Job Results:
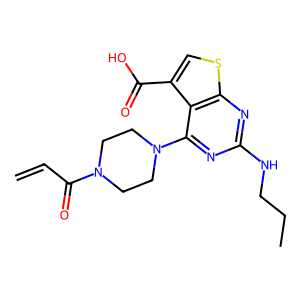
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
57b30c77c1e7b273b1e911481965e4cd
Job name
NA
Time
2025-10-13 17:21:20
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | 2IIP | 7.02 | |
Target general information Gen name NNMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, NNMT/PNMT/TEMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase activity.Pyridine N-methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00627 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Citrullination; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 27886.8 Length 251 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.66 Isoelectric point 5.23 Charge (pH=7) -5.11 3D Binding mode Sequence GFTSKDTYLSHFNPRDYLEKYYSAESQILKHLLKNLFKIFCLDGVKGDLLIDIGSGPTIYQLLSACESFKEIVVTDYSDQNLQELEKWLKAAPAAFDWSPVVTYVCDLEGNRVKGPEKEEKLRQAVKQVLKCDVTQSQPLGAVPLPPADCVLSTLCLDAACPDLPTYCRALRNLGSLLKPGGFLVIMDALKSSYYMIGEQKFSSLPLGREAVEAAVKEAGYTIEWFEVISQSYSSTMANNEGLFSLVARKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 2 | Bacterial Oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase II (Bact fabF) | 2GFX | 7.02 | |
Target general information Gen name Bact fabF Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms KASB; KAS II; KAS 2; FabF; Condensing enzyme FabF; Beta-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase B; Beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase II; Beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase 2; 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase Protein family Thiolase-like superfamily, Beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthases family Biochemical class Acyltransferase Function Catalyzes the condensation reaction of fatty acid synthesis by the addition to an acyl acceptor of two carbons from malonyl-ACP. Has a preference for short chain acid substrates and may function to supply the octanoic substrates for lipoic acid biosynthesis. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08366; DB01034; DB03017; DB08407 Interacts with P0A6Y8 EC number EC 2.3.1.179 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acyltransferase; Direct protein sequencing; Fatty acid biosynthesis; Fatty acid metabolism; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 42852 Length 411 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 31.41 Isoelectric point 5.72 Charge (pH=7) -7.34 3D Binding mode Sequence KRRVVVTGLGMLSPVGNTVESTWKALLAGQSGISLIDHFDTSAYATKFAGLVKDFNCEDIISRKEQRKMDAFIQYGIVAGVQAMQDSGLEITEENATRIGAAIGSGIGGLGLIEENHTSLMNGGPRKISPFFVPSTIVNMVAGHLTIMYGLRGPSISIATAQTSGVHNIGHAARIIAYGDADVMVAGGAEKASTPLGVGGFGAARALSTRNDNPQAASRPWDKERDGFVLGDGAGMLVLEEYEHAKKRGAKIYAELVGFGMSSDAYHMTSPPENGAGAALAMANALRDAGIEASQIGYVNAHGTSTPAGDKAEAQAVKTIFGEAASRVLVSSTKSMTGHLLGAAGAVESIYSILALRDQAVPPTINLDNPDEGCDLDFVPHEARQVSGMEYTLCNSFGFGGTNGSLIFKKI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 3 | L-aspartate oxidase | 1KNR | 6.96 | |
Target general information Gen name nadB Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms JW2558;nicB;b2574 Protein family FAD-dependent oxidoreductase 2 family, NadB subfamily Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.L-aspartate:fumarate oxidoreductase activity.L-aspartate oxidase activity. Related diseases Thyroid hormone resistance, generalized, autosomal dominant (GRTHD) [MIM:188570]: An autosomal dominant disease characterized by high levels of circulating thyroid hormones (T3-T4), goiter, abnormal mental functions, increased susceptibility to infections, abnormal growth and bone maturation, tachycardia and deafness. Affected individuals may also have attention deficit-hyperactivity disorders (ADHD) and language difficulties. Patients have normal or slightly elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10660344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12511610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12554782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1314846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1324420, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1563081, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1587388, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1619012, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1661299, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16804041, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1846005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19268523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2153155, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2510172, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7833659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8175986, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8514853, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8664910, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8889584}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thyroid hormone resistance, generalized, autosomal recessive (GRTHR) [MIM:274300]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by goiter, clinical euthyroidism, end-organ unresponsiveness to thyroid hormone, abnormal growth and bone maturation, and deafness. Patients also have high levels of circulating thyroid hormones, with elevated thyroid stimulating hormone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1653889}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Selective pituitary thyroid hormone resistance (PRTH) [MIM:145650]: Variant form of thyroid hormone resistance and is characterized by clinical hyperthyroidism, with elevated free thyroid hormones, but inappropriately normal serum TSH. Unlike GRTH, where the syndrome usually segregates with a dominant allele, the mode of inheritance in PRTH has not been established. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7528740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8381821}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147 Interacts with NA EC number 1.4.3.16; 1.5.99.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Nucleotide-binding; Oxidoreductase; Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 58993.2 Length 529 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 36.96 Isoelectric point 5.76 Charge (pH=7) -15.84 3D Binding mode Sequence PEHSCDVLIIGSGAAGLSLALRLADQHQVIVLSKGPVTEGSTFYAQGGIAAVFDETDSIDSHVEDTLIAGAGICDRHAVEFVASNARSCVQWLIDQGVLFDTHIQPNGEESYHLTREGGHSHRRILHAADATGREVETTLVSKALNHPNIRVLERTNAVDLIVSDKIGLPGTRRVVGAWVWNRNKETVETCHAKAVVLATGGASKVYQYTTNPDISSGDGIAMAWRAGCRVANLEFNQFHPTALYHPQARNFLLTEALRGEGAYLKRPDGTRFMPDFDERGELAPRDIVARAIDHEMKRLGADCMFLDISHKPADFIRQHFPMIYEKLLGLGIDLTQEPVPIVPAAHYTCGGVMVDDHGRTDVEGLYAIGEVSYTGLHGANLMASNSLLECLVYGWSAAEDITRRMPYAHDISTLPPWDESRVENPDERVVIQHNWHELRLFMWDYVGIVRTTKRLERALRRITMLQQEIDEYYAHFRVSNNLLELRNLVQVAELIVRCAMMRKESRGLHFTLDYPELLTHSGPSILSP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 4 | Folate receptor alpha (FOLR1) | 4LRH | 6.92 | |
Target general information Gen name FOLR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Ovarian tumorassociated antigen MOv18; KB cells FBP; Folate receptor, adult; Folate receptor 1; FRalpha; FOLR1; Adult folatebinding protein Protein family Folate receptor family Biochemical class Folate receptor Function Binds to folate and reduced folic acid derivatives and mediates delivery of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and folate analogs into the interior of cells. Has high affinity for folate and folic acid analogs at neutral pH. Exposure to slightly acidic pHafter receptor endocytosis triggers a conformation change that strongly reduces its affinity for folates and mediates their release. Required for normal embryonic development and normal cell proliferation. Related diseases Neurodegeneration due to cerebral folate transport deficiency (NCFTD) [MIM:613068]: An autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder resulting from brain-specific folate deficiency early in life. Onset is apparent in late infancy with severe developmental regression, movement disturbances, epilepsy and leukodystrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19732866}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05595; DB00158; DB00563; DB12489; DB15413; DB05168 Interacts with Q8N357 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Endosome; Folate-binding; Glycoprotein; GPI-anchor; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Neurodegeneration; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 24216 Length 207 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 49.36 Isoelectric point 8.14 Charge (pH=7) 3.41 3D Binding mode Sequence RTELLNVCMNAKHHKEKPGPEDKLHEQCRPWRKNACCSTNTSQEAHKDVSYLYRFNWNHCGEMAPACKRHFIQDTCLYECSPNLGPWIQQVDQSWRKERVLNVPLCKEDCEQWWEDCRTSYTCKSNWHKGWNWTSGFNKCAVGAACQPFHFYFPTPTVLCNEIWTHSYKVSNYSRGSGRCIQMWFDPAQGNPNEEVARFYAAAMSGT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 5 | Gamma-butyrobetaine dioxygenase | 4C5W | 6.91 | |
Target general information Gen name BBOX1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms BBH;BBOX Protein family Gamma-BBH/TMLD family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Gamma-butyrobetaine dioxygenase activity.Identical protein binding.Iron ion binding.Zinc ion binding. Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder with poor language and loss of hand skills (NDPLHS) [MIM:617903]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by psychomotor developmental stagnation or regression. NDPLHS manifest in the first years of life as loss of purposeful hand movements, loss of language, and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26740508, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28856709, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29369404}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 59 (DEE59) [MIM:617904]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of severe early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE59 is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by onset of refractory seizures in early infancy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28856709, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29100083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29369404}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00126 Interacts with O75936; A0MZ66-7 EC number 1.14.11.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Carnitine biosynthesis; Cytoplasm; Dioxygenase; Iron; Metal-binding; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 31642.5 Length 275 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 35.68 Isoelectric point 6.33 Charge (pH=7) -2.46 3D Binding mode Sequence FPECQYWGSELQLPTLDFEDVLRYDEHAYKWLSTLKKVGIVRLTGASDKPGEVSKLGKRMGFLYLTFYGHTWQVQDKIDANNVAYTTGKLSFHTDYPALHHPPGVQLLHCIKQTVTGGDSEIVDGFNVCQKLKKNNPQAFQILSSTFVDFTDIGVDYCDFSVQSKHKIIELDDKGQVVRINFNNATRDTIFDVPVERVQPFYAALKEFVDLMNSKESKFTFKMNPGDVITFDNWRLLHGRRSYEAGTEISRHLEGAYADWDVVMSRLRILRQRVE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 6 | Dimethylglycine oxidase | 1PJ5 | 6.90 | |
Target general information Gen name dmg Organism Arthrobacter globiformis Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family GcvT family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Dimethylglycine oxidase activity.Nucleotide binding. Related diseases Curry-Jones syndrome (CRJS) [MIM:601707]: A multisystem disorder characterized by patchy skin lesions, polysyndactyly, diverse cerebral malformations, unicoronal craniosynostosis, iris colobomas, microphthalmia, and intestinal malrotation with myofibromas or hamartomas. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24859340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27236920}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. 8 individuals have been identified with the disease-causing mutation Phe-412 and all were mosaic. The mutation could not be reliably detected in blood, greatest success rates were obtained with affected tissues obtained by invasive procedures. It is thought that the mutation has arisen postzygotically early during embryonic development (PubMed:27236920). This mutation has also been identified in ameloblastoma, medulloblastoma, meningioma, and basal cell carcinoma, and has been reported as the oncogenic driver in some of these tumors (PubMed:24859340). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24859340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27236920}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03256; DB03147 Interacts with NA EC number 1.5.3.10 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Nucleotide-binding; Oxidoreductase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 45912.2 Length 427 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 43.46 Isoelectric point 4.83 Charge (pH=7) -20.69 3D Binding mode Sequence TPRIVIIGAGIVGTNLADELVTRGWNNITVLDQGPLNMPGGSTSHAPGLVFQTNPSKTMASFAKYTVEKLLSLTEDGVSCFNQVGGLEVATTETRLADLKRKLGYAAAWGIEGRLLSPAECQELYPLLDGENILGGLHVPSDGLASAARAVQLLIKRTESAGVTYRGSTTVTGIEQSGGRVTGVQTADGVIPADIVVSCAGFWGAKIGAMIGMAVPLLPLAHQYVKTTPVPAQQGRNDQPNGARLPILRHQDQDLYYREHGDRYGIGSYAHRPMPVDVDTLGAYAPETVSEHHMPSRLDFTLEDFLPAWEATKQLLPALADSEIEDGFNGIFSFTPDGGPLLGESKELDGFYVAEAVWVTHSAGVAKAMAELLTTGRSETDLGECDITRFEDVQLTPEYVSETSQQNFVEIYDVLHPLQPRLSPRNL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 7 | Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1B (KDM1B) | 4HSU | 6.90 | |
Target general information Gen name KDM1B Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Lysine-specific histone demethylase 2; LSD2; Flavin-containing amine oxidase domain-containing protein 1; C6orf193; AOF1 Protein family Flavin monoamine oxidase family Biochemical class CH-NH(2) donor oxidoreductase Function Required for de novo DNA methylation of a subset of imprinted genes during oogenesis. Acts by oxidizing the substrate by FAD to generate the corresponding imine that is subsequently hydrolyzed. Demethylates both mono- and di-methylated 'Lys-4' of histone H3. Has no effect on tri-methylated 'Lys-4', mono-, di- or tri-methylated 'Lys-9', mono-, di- or tri-methylated 'Lys-27', mono-, di- or tri-methylated 'Lys-36' of histone H3, or on mono-, di- or tri-methylated 'Lys-20' of histone H4. Histone demethylase that demethylates 'Lys-4' of histone H3, a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional activation, thereby acting as a corepressor. Related diseases Angioedema, hereditary, 1 (HAE1) [MIM:106100]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by episodic local swelling involving subcutaneous or submucous tissue of the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts, face, extremities, and genitalia. Hereditary angioedema due to C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency is comprised of two clinically indistinguishable forms. In hereditary angioedema type 1, serum levels of C1 esterase inhibitor are decreased, while in type 2, the levels are normal or elevated, but the protein is non-functional. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12773530, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1363816, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1451784, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14635117, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16409206, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2118657, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2296585, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22994404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2365061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24456027, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3178731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7814636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7883978, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8172583, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8529136, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8755917, ECO:0000269|Ref.41}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q96L03 EC number EC 1.-.-.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Chromosome; Developmental protein; FAD; Flavoprotein; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 85795.5 Length 763 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.87 Isoelectric point 8.41 Charge (pH=7) 9.16 3D Binding mode Sequence GSRKCEKAGCTATCPVCFASASERCAKNGYTSRWYHLSCGEHFCNECFDHYYRSHKDGYDKYTTWKKIWTSNGKTEPSPKAFMADQQLPYWVQCTKPECRKWRQLTKEIQLTPQIAKTYRCGMKSDHCSLPEDLRVLEVSNHWWYSMLILPPLLKDSVAAPLLSAYYPDCVGMSPSCTGMNRYFQPFYQPNECGKALCVRPDVMELDELYEFPEYSRDPTMYLALRNLILALWYTNCKEALTPQKCIPHIIVRGLVRIRCVQEVERILYFMTRKGLINTGVLSVGADQYLLPKDYHNKSVIIIGAGPAGLAAARQLHNFGIKVTVLEAKDRIGGRVWDDKSFKGVTVGRGAQIVNGCINNPVALMCEQLGISMHKFGERCDLIQEGGRITDPTIDKRMDFHFNALLDVVSEWRKDKTQLQDVPLGEKIEEIYKAFIKESGIQFSELEGQVLQFHLSNLEYACGSNLHQVSARSWDHNEFFAQFAGDHTLLTPGYSVIIEKLAEGLDIQLKSPVQCIDYSGDEVQVTTTDGTGYSAQKVLVTVPLALLQKGAIQFNPPLSEKKMKAINSLGAGIIEKIALQFPYRFWDSKVQGADFFGHVPPSASKRGLFAVFYDMDPQKKHSVLMSVIAGEAVASVRTLDDKQVLQQCMATLRELFKEQEVPDPTKYFVTRWSTDPWIQMAYSFVKTGGSGEAYDIIAEDIQGTVFFAGEATNRHFPQTVTGAYLSGVREASKIAAFARTMQTARKSTGGKAPRKQLATKAAR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 8 | Histidine decarboxylase (HDC) | 4E1O | 6.88 | |
Target general information Gen name HDC Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Human histidine decarboxylase Protein family Group II decarboxylase family Biochemical class Carbon-carbon lyase Function Catalyzes the biosynthesis of histamine from histidine. Related diseases Corticosterone methyloxidase 1 deficiency (CMO-1 deficiency) [MIM:203400]: Autosomal recessive disorder of aldosterone biosynthesis. There are two biochemically different forms of selective aldosterone deficiency be termed corticosterone methyloxidase (CMO) deficiency type 1 and type 2. In CMO-1 deficiency, aldosterone is undetectable in plasma, while its immediate precursor, 18-hydroxycorticosterone, is low or normal. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11238478, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8439335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9177280}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Corticosterone methyloxidase 2 deficiency (CMO-2 deficiency) [MIM:610600]: Autosomal recessive disorder of aldosterone biosynthesis. In CMO-2 deficiency, aldosterone can be low or normal, but at the expense of increased secretion of 18-hydroxycorticosterone. Consequently, patients have a greatly increased ratio of 18-hydroxycorticosterone to aldosterone and a low ratio of corticosterone to 18-hydroxycorticosterone in serum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12788848, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1346492, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1594605, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9625333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9814506}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00117; DB00114 Interacts with Q86UW9 EC number EC 4.1.1.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Catecholamine biosynthesis; Decarboxylase; Lyase; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F Molecular weight (Da) 107706 Length 956 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 55.17 Isoelectric point 6.23 Charge (pH=7) -9.63 3D Binding mode Sequence GSMEPEEYRERGREMVDYICQYLSTVRERRVTPDVQPGYLRAQLPESAPEDPDSWDSIFGDIERIIMPGVVHWQSPHMHAYYPALTSWPSLLGDMLADAINCLGFTWASSPACTELEMNVMDWLAKMLGLPEHFLHHHPSSQGGGVLQSTVSESTLIALLAARKNKILEMKTSEPDADESSLNARLVAYASDQAHSSVEKAGLISLVKMKFLPVDDNFSLRGEALQKAIEEDKQRGLVPVFVCATLGTTGVCAFDXLSELGPICAREGLWLHIDAAYAGTAFLCPEFRGFLKGIEYADSFTFNPSKWMMVHFDCTGFWVKDKYKLQQTFSVNPIYLRHANSGVATDFMHWQIPLSRRFRSVKLWFVIRSFGVKNLQAHVRHGTEMAKYFESLVRNDPSFEIPAKRHLGLVVFRLKGPNSLTENVLKEIAKAGRLFLIPATIQDKLIIRFTVTSQFTTRDDILRDWNLIRDAATLILSQGSMEPEEYRERGREMVDYICQYLSTVRERRVTPDVQPGYLRAQLPESAPEDPDSWDSIFGDIERIIMPGVVHWQSPHMHAYYPALTSWPSLLGDMLADAINCLGFTWASSPACTELEMNVMDWLAKMLGLPEHFLHHHPSSQGGGVLQSTVSESTLIALLAARKNKILEMKTSEPDADESSLNARLVAYASDQAHSSVEKAGLISLVKMKFLPVDDNFSLRGEALQKAIEEDKQRGLVPVFVCATLGTTGVCAFDXLSELGPICAREGLWLHIDAAYAGTAFLCPEFRGFLKGIEYADSFTFNPSKWMMVHFDCTGFWVKDKYKLQQTFSVNPIYLRHANSGVATDFMHWQIPLSRRFRSVKLWFVIRSFGVKNLQAHVRHGTEMAKYFESLVRNDPSFEIPAKRHLGLVVFRLKGPNSLTENVLKEIAKAGRLFLIPATIQDKLIIRFTVTSQFTTRDDILRDWNLIRDAATLILSQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 9 | Pseudomonas Transcriptional activator protein LasR (Pseudo LasR) | 3IX3 | 6.88 | |
Target general information Gen name Pseudo LasR Organism Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NA Protein family Autoinducer-regulated transcriptional regulatory protein family Biochemical class NA Function Transcriptional activator of elastase structural gene (LasB). Binds to the PAI autoinducer. Related diseases Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1A (IGHD1A) [MIM:262400]: An autosomal recessive, severe deficiency of growth hormone leading to dwarfism. Patients often develop antibodies to administered growth hormone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8364549}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1B (IGHD1B) [MIM:612781]: An autosomal recessive deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Patients have low but detectable levels of growth hormone, significantly retarded bone age, and a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655557}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Kowarski syndrome (KWKS) [MIM:262650]: A syndrome clinically characterized by short stature associated with bioinactive growth hormone, normal or slightly increased growth hormone secretion, pathologically low insulin-like growth factor 1 levels, and normal catch-up growth on growth hormone replacement therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17519310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8552145, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9276733}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 2 (IGHD2) [MIM:173100]: An autosomal dominant deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Clinical severity is variable. Patients have a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11502836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9152628}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08324 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; DNA-binding; Quorum sensing; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 18305.5 Length 163 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.52 Isoelectric point 5.19 Charge (pH=7) -6.78 3D Binding mode Sequence FLELERSSGKLEWSAILQKMASDLGFSKILFGLLPKDSQDYENAFIVGNYPAAWREHYDRAGYARVDPTVSHCTQSVLPIFWEPSIYQTRKQHEFFEEASAAGLVYGLTMPLHGARGELGALSLSVEAENRAEANRFMESVLPTLWMLKDYALQSGAGLAFEH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 10 | Aldehyde oxidoreductase | 4USA | 6.87 | |
Target general information Gen name mop Organism Megalodesulfovibrio gigas (Desulfovibrio gigas) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Xanthine dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding.Aldehyde dehydrogenase (FAD-independent) activity.Electron carrier activity.Metal ion binding. Related diseases LTC4 synthase deficiency is associated with a neurometabolic developmental disorder characterized by muscular hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, and microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10896305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9820300}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02137 Interacts with NA EC number 1.2.99.7 Uniprot keywords 2Fe-2S; 3D-structure; FAD; Flavoprotein; Iron; Iron-sulfur; Metal-binding; Molybdenum; NAD; Oxidoreductase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 96930.4 Length 907 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 29.17 Isoelectric point 5.69 Charge (pH=7) -17.56 3D Binding mode Sequence MIQKVITVNGIEQNLFVDAEALLSDVLRQQLGLTGVKVGCEQGQCGACSVILDGKVVRACVTKMKRVADGAQITTIEGVGQPENLHPLQKAWVLHGGAQCGFCSPGFIVSAKGLLDTNADPSREDVRDWFQKHRNACRCTGYKPLVDAVMDAAAVINGKKPETDLEFKMPADGRIWGSKYPRPTAVAKVTGTLDYGADLGLKMPAGTLHLAMVQAKVSHANIKGIDTSEALTMPGVHSVITHKDVKGKNRITGLITFPTNKGDGWDRPILXDEKVFQYGDCIALVCADSEANARAAAEKVKVDLEELPAYMSGPAAAAEDAIEIHPGTPNVYFEQPIVKGEDTGPIFASADVTVEGDFYVGRQPHMPIEPDVAFAYMGDDGKCYIHSKSIGVHLHLYMIAPGVGLEPDQLVLVANPMGGTFGYKFSPTSEALVAVAAMATGRPVHLRYNYQQQQQYTGKRSPWEMNVKFAAKKDGTLLAMESDWLVDHGPYSEFGDLLTLRGAQFIGAGYNIPNIRGLGRTVATNHVWGSAFRGYGAPQSMFASECLMDMLAEKLGMDPLELRYKNAYRPGDTNPTGQEPEVFSLPDMIDQLRPKYQAALEKAQKESTATHKKGVGISIGVYGSGLDGPDASEAWAELNADGTITVHTAWEDHGQGADIGCVGTAHEALRPMGVAPEKIKFTWPNTATTPNSGPSGGSRQQVMTGNAIRVACENLLKACEKPGGGYYTYDELKAADKPTKITGNWTASGATHCDAVTGLGKPFVVYMYGVFMAEVTVDVATGQTTVDGMTLMADLGSLCNQLATDGQIYGGLAQGIGLALSEDFEDIKKHATLVGAGFPFIKQIPDKLDIVYVNHPRPDGPFGASGVGELPLTSPHAAIINAIKSATGVRIYRLPAYPEKVLEALKA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 11 | Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex 1 (VKORC1) | 6WV3 | 6.86 | |
Target general information Gen name VKORC1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Vitamin K1 2,3-epoxide reductase subunit 1; VKORC1; VKOR; UNQ308/PRO351; MSTP576; MSTP134 Protein family VKOR family Biochemical class Short-chain dehydrogenases reductase Function Involved invitamin K metabolism. Catalytic subunit of the vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) complex which reduces inactive vitamin K 2,3-epoxide to active vitamin K. Vitamin K is required for the gamma-carboxylation of various proteins, including clotting factors, and is required for normal blood coagulation, but also for normal bone development. Related diseases Combined deficiency of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors 2 (VKCFD2) [MIM:607473]: VKCFD leads to a bleeding tendency that is usually reversed by oral administration of vitamin K. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14765194, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16270630}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Coumarin resistance (CMRES) [MIM:122700]: A condition characterized by partial or complete resistance to warfarin or other 4-hydroxycoumarin derivatives. These drugs are used as anti-coagulants for the prevention of thromboembolic diseases in subjects with deep vein thrombosis, atrial fibrillation, or mechanical heart valve replacement. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14765194, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20946155}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01418; DB00266; DB09332; DB00170; DB00498; DB00946; DB01022; DB00682 Interacts with Q13323; Q7Z7G2; Q96BA8; Q9Y282; Q5JX71; Q96KR6; Q5T7V8; Q8TDT2; Q9NQG1; P15941-11; Q96TC7; Q9NR31; A0A0S2Z4U3; Q8TBB6; O15393-2; Q19QW4 EC number EC 1.17.4.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Membrane; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Quinone; Redox-active center; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 42656.4 Length 381 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 32.12 Isoelectric point 7.73 Charge (pH=7) 1.93 3D Binding mode Sequence KGEELFTGVVPILVELDGDVNGHKFSVRGEGEGDATNGKLTLKFICTTGKLPVPWPTLVTTLXVQCFSRYPDHMKRHDFFKSAMPEGYVQERTISFKDDGTYKTRAEVKFEGDTLVNRIELKGIDFKEDGNILGHKLEYNSTWGSPGWVRLALCLTGLVLSLYALHVKAARARDRDYRALCDVGTAISCSRVFSSRWGRGFGLVEHVLGQDSILNQSNSIFGCIFYTLQLLLGCLRTRWASVLMLLSSLVSLAGSVYLAWILFFVLYDFCIVCITTYAINVSLMWLSFRKVQENSHNVYITADKQKNGIKANFKIRHNVEDGSVQLADHYQQNTPIGDGPVLLPDNHYLSTQSVLSKDPNEKRDHMVLLEFVTAAGITHHH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 12 | Xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase (XDH) | 2E1Q | 6.84 | |
Target general information Gen name XDH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Xanthine oxidase; Xanthine dehydrogenase; XDHA Protein family Xanthine dehydrogenase family Biochemical class CH/CH(2) oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine. Catalyzes the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. Contributes to the generation of reactive oxygen species. Has also low oxidase activity towards aldehydes (in vitro). Key enzyme in purine degradation. Related diseases Xanthinuria 1 (XAN1) [MIM:278300]: A disorder characterized by excretion of very large amounts of xanthine in the urine and a tendency to form xanthine stones. Uric acid is strikingly diminished in serum and urine. XAN1 is due to isolated xanthine dehydrogenase deficiency. Patients can metabolize allopurinol. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10844591, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11379872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14551354, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9153281}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00640; DB00041; DB00437; DB00993; DB00958; DB01136; DB00856; DB00515; DB00746; DB03328; DB00997; DB03516; DB12466; DB04854; DB03147; DB04335; DB01020; DB00583; DB00170; DB01033; DB00157; DB03841; DB00336; DB01250; DB05262; DB06478; DB01168; DB00339; DB00127; DB01685; DB00831 Interacts with Q9Y3R0-3 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 2Fe-2S; 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; FAD; Flavoprotein; Iron; Iron-sulfur; Metal-binding; Molybdenum; NAD; Oxidoreductase; Peroxisome; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 143697 Length 1307 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 37.9 Isoelectric point 8.01 Charge (pH=7) 7.07 3D Binding mode Sequence ADKLVFFVNGRKVVEKNADPETTLLAYLRRKLGLSGTKLGCGEGGCGACTVMLSKYDRLQNKIVHFSANACLAPICSLHHVAVTTVEGIGSTKTRLHPVQERIAKSHGSQCGFCTPGIVMSMYTLLRNQPEPTMEEIENAFQGNLCRCTGYRPILQGFRTFARDGSPSLFKPEEFTPLDPTQEPIFPPELLRLKDTPRKQLRFEGERVTWIQASTLKELLDLKAQHPDAKLVVGNTEIGIEMKFKNMLFPMIVCPAWIPELNSVEHGPDGISFGAACPLSIVEKTLVDAVAKLPAQKTEVFRGVLEQLRWFAGKQVKSVASVGGNIITASPISDLNPVFMASGAKLTLVSRGTRRTVQMDHTFFPGYRKTLLSPEEILLSIEIPYSREGEYFSAFKQASRREDDIAKVTSGMRVLFKPGTTEVQELALCYGGMANRTISALKTTQRQLSKLWKEELLQDVCAGLAEELHLPPDAPGGMVDFRCTLTLSFFFKFYLTVLQKLGQENLEDKCGKLDPTFASATLLFQKDPPADVQLFQEVPKGQSEEDMVGRPLPHLAADMQASGEAVYCDDIPRYENELSLRLVTSTRAHAKIKSIDTSEAKKVPGFVCFISADDVPGSNITGICNDETVFAKDKVTCVGHIIGAVVADTPEHTQRAAQGVKITYEELPAIITIEDAIKNNSFYGPELKIEKGDLKKGFSEADNVVSGEIYIGGQEHFYLETHCTIAVPKGEAGEMELFVSTQNTMKTQSFVAKMLGVPANRIVVRVKRMGGGFGGKVTRSTVVSTAVALAAYKTGRPVRCMLDRDEDMLITGGRHPFLARYKVGFMKTGTVVALEVDHFSNVGNTQDLSQSIMERALFHMDNCYKIPNIRGTGRLCKTNLPSNTAFRGFGGPQGMLIAECWMSEVAVTCGMPAEEVRRKNLYKEGDLTHFNQKLEGFTLPRCWEECLASSQYHARKSEVDKFNKENCWKKRGLCIIPTKFGISFTVPFLNQAGALLHVYTDGSVLLTHGGTEMGQGLHTKMVQVASRALKIPTSKIYISETSTNTVPNTSPTAASVSADLNGQAVYAACQTILKRLEPYKKKNPSGSWEDWVTAAYMDTVSLSATGFYRTPNLGYSFETNSGNPFHYFSYGVACSEVEIDCLTGDHKNLRTDIVMDVGSSLNPAIDIGQVEGAFVQGLGLFTLEELHYSPEGSLHTRGPSTYKIPAFGSIPIEFRVSLLRDCPNKKAIYASKAVGEPPLFLAASIFFAIKDAIRAARAQHTGNNVKELFRLDSPATPEKIRNACVDKFTTLCVTGVPENCKPWSVRV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 13 | Orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase (UMPS) | 3MI2 | 6.84 | |
Target general information Gen name UMPS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Uridine 5'-monophosphate synthase; UMP synthase Protein family Purine/pyrimidine phosphoribosyltransferase family; OMP decarboxylase family Biochemical class Pentosyltransferase Function Catalyses the formation of uridine monophosphate (UMP), an energy-carrying molecule in many important biosynthetic pathways. Related diseases Orotic aciduria 1 (ORAC1) [MIM:258900]: A disorder of pyrimidine metabolism resulting in megaloblastic anemia and orotic acid crystalluria that is frequently associated with some degree of physical and intellectual disability. A minority of cases have additional features, particularly congenital malformations and immune deficiencies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9042911}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02890; DB00544 Interacts with P54764; P11172-1 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Decarboxylase; Disease variant; Glycosyltransferase; Lyase; Multifunctional enzyme; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Pyrimidine biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 55844 Length 514 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 22.7 Isoelectric point 6.44 Charge (pH=7) -2.99 3D Binding mode Sequence KELSFGARAELPRIHPVASKLLRLMQKKETNLCLSADVSLARELLQLADALGPSICMLKTHVDILNDFTLDVMKELITLAKXHEFLIFEDRKFADIGNTVKKQYEGGIFKIASWADLVNAHVVPGSGVVKGLQEVGLPLHRGCLLIAEMSSTGSLATGDYTRAAVRMAEEHSEFVVGFISGSRVSMKPEFLHLTPGVQLEAGGDNLGQQYNSPQEVIGKRGSDIIIVGRGIISAADRLEAAEMYRKAAWEAYLSRLGKELSFGARAELPRIHPVASKLLRLMQKKETNLCLSADVSLARELLQLADALGPSICMLKTHVDILNDFTLDVMKELITLAKXHEFLIFEDRKFADIGNTVKKQYEGGIFKIASWADLVNAHVVPGSGVVKGLQEVGLPLHRGCLLIAEMSSTGSLATGDYTRAAVRMAEEHSEFVVGFISGSRVSMKPEFLHLTPGVQLEAGGDNLGQQYNSPQEVIGKRGSDIIIVGRGIISAADRLEAAEMYRKAAWEAYLSRLG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 14 | Plasmodium Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (Malaria LACZ) | 3OZF | 6.84 | |
Target general information Gen name Malaria LACZ Organism Plasmodium falciparum (isolate FCR-3 / Gambia) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms LACZ of Plasmodium falciparum (isolate FCR-3 / Gambia); Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase; HPRT; HGPRTase; HGPRT of Plasmodium falciparum (isolate FCR-3 / Gambia); Guanine phosphoribosyltransfera Protein family Purine/pyrimidine phosphoribosyltransferase family Biochemical class Pentosyltransferase Function Converts guanine to guanosine monophosphate, and hypoxanthine to inosine monophosphate. Transfers the 5- phosphoribosyl group from 5-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate onto the purine. Plays a central role in the generation of purine nucleotides through the purine salvage pathway. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder with dysmorphic facies and ptosis (IDDDFP) [MIM:617333]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by delayed psychomotor development, intellectual disability, delayed language, and facial dysmorphisms, most notably ptosis. Additional features may include poor growth, hypotonia, and seizures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27939639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27939640}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02075; DB11638 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Glycosyltransferase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Purine salvage; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 26581.3 Length 233 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 29.77 Isoelectric point 7.92 Charge (pH=7) 1.69 3D Binding mode Sequence PRGSHMPIPNNPGAGENAFDPVFVNDDDGYDLDSFMIPAHYKKYLTKVLVPNGVIKNRIEKLAYDIKKVYNNEEFHILCLLKGSRGFFTALLKHLSRIHNYSAVETSKPLFGEHYVRVKSYCNDQSTGTLEIVSEDLSCLKGKHVLIVEDIIDTGKTLVKFCEYLKKFEIKTVAIACLFIKRTPLWNGFKADFVGFSIPDHFVVGYSLDYNEIFRDLDHCCLVNDEGKKKYKA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 15 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase (HLNM) | 3QOW | 6.84 | |
Target general information Gen name DOT1L Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Lysine N-methyltransferase 4; KMT4; KIAA1814; Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase, H3 lysine-79 specific; Histone H3-K79 methyltransferase; H3-K79-HMTase; DOT1-like protein Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, DOT1 family Biochemical class Methyltransferase Function Histone methyltransferase. Methylates 'Lys-79' of histone H3. Nucleosomes are preferred as substrate compared to free histones. Binds to DNA. Related diseases Defects in DOTL1 are associated with an autosomal dominant form of global developmental delay and intellectual disability, with or without one or more major congenital anomalies (PubMed:37827158). The patient phenotypes are characterized by central nervous system (CNS) dysfunction, such as mild motor delay and significant speech and language delay, and a range of congenital anomalies, including brain structural anomalies, cardiac defects, varied urogenital features and growth restriction (PubMed:37827158). Variants may cause a gain-of-function effect leading to an increase in cellular H3K79 methylation levels (PubMed:37827158). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:37827158}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q03111; P42568 EC number EC 2.1.1.43 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Disease variant; DNA-binding; Methyltransferase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 37367.1 Length 322 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 32.71 Isoelectric point 6.03 Charge (pH=7) -5.25 3D Binding mode Sequence KLELRLKSPVGAEPAVYPWPLPVYDKHHDAAHEIIETIRWVCEEIPDLKLAMENYLIDYDTKSFESMQRLCDKYNRAIDSIHQLWKGTTQPMKLNTRPSTGLLRHILQQVYNHSVTDPEKLNNYEPFSPEVYGETSFDLVAQMIDEIKMTDDDLFVDLGSGVGQVVLQVAAATNCKHHYGVEKADIPAKYAETMDREFRKWMKWYGKKHAEYTLERGDFLSEEWRERIANTSVIFVNNFAFGPEVDHQLKERFANMKEGGRIVSSKPFAPLNFRINSRNLSDIGTIMRVVELSPLKWTGKPVSYYLHTIDRTILENYFSSLK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 16 | Folate receptor beta (FOLR2) | 4KN0 | 6.83 | |
Target general information Gen name FOLR2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Placental folate-binding protein; Folate receptor, fetal/placental; Folate receptor type-beta; Folate receptor 2; FR-beta; FOLR2 Protein family Folate receptor family Biochemical class Folate receptor Function Binds to folate and reduced folic acid derivatives and mediates delivery of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and folate analogs into the interior of cells. Has high affinity for folate and folic acid analogs at neutral pH. Exposure to slightly acidic pH after receptor endocytosis triggers a conformation change that strongly reduces its affinity for folates and mediates their release. Related diseases Acute hepatic porphyria (AHEPP) [MIM:612740]: A form of porphyria. Porphyrias are inherited defects in the biosynthesis of heme, resulting in the accumulation and increased excretion of porphyrins or porphyrin precursors. They are classified as erythropoietic or hepatic, depending on whether the enzyme deficiency occurs in red blood cells or in the liver. AHP is characterized by attacks of gastrointestinal disturbances, abdominal colic, paralyses and peripheral neuropathy. Most attacks are precipitated by drugs, alcohol, caloric deprivation, infections, or endocrine factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10706561, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1309003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1569184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17236137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2063868}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00158; DB00563; DB05168 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Folate-binding; Glycoprotein; GPI-anchor; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23841.6 Length 205 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 56.78 Isoelectric point 7.92 Charge (pH=7) 2.58 3D Binding mode Sequence RTDLLNVCMDAKHHKTKPGPEDKLHDQCSPWKKNACCTASTSQELHKDTSRLYNFNWDHCGKMEPACKRHFIQDTCLYECSPNLGPWIQQVNQSWRKERFLDVPLCKEDCQRWWEDCHTSHTCKSNWHRGWDWTSGVNKCPAGALCRTFESYFPTPAALCEGLWSHSYKVSNYSRGSGRCIQMWFDSAQGNPNEEVARFYAAAMH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 17 | Tryptophan 5-hydroxylase 1 (TPH1) | 5TPG | 6.82 | |
Target general information Gen name TPH1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tryptophan 5-monooxygenase 1; TRPH; TPRH Protein family Biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylase family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Responsible for addition of the -HO group (hydroxylation) to the 5 position to form the amino acid 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), which is the initial and rate-limiting step in the synthesis of the neurotransmitter serotonin. Related diseases Tyrosinemia 2 (TYRSN2) [MIM:276600]: An inborn error of metabolism characterized by elevations of tyrosine in the blood and urine, and oculocutaneous manifestations. Typical features include palmoplantar keratosis, painful corneal ulcers, and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1357662}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05199; DB00360; DB12095; DB00150 Interacts with Q14457; Q96IK1-2; Q9UKB3; Q9H8Y8; O43586; O95789-4 EC number EC 1.14.16.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Iron; Metal-binding; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serotonin biosynthesis; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 31138.2 Length 271 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 43.43 Isoelectric point 6.73 Charge (pH=7) -0.86 3D Binding mode Sequence TVPWFPKKISDLDHCNVYRKRRKYFADLAMNYKHGDPIPKVEFTEEEIKTWGTVFQELNKLYPTHACREYLKNLPLLSKYCGYREDNIPQLEDVSNFLKERTGFSIRPVAGYLSPRDFLSGLAFRVFHCTQYVRHSSDPFYTPEPDTCHELLGHVPLLAEPSFAQFSQEIGLASLGASEEAVQKLATCYFFTVEFGLCKQDGQLRVFGAGLLSSISELKHALSGHAKVKPFDPKITCKQECLITTFQDVYFVSESFEDAKEKMREFTKTIK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 18 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Kit (KIT) | 1T46 | 6.79 | |
Target general information Gen name KIT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms v-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; p145 c-kit; Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Kit; Proto-oncogene c-Kit; Piebald trait protein; PBT; Mast/stem cell growth factor re Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function In response to KITLG/SCF binding, KIT can activate several signaling pathways. Phosphorylates PIK3R1, PLCG1, SH2B2/APS and CBL. Activates the AKT1 signaling pathway by phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Activated KIT also transmits signals via GRB2 and activation of RAS, RAF1 and the MAP kinases MAPK1/ERK2 and/or MAPK3/ERK1. Promotes activation of STAT family members STAT1, STAT3, STAT5A and STAT5B. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. KIT signaling is modulated by protein phosphatases, and by rapid internalization and degradation of the receptor. Activated KIT promotes phosphorylation of the protein phosphatases PTPN6/SHP-1 and PTPRU, and of the transcription factors STAT1, STAT3, STAT5A and STAT5B. Promotes phosphorylation of PIK3R1, CBL, CRK (isoform Crk-II), LYN, MAPK1/ERK2 and/or MAPK3/ERK1, PLCG1, SRC and SHC1. Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for the cytokine KITLG/SCF and plays an essential role in the regulation of cell survival and proliferation, hematopoiesis, stem cell maintenance, gametogenesis, mast cell development, migration and function, and in melanogenesis. Related diseases Piebald trait (PBT) [MIM:172800]: Autosomal dominant genetic developmental abnormality of pigmentation characterized by congenital patches of white skin and hair that lack melanocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11074500, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1370874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1376329, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1717985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7687267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8680409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9450866, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9699740}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) [MIM:606764]: Common mesenchymal neoplasms arising in the gastrointestinal tract, most often in the stomach. They are histologically, immunohistochemically, and genetically different from typical leiomyomas, leiomyosarcomas, and schwannomas. Most GISTs are composed of a fairly uniform population of spindle-shaped cells. Some tumors are dominated by epithelioid cells or contain a mixture of spindle and epithelioid morphologies. Primary GISTs in the gastrointestinal tract commonly metastasize in the omentum and mesenteries, often as multiple nodules. However, primary tumors may also occur outside of the gastrointestinal tract, in other intra-abdominal locations, especially in the omentum and mesentery. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11505412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15824741, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9438854, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9697690}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Testicular germ cell tumor (TGCT) [MIM:273300]: A common malignancy in males representing 95% of all testicular neoplasms. TGCTs have various pathologic subtypes including: unclassified intratubular germ cell neoplasia, seminoma (including cases with syncytiotrophoblastic cells), spermatocytic seminoma, embryonal carcinoma, yolk sac tumor, choriocarcinoma, and teratoma. The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML) [MIM:601626]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. AML is a malignant disease of bone marrow characterized by maturational arrest of hematopoietic precursors at an early stage of development. Clonal expansion of myeloid blasts occurs in bone marrow, blood, and other tissue. Myelogenous leukemias develop from changes in cells that normally produce neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils and monocytes. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. Somatic mutations that lead to constitutive activation of KIT are detected in AML patients. These mutations fall into two classes, the most common being in-frame internal tandem duplications of variable length in the juxtamembrane region that disrupt the normal regulation of the kinase activity. Likewise, point mutations in the kinase domain can result in a constitutively activated kinase.; DISEASE: Mastocytosis, cutaneous (MASTC) [MIM:154800]: A form of mastocytosis, a heterogeneous group of disorders associated with abnormal proliferation and accumulation of mast cells in various tissues, especially in the skin and hematopoietic organs. MASTC is an autosomal dominant form characterized by macules, papules, nodules, or diffuse infiltration of the skin, often associated with localized hyperpigmentation. Gentle rubbing of the lesions induces histamine release from mechanically activated mast cells, causing local wheals, erythema, and often pruritus, a phenomenon termed Darier sign. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15173254, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19865100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21689725, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24289326, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9990072}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Mastocytosis, systemic (MASTSYS) [MIM:154800]: A severe form of mastocytosis characterized by abnormal proliferation and accumulation of mast cells in several organs, resulting in a systemic disease that may affect bone, gastrointestinal tract, lymphatics, spleen, and liver. In some cases, it is associated with a clonal hematologic non-mast-cell lineage disease, such as a myelodysplastic or myeloproliferative disorder. It can also lead to mast cell leukemia, which carries a high risk of mortality. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9990072}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12742; DB09103; DB15233; DB01254; DB12147; DB12010; DB00619; DB09078; DB06080; DB06595; DB04868; DB05913; DB06589; DB12978; DB01962; DB08901; DB08896; DB14840; DB00398; DB01268; DB11800; DB05146 Interacts with P00519; P42684; O75815; P51451; Q8WV28; P46108; P07332; P09769; O75791; P62993; Q14451; P08631; Q96JZ2; P21583; P06239; P07948; P16333; O43639; P27986; O00459; Q92569; P19174; P16885; Q13882; Q06124; Q92729; P20936; Q9UQQ2; O14796; Q9NP31; Q8N5H7; P78314; Q15464; P29353; P98077; Q92529; Q9H6Q3; O14508; O14543; O14544; P12931; Q9ULZ2; Q9HBL0; Q63HR2; Q68CZ2; P42681; P07947; P43403; Q8VBX6; P35235 EC number EC 2.7.10.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Immunoglobulin domain; Kinase; Magnesium; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Proto-oncogene; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33575.6 Length 297 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 45.37 Isoelectric point 8.37 Charge (pH=7) 3.24 3D Binding mode Sequence GNNYVYIDPTQLPYDHKWEFPRNRLSFGKTLGAGAFGKVVEATAYGLIKSDAAMTVAVKMLKPSAHLTEREALMSELKVLSYLGNHMNIVNLLGACTIGGPTLVITEYCCYGDLLNFLRRKRDSFLALDLEDLLSFSYQVAKGMAFLASKNCIHRDLAARNILLTHGRITKICDFGLARDIKNDSNYVVKGNARLPVKWMAPESIFNCVYTFESDVWSYGIFLWELFSLGSSPYPGMPVDSKFYKMIKEGFRMLSPEHAPAEMYDIMKTCWDADPLKRPTFKQIVQLIEKQISESTN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 19 | "Periplasmic trehalase (EC 3.2.1.28) (Alpha,alpha-trehalase) (Alpha,alpha-trehalose glucohydrolase) (Tre37A)" | 2JG0 | 6.79 | |
Target general information Gen name treA Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms JW1186;osmA;b1197 Protein family Glycosyl hydrolase 37 family Biochemical class NA Function Provides the cells with the ability to utilize trehalose at high osmolarity by splitting it into glucose molecules that can subsequently be taken up by the phosphotransferase-mediated uptake system. Related diseases SRC kinase activity has been shown to be increased in several tumor tissues and tumor cell lines such as colon carcinoma cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2498394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3093483}.; DISEASE: Thrombocytopenia 6 (THC6) [MIM:616937]: A form of thrombocytopenia, a hematologic disorder defined by a decrease in the number of platelets in circulating blood, resulting in the potential for increased bleeding and decreased ability for clotting. THC6 is an autosomal dominant form. Affected individuals may also have bone abnormalities and an increased risk for myelofibrosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26936507}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 3.2.1.28 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Glycosidase; Hydrolase; Periplasm; Reference proteome; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 57508.9 Length 507 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 48.32 Isoelectric point 5.48 Charge (pH=7) -10.13 3D Binding mode Sequence PQPPDILLGPLFNDVQNAKLFPDQKTFADAVPNSDPLMILADYRMQQNQSGFDLRHFVNVNFTLPKYVPPEGQSLREHIDGLWPVLTRSTENTEKWDSLLPLPEPYVVPGGRFREVYYWDSYFTMLGLAESGHWDKVADMVANFAHEIDTYGHIPNGNRSYYLSRSQPPFFALMVELLAQHEGDAALKQYLPQMQKEYAYWMDGVENLQAGQQEKRVVKLQDGTLLNRYWDDRDTPRPESWVEDIATAKSNPNRPATEIYRDLRSAAASGWDFSSRWMDNPQQLNTLRTTSIVPVDLNSLMFKMEKILARASKAAGDNAMANQYETLANARQKGIEKYLWNDQQGWYADYDLKSHKVRNQLTAAALFPLYVNAAAKDRANKMATATKTHLLQPGGLNTTSVKSGQQWDAPNGWAPLQWVATEGLQNYGQKEVAMDISWHFLTNVQHTYDREKKLVEKYDVSTTGTGGGGGEYPLQDGFGWTNGVTLKMLDLICPKEQPCDNVPATRP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 20 | Sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) | 7VSI | 6.79 | |
Target general information Gen name SLC5A2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Solute carrier family 5 member 2; Na(+)/glucose cotransporter 2; Low affinity sodium-glucose cotransporter Protein family Sodium:solute symporter (SSF) (TC 2.A.21) family Biochemical class Solute:sodium symporter Function Has a Na(+) to glucose coupling ratio of 1:1. Sodium-dependent glucose transporter. Related diseases Renal glucosuria (GLYS) [MIM:233100]: A disorder characterized by persistent isolated glucosuria, normal fasting serum glucose concentration, decreased renal tubular resorption of glucose from the urine, and absence of any other signs of tubular dysfunction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14614622}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12236; DB08907; DB01914; DB06292; DB09038; DB11827; DB12713 Interacts with O14556; Q13113 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Ion transport; Membrane; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Sodium; Sodium transport; Sugar transport; Symport; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 63858.9 Length 586 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 39.46 Isoelectric point 8.62 Charge (pH=7) 7.41 3D Binding mode Sequence DNPADILVIAAYFLLVIGVGLWSMCRTNRGTVGGYFLAGRSMVWWPVGASLFASNIGSGHFVGLAGTGAASGLAVAGFEWNALFVVLLLGWLFAPVYLTAGVITMPQYLRKRFGGRRIRLYLSVLSLFLYIFTKISVDMFSGAVFIQQALGWNIYASVIALLGITMIYTVTGGLAALMYTDTVQTFVILGGACILMGYAFHEVGGYSGLFDKYLGAATSLTVSEDPAVGNISSFCYRPRPDSYHLLRHPVTGDLPWPALLLGLTIVSGWYWCSDQVIVQRCLAGKSLTHIKAGCILCGYLKLTPMFLMVMPGMISRILYPDEVACVVPEVCRRVCGTEVGCSNIAYPRLVVKLMPNGLRGLMLAVMLAALMSSLASIFNSSSTLFTMDIYTRLRPRAGDRELLLVGRLWVVFIVVVSVAWLPVVQAAQGGQLFDYIQAVSSYLAPPVSAVFVLALFVPRVNEQGAFWGLIGGLLMGLARLIPEFSFGSGSCVQPSACPAFLCGVHYLYFAIVLFFCSGLLTLTVSLCTAPIPRKHLHRLVFSLRHSKEEREDLDEDISEDPSWARVVNLNALLMMAVAVFLWGFYA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||