Job Results:
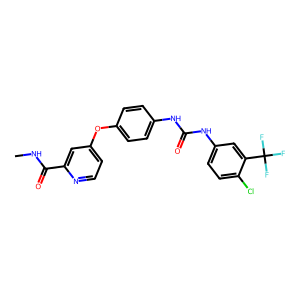
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
2f26746d3788b5c615eb3e0507a308ea
Job name
NA
Time
2025-01-23 16:35:41
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | 2IIP | 8.23 | |
Target general information Gen name NNMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, NNMT/PNMT/TEMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase activity.Pyridine N-methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00627 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Citrullination; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 27886.8 Length 251 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.66 Isoelectric point 5.23 Charge (pH=7) -5.11 3D Binding mode Sequence GFTSKDTYLSHFNPRDYLEKYYSAESQILKHLLKNLFKIFCLDGVKGDLLIDIGSGPTIYQLLSACESFKEIVVTDYSDQNLQELEKWLKAAPAAFDWSPVVTYVCDLEGNRVKGPEKEEKLRQAVKQVLKCDVTQSQPLGAVPLPPADCVLSTLCLDAACPDLPTYCRALRNLGSLLKPGGFLVIMDALKSSYYMIGEQKFSSLPLGREAVEAAVKEAGYTIEWFEVISQSYSSTMANNEGLFSLVARKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 2 | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | 2IIP | 8.23 | |
Target general information Gen name NNMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, NNMT/PNMT/TEMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase activity.Pyridine N-methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00627 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Citrullination; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 27886.8 Length 251 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.66 Isoelectric point 5.23 Charge (pH=7) -5.11 3D Binding mode Sequence GFTSKDTYLSHFNPRDYLEKYYSAESQILKHLLKNLFKIFCLDGVKGDLLIDIGSGPTIYQLLSACESFKEIVVTDYSDQNLQELEKWLKAAPAAFDWSPVVTYVCDLEGNRVKGPEKEEKLRQAVKQVLKCDVTQSQPLGAVPLPPADCVLSTLCLDAACPDLPTYCRALRNLGSLLKPGGFLVIMDALKSSYYMIGEQKFSSLPLGREAVEAAVKEAGYTIEWFEVISQSYSSTMANNEGLFSLVARKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 3 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 8 (CDK8) | 3RGF | 8.04 | |
Target general information Gen name CDK8 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein kinase K35; Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit CDK8; Mediator complex subunit CDK8; Cell division protein kinase 8 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CDC2/CDKX subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Mediator functions as a bridge to convey information from gene-specific regulatory proteins to the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Mediator is recruited to promoters by direct interactions with regulatory proteins and serves as a scaffold for the assembly of a functional preinitiation complex with RNA polymerase II and the general transcription factors. Phosphorylates the CTD (C-terminal domain) of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAp II), which may inhibit the formation of a transcription initiation complex. Phosphorylates CCNH leading to down-regulation of the TFIIH complex and transcriptional repression. Recruited through interaction with MAML1 to hyperphosphorylate the intracellular domain of NOTCH, leading to its degradation. Component of the Mediator complex, a coactivator involved in regulated gene transcription of nearly all RNA polymerase II-dependent genes. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder with hypotonia and behavioral abnormalities (IDDHBA) [MIM:618748]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder with onset in infancy. IDDHBA is characterized by hypotonia, global developmental delay, learning disability, and behavioral abnormalities, such as autistic features and attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Additional variable features may include non-specific facial dysmorphism, congenital heart defects, ocular anomalies, and poor feeding. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30905399}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03496 Interacts with P24863; Q01094; P02489; Q14204; Q92876 EC number EC 2.7.11.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Autism spectrum disorder; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Kinase; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repressor; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 37655.2 Length 321 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.04 Isoelectric point 8.56 Charge (pH=7) 5.13 3D Binding mode Sequence DKMDYDFKVKLSSERERVEDLFEYEGCKVGHVYKAKRKDGKDDKDYALKQIEGTGISMSACREIALLRELKHPNVISLQKVFLSHADRKVWLLFDYAEHDLWHIIKFHRASKLPRGMVKSLLYQILDGIHYLHANWVLHRDLKPANILVMGEGPERGRVKIADMGFARVTFWYRAPELLLGARHYTKAIDIWAIGCIFAELLTSEPIFHCRQNPYHHDQLDRIFNVMGFPADKDWEDIKKMPEHSTLMKDFRRNTYTNCSLIKYMEKHKVKPDSKAFHLLQKLLTMDPIKRITSEQAMQDPYFLEDPLPTSDVFAGCQIPY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 4 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 8 (CDK8) | 3RGF | 8.04 | |
Target general information Gen name CDK8 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein kinase K35; Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit CDK8; Mediator complex subunit CDK8; Cell division protein kinase 8 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CDC2/CDKX subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Mediator functions as a bridge to convey information from gene-specific regulatory proteins to the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Mediator is recruited to promoters by direct interactions with regulatory proteins and serves as a scaffold for the assembly of a functional preinitiation complex with RNA polymerase II and the general transcription factors. Phosphorylates the CTD (C-terminal domain) of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAp II), which may inhibit the formation of a transcription initiation complex. Phosphorylates CCNH leading to down-regulation of the TFIIH complex and transcriptional repression. Recruited through interaction with MAML1 to hyperphosphorylate the intracellular domain of NOTCH, leading to its degradation. Component of the Mediator complex, a coactivator involved in regulated gene transcription of nearly all RNA polymerase II-dependent genes. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder with hypotonia and behavioral abnormalities (IDDHBA) [MIM:618748]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder with onset in infancy. IDDHBA is characterized by hypotonia, global developmental delay, learning disability, and behavioral abnormalities, such as autistic features and attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Additional variable features may include non-specific facial dysmorphism, congenital heart defects, ocular anomalies, and poor feeding. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30905399}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03496 Interacts with P24863; Q01094; P02489; Q14204; Q92876 EC number EC 2.7.11.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Autism spectrum disorder; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Kinase; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repressor; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 37655.2 Length 321 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.04 Isoelectric point 8.56 Charge (pH=7) 5.13 3D Binding mode Sequence DKMDYDFKVKLSSERERVEDLFEYEGCKVGHVYKAKRKDGKDDKDYALKQIEGTGISMSACREIALLRELKHPNVISLQKVFLSHADRKVWLLFDYAEHDLWHIIKFHRASKLPRGMVKSLLYQILDGIHYLHANWVLHRDLKPANILVMGEGPERGRVKIADMGFARVTFWYRAPELLLGARHYTKAIDIWAIGCIFAELLTSEPIFHCRQNPYHHDQLDRIFNVMGFPADKDWEDIKKMPEHSTLMKDFRRNTYTNCSLIKYMEKHKVKPDSKAFHLLQKLLTMDPIKRITSEQAMQDPYFLEDPLPTSDVFAGCQIPY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 5 | Pseudomonas Transcriptional activator protein LasR (Pseudo LasR) | 3IX3 | 8.03 | |
