Job Results:
Ligand
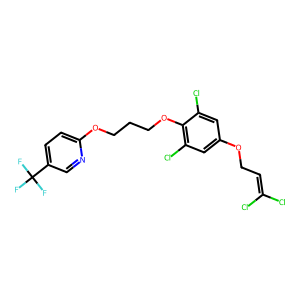
Structure
Job ID
eb2dc74daae6d1f1ffd56809732feeb9
Job name
chm
Time
2025-01-23 17:13:15
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aldose reductase (AKR1B1) | 1US0 | 7.62 | |
Target general information Gen name AKR1B1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Aldehyde reductase; AKR1B1 Protein family Aldo/keto reductase family Biochemical class Short-chain dehydrogenases reductase Function Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a wide variety of carbonyl-containing compounds to their corresponding alcohols with a broad range of catalytic efficiencies. Related diseases Glutamine deficiency, congenital (GLND) [MIM:610015]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by variable brain malformations, encephalopathy, severe developmental delay, seizures, and decreased glutamine levels in bodily fluids. Death in early infancy may occur. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16267323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26711351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 116 (DEE116) [MIM:620806]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE116 is autosomal dominant form characterized by severe developmental delay, seizures, and white matter abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. DEE116 is caused by variants that disrupt the canonical translation start codon in GLUL resulting in initiation of translation at Met-18 (PubMed:38579670). The resulting protein is enzymatically competent but insensitive to negative feedback regulation via glutamine-induced degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07028; DB07030; DB07450; DB02101; DB08449; DB08000; DB07139; DB07498; DB02007; DB02020; DB11859; DB02994; DB04272; DB07187; DB00694; DB00997; DB06246; DB01039; DB02021; DB16707; DB00143; DB02834; DB08084; DB01689; DB07063; DB06077; DB02518; DB00157; DB03461; DB05383; DB05533; DB05327; DB02712; DB00605; DB02383; DB02132; DB08772; DB07093; DB07999; DB08098 Interacts with Q9BUY7 EC number EC 1.1.1.300 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Lipid metabolism; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35447.6 Length 313 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 36.41 Isoelectric point 7.1 Charge (pH=7) 0.26 3D Binding mode Sequence MASRILLNNGAKMPILGLGTWKSPPGQVTEAVKVAIDVGYRHIDCAHVYQNENEVGVAIQEKLREQVVKREELFIVSKLWCTYHEKGLVKGACQKTLSDLKLDYLDLYLIHWPTGFKPGKEFFPLDESGNVVPSDTNILDTWAAMEELVDEGLVKAIGISNFNHLQVEMILNKPGLKYKPAVNQIECHPYLTQEKLIQYCQSKGIVVTAYSPLGSPDRPWAKPEDPSLLEDPRIKAIAAKHNKTTAQVLIRFPMQRNLVVIPKSVTPERIAENFKVFDFELSSQDMTTLLSYNRNWRVCALLSCTSHKDYPFH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 2 | Aldose reductase (AKR1B1) | 1US0 | 7.62 | |
Target general information Gen name AKR1B1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Aldehyde reductase; AKR1B1 Protein family Aldo/keto reductase family Biochemical class Short-chain dehydrogenases reductase Function Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a wide variety of carbonyl-containing compounds to their corresponding alcohols with a broad range of catalytic efficiencies. Related diseases Glutamine deficiency, congenital (GLND) [MIM:610015]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by variable brain malformations, encephalopathy, severe developmental delay, seizures, and decreased glutamine levels in bodily fluids. Death in early infancy may occur. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16267323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26711351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 116 (DEE116) [MIM:620806]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE116 is autosomal dominant form characterized by severe developmental delay, seizures, and white matter abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. DEE116 is caused by variants that disrupt the canonical translation start codon in GLUL resulting in initiation of translation at Met-18 (PubMed:38579670). The resulting protein is enzymatically competent but insensitive to negative feedback regulation via glutamine-induced degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07028; DB07030; DB07450; DB02101; DB08449; DB08000; DB07139; DB07498; DB02007; DB02020; DB11859; DB02994; DB04272; DB07187; DB00694; DB00997; DB06246; DB01039; DB02021; DB16707; DB00143; DB02834; DB08084; DB01689; DB07063; DB06077; DB02518; DB00157; DB03461; DB05383; DB05533; DB05327; DB02712; DB00605; DB02383; DB02132; DB08772; DB07093; DB07999; DB08098 Interacts with Q9BUY7 EC number EC 1.1.1.300 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Lipid metabolism; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35447.6 Length 313 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 36.41 Isoelectric point 7.1 Charge (pH=7) 0.26 3D Binding mode Sequence MASRILLNNGAKMPILGLGTWKSPPGQVTEAVKVAIDVGYRHIDCAHVYQNENEVGVAIQEKLREQVVKREELFIVSKLWCTYHEKGLVKGACQKTLSDLKLDYLDLYLIHWPTGFKPGKEFFPLDESGNVVPSDTNILDTWAAMEELVDEGLVKAIGISNFNHLQVEMILNKPGLKYKPAVNQIECHPYLTQEKLIQYCQSKGIVVTAYSPLGSPDRPWAKPEDPSLLEDPRIKAIAAKHNKTTAQVLIRFPMQRNLVVIPKSVTPERIAENFKVFDFELSSQDMTTLLSYNRNWRVCALLSCTSHKDYPFH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 3 | Aldose reductase (AKR1B1) | 1US0 | 7.62 | |
Target general information Gen name AKR1B1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Aldehyde reductase; AKR1B1 Protein family Aldo/keto reductase family Biochemical class Short-chain dehydrogenases reductase Function Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a wide variety of carbonyl-containing compounds to their corresponding alcohols with a broad range of catalytic efficiencies. Related diseases Glutamine deficiency, congenital (GLND) [MIM:610015]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by variable brain malformations, encephalopathy, severe developmental delay, seizures, and decreased glutamine levels in bodily fluids. Death in early infancy may occur. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16267323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26711351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 116 (DEE116) [MIM:620806]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE116 is autosomal dominant form characterized by severe developmental delay, seizures, and white matter abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. DEE116 is caused by variants that disrupt the canonical translation start codon in GLUL resulting in initiation of translation at Met-18 (PubMed:38579670). The resulting protein is enzymatically competent but insensitive to negative feedback regulation via glutamine-induced degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07028; DB07030; DB07450; DB02101; DB08449; DB08000; DB07139; DB07498; DB02007; DB02020; DB11859; DB02994; DB04272; DB07187; DB00694; DB00997; DB06246; DB01039; DB02021; DB16707; DB00143; DB02834; DB08084; DB01689; DB07063; DB06077; DB02518; DB00157; DB03461; DB05383; DB05533; DB05327; DB02712; DB00605; DB02383; DB02132; DB08772; DB07093; DB07999; DB08098 Interacts with Q9BUY7 EC number EC 1.1.1.300 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Lipid metabolism; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35447.6 Length 313 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 36.41 Isoelectric point 7.1 Charge (pH=7) 0.26 3D Binding mode Sequence MASRILLNNGAKMPILGLGTWKSPPGQVTEAVKVAIDVGYRHIDCAHVYQNENEVGVAIQEKLREQVVKREELFIVSKLWCTYHEKGLVKGACQKTLSDLKLDYLDLYLIHWPTGFKPGKEFFPLDESGNVVPSDTNILDTWAAMEELVDEGLVKAIGISNFNHLQVEMILNKPGLKYKPAVNQIECHPYLTQEKLIQYCQSKGIVVTAYSPLGSPDRPWAKPEDPSLLEDPRIKAIAAKHNKTTAQVLIRFPMQRNLVVIPKSVTPERIAENFKVFDFELSSQDMTTLLSYNRNWRVCALLSCTSHKDYPFH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 4 | Pseudomonas Transcriptional activator protein LasR (Pseudo LasR) | 3IX3 | 7.50 | |
Target general information Gen name Pseudo LasR Organism Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NA Protein family Autoinducer-regulated transcriptional regulatory protein family Biochemical class NA Function Transcriptional activator of elastase structural gene (LasB). Binds to the PAI autoinducer. Related diseases Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1A (IGHD1A) [MIM:262400]: An autosomal recessive, severe deficiency of growth hormone leading to dwarfism. Patients often develop antibodies to administered growth hormone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8364549}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1B (IGHD1B) [MIM:612781]: An autosomal recessive deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Patients have low but detectable levels of growth hormone, significantly retarded bone age, and a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655557}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Kowarski syndrome (KWKS) [MIM:262650]: A syndrome