Job Results:
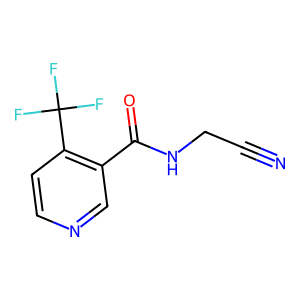
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
5c976aa63f0cd6d4251a6978fa589574
Job name
NA
Time
2025-07-21 16:39:34
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | Bifunctional aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (EPRS) | 4HVC | 5.35 | |
Target general information Gen name EPRS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms QPRS; QARS; ProlinetRNA ligase; PIG32; GlutamatylprolyltRNA synthetase; Glutamatyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase; GluRS; EPRS; Cell proliferationinducing gene 32 protein; Cell proliferation-inducing gene 32 Protein family Class-I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family, Glutamate--tRNA ligase type 2 subfamily; Class-II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family Biochemical class Carbon-oxygen ligase Function The phosphorylation of EPRS, induced by interferon-gamma, dissociates the protein from the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase multienzyme complex and recruits it to the GAIT complex that binds to stem loop-containing GAIT elements in the 3'-UTR of diverse inflammatory mRNAs (such as ceruplasmin), suppressing their translation. Interferon-gamma can therefore redirect, in specific cells, the EPRS function from protein synthesis to translation inhibition. Also functions as an effector of the mTORC1 signaling pathway by promoting, through SLC27A1, the uptake of long-chain fatty acid by adipocytes. Thereby, it also plays a role in fat metabolism and more indirectly influences lifespan. Multifunctional protein which is primarily part of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase multienzyme complex, also know as multisynthetase complex, that catalyzes the attachment of the cognate amino acid to the corresponding tRNA in a two-step reaction: the amino acid is first activated by ATP to form a covalent intermediate with AMP and is then transferred to the acceptor end of the cognate tRNA. Related diseases Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, 15 (HLD15) [MIM:617951]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by hypomyelinating leukodystrophy with thinning of the corpus callosum. Clinical features include motor and cognitive impairment appearing in the first or second decade of life, dystonia, ataxia, spasticity, and dysphagia. Most patients develop severe optic atrophy, and some have hearing loss. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29576217}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02684; DB02510; DB03376; DB00142; DB00172 Interacts with P07814; Q8IWL3; P41252; Q15046; P42695; P54136; O60506 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Leukodystrophy; Ligase; Membrane; Metal-binding; Methylation; Multifunctional enzyme; Neurodegeneration; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Protein biosynthesis; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; RNA-binding; Translation regulation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 55039.7 Length 483 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 39.15 Isoelectric point 5.92 Charge (pH=7) -6.4 3D Binding mode Sequence GLEAKKEENLADWYSQVITKSEMIEYHDISGCYILRPWAYAIWEAIKDFFDAEIKKLGVENCYFPMFVSQSALEKEKTHVADFAPEVAWVTRSGKTELAEPIAIRPTSETVMYPAYAKWVQSHRDLPIKLNQWCNVVRWEFKHPQPFLRTREFLWQEGHSAFATMEEAAEEVLQILDLYAQVYEELLAIPVVKGRKTEKEKFAGGDYTTTIEAFISASGRAIQGGTSHHLGQNFSKMFEIVFEDPKIPGEKQFAYQNSWGLTTRTIGVMTMVHGDNMGLVLPPRVACVQVVIIPCGISEEDKEALIAKCNDYRRRLLSVNIRVRADLRDNYSPGWKFNHWELKGVPIRLEVGPRDMKSCQFVAVRRDTGEKLTVAENEAETKLQAILEDIQVTLFTRASEDLKTHMVVANTMEDFQKILDSGKIVQIPFCGEIDCEDWIKKTTAMGAKSLCIPFKPLCELQPGAKCVCGKNPAKYYTLFGRSY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 42 | Matrix metalloproteinase-10 (MMP-10) | 1Q3A | 5.35 | |
Target general information Gen name MMP10 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Transin-2; Stromelysin-2; STMY2; SL-2 Protein family Peptidase M10A family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Activates procollagenase. Can degrade fibronectin, gelatins of type I, III, IV, and V; weakly collagens III, IV, and V. Related diseases Orthostatic hypotension 1 (ORTHYP1) [MIM:223360]: A form of orthostatic hypotension due to congenital dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a finding defined as a 20-mm Hg decrease in systolic pressure or a 10-mm Hg decrease in diastolic pressure occurring 3 minutes after a person has risen from supine to standing. Symptoms include dizziness, blurred vision, and sometimes syncope. ORTHYP1 is an autosomal recessive condition apparent from infancy or early childhood and characterized by low plasma and urinary levels of norepinephrine and epinephrine, and episodic hypoglycemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11857564}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00786; DB08271 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.4.24.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Calcium; Collagen degradation; Disulfide bond; Extracellular matrix; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Zinc; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 52822 Length 471 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 21.13 Isoelectric point 4.83 Charge (pH=7) -35.32 3D Binding mode Sequence MPKWRKTHLTYRIVNYTPDLPRDAVDSAIEKALKVWEEVTPLTFSRLYEGEADIMISFAVKEHGDNYSFDGPGHSLAHAYPPGPGLYGDIHFDDDEKWTEDASGTNLFLVAAHELGHSLGLFHSANTEALMYPLYNSLAQFRLSQDDVNGIQSLYGPKWRKTHLTYRIVNYTPDLPRDAVDSAIEKALKVWEEVTPLTFSRLYEGEADIMISFAVKEHGDNYSFDGPGHSLAHAYPPGPGLYGDIHFDDDEKWTEDASGTNLFLVAAHELGHSLGLFHSANTEALMYPLYNSLAQFRLSQDDVNGIQSLYGGMPKWRKTHLTYRIVNYTPDLPRDAVDSAIEKALKVWEEVTPLTFSRLYEGEADIMISFAVKEHGDNYSFDGPGHSLAHAYPPGPGLYGDIHFDDDEKWTEDASGTNLFLVAAHELGHSLGLFHSANTEALMYPLYNSFTELAQFRLSQDDVNGIQSLYG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 43 | Cytochrome b (Complex III subunit 3) (Complex III subunit III) (Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 3) (Ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase complex cytochrome b subunit) | 1SQB | 5.35 | |
