Job Results:
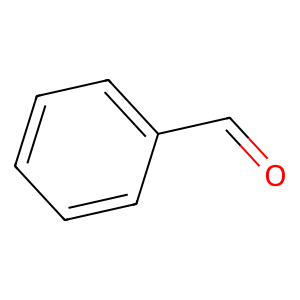
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
0cb0764e79e22b0da515513ec30e42ef
Job name
NA
Time
2025-06-05 10:48:27
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | 2IIP | 5.26 | |
Target general information Gen name NNMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, NNMT/PNMT/TEMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase activity.Pyridine N-methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00627 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Citrullination; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 27886.8 Length 251 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.66 Isoelectric point 5.23 Charge (pH=7) -5.11 3D Binding mode Sequence GFTSKDTYLSHFNPRDYLEKYYSAESQILKHLLKNLFKIFCLDGVKGDLLIDIGSGPTIYQLLSACESFKEIVVTDYSDQNLQELEKWLKAAPAAFDWSPVVTYVCDLEGNRVKGPEKEEKLRQAVKQVLKCDVTQSQPLGAVPLPPADCVLSTLCLDAACPDLPTYCRALRNLGSLLKPGGFLVIMDALKSSYYMIGEQKFSSLPLGREAVEAAVKEAGYTIEWFEVISQSYSSTMANNEGLFSLVARKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 42 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | 3EQC | 5.26 | |
Target general information Gen name MAP2K1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms PRKMK1;MEK1 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family, MAP kinase kinase subfamily Biochemical class Transferase Function ATP binding.MAP kinase kinase activity.Protein C-terminus binding.Protein kinase activity.Protein N-terminus binding.Protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity.Protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity.Protein serine/threonine kinase activity.Protein tyrosine kinase activity.Signal transducer, downstream of receptor, with protein tyrosine phosphatase activity. Related diseases Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome 3 (CFC3) [MIM:615279]: A form of cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, a multiple congenital anomaly disorder characterized by a distinctive facial appearance, heart defects and intellectual disability. Heart defects include pulmonic stenosis, atrial septal defects and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Some affected individuals present with ectodermal abnormalities such as sparse, friable hair, hyperkeratotic skin lesions and a generalized ichthyosis-like condition. Typical facial features are similar to Noonan syndrome. They include high forehead with bitemporal constriction, hypoplastic supraorbital ridges, downslanting palpebral fissures, a depressed nasal bridge, and posteriorly angulated ears with prominent helices. Distinctive features of CFC3 include macrostomia and horizontal shape of palpebral fissures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16439621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18042262}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Melorheostosis, isolated (MEL) [MIM:155950]: A sclerosing bone disorder characterized by hyperostosis of the cortex of tubular bones, frequently involving one limb. The lesions may be accompanied by abnormalities of adjacent soft tissue, joint contractures, sclerodermatous skin lesions, muscle atrophy, or hemangioma. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29643386}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06892; DB07046; DB08208; DB03115; DB11967; DB06616; DB05239; DB02152; DB07101; DB08130; DB14904; DB11689; DB08911 Interacts with Q8N9N5; Q8N9N5-2; Q9NR09; P15056; Q9Y297; O15519-1; P28482; P27361; Q13526; Q9H8W4; P04049; Q8WWU5-7; Q86Y07; Q86Y07-1; P46937 EC number 2.7.12.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cardiomyopathy; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Ectodermal dysplasia; Intellectual disability; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Tyrosine-protein kinase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34949.2 Length 312 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 45.3 Isoelectric point 5.96 Charge (pH=7) -4.47 3D Binding mode Sequence ELELDEQQRKRLEAFLTQKQKVGELKDDDFEKISELGAGNGGVVFKVSHKPSGLVMARKLIHLEIKPAIRNQIIRELQVLHECNSPYIVGFYGAFYSDGEISICMEHMDGGSLDQVLKKAGRIPEQILGKVSIAVIKGLTYLREKHKIMHRDVKPSNILVNSRGEIKLCDFGVSGQLIDSMAVGTRSYMSPERLQGTHYSVQSDIWSMGLSLVEMAVGRYPIPPPDAKELELMFGCPMAIFELLDYIVNEPPPKLPSGVFSLEFQDFVNKCLIKNPAERADLKQLMVHAFIKRSDAEEVDFAGWLCSTIGLN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 43 | Wnt-7a protein (WNT7A) | 4UZQ | 5.26 | |
Target general information Gen name WNT7A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein Wnt-7a Protein family Wnt family Biochemical class NA Function Plays an important role in embryonic development, including dorsal versus ventral patterning during limb development, skeleton development and urogenital tract development. Required for central nervous system (CNS) angiogenesis and blood-brain barrier regulation. Required for normal, sexually dimorphic development of the Mullerian ducts, and for normal fertility in both sexes. Required for normal neural stem cell proliferation in the hippocampus dentate gyrus. Required for normal progress through the cell cycle in neural progenitor cells, for self-renewal of neural stem cells, and for normal neuronal differentiation and maturation. Promotes formation of synapses via its interaction with FZD5. Ligand for members of the frizzled family of seven transmembrane receptors that functions in the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Related diseases Limb pelvis hypoplasia aplasia syndrome (LPHAS) [MIM:276820]: A syndrome of severe deficiency of the extremities due to hypo- or aplasia of one or more long bones of one or more limbs. Pelvic manifestations include hip dislocation, hypoplastic iliac bone and aplastic pubic bones. Thoracic deformity, unusual facies and genitourinary anomalies can be present. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16826533, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17431918, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20949531, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21271649, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27638328}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Fuhrmann syndrome (FUHRS) [MIM:228930]: Distinct limb-malformation disorder characterized also by various degrees of limb aplasia/hypoplasia and joint dysplasia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16826533}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P55212; P22607; P06396; P13473-2; Q9UMX0; Q9Y5W5; Q5T9L3; Q9Z0J1 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Developmental protein; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Extracellular matrix; Glycoprotein; Lipoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Wnt signaling pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 40475.5 Length 356 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 50.49 Isoelectric point 7.67 Charge (pH=7) 1.62 3D Binding mode Sequence EDLRLHLLLNTSVTCNDGSPAGYYLKESRGSRRWLLFLEGGWYCFNRENCDSRYDTMRRLMSSRDWPRTRTGTGILSSQPEENPYWWNANMVFIPYCSSDVWSGASSKSEKNEYAFMGALIIQEVVRELLGRGLSGAKVLLLAGSAAGGTGVLLNVDRVAEQLEKLGYPAIQVRGLADSGWFLDNKQYRHTDCVDTITCAPTEAIRRGIRYWNGVVPERCRRQFQEGEEWNCFFGYKVYPTLRSPVFVVQWLFDEAQLTVDNVHLTGQPVQEGLRLYIQNLGRELRHTLKDVPASFAPACLSHEIIIRSHWTDVQVKGTSLPRALHCWDRSLHKGCPVHLVDSCPWPHCNPSCPTS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 44 | Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH2) | 1O04 | 5.25 | |
Target general information Gen name ALDH2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial; ALDM; ALDHI; ALDH-E2; ALDH class 2 Protein family Aldehyde dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Aldehyde/oxo donor oxidoreductase Function Second enzyme of the major oxidative pathway of alcohol metabolism. Catalyzes the chemical transformation from acetaldehyde to acetic acid. Additionally, functions as a protector against oxidative stress. Related diseases AMED syndrome, digenic (AMEDS) [MIM:619151]: A form of bone marrow failure syndrome, a heterogeneous group of life-threatening disorders characterized by hematopoietic defects in association with a range of variable extra-hematopoietic manifestations. AMEDS is an autosomal recessive, digenic form characterized by childhood onset of bone marrow failure resulting in aplastic anemia, in association with global developmental delay, intellectual disability, and poor overall growth with short stature. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33355142}. The disease is caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry. AMEDS patients carry ADH5 biallelic variants and homozygous or heterozygous ALDH2 variant p.Glu504Lys, affecting protein activity. Cellular and animal studies demonstrate that the simultaneous loss of ALDH2 and ADH5 activities leads to an increase of cellular formaldehyde sensitivity and multisystem abnormalities including hematopoietic failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33355142}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01612; DB06770; DB04381; DB02115; DB00822; DB00536; DB00157; DB00435; DB00727; DB09117; DB06154; DB06207 Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.2.1.3 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Dwarfism; Intellectual disability; Mitochondrion; NAD; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transit peptide; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H Molecular weight (Da) 50223.5 Length 462 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 33.68 Isoelectric point 5.29 Charge (pH=7) -7.87 3D Binding mode Sequence AVPAPNQQPEVFCNQIFINNEWHDAVSRKTFPTVNPSTGEVICQVAEGDKEDVDKAVKAARAAFQLGSPWRRMDASHRGRLLNRLADLIERDRTYLAALETLDNGKPYVISYLVDLDMVLKCLRYYAGWADKEPVGVCGQIIPWNFPLLMQAWKLGPALATGNVVVMKVAEQTPLTALYVANLIKEAGFPPGVVNIVPGFGPTAGAAIASHEDVDKVAFTGSTEIGRVIQVAAGSSNLKRVTLELGGKSPNIIMSDADMDWAVEQAHFALFFNQGQCSCAGSRTFVQEDIYDEFVERSVARAKSRVVGNPFDSKTEQGPQVDETQFKKILGYINTGKQEGAKLLCGGGIAADRGYFIQPTVFGDVQDGMTIAKEEIFGPVMQILKFKTIEEVVGRANNSTYGLAAAVFTKDLDKANYLSQALQAGTVWVNCYDVFGAQSPFGGYKMSGSGRELGEYGLQAYT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 45 | Retinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha (RXRA) | 2P1T | 5.25 | |
Target general information Gen name RXRA Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Retinoid X receptor alpha; RXRalpha; Nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group B member 1; NR2B1 Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR2 subfamily Biochemical class Nuclear hormone receptor Function Retinoic acid receptors bind as heterodimers to their target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, and regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RAR/RXR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5. The high affinity ligand for RXRs is 9-cis retinoic acid. RXRA serves as a common heterodimeric partner for a number of nuclear receptors. In the absence of ligand, the RXR-RAR heterodimers associate with a multiprotein complex containing transcription corepressors that induce histone acetylation, chromatin condensation and transcriptional suppression. On ligand binding, the corepressors dissociate from the receptors and associate with the coactivators leading to transcriptional activation. The RXRA/PPARA heterodimer is required for PPARA transcriptional activity on fatty acid oxidation genes such as ACOX1 and the P450 system genes. Receptor for retinoic acid. Related diseases Lichtenstein-Knorr syndrome (LIKNS) [MIM:616291]: An autosomal recessive neurologic disorder characterized by progressive cerebellar ataxia and severe progressive sensorineural hearing loss. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25205112, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30237576}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08063; DB08402; DB07863; DB07557; DB00459; DB00210; DB01436; DB00523; DB00132; DB04557; DB00307; DB01393; DB03756; DB00749; DB00926; DB05956; DB04224; DB02746; DB00412; DB00755; DB08601 Interacts with O14503; P35637; Q15648; Q71SY5; Q15788; Q15596; P55055; P55055-1; Q13133; P27986; P37231; P37231-1; P10276; P42224; P11473; P97792-1; Q9JLI4; P04625; PRO_0000278730 [Q03463] EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; DNA-binding; Host-virus interaction; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 24958.9 Length 221 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 39.47 Isoelectric point 6.16 Charge (pH=7) -3.45 3D Binding mode Sequence DMPVERILEAELAVEDPVTNICQAADKQLFTLVEWAKRIPHFSELPLDDQVILLRAGWNELLIASFSHRSIAVKDGILLATGLHVHRNSAHSAGVGAIFDRVLTELVSKMRDMQMDKTELGCLRAIVLFNPDSKGLSNPAEVEALREKVYASLEAYCKHKYPEQPGRFAKLLLRLPALRSIGLKCLEHLFFFKLIGDTPIDTFLMEMLEAPHKILHRLLQD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 46 | Spermine synthase | 3C6K | 5.25 | |
Target general information Gen name SMS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Spermidine/spermine synthase family Biochemical class Transferase Function Spermine synthase activity. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked, syndromic, Snyder-Robinson type (MRXSSR) [MIM:309583]: An X-linked intellectual disability syndrome characterized by a collection of clinical features including facial asymmetry, marfanoid habitus, hypertonia, osteoporosis and unsteady gait. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14508504, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18550699, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19206178, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22612257, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23696453, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23897707}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00127 Interacts with NA EC number 2.5.1.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Direct protein sequencing; Intellectual disability; Phosphoprotein; Polyamine biosynthesis; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 27177.1 Length 238 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 41.31 Isoelectric point 4.82 Charge (pH=7) -9.19 3D Binding mode Sequence RYWPTADGRLVEYDIDEVVYDEDSPYQNIKILHSKQFGNILILSGDVNLAESDLAYTRAIMGSGKEDYTGKDVLILGGGDGGILCEIVKLKPKMVTMVEIDQMVIDGCKKYMRKDVLDNLKGDCYQVLIEDCIPVLKRYAKEGREFDYVINDLTAVPISTSPSTWEFLRLILDLSMKVLKQDGKYFTQGNCVNLTEALSLYEEQLGRLYCPVEFSKEIVCVPSYLELWVFYTVWKKAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 47 | Hyperpolarization cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 4 (HCN4) | 3OTF | 5.25 | |
Target general information Gen name HCN4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 4 Protein family Potassium channel HCN family Biochemical class Voltage-gated ion channel Function Contributes to the native pacemaker currents in heart (If) that regulate the rhythm of heart beat. May contribute to the native pacemaker currents in neurons (Ih). May mediate responses to sour stimuli. Hyperpolarization-activated ion channel with very slow activation and inactivation exhibiting weak selectivity for potassium over sodium ions. Related diseases Sick sinus syndrome 2 (SSS2) [MIM:163800]: The term 'sick sinus syndrome' encompasses a variety of conditions caused by sinus node dysfunction. The most common clinical manifestations are syncope, presyncope, dizziness, and fatigue. Electrocardiogram typically shows sinus bradycardia, sinus arrest, and/or sinoatrial block. Episodes of atrial tachycardias coexisting with sinus bradycardia ('tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome') are also common in this disorder. SSS occurs most often in the elderly associated with underlying heart disease or previous cardiac surgery, but can also occur in the fetus, infant, or child without heart disease or other contributing factors. SSS2 onset is in utero or at birth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15123648, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16407510, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20662977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23103389}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Brugada syndrome 8 (BRGDA8) [MIM:613123]: A tachyarrhythmia characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs, the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19165230}. The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Epilepsy, idiopathic generalized 18 (EIG18) [MIM:619521]: An autosomal dominant form of idiopathic generalized epilepsy, a disorder characterized by recurring generalized seizures in the absence of detectable brain lesions and/or metabolic abnormalities. Generalized seizures arise diffusely and simultaneously from both hemispheres of the brain. Seizure types include juvenile myoclonic seizures, absence seizures, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. EIG18 is characterized by onset of myoclonic seizures in infancy. Although the seizures remit, some patients may have later speech or cognitive impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30127718}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with O60741; Q9Y3Q4 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Brugada syndrome; cAMP; cAMP-binding; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Epilepsy; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Potassium; Potassium channel; Potassium transport; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Sodium; Sodium channel; Sodium transport; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Voltage-gated channel Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23211.2 Length 197 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 42.69 Isoelectric point 8.67 Charge (pH=7) 3.11 3D Binding mode Sequence DSSRRQYQEKYKQVEQYMSFHKLPPDTRQRIHDYYEHRYQGKMFDEESILGELSEPLREEIINFNCRKLVASMPLFANADPNFVTSMLTKLRFEVFQPGDYIIREGTIGKKMYFIQHGVVSVLTKGNKETKLADGSYFGEICLLTRGRRTASVRADTYCRLYSLSVDNFNEVLEEYPMMRRAFETVALDRLDRIGKK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 48 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor alpha-2 (CHRNA2) | 5FJV | 5.25 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CHRNA2 Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-2/CHRNA2 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. Related diseases Epilepsy, nocturnal frontal lobe, 4 (ENFL4) [MIM:610353]: An autosomal dominant focal epilepsy characterized by nocturnal seizures associated with fear sensation, tongue movements, and nocturnal wandering, closely resembling nightmares and sleep walking. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16826524}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Seizures, benign familial infantile, 6 (BFIS6) [MIM:610353]: A form of benign familial infantile epilepsy, a neurologic disorder characterized by afebrile seizures occurring in clusters during the first year of life, without neurologic sequelae. BFIS6 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25847220}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00732; DB00237; DB00411; DB00565; DB01245; DB00514; DB01135; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB00483; DB08960; DB00657; DB01336; DB00416; DB01226; DB00184; DB01337; DB01338; DB00721; DB00728; DB05740; DB00202; DB01199; DB01339 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Epilepsy; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 48323.4 Length 413 Aromaticity 0.15 Instability index 32 Isoelectric point 5.69 Charge (pH=7) -6.58 3D Binding mode Sequence DRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLPEDRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 49 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor alpha-3/beta-4 (CHRNA3/B4) | 6PV7 | 5.25 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA3-CHRNB4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Neuronal acetylcholine receptor Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-3/CHRNA3 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function A type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting of 3 and 4 subunits. Related diseases Bladder dysfunction, autonomic, with impaired pupillary reflex and secondary CAKUT (BAIPRCK) [MIM:191800]: An autosomal recessive disease characterized by impaired innervation and autonomic dysfunction of the urinary bladder, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, small kidneys, recurrent urinary tract infections, and progressive renal insufficiency. Additional autonomic features are impaired pupillary reflex and orthostatic hypotension. The disease manifests in utero or early childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31708116}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00915; DB01156; DB00237; DB00565; DB09028; DB00514; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB05710; DB01227; DB00848; DB00333; DB00184; DB01090; DB00202; DB01273 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 89661.2 Length 775 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 35.11 Isoelectric point 6.07 Charge (pH=7) -5.67 3D Binding mode Sequence SEAEHRLFERLFEDYNEIIRPVANVSDPVIIHFEVSMSQLVKVDEVNQIMETNLWLKQIWNDYKLKWNPSDYGGAEFMRVPAQKIWKPDIVLYNNAVGDFQVDDKTKALLKYTGEVTWIPPAIFKSSCKIDVTYFPFDYQNCTMKFGSWSYDKAKIDLVLIGSSMNLKDYWESGEWAIIKAPGYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDITYSLYIRRLPLFYTINLIIPCLLISFLTVLVFYLPSDCGEKVTLCISVLLSLTVFLLVITETIPSTSLVIPLIGEYLLFTMIFVTLSIVITVFVLNVHYRTPTTHTMPSWVKTVFLNLLPRVMFMTRIKEAIQSVKYIAENMKAQNEAKEIQDDWKYVAMVIDRIFLWVFTLVCILGTAGLFLQPLMRVANAEEKLMDDLLNKTRYNNLIRPATSSSQLISIKLQLSLAQLISVNEREQIMTTNVWLKQEWTDYRLTWNSSRYEGVNILRIPAKRIWLPDIVLYNNADGTYEVSVYTNLIVRSNGSVLWLPPAIYKSACKIEVKYFPFDQQNCTLKFRSWTYDHTEIDMVLMTPTASMDDFTPSGEWDIVALPGRRTVNPQDPSYVDVTYDFIIKRKPLFYTINLIIPCVLTTLLAILVFYLPSDCGEKMTLCISVLLALTFFLLLISKIVPPTSLDVPLIGKYLMFTMVLVTFSIVTSVCVLNVHHRSPSTHTMAPWVKRCFLHKLPTFLFMKRRQDVQEALEGVSFIAQHMKNDDEDQSVVEDWKYVAMVVDRLFLWVFMFVCVLGTVGLFLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 50 | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) | 5J89 | 5.25 | |
Target general information Gen name CD274 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hPD-L1; Programmed death ligand 1; PDL1; PDCD1LG1; PDCD1L1; PDCD1 ligand 1; B7H1; B7-H1; B7 homolog 1 Protein family Immunoglobulin superfamily, BTN/MOG family Biochemical class Immunoglobulin Function As a ligand for the inhibitory receptor PDCD1/PD-1, modulates the activation threshold of T-cells and limits T-cell effector response. Through a yet unknown activating receptor, may costimulate T-cell subsets that predominantly produce interleukin-10 (IL10). Plays a critical role in induction and maintenance of immune tolerance to self. Related diseases Truncation of the 3'-untranslated (3'-UTR) region of CD274 transcripts leads to elevated expression of CD274 in multiple cancers including T-cell leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and stomach adenocarcinoma (PubMed:27281199). Disruption of 3'-UTR region is caused by structural variants that stabilize CD274 transcripts, leading to overexpression (PubMed:27281199). Increased expression in tumors promotes immune evasion and tumor cell growth by allowing malignant cells to escape destruction by the immune system (PubMed:27281199). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27281199}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB15773; DB11595; DB15771; DB11945; DB15772; DB14776; DB15770; DB11714; DB15769; DB09035; DB09037; DB00203; DB00313 Interacts with P33681; Q8IZR5; Q9NX76; Q15116; Q15116 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Endosome; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Immunoglobulin domain; Membrane; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C,D Molecular weight (Da) 28335.2 Length 249 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 35.39 Isoelectric point 6.15 Charge (pH=7) -3.43 3D Binding mode Sequence AFTVTVPKDLYVVEYGSNMTIECKFPVEKQLDLAALIVYWEMEDKNIIQFVHGEEDLKVQHSSYRQRARLLKDQLSLGNAALQITDVKLQDAGVYRCMISYGGADYKRITVKVNAPYAAALEHHHAFTVTVPKDLYVVEYGSNMTIECKFPVEKQLDLAALIVYWEMEDKNIIQFVHGEEDLKVQHSSYRQRARLLKDQLSLGNAALQITDVKLQDAGVYRCMISYGGADYKRITVKVNAPYAAALEHH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 51 | Erbb2 tyrosine kinase receptor (HER2) | 3PP0 | 5.24 | |
Target general information Gen name ERBB2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms p185erbB2; Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2; Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2; Proto-oncogene c-ErbB-2; Proto-oncogene Neu; NGL; NEU; Metastatic lymph node gene 19 protein; MLN19 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, EGF receptor subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Protein tyrosine kinase that is part of several cell surface receptor complexes, but that apparently needs a coreceptor for ligand binding. Essential component of a neuregulin-receptor complex, although neuregulins do not interact with it alone. GP30 is a potential ligand for this receptor. Regulates outgrowth and stabilization of peripheral microtubules (MTs). Upon ERBB2 activation, the MEMO1-RHOA-DIAPH1 signaling pathway elicits the phosphorylation and thus the inhibition of GSK3B at cell membrane. This prevents the phosphorylation of APC and CLASP2, allowing its association with the cell membrane. In turn, membrane-bound APC allows the localization of MACF1 to the cell membrane, which is required for microtubule capture and stabilization. Related diseases Glioma (GLM) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15457249}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Ovarian cancer (OC) [MIM:167000]: The term ovarian cancer defines malignancies originating from ovarian tissue. Although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, epithelial ovarian carcinoma is the most common form. Ovarian cancers are often asymptomatic and the recognized signs and symptoms, even of late-stage disease, are vague. Consequently, most patients are diagnosed with advanced disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15457249, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17344846}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Lung cancer (LNCR) [MIM:211980]: A common malignancy affecting tissues of the lung. The most common form of lung cancer is non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that can be divided into 3 major histologic subtypes: squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and large cell lung cancer. NSCLC is often diagnosed at an advanced stage and has a poor prognosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15457249}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Gastric cancer (GASC) [MIM:613659]: A malignant disease which starts in the stomach, can spread to the esophagus or the small intestine, and can extend through the stomach wall to nearby lymph nodes and organs. It also can metastasize to other parts of the body. The term gastric cancer or gastric carcinoma refers to adenocarcinoma of the stomach that accounts for most of all gastric malignant tumors. Two main histologic types are recognized, diffuse type and intestinal type carcinomas. Diffuse tumors are poorly differentiated infiltrating lesions, resulting in thickening of the stomach. In contrast, intestinal tumors are usually exophytic, often ulcerating, and associated with intestinal metaplasia of the stomach, most often observed in sporadic disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15457249, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17344846}. The protein represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Chromosomal aberrations involving ERBB2 may be a cause gastric cancer. Deletions within 17q12 region producing fusion transcripts with CDK12, leading to CDK12-ERBB2 fusion leading to truncated CDK12 protein not in-frame with ERBB2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21097718}.; DISEASE: Visceral neuropathy, familial, 2, autosomal recessive (VSCN2) [MIM:619465]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by intestinal dysmotility due to aganglionosis (Hirschsprung disease), hypoganglionosis, and/or chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Patients also show peripheral axonal neuropathy, hypotonia, mild developmental delay, unilateral ptosis, and sensorineural hearing loss. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33497358}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08916; DB06021; DB12267; DB12010; DB04988; DB01259; DB14967; DB06366; DB11973; DB00072; DB05773; DB11652; DB05944; DB15035 Interacts with P00519; P42684; P15309; P60709; Q92625; O00213; O75815; Q9HB71; Q16543; Q9NSE2; Q7Z7G1; P46109; Q93034; Q99704; Q8TEW6; Q15075; P98172; P00533; P04626; P21860; Q15303; Q9UJM3; P09769; P06241; O75791; P62993; Q14451; P07900; P08238; P14625; P11021; P46940; P35568; Q08881; P23458; Q14974; Q96JA1; O75367; O75367-3; Q9UQF2; Q13387; P42679; Q9Y316; O43639; Q02297-7; O00750; P27986; O00459; Q92569; P19174; P16885; O95602; Q13882; Q06124; Q05209; Q99952; Q99952-1; P23467; P08575; Q12913; Q15262; Q16827; Q15256; P49792; P20936; O95980; Q9NP31; P29353; P98077; Q92529; Q9H6Q3; O15524; P12931; P42224; P40763; P31948; Q7KZ85; P43405; Q9Y490; Q63HR2; Q68CZ2; Q96D37; P52735; O14980; P62258 EC number EC 2.7.10.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; Alternative initiation; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Chromosomal rearrangement; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endosome; Glycoprotein; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tyrosine-protein kinase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 33776.1 Length 296 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 47.13 Isoelectric point 8.67 Charge (pH=7) 4.22 3D Binding mode Sequence APNQALLRILKETELRKVKVLGSGAFGTVYKGIWIPDGENVKIPVAIKVLRENTSPKANKEILDEAYVMAGVGSPYVSRLLGICLTSTVQLVTQLMPYGCLLDHVRENRGRLGSQDLLNWCMQIAKGMSYLEDVRLVHRDLAARNVLVKSPNHVKITDFGLARLLDIDETEYHAGKVPIKWMALESILRRRFTHQSDVWSYGVTVWELMTFGAKPYDGIPAREIPDLLEKGERLPQPPICTIDVYMIMVKCWMIDSECRPRFRELVSEFSRMARDPQRFVVIQNEPLDSTFYRSLL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 52 | Acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha | 4ZJS | 5.24 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms ACHRA;CHNRA Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-1/CHRNA1 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Immune system Function Acetylcholine binding.Acetylcholine-gated cation-selective channel activity.Acetylcholine receptor activity.Ion channel activity.Ligand-gated ion channel activity. Related diseases Multiple pterygium syndrome, lethal type (LMPS) [MIM:253290]: Multiple pterygia are found infrequently in children with arthrogryposis and in fetuses with fetal akinesia syndrome. In lethal multiple pterygium syndrome there is intrauterine growth retardation, multiple pterygia, and flexion contractures causing severe arthrogryposis and fetal akinesia. Subcutaneous edema can be severe, causing fetal hydrops with cystic hygroma and lung hypoplasia. Oligohydramnios and facial anomalies are frequent. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18252226}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: The alpha subunit is the main focus for antibody binding in myasthenia gravis. Myasthenia gravis is characterized by sporadic muscular fatigability and weakness, occurring chiefly in muscles innervated by cranial nerves, and characteristically improved by cholinesterase-inhibiting drugs.; DISEASE: Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 1A, slow-channel (CMS1A) [MIM:601462]: A common congenital myasthenic syndrome. Congenital myasthenic syndromes are characterized by muscle weakness affecting the axial and limb muscles (with hypotonia in early-onset forms), the ocular muscles (leading to ptosis and ophthalmoplegia), and the facial and bulbar musculature (affecting sucking and swallowing, and leading to dysphonia). The symptoms fluctuate and worsen with physical effort. CMS1A is a slow-channel myasthenic syndrome. It is caused by kinetic abnormalities of the AChR, resulting in prolonged AChR channel opening episodes, prolonged endplate currents, and depolarization block. This is associated with calcium overload, which may contribute to subsequent degeneration of the endplate and postsynaptic membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16685696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7619526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8872460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9158151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9221765}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 1B, fast-channel (CMS1B) [MIM:608930]: A form of congenital myasthenic syndrome, a group of disorders characterized by failure of neuromuscular transmission, including pre-synaptic, synaptic, and post-synaptic disorders that are not of autoimmune origin. Clinical features are easy fatigability and muscle weakness affecting the axial and limb muscles (with hypotonia in early-onset forms), the ocular muscles (leading to ptosis and ophthalmoplegia), and the facial and bulbar musculature (affecting sucking and swallowing, and leading to dysphonia). The symptoms fluctuate and worsen with physical effort. CMS1B is a fast-channel myasthenic syndrome. It is caused by kinetic abnormalities of the AChR, resulting in brief opening and activity of the channel, with a rapid decay in endplate current, failure to achieve threshold depolarization of the endplate and consequent failure to fire an action potential. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10195214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12588888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15079006}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08838; DB00565; DB00555 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Congenital myasthenic syndrome; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E Molecular weight (Da) 46717.8 Length 411 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 38.02 Isoelectric point 4.77 Charge (pH=7) -22.31 3D Binding mode Sequence EHETRLVAKLFKDYSSVVRPVEDHRQVVEVTLGFTLQDIVKADSSTNEVDLVYYEQQRWVDYNLKWNPDDYGGVKKIHIPAADIWTPDITAYSSTRPVQVLSPQIAVVTHDGSVMFIPAQRLSFMCDPTGVDSEEGATCAVKFGSWVYSGFEIDLKTDTDQVDLSSYYASSKYEILSATQTRQVQHYSCCPEPYIDVNLVVKFREEHETRLVAKLFKDYSSVVRPVEDHRQVVEVTLGFTLQDIVKADSSTNEVDLVYYEQQRWVDYNLKWNPDDYGGVKKIHIPAADIWTPDITAYSSTRPVQVLSPQIAVVTHDGSVMFIPAQRLSFMCDPTGVDSEEGATCAVKFGSWVYSGFEIDLKTDTDQVDLSSYYASSKYEILSATQTRQVQHYSCCPEPYIDVNLVVKFRER Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 53 | Non-heme chloroperoxidase | 1A8U | 5.24 | |
Target general information Gen name cpo Organism Kitasatospora aureofaciens (Streptomyces aureofaciens) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms cpoT Protein family AB hydrolase superfamily, Bacterial non-heme haloperoxidase / perhydrolase family Biochemical class Haloperoxidase Function Chloride peroxidase activity. Related diseases Hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia (HVLI) [MIM:618850]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by highly elevated plasma concentrations of valine and leucine/isoleucine. Affected individuals suffer from headache and mild memory impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. A patient with hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia was identified as compound heterozygote for Gln-170 (inherited from his father) and Lys-264 (inherited from his mother), both variants reduced the catalytic activity of the enzyme. After treatment with vitamin B6, a precursor of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, a BCAT2 cofactor, the blood levels of branched chain amino acids, especially valine, were decreased and brain lesions were improved. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03793 Interacts with NA EC number 1.11.1.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Chloride; Oxidoreductase; Peroxidase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 60428.4 Length 554 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 31.26 Isoelectric point 4.65 Charge (pH=7) -32.72 3D Binding mode Sequence PFITVGQENSTSIDLYYEDHGAGQPVVLIHGFPLSGHSWERQSAALLDAGYRVITYDRRGFGQSSQPTTGYDYDTFAADLNTVLETLDLQDAVLVGFSMGTGEVARYVSSYGTARIAKVAFLASLEPFLLKTDDNPDGAAPKEFFDGIVAAVKADRYAFYTGFFNDFYNLDENLGTRISEEAVRNSWNTAASGGFFAAAAAPTTWYTDFRADIPRIDVPALILHGTGDRTLPIENTARVFHKALPSAEYVEVEGAPHGLLWTHAEEVNTALLAFLAKPFITVGQENSTSIDLYYEDHGAGQPVVLIHGFPLSGHSWERQSAALLDAGYRVITYDRRGFGQSSQPTTGYDYDTFAADLNTVLETLDLQDAVLVGFSMGTGEVARYVSSYGTARIAKVAFLASLEPFLLKTDDNPDGAAPKEFFDGIVAAVKADRYAFYTGFFNDFYNLDENLGTRISEEAVRNSWNTAASGGFFAAAAAPTTWYTDFRADIPRIDVPALILHGTGDRTLPIENTARVFHKALPSAEYVEVEGAPHGLLWTHAEEVNTALLAFLAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 54 | Nitric-oxide synthase inducible (NOS2) | 3E7G | 5.24 | |
Target general information Gen name NOS2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms iNOS; Peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylase NOS2; Nitric oxide synthase, inducible; NOS2A; NOS type II; Inducible NOS; Inducible NO synthase; Hepatocyte NOS; HEP-NOS Protein family NOS family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Produces nitric oxide (NO) which is a messenger molecule with diverse functions throughout the body. In macrophages, NO mediates tumoricidal and bactericidal actions. Also has nitrosylase activity and mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of cytoplasmic target proteins such PTGS2/COX2 (By similarity). As component of the iNOS-S100A8/9 transnitrosylase complex involved in the selective inflammatory stimulus-dependent S-nitrosylation of GAPDH on 'Cys-247' implicated in regulation of the GAIT complex activity and probably multiple targets including ANXA5, EZR, MSN and VIM. Involved in inflammation, enhances the synthesis of proinflammatory mediators such as IL6 and IL8. Related diseases Cerebellar ataxia, impaired intellectual development, and dysequilibrium syndrome 3 (CAMRQ3) [MIM:613227]: An autosomal recessive, congenital cerebellar ataxia associated with dysarthia, quadrupedal gait and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19461874}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07003; DB07007; DB07011; DB07405; DB08750; DB01997; DB07029; DB07008; DB08214; DB07002; DB01835; DB06879; DB04534; DB03100; DB02207; DB00125; DB00155; DB01234; DB14649; DB11327; DB00997; DB07306; DB07388; DB05252; DB01381; DB03366; DB05214; DB04400; DB09237; DB00244; DB01110; DB01017; DB03144; DB01686; DB03449; DB06916; DB07318; DB07389; DB02044; DB02644; DB05383; DB02234; DB03953; DB02462; DB08814 Interacts with P04406 EC number EC 1.14.13.39 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Calmodulin-binding; Cytoplasm; FAD; Flavoprotein; FMN; Heme; Iron; Metal-binding; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 48633 Length 421 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.5 Isoelectric point 6.75 Charge (pH=7) -1.04 3D Binding mode Sequence RHVRIKNWGSGMTFQDTLHHKAKGILTCRSKSCLGSIMTPKSLTRGPRDKPTPPDELLPQAIEFVNQYYGSFKEAKIEEHLARVEAVTKEIETTGTYQLTGDELIFATKQAWRNAPRCIGRIQWSNLQVFDARSCSTAREMFEHICRHVRYSTNNGNIRSAITVFPQRSDGKHDFRVWNAQLIRYAGYQMPDGSIRGDPANVEFTQLCIDLGWKPKYGRFDVVPLVLQANGRDPELFEIPPDLVLEVAMEHPKYEWFRELELKWYALPAVANMLLEVGGLEFPGCPFNGWYMGTEIGVRDFCDVQRYNILEEVGRRMGLETHKLASLWKDQAVVEINIAVLHSFQKQNVTIMDHHSAAESFMKYMQNEYRSRGGCPADWIWLVPPMSGSITPVFHQEMLNYVLSPFYYYQVEAWKTHVWQD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 55 | cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4C | 2QYM | 5.24 | |
Target general information Gen name PDE4C Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms DPDE1 Protein family Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family, PDE4 subfamily Biochemical class Hydrolase Function 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity.Metal ion binding. Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 33 (COXPD33) [MIM:617713]: An autosomal recessive disorder caused by multiple mitochondrial respiratory chain defects and impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism. Clinical manifestations are highly variable. Affected infants present with cardiomyopathy accompanied by multisystemic features involving liver, kidney, and brain. Death in infancy is observed in some patients. Children and adults present with myopathy and progressive external ophthalmoplegia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28942965}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01427; DB00201; DB05219; DB00651; DB06246; DB05266; DB01088; DB01791; DB01656; DB01954; DB09283 Interacts with Q96D03; O15499; P26718; P50221; Q6FHY5; Q9UJX0; P26367; P30626; P59817; P30626 EC number 3.1.4.53 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; cAMP; Cell projection; Cilium; Hydrolase; Manganese; Metal-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33042.2 Length 291 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 23.45 Isoelectric point 4.91 Charge (pH=7) -18.1 3D Binding mode Sequence VPRFGVQTDQEEQLAKELEDTNKWGLDVFKVAELSGNRPLTAIIFSIFQERDLLKTFQIPADTLATYLLMLEGHYHANVAYHNSLHAADVAQSTHVLLATPALEAVFTDLEILAALFASAIHDVDHPGVSNQNDASVLENHHLAVGFKLLQAENCDIFQNLSAKQRLSLRRMVIDMVLATDMSKHMNLLADLKTMVETKKVTSLGVLLLDNYSDRIQVLQNLVHCADLSNPTKPLPLYRQWTDRIMAEFFQQQVGFIDYIAHPLWETWADLVHPDAQDLLDTLEDNREWYQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 56 | Lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase (EC 1.14.13.70) | 4G3J | 5.24 | |
Target general information Gen name Tb11.02.4080 Organism Trypanosoma brucei brucei (strain 927/4 GUTat10.1) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Cytochrome P450 family Biochemical class NA Function NA Related diseases LTC4 synthase deficiency is associated with a neurometabolic developmental disorder characterized by muscular hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, and microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10896305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9820300}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 1.14.13.70 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Heme; Iron; Metal-binding; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID D Molecular weight (Da) 50691.4 Length 448 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 54.09 Isoelectric point 6.99 Charge (pH=7) -0.03 3D Binding mode Sequence GKLPPVYPVTVPILGHIIQFGKSPLGFMQECKRQLKSGIFTINIVGKRVTIVGDPHEHSRFFLPRNEVLSPREVYSFMVPVFGEGVAYAAPYPRMREQLNFLAEELTIAKFQNFVPAIQHEVRKFMAANWDKDEGEINLLEDCSTMIINTACQCLFGEDLRKRLDARRFAQLLAKMESSLIPAAVFLPILLKLPLPQSARCHEARTELQKILSEIIIARKEEEVNKDSSTSDLLSGLLSAVYRDGTPMSLHEVCGMIVAAMFAGQHTSSITTTWSMLHLMHPANVKHLEALRKEIEEFPAQLNYNNVMDEMPFAERCARESIRRDPPLLMLMRKVMADVKVGSYVVPKGDIIACSPLLSHHDEEAFPEPRRWDPERDEKVEGAFIGFGAGVHKCIGQKFGLLQVKTILATAFRSYDFQLLRDEVPDPDYHTMVVGPTASQCRVKYIRR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 57 | Influenza Polymerase acidic endonuclease (Influ PA) | 4ZI0 | 5.24 | |
Target general information Gen name Influ PA Organism Influenza A virus (strain A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 H1N1) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms RNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit P2; Polymerase acidic protein Protein family Influenza viruses PA family Biochemical class NA Function Plays an essential role in viral RNA transcription and replication by forming the heterotrimeric polymerase complex together with PB1 and PB2 subunits. The complex transcribes viral mRNAs by using a unique mechanism called cap-snatching. It consists in the hijacking and cleavage of host capped pre-mRNAs. These short capped RNAs are then used as primers for viral mRNAs. The PB2 subunit is responsible for the binding of the 5' cap of cellular pre-mRNAs which are subsequently cleaved after 10-13 nucleotides by the PA subunit that carries the endonuclease activity. Related diseases Lymphatic malformation 8 (LMPHM8) [MIM:618773]: A form of primary lymphedema, a disease characterized by swelling of body parts due to developmental anomalies and functional defects of the lymphatic system. Adult patients with lymphedema may suffer from recurrent local infections. Impaired lymphatic drainage in the fetus can develop into hydrops fetalis, a severe condition characterized by excessive fluid accumulation in more than two fetal extra-vascular compartments and body cavities, placental enlargement and edema, pericardial or pleural effusion, or ascites. LMPHM8 is an autosomal recessive form characterized by onset in utero and fetal death due to non-immune hydrops fetalis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30115739}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB13997 Interacts with P03485; P03466; P03431 EC number EC 3.1.-.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cap snatching; Endonuclease; Eukaryotic host gene expression shutoff by virus; Eukaryotic host transcription shutoff by virus; Host cytoplasm; Host gene expression shutoff by virus; Host nucleus; Host-virus interaction; Hydrolase; Inhibition of host RNA polymerase II by virus; Manganese; Metal-binding; Nuclease; Phosphoprotein; Reference proteome; Ribosomal frameshifting Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 21288.1 Length 181 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 49.23 Isoelectric point 6.27 Charge (pH=7) -1.8 3D Binding mode Sequence GPLGSMEDFVRQCFNPMIVELAEKTMKEYGEDLKIETNKFAAICTHLEVCFMYSDASKHRFEIIEGRDRTMAWTVVNSICNTTGAEKPKFLPDLYDYKENRFIEIGVTRREVHIYYLEKANKIKSEKTHIHIFSFTGEEMATKADYTLDEESRARIKTRLFTIRQEMASRGLWDSFRQSER Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 58 | Tankyrase-2 (TNKS-2) | 3U9H | 5.24 | |
Target general information Gen name TNKS2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tankyrase-related protein; Tankyrase-like protein; Tankyrase II; TRF1-interacting ankyrin-related ADP-ribose polymerase 2; TNKL; TANK2; Protein poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase tankyrase-2; Poly [ADP-ribos Protein family ARTD/PARP family Biochemical class Glycosyltransferases Function Acts as an activator of the Wnt signaling pathway by mediating poly-ADP-ribosylation of AXIN1 and AXIN2, 2 key components of the beta-catenin destruction complex: poly-ADP-ribosylated target proteins are recognized by RNF146, which mediates their ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. Also mediates poly-ADP-ribosylation of BLZF1 and CASC3, followed by recruitment of RNF146 and subsequent ubiquitination. Mediates poly-ADP-ribosylation of TERF1, thereby contributing to the regulation of telomere length. Stimulates 26S proteasome activity. Poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase involved in various processes such as Wnt signaling pathway, telomere length and vesicle trafficking. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder with macrocephaly, seizures, and speech delay (IDDMSSD) [MIM:618158]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impaired intellectual development, poor speech, postnatal macrocephaly, and seizures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30290153}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with O15084; Q7Z6K5-1; O15169; Q9NWV8; P11274; Q13698; Q9NRI5; Q6V0I7; Q9NWT6; P14652; Q9UIQ6; Q14980; Q9BZL4; Q92698; P78314; O43815; P54274; Q9C0C2; Q9UHP3; Q06649 EC number EC 2.4.2.30 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ADP-ribosylation; ANK repeat; Chromosome; Cytoplasm; Glycosyltransferase; Golgi apparatus; Hydroxylation; Membrane; Metal-binding; NAD; Nucleotidyltransferase; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Telomere; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Wnt signaling pathway; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23695.5 Length 208 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 47.61 Isoelectric point 8.28 Charge (pH=7) 2.88 3D Binding mode Sequence GTILIDLSPDDKEFQSVEEEMQSTVREHRDGGHAGGIFNRYNILKIQKVCNKKLWERYTHRRKEVSEENHNHANERMLFHGSPFVNAIIHKGFDERHAYIGGMFGAGIYFAENSSKSNQYVYGIGGGTGCPVHKDRSCYICHRQLLFCRVTLGKSFLQFSAMAHSPPGHHSVTGRPSVNGLALAEYVIYRGEQAYPEYLITYQIMRPE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 59 | Toll-like receptor 1 (TLR1) | 2Z7X | 5.24 | |
Target general information Gen name TLR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Toll/interleukin-1 receptor-like protein; TIL; KIAA0012; CD281 Protein family Toll-like receptor family Biochemical class Toll-like receptor Function Specifically recognizes diacylated and triacylated lipopeptides. Cooperates with TLR2 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins or lipopeptides. Forms the activation cluster TLR2:TLR1:CD14 in response to triacylated lipopeptides, this cluster triggers signaling from the cell surface and subsequently is targeted to the Golgi in a lipid-raft dependent pathway. Acts via MYD88 and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Participates in the innate immune response to microbial agents. Related diseases Hao-Fountain syndrome (HAFOUS) [MIM:616863]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by global developmental delay, varying degrees of intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorder, poor or absent speech, and mild facial dysmorphism. Most patients develop seizures. Additional variable features include hypotonia, hypogonadism in males, and ocular anomalies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26365382, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30679821}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q15399; Q9BXR5; O60603; Q9Y2C9 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; Immunity; Inflammatory response; Innate immunity; Leucine-rich repeat; Membrane; NAD; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 62767.4 Length 555 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 38.79 Isoelectric point 6.85 Charge (pH=7) -0.55 3D Binding mode Sequence SLSCDRNGICKGSSGSLNSIPSGLTEAVKSLDLSNNRITYISNSDLQRCVNLQALVLTSNGINTIEEDSFSSLGSLEHLDLSYNYLSNLSSSWFKPLSSLTFLNLLGNPYKTLGETSLFSHLTKLQILRVGNMDTFTKIQRKDFAGLTFLEELEIDASDLQSYEPKSLKSIQNVSHLILHMKQHILLLEIFVDVTSSVECLELRDTDLDTFHFSELSTGETNSLIKKFTFRNVKITDESLFQVMKLLNQISGLLELEFDDCTLNGVGNFRASDNDRVIDPGKVETLTIRRLHIPRFYLFYDLSTLYSLTERVKRITVENSKVFLVPCLLSQHLKSLEYLDLSENLMVEEYLKNSACEDAWPSLQTLILRQNHLASLEKTGETLLTLKNLTNIDISKNSFHSMPETCQWPEKMKYLNLSSTRIHSVTGCIPKTLEILDVSNNNLNLFSLNLPQLKELYISRNKLMTLPDASLLPMLLVLKISRNQLKSVPDGIFDRLTSLQKIWLHTNPWDCSCPRIDYLSRWLNKNSQKEQGSAKCSGSGKPVRSIICPXSKKKK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 60 | Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) | 2Z7X | 5.24 | |
Target general information Gen name TLR2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Toll/interleukin-1 receptor-like protein 4; TIL4; CD282 Protein family Toll-like receptor family Biochemical class Toll-like receptor Function Cooperates with TLR1 or TLR6 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins or lipopeptides. Acts via MYD88 and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. May also activate immune cells and promote apoptosis in response to the lipid moiety of lipoproteins. Recognizes mycoplasmal macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2kD (MALP-2), soluble tuberculosis factor (STF), phenol-soluble modulin (PSM) and B. burgdorferi outer surface protein A lipoprotein (OspA-L) cooperatively with TLR6. Stimulation of monocytes in vitro with M. tuberculosis PstS1 induces p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 activation primarily via this receptor, but also partially via TLR4. MAPK activation in response to bacterial peptidoglycan also occurs via this receptor. Acts as a receptor for M. tuberculosis lipoproteins LprA, LprG, LpqH and PstS1, some lipoproteins are dependent on other coreceptors (TLR1, CD14 and/or CD36); the lipoproteins act as agonists to modulate antigen presenting cell functions in response to the pathogen. M. tuberculosis HSP70 (dnaK) but not HSP65 (groEL-2) acts via this protein to stimulate NF-kappa-B expression. Recognizes M. tuberculosis major T-antigen EsxA (ESAT-6) which inhibits downstream MYD88-dependent signaling (shown in mouse). Forms activation clusters composed of several receptors depending on the ligand, these clusters trigger signaling from the cell surface and subsequently are targeted to the Golgi in a lipid-raft dependent pathway. Forms the cluster TLR2:TLR6:CD14:CD36 in response to diacylated lipopeptides and TLR2:TLR1:CD14 in response to triacylated lipopeptides. Required for normal uptake of M. tuberculosis, a process that is inhibited by M. tuberculosis LppM. Cooperates with LY96 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins and other microbial cell wall components. Related diseases Squalene synthase deficiency (SQSD) [MIM:618156]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by profound developmental delay, brain abnormalities, 2/3 syndactyly of the toes, facial dysmorphisms, low total and LDL-cholesterol, and abnormal urine organic acids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29909962}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00210; DB05475; DB00045; DB16474; DB03963; DB11601 Interacts with P61073; P00533; Q99836; Q15399; Q9BXR5; O60603; Q9Y2C9; Q96DA0 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Inflammatory response; Innate immunity; Isopeptide bond; Leucine-rich repeat; Membrane; NAD; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 62767.4 Length 555 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 38.79 Isoelectric point 6.85 Charge (pH=7) -0.55 3D Binding mode Sequence SLSCDRNGICKGSSGSLNSIPSGLTEAVKSLDLSNNRITYISNSDLQRCVNLQALVLTSNGINTIEEDSFSSLGSLEHLDLSYNYLSNLSSSWFKPLSSLTFLNLLGNPYKTLGETSLFSHLTKLQILRVGNMDTFTKIQRKDFAGLTFLEELEIDASDLQSYEPKSLKSIQNVSHLILHMKQHILLLEIFVDVTSSVECLELRDTDLDTFHFSELSTGETNSLIKKFTFRNVKITDESLFQVMKLLNQISGLLELEFDDCTLNGVGNFRASDNDRVIDPGKVETLTIRRLHIPRFYLFYDLSTLYSLTERVKRITVENSKVFLVPCLLSQHLKSLEYLDLSENLMVEEYLKNSACEDAWPSLQTLILRQNHLASLEKTGETLLTLKNLTNIDISKNSFHSMPETCQWPEKMKYLNLSSTRIHSVTGCIPKTLEILDVSNNNLNLFSLNLPQLKELYISRNKLMTLPDASLLPMLLVLKISRNQLKSVPDGIFDRLTSLQKIWLHTNPWDCSCPRIDYLSRWLNKNSQKEQGSAKCSGSGKPVRSIICPXSKKKK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||