Job Results:
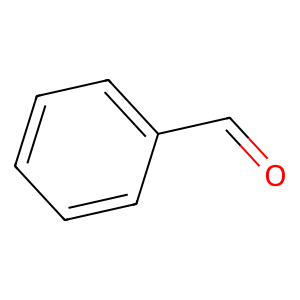
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
0cb0764e79e22b0da515513ec30e42ef
Job name
NA
Time
2025-06-05 10:48:27
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61 | Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase subunit M2 | 3OLJ | 5.23 | |
Target general information Gen name RRM2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms RR2 Protein family Ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase small chain family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Metal ion binding.Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase activity, thioredoxin disulfide as acceptor. Related diseases Pyruvate kinase hyperactivity (PKHYP) [MIM:102900]: Autosomal dominant phenotype characterized by increase of red blood cell ATP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9090535}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Pyruvate kinase deficiency of red cells (PKRD) [MIM:266200]: A frequent cause of hereditary non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia. Clinically, pyruvate kinase-deficient patients suffer from a highly variable degree of chronic hemolysis, ranging from severe neonatal jaundice and fatal anemia at birth, severe transfusion-dependent chronic hemolysis, moderate hemolysis with exacerbation during infection, to a fully compensated hemolysis without apparent anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10087985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10772876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11328279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11960989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1536957, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1896471, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19085939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2018831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21794208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7706479, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8161798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8180378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8476433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8481523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8483951, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8664896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8807089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9075576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9482576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9827908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9886305, ECO:0000269|Ref.24}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00242; DB05260; DB05801; DB05003; DB05428 Interacts with P41002; Q9UM11; P23921; O00560 EC number 1.17.4.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Deoxyribonucleotide synthesis; Iron; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 33579.4 Length 286 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 43.7 Isoelectric point 5.12 Charge (pH=7) -12.86 3D Binding mode Sequence MGVEDEPLLRENPRRFVIFPIEYHDIWQMYKKAEASFWTAEEVDLSKDIQHWESLKPEERYFISHVLAFFAASDGIVNENLVERFSQEVQITEARCFYGFQIAMENIHSEMYSLLIDTYIKDPKEREFLFNAIETMPCVKKKADWALRWIGDKEATYGERVVAFAAVEGIFFSGSFASIFWLKKRGLMPGLTFSNELISRDEGLHCDFACLMFKHLVHKPSEERVREIIINAVRIEQEFLTEALPVKLIGMNCTLMKQYIEFVADRLMLELGFSKVFRVENPFDFM Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 62 | Plasmepsin-2 | 2BJU | 5.23 | |
Target general information Gen name N/A Organism Plasmodium falciparum (isolate HB3) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Peptidase A1 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Aspartic-type endopeptidase activity. Related diseases Short/branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (SBCADD) [MIM:610006]: Autosomal recessive disorder and consists of a defect in catabolism of L-isoleucine which is characterized by an increase of 2-methylbutyrylglycine and 2-methylbutyrylcarnitine in blood and urine. Affected individuals have seizures and psychomotor delay as the main clinical features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10832746, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11013134, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16317551}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04378; DB04373; DB11638; DB01218; DB02505; DB03063 Interacts with NA EC number 3.4.23.39 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Aspartyl protease; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Hydrolase; Membrane; Protease; Reference proteome; Signal-anchor; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Vacuole; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 36923.5 Length 329 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 44.31 Isoelectric point 4.67 Charge (pH=7) -17.94 3D Binding mode Sequence SSNDNIELVDFQNIMFYGDAEVGDNQQPFTFILDTGSANLWVPSVKCTTAGCLTKHLYDSSKSRTYEKDGTKVEMNYVSGTVSGFFSKDLVTVGNLSLPYKFIEVIDTNGFEPTYTASTFDGILGLGWKDLSIGSVDPIVVELKNQNKIENALFTFYLPVHDKHTGFLTIGGIEERFYEGPLTYEKLNHDLYWQITLDAHVGNIMLEKANCIVDSGTSAITVPTDFLNKMLQNLDVIKVPFLPFYVTLCNNSKLPTFEFTSENGKYTLEPEYYLQHIEDVGPGLCMLNIIGLDFPVPTFILGDPFMRKYFTVFDYDNHSVGIALAKKNL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 63 | Sterol 14alpha-demethylase (EC 1.14.15.36) (CYPLI) (Cytochrome P450 51) (Cytochrome P450-14DM) (Cytochrome P450-LIA1) (Sterol 14-alpha demethylase) | 2W0B | 5.23 | |
Target general information Gen name cyp51 Organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms MTCY369.09c;Rv0764c Protein family Cytochrome P450 family Biochemical class NA Function Sterol 14alpha-demethylase whose physiological substrate is not known. Accepts electrons from the iron-sulfur ferredoxin Fdx encoded by an adjacent gene (PubMed:10430874, PubMed:16819841). In vitro, catalyzes C14-demethylation of lanosterol, 24,25-dihydrolanosterol and obtusifoliol, to produce the 8,14-dienes stereoselectively (PubMed:10430874). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10430874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16819841}." Related diseases Thrombocytopenia 4 (THC4) [MIM:612004]: A form of thrombocytopenia, a hematologic disorder defined by a decrease in the number of platelets in circulating blood, resulting in the potential for increased bleeding and decreased ability for clotting. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18345000}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 1.14.15.36 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Heme; Iron; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Metal-binding; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome; Steroid biosynthesis; Steroid metabolism; Sterol biosynthesis; Sterol metabolism Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 49740 Length 440 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 36.42 Isoelectric point 5.61 Charge (pH=7) -13.63 3D Binding mode Sequence AVALPRVSGGHDEHGHLEEFRTDPIGLMQRVRDELGDVGTFQLAGKQVVLLSGSHANEFFFRAGDDDLDQAKAYPFMTPIFGEGVVFDASPERRKEMLHNAALRGEQMKGHAATIEDQVRRMIADWGEAGEIDLLDFFAELTIYTSSACLIGKKFRDQLDGRFAKLYHELERGTDPLAYVDPYLPIESFRRRDEARNGLVALVADIMNGRIANRDMLDVLIAVKAETGTPRFSADEITGMFISMMFAGHHTSSGTASWTLIELMRHRDAYAAVIDELDELYGDGRSVSFHALRQIPQLENVLKETLRLHPPLIILMRVAKGEFEVQGHRIHEGDLVAASPAISNRIPEDFPDPHDFVPARYEQPRQEDLLNRWTWIPFGAGRHRCVGAAFAIMQIKAIFSVLLREYEFEMAQPPESYRNDHSKMVVQLAQPAAVRYRRRT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 64 | Opioid receptor sigma 1 (OPRS1) | 5HK1 | 5.23 | |