Target general information Gen name Pseudo LasR Organism Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NA Protein family Autoinducer-regulated transcriptional regulatory protein family Biochemical class NA Function Transcriptional activator of elastase structural gene (LasB). Binds to the PAI autoinducer. Related diseases Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1A (IGHD1A) [MIM:262400]: An autosomal recessive, severe deficiency of growth hormone leading to dwarfism. Patients often develop antibodies to administered growth hormone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8364549}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1B (IGHD1B) [MIM:612781]: An autosomal recessive deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Patients have low but detectable levels of growth hormone, significantly retarded bone age, and a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655557}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Kowarski syndrome (KWKS) [MIM:262650]: A syndrome clinically characterized by short stature associated with bioinactive growth hormone, normal or slightly increased growth hormone secretion, pathologically low insulin-like growth factor 1 levels, and normal catch-up growth on growth hormone replacement therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17519310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8552145, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9276733}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 2 (IGHD2) [MIM:173100]: An autosomal dominant deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Clinical severity is variable. Patients have a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11502836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9152628}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08324 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; DNA-binding; Quorum sensing; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 18305.5 Length 163 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.52 Isoelectric point 5.19 Charge (pH=7) -6.78 3D Binding mode Sequence FLELERSSGKLEWSAILQKMASDLGFSKILFGLLPKDSQDYENAFIVGNYPAAWREHYDRAGYARVDPTVSHCTQSVLPIFWEPSIYQTRKQHEFFEEASAAGLVYGLTMPLHGARGELGALSLSVEAENRAEANRFMESVLPTLWMLKDYALQSGAGLAFEH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 6 | Pseudomonas Transcriptional activator protein LasR (Pseudo LasR) | 3IX3 | 8.03 | |
Target general information Gen name Pseudo LasR Organism Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NA Protein family Autoinducer-regulated transcriptional regulatory protein family Biochemical class NA Function Transcriptional activator of elastase structural gene (LasB). Binds to the PAI autoinducer. Related diseases Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1A (IGHD1A) [MIM:262400]: An autosomal recessive, severe deficiency of growth hormone leading to dwarfism. Patients often develop antibodies to administered growth hormone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8364549}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1B (IGHD1B) [MIM:612781]: An autosomal recessive deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Patients have low but detectable levels of growth hormone, significantly retarded bone age, and a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655557}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Kowarski syndrome (KWKS) [MIM:262650]: A syndrome clinically characterized by short stature associated with bioinactive growth hormone, normal or slightly increased growth hormone secretion, pathologically low insulin-like growth factor 1 levels, and normal catch-up growth on growth hormone replacement therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17519310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8552145, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9276733}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 2 (IGHD2) [MIM:173100]: An autosomal dominant deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Clinical severity is variable. Patients have a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11502836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9152628}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08324 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; DNA-binding; Quorum sensing; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 18305.5 Length 163 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.52 Isoelectric point 5.19 Charge (pH=7) -6.78 3D Binding mode Sequence FLELERSSGKLEWSAILQKMASDLGFSKILFGLLPKDSQDYENAFIVGNYPAAWREHYDRAGYARVDPTVSHCTQSVLPIFWEPSIYQTRKQHEFFEEASAAGLVYGLTMPLHGARGELGALSLSVEAENRAEANRFMESVLPTLWMLKDYALQSGAGLAFEH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 7 | Cyclopropane mycolic acid synthase MmaA2 | 1TPY | 8.02 | |
Target general information Gen name mmaA2 Organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms Rv0644c;mma2 Protein family CFA/CMAS family Biochemical class Transferase Function Cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase activity.Methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 16 (OZEMA16) [MIM:617234]: A rare cause of female primary infertility. In affected women, ovulation and fertilization proceed normally but embryos are arrested at early stages of development. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27545678}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01718; DB01752 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.79 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Methyltransferase; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32493.6 Length 285 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.61 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -10.17 3D Binding mode Sequence NDLTPHFEDVQAHYDLSDDFFRLFLDPTQTYSCAHFEREDMTLEEAQIAKIDLALGKLGLQPGMTLLDIGCGWGATMRRAIAQYDVNVVGLTLSKNQAAHVQKSFDEMDTPRDRRVLLAGWEQFNEPVDRIVSIGAFEHFGHDRHADFFARAHKILPPDGVLLLHTITGLTRQQMVDHGLPLTLWLARFLKFIATEIFPGGQPPTIEMVEEQSAKTGFTLTRRQSLQPHYARTLDLWAEALQEHKSEAIAIQSEEVYERYMKYLTGCAKLFRVGYIDVNQFTLAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 8 | Cyclopropane mycolic acid synthase MmaA2 | 1TPY | 8.02 | |