Target general information Gen name MT-CYB Organism Bos taurus (Bovine) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CYTB;MTCYB;COB Protein family Cytochrome b family Biochemical class NA Function Component of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex (complex III or cytochrome b-c1 complex) that is part of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The b-c1 complex mediates electron transfer from ubiquinol to cytochrome c. Contributes to the generation of a proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane that is then used for ATP synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1327781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20025846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9485330, ECO:0000305|PubMed:189810}." Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 6 (COXPD6) [MIM:300816]: A mitochondrial disease resulting in a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by psychomotor delay, hypotonia, areflexia, muscle weakness and wasting. Some patients manifest prenatal ventriculomegaly and severe postnatal encephalomyopathy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20362274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22019070, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25583628, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26004228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26173962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27178839}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, X-linked recessive, 4, with or without cerebellar ataxia (CMTX4) [MIM:310490]: A neuromuscular disorder characterized by progressive sensorimotor axonal neuropathy, distal sensory impairment, difficulty walking due to peripheral neuropathy and/or cerebellar ataxia, and deafness due to auditory neuropathy. Additional features include cognitive impairment, cerebellar atrophy, dysarthria, abnormal extraocular movements, tremor, dysmetria and spasticity. The age at onset ranges from infancy to young adulthood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23217327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26004228}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Deafness, X-linked, 5, with peripheral neuropathy (DFNX5) [MIM:300614]: A form of hearing loss characterized by absent or severely abnormal auditory brainstem response, abnormal middle ear reflexes, abnormal speech discrimination, loss of outer hair cell function, and cochlear nerve hypoplasia. DFNX5 patients manifest auditory neuropathy with childhood onset, associated with distal sensory impairment affecting the peripheral nervous system. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25986071}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, X-linked, with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy (SEMDHL) [MIM:300232]: An X-linked recessive developmental disorder characterized by slowly progressive skeletal and neurologic abnormalities, including short stature, large and deformed joints, significant motor impairment, visual defects, and sometimes cognitive deficits. Affected individuals typically have normal early development in the first year or so of life, followed by development regression and the development of symptoms. Brain imaging shows white matter abnormalities consistent with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842795}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Electron transport; Heme; Iron; Membrane; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Reference proteome; Respiratory chain; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubiquinone Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C,D,F,G,H Molecular weight (Da) 99281.2 Length 866 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 43.81 Isoelectric point 8.32 Charge (pH=7) 7.12 3D Binding mode Sequence VSASSRWLEGIRKWYYNAAGFNKLGLMRDDTIHENDDVKEAIRRLPENLYDDRVFRIKRALDLSMRQQILPKEQWTKYEEDKSYLEPYLKEVIRERKEREEWAKKELVDPLTTVREQCEQLEKCVKARERLELCDERVSSRSQTEEDCTEELLDFLHARDHCVAHKLFNSLKTNIRKSHPLMKIVNNAFIDLPAPSNISSWWNFGSLLGICLILQILTGLFLAMHYTSDTTTAFSSVTHICRDVNYGWIIRYMHANGASMFFICLYMHVGRGLYYGSYTFLETWNIGVILLLTVMATAFMGYVLPWGQMSFWGATVITNLLSAIPYIGTNLVEWIWGGFSVDKATLTRFFAFHFILPFIIMAIAMVHLLFLHETGSNNPTGISSDVDKIPFHPYYTIKDILGALLLILALMLLVLFAPDLLGDPDNYTPANPLNTPPHIKPEWYFLFAYAILRSIPNKLGGVLALAFSILILALIPLLHTSKQRSMMFRPLSQCLFWALVADLLTLTWIGGQPVEHPYITIGQLASVLYFLLILVLMPTAGTIENKLLKWSDLELHPPSYPWSHRGLLSSLDHTSIRRGFQVYKQVCSSCHSMDYVAYRHLVGVCYTEDEAKALAEEVEVQDGPNEDGEMFMRPGKLSDYFPKPYPNPEAARAANNGALPPDLSYIVRARHGGEDYVFSLLTGYCEPPTGVSLREGLYFNPYFPGQAIGMAPPIYNEVLEFDDGTPATMSQVAKDVCTFLRWAAEPEHDHRKRMGLKMLLMMGLLLPLVYAMKRHKWSVLKSRKLAYRPPKGRQFGHLTRVRHVITYSLSPFEQRAFPHYFSKGIPNVLRRTRACILRVAPPFVAFYLVYTWGTQEFEKSKRKNPA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 44 | Pyruvate kinase PKLR | 4IP7 | 5.35 | |
Target general information Gen name PKLR Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms PKL;PK1 Protein family Pyruvate kinase family Biochemical class Transferase Function ATP binding.Kinase activity.Magnesium ion binding.Potassium ion binding.Pyruvate kinase activity. Related diseases Pyruvate kinase hyperactivity (PKHYP) [MIM:102900]: Autosomal dominant phenotype characterized by increase of red blood cell ATP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9090535}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Pyruvate kinase deficiency of red cells (PKRD) [MIM:266200]: A frequent cause of hereditary non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia. Clinically, pyruvate kinase-deficient patients suffer from a highly variable degree of chronic hemolysis, ranging from severe neonatal jaundice and fatal anemia at birth, severe transfusion-dependent chronic hemolysis, moderate hemolysis with exacerbation during infection, to a fully compensated hemolysis without apparent anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10087985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10772876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11328279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11960989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1536957, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1896471, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19085939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2018831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21794208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7706479, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8161798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8180378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8476433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8481523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8483951, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8664896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8807089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9075576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9482576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9827908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9886305, ECO:0000269|Ref.24}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02726; DB00787; DB04551; DB16236; DB00119 Interacts with Q9UBL6-2 EC number 2.7.1.40 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Allosteric enzyme; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Disease variant; Glycolysis; Hereditary hemolytic anemia; Kinase; Magnesium; Manganese; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Potassium; Proteomics identification; Pyruvate; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 45695.1 Length 421 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 34.44 Isoelectric point 6.88 Charge (pH=7) -0.35 3D Binding mode Sequence GTAFFQQQQLPAAMADTFLEHLCLLDIDSEPVAARSTSIIATIGPASRSVERLKEMIKAGMNIARLNFSHGSHEYHAESIANVREAVESFSPLSYRPVAIALDTKGPEIGLSEQDVRDLRFGVEHGVDIVFASFVRKASDVAAVRAALGPEGHGIKIISKIENHEGVKRFDEILEVSDGIMVARGDLGIEIPAEKVFLAQKMMIGRCNLAGKPVVCATQMLESMITKPRPTRAETSDVANAVLDGADCIMLSGETAKGNFPVEAVKMQHAIAREAEAAVYHRQLFEELRRAAPLSRDPTEVTAIGAVEAAFKCCAAAIIVLTTTGRSAQLLSRYRPRAAVIAVTRSAQAARQVHLCRGVFPLLYREPPEAIWADDVDRRVQFGIESGKLRGFLRVGDLVIVVTGWRPGSGYTNIMRVLSIS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 45 | Matrix metalloproteinase-12 (MMP-12) | 1Y93 | 5.35 | |
Target general information Gen name MMP12 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Macrophage metalloelastase; Macrophage elastase; MME; ME; HME Protein family Peptidase M10A family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Has significant elastolytic activity. Can accept large and small amino acids at the P1' site, but has a preference for leucine. Aromatic or hydrophobic residues are preferred at the P1 site, with small hydrophobic residues (preferably alanine) occupying P3. May be involved in tissue injury and remodeling. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07026; DB07921; DB04405; DB00551; DB03880; DB07556; DB02118; DB00786; DB07446; DB07683; DB08599; DB08271; DB07922; DB07920; DB05387; DB03367; DB00013 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.4.24.65 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Calcium; Disulfide bond; Extracellular matrix; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Zinc; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 17461.3 Length 158 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 13.25 Isoelectric point 6.11 Charge (pH=7) -3.44 3D Binding mode Sequence GPVWRKHYITYRINNYTPDMNREDVDYAIRKAFQVWSNVTPLKFSKINTGMADILVVFARGAHGDDHAFDGKGGILAHAFGPGSGIGGDAHFDEDEFWTTHSGGTNLFLTAVHEIGHSLGLGHSSDPKAVMFPTYKYVDINTFRLSADDIRGIQSLYG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 46 | Plasmodium Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (Malaria DHOdehase) | 1TV5 | 5.35 | |
Target general information Gen name Malaria DHOdehase Organism Plasmodium falciparum (isolate 3D7) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PFF0160c; Mitochondrially bound dihydroorotate-ubiqui oxidoreductase; Dihydroorotate oxidase of Plasmodium falciparum; Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase of Plasmodium falciparum; DHOdehase of Plasmodium fa Protein family Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase family, Type 2 subfamily Biochemical class CH-CH donor oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the conversion of dihydroorotate to orotate with quinone as electron acceptor. Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 33 (COXPD33) [MIM:617713]: An autosomal recessive disorder caused by multiple mitochondrial respiratory chain defects and impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism. Clinical manifestations are highly variable. Affected infants present with cardiomyopathy accompanied by multisystemic features involving liver, kidney, and brain. Death in infancy is observed in some patients. Children and adults present with myopathy and progressive external ophthalmoplegia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28942965}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01117 Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.3.5.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Flavoprotein; FMN; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Oxidoreductase; Pyrimidine biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Transit peptide; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 41846.8 Length 371 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.25 Isoelectric point 8.21 Charge (pH=7) 3.13 3D Binding mode Sequence FESYNPEFFLYDIFLKFCLKYIDGEICHDLFLLLGKYNILPYDTSNDSIYACTNIKHLDFINPFGVAAGFDKNGVCIDSILKLGFSFIEIGTITPRGQTGNAKPRIFRDVESRSIINSCGFNNMGCDKVTENLILFRKRQEEDKLLSKHIVGVSIGKNKDTVNIVDDLKYCINKIGRYADYIAINVSSPNTPGLRDNQEAGKLKNIILSVKEEIDNLEFLWFNTTKKKPLVFVKLAPDLNQEQKKEIADVLLETNIDGMIISNTTTQINDIKSFENKKGGVSGAKLKDISTKFICEMYNYTNKQIPIIASGGIFSGLDALEKIEAGASVCQLYSCLVFNGMKSAVQIKRELNHLLYQRGYYNLKEAIGRKH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 47 | Matrix metalloproteinase-12 (MMP-12) | 1JK3 | 5.35 | |
Target general information Gen name MMP12 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Macrophage metalloelastase; Macrophage elastase; MME; ME; HME Protein family Peptidase M10A family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Has significant elastolytic activity. Can accept large and small amino acids at the P1' site, but has a preference for leucine. Aromatic or hydrophobic residues are preferred at the P1 site, with small hydrophobic residues (preferably alanine) occupying P3. May be involved in tissue injury and remodeling. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07026; DB07921; DB04405; DB00551; DB03880; DB07556; DB02118; DB00786; DB07446; DB07683; DB08599; DB08271; DB07922; DB07920; DB05387; DB03367; DB00013 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.4.24.65 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Calcium; Disulfide bond; Extracellular matrix; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Zinc; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 17435.3 Length 158 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 11.56 Isoelectric point 6.52 Charge (pH=7) -1.45 3D Binding mode Sequence GPVWRKHYITYRINNYTPDMNREDVDYAIRKAFQVWSNVTPLKFSKINTGMADILVVFARGAHGDFHAFDGKGGILAHAFGPGSGIGGDAHFDEDEFWTTHSGGTNLFLTAVHAIGHSLGLGHSSDPKAVMFPTYKYVDINTFRLSADDIRGIQSLYG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 48 | Plasmodium Adenylosuccinate synthetase (Malaria Adss) | 1P9B | 5.35 | |
Target general information Gen name Malaria Adss Organism Plasmodium falciparum Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms IMP--aspartate ligase; Adenylosuccinate synthase; AdSS; AMPSase Protein family Adenylosuccinate synthetase family Biochemical class Carbon-nitrogen ligase Function Plays an important role in the salvage pathway for purine nucleotide biosynthesis. Catalyzes the first committed step in the biosynthesis of AMP from IMP. Related diseases Hypertension and brachydactyly syndrome (HTNB) [MIM:112410]: A syndrome characterized by brachydactyly type E, severe salt-independent but age-dependent hypertension, an increased fibroblast growth rate, neurovascular contact at the rostral-ventrolateral medulla, and altered baroreflex blood pressure regulation. It results in death from stroke before age 50 years when untreated. Brachydactyly type E is characterized by shortening of the fingers mainly in the metacarpals and metatarsals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25961942}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03510; DB04315; DB02109 Interacts with NA EC number EC 6.3.4.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; GTP-binding; Ligase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Purine biosynthesis Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 47877.9 Length 424 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 31.72 Isoelectric point 7.63 Charge (pH=7) 1.58 3D Binding mode Sequence GNVVAILGAQWGDEGKGKIIDMLSEYSDITCRFNGGANAGHTISVNDKKYALHLLPCGVLYDNNISVLGNGMVIHVKSLMEEIESVGGKLLDRLYLSNKAHILFDIHQIIDSIQETKKLKEGKQIGTTKRGIGPCYSTKASRIGIRLGTLKNFENFKNMYSKLIDHLMDLYNITEYDKEKELNLFYNYHIKLRDRIVDVISFMNTNLENNKKVLIEGANAAMLDIDFGTYPYVTSSCTTVGGVFSGLGIHHKKLNLVVGVVKSYLTRVGCGPFLTELNNDVGQYLREKGHEYGTTTKRPRRCGWLDIPMLLYVKCINSIDMINLTKLDVLSGLEEILLCVNFKNKKTGELLEKGCYPVEEEISEEYEPVYEKFSGWKEDISTCNEFDELPENAKKYILAIEKYLKTPIVWIGVGPNRKNMIVKK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 49 | Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase (DDC) | 3RCH | 5.34 | |
Target general information Gen name DDC Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms DOPA decarboxylase; AADC Protein family Group II decarboxylase family Biochemical class Carbon-carbon lyase Function Catalyzes the decarboxylation of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) to dopamine, L-5-hydroxytryptophan to serotonin and L-tryptophan to tryptamine. Related diseases Aromatic L-amino-acid decarboxylase deficiency (AADCD) [MIM:608643]: An inborn error in neurotransmitter metabolism that leads to combined serotonin and catecholamine deficiency. It causes developmental and psychomotor delay, poor feeding, lethargy, ptosis, intermittent hypothermia, gastrointestinal disturbances. The onset is early in infancy and inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14991824, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15079002, ECO:0000269|Ref.12}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00915; DB12783; DB00190; DB00260; DB06262; DB13848; DB00875; DB01235; DB00968; DB00114; DB00150 Interacts with P10275 EC number EC 4.1.1.28 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Catecholamine biosynthesis; Decarboxylase; Disease variant; Lyase; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome; Repeat Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 41117.4 Length 369 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 37.52 Isoelectric point 8.26 Charge (pH=7) 3.76 3D Binding mode Sequence HSPYFFAYFPTASSYPAMLADMLCGAIGASPACTELETVMMDWLGKMLELPKAFLNEKAGEGGGVIQGSASEATLVALLAARTKVIHRLQAASPELTQAAIMEKLVAYSSDQAHSSVERAGLIGGVKLKAIPSDGNFAMRASALQEALERDKAAGLIPFFMVATLGTTTCCSFDNLLEVGPICNKEDIWLHVDAAYAGSAFICPEFRHLLNGVEFADSFNFNPHKWLLVNFDCSAMWVKKRTDLRFRSLKMWFVFRMYGVKGLQAYIRKHVQLSHEFESLVRQDPRFEICVEVILGLVCFRLKGSNKVNEALLQRINSAKKIHLVPCHLRDKFVLRFAICSRTVESAHVQRAWEHIKELAADVLRAERE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 50 | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | 2IIP | 5.34 | |
Target general information Gen name NNMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, NNMT/PNMT/TEMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase activity.Pyridine N-methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00627 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Citrullination; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 27886.8 Length 251 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.66 Isoelectric point 5.23 Charge (pH=7) -5.11 3D Binding mode Sequence GFTSKDTYLSHFNPRDYLEKYYSAESQILKHLLKNLFKIFCLDGVKGDLLIDIGSGPTIYQLLSACESFKEIVVTDYSDQNLQELEKWLKAAPAAFDWSPVVTYVCDLEGNRVKGPEKEEKLRQAVKQVLKCDVTQSQPLGAVPLPPADCVLSTLCLDAACPDLPTYCRALRNLGSLLKPGGFLVIMDALKSSYYMIGEQKFSSLPLGREAVEAAVKEAGYTIEWFEVISQSYSSTMANNEGLFSLVARKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 51 | Thiamin pyrophosphokinase 1 | 3S4Y | 5.34 | |
Target general information Gen name TPK1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Thiamine pyrophosphokinase family Biochemical class Transferase Function ATP binding.Kinase activity.Thiamine binding.Thiamine diphosphokinase activity. Related diseases Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 5, episodic encephalopathy type (THMD5) [MIM:614458]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder due to an inborn error of thiamine metabolism. The phenotype is highly variable, but in general, affected individuals have onset in early childhood of acute encephalopathic episodes associated with increased serum and CSF lactate. These episodes result in progressive neurologic dysfunction manifest as gait disturbances, ataxia, dystonia, and spasticity, which in some cases may result in loss of ability to walk. Cognitive function is usually preserved, although mildly delayed development has been reported. These episodes are usually associated with infection and metabolic decompensation. Some patients may have recovery of some neurologic deficits. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22152682}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04768; DB00152 Interacts with O14841; Q9H3S4 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Disease variant; Kinase; Nucleotide-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 16268.5 Length 142 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 48.41 Isoelectric point 5.34 Charge (pH=7) -3.99 3D Binding mode Sequence NLKYCLVILNQPLDNYFRHLWNKALLRACADGGANRLYDITEGERESFLPEFINGDFDSIRPEVREYYATKGCELISTPDQDHTDFTKCLKMLQKKIEEKDLKVDVIVTLGGLAGRFDQIMASVNTLFQATHITPFPIIIIQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 52 | Sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) | 7VSI | 5.34 | |
Target general information Gen name SLC5A2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Solute carrier family 5 member 2; Na(+)/glucose cotransporter 2; Low affinity sodium-glucose cotransporter Protein family Sodium:solute symporter (SSF) (TC 2.A.21) family Biochemical class Solute:sodium symporter Function Has a Na(+) to glucose coupling ratio of 1:1. Sodium-dependent glucose transporter. Related diseases Renal glucosuria (GLYS) [MIM:233100]: A disorder characterized by persistent isolated glucosuria, normal fasting serum glucose concentration, decreased renal tubular resorption of glucose from the urine, and absence of any other signs of tubular dysfunction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14614622}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12236; DB08907; DB01914; DB06292; DB09038; DB11827; DB12713 Interacts with O14556; Q13113 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Ion transport; Membrane; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Sodium; Sodium transport; Sugar transport; Symport; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 63858.9 Length 586 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 39.46 Isoelectric point 8.62 Charge (pH=7) 7.41 3D Binding mode Sequence DNPADILVIAAYFLLVIGVGLWSMCRTNRGTVGGYFLAGRSMVWWPVGASLFASNIGSGHFVGLAGTGAASGLAVAGFEWNALFVVLLLGWLFAPVYLTAGVITMPQYLRKRFGGRRIRLYLSVLSLFLYIFTKISVDMFSGAVFIQQALGWNIYASVIALLGITMIYTVTGGLAALMYTDTVQTFVILGGACILMGYAFHEVGGYSGLFDKYLGAATSLTVSEDPAVGNISSFCYRPRPDSYHLLRHPVTGDLPWPALLLGLTIVSGWYWCSDQVIVQRCLAGKSLTHIKAGCILCGYLKLTPMFLMVMPGMISRILYPDEVACVVPEVCRRVCGTEVGCSNIAYPRLVVKLMPNGLRGLMLAVMLAALMSSLASIFNSSSTLFTMDIYTRLRPRAGDRELLLVGRLWVVFIVVVSVAWLPVVQAAQGGQLFDYIQAVSSYLAPPVSAVFVLALFVPRVNEQGAFWGLIGGLLMGLARLIPEFSFGSGSCVQPSACPAFLCGVHYLYFAIVLFFCSGLLTLTVSLCTAPIPRKHLHRLVFSLRHSKEEREDLDEDISEDPSWARVVNLNALLMMAVAVFLWGFYA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 53 | Free fatty acid receptor 1 | 4PHU | 5.33 | |
Target general information Gen name FFAR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms GPR40 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class Fatty acid binding protein / hydrolase Function Bioactive lipid receptor activity.G-protein coupled receptor activity.Guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity.Lipid binding. Related diseases Refsum disease (RD) [MIM:266500]: A rare autosomal recessive peroxisomal disorder characterized by the accumulation of the branched-chain fatty acid, phytanic acid, in blood and tissues. Cardinal clinical features are retinitis pigmentosa, peripheral neuropathy, cerebellar ataxia, and elevated protein levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Half of all patients exhibit generalized, mild to moderate ichthyosis resembling ichthyosis vulgaris. Less constant features are nerve deafness, anosmia, skeletal abnormalities, cataracts and cardiac impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10709665, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10767344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14974078, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9326939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9326940}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00159 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Lipid-binding; Membrane; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 28319.1 Length 272 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 27.3 Isoelectric point 9.07 Charge (pH=7) 6.85 3D Binding mode Sequence MDLPPQLSFGLYVAAFALGFPLNVLAIRGATAHARLRLTPSAVYALNLGCSDLLLTVSLPLKAVEALASGAWPLPASLCPVFAVAHFAPLYAGGGFLAALSAARYLGAAFPPCYSWGVCAAIWALVLCHLGLVFGLEAPGGWLDHSNTSLGINTPVNGSPVCLEAWDPASAGPARFSLSLLLFFLPLAITAFCFVGCLRALARGSLTHRRKLRAAWVAGGALLTLLLCVGPYNASNVASFLYPNLGGSWRKLGLITGAWSVVLNPLVTGYLG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 54 | Tryptophan 5-hydroxylase 1 (TPH1) | 5TPG | 5.33 | |
Target general information Gen name TPH1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tryptophan 5-monooxygenase 1; TRPH; TPRH Protein family Biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylase family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Responsible for addition of the -HO group (hydroxylation) to the 5 position to form the amino acid 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), which is the initial and rate-limiting step in the synthesis of the neurotransmitter serotonin. Related diseases Tyrosinemia 2 (TYRSN2) [MIM:276600]: An inborn error of metabolism characterized by elevations of tyrosine in the blood and urine, and oculocutaneous manifestations. Typical features include palmoplantar keratosis, painful corneal ulcers, and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1357662}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05199; DB00360; DB12095; DB00150 Interacts with Q14457; Q96IK1-2; Q9UKB3; Q9H8Y8; O43586; O95789-4 EC number EC 1.14.16.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Iron; Metal-binding; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serotonin biosynthesis; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 31138.2 Length 271 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 43.43 Isoelectric point 6.73 Charge (pH=7) -0.86 3D Binding mode Sequence TVPWFPKKISDLDHCNVYRKRRKYFADLAMNYKHGDPIPKVEFTEEEIKTWGTVFQELNKLYPTHACREYLKNLPLLSKYCGYREDNIPQLEDVSNFLKERTGFSIRPVAGYLSPRDFLSGLAFRVFHCTQYVRHSSDPFYTPEPDTCHELLGHVPLLAEPSFAQFSQEIGLASLGASEEAVQKLATCYFFTVEFGLCKQDGQLRVFGAGLLSSISELKHALSGHAKVKPFDPKITCKQECLITTFQDVYFVSESFEDAKEKMREFTKTIK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 55 | NADH peroxidase | 1NHP | 5.33 | |
Target general information Gen name npr Organism Enterococcus faecalis (strain ATCC 700802 / V583) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms EF_1211 Protein family Class-III pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase (h2o2(a)) Function Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.NADH peroxidase activity. Related diseases Telangiectasia, hereditary hemorrhagic, 2 (HHT2) [MIM:600376]: A multisystemic vascular dysplasia leading to dilation of permanent blood vessels and arteriovenous malformations of skin, mucosa, and viscera. The disease is characterized by recurrent epistaxis and gastro-intestinal hemorrhage. Visceral involvement includes arteriovenous malformations of the lung, liver, and brain. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10694922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10767348, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11170071, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11484689, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14684682, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15024723, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15712270, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16525724, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16752392, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20414677, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26176610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8640225, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9245985}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147; DB03382 Interacts with NA EC number 1.11.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; NAD; Oxidation; Oxidoreductase; Peroxidase; Redox-active center; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 49518.8 Length 447 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 27.53 Isoelectric point 4.83 Charge (pH=7) -19.06 3D Binding mode Sequence MKVIVLGSSHGGYEAVEELLNLHPDAEIQWYEKGDFISFLSAGMQLYLEGKVKDVNSVRYMTGEKMESRGVNVFSNTEITAIQPKEHQVTVKDLVSGEERVENYDKLIISPGAVPFELDIPGKDLDNIYLMRGRQWAIKLKQKTVDPEVNNVVVIGSGYIGIEAAEAFAKAGKKVTVIDILDRPLGVYLDKEFTDVLTEEMEANNITIATGETVERYEGDGRVQKVVTDKNAYDADLVVVAVGVRPNTAWLKGTLELHPNGLIKTDEYMRTSEPDVFAVGDATLIKYNPADTEVNIALATNARKQGRFAVKNLEEPVKPFPGVQGSSGLAVFDYKFASTGINEVMAQKLGKETKAVTVVEDYLMDFNPDKQKAWFKLVYDPETTQILGAQLMSKADLTANINAISLAIQAKMTIEDLAYADFFFQPAFDKPWNIINTAALEAVKQER Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 56 | Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) | 4OQV | 5.33 | |
Target general information Gen name DHODH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Dihydroorotate oxidase; Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone), mitochondrial; DHOdehase; DHODH Protein family Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase family, Type 2 subfamily Biochemical class CH-CH donor oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the conversion of dihydroorotate to orotate with quinone as electron acceptor. Related diseases Postaxial acrofacial dysostosis (POADS) [MIM:263750]: POADS is characterized by severe micrognathia, cleft lip and/or palate, hypoplasia or aplasia of the posterior elements of the limbs, coloboma of the eyelids and supernumerary nipples. POADS is a very rare disorder: only 2 multiplex families, each consisting of 2 affected siblings born to unaffected, nonconsanguineous parents, have been described among a total of around 30 reported cases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19915526}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07559; DB07561; DB08172; DB08169; DB07443; DB07978; DB07975; DB04281; DB08249; DB07977; DB07976; DB04583; DB08008; DB01117; DB03523; DB03480; DB02613; DB04147; DB03247; DB01097; DB06481; DB08006; DB02262; DB05125; DB08880; DB07646 Interacts with Q6ZMZ0; P49638 EC number EC 1.3.5.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Disease variant; Flavoprotein; FMN; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Pyrimidine biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Transit peptide; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 38341.4 Length 353 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 39.27 Isoelectric point 9.28 Charge (pH=7) 5.52 3D Binding mode Sequence DERFYAEHLMPTLQGLLDPESAHRLAVRFTSLGLLPRARFQDSDMLEVRVLGHKFRNPVGIAAGFDKHGEAVDGLYKMGFGFVEIGSVTPKPQEGNPRPRVFRLPEDQAVINRYGFNSHGLSVVEHRLRARQQKQAKLTEDGLPLGVNLGKNKTSVDAAEDYAEGVRVLGPLADYLVVNVSSPGKAELRRLLTKVLQERDGLRRVHRPAVLVKIAPDLTSQDKEDIASVVKELGIDGLIVTNTTVSRPAGLQGALRSETGGLSGKPLRDLSTQTIREMYALTQGRVPIIGVGGVSSGQDALEKIRAGASLVQLYTALTFWGPPVVGKVKRELEALLKEQGFGGVTDAIGADHR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 57 | Cocaine esterase | 3I2K | 5.33 | |
Target general information Gen name cocE Organism Rhodococcus sp. (strain MB1 Bresler) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family CocE/NonD hydrolase family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Carboxylic ester hydrolase activity.Dipeptidyl-peptidase activity. Related diseases Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 5, episodic encephalopathy type (THMD5) [MIM:614458]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder due to an inborn error of thiamine metabolism. The phenotype is highly variable, but in general, affected individuals have onset in early childhood of acute encephalopathic episodes associated with increased serum and CSF lactate. These episodes result in progressive neurologic dysfunction manifest as gait disturbances, ataxia, dystonia, and spasticity, which in some cases may result in loss of ability to walk. Cognitive function is usually preserved, although mildly delayed development has been reported. These episodes are usually associated with infection and metabolic decompensation. Some patients may have recovery of some neurologic deficits. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22152682}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03793; DB01795 Interacts with NA EC number 3.1.1.84 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Hydrolase; Serine esterase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 62127.9 Length 574 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 26.62 Isoelectric point 4.56 Charge (pH=7) -33.24 3D Binding mode Sequence VDGNYSVASNVMVPMRDGVRLAVDLYRPDADGPVPVLLVRNPYDKFDVFAWSTQSTNWLEFVRDGYAVVIQDTRGLFASEGEFVPHVDDEADAEDTLSWILEQAWCDGNVGMFGVSYLGVTQWQAAVSGVGGLKAIAPSMASADLYRAPWYGPGGALSVEALLGWSALIGTGLITSRSDARPEDAADFVQLAAILNDVAGAASVTPLAEQPLLGRLIPWVIDQVVDHPDNDESWQSISLFERLGGLATPALITAGWYDGFVGESLRTFVAVKDNADARLVVGPWSHSNLTGRNADRKFGIAATYPIQEATTMHKAFFDRHLRGETDALAGVPKVRLFVMGIDEWRDETDWPLPDTAYTPFYLGGSGAANTSTGGGTLSTSISGTESADTYLYDPADPVPSLGGTLLFHNGDNGPADQRPIHDRDDVLCYSTEVLTDPVEVTGTVSARLFVSSSAVDTDFTAKLVDVFPDGRAIALCDGIVRMRYRETLVNPTLIEAGEIYEVAIDMLATSNVFLPGHRIMVQVSSSNFPKYDRNSNTGGVIAREQLEEMCTAVNRIHRGPEHPSHIVLPIIKRK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 58 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase KMT5C (KMT5C) | 3RQ4 | 5.33 | |
Target general information Gen name KMT5C Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Lysine N-methyltransferase 5C; Lysine-specific methyltransferase 5C; Suppressor of variegation 4-20 homolog 2; Su(var)4-20 homolog 2; Suv4-20h2; [histone H4]-N-methyl-L-lysine20 N-methyltransferase KM Protein family Class V-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, Histone-lysine methyltransferase family, Suvar4-20 subfamily Biochemical class NA Function Histone methyltransferase that specifically methylates monomethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me1) and dimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me2) of histone H4 to produce respectively dimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me2) and trimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me3) and thus regulates transcription and maintenance of genome integrity. In vitro also methylates unmodified 'Lys-20' (H4K20me0) of histone H4 and nucleosomes. H4 'Lys-20' trimethylation represents a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional repression. Mainly functions in pericentric heterochromatin regions, thereby playing a central role in the establishment of constitutive heterochromatin in these regions. KMT5C is targeted to histone H3 via its interaction with RB1 family proteins (RB1, RBL1 and RBL2) (By similarity). Facilitates TP53BP1 foci formation upon DNA damage and proficient non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ)-directed DNA repair by catalyzing the di- and trimethylation of 'Lys-20' of histone H4. May play a role in class switch reconbination by catalyzing the di- and trimethylation of 'Lys-20' of histone H4 (By similarity). Related diseases Brachydactyly A2 (BDA2) [MIM:112600]: A form of brachydactyly. Brachydactyly defines a group of inherited malformations characterized by shortening of the digits due to abnormal development of the phalanges and/or the metacarpals. In brachydactyly type A2 shortening of the middle phalanges is confined to the index finger and the second toe, all other digits being more or less normal. Because of a rhomboid or triangular shape of the affected middle phalanx, the end of the second finger usually deviates radially. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19327734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357617}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. Duplications of a cis-regulatory element located approximately 110 kb downstream of BMP2 have been found in BDA2 families. They likely cause altered BMP2 expression with pathological consequences. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19327734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357617}.; DISEASE: Short stature, facial dysmorphism, and skeletal anomalies with or without cardiac anomalies 1 (SSFSC1) [MIM:617877]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by short stature, facial dysmorphism, skeletal anomalies, and variable cardiac defects. Distinctive facial features include midface retrusion, short upturned nose, long philtrum, high-arched or cleft palate, and variable degrees of micrognathia and dental crowding. Skeletal anomalies include patterning defects of the axial skeleton, characterized by 11 pairs of ribs and brachydactyly of the fifth ray. Congenital heart defects are variably observed and appear to involve primarily the cardiac outflow tract. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29198724}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q13185 EC number EC 2.1.1.361 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Chromosome; Metal-binding; Methyltransferase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repressor; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 27285.8 Length 240 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 42.74 Isoelectric point 8.32 Charge (pH=7) 3.24 3D Binding mode Sequence DRVTARELCENDDLATSLVLDPYLGFRTHKMNVSPVPPLRRQQHLRSALETFLRQRDLEAAYRALTLGGWTARYFQSRGPRQEAALKTHVYRYLRAFLPESGFTILPCTRYSMETNGAKIVSTRAWKKNEKLELLVGCIAELREADEGLLRAGENDFSIMYSTRKRSAQLWLGPAAFINHDCKPNCKFVPADGNAACVKVLRDIEPGDEVTCFYGEGFFGEKNEHCECHTCERKGEGAFR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 59 | Quinone-dependent D-lactate dehydrogenase | 1F0X | 5.32 | |
Target general information Gen name dld Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms JW2121;b2133 Protein family Quinone-dependent D-lactate dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase activity.D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome) activity.Electron carrier activity.FAD binding.Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.NAD binding.Oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, quinone or similar compound as acceptor.Quinone binding. Related diseases Myeloperoxidase deficiency (MPOD) [MIM:254600]: A disorder characterized by decreased myeloperoxidase activity in neutrophils and monocytes that results in disseminated candidiasis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:37198333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7904599, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8142659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8621627, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9354683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9637725}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147; DB00756 Interacts with NA EC number 1.1.5.12 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell inner membrane; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Membrane; Oxidoreductase; Quinone; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 56475.2 Length 502 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 32.5 Isoelectric point 5.97 Charge (pH=7) -10.38 3D Binding mode Sequence NKAFLNELARLVGSSHLLTDPAKTARYRKGFRSGQGDALAVVFPGSLLELWRVLKACVTADKIILMQAANTGLTEGSTPNGNDYDRDVVIISTLRLDKLHVLGKGEQVLAYPGTTLYSLEKALKPLGREPHSVIGSSCIGASVIGGICNNSGGSLVQRGPAYTEMSLFARINEDGKLTLVNHLGIDLGETPEQILSKLDDDRIKDDDVRHDGRHAHDYDYVHRVRDIEADTPARYNADPDRLFESSGCAGKLAVFAVRLDTFEAEKNQQVFYIGTNQPEVLTEIRRHILANFENLPVAGEYMHRDIYDIAELPPRMKNWRDKYEHHLLLKMAGDGVGEAKSWLVDYFKQAEGDFFVCTPEEGSKAFLHRFAAAGAAIRYQAVHSDEVEDILALDIALRRNDTEWYEHLPPEIDSQLVHKLYYGHFMCYVFHQDYIVKKGVDVHALKEQMLELLQQRGAQYPAEHNVGHLYKAPETLQKFYRENDPTNSMNPGIGKTSKRKNW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 60 | Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase large subunit | 2WGH | 5.32 | |
Target general information Gen name RRM1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms RR1 Protein family Ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase large chain family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function ATP binding.Identical protein binding.Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase activity, thioredoxin disulfide as acceptor. Related diseases Progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions, autosomal recessive 6 (PEOB6) [MIM:620647]: A form of progressive external ophthalmoplegia, a mitochondrial myopathy characterized by progressive paralysis of the levator palpebrae, orbicularis oculi, and extraocular muscles. Ragged red fibers are seen on muscle biopsy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:35617047}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00242; DB00631; DB01073; DB05420; DB00441; DB01005; DB05003; DB01280; DB06433 Interacts with P23921; P31350; Q8N720 EC number 1.17.4.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Allosteric enzyme; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Deoxyribonucleotide synthesis; Disulfide bond; Nucleotide-binding; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Primary mitochondrial disease; Progressive external ophthalmoplegia; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 147968 Length 1301 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.58 Isoelectric point 7.14 Charge (pH=7) 0.86 3D Binding mode Sequence LAARIAVSNLHKETKKVFSDVMEDLYNYINPHNGKHSPMVAKSTLDIVLANKDRLNSAIIYDRDFSYNYFGFKTLERSYLLKINGKVAERPQHMLMRVSVGIHKEDIDAAIETYNLLSERWFTHASPTLFNAGTNRPQLSSCFLLSMKDDSIEGIYDTLKQCALISKSAGGIGVAVSCIRATGSYIAGTNGNSNGLVPMLRVYNNTARYVDQGGNKRPGAFAIYLEPWHLDIFEFLDLKKNTGKEEQRARDLFFALWIPDLFMKRVETNQDWSLMCPNECPGLDEVWGEEFEKLYASYEKQGRVRKVVKAQQLWYAIIESQTETGTPYMLYKDSCNRKSNQQNLGTIKCSNLCTEIVEYTSKDEVAVCNLASLALNMYVTSEHTYDFKKLAEVTKVVVRNLNKIIDINYYPVPEACLSNKRHRPIGIGVQGLADAFILMRYPFESAEAQLLNKQIFETIYYGALEASCDLAKEQGPYETYEGSPVSKGILQYDMWNVTPTDLWDWKVLKEKIAKYGIRNSLLIAPMPTASTAQILGNNESIEPYTSNIYQIVNPHLLKDLTERGLGSIQSIPEIPDDLKQLYKTVWEISQKTVLKMAAERGAFIDQSQSLNIHIAEPNYGKLTSMHFYGWKQGLKTGMYYLRTRAARIAVSNLHKETKKVFSDVMEDLYNYINPHNGKHSPMVAKSTLDIVLANKDRLNSAIIYDRDFSYNYFGFKTLERSYLLKINGKVAERPQHMLMRVSVGIHKEDIDAAIETYNLLSERWFTHASPTLFNAGTNRPQLSSCFLLSMKDDSIEGIYDTLKQCALISKSAGGIGVAVSCIRATGSYIAGTNGNSNGLVPMLRVYNNTARYVDQGGNKRPGAFAIYLEPWHLDIFEFLDLKKNTGKEEQRARDLFFALWIPDLFMKRVETNQDWSLMCPNECPGLDEVWGEEFEKLYASYEKQGRVRKVVKAQQLWYAIIESQTETGTPYMLYKDSCNRKSNQQNLGTIKCSNLCTEIVEYTSKDEVAVCNLASLALNMYVTSEHTYDFKKLAEVTKVVVRNLNKIIDINYYPVPEACLSNKRHRPIGIGVQGLADAFILMRYPFESAEAQLLNKQIFETIYYGALEASCDLAKEQGPYETYEGSPVSKGILQYDMWNVTPTDLWDWKVLKEKIAKYGIRNSLLIAPMPTASTAQILGNNESIEPYTSNIYQIVNPHLLKDLTERGLWEEMKNQIIACNGSIQSIPEIPDDLKQLYKTVWEISQKTVLKMAAERGAFIDQSQSLNIHIAEPNYGKLTSMHFYGWKQGLKTGMYYLRTRAH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||