Target general information Gen name SIGMAR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hSigmaR1; Sigma1R; Sigma1-receptor; Sigma non-opioid intracellular receptor 1; Sigma 1-type opioid receptor; SRBP; SR31747-binding protein; SR31747 binding protein 1; SR-BP; SIG-1R; Opioid receptor, s Protein family ERG2 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Involved in the regulation of different receptors it plays a role in BDNF signaling and EGF signaling. Also regulates ion channels like the potassium channel and could modulate neurotransmitter release. Plays a role in calcium signaling through modulation together with ANK2 of the ITP3R-dependent calcium efflux at the endoplasmic reticulum. Plays a role in several other cell functions including proliferation, survival and death. Originally identified for its ability to bind various psychoactive drugs it is involved in learning processes, memory and mood alteration. Necessary for proper mitochondrial axonal transport in motor neurons, in particular the retrograde movement of mitochondria. Plays a role in protecting cells against oxidative stress-induced cell death via its interaction with RNF112. Functions in lipid transport from the endoplasmic reticulum and is involved in a wide array of cellular functions probably through regulation of the biogenesis of lipid microdomains at the plasma membrane. Related diseases Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 16, juvenile (ALS16) [MIM:614373]: A neurodegenerative disorder affecting upper motor neurons in the brain and lower motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord, resulting in fatal paralysis. Sensory abnormalities are absent. The pathologic hallmarks of the disease include pallor of the corticospinal tract due to loss of motor neurons, presence of ubiquitin-positive inclusions within surviving motor neurons, and deposition of pathologic aggregates. The etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is likely to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. The disease is inherited in 5-10% of the cases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21842496}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Neuronopathy, distal hereditary motor, autosomal recessive 2 (HMNR2) [MIM:605726]: A form of distal hereditary motor neuronopathy, a heterogeneous group of neuromuscular disorders caused by selective degeneration of motor neurons in the anterior horn of the spinal cord, without sensory deficit in the posterior horn. The overall clinical picture consists of a classical distal muscular atrophy syndrome in the legs without clinical sensory loss. The disease starts with weakness and wasting of distal muscles of the anterior tibial and peroneal compartments of the legs. Later on, weakness and atrophy may expand to the proximal muscles of the lower limbs and/or to the distal upper limbs. HMNR2 is characterized by onset of distal muscle weakness and wasting affecting the lower and upper limbs in the first decade. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26078401, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27629094}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00321; DB09014; DB00907; DB00514; DB01488; DB00574; DB00502; DB00956; DB00704; DB00540; DB06174; DB00652; DB11186; DB03575; DB05316; DB01708; DB00409; DB01104 Interacts with Q92847-1; Q99720-1; O00213-2; P17612; P50454; P37173 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Cell junction; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Endoplasmic reticulum; Lipid droplet; Lipid transport; Membrane; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathy; Nucleus; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 20805.3 Length 185 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 31.72 Isoelectric point 5.44 Charge (pH=7) -6.63 3D Binding mode Sequence VFQREEIAQLARQYAGLDHELAFSRLIVELRRLHPGHVLPDEELQWVFVNAGGWMGAMCLLHASLSEYVLLFGTALGSRGHSGRYWAEISDTIISGTFHQWREGTTKSEVFYPGETVVHGPGEATAVEWGPNTWMVEYGRGVIPSTLAFALADTVFSTQDFLTLFYTLRSYARGLRLELTTYLFG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 65 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 14 (USP14) | 6IIK | 5.23 | |
Target general information Gen name USP14 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Ubiquitin-specific-processing protease 14; Ubiquitin thioesterase 14; TGT; Deubiquitinating enzyme 14 Protein family Peptidase C19 family, USP14/UBP6 subfamily Biochemical class Peptidase Function Ensures the regeneration of ubiquitin at the proteasome. Is a reversibly associated subunit of the proteasome and a large fraction of proteasome-free protein exists within the cell. Required for the degradation of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 which is critical for CXCL12-induced cell chemotaxis. Serves also as a physiological inhibitor of endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) under the non-stressed condition by inhibiting the degradation of unfolded endoplasmic reticulum proteins via interaction with ERN1. Indispensable for synaptic development and function at neuromuscular junctions (NMJs). Plays a role in the innate immune defense against viruses by stabilizing the viral DNA sensor CGAS and thus inhibiting its autophagic degradation. Proteasome-associated deubiquitinase which releases ubiquitin from the proteasome targeted ubiquitinated proteins. Related diseases Hypophosphatemic rickets, autosomal dominant (ADHR) [MIM:193100]: A disease characterized by isolated renal phosphate wasting, hypophosphatemia, and inappropriately normal 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) levels. Patients frequently present with bone pain, rickets, and tooth abscesses. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11062477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11409890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16638743}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Tumoral calcinosis, hyperphosphatemic, familial, 2 (HFTC2) [MIM:617993]: A form of hyperphosphatemic tumoral calcinosis, a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that manifests with hyperphosphatemia and massive calcium deposits in the skin and subcutaneous tissues. Some patients have recurrent, transient, painful swellings of the long bones associated with the radiographic findings of periosteal reaction and cortical hyperostosis and absence of skin involvement. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15590700, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16030159, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16151858, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24680727}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12695 Interacts with Q08209 EC number EC 3.4.19.12 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Hydrolase; Immunity; Innate immunity; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteasome; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Thiol protease; Ubl conjugation pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 38476.7 Length 335 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 61.05 Isoelectric point 5.6 Charge (pH=7) -4.84 3D Binding mode Sequence ELPCGLTNLGNTCYMNATVQCIRSVPELKDALKRYAGALRASGEMASAQYITAALRDLFDSMDKTSSSIPPIILLQFLHMAFPQFAEKGEQGQYLQQDANECWIQMMRVLQQKLEAIEDKSLIDQFFGVEFETTMKCTESEEEEVTKGKENQLQLSCFINQEVKYLFTGLKLRLQEEITKQSPTLQRNALYIKSSKISRLPAYLTIQMVRFFNAKVLKDVKFPLMLDMYELCTPELQEKMVSFRSKFKDLYEPFSFADDIGSNNCGYYDLQAVLTHQGRSSSSGHYVSWVKRKQDEWIKFDDDKVSIVTPEDILRLSGGGDWHIAYVLLYGPRRV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 66 | Bacterial Nicotinate-nucleotide adenylyltransferase (Bact nadD) | 1K4K | 5.23 | |
Target general information Gen name Bact nadD Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms nadD of Escherichia coli (strain K12); Nicotinate mononucleotide adenylyltransferase of Escherichia coli (strain K12); NaMN adenylyltransferase of Escherichia coli (strain K12); Deamido-NAD(+)Nicotina Protein family NadD family Biochemical class Kinase Function Catalyzes the reversible adenylation of nicotinate mononucleotide (namn) to nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide (naad). Related diseases Asthma-related traits 5 (ASRT5) [MIM:611064]: Asthma-related traits include clinical symptoms of asthma, such as coughing, wheezing, dyspnea, bronchial hyperresponsiveness as assessed by methacholine challenge test, serum IgE levels, atopy and atopic dermatitis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17503328}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 2.7.7.18 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ATP-binding; NAD; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleotidyltransferase; Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 24527.6 Length 213 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 48.92 Isoelectric point 5.46 Charge (pH=7) -7.78 3D Binding mode Sequence MKSLQALFGGTFDPVHYGHLKPVETLANLIGLTRVTIIPNNVPPHRPQPEANSVQRKHMLELAIADKPLFTLDERELKRNAPSYTAQTLKEWRQEQGPDVPLAFIIGQDSLLTFPTWYEYETILDNAHLIVCRRPGYPLEMAQPQYQQWLEDHLTHNPEDLHLQPAGKIYLAETPWFNISATIIRERLQNGESCEDLLPEPVLTYINQQGLYR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 67 | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor (GPR119) | 7XZ6 | 5.23 | |
Target general information Gen name GPR119 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms GPR119; G-protein coupled receptor 119 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Receptor for the endogenous fatty-acid ethanolamide oleoylethanolamide (OEA) and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC). Functions as a glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylate cyclase. Seems to act through a G(s) mediated pathway. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 24 (DEE24) [MIM:615871]: A disease characterized by early-onset seizures, intellectual disability of varying degrees, and behavioral disturbances or autistic features in most individuals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24747641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27864847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 10 (GEFSP10) [MIM:618482]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder with incomplete penetrance, characterized by variable types of seizures including absence, tonic-clonic, febrile, focal, and eyelid myoclonia. Some patients have normal neurologic development. Others have mild-to-moderate intellectual disability or autism spectrum disorder. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29936235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05166 Interacts with Q12797-6 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; G-protein coupled receptor; Lipid-binding; Membrane; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 32134.1 Length 292 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 34.96 Isoelectric point 9.12 Charge (pH=7) 8.03 3D Binding mode Sequence MESSFSFGVILAVLASLIIATNTLVAVAVLLLIHKNDGVSLCFTLNLAVADTLIGVAISGLLTDQLSSPSRPTQKTLCSLRMAFVTSSAAASVLTVMLITFDRYLAIKQPFRYLKIMSGFVAGACIAGLWLVSYLIGFLPLGIPMFQQTAYKGQCSFFAVFHPHFVLTLSCVGFFPAMLLFVFFYCDMLKIASMHSQQIRKMEHAGAMAGSDFKALRTVSVLIGSFALSWTPFLITGIVQVACQECHLYLVLERYLWLLGVGNSLLNPLIYAYWQKEVRLQLYHMALGVKKV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 68 | Serum albumin (ALB) | 4L8U | 5.22 | |
Target general information Gen name ALB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Serum albumin Protein family ALB/AFP/VDB family Biochemical class NA Function Serum albumin, the main protein of plasma, has a good binding capacity for water, Ca(2+), Na(+), K(+), fatty acids, hormones, bilirubin and drugs. Its main function is the regulation of the colloidal osmotic pressure of blood. Major zinc transporter in plasma, typically binds about 80% of all plasma zinc. Related diseases Hyperthyroxinemia, familial dysalbuminemic (FDAH) [MIM:615999]: A disorder characterized by abnormally elevated levels of total serum thyroxine (T4) in euthyroid patients. It is due to abnormal serum albumin that binds T4 with enhanced affinity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7852505, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8048949, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9329347, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9589637}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Analbuminemia (ANALBA) [MIM:616000]: A rare autosomal recessive disorder manifested by the presence of a very low amount of circulating serum albumin. Affected individuals manifest mild edema, hypotension, fatigue, and, occasionally, lower body lipodystrophy (mainly in adult females). The most common biochemical finding is hyperlipidemia, with a significant increase in the total and LDL cholesterol concentrations, but normal concentrations of HDL cholesterol and triglycerides. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8134387}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08496; DB07517; DB12001; DB05812; DB14973; DB11703; DB01418; DB01614; DB00316; DB00414; DB09347; DB06151; DB00459; DB00787; DB00640; DB00802; DB00346; DB00404; DB00770; DB01370; DB14517; DB14518; DB01118; DB00321; DB01060; DB00415; DB00276; DB06728; DB11901; DB00714; DB04557; DB09229; DB11217; DB00278; DB01238; DB14185; DB09204; DB01169; DB11638; DB09274; DB00126; DB06216; DB01072; DB00335; DB00289; DB01076; DB00995; DB06237; DB07402; DB00993; DB08822; DB08903; DB16703; DB00245; DB01086; DB01053; DB00443; DB14669; DB11967; DB13909; DB01294; DB09223; DB00083; DB09128; DB01222; DB15248; DB00490; DB00237; DB11148; DB06772; DB11751; DB11093; DB11348; DB14481; DB04690; DB01101; DB03600; DB01197; DB01136; DB00456; DB01327; DB14879; DB00274; DB01328; DB01329; DB00493; DB01330; DB00430; DB00438; DB01212; DB06119; DB00567; DB07565; DB08936; DB00878; DB00608; DB00477; DB09093; DB00310; DB00501; DB00568; DB00537; DB00515; DB00349; DB01013; DB00845; DB01242; DB01068; DB00575; DB00758; DB01147; DB00363; DB15534; DB01394; DB00286; DB12483; DB09130; DB01380; DB08865; DB11134; DB06778; DB01176; DB00924; DB00434; DB00847; DB01914; DB06695; DB08912; DB11963; DB04816; DB00080; DB12941; DB01264; DB11943; DB11637; DB01189; DB00304; DB01234; DB14649; DB09213; DB00829; DB01119; DB11397; DB00586; DB00485; DB00266; DB00900; DB00861; DB01396; DB00343; DB08995; DB08930; DB01142; DB00997; DB00254; DB00366; DB04855; DB00476; DB01126; DB01057; DB12243; DB13421; DB00625; DB15444; DB00879; DB00584; DB13874; DB11718; DB00228; DB08899; DB01364; DB00530; DB00303; DB11827; DB12235; DB00783; DB13952; DB13953; DB13954; DB13955; DB13956; DB00655; DB04574; DB00903; DB00977; DB00749; DB00294; DB01276; DB12466; DB04854; DB01039; DB00573; DB00813; DB00950; DB16165; DB01195; DB00687; DB15690; DB00544; DB00472; DB00712; DB08906; DB00983; DB01320; DB06716; DB11796; DB00695; DB15149; DB00743; DB06705; DB01044; DB00317; DB01241; DB12141; DB11978; DB01120; DB01067; DB01016; DB00986; DB13751; DB04539; DB12836; DB11575; DB11359; DB01159; DB14999; DB00070; DB01275; DB00999; DB00774; DB00327; DB09526; DB01611; DB01005; DB00557; DB13014; DB12471; DB09053; DB01050; DB00159; DB01088; DB00619; DB09262; DB00458; DB00808; DB00328; DB07992; DB09564; DB01307; DB05382; DB04711; DB09333; DB00332; DB16200; DB01029; DB00762; DB06636; DB00753; DB00677; DB00951; DB01064; DB00982; DB11757; DB01167; DB08820; DB01587; DB01026; DB01009; DB00598; DB09236; DB00709; DB00555; DB03017; DB01006; DB09237; DB06282; DB01235; DB01137; DB00451; DB00601; DB17083; DB00279; DB01583; DB06655; DB01601; DB09195; DB00678; DB00227; DB09280; DB15935; DB12674; DB00137; DB08932; DB14513; DB01397; DB06796; DB06234; DB00737; DB13959; DB09124; DB00603; DB00784; DB00814; DB01042; DB00454; DB09383; DB00931; DB00333; DB00563; DB00968; DB09241; DB00959; DB06710; DB00264; DB01110; DB00683; DB08893; DB00295; DB01024; DB08231; DB00461; DB00607; DB01183; DB00788; DB00731; DB04861; DB00220; DB11828; DB00238; DB01115; DB11820; DB09079; DB11793; DB12005; DB06713; DB00717; DB00957; DB00540; DB00104; DB00334; DB09074; DB04224; DB00768; DB12455; DB11130; DB04911; DB01083; DB13310; DB01173; DB00526; DB00842; DB00776; DB01062; DB00497; DB06412; DB03585; DB00595; DB15575; DB09073; DB03796; DB13967; DB14582; DB00642; DB00850; DB12978; DB01619; DB03255; DB00946; DB00252; DB01132; DB01621; DB04951; DB00554; DB08860; DB11642; DB01324; DB09087; DB09418; DB06813; DB13514; DB06209; DB01058; DB00860; DB15566; DB14631; DB00635; DB01032; DB01069; DB09348; DB00818; DB00571; DB06480; DB00852; DB00165; DB04216; DB00881; DB00908; DB12874; DB08735; DB00481; DB11853; DB12404; DB00912; DB02709; DB11855; DB01045; DB11753; DB08864; DB08931; DB14840; DB15305; DB00734; DB00503; DB11182; DB00412; DB01098; DB04847; DB06201; DB08877; DB08736; DB00936; DB00938; DB01232; DB11689; DB13928; DB01104; DB01236; DB12965; DB06290; DB00877; DB00815; DB15093; DB00421; DB00649; DB03193; DB06150; DB01581; DB01582; DB00576; DB01015; DB00795; DB00605; DB00391; DB00870; DB00864; DB00675; DB05134; DB09139; DB05521; DB00853; DB14126; DB09299; DB15133; DB00857; DB00342; DB00624; DB13943; DB13944; DB01420; DB13946; DB00759; DB00152; DB11590; DB01622; DB01623; DB09100; DB09070; DB08816; DB01133; DB15171; DB11800; DB01056; DB08895; DB01124; DB00500; DB00273; DB01685; DB00214; DB00755; DB00620; DB00432; DB08814; DB11677; DB00376; DB09069; DB00792; DB00427; DB08867; DB09076; DB12255; DB00313; DB00512; DB05294; DB08881; DB00661; DB15456; DB11641; DB08828; DB00162; DB11739; DB16699; DB00682; DB00943; DB00495; DB00744; DB14533; DB14548; DB00246; DB04828 Interacts with P02768; P02786; Q8N5Z5; Q6GQQ9-2; Q07869; Q09028; Q86WT6-2; O76024 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Cleavage on pair of basic residues; Copper; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycation; Glycoprotein; Lipid-binding; Metal-binding; Methylation; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34028.4 Length 298 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 43.45 Isoelectric point 5.49 Charge (pH=7) -10.44 3D Binding mode Sequence AHKSEVAHRFKDLGEENFKALVLIAFAQYLQQCPFEDHVKLVNEVTEFAKTCVADESAENCDKSLHTLFGDKLCTVATLRETYGEMADCCAKQEPERNECFLQHKDDNPNLPRLVRPEVDVMCTAFHDNEETFLKKYLYEIARRHPYFYAPELLFFAKRYKAAFTECCQAADKAACLLPKLDELRDEGKASSAKQRLKCASLQKFGERAFKAWAVARLSQRFPKAEFAEVSKLVTDLTKVHTECCHGDLLECADDRADLAKYICENQDSISSKLKECCEKPLLEKSHCIAEVENDEMP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 69 | Glutathione-dependent PGD synthase (HPGDS) | 2CVD | 5.22 | |
Target general information Gen name HPGDS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms HPGDS; Glutathione-S-transferase; GST class-alpha Protein family GST superfamily, Sigma family Biochemical class Intramolecular oxidoreductases Function Bifunctional enzyme which catalyzes both the conversion of PGH2 to PGD2, a prostaglandin involved in smooth muscle contraction/relaxation and a potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation, and the conjugation of glutathione with a widerange of aryl halides and organic isothiocyanates. Also exhibits low glutathione-peroxidase activity towards cumene hydroperoxide. Related diseases Chromosomal aberrations involving JAK2 are found in both chronic and acute forms of eosinophilic, lymphoblastic and myeloid leukemia. Translocation t(8;9)(p22;p24) with PCM1 links the protein kinase domain of JAK2 to the major portion of PCM1. Translocation t(9;12)(p24;p13) with ETV6.; DISEASE: Budd-Chiari syndrome (BDCHS) [MIM:600880]: A syndrome caused by obstruction of hepatic venous outflow involving either the hepatic veins or the terminal segment of the inferior vena cava. Obstructions are generally caused by thrombosis and lead to hepatic congestion and ischemic necrosis. Clinical manifestations observed in the majority of patients include hepatomegaly, right upper quadrant pain and abdominal ascites. Budd-Chiari syndrome is associated with a combination of disease states including primary myeloproliferative syndromes and thrombophilia due to factor V Leiden, protein C deficiency and antithrombin III deficiency. Budd-Chiari syndrome is a rare but typical complication in patients with polycythemia vera. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16707754}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Polycythemia vera (PV) [MIM:263300]: A myeloproliferative disorder characterized by abnormal proliferation of all hematopoietic bone marrow elements, erythroid hyperplasia, an absolute increase in total blood volume, but also by myeloid leukocytosis, thrombocytosis and splenomegaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15781101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15793561, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15858187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16603627, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25644777}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thrombocythemia 3 (THCYT3) [MIM:614521]: A myeloproliferative disorder characterized by excessive platelet production, resulting in increased numbers of circulating platelets. It can be associated with spontaneous hemorrhages and thrombotic episodes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16325696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22397670}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Myelofibrosis (MYELOF) [MIM:254450]: A disorder characterized by replacement of the bone marrow by fibrous tissue, occurring in association with a myeloproliferative disorder. Clinical manifestations may include anemia, pallor, splenomegaly, hypermetabolic state, petechiae, ecchymosis, bleeding, lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, portal hypertension. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML) [MIM:601626]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. AML is a malignant disease of bone marrow characterized by maturational arrest of hematopoietic precursors at an early stage of development. Clonal expansion of myeloid blasts occurs in bone marrow, blood, and other tissue. Myelogenous leukemias develop from changes in cells that normally produce neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils and monocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16247455}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08790; DB01897; DB08695; DB07613; DB07917; DB07616; DB00321; DB00291; DB03619; DB00143; DB03310; DB08313; DB07614; DB07615 Interacts with Q96GS6; Q96B67; P15018; P08582-2; Q13370; Q8N1H7 EC number EC 5.3.99.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Calcium; Cytoplasm; Fatty acid biosynthesis; Fatty acid metabolism; Isomerase; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Prostaglandin biosynthesis; Prostaglandin metabolism; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 46441 Length 396 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 29.82 Isoelectric point 5.55 Charge (pH=7) -9.17 3D Binding mode Sequence PNYKLTYFNMRGRAEIIRYIFAYLDIQYEDHRIEQADWPEIKSTLPFGKIPILEVDGLTLHQSLAIARYLTKNTDLAGNTEMEQCHVDAIVDTLDDFMSCFPWAEKKQDVKEQMFNELLTYNAPHLMQDLDTYLGGREWLIGMSVTWADFYWEICSTTLLVFKPDLLDNHPRLVTLRKKVQAIPAVANWIKRRPQTKLPNYKLTYFNMRGRAEIIRYIFAYLDIQYEDHRIEQADWPEIKSTLPFGKIPILEVDGLTLHQSLAIARYLTKNTDLAGNTEMEQCHVDAIVDTLDDFMSCFPWAEKKQDVKEQMFNELLTYNAPHLMQDLDTYLGGREWLIGMSVTWADFYWEICSTTLLVFKPDLLDNHPRLVTLRKKVQAIPAVANWIKRRPQTKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 70 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member A3 | 5FHZ | 5.22 | |
Target general information Gen name ALDH1A3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms ALDH6 Protein family Aldehyde dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD) activity.Aldehyde dehydrogenase [NAD(P)+] activity.NAD+ binding.Protein homodimerization activity.Retinal dehydrogenase activity.Thyroid hormone binding. Related diseases Microphthalmia, isolated, 8 (MCOP8) [MIM:615113]: A disorder of eye formation, ranging from small size of a single eye to complete bilateral absence of ocular tissues. Ocular abnormalities like opacities of the cornea and lens, scaring of the retina and choroid, and other abnormalities may also be present. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23312594, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23591992, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23646827, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23881059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24024553, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24568872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24777706}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00157; DB00162 Interacts with NA EC number 1.2.1.36 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Lipid metabolism; Microphthalmia; NAD; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H Molecular weight (Da) 50635.7 Length 461 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 33.75 Isoelectric point 7.07 Charge (pH=7) 0.15 3D Binding mode Sequence LPRPIRNLEVKFTKIFINNEWHESKSGKKFATCNPSTREQICEVEEGDKPDVDKAVEAAQVAFQRGSPWRRLDALSRGRLLHQLADLVERDRATLAALETMDTGKPFLHAFFIDLEGCIRTLRYFAGWADKIPIGVCGAITPWNFPLLMLVWKLAPALCCGNTMVLKPAEQTPLTALYLGSLIKEAGFPPGVVNIVPGFGPTVGAAISSHPQINKIAFTGSTEVGKLVKEAASRSNLKRVTLELGGKNPCIVCADADLDLAVECAHQGVFFNQGQCCTAASRVFVEEQVYSEFVRRSVEYAKKRPVGDPFDVKTEQGPQIDQKQFDKILELIESGKKEGAKLECGGSAMEDKGLFIKPTVFSEVTDNMRIAKEEIFGPVQPILKFKSIEEVIKRANSTDYGLTAAVFTKNLDKALKLASALESGTVWINCYNALYAQAPFGGFKMSGNGRELGEYALAEYT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 71 | Cyclopropane mycolic acid synthase MmaA2 | 1TPY | 5.22 | |
Target general information Gen name mmaA2 Organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms Rv0644c;mma2 Protein family CFA/CMAS family Biochemical class Transferase Function Cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase activity.Methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 16 (OZEMA16) [MIM:617234]: A rare cause of female primary infertility. In affected women, ovulation and fertilization proceed normally but embryos are arrested at early stages of development. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27545678}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01718; DB01752 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.79 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Methyltransferase; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32493.6 Length 285 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.61 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -10.17 3D Binding mode Sequence NDLTPHFEDVQAHYDLSDDFFRLFLDPTQTYSCAHFEREDMTLEEAQIAKIDLALGKLGLQPGMTLLDIGCGWGATMRRAIAQYDVNVVGLTLSKNQAAHVQKSFDEMDTPRDRRVLLAGWEQFNEPVDRIVSIGAFEHFGHDRHADFFARAHKILPPDGVLLLHTITGLTRQQMVDHGLPLTLWLARFLKFIATEIFPGGQPPTIEMVEEQSAKTGFTLTRRQSLQPHYARTLDLWAEALQEHKSEAIAIQSEEVYERYMKYLTGCAKLFRVGYIDVNQFTLAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 72 | Carbonic anhydrase 13 | 4KNN | 5.22 | |
Target general information Gen name CA13 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Alpha-carbonic anhydrase family Biochemical class Lyase / lyase inhibitor Function Carbonate dehydratase activity.Zinc ion binding. Related diseases Long QT syndrome 10 (LQT10) [MIM:611819]: A heart disorder characterized by a prolonged QT interval on the ECG and polymorphic ventricular arrhythmias. They cause syncope and sudden death in response to exercise or emotional stress, and can present with a sentinel event of sudden cardiac death in infancy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17592081}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Atrial fibrillation, familial, 17 (ATFB17) [MIM:611819]: A familial form of atrial fibrillation, a common sustained cardiac rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity and ineffective atrial contraction promoting blood stasis in the atria and reduces ventricular filling. It can result in palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23604097}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00562; DB00606; DB07115; DB00909 Interacts with Q8N4Y2-3; Q6UUV7 EC number 4.2.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Lyase; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 28955.1 Length 258 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.81 Isoelectric point 6.3 Charge (pH=7) -3.47 3D Binding mode Sequence SWGYREHNGPIHWKEFFPIADGDQQSPIEIKTKEVKYDSSLRPLSIKYDPSSAKIISNSGHSFNVDFDDTENKSVLRGGPLTGSYRLRQVHLHWGSADDHGSEHIVDGVSYAAELHVVHWNSDKYPSFVEAAHEPDGLAVLGVFLQIGEPNSQLQKITDTLDSIKEKGKQTRFTNFDLLSLLPPSWDYWTYPGSLTVPPLLESVTWIVLKQPINISSQQLAKFRSLLCTAEGEAAAFLVSNHRPPQPLKGRKVRASFH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 73 | p53-binding protein Mdm4 (MDM4) | 6Q9Y | 5.22 | |
Target general information Gen name MDM4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein Mdmx; Mdm2-like p53-binding protein; Double minute 4 protein Protein family MDM2/MDM4 family Biochemical class MDM2/MDM4 family Function Inhibits p53/TP53- and TP73/p73-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by binding its transcriptional activation domain. Inhibits degradation of MDM2. Can reverse MDM2-targeted degradation of TP53 while maintaining suppression of TP53 transactivation and apoptotic functions. Related diseases Bone marrow failure syndrome 6 (BMFS6) [MIM:618849]: A form of bone marrow failure syndrome, a heterogeneous group of life-threatening disorders characterized by hematopoietic defects in association with a range of variable extra-hematopoietic manifestations. BMFS6 is an autosomal dominant form characterized by intermittent neutropenia, lymphopenia, or anemia associated with hypocellular bone marrow, and increased susceptibility to cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32300648}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9NX04; P10415; Q7Z479; O95971; P48729; Q00987; Q13064; P41227; P06400; Q9Y4L5; P23297; P29034; P33763; P04271; P31947; P04637; P62837; Q93009; O14972; P61964; P62258; P61981; P63104; Q9BRR0; A0A0S2Z6X0; Q3YBA8; P03255-2 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Disease variant; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 19722 Length 173 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 50.78 Isoelectric point 8.48 Charge (pH=7) 2.27 3D Binding mode Sequence QVRPKLPLLKILHAAGAQGEMFTVKEVMHYLGQYIMVKQLYDQQEQHMVYCGGDLLGELLGRQSFSVKDPSPLYDMLRKNLVTLAQINQVRPKLPLLKILHAAGAQGEMFTVKEVMHYLGQYIMVKQLYDQQEQHMVYCGGDLLGELLGRQSFSVKDPSPLYDMLRKNLVTLA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 74 | Scavenger decapping enzyme DcpS (DCPS) | 1ST4 | 5.22 | |
Target general information Gen name DCPS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Scavenger mRNA-decapping enzyme DcpS; Histidine triad protein member5; Hint-related 7meGMP-directed hydrolase; HINT-5; DCS-1; DCPS Protein family HIT family Biochemical class Acid anhydrides hydrolase Function Decapping scavenger enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of a residual cap structure following the degradation of mRNAs by the 3'->5' exosome-mediated mRNA decay pathway. Hydrolyzes cap analog structures like 7-methylguanosine nucleoside triphosphate (m7GpppG) with up to 10 nucleotide substrates (small capped oligoribonucleotides) and specifically releases 5'-phosphorylated RNA fragments and 7-methylguanosine monophosphate (m7GMP). Cleaves cap analog structures like tri-methyl guanosine nucleoside triphosphate (m3(2,2,7)GpppG) with very poor efficiency. Does not hydrolyze unmethylated cap analog (GpppG) and shows no decapping activity on intact m7GpppG-capped mRNA molecules longer than 25 nucleotides. Does not hydrolyze 7-methylguanosine diphosphate (m7GDP) to m7GMP (PubMed:22985415). May also play a role in the 5'->3 mRNA decay pathway; m7GDP, the downstream product released by the 5'->3' mRNA mediated decapping activity, may be also converted by DCPS to m7GMP (PubMed:14523240). Binds to m7GpppG and strongly to m7GDP. Plays a role in first intron splicing of pre- mRNAs. Inhibits activation-induced cell death. Related diseases Al-Raqad syndrome (ARS) [MIM:616459]: A syndrome characterized by delayed psychomotor development, moderate to severe intellectual disability, poor or absent speech, microcephaly, congenital hypotonia, and severe growth delay. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25701870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25712129}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07644; DB07643; DB07642; DB03593; DB01960; DB01649; DB03958 Interacts with Q96C86; P52292; O15131; O60684 EC number EC 3.6.1.59 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Intellectual disability; mRNA processing; mRNA splicing; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B,A Molecular weight (Da) 69192.9 Length 597 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 54.62 Isoelectric point 6.12 Charge (pH=7) -9.94 3D Binding mode Sequence VRLPFSGFRLQKVLRESARDKIIFLHGKVNEASGDGDGEDAVVILEKTPFQVEQVAQLLTGSPELQLQFSNDIYSTYHLFPPRQLNDVKTTVVYPATEKHLQKYLRQDLRLIRETGDDYRNITLPHLESQSLSIQWVYNILDKKAEADRIVFENPDPSDGFVLIPDLKWNQQQLDDLYLIAICHRRGIRSLRDLTPEHLPLLRNILHQGQEAILQRYRMKGDHLRVYLHYLPSYYHLNVHFTALGFEAPGSGVERAHLLAEVIENLECDPRHYQQRTLTFALRADDPLLKLLQEAQQAPVRLPFSGFRLQKVLRESARDKIIFLHGKVNEASGDGDGEDAVVILEKTPFQVEQVAQLLTGSPELQLQFSNDIYSTYHLFPPRQLNDVKTTVVYPATEKHLQKYLRQDLRLIRETGDDYRNITLPHLESQSLSIQWVYNILDKKAEADRIVFENPDPSDGFVLIPDLKWNQQQLDDLYLIAICHRRGIRSLRDLTPEHLPLLRNILHQGQEAILQRYRMKGDHLRVYLHYLPSYYHLNVHFTALGFEAPGSGVERAHLLAEVIENLECDPRHYQQRTLTFALRADDPLLKLLQEAQQS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 75 | Casein kinase II alpha prime (CSNK2A2) | 5YF9 | 5.22 | |
Target general information Gen name CSNK2A2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Casein kinase II subunit alpha'; CK2A2; CK II alpha' Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CK2 subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Regulates numerous cellular processes, such as cell cycle progression, apoptosis and transcription, as well as viral infection. May act as a regulatory node which integrates and coordinates numerous signals leading to an appropriate cellular response. During mitosis, functions as a component of the p53/TP53-dependent spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) that maintains cyclin-B-CDK1 activity and G2 arrest in response to spindle damage. Also required for p53/TP53-mediated apoptosis, phosphorylating 'Ser-392' of p53/TP53 following UV irradiation. Can also negatively regulate apoptosis. Phosphorylates the caspases CASP9 and CASP2 and the apoptotic regulator NOL3. Phosphorylation protects CASP9 from cleavage and activation by CASP8, and inhibits the dimerization of CASP2 and activation of CASP8. Regulates transcription by direct phosphorylation of RNA polymerases I, II, III and IV. Also phosphorylates and regulates numerous transcription factors including NF-kappa-B, STAT1, CREB1, IRF1, IRF2, ATF1, SRF, MAX, JUN, FOS, MYC and MYB. Phosphorylates Hsp90 and its co-chaperones FKBP4 and CDC37, which is essential for chaperone function. Regulates Wnt signaling by phosphorylating CTNNB1 and the transcription factor LEF1. Acts as an ectokinase that phosphorylates several extracellular proteins. During viral infection, phosphorylates various proteins involved in the viral life cycles of EBV, HSV, HBV, HCV, HIV, CMV and HPV. Catalytic subunit of a constitutively active serine/threonine-protein kinase complex that phosphorylates a large number of substrates containing acidic residues C-terminal to the phosphorylated serine or threonine. Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder with language delay and seizures (NEDLDS) [MIM:619908]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by global developmental delay, intellectual disability, speech delay, and seizures. Additional features may include axial hypotonia, peripheral hypertonia, hypothyroidism, and non-specific dysmorphic features or brain imaging abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:35240055}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07546; DB12010 Interacts with Q8NDY6; P68400; P67870; O60282; Q9NRD5; Q8WV44; Q9BS34 EC number EC 2.7.11.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Apoptosis; ATP-binding; Cell cycle; Cytoplasm; Kinase; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Wnt signaling pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID X Molecular weight (Da) 38039.2 Length 319 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 43.61 Isoelectric point 8.29 Charge (pH=7) 3.03 3D Binding mode Sequence AGSRARVYAEVNSLRSREYWDYEAHVPSWGNQDDYQLVRKLGEVFEAINITNNERVVVKILKPVKKKKIKREVKILENLRGGTNIIKLIDTVKDPVSKTPALVFEYINNTDFKQLYQILTDFDIRFYMYELLKALDYCHSKGIMHRDVKPHNVMIDHQQKKLRLIDWGLAEFYHPAQEYNVRVASRYFKGPELLVDYQMYDYSLDMWSLGCMLASMIFRREPFFHGQDNYDQLVRIAKVLGTEELYGYLKKYHIDLDPHFNDILGQHSRKRWENFIHSENRHLVSPEALDLLDKLLRYDHQQRLTAKEAMEHPYFYPVV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 76 | Cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1) | 3PM0 | 5.22 | |
Target general information Gen name CYP1B1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CYPIB1 Protein family Cytochrome P450 family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, retinoid and xenobiotics. Preferentially oxidizes 17beta-estradiol to the carcinogenic 4-hydroxy derivative, and a variety of procarcinogenic compounds to their activated forms, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Promotes angiogenesis by removing cellular oxygenation products, thereby decreasing oxidative stress, release of antiangiogenic factor THBS2, then allowing endothelial cells migration, cell adhesion and capillary morphogenesis. These changes are concommitant with the endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity and nitric oxide synthesis. Plays an important role in the regulation of perivascular cell proliferation, migration, and survival through modulation of the intracellular oxidative state and NF-kappa-B expression and/or activity, during angiogenesis. Contributes to oxidative homeostasis and ultrastructural organization and function of trabecular meshwork tissue through modulation of POSTN expression. Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. Related diseases Anterior segment dysgenesis 6 (ASGD6) [MIM:617315]: A form of anterior segment dysgenesis, a group of defects affecting anterior structures of the eye including cornea, iris, lens, trabecular meshwork, and Schlemm canal. Anterior segment dysgeneses result from abnormal migration or differentiation of the neural crest derived mesenchymal cells that give rise to components of the anterior chamber during eye development. Different anterior segment anomalies may exist alone or in combination, including iris hypoplasia, enlarged or reduced corneal diameter, corneal vascularization and opacity, posterior embryotoxon, corectopia, polycoria, abnormal iridocorneal angle, ectopia lentis, and anterior synechiae between the iris and posterior corneal surface. Clinical conditions falling within the phenotypic spectrum of anterior segment dysgeneses include aniridia, Axenfeld anomaly, Reiger anomaly/syndrome, Peters anomaly, and iridogoniodysgenesis. ASGD6 patients predominantly manifest Peters anomaly. Peters anomaly consists of corneal leukoma, defects in the posterior structures of the cornea such as absence of the posterior corneal stroma and Descemet membrane, and a variable degree of iridocorneal and/or keratolenticular adhesions. Over 50% of patients develop glaucoma in childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11403040}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glaucoma 3, primary congenital, A (GLC3A) [MIM:231300]: An autosomal recessive form of primary congenital glaucoma (PCG). PCG is characterized by marked increase of intraocular pressure at birth or early childhood, large ocular globes (buphthalmos) and corneal edema. It results from developmental defects of the trabecular meshwork and anterior chamber angle of the eye that prevent adequate drainage of aqueous humor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10227395, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10655546, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11184479, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11527932, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11774072, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11980847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12036985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12525557, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14635112, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14640114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15255109, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15342693, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15475877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16490498, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16688110, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16735994, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16862072, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18470941, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9463332, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9497261}. The disease is caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glaucoma 1, open angle, A (GLC1A) [MIM:137750]: A form of primary open angle glaucoma (POAG). POAG is characterized by a specific pattern of optic nerve and visual field defects. The angle of the anterior chamber of the eye is open, and usually the intraocular pressure is increased. However, glaucoma can occur at any intraocular pressure. The disease is generally asymptomatic until the late stages, by which time significant and irreversible optic nerve damage has already taken place. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11774072}. The gene represented in this entry acts as a disease modifier. Digenic mutations in CYP1B1 and MYOC have been found in a family segregating both primary adult-onset and juvenile forms of open angle glaucoma (PubMed:11774072). All affected family members with mutations in both MYOC and CYP1B1 had juvenile glaucoma, whereas those with only the MYOC mutation had the adult-onset form (PubMed:11774072). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11774072}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02342; DB00613; DB06732; DB00443; DB00121; DB01222; DB00201; DB09061; DB14737; DB01254; DB00694; DB01248; DB00997; DB00470; DB00530; DB00783; DB13952; DB13953; DB13954; DB13955; DB13956; DB00655; DB07776; DB00499; DB01645; DB01381; DB00741; DB01064; DB01026; DB00448; DB14009; DB01065; DB00170; DB00959; DB01204; DB14011; DB03467; DB00338; DB01229; DB14631; DB00635; DB01087; DB00396; DB00818; DB04216; DB02709; DB00675; DB00624; DB13946; DB00277; DB12245; DB11155 Interacts with Q02763 EC number EC 1.14.14.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Disease variant; Endoplasmic reticulum; Fatty acid metabolism; Glaucoma; Heme; Iron; Lipid metabolism; Lyase; Membrane; Metal-binding; Microsome; Mitochondrion; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Peters anomaly; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Steroid metabolism Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 51875.9 Length 459 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 34.16 Isoelectric point 8.64 Charge (pH=7) 4.89 3D Binding mode Sequence QAAHLSFARLARRYGDVFQIRLGSCPIVVLNGERAIHQALVQQGSAFADRPSFASFRVVSGGRSMAFGHYSEHWKVQRRAAHSMMRNFFTRQPRSRQVLEGHVLSEARELVALLVRGSADGAFLDPRPLTVVAVANVMSAVCFGCRYSHDDPEFRELLSHNEEFGRTVGAGSLVDVMPWLQYFPNPVRTVFREFEQLNRNFSNFILDKFLRHCESLRPGAAPRDMMDAFILSAEKKAAGDGARLDLENVPATITDIFGASQDTLSTALQWLLLLFTRYPDVQTRVQAELDQVVGRDRLPCMGDQPNLPYVLAFLYEAMRFSSFVPVTIPHATTANTSVLGYHIPKDTVVFVNQWSVNHDPLKWPNPENFDPARFLDKDGLINKDLTSRVMIFSVGKRRCIGEELSKMQLFLFISILAHQCDFRANPNEPAKMNFSYGLTIKPKSFKVNVTLRESMELLD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 77 | Dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation regulated kinase 3 (DYRK3) | 5Y86 | 5.22 | |
Target general information Gen name DYRK3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Regulatory erythroid kinase; REDK; Dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 3 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, MNB/DYRK subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Dual-specificity tyrosine-regulated kinases (DYRKs) autophosphorylate a critical tyrosine residue in their activation loop and phosphorylate their substrate on serine and threonine residues. Acts as a central dissolvase of membraneless organelles during the G2-to-M transition, after the nuclear-envelope breakdown: acts by mediating phosphorylation of multiple serine and threonine residues in unstructured domains of proteins, such as SRRM1 and PCM1. Does not mediate disassembly of all membraneless organelles: disassembly of P-body and nucleolus is not regulated by DYRK3. Dissolution of membraneless organelles at the onset of mitosis is also required to release mitotic regulators, such as ZNF207, from liquid-unmixed organelles where they are sequestered and keep them dissolved during mitosis. Regulates mTORC1 by mediating the dissolution of stress granules: during stressful conditions, DYRK3 partitions from the cytosol to the stress granule, together with mTORC1 components, which prevents mTORC1 signaling. When stress signals are gone, the kinase activity of DYRK3 is required for the dissolution of stress granule and mTORC1 relocation to the cytosol: acts by mediating the phosphorylation of the mTORC1 inhibitor AKT1S1, allowing full reactivation of mTORC1 signaling. Also acts as a negative regulator of EPO-dependent erythropoiesis: may place an upper limit on red cell production during stress erythropoiesis. Inhibits cell death due to cytokine withdrawal in hematopoietic progenitor cells. Promotes cell survival upon genotoxic stress through phosphorylation of SIRT1: this in turn inhibits p53/TP53 activity and apoptosis. Dual-specificity protein kinase that promotes disassembly of several types of membraneless organelles during mitosis, such as stress granules, nuclear speckles and pericentriolar material. Related diseases Defects in MELK are associated with some cancers, such as brain or breast cancers. Expression is dramatically increased in aggressive undifferentiated tumors, correlating with poor patient outcome in breast and brain cancers, suggesting a role in tumor-initiating cells and proliferation via its function in cell proliferation regulation. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9H8Y8 EC number EC 2.7.12.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cell cycle; Cell division; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Kinase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Mitosis; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 44821.5 Length 395 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 49.38 Isoelectric point 9.52 Charge (pH=7) 21.08 3D Binding mode Sequence VVPLTPEQALKQYKHHLTAYEKLEIINYPEIYFVGPNAKKRHGVIGGPNNGGYDDADGAYIHVPRDHLAYRYEVLKIIGKGSFGQVARVYDHKLRQYVALKMVRNEKRFHRQAAEEIRILEHLKKQDKTGSMNVIHMLESFTFRNHVCMAFELLSIDLYELIKKNKFQGFSVQLVRKFAQSILQSLDALHKNKIIHCDLKPENILLKHHGRSXTKVIDFGSSCFEYQKLYTXIQSRFYRAPEIILGSRYSTPIDIWSFGCILAELLTGQPLFPGEDEGDQLACMMELLGMPPPKLLEQSKRAKYFINXKGIPRYCSVTTQADGRVVLVGGRSRRGKKRGPPGSKDWGTALKGCDDYLFIEFLKRCLHWDPSARLXPAQALRHPWISKSVPRPLTT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 78 | Neprilysin | 1R1H | 5.21 | |
Target general information Gen name MME Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms EPN Protein family Peptidase M13 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Endopeptidase activity.Exopeptidase activity.Metalloendopeptidase activity.Metallopeptidase activity.Peptide binding.Zinc ion binding. Related diseases Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, 2T (CMT2T) [MIM:617017]: An axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal degeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26991897, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27588448}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spinocerebellar ataxia 43 (SCA43) [MIM:617018]: A form of spinocerebellar ataxia, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of cerebellar disorders. Patients show progressive incoordination of gait and often poor coordination of hands, speech and eye movements, due to degeneration of the cerebellum with variable involvement of the brainstem and spinal cord. SCA43 is a slowly progressive, autosomal dominant form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27583304}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08575; DB02597; DB00616; DB11623; DB05796; DB06655; DB02558; DB02062; DB00886; DB02557; DB09292; DB13928; DB08626 Interacts with P05067; P21926; Q06787-7; P08107; P04792 EC number 3.4.24.11 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Myristate; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathy; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal-anchor; Spinocerebellar ataxia; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 79435.8 Length 696 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.5 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -11.46 3D Binding mode Sequence GICKSSDCIKSAARLIQNMDATTEPCTDFFKYACGGWLKRNVIPETSSRYGNFDILRDELEVVLKDVLQEPKTEDIVAVQKAKALYRSCINESAIDSRGGEPLLKLLPDIYGWPVATENWEQKYGASWTAEKAIAQLNSKYGKKVLINLFVGTDDKNSVNHVIHIDQPRLGLPSRDYYECTGIYKEACTAYVDFMISVARLIRQEERLPIDENQLALEMNKVMELEKEIANATAKPEDRNDPMLLYNKMTLAQIQNNFSLEINGKPFSWLNFTNEIMSTVNISITNEEDVVVYAPEYLTKLKPILTKYSARDLQNLMSWRFIMDLVSSLSRTYKESRNAFRKALYGTTSETATWRRCANYVNGNMENAVGRLYVEAAFAGESKHVVEDLIAQIREVFIQTLDDLTWMDAETKKRAEEKALAIKERIGYPDDIVSNDNKLNNEYLELNYKEDEYFENIIQNLKFSQSKQLKKLREKVDKDEWISGAAVVNAFYSSGRNQIVFPAGILQPPFFSAQQSNSLNYGGIGMVIGHEITHGFDDNGRNFNKDGDLVDWWTQQSASNFKEQSQCMVYQYGNFSWDLAGGQHLNGINTLGENIADNGGLGQAYRAYQNYIKKNGEEKLLPGLDLNHKQLFFLNFAQVWCGTYRPEYAVNSIKTDVHSPGNFRIIGTLQNSAEFSEAFHCRKNSYMNPEKKCRVW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 79 | Cytochrome b (Complex III subunit 3) (Complex III subunit III) (Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 3) (Ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase complex cytochrome b subunit) | 1SQB | 5.21 | |
Target general information Gen name MT-CYB Organism Bos taurus (Bovine) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CYTB;MTCYB;COB Protein family Cytochrome b family Biochemical class NA Function Component of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex (complex III or cytochrome b-c1 complex) that is part of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The b-c1 complex mediates electron transfer from ubiquinol to cytochrome c. Contributes to the generation of a proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane that is then used for ATP synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1327781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20025846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9485330, ECO:0000305|PubMed:189810}." Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 6 (COXPD6) [MIM:300816]: A mitochondrial disease resulting in a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by psychomotor delay, hypotonia, areflexia, muscle weakness and wasting. Some patients manifest prenatal ventriculomegaly and severe postnatal encephalomyopathy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20362274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22019070, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25583628, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26004228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26173962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27178839}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, X-linked recessive, 4, with or without cerebellar ataxia (CMTX4) [MIM:310490]: A neuromuscular disorder characterized by progressive sensorimotor axonal neuropathy, distal sensory impairment, difficulty walking due to peripheral neuropathy and/or cerebellar ataxia, and deafness due to auditory neuropathy. Additional features include cognitive impairment, cerebellar atrophy, dysarthria, abnormal extraocular movements, tremor, dysmetria and spasticity. The age at onset ranges from infancy to young adulthood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23217327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26004228}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Deafness, X-linked, 5, with peripheral neuropathy (DFNX5) [MIM:300614]: A form of hearing loss characterized by absent or severely abnormal auditory brainstem response, abnormal middle ear reflexes, abnormal speech discrimination, loss of outer hair cell function, and cochlear nerve hypoplasia. DFNX5 patients manifest auditory neuropathy with childhood onset, associated with distal sensory impairment affecting the peripheral nervous system. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25986071}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, X-linked, with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy (SEMDHL) [MIM:300232]: An X-linked recessive developmental disorder characterized by slowly progressive skeletal and neurologic abnormalities, including short stature, large and deformed joints, significant motor impairment, visual defects, and sometimes cognitive deficits. Affected individuals typically have normal early development in the first year or so of life, followed by development regression and the development of symptoms. Brain imaging shows white matter abnormalities consistent with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842795}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Electron transport; Heme; Iron; Membrane; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Reference proteome; Respiratory chain; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubiquinone Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C,D,F,G,H Molecular weight (Da) 99281.2 Length 866 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 43.81 Isoelectric point 8.32 Charge (pH=7) 7.12 3D Binding mode Sequence VSASSRWLEGIRKWYYNAAGFNKLGLMRDDTIHENDDVKEAIRRLPENLYDDRVFRIKRALDLSMRQQILPKEQWTKYEEDKSYLEPYLKEVIRERKEREEWAKKELVDPLTTVREQCEQLEKCVKARERLELCDERVSSRSQTEEDCTEELLDFLHARDHCVAHKLFNSLKTNIRKSHPLMKIVNNAFIDLPAPSNISSWWNFGSLLGICLILQILTGLFLAMHYTSDTTTAFSSVTHICRDVNYGWIIRYMHANGASMFFICLYMHVGRGLYYGSYTFLETWNIGVILLLTVMATAFMGYVLPWGQMSFWGATVITNLLSAIPYIGTNLVEWIWGGFSVDKATLTRFFAFHFILPFIIMAIAMVHLLFLHETGSNNPTGISSDVDKIPFHPYYTIKDILGALLLILALMLLVLFAPDLLGDPDNYTPANPLNTPPHIKPEWYFLFAYAILRSIPNKLGGVLALAFSILILALIPLLHTSKQRSMMFRPLSQCLFWALVADLLTLTWIGGQPVEHPYITIGQLASVLYFLLILVLMPTAGTIENKLLKWSDLELHPPSYPWSHRGLLSSLDHTSIRRGFQVYKQVCSSCHSMDYVAYRHLVGVCYTEDEAKALAEEVEVQDGPNEDGEMFMRPGKLSDYFPKPYPNPEAARAANNGALPPDLSYIVRARHGGEDYVFSLLTGYCEPPTGVSLREGLYFNPYFPGQAIGMAPPIYNEVLEFDDGTPATMSQVAKDVCTFLRWAAEPEHDHRKRMGLKMLLMMGLLLPLVYAMKRHKWSVLKSRKLAYRPPKGRQFGHLTRVRHVITYSLSPFEQRAFPHYFSKGIPNVLRRTRACILRVAPPFVAFYLVYTWGTQEFEKSKRKNPA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 80 | Fatty acid-binding protein, intestinal | 3AKM | 5.21 | |
Target general information Gen name FABP2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms FABPI Protein family Calycin superfamily, Fatty-acid binding protein (FABP) family Biochemical class Transport protein Function Fatty acid binding.Transporter activity. Related diseases Usher syndrome 3B (USH3B) [MIM:614504]: A syndrome characterized by progressive vision and hearing loss during early childhood. Some patients have the so-called 'Charles Bonnet syndrome,' involving decreased visual acuity and vivid visual hallucinations. USH is a genetically heterogeneous condition characterized by the association of retinitis pigmentosa with sensorineural deafness. Age at onset and differences in auditory and vestibular function distinguish Usher syndrome type 1 (USH1), Usher syndrome type 2 (USH2) and Usher syndrome type 3 (USH3). USH3 is characterized by postlingual, progressive hearing loss, variable vestibular dysfunction, and onset of retinitis pigmentosa symptoms, including nyctalopia, constriction of the visual fields, and loss of central visual acuity, usually by the second decade of life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22279524}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, 2W (CMT2W) [MIM:616625]: An autosomal dominant, axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal degeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. CMT2W patients manifest a peripheral neuropathy mainly affecting the lower limbs and resulting in gait difficulties and distal sensory impairment. Most patients also have upper limb involvement. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22930593, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26072516, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29235198}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04557; DB09213; DB00783; DB13952; DB13953; DB13954; DB13955; DB13956; DB01050; DB08231; DB03796; DB01138 Interacts with O95994; Q9NYB0 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Lipid-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 15075.9 Length 131 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 32.01 Isoelectric point 6.88 Charge (pH=7) -0.09 3D Binding mode Sequence AFDSTWKVDRSENYDKFMEKMGVNIVKRKLAAHDNLKLTITQEGNKFTVKESSAFRNIEVVFELGVTFNYNLADGTELRGTWSLEGNKLIGKFKRTDNGNELNTVREIIGDELVQTYVYEGVEAKRIFKKD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||