Target general information Gen name mmaA2 Organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms Rv0644c;mma2 Protein family CFA/CMAS family Biochemical class Transferase Function Cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase activity.Methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 16 (OZEMA16) [MIM:617234]: A rare cause of female primary infertility. In affected women, ovulation and fertilization proceed normally but embryos are arrested at early stages of development. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27545678}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01718; DB01752 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.79 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Methyltransferase; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32493.6 Length 285 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.61 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -10.17 3D Binding mode Sequence NDLTPHFEDVQAHYDLSDDFFRLFLDPTQTYSCAHFEREDMTLEEAQIAKIDLALGKLGLQPGMTLLDIGCGWGATMRRAIAQYDVNVVGLTLSKNQAAHVQKSFDEMDTPRDRRVLLAGWEQFNEPVDRIVSIGAFEHFGHDRHADFFARAHKILPPDGVLLLHTITGLTRQQMVDHGLPLTLWLARFLKFIATEIFPGGQPPTIEMVEEQSAKTGFTLTRRQSLQPHYARTLDLWAEALQEHKSEAIAIQSEEVYERYMKYLTGCAKLFRVGYIDVNQFTLAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 9 | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor (GPR119) | 7XZ6 | 8.00 | |
Target general information Gen name GPR119 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms GPR119; G-protein coupled receptor 119 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Receptor for the endogenous fatty-acid ethanolamide oleoylethanolamide (OEA) and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC). Functions as a glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylate cyclase. Seems to act through a G(s) mediated pathway. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 24 (DEE24) [MIM:615871]: A disease characterized by early-onset seizures, intellectual disability of varying degrees, and behavioral disturbances or autistic features in most individuals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24747641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27864847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 10 (GEFSP10) [MIM:618482]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder with incomplete penetrance, characterized by variable types of seizures including absence, tonic-clonic, febrile, focal, and eyelid myoclonia. Some patients have normal neurologic development. Others have mild-to-moderate intellectual disability or autism spectrum disorder. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29936235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05166 Interacts with Q12797-6 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; G-protein coupled receptor; Lipid-binding; Membrane; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 32134.1 Length 292 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 34.96 Isoelectric point 9.12 Charge (pH=7) 8.03 3D Binding mode Sequence MESSFSFGVILAVLASLIIATNTLVAVAVLLLIHKNDGVSLCFTLNLAVADTLIGVAISGLLTDQLSSPSRPTQKTLCSLRMAFVTSSAAASVLTVMLITFDRYLAIKQPFRYLKIMSGFVAGACIAGLWLVSYLIGFLPLGIPMFQQTAYKGQCSFFAVFHPHFVLTLSCVGFFPAMLLFVFFYCDMLKIASMHSQQIRKMEHAGAMAGSDFKALRTVSVLIGSFALSWTPFLITGIVQVACQECHLYLVLERYLWLLGVGNSLLNPLIYAYWQKEVRLQLYHMALGVKKV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 10 | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor (GPR119) | 7XZ6 | 8.00 | |
Target general information Gen name GPR119 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms GPR119; G-protein coupled receptor 119 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Receptor for the endogenous fatty-acid ethanolamide oleoylethanolamide (OEA) and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC). Functions as a glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylate cyclase. Seems to act through a G(s) mediated pathway. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 24 (DEE24) [MIM:615871]: A disease characterized by early-onset seizures, intellectual disability of varying degrees, and behavioral disturbances or autistic features in most individuals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24747641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27864847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 10 (GEFSP10) [MIM:618482]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder with incomplete penetrance, characterized by variable types of seizures including absence, tonic-clonic, febrile, focal, and eyelid myoclonia. Some patients have normal neurologic development. Others have mild-to-moderate intellectual disability or autism spectrum disorder. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29936235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05166 Interacts with Q12797-6 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; G-protein coupled receptor; Lipid-binding; Membrane; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 32134.1 Length 292 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 34.96 Isoelectric point 9.12 Charge (pH=7) 8.03 3D Binding mode Sequence MESSFSFGVILAVLASLIIATNTLVAVAVLLLIHKNDGVSLCFTLNLAVADTLIGVAISGLLTDQLSSPSRPTQKTLCSLRMAFVTSSAAASVLTVMLITFDRYLAIKQPFRYLKIMSGFVAGACIAGLWLVSYLIGFLPLGIPMFQQTAYKGQCSFFAVFHPHFVLTLSCVGFFPAMLLFVFFYCDMLKIASMHSQQIRKMEHAGAMAGSDFKALRTVSVLIGSFALSWTPFLITGIVQVACQECHLYLVLERYLWLLGVGNSLLNPLIYAYWQKEVRLQLYHMALGVKKV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 11 | Plasmodium Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (Malaria DHOdehase) | 1TV5 | 7.90 | |
Target general information Gen name Malaria DHOdehase Organism Plasmodium falciparum (isolate 3D7) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PFF0160c; Mitochondrially bound dihydroorotate-ubiqui oxidoreductase; Dihydroorotate oxidase of Plasmodium falciparum; Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase of Plasmodium falciparum; DHOdehase of Plasmodium fa Protein family Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase family, Type 2 subfamily Biochemical class CH-CH donor oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the conversion of dihydroorotate to orotate with quinone as electron acceptor. Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 33 (COXPD33) [MIM:617713]: An autosomal recessive disorder caused by multiple mitochondrial respiratory chain defects and impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism. Clinical manifestations are highly variable. Affected infants present with cardiomyopathy accompanied by multisystemic features involving liver, kidney, and brain. Death in infancy is observed in some patients. Children and adults present with myopathy and progressive external ophthalmoplegia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28942965}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01117 Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.3.5.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Flavoprotein; FMN; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Oxidoreductase; Pyrimidine biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Transit peptide; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 41846.8 Length 371 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.25 Isoelectric point 8.21 Charge (pH=7) 3.13 3D Binding mode Sequence FESYNPEFFLYDIFLKFCLKYIDGEICHDLFLLLGKYNILPYDTSNDSIYACTNIKHLDFINPFGVAAGFDKNGVCIDSILKLGFSFIEIGTITPRGQTGNAKPRIFRDVESRSIINSCGFNNMGCDKVTENLILFRKRQEEDKLLSKHIVGVSIGKNKDTVNIVDDLKYCINKIGRYADYIAINVSSPNTPGLRDNQEAGKLKNIILSVKEEIDNLEFLWFNTTKKKPLVFVKLAPDLNQEQKKEIADVLLETNIDGMIISNTTTQINDIKSFENKKGGVSGAKLKDISTKFICEMYNYTNKQIPIIASGGIFSGLDALEKIEAGASVCQLYSCLVFNGMKSAVQIKRELNHLLYQRGYYNLKEAIGRKH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 12 | Plasmodium Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (Malaria DHOdehase) | 1TV5 | 7.90 | |
Target general information Gen name Malaria DHOdehase Organism Plasmodium falciparum (isolate 3D7) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PFF0160c; Mitochondrially bound dihydroorotate-ubiqui oxidoreductase; Dihydroorotate oxidase of Plasmodium falciparum; Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase of Plasmodium falciparum; DHOdehase of Plasmodium fa Protein family Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase family, Type 2 subfamily Biochemical class CH-CH donor oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the conversion of dihydroorotate to orotate with quinone as electron acceptor. Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 33 (COXPD33) [MIM:617713]: An autosomal recessive disorder caused by multiple mitochondrial respiratory chain defects and impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism. Clinical manifestations are highly variable. Affected infants present with cardiomyopathy accompanied by multisystemic features involving liver, kidney, and brain. Death in infancy is observed in some patients. Children and adults present with myopathy and progressive external ophthalmoplegia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28942965}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01117 Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.3.5.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Flavoprotein; FMN; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Oxidoreductase; Pyrimidine biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Transit peptide; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 41846.8 Length 371 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.25 Isoelectric point 8.21 Charge (pH=7) 3.13 3D Binding mode Sequence FESYNPEFFLYDIFLKFCLKYIDGEICHDLFLLLGKYNILPYDTSNDSIYACTNIKHLDFINPFGVAAGFDKNGVCIDSILKLGFSFIEIGTITPRGQTGNAKPRIFRDVESRSIINSCGFNNMGCDKVTENLILFRKRQEEDKLLSKHIVGVSIGKNKDTVNIVDDLKYCINKIGRYADYIAINVSSPNTPGLRDNQEAGKLKNIILSVKEEIDNLEFLWFNTTKKKPLVFVKLAPDLNQEQKKEIADVLLETNIDGMIISNTTTQINDIKSFENKKGGVSGAKLKDISTKFICEMYNYTNKQIPIIASGGIFSGLDALEKIEAGASVCQLYSCLVFNGMKSAVQIKRELNHLLYQRGYYNLKEAIGRKH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 13 | Thiopurine S-methyltransferase | 2BZG | 7.89 | |
Target general information Gen name TPMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, TPMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Thiopurine S-methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 3 (CCDS3) [MIM:612718]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by developmental delay/regression, intellectual disability, severe disturbance of expressive and cognitive speech, and severe depletion of creatine/phosphocreatine in the brain. Most patients develop a myopathy characterized by muscle weakness and atrophy later in life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11555793, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20682460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22386973, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23660394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23770102, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26490222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27233232}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Fanconi renotubular syndrome 1 (FRTS1) [MIM:134600]: A form of Fanconi renotubular syndrome, a disease due to a generalized dysfunction of the proximal kidney tubule resulting in decreased solute and water reabsorption. Patients have polydipsia and polyuria with phosphaturia, glycosuria and aminoaciduria. They may develop hypophosphatemic rickets or osteomalacia, acidosis and a tendency toward dehydration. Some eventually develop renal insufficiency. FRTS1 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29654216}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00993; DB00436; DB01327; DB01033; DB01250; DB01021 Interacts with Q8TAP4-4; Q15047-2; P61981 EC number 2.1.1.67 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 25971.5 Length 229 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 32.58 Isoelectric point 6.74 Charge (pH=7) -0.6 3D Binding mode Sequence EVQKNQVLTLEEWQDKWVNGKTAFHQEQGHQLLKKHLDTFLKGKSGLRVFFPLCGKAVEXKWFADRGHSVVGVEISELGIQEFFTEQNLSYSEEPITEIPGTKVFKSSSGNISLYCCSIFDLPRTNIGKFDXIWDRGALVAINPGDRKCYADTXFSLLGKKFQYLLCVLSYDPTKHPGPPFYVPHAEIERLFGKICNIRCLEKVDAFEERHKSWGIDCLFEKLYLLTEK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 14 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (KDR) | 2XIR | 7.88 | |
Target general information Gen name KDR Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms VEGFR2; VEGFR-2; VEGF-2 receptor; Protein-tyrosine kinase receptor flk-1; Kinase insert domain receptor; Fetal liver kinase 1; FLK1; FLK-1; CD309 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Plays an essential role in the regulation of angiogenesis, vascular development, vascular permeability, and embryonic hematopoiesis. Promotes proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation of endothelial cells. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. Isoforms lacking a transmembrane domain, such as isoform 2 and isoform 3, may function as decoy receptors for VEGFA, VEGFC and/or VEGFD. Isoform 2 plays an important role as negative regulator of VEGFA- and VEGFC-mediated lymphangiogenesis by limiting the amount of free VEGFA and/or VEGFC and preventing their binding to FLT4. Modulates FLT1 and FLT4 signaling by forming heterodimers. Binding of vascular growth factors to isoform 1 leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the activation of protein kinase C. Mediates activation of MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Mediates phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and activation of PTK2/FAK1. Required for VEGFA-mediated induction of NOS2 and NOS3, leading to the production of the signaling molecule nitric oxide (NO) by endothelial cells. Phosphorylates PLCG1. Promotes phosphorylation of FYN, NCK1, NOS3, PIK3R1, PTK2/FAK1 and SRC. Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFC and VEGFD. Related diseases Hemangioma, capillary infantile (HCI) [MIM:602089]: A condition characterized by dull red, firm, dome-shaped hemangiomas, sharply demarcated from surrounding skin, usually presenting at birth or occurring within the first two or three months of life. They result from highly proliferative, localized growth of capillary endothelium and generally undergo regression and involution without scarring. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11807987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18931684}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Plays a major role in tumor angiogenesis. In case of HIV-1 infection, the interaction with extracellular viral Tat protein seems to enhance angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04727; DB07514; DB07528; DB06938; DB07326; DB06626; DB08875; DB04849; DB05198; DB12147; DB12307; DB12010; DB11679; DB06101; DB09078; DB06080; DB06595; DB07537; DB07183; DB07333; DB07334; DB07274; DB09079; DB08519; DB08042; DB16265; DB06589; DB05931; DB08901; DB15822; DB05984; DB05578; DB08896; DB14840; DB06436; DB00398; DB01268; DB05075; DB11800; DB04879; DB05146; DB05014 Interacts with P35916; O60565; P98160; PRO_0000391621 [P98160]; PRO_0000391622 [P98160]; P17301; P35968; P09382; P08581; P16333; O14786; O75340; P09619; P29350; Q12913; P12931; P15692; P15692-4; P49767; Q9MYV3-3 EC number EC 2.7.10.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Angiogenesis; ATP-binding; Cell junction; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Developmental protein; Differentiation; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Endosome; Glycoprotein; Host-virus interaction; Immunoglobulin domain; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33863.9 Length 296 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.01 Isoelectric point 8.5 Charge (pH=7) 4.59 3D Binding mode Sequence HCERLPYDASKWEFPRDRLKLGKPLGRGAFGQVIEADAFGIDKTATCRTVAVKMLKEGATHSEHRALMSELKILIHIGHHLNVVNLLGACTKPGGPLMVIVEFCKFGNLSTYLRSKRNEFVPYYKDFLTLEHLICYSFQVAKGMEFLASRKCIHRDLAARNILLSEKNVVKICDFGLARDIYKDPDYVRKGDARLPLKWMAPETIFDRVYTIQSDVWSFGVLLWEIFSLGASPYPGVKIDEEFCRRLKEGTRMRAPDYTTPEMYQTMLDCWHGEPSQRPTFSELVEHLGNLLQANA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 15 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (KDR) | 2XIR | 7.88 | |
Target general information Gen name KDR Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms VEGFR2; VEGFR-2; VEGF-2 receptor; Protein-tyrosine kinase receptor flk-1; Kinase insert domain receptor; Fetal liver kinase 1; FLK1; FLK-1; CD309 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Plays an essential role in the regulation of angiogenesis, vascular development, vascular permeability, and embryonic hematopoiesis. Promotes proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation of endothelial cells. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. Isoforms lacking a transmembrane domain, such as isoform 2 and isoform 3, may function as decoy receptors for VEGFA, VEGFC and/or VEGFD. Isoform 2 plays an important role as negative regulator of VEGFA- and VEGFC-mediated lymphangiogenesis by limiting the amount of free VEGFA and/or VEGFC and preventing their binding to FLT4. Modulates FLT1 and FLT4 signaling by forming heterodimers. Binding of vascular growth factors to isoform 1 leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the activation of protein kinase C. Mediates activation of MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Mediates phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and activation of PTK2/FAK1. Required for VEGFA-mediated induction of NOS2 and NOS3, leading to the production of the signaling molecule nitric oxide (NO) by endothelial cells. Phosphorylates PLCG1. Promotes phosphorylation of FYN, NCK1, NOS3, PIK3R1, PTK2/FAK1 and SRC. Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFC and VEGFD. Related diseases Hemangioma, capillary infantile (HCI) [MIM:602089]: A condition characterized by dull red, firm, dome-shaped hemangiomas, sharply demarcated from surrounding skin, usually presenting at birth or occurring within the first two or three months of life. They result from highly proliferative, localized growth of capillary endothelium and generally undergo regression and involution without scarring. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11807987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18931684}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Plays a major role in tumor angiogenesis. In case of HIV-1 infection, the interaction with extracellular viral Tat protein seems to enhance angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04727; DB07514; DB07528; DB06938; DB07326; DB06626; DB08875; DB04849; DB05198; DB12147; DB12307; DB12010; DB11679; DB06101; DB09078; DB06080; DB06595; DB07537; DB07183; DB07333; DB07334; DB07274; DB09079; DB08519; DB08042; DB16265; DB06589; DB05931; DB08901; DB15822; DB05984; DB05578; DB08896; DB14840; DB06436; DB00398; DB01268; DB05075; DB11800; DB04879; DB05146; DB05014 Interacts with P35916; O60565; P98160; PRO_0000391621 [P98160]; PRO_0000391622 [P98160]; P17301; P35968; P09382; P08581; P16333; O14786; O75340; P09619; P29350; Q12913; P12931; P15692; P15692-4; P49767; Q9MYV3-3 EC number EC 2.7.10.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Angiogenesis; ATP-binding; Cell junction; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Developmental protein; Differentiation; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Endosome; Glycoprotein; Host-virus interaction; Immunoglobulin domain; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33863.9 Length 296 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.01 Isoelectric point 8.5 Charge (pH=7) 4.59 3D Binding mode Sequence HCERLPYDASKWEFPRDRLKLGKPLGRGAFGQVIEADAFGIDKTATCRTVAVKMLKEGATHSEHRALMSELKILIHIGHHLNVVNLLGACTKPGGPLMVIVEFCKFGNLSTYLRSKRNEFVPYYKDFLTLEHLICYSFQVAKGMEFLASRKCIHRDLAARNILLSEKNVVKICDFGLARDIYKDPDYVRKGDARLPLKWMAPETIFDRVYTIQSDVWSFGVLLWEIFSLGASPYPGVKIDEEFCRRLKEGTRMRAPDYTTPEMYQTMLDCWHGEPSQRPTFSELVEHLGNLLQANA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 16 | Mutated Histone H3.3 (H3F3A) | 4GUS | 7.85 | |
Target general information Gen name H3F3A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PP781; Histone H3.3; H3F3; H3.3B; H3.3A Protein family Histone H3 family Biochemical class NA Function Variant histone H3 which replaces conventional H3 in a wide range of nucleosomes in active genes. Constitutes the predominant form of histone H3 in non-dividing cells and is incorporated into chromatin independently of DNA synthesis. Deposited at sites of nucleosomal displacement throughout transcribed genes, suggesting that it represents an epigenetic imprint of transcriptionally active chromatin. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. Related diseases Glioma (GLM) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539269}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. H3F3A mutations affecting residues involved in post-translational modifications of histone H3.3 are recurrent in malignant, aggressive gliomas including glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) (PubMed:22286061, PubMed:22286216). The mechanism through which mutations lead to tumorigenesis involves altered histones methylation, impaired regulation of Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) activity, and aberrant epigenetic regulation of gene expression (PubMed:23539183, PubMed:23539269, PubMed:23603901). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23603901}.; DISEASE: Bryant-Li-Bhoj neurodevelopmental syndrome 1 (BRYLIB1) [MIM:619720]: An autosomal dominant disorder predominantly characterized by global developmental delay, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and delayed motor milestones. Clinical manifestations are highly variable, including abnormal head shape, dysmorphic facial features, oculomotor abnormalities, feeding problems, and non-specific brain imaging abnormalities. Additional features may include hearing loss, seizures, short stature, and mild skeletal defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BRYLIB1 is caused by variants in H3-3A. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}.; DISEASE: Bryant-Li-Bhoj neurodevelopmental syndrome 2 (BRYLIB2) [MIM:619721]: An autosomal dominant disorder predominantly characterized by global developmental delay, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and delayed motor milestones. Clinical manifestations are highly variable, including abnormal head shape, dysmorphic facial features, oculomotor abnormalities, feeding problems, and non-specific brain imaging abnormalities. Additional features may include hearing loss, seizures, short stature, and mild skeletal defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BRYLIB2 is caused by variants in H3-3B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}.; DISEASE: H3F3A and H3F3B mutations affecting residues involved in post-translational modifications of histone H3.3 are implicated in the pathogenesis of some bone and cartilage neoplasms. Mutations have been found with high prevalence in chondroblastoma and giant cell tumors of bone, and with low frequency in osteosarcoma, conventional chondrosarcoma and clear cell chondrosarcoma. Chondroblastoma samples frequently carry a H3F3B mutation affecting residue Lys-37 (H3K36), although H3F3A is mutated in some cases. Most giant cell tumors of bone harbor H3F3A mutations affecting residue Gly-35 (H3G34). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24162739}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9NVP2; P45973; Q13111; Q9UER7; Q9UER7-1; Q9Y6K1; P62805; P49321-2; Q8IZL8; Q5VWG9; Q9VK33; Q8R5C8 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; ADP-ribosylation; Chromosome; Citrullination; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; DNA-binding; Hydroxylation; Intellectual disability; Lipoprotein; Methylation; Nucleosome core; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 86148.9 Length 766 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.57 Isoelectric point 8.25 Charge (pH=7) 7.16 3D Binding mode Sequence GSRKCEKAGCTATCPVCFASASERCAKNGYTSRWYHLSCGEHFCNECFDHYYRSHKDGYDKYTTWKKIWTSNGKTEPSPKAFMADQQLPYWVQCTKPECRKWRQLTKEIQLTPQIAKTYRCGMKPNTAIKPETSDHCSLPEDLRVLEVSNHWWYSMLILPPLLKDSVAAPLLSAYYPDCVGMSPSCTGMNRYFQPFYQPNECGKALCVRPDVMELDELYEFPEYSRDPTMYLALRNLILALWYTNCKEALTPQKCIPHIIVRGLVRIRCVQEVERILYFMTRKGLINTGVLSVGADQYLLPKDYHNKSVIIIGAGPAGLAAARQLHNFGIKVTVLEAKDRIGGRVWDDKSFKGVTVGRGAQIVNGCINNPVALMCEQLGISMHKFGERCDLIQEGGRITDPTIDKRMDFHFNALLDVVSEWRKDKTQLQDVPLGEKIEEIYKAFIKESGIQFSELEGQVLQFHLSNLEYACGSNLHQVSARSWDHNEFFAQFAGDHTLLTPGYSVIIEKLAEGLDIQLKSPVQCIDYSGDEVQVTTTDGTGYSAQKVLVTVPLALLQKGAIQFNPPLSEKKMKAINSLGAGIIEKIALQFPYRFWDSKVQGADFFGHVPPSASKRGLFAVFYDMDPQKKHSVLMSVIAGEAVASVRTLDDKQVLQQCMATLRELFKEQEVPDPTKYFVTRWSTDPWIQMAYSFVKTGGSGEAYDIIAEDIQGTVFFAGEATNRHFPQTVTGAYLSGVREASKIAAFARTMQTARKSTGGKAPRKQL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 17 | Mutated Histone H3.3 (H3F3A) | 4GUS | 7.85 | |
Target general information Gen name H3F3A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PP781; Histone H3.3; H3F3; H3.3B; H3.3A Protein family Histone H3 family Biochemical class NA Function Variant histone H3 which replaces conventional H3 in a wide range of nucleosomes in active genes. Constitutes the predominant form of histone H3 in non-dividing cells and is incorporated into chromatin independently of DNA synthesis. Deposited at sites of nucleosomal displacement throughout transcribed genes, suggesting that it represents an epigenetic imprint of transcriptionally active chromatin. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. Related diseases Glioma (GLM) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539269}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. H3F3A mutations affecting residues involved in post-translational modifications of histone H3.3 are recurrent in malignant, aggressive gliomas including glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) (PubMed:22286061, PubMed:22286216). The mechanism through which mutations lead to tumorigenesis involves altered histones methylation, impaired regulation of Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) activity, and aberrant epigenetic regulation of gene expression (PubMed:23539183, PubMed:23539269, PubMed:23603901). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23603901}.; DISEASE: Bryant-Li-Bhoj neurodevelopmental syndrome 1 (BRYLIB1) [MIM:619720]: An autosomal dominant disorder predominantly characterized by global developmental delay, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and delayed motor milestones. Clinical manifestations are highly variable, including abnormal head shape, dysmorphic facial features, oculomotor abnormalities, feeding problems, and non-specific brain imaging abnormalities. Additional features may include hearing loss, seizures, short stature, and mild skeletal defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BRYLIB1 is caused by variants in H3-3A. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}.; DISEASE: Bryant-Li-Bhoj neurodevelopmental syndrome 2 (BRYLIB2) [MIM:619721]: An autosomal dominant disorder predominantly characterized by global developmental delay, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and delayed motor milestones. Clinical manifestations are highly variable, including abnormal head shape, dysmorphic facial features, oculomotor abnormalities, feeding problems, and non-specific brain imaging abnormalities. Additional features may include hearing loss, seizures, short stature, and mild skeletal defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BRYLIB2 is caused by variants in H3-3B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}.; DISEASE: H3F3A and H3F3B mutations affecting residues involved in post-translational modifications of histone H3.3 are implicated in the pathogenesis of some bone and cartilage neoplasms. Mutations have been found with high prevalence in chondroblastoma and giant cell tumors of bone, and with low frequency in osteosarcoma, conventional chondrosarcoma and clear cell chondrosarcoma. Chondroblastoma samples frequently carry a H3F3B mutation affecting residue Lys-37 (H3K36), although H3F3A is mutated in some cases. Most giant cell tumors of bone harbor H3F3A mutations affecting residue Gly-35 (H3G34). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24162739}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9NVP2; P45973; Q13111; Q9UER7; Q9UER7-1; Q9Y6K1; P62805; P49321-2; Q8IZL8; Q5VWG9; Q9VK33; Q8R5C8 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; ADP-ribosylation; Chromosome; Citrullination; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; DNA-binding; Hydroxylation; Intellectual disability; Lipoprotein; Methylation; Nucleosome core; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 86148.9 Length 766 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.57 Isoelectric point 8.25 Charge (pH=7) 7.16 3D Binding mode Sequence GSRKCEKAGCTATCPVCFASASERCAKNGYTSRWYHLSCGEHFCNECFDHYYRSHKDGYDKYTTWKKIWTSNGKTEPSPKAFMADQQLPYWVQCTKPECRKWRQLTKEIQLTPQIAKTYRCGMKPNTAIKPETSDHCSLPEDLRVLEVSNHWWYSMLILPPLLKDSVAAPLLSAYYPDCVGMSPSCTGMNRYFQPFYQPNECGKALCVRPDVMELDELYEFPEYSRDPTMYLALRNLILALWYTNCKEALTPQKCIPHIIVRGLVRIRCVQEVERILYFMTRKGLINTGVLSVGADQYLLPKDYHNKSVIIIGAGPAGLAAARQLHNFGIKVTVLEAKDRIGGRVWDDKSFKGVTVGRGAQIVNGCINNPVALMCEQLGISMHKFGERCDLIQEGGRITDPTIDKRMDFHFNALLDVVSEWRKDKTQLQDVPLGEKIEEIYKAFIKESGIQFSELEGQVLQFHLSNLEYACGSNLHQVSARSWDHNEFFAQFAGDHTLLTPGYSVIIEKLAEGLDIQLKSPVQCIDYSGDEVQVTTTDGTGYSAQKVLVTVPLALLQKGAIQFNPPLSEKKMKAINSLGAGIIEKIALQFPYRFWDSKVQGADFFGHVPPSASKRGLFAVFYDMDPQKKHSVLMSVIAGEAVASVRTLDDKQVLQQCMATLRELFKEQEVPDPTKYFVTRWSTDPWIQMAYSFVKTGGSGEAYDIIAEDIQGTVFFAGEATNRHFPQTVTGAYLSGVREASKIAAFARTMQTARKSTGGKAPRKQL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 18 | Opioid receptor sigma 1 (OPRS1) | 5HK1 | 7.83 | |
Target general information Gen name SIGMAR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hSigmaR1; Sigma1R; Sigma1-receptor; Sigma non-opioid intracellular receptor 1; Sigma 1-type opioid receptor; SRBP; SR31747-binding protein; SR31747 binding protein 1; SR-BP; SIG-1R; Opioid receptor, s Protein family ERG2 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Involved in the regulation of different receptors it plays a role in BDNF signaling and EGF signaling. Also regulates ion channels like the potassium channel and could modulate neurotransmitter release. Plays a role in calcium signaling through modulation together with ANK2 of the ITP3R-dependent calcium efflux at the endoplasmic reticulum. Plays a role in several other cell functions including proliferation, survival and death. Originally identified for its ability to bind various psychoactive drugs it is involved in learning processes, memory and mood alteration. Necessary for proper mitochondrial axonal transport in motor neurons, in particular the retrograde movement of mitochondria. Plays a role in protecting cells against oxidative stress-induced cell death via its interaction with RNF112. Functions in lipid transport from the endoplasmic reticulum and is involved in a wide array of cellular functions probably through regulation of the biogenesis of lipid microdomains at the plasma membrane. Related diseases Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 16, juvenile (ALS16) [MIM:614373]: A neurodegenerative disorder affecting upper motor neurons in the brain and lower motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord, resulting in fatal paralysis. Sensory abnormalities are absent. The pathologic hallmarks of the disease include pallor of the corticospinal tract due to loss of motor neurons, presence of ubiquitin-positive inclusions within surviving motor neurons, and deposition of pathologic aggregates. The etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is likely to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. The disease is inherited in 5-10% of the cases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21842496}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Neuronopathy, distal hereditary motor, autosomal recessive 2 (HMNR2) [MIM:605726]: A form of distal hereditary motor neuronopathy, a heterogeneous group of neuromuscular disorders caused by selective degeneration of motor neurons in the anterior horn of the spinal cord, without sensory deficit in the posterior horn. The overall clinical picture consists of a classical distal muscular atrophy syndrome in the legs without clinical sensory loss. The disease starts with weakness and wasting of distal muscles of the anterior tibial and peroneal compartments of the legs. Later on, weakness and atrophy may expand to the proximal muscles of the lower limbs and/or to the distal upper limbs. HMNR2 is characterized by onset of distal muscle weakness and wasting affecting the lower and upper limbs in the first decade. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26078401, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27629094}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00321; DB09014; DB00907; DB00514; DB01488; DB00574; DB00502; DB00956; DB00704; DB00540; DB06174; DB00652; DB11186; DB03575; DB05316; DB01708; DB00409; DB01104 Interacts with Q92847-1; Q99720-1; O00213-2; P17612; P50454; P37173 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Cell junction; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Endoplasmic reticulum; Lipid droplet; Lipid transport; Membrane; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathy; Nucleus; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 20805.3 Length 185 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 31.72 Isoelectric point 5.44 Charge (pH=7) -6.63 3D Binding mode Sequence VFQREEIAQLARQYAGLDHELAFSRLIVELRRLHPGHVLPDEELQWVFVNAGGWMGAMCLLHASLSEYVLLFGTALGSRGHSGRYWAEISDTIISGTFHQWREGTTKSEVFYPGETVVHGPGEATAVEWGPNTWMVEYGRGVIPSTLAFALADTVFSTQDFLTLFYTLRSYARGLRLELTTYLFG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 19 | Monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) | 2V5Z | 7.83 | |
Target general information Gen name MAOB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms MAO-B; Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] B Protein family Flavin monoamine oxidase family Biochemical class CH-NH(2) donor oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the oxidative deamination of biogenic and xenobiotic amines and has important functions in the metabolism of neuroactive and vasoactive amines in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. MAOB preferentially degrades benzylamine and phenylethylamine. Related diseases Microvascular complications of diabetes 5 (MVCD5) [MIM:612633]: Pathological conditions that develop in numerous tissues and organs as a consequence of diabetes mellitus. They include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy leading to end-stage renal disease, and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic retinopathy remains the major cause of new-onset blindness among diabetic adults. It is characterized by vascular permeability and increased tissue ischemia and angiogenesis. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Homozygosity for the Leu-55 allele is strongly associated with the development of retinal disease in diabetic patients. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08176; DB02211; DB08516; DB08480; DB01472; DB04307; DB07512; DB07513; DB00915; DB00182; DB06698; DB04889; DB00215; DB09130; DB04147; DB00988; DB01363; DB00668; DB01175; DB02509; DB03147; DB14914; DB00614; DB04818; DB02095; DB01247; DB00601; DB01577; DB01442; DB01171; DB08082; DB02643; DB04677; DB03894; DB08804; DB04820; DB00184; DB04821; DB12612; DB01626; DB00780; DB00191; DB00388; DB01132; DB00721; DB01168; DB01367; DB09363; DB06654; DB01037; DB01104; DB14569; DB09042; DB00752; DB16446; DB09185; DB04832; DB00909 Interacts with P55212; P28329-3; Q8NI60; Q5RI15; Q92915-2; P22607; Q53GS7; P06396; P01112; O14901; P13473-2; P21397; Q9BVL2; O75400-2; P62826; Q6NTF9-3; Q9Y371; Q7Z699; Q9UMX0; Q9Y649 EC number EC 1.4.3.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion outer membrane; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 56019.9 Length 494 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 34.81 Isoelectric point 6.51 Charge (pH=7) -2.2 3D Binding mode Sequence NKCDVVVVGGGISGMAAAKLLHDSGLNVVVLEARDRVGGRTYTLRNQKVKYVDLGGSYVGPTQNRILRLAKELGLETYKVNEVERLIHHVKGKSYPFRGPFPPVWNPITYLDHNNFWRTMDDMGREIPSDAPWKAPLAEEWDNMTMKELLDKLCWTESAKQLATLFVNLCVTAETHEVSALWFLWYVKQCGGTTRIISTTNGGQERKFVGGSGQVSERIMDLLGDRVKLERPVIYIDQTRENVLVETLNHEMYEAKYVISAIPPTLGMKIHFNPPLPMMRNQMITRVPLGSVIKCIVYYKEPFWRKKDYCGTMIIDGEEAPVAYTLDDTKPEGNYAAIMGFILAHKARKLARLTKEERLKKLCELYAKVLGSLEALEPVHYEEKNWCEEQYSGGCYTTYFPPGILTQYGRVLRQPVDRIYFAGTETATHWSGYMEGAVEAGERAAREILHAMGKIPEDEIWQSEPESVDVPAQPITTTFLERHLPSVPGLLRLI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 20 | Opioid receptor sigma 1 (OPRS1) | 5HK1 | 7.83 | |
Target general information Gen name SIGMAR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hSigmaR1; Sigma1R; Sigma1-receptor; Sigma non-opioid intracellular receptor 1; Sigma 1-type opioid receptor; SRBP; SR31747-binding protein; SR31747 binding protein 1; SR-BP; SIG-1R; Opioid receptor, s Protein family ERG2 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Involved in the regulation of different receptors it plays a role in BDNF signaling and EGF signaling. Also regulates ion channels like the potassium channel and could modulate neurotransmitter release. Plays a role in calcium signaling through modulation together with ANK2 of the ITP3R-dependent calcium efflux at the endoplasmic reticulum. Plays a role in several other cell functions including proliferation, survival and death. Originally identified for its ability to bind various psychoactive drugs it is involved in learning processes, memory and mood alteration. Necessary for proper mitochondrial axonal transport in motor neurons, in particular the retrograde movement of mitochondria. Plays a role in protecting cells against oxidative stress-induced cell death via its interaction with RNF112. Functions in lipid transport from the endoplasmic reticulum and is involved in a wide array of cellular functions probably through regulation of the biogenesis of lipid microdomains at the plasma membrane. Related diseases Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 16, juvenile (ALS16) [MIM:614373]: A neurodegenerative disorder affecting upper motor neurons in the brain and lower motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord, resulting in fatal paralysis. Sensory abnormalities are absent. The pathologic hallmarks of the disease include pallor of the corticospinal tract due to loss of motor neurons, presence of ubiquitin-positive inclusions within surviving motor neurons, and deposition of pathologic aggregates. The etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is likely to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. The disease is inherited in 5-10% of the cases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21842496}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Neuronopathy, distal hereditary motor, autosomal recessive 2 (HMNR2) [MIM:605726]: A form of distal hereditary motor neuronopathy, a heterogeneous group of neuromuscular disorders caused by selective degeneration of motor neurons in the anterior horn of the spinal cord, without sensory deficit in the posterior horn. The overall clinical picture consists of a classical distal muscular atrophy syndrome in the legs without clinical sensory loss. The disease starts with weakness and wasting of distal muscles of the anterior tibial and peroneal compartments of the legs. Later on, weakness and atrophy may expand to the proximal muscles of the lower limbs and/or to the distal upper limbs. HMNR2 is characterized by onset of distal muscle weakness and wasting affecting the lower and upper limbs in the first decade. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26078401, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27629094}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00321; DB09014; DB00907; DB00514; DB01488; DB00574; DB00502; DB00956; DB00704; DB00540; DB06174; DB00652; DB11186; DB03575; DB05316; DB01708; DB00409; DB01104 Interacts with Q92847-1; Q99720-1; O00213-2; P17612; P50454; P37173 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Cell junction; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Endoplasmic reticulum; Lipid droplet; Lipid transport; Membrane; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathy; Nucleus; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 20805.3 Length 185 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 31.72 Isoelectric point 5.44 Charge (pH=7) -6.63 3D Binding mode Sequence VFQREEIAQLARQYAGLDHELAFSRLIVELRRLHPGHVLPDEELQWVFVNAGGWMGAMCLLHASLSEYVLLFGTALGSRGHSGRYWAEISDTIISGTFHQWREGTTKSEVFYPGETVVHGPGEATAVEWGPNTWMVEYGRGVIPSTLAFALADTVFSTQDFLTLFYTLRSYARGLRLELTTYLFG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||