Job Results:
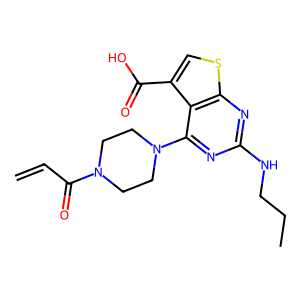
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
57b30c77c1e7b273b1e911481965e4cd
Job name
NA
Time
2025-10-13 17:21:20
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | 4-cresol dehydrogenase [hydroxylating] flavoprotein subunit | 1WVF | 6.66 | |
Target general information Gen name pchF Organism Pseudomonas putida (Arthrobacter siderocapsulatus) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family NA Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function 4-cresol dehydrogenase (hydroxylating) activity.Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.Oxidoreductase activity, acting on CH-OH group of donors. Related diseases Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency (DLDD) [MIM:246900]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized biochemically by a combined deficiency of the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC), pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC), and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (KGDC). Clinically, affected individuals have lactic acidosis and neurologic deterioration due to sensitivity of the central nervous system to defects in oxidative metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10448086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11687750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12925875, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15712224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16442803, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16770810, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17404228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20160912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8506365, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8968745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9540846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9934985}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147 Interacts with NA EC number 1.17.9.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Oxidoreductase; Plasmid Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 57240.8 Length 515 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 30.94 Isoelectric point 6.06 Charge (pH=7) -4.42 3D Binding mode Sequence AVLPKGVTQGEFNKAVQKFRALLGDDNVLVESDQLVPYNKIMMPVENAAHAPSAAVTATTVEQVQGVVKICNEHKIPIWTISTGRNFGYGSAAPVQRGQVILDLKKMNKIIKIDPEMCYALVEPGVTFGQMYDYIQENNLPVMLSFSAPSAIAGPVGNTMDRGVGYTPYGEHFMMQCGMEVVLANGDVYRTGMGGVPGSNTWQIFKWGYGPTLDGMFTQANYGICTKMGFWLMPKPPVFKPFEVIFEDEADIVEIVDALRPLRMSNTIPNSVVIASTLWEAGSAHLTRAQYTTEPGHTPDSVIKQMQKDTGMGAWNLYAALYGTQEQVDVNWKIVTDVFKKLGKGRIVTQEEAGDTQPFKYRAQLMSGVPNLQEFGLYNWRGGGGSMWFAPVSEARGSECKKQAAMAKRVLHKYGLDYVAEFIVAPRDMHHVIDVLYDRTNPEETKRADACFNELLDEFEKEGYAVYRVNTRFQDRVAQSYGPVKRKLEHAIKRAVDPNNILAPGRSGIDLNNDF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 42 | Benzoate 1,2-dioxygenase electron transfer component | 1KRH | 6.66 | |
Target general information Gen name benC Organism Acinetobacter baylyi (strain ATCC 33305 / BD413 / ADP1) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms ACIAD1438 Protein family Bacterial ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase ferredoxin reductase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding.Electron carrier activity.Ferredoxin-NAD+ reductase activity.Metal ion binding. Related diseases Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency (APRTD) [MIM:614723]: An enzymatic deficiency that can lead to urolithiasis and renal failure. Patients have 2,8-dihydroxyadenine (DHA) urinary stones. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11243733, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1353080, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15571218, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1746557, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21635362, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3343350, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3680503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7915931}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147 Interacts with NA EC number 1.18.1.3 Uniprot keywords 2Fe-2S; 3D-structure; Aromatic hydrocarbons catabolism; FAD; Flavoprotein; Iron; Iron-sulfur; Metal-binding; NAD; Oxidoreductase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 37496.7 Length 337 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 47.02 Isoelectric point 4.75 Charge (pH=7) -18.87 3D Binding mode Sequence SNHQVALQFEDGVTRFICIAQGETLSDAAYRQQINIPMDCREGECGTCRAFCESGNYDMPEDNYIEDALTPEEAQQGYVLACQCRPTSDAVFQIQASSEVCKTKIHHFEGTLARVENLSDSTITFDIQLDDGQPDIHFLAGQYVNVTLPGTTETRSYSFSSQPGNRLTGFVVRNVPQGKMSEYLSVQAKAGDKMSFTGPFGSFYLRDVKRPVLMLAGGTGIAPFLSMLQVLEQKGSEHPVRLVFGVTQDCDLVALEQLDALQQKLPWFEYRTVVAHAESQHERKGYVTGHIEYDWLNGGEVDVYLCGPVPMVEAVRSWLDTQGIQPANFLFEKFSAN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 43 | Monoamine oxidase type A (MAO-A) | 2Z5Y | 6.66 | |
Target general information Gen name MAOA Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Monoamine oxidase A; Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] A Protein family Flavin monoamine oxidase family Biochemical class CH-NH(2) donor oxidoreductase Function MAOA preferentially oxidizes biogenic amines such as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), norepinephrine and epinephrine. Catalyzes the oxidative deamination of biogenic and xenobiotic amines and has important functions in the metabolism of neuroactive and vasoactive amines in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. Related diseases Brunner syndrome (BRNRS) [MIM:300615]: A form of X-linked non-dysmorphic mild intellectual disability. Male patients are affected by borderline intellectual deficit and exhibit abnormal behavior, including disturbed regulation of impulsive aggression. Obligate female carriers have normal intelligence and behavior. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8211186}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01472; DB00918; DB00182; DB06698; DB04889; DB13876; DB01445; DB06774; DB00215; DB04017; DB09130; DB05205; DB07641; DB00988; DB01363; DB00668; DB12329; DB01175; DB03147; DB14914; DB00614; DB01381; DB07919; DB04818; DB01247; DB00601; DB01577; DB00805; DB01442; DB01171; DB08804; DB00952; DB04820; DB00184; DB04821; DB06412; DB01626; DB00780; DB00191; DB00388; DB00397; DB09244; DB04850; DB00721; DB01168; DB00571; DB00852; DB09363; DB00140; DB00953; DB06654; DB01037; DB01104; DB00669; DB14569; DB09042; DB00624; DB13943; DB13944; DB13946; DB09245; DB00752; DB15328; DB09185; DB04832; DB00315; DB00909 Interacts with P27338 EC number EC 1.4.3.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Catecholamine metabolism; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; FAD; Flavoprotein; Intellectual disability; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion outer membrane; Neurotransmitter degradation; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 58195.3 Length 513 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 34.97 Isoelectric point 7.98 Charge (pH=7) 2.87 3D Binding mode Sequence HMFDVVVIGGGISGLSAAKLLTEYGVSVLVLEARDRVGGRTYTIRNEHVDYVDVGGAYVGPTQNRILRLSKELGIETYKVNVSERLVQYVKGKTYPFRAAFPPVWNPIAYLDYNNLWRTIDNMGKEIPTDAPWEAQHADKWDKMTMKELIDKICWTKTARRFAYLFVNINVTSEPHEVSALWFLWYVKQCGGTTRIFSVTNGGQERKFVGGSGQVSERIMDLLGDQVKLNHPVTHVDQSSDNIIIETLNHEHYECKYVINAIPPTLTAKIHFRPELPAERNQLIQRLPMGAVIKCMMYYKEAFWKKKDYCGCMIIEDEDAPISITLDDTKPDGSLPAIMGFILARKADRLAKLHKEIRKKKICELYAKVLGSQEALHPVHYEEKNWCEEQYSGGCYTAYFPPGIMTQYGRVIRQPVGRIFFAGTETATKWSGYMEGAVEAGERAAREVLNGLGKVTEKDIWVQEPESKDVPAVEITHTFWERNLPSVSGLLKIIGFSTSVTALGFVLYKYKLL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 44 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EHMT2 (EHMT2) | 5VSC | 6.65 | |
Target general information Gen name EHMT2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein G9a; NG36; Lysine N-methyltransferase 1C; KMT1C; Histone H3-K9 methyltransferase 3; HLA-B-associated transcript 8; H3-K9-HMTase 3; G9A; Euchromatic histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2; C6orf3 Protein family Class V-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, Histone-lysine methyltransferase family, Suvar3-9 subfamily Biochemical class Methyltransferase Function H3K9me represents a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional repression by recruiting HP1 proteins to methylated histones. Also mediates monomethylation of 'Lys-56' of histone H3 (H3K56me1) in G1 phase, leading to promote interaction between histone H3 and PCNA and regulating DNA replication. Also weakly methylates 'Lys-27' of histone H3 (H3K27me). Also required for DNA methylation, the histone methyltransferase activity is not required for DNA methylation, suggesting that these 2 activities function independently. Probably targeted to histone H3 by different DNA-binding proteins like E2F6, MGA, MAX and/or DP1. May also methylate histone H1. In addition to the histone methyltransferase activity, also methylates non-histone proteins: mediates dimethylation of 'Lys-373' of p53/TP53. Also methylates CDYL, WIZ, ACIN1, DNMT1, HDAC1, ERCC6, KLF12 and itself. Histone methyltransferase that specifically mono- and dimethylates 'Lys-9' of histone H3 (H3K9me1 and H3K9me2, respectively) in euchromatin. Related diseases Pseudohypoaldosteronism 2C (PHA2C) [MIM:614492]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by severe hypertension, hyperkalemia, hyperchloremia, mild hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis in some cases, and correction of physiologic abnormalities by thiazide diuretics. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11498583}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Neuropathy, hereditary sensory and autonomic, 2A (HSAN2A) [MIM:201300]: A form of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy, a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by degeneration of dorsal root and autonomic ganglion cells, and by sensory and/or autonomic abnormalities. HSAN2A is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by impairment of pain, temperature and touch sensation, onset of symptoms in infancy or early childhood, occurrence of distal extremity pathologies (paronychia, whitlows, ulcers, and Charcot joints), frequent amputations, sensory loss that affects all modalities of sensation (lower and upper limbs and perhaps the trunk as well), absence or diminution of tendon reflexes (usually in all limbs), minimal autonomic dysfunction, absence of sensory nerve action potentials, and virtual absence of myelinated fibers with decreased numbers of unmyelinated fibers in sural nerves. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15060842, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15911806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18521183}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q6VMQ6-2; Q6P1J9; Q9UBC3; P38919; Q9UM22; P23771; Q99684; Q13547; Q96JB3; Q92831; O60341-1; Q9Y4X4; P57682; Q13330; O94776; Q9BTC8; P20592; Q9BSU3; Q99801-1; O60568; Q9NQX1; Q5JSZ5; Q7Z3Z2; Q9P2R6; Q14119; Q96GT9; O60315; Q9NWS9-2; Q96JM2; A0A0S2Z5X4; Q96BV0; Q96EG3; Q07120; O60341-1 EC number EC 2.1.1.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ANK repeat; Chromatin regulator; Chromosome; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Methylation; Methyltransferase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 31010.9 Length 269 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 47.49 Isoelectric point 5.16 Charge (pH=7) -9.31 3D Binding mode Sequence TEKIICRDVARGYENVPIPCVNGVDGEPCPEDYKYISENCETSTMNIDRNITHLQHCTCVDDCSSSNCLCGQLSIRCWYDKDGRLLQEFNKIEPPLIFECNQACSCWRNCKNRVVQSGIKVRLQLYRTAKMGWGVRALQTIPQGTFICEYVGELISDAEADVREDDSYLFDLDEVYCIDARYYGNISRFINHLCDPNIIPVRVFMLHQDLRFPRIAFFSSRDIRTGEELGFDYGDRFWDIKSKYFTCQCGSEKCKHSAEAIALEQSRLA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 45 | Lysine N-methyltransferase 3A (SETD2) | 7LZD | 6.65 | |
Target general information Gen name SETD2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms p231HBP; hSET2; SET2; SET domain-containing protein 2; Protein-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD2; KMT3A; KIAA1732; Huntingtin-interacting protein B; Huntingtin-interacting protein 1; Huntingtin yeast p Protein family Class V-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, Histone-lysine methyltransferase family, SET2 subfamily Biochemical class Methyltransferase Function Represents the main enzyme generating H3K36me3, a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional activation. Plays a role in chromatin structure modulation during elongation by coordinating recruitment of the FACT complex and by interacting with hyperphosphorylated POLR2A. Acts as a key regulator of DNA mismatch repair in G1 and early S phase by generating H3K36me3, a mark required to recruit MSH6 subunit of the MutS alpha complex: early recruitment of the MutS alpha complex to chromatin to be replicated allows a quick identification of mismatch DNA to initiate the mismatch repair reaction. Required for DNA double-strand break repair in response to DNA damage: acts by mediating formation of H3K36me3, promoting recruitment of RAD51 and DNA repair via homologous recombination (HR). Acts as a tumor suppressor. H3K36me3 also plays an essential role in the maintenance of a heterochromatic state, by recruiting DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A. H3K36me3 is also enhanced in intron-containing genes, suggesting that SETD2 recruitment is enhanced by splicing and that splicing is coupled to recruitment of elongating RNA polymerase. Required during angiogenesis. Required for endoderm development by promoting embryonic stem cell differentiation toward endoderm: acts by mediating formation of H3K36me3 in distal promoter regions of FGFR3, leading to regulate transcription initiation of FGFR3. In addition to histones, also mediates methylation of other proteins, such as tubulins and STAT1. Trimethylates 'Lys-40' of alpha-tubulins such as TUBA1B (alpha-TubK40me3); alpha-TubK40me3 is required for normal mitosis and cytokinesis and may be a specific tag in cytoskeletal remodeling. Involved in interferon-alpha-induced antiviral defense by mediating both monomethylation of STAT1 at 'Lys-525' and catalyzing H3K36me3 on promoters of some interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) to activate gene transcription. Histone methyltransferase that specifically trimethylates 'Lys-36' of histone H3 (H3K36me3) using dimethylated 'Lys-36' (H3K36me2) as substrate. Related diseases Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) [MIM:144700]: Renal cell carcinoma is a heterogeneous group of sporadic or hereditary carcinoma derived from cells of the proximal renal tubular epithelium. It is subclassified into clear cell renal carcinoma (non-papillary carcinoma), papillary renal cell carcinoma, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, collecting duct carcinoma with medullary carcinoma of the kidney, and unclassified renal cell carcinoma. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma is the most common subtype. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20054297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23622243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23792563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25728682}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Defects of SETD2 are associated with loss of DNA methylation at non-promoter regions (PubMed:23792563). SETD2 defects lead to aberrant and reduced nucleosome compaction and chromatin association of key replication proteins, such as MCM7 and DNA polymerase delta, leading to hinder replication fork progression and prevent loading of RAD51 homologous recombination repair factor at DNA breaks (PubMed:25728682). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23792563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25728682}.; DISEASE: Luscan-Lumish syndrome (LLS) [MIM:616831]: An autosomal dominant syndrome with a variable phenotype. Clinical features include macrocephaly, distinctive facial appearance, postnatal overgrowth, various degrees of learning difficulties, autism spectrum disorder, and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23160955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24852293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26084711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27317772}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute lymphoblastic (ALL) [MIM:613065]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. ALL is a malignant disease of bone marrow and the most common malignancy diagnosed in children. The malignant cells are lymphoid precursor cells (lymphoblasts) that are arrested in an early stage of development. The lymphoblasts replace the normal marrow elements, resulting in a marked decrease in the production of normal blood cells. Consequently, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia occur to varying degrees. The lymphoblasts also proliferate in organs other than the marrow, particularly the liver, spleen, and lymphnodes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24509477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24662245}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML) [MIM:601626]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. AML is a malignant disease of bone marrow characterized by maturational arrest of hematopoietic precursors at an early stage of development. Clonal expansion of myeloid blasts occurs in bone marrow, blood, and other tissue. Myelogenous leukemias develop from changes in cells that normally produce neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils and monocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16314571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24509477}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 70 (MRD70) [MIM:620157]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by mild global developmental delay, moderately impaired intellectual disability with speech difficulties, and behavioral abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32710489}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Rabin-Pappas syndrome (RAPAS) [MIM:620155]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by severely impaired global development, intellectual disability, microcephaly, facial dysmorphism, and variable congenital anomalies affecting the skeletal, genitourinary, cardiac, and other organ systems. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32710489}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P42858; P84022 EC number EC 2.1.1.43 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; Alternative splicing; Antiviral defense; Autism spectrum disorder; Chromatin regulator; Chromosome; Coiled coil; Developmental protein; Differentiation; Disease variant; DNA damage; DNA repair; Host-virus interaction; Immunity; Innate immunity; Intellectual disability; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Methyltransferase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Tumor suppressor; Ubl conjugation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 27416.8 Length 237 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 55.47 Isoelectric point 7.51 Charge (pH=7) 0.99 3D Binding mode Sequence GPSCVMDDFRDPQRWKECAKQGKMPCYFDLIEENVYLTERRMQCECTPLSKDERAQGEIACGEDCLNRLLMIECSSRCPNGDYCSNRRFQRKQHADVEVILTEKKGWGLRAAKDLPSNTFVLEYCGEVLDHKEFKARVKEYARNKNIHYYFMALKNDEIIDATQKGNCSRFMNHSCEPNCETQKWTVNGQLRVGFFTTKLVPSGSELTFDYQFQRYGKEAQKCFCGSANCRGYLGGE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 46 | GTPase HRas (HRAS) | 7L0F | 6.65 | |
Target general information Gen name HRAS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms p21ras; cHras; c-H-ras; Transforming protein p21; HaRas; Ha-Ras; H-Ras-1; GTPase HRas, Nterminally processed Protein family Small GTPase superfamily, Ras family Biochemical class Small GTPase Function Ras proteins bind GDP/GTP and possess intrinsic GTPase activity. Involved in the activation of Ras protein signal transduction. Related diseases Costello syndrome (CSTLO) [MIM:218040]: A rare condition characterized by prenatally increased growth, postnatal growth deficiency, intellectual disability, distinctive facial appearance, cardiovascular abnormalities (typically pulmonic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and/or atrial tachycardia), tumor predisposition, skin and musculoskeletal abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16170316, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16329078, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16443854, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17054105, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18039947, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18247425, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19995790}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Congenital myopathy with excess of muscle spindles (CMEMS) [MIM:218040]: Variant of Costello syndrome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17412879}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thyroid cancer, non-medullary, 2 (NMTC2) [MIM:188470]: A form of non-medullary thyroid cancer (NMTC), a cancer characterized by tumors originating from the thyroid follicular cells. NMTCs represent approximately 95% of all cases of thyroid cancer and are classified into papillary, follicular, Hurthle cell, and anaplastic neoplasms. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12727991}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Mutations which change positions 12, 13 or 61 activate the potential of HRAS to transform cultured cells and are implicated in a variety of human tumors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:3670300}.; DISEASE: Bladder cancer (BLC) [MIM:109800]: A malignancy originating in tissues of the urinary bladder. It often presents with multiple tumors appearing at different times and at different sites in the bladder. Most bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas that begin in cells that normally make up the inner lining of the bladder. Other types of bladder cancer include squamous cell carcinoma (cancer that begins in thin, flat cells) and adenocarcinoma (cancer that begins in cells that make and release mucus and other fluids). Bladder cancer is a complex disorder with both genetic and environmental influences. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:6298635, ECO:0000269|PubMed:6844927}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Schimmelpenning-Feuerstein-Mims syndrome (SFM) [MIM:163200]: A disease characterized by sebaceous nevi, often on the face, associated with variable ipsilateral abnormalities of the central nervous system, ocular anomalies, and skeletal defects. Many oral manifestations have been reported, not only including hypoplastic and malformed teeth, and mucosal papillomatosis, but also ankyloglossia, hemihyperplastic tongue, intraoral nevus, giant cell granuloma, ameloblastoma, bone cysts, follicular cysts, oligodontia, and odontodysplasia. Sebaceous nevi follow the lines of Blaschko and these can continue as linear intraoral lesions, as in mucosal papillomatosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22683711}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04315; DB04137; DB02210; DB08751; DB03226; DB15588 Interacts with Q99996-3; P53677-2; P10398; Q9NXL2-1; Q9UII2; Q9H7T9; Q00994; Q9H2G9; P15056; Q7Z569; Q5PSV4; Q9ULD4-2; Q96LL4; Q96HB5; Q49A88-3; Q96GN5-2; P24941; O95674; Q9H3R5; Q9Y4F5-3; Q86XR8; Q494V2-2; Q8WUX9; Q14117; Q9Y6W6; O14641; A0AVK6; Q8NB25; Q8IZU1; O94868-3; P15407; P15408; P52655; Q96CS2; Q9BT25; Q8IV36; O43248; Q53GQ0; P10809; Q8NDH6-2; Q8IY31-2; Q8NA54; Q13352; P28290-2; Q9BVG8-5; Q2M2Z5; Q6P597; P57682; Q9UH77; P08727; Q14525; Q14847-2; Q96LR2; P27338; Q99558; Q96EZ8; Q8TAC0; Q5JXC2; Q8NEH6; Q9Y605; Q96HT8; Q9GZM8; P21359; Q8N5V2; Q6PHZ7; Q9BZ95-3; A5D8V7; O43482; Q9BR81; O15534; Q9BUL5; O00329; O00329-2; Q9UPR0; Q96I34; Q15435-3; P04049; P11233; Q15311; Q12967; Q9NS23-2; Q9NS23-4; Q8WWW0; Q8TBY0; Q9P2K3-2; Q9NZL6; O15211; Q8IXN7; Q13671; Q13671-1; Q8WVD3; Q9BY12-3; Q13435; Q12824; Q13573; Q07889; Q86W54-2; Q92783-2; O75886; Q13586; Q8N4C7; O75528; P54274-2; Q9BXU0; Q5T0J7-2; Q5T1C6; Q8IUR5-4; P36406; Q86WT6-2; Q99598; Q6PF05; Q9UGJ1-2; Q9Y5Z9; P22415; Q495M9; Q9H270; Q8NEZ2; P19544-6; O43829; Q9C0F3; Q7Z637; Q86V28; P42337; Q9Z0S9; Q9EQZ6; P27671; Q5EBH1; Q5EBH1-1; P52306-5 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; GTP-binding; Hydrolase; Isopeptide bond; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Methylation; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Palmitate; Prenylation; Proteomics identification; Proto-oncogene; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID E,F Molecular weight (Da) 28737.2 Length 259 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 30.69 Isoelectric point 5.64 Charge (pH=7) -4.15 3D Binding mode Sequence MTEYKLVVVGAGGVGKSALTIQLIQNHFVDEYDPTIEDSYRKQVVIDGETCLLDILDTAGQEEYSAMRDQYMRTGEGFLCVFAINNTKSFEDIHQYREQIKRVKDSDDVPMVLVGNKCDLAARTVESRQAQDLARSYGIPYIETSAKTRQGVEDAFYTLVREIRQHSVPTKLEVVAATPTSLLISWDAPAVTVFFYIIAYGETGHGVGAFQAFRVPGSKSTATISGLKPGVDYTITVYARGYSKQGPYKPSPISINYRT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 47 | Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 1ZMD | 6.63 | |
Target general information Gen name DLD Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms PHE3;LAD;GCSL Protein family Class-I pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase activity.Electron carrier activity.Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.Lipoamide binding.NAD binding. Related diseases Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency (DLDD) [MIM:246900]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized biochemically by a combined deficiency of the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC), pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC), and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (KGDC). Clinically, affected individuals have lactic acidosis and neurologic deterioration due to sensitivity of the central nervous system to defects in oxidative metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10448086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11687750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12925875, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15712224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16442803, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16770810, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17404228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20160912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8506365, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8968745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9540846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9934985}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147; DB00145; DB00157 Interacts with P42858; O14713; O00330; P30041; P62258 EC number 1.8.1.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cell projection; Cilium; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; FAD; Flagellum; Flavoprotein; Mitochondrion; NAD; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Redox-active center; Reference proteome; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H Molecular weight (Da) 49832.7 Length 471 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 26.19 Isoelectric point 6.51 Charge (pH=7) -2.02 3D Binding mode Sequence PIDADVTVIGSGPGGYVAAIKAAQLGFKTVCIEKNETLGGTCLNVGCIPSKALLNNSHYYHMAHGTDFASRGIEMSEVRLNLDKMMEQKSTAVKALTGGIAHLFKQNKVVHVNGYGKITGKNQVTATKADGGTQVIDTKNILIATGSEVTPFPGITIDEDTIVSSTGALSLKKVPEKMVVIGAGVIGVELGSVWQRLGADVTAVEFLGHVGGVGIDMEISKNFQRILQKQGFKFKLNTKVTGATKKSDGKIDVSIEAASGGKAEVITCDVLLVCIGRRPFTKNLGLEELGIELDPRGRIPVNTRFQTKIPNIYAIGDVVAGPMLAHKAEDEGIICVEGMAGGAVHIDYNCVPSVIYTHPEVAWVGKSEEQLKEEGIEYKVGKFPFAANSRAKTNADTDGMVKILGQKSTDRVLGAHILGPGAGEMVNEAALALEYGASCEDIARVCHAHPTLSEAFREANLAASFGKSINF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 48 | 2-oxopropyl-CoM reductase, carboxylating | 1MO9 | 6.63 | |
Target general information Gen name xecC Organism Xanthobacter autotrophicus (strain ATCC BAA-1158 / Py2) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms Xaut_4867 Protein family Class-I pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function 2-oxopropyl-CoM reductase (carboxylating) activity.Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding. Related diseases LTC4 synthase deficiency is associated with a neurometabolic developmental disorder characterized by muscular hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, and microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10896305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9820300}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03163; DB03147 Interacts with NA EC number 1.8.1.5 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Disulfide bond; FAD; Flavoprotein; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Plasmid; Redox-active center; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 114413 Length 1044 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 25.66 Isoelectric point 5.68 Charge (pH=7) -21.74 3D Binding mode Sequence KVWNARNDHLTINQWATRIDEILEAPDGGEVIYNVDENDPREYDAIFIGGGAAGRFGSAYLRAMGGRQLIVDRWPFLGGSCPHNACVPHHLFSDCAAELMLARTFSGQYWFPDMTEKVVGIKEVVDLFRAGRNGPHGIMNFQSKEQLNLEYILNCPAKVIDNHTVEAAGKVFKAKNLILAVGAGPGTLDVPGVNAKGVFDHATLVEELDYEPGSTVVVVGGSKTAVEYGCFFNATGRRTVMLVRTEPLKLIKDNETRAYVLDRMKEQGMEIISGSNVTRIEEDANGRVQAVVAMTPNGEMRIETDFVFLGLGEQPRSAELAKILGLDLGPKGEVLVNEYLQTSVPNVYAVGDLIGGPMEMFKARKSGCYAARNVMGEKISYTPKNYPDFLHTHYEVSFLGMGEEEARAAGHEIVTIKMPPDTENGLNVALPASDRTMLYAFGKGTAHMSGFQKIVIDAKTRKVLGAHHVGYGAKDAFQYLNVLIKQGLTVDELGDMDELFLNPTHFIQLSRLRAGSKNLVSLKVWNARNDHLTINQWATRIDEILEAPDGGEVIYNVDENDPREYDAIFIGGGAAGRFGSAYLRAMGGRQLIVDRWPFLGGSCPHNACVPHHLFSDCAAELMLARTFSGQYWFPDMTEKVVGIKEVVDLFRAGRNGPHGIMNFQSKEQLNLEYILNCPAKVIDNHTVEAAGKVFKAKNLILAVGAGPGTLDVPGVNAKGVFDHATLVEELDYEPGSTVVVVGGSKTAVEYGCFFNATGRRTVMLVRTEPLKLIKDNETRAYVLDRMKEQGMEIISGSNVTRIEEDANGRVQAVVAMTPNGEMRIETDFVFLGLGEQPRSAELAKILGLDLGPKGEVLVNEYLQTSVPNVYAVGDLIGGPMEMFKARKSGCYAARNVMGEKISYTPKNYPDFLHTHYEVSFLGMGEEEARAAGHEIVTIKMPPDTENGLNVALPASDRTMLYAFGKGTAHMSGFQKIVIDAKTRKVLGAHHVGYGAKDAFQYLNVLIKQGLTVDELGDMDELFLNPTHFIQLSRLRAGSKNLVSL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 49 | Matrix metalloproteinase-10 (MMP-10) | 1Q3A | 6.61 | |
Target general information Gen name MMP10 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Transin-2; Stromelysin-2; STMY2; SL-2 Protein family Peptidase M10A family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Activates procollagenase. Can degrade fibronectin, gelatins of type I, III, IV, and V; weakly collagens III, IV, and V. Related diseases Orthostatic hypotension 1 (ORTHYP1) [MIM:223360]: A form of orthostatic hypotension due to congenital dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a finding defined as a 20-mm Hg decrease in systolic pressure or a 10-mm Hg decrease in diastolic pressure occurring 3 minutes after a person has risen from supine to standing. Symptoms include dizziness, blurred vision, and sometimes syncope. ORTHYP1 is an autosomal recessive condition apparent from infancy or early childhood and characterized by low plasma and urinary levels of norepinephrine and epinephrine, and episodic hypoglycemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11857564}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00786; DB08271 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.4.24.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Calcium; Collagen degradation; Disulfide bond; Extracellular matrix; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Zinc; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 52822 Length 471 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 21.13 Isoelectric point 4.83 Charge (pH=7) -35.32 3D Binding mode Sequence MPKWRKTHLTYRIVNYTPDLPRDAVDSAIEKALKVWEEVTPLTFSRLYEGEADIMISFAVKEHGDNYSFDGPGHSLAHAYPPGPGLYGDIHFDDDEKWTEDASGTNLFLVAAHELGHSLGLFHSANTEALMYPLYNSLAQFRLSQDDVNGIQSLYGPKWRKTHLTYRIVNYTPDLPRDAVDSAIEKALKVWEEVTPLTFSRLYEGEADIMISFAVKEHGDNYSFDGPGHSLAHAYPPGPGLYGDIHFDDDEKWTEDASGTNLFLVAAHELGHSLGLFHSANTEALMYPLYNSLAQFRLSQDDVNGIQSLYGGMPKWRKTHLTYRIVNYTPDLPRDAVDSAIEKALKVWEEVTPLTFSRLYEGEADIMISFAVKEHGDNYSFDGPGHSLAHAYPPGPGLYGDIHFDDDEKWTEDASGTNLFLVAAHELGHSLGLFHSANTEALMYPLYNSFTELAQFRLSQDDVNGIQSLYG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 50 | "15-cis-phytoene desaturase, chloroplastic/chromoplastic (EC 1.3.5.5) (Phytoene dehydrogenase) (Phytoene desaturase)" | 5MOG | 6.60 | |
Target general information Gen name PDS1 Organism Oryza sativa subsp. indica (Rice) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms PDS;OsI_010044 Protein family Carotenoid/retinoid oxidoreductase family Biochemical class NA Function Converts phytoene into zeta-carotene via the intermediary of phytofluene by the symmetrical introduction of two double bonds at the C-11 and C-11' positions of phytoene with a concomitant isomerization of two neighboring double bonds at the C9 and C9' positions from trans to cis. Active with decylplastoquinone (DPQ) as substrate (PubMed:26147209, PubMed:29176862). Also active with other benzoquinones, which are strongly preferred over naphthoquinones as substrates (PubMed:26147209). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26147209, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29176862}." Related diseases NA Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 1.3.5.5 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Carotenoid biosynthesis; Chloroplast; Chromoplast; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Membrane; Oxidoreductase; Plastid; Reference proteome; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID E Molecular weight (Da) 52485.1 Length 466 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 45.53 Isoelectric point 5.93 Charge (pH=7) -5.81 3D Binding mode Sequence TKPLQVVIAGAGLAGLSTAKYLADAGHKPILLEARDVLGGKIAAWKDEDGDWYETGLHIFFGAYPNIQNLFGELGINDRLQWKEHSMIFAMPNKPGEFSRFDFPETLPAPLNGIWAILRNNEMLTWPEKVKFALGLLPAMVGGQAYVEAQDGFTVSEWMKKQGVPDRVNDEVFIAMSKALNFINPDELSMQCILIALNRFLQEKHGSKMAFLDGNPPERLCMPIVDHVRSLGGEVRLNSRIQKIELNPDGTVKHFALTDGTQITGDAYVFATPVDILKLLVPQEWKEISYFKKLEKLVGVPVINVHIWFDRKLKNTYDHLLFSRSSLLSVYADMSVTCKEYYDPNRSMLELVFAPAEEWVGRSDTEIIEATMQELAKLFPDEIAADQSKAKILKYHVVKTPRSVYKTIPDCEPCRPLQRSPIEGFYLAGDYTKQKYLASMEGAVLSGKLCAQSVVEDYKMLSRRSL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 51 | Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C1 | 1MRQ | 6.60 | |
Target general information Gen name AKR1C1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms DDH1;DDH Protein family Aldo/keto reductase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function 17-alpha,20-alpha-dihydroxypregn-4-en-3-one dehydrogenase activity.Alditol:NADP+ 1-oxidoreductase activity.Aldo-keto reductase (NADP) activity.Androsterone dehydrogenase (B-specific) activity.Bile acid binding.Carboxylic acid binding.Indanol dehydrogenase activity.Ketosteroid monooxygenase activity.Oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, quinone or similar compound as acceptor.Phenanthrene 9,10-monooxygenase activity.Trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol dehydrogenase activity. Related diseases Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) [MIM:135100]: A rare autosomal dominant connective tissue disorder resulting in skeletal malformations and progressive extraskeletal ossification. Heterotopic ossification begins in childhood and can be induced by trauma or may occur without warning. Bone formation is episodic and progressive, leading to a debilitating ankylosis of all major joints of the axial and appendicular skeleton, rendering movement impossible. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16642017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19085907, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19330033}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04674; DB00945; DB07768; DB01039; DB07931; DB06077; DB00959; DB00461; DB00157; DB03467; DB03461; DB00776; DB12612; DB00936 Interacts with P51857; P26045; Q7Z699 EC number 1.1.1.-; 1.1.1.112; 1.1.1.149; 1.1.1.209; 1.1.1.210; 1.1.1.357; 1.1.1.51; 1.1.1.53; 1.1.1.62; 1.3.1.20 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Lipid metabolism; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 36784.9 Length 323 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 42.07 Isoelectric point 8.06 Charge (pH=7) 2.42 3D Binding mode Sequence QDSKYQCVKLNDGHFMPVLGFGTYAPAEVPKSKALEATKLAIEAGFRHIDSAHLYNNEEQVGLAIRSKIADGSVKREDIFYTSKLWCNSHRPELVRPALERSLKNLQLDYVDLYLIHFPVSVKPGEEVIPKDENGKILFDTVDLCATWEAVEKCKDAGLAKSIGVSNFNRRQLEMILNKPGLKYKPVCNQVECHPYFNQRKLLDFCKSKDIVLVAYSALGSHREEPWVDPNSPVLLEDPVLCALAKKHKRTPALIALRYQLQRGVVVLAKSYNEQRIRQNVQVFEFQLTSEEMKAIDGLNRNVRYLTLDIFAGPPNYPFSDEY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 52 | Plasmodium Adenylosuccinate synthetase (Malaria Adss) | 1P9B | 6.60 | |
Target general information Gen name Malaria Adss Organism Plasmodium falciparum Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms IMP--aspartate ligase; Adenylosuccinate synthase; AdSS; AMPSase Protein family Adenylosuccinate synthetase family Biochemical class Carbon-nitrogen ligase Function Plays an important role in the salvage pathway for purine nucleotide biosynthesis. Catalyzes the first committed step in the biosynthesis of AMP from IMP. Related diseases Hypertension and brachydactyly syndrome (HTNB) [MIM:112410]: A syndrome characterized by brachydactyly type E, severe salt-independent but age-dependent hypertension, an increased fibroblast growth rate, neurovascular contact at the rostral-ventrolateral medulla, and altered baroreflex blood pressure regulation. It results in death from stroke before age 50 years when untreated. Brachydactyly type E is characterized by shortening of the fingers mainly in the metacarpals and metatarsals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25961942}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03510; DB04315; DB02109 Interacts with NA EC number EC 6.3.4.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; GTP-binding; Ligase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Purine biosynthesis Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 47877.9 Length 424 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 31.72 Isoelectric point 7.63 Charge (pH=7) 1.58 3D Binding mode Sequence GNVVAILGAQWGDEGKGKIIDMLSEYSDITCRFNGGANAGHTISVNDKKYALHLLPCGVLYDNNISVLGNGMVIHVKSLMEEIESVGGKLLDRLYLSNKAHILFDIHQIIDSIQETKKLKEGKQIGTTKRGIGPCYSTKASRIGIRLGTLKNFENFKNMYSKLIDHLMDLYNITEYDKEKELNLFYNYHIKLRDRIVDVISFMNTNLENNKKVLIEGANAAMLDIDFGTYPYVTSSCTTVGGVFSGLGIHHKKLNLVVGVVKSYLTRVGCGPFLTELNNDVGQYLREKGHEYGTTTKRPRRCGWLDIPMLLYVKCINSIDMINLTKLDVLSGLEEILLCVNFKNKKTGELLEKGCYPVEEEISEEYEPVYEKFSGWKEDISTCNEFDELPENAKKYILAIEKYLKTPIVWIGVGPNRKNMIVKK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 53 | UDP-galactopyranose mutase | 1I8T | 6.59 | |
Target general information Gen name glf Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b2036;JW2021;yefE Protein family UDP-galactopyranose/dTDP-fucopyranose mutase family Biochemical class Isomerase Function Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.UDP-galactopyranose mutase activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147 Interacts with P11868 EC number 5.4.99.9 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Isomerase; Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 42965.3 Length 367 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 32.48 Isoelectric point 6.62 Charge (pH=7) -1.52 3D Binding mode Sequence MYDYIIVGSGLFGAVCANELKKLNKKVLVIEKRNHIGGNAYTEDCEGIQIHKYGAHIFHTNDKYIWDYVNDLVEFNRFTNSPLAIYKDKLFNLPFNMNTFHQMWGVKDPQEAQNIINAQKKKYGDKVPENLEEQAISLVGEDLYQALIKGYTEKQWGRSAKELPAFIIKRIPVRFTFDNNYFSDRYQGIPVGGYTKLIEKMLEGVDVKLGIDFLKDKDSLASKAHRIIYTGPIDQYFDYRFGALEYRSLKFETERHEFPNFQGNAVINFTDANVPYTRIIEHKHFDYVETKHTVVTKEYPLEWKVGDEPYYPVNDNKNMELFKKYRELASREDKVIFGGRLAEYKYYDMHQVISAALYQVKNIMSTD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 54 | Progesterone receptor (PGR) | 1SQN | 6.58 | |
Target general information Gen name PGR Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PR; Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 3; NR3C3 Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR3 subfamily Biochemical class Nuclear hormone receptor Function Depending on the isoform, progesterone receptor functions as transcriptional activator or repressor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Related diseases Butyrylcholinesterase deficiency (BCHED) [MIM:617936]: An autosomal recessive metabolic condition characterized by increased sensitivity to certain anesthetic drugs, including the muscle relaxants succinylcholine or mivacurium. BCHED results in slower hydrolysis of these drugs and, consequently, a prolonged neuromuscular block, leading to apnea. The duration of the prolonged apnea varies significantly depending on the extent of the enzyme deficiency. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10404729, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11928765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12881446, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1306123, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1349196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1415224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15563885, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15781196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1611188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16788378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17700357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18075469, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18300943, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25054547, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25264279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2915989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7634491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8554068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8680411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9110359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9191541, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9388484, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9543549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9694584}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01431; DB06680; DB01406; DB12941; DB13857; DB00304; DB09123; DB01395; DB00378; DB11219; DB00823; DB00294; DB13867; DB08906; DB00588; DB06730; DB11619; DB11064; DB06789; DB00367; DB00431; DB09124; DB00603; DB00351; DB02998; DB00834; DB00648; DB00764; DB14512; DB06713; DB00717; DB00957; DB09389; DB01428; DB02746; DB00396; DB14583; DB00421; DB04787; DB05253; DB08867 Interacts with Q9H467; P03372; P06401; P40763; P03372 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative promoter usage; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; DNA-binding; Isopeptide bond; Lipid-binding; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion outer membrane; Nucleus; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Steroid-binding; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 28853.6 Length 250 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 54.82 Isoelectric point 8.4 Charge (pH=7) 2.28 3D Binding mode Sequence LIPPLINLLMSIEPDVIYAGHDNTKPDTSSSLLTSLNQLGERQLLSVVKWSKSLPGFRNLHIDDQITLIQYSWMSLMVFGLGWRSYKHVSGQMLYFAPDLILNEQRMKESSFYSLCLTMWQIPQEFVKLQVSQEEFLCMKVLLLLNTIPLEGLRSQTQFEEMRSSYIRELIKAIGLRQGVVSSSQRFYQLTKLLDNLHDLVKQLHLYCLNTFIQSRALSVEFPEMMSEVIAAQLPKILAGMVKPLLFHKK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 55 | Retinoic acid receptor beta (RARB) | 4DM6 | 6.58 | |
Target general information Gen name RARB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms RAR-epsilon; RAR-beta; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 2; NR1B2; HBV-activated protein; HAP Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily Biochemical class Nuclear hormone receptor Function Retinoic acid receptors bind as heterodimers to their target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, and regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RXR/RAR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5. In the absence or presence of hormone ligand, acts mainly as an activator of gene expression due to weak binding to corepressors. In concert with RARG, required for skeletal growth, matrix homeostasis and growth plate function. Receptor for retinoic acid. Related diseases Microphthalmia, syndromic, 12 (MCOPS12) [MIM:615524]: A form of microphthalmia, a disorder of eye formation, ranging from small size of a single eye to complete bilateral absence of ocular tissues (anophthalmia). In many cases, microphthalmia/anophthalmia occurs in association with syndromes that include non-ocular abnormalities. MCOPS12 patients manifest variable features, including diaphragmatic hernia, pulmonary hypoplasia, and cardiac abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24075189, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27120018}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00459; DB00210; DB00523; DB02877; DB00926; DB05785; DB04942; DB00799; DB00755; DB12808 Interacts with O95273; P50222; Q9UBK2; P62195; P28702; P28702-3; P48443; P03255 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; DNA-binding; Metal-binding; Microphthalmia; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proto-oncogene; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 25904.1 Length 229 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 44.34 Isoelectric point 7.55 Charge (pH=7) 0.73 3D Binding mode Sequence TEKIRKAHQETFPSLCQLGKYTTNSSADHRVRLDLGLWDKFSELATKCIIKIVEFAKRLPGFTGLTIADQITLLKAACLDILILRICTRYTPEQDTMTFSDGLTLNRTQMHNAGFGPLTDLVFTFANQLLPLEMDDTETGLLSAICLICGDRQDLEEPTKVDKLQEPLLEALKIYIRKRRPSKPHMFPKILMKITDLRSISAKGAERVITLKMEIPGSMPPLIQEMLEN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 56 | Thiopurine S-methyltransferase | 2BZG | 6.58 | |
Target general information Gen name TPMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, TPMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Thiopurine S-methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 3 (CCDS3) [MIM:612718]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by developmental delay/regression, intellectual disability, severe disturbance of expressive and cognitive speech, and severe depletion of creatine/phosphocreatine in the brain. Most patients develop a myopathy characterized by muscle weakness and atrophy later in life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11555793, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20682460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22386973, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23660394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23770102, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26490222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27233232}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Fanconi renotubular syndrome 1 (FRTS1) [MIM:134600]: A form of Fanconi renotubular syndrome, a disease due to a generalized dysfunction of the proximal kidney tubule resulting in decreased solute and water reabsorption. Patients have polydipsia and polyuria with phosphaturia, glycosuria and aminoaciduria. They may develop hypophosphatemic rickets or osteomalacia, acidosis and a tendency toward dehydration. Some eventually develop renal insufficiency. FRTS1 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29654216}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00993; DB00436; DB01327; DB01033; DB01250; DB01021 Interacts with Q8TAP4-4; Q15047-2; P61981 EC number 2.1.1.67 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 25971.5 Length 229 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 32.58 Isoelectric point 6.74 Charge (pH=7) -0.6 3D Binding mode Sequence EVQKNQVLTLEEWQDKWVNGKTAFHQEQGHQLLKKHLDTFLKGKSGLRVFFPLCGKAVEXKWFADRGHSVVGVEISELGIQEFFTEQNLSYSEEPITEIPGTKVFKSSSGNISLYCCSIFDLPRTNIGKFDXIWDRGALVAINPGDRKCYADTXFSLLGKKFQYLLCVLSYDPTKHPGPPFYVPHAEIERLFGKICNIRCLEKVDAFEERHKSWGIDCLFEKLYLLTEK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 57 | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) | 5FY9 | 6.58 | |
Target general information Gen name KDM5B Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Retinoblastomabinding protein 2 homolog 1; Retinoblastoma-binding protein 2 homolog 1; RBP2H1; RBP2-H1; RBBP2H1; PLU1; PLU-1; Lysinespecific demethylase 5B; Jumonji/ARID domaincontaining protein 1B; J Protein family JARID1 histone demethylase family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Does not demethylate histone H3 'Lys-9' or H3 'Lys-27'. Demethylates trimethylated, dimethylated and monomethylated H3 'Lys-4'. Acts as a transcriptional corepressor for FOXG1B and PAX9. Favors the proliferation of breast cancer cells by repressing tumor suppressor genes such as BRCA1 and HOXA5. In contrast, may act as a tumor suppressor for melanoma. Represses the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer-mediated transcriptional activation of the core clock component PER2. Histone demethylase that demethylates 'Lys-4' of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 65 (MRT65) [MIM:618109]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRT65 patients have moderate to severe intellectual disability, developmental delay, and facial dysmorphism. Camptodactyly is present in some patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29276005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30409806}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P49711 EC number EC 1.14.11.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Biological rhythms; Chromatin regulator; Dioxygenase; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Iron; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 53020.6 Length 460 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 44.23 Isoelectric point 5.28 Charge (pH=7) -18.32 3D Binding mode Sequence SMFLPPPECPVFEPSWEEFADPFAFIHKIRPIAEQTGICKVRPPPDWQPPFACDVDKLHFTPRIQRLNELEAQTRVKLGGGGARDYTLRTFGEMADAFKSDYFNMPVHMVPTELVEKEFWRLVSTIEEDVTVEYGADIASKEFGSGFPVRDIKLSPEEEEYLDSGWNLNNMPVMEQSVLAHITADICGMKLPWLYVGMCFSSFCWHIEDHWSYSINYLHWGEPKTWYGVPGYAAEQLENVMKKLAPELFVSQPDLLHQLVTIMNPNTLMTHEVPVYRTNQCAGEFVITFPRAYHSGFNQGFNFAEAVNFCTVDWLPLGRQCVEHYRLLHRYCVFSHDEMICKMASKADVLDVVVASTVQKDMAIMIEDEKALRETVRKLGVIDSERMDFELLPDDERQCVKCKTTCFMSAISCSCKPGLLVCLHHVKELCSCPPYKYKLRYRYTLDDLYPMMNALKLRAE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 58 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase KMT5C (KMT5C) | 3RQ4 | 6.58 | |
Target general information Gen name KMT5C Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Lysine N-methyltransferase 5C; Lysine-specific methyltransferase 5C; Suppressor of variegation 4-20 homolog 2; Su(var)4-20 homolog 2; Suv4-20h2; [histone H4]-N-methyl-L-lysine20 N-methyltransferase KM Protein family Class V-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, Histone-lysine methyltransferase family, Suvar4-20 subfamily Biochemical class NA Function Histone methyltransferase that specifically methylates monomethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me1) and dimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me2) of histone H4 to produce respectively dimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me2) and trimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me3) and thus regulates transcription and maintenance of genome integrity. In vitro also methylates unmodified 'Lys-20' (H4K20me0) of histone H4 and nucleosomes. H4 'Lys-20' trimethylation represents a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional repression. Mainly functions in pericentric heterochromatin regions, thereby playing a central role in the establishment of constitutive heterochromatin in these regions. KMT5C is targeted to histone H3 via its interaction with RB1 family proteins (RB1, RBL1 and RBL2) (By similarity). Facilitates TP53BP1 foci formation upon DNA damage and proficient non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ)-directed DNA repair by catalyzing the di- and trimethylation of 'Lys-20' of histone H4. May play a role in class switch reconbination by catalyzing the di- and trimethylation of 'Lys-20' of histone H4 (By similarity). Related diseases Brachydactyly A2 (BDA2) [MIM:112600]: A form of brachydactyly. Brachydactyly defines a group of inherited malformations characterized by shortening of the digits due to abnormal development of the phalanges and/or the metacarpals. In brachydactyly type A2 shortening of the middle phalanges is confined to the index finger and the second toe, all other digits being more or less normal. Because of a rhomboid or triangular shape of the affected middle phalanx, the end of the second finger usually deviates radially. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19327734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357617}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. Duplications of a cis-regulatory element located approximately 110 kb downstream of BMP2 have been found in BDA2 families. They likely cause altered BMP2 expression with pathological consequences. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19327734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357617}.; DISEASE: Short stature, facial dysmorphism, and skeletal anomalies with or without cardiac anomalies 1 (SSFSC1) [MIM:617877]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by short stature, facial dysmorphism, skeletal anomalies, and variable cardiac defects. Distinctive facial features include midface retrusion, short upturned nose, long philtrum, high-arched or cleft palate, and variable degrees of micrognathia and dental crowding. Skeletal anomalies include patterning defects of the axial skeleton, characterized by 11 pairs of ribs and brachydactyly of the fifth ray. Congenital heart defects are variably observed and appear to involve primarily the cardiac outflow tract. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29198724}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q13185 EC number EC 2.1.1.361 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Chromosome; Metal-binding; Methyltransferase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repressor; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 27285.8 Length 240 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 42.74 Isoelectric point 8.32 Charge (pH=7) 3.24 3D Binding mode Sequence DRVTARELCENDDLATSLVLDPYLGFRTHKMNVSPVPPLRRQQHLRSALETFLRQRDLEAAYRALTLGGWTARYFQSRGPRQEAALKTHVYRYLRAFLPESGFTILPCTRYSMETNGAKIVSTRAWKKNEKLELLVGCIAELREADEGLLRAGENDFSIMYSTRKRSAQLWLGPAAFINHDCKPNCKFVPADGNAACVKVLRDIEPGDEVTCFYGEGFFGEKNEHCECHTCERKGEGAFR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 59 | Poly [ADP-ribose] glycohydrolase (PARG) | 7KG8 | 6.58 | |
Target general information Gen name PARG Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase Protein family Poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase family Biochemical class Glycosylase Function Poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase that degrades poly(ADP-ribose) by hydrolyzing the ribose-ribose bonds present in poly(ADP-ribose). PARG acts both as an endo- and exoglycosidase, releasing poly(ADP-ribose) of different length as well as ADP-ribose monomers. It is however unable to cleave the ester bond between the terminal ADP-ribose and ADP-ribosylated residues, leaving proteins that are mono-ADP-ribosylated. Poly(ADP-ribose) is synthesized after DNA damage is only present transiently and is rapidly degraded by PARG. Required to prevent detrimental accumulation of poly(ADP-ribose) upon prolonged replicative stress, while it is not required for recovery from transient replicative stress. Required for retinoid acid-dependent gene transactivation, probably by removing poly(ADP-ribose) from histone demethylase KDM4D, allowing chromatin derepression at RAR-dependent gene promoters. Involved in the synthesis of ATP in the nucleus, together with PARP1, NMNAT1 and NUDT5. Nuclear ATP generation is required for extensive chromatin remodeling events that are energy-consuming. Related diseases Familial adenomatous polyposis 2 (FAP2) [MIM:608456]: A condition characterized by the development of multiple colorectal adenomatous polyps, benign neoplasms derived from glandular epithelium. Some affected individuals may develop colorectal carcinoma. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11818965, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12606733, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12853198, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15366000, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16134147, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16287072, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16557584, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16941501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18091433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18515411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19953527, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20418187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20848659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25820570, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26694661}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Gastric cancer (GASC) [MIM:613659]: A malignant disease which starts in the stomach, can spread to the esophagus or the small intestine, and can extend through the stomach wall to nearby lymph nodes and organs. It also can metastasize to other parts of the body. The term gastric cancer or gastric carcinoma refers to adenocarcinoma of the stomach that accounts for most of all gastric malignant tumors. Two main histologic types are recognized, diffuse type and intestinal type carcinomas. Diffuse tumors are poorly differentiated infiltrating lesions, resulting in thickening of the stomach. In contrast, intestinal tumors are usually exophytic, often ulcerating, and associated with intestinal metaplasia of the stomach, most often observed in sporadic disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15273732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25820570}. The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis. Somatic mutations contribute to the development of a sub-set of sporadic gastric cancers in carriers of Helicobacter pylori (PubMed:15273732). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15273732}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.2.1.143 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; DNA damage; Hydrolase; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 57587.3 Length 501 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 58.01 Isoelectric point 7.65 Charge (pH=7) 1.7 3D Binding mode Sequence KKWLGTPIEEMRRMPRCGIRLPLLRPSANHTVTIRVDLLRAGEVPKPFPTHYKDLWDNKHVKMPCSEQNLYAGSRWELIQTALLNKFTRPQNLKDAILKYNVAYSKKWDFTALIDFWDKVLEEAEAQHLYQSILPDMVKIALXLPNICTQPIPLLAAAMNHSITMSQEQIASLLANAFFCTFPRRNAKMKSEYSSYPDINFNRLFEGRSSRKPEKLKTLFCYFRRVTAAAPTGLVTFTRQSLEDFPEWERXEKPLTRLHVTYEGTIEENGQGMLQVDFANRFVGGGVTSAGLVQEEIRFLINPELIISRLFTEVLDHNECLIITGTEQYSEYTGYAETYRWSRSHEDGSERDDWQRRCTEIVAIDALHFRRYLDQFVPEKMRRELNKAYCGFLRPGVSSENLSAVATGNWGCGAFGGDARLKALIQILAAAAAERDVVYFTFGDSELMRDIYSMHIFLTERKLTVGDVYKLLLRYYNEECRNCTPGPDIKLYPFIYHAVES Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 60 | Oxalosuccinate decarboxylase (IDH1) | 6ADG | 6.58 | |
Target general information Gen name IDH1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PICD; NADP(+)-specific ICDH; Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP] cytoplasmic; IDP; IDH; Cytosolic NADP-isocitrate dehydrogenase Protein family Isocitrate and isopropylmalate dehydrogenases family Biochemical class Short-chain dehydrogenases reductase Function Catalyses the NADPH-dependent reduction of alpha-ketoglutarate to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG). Related diseases Glioma (GLM) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19117336, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. Mutations affecting Arg-132 are tissue-specific, and suggest that this residue plays a unique role in the development of high-grade gliomas. Mutations of Arg-132 to Cys, His, Leu or Ser abolish magnesium binding and abolish the conversion of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate. Instead, alpha-ketoglutarate is converted to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate. Elevated levels of R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate are correlated with an elevated risk of malignant brain tumors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646}.; DISEASE: Genetic variations are associated with cartilaginous tumors such as enchondroma or chondrosarcoma. Mutations of Arg-132 to Cys, Gly or His abolish the conversion of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate. Instead, alpha-ketoglutarate is converted to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26161668}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09374; DB01727; DB14568; DB03461; DB16267 Interacts with P0DP23; P27797; P36957; O75874; Q8TDX7; P16284; P17612; P50454; P37173; Q05086-3 EC number EC 1.1.1.42 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Glyoxylate bypass; Magnesium; Manganese; Metal-binding; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Peroxisome; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Tricarboxylic acid cycle Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 92711.7 Length 823 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 26.74 Isoelectric point 6.42 Charge (pH=7) -4.48 3D Binding mode Sequence KKISGGSVVEMQGDEMTRIIWELIKEKLIFPYVELDLHSYDLGIENRDATNDQVTKDAAEAIKKHNVGVKCATITPDEKRVEEFKLKQMWKSPNGTIRNILGGTVFREAIICKNIPRLVSGWVKPIIIGHHAYGDQYRATDFVVPGPGKVEITYTPSDGTQKVTYLVHNFEEGGGVAMGMYNQDKSIEDFAHSSFQMALSKGWPLYLSTKNTILKKYDGRFKDIFQEIYDKQYKSQFEAQKIWYEHRLIDDMVAQAMKSEGGFIWACKNYDGDVQSDSVAQGYGSLGMMTSVLVCPDGKTVEAEAAHGTVTRHYRMYQKGQETSTNPIASIFAWTRGLAHRAKLDNNKELAFFANALEEVSIETIEAGFMTKDLAACIKGLPNVQRSDYLNTFEFMDKLGENLKIKLAQAKLKKISGGSVVEMQGDEMTRIIWELIKEKLIFPYVELDLHSYDLGIENRDATNDQVTKDAAEAIKKHNVGVKCATITPDEKRVEEFKLKQMWKSPNGTIRNILGGTVFREAIICKNIPRLVSGWVKPIIIGHHAYGDQYRATDFVVPGPGKVEITYTPSDGTQKVTYLVHNFEEGGGVAMGMYNQDKSIEDFAHSSFQMALSKGWPLYLSTKNTILKKYDGRFKDIFQEIYDKQYKSQFEAQKIWYEHRLIDDMVAQAMKSEGGFIWACKNYDGDVQSDSVAQGYGSLGMMTSVLVCPDGKTVEAEAAHGTVTRHYRMYQKGQETSTNPIASIFAWTRGLAHRAKLDNNKELAFFANALEEVSIETIEAGFMTKDLAACIKGLPNVQRSDYLNTFEFMDKLGENLKIKLAQAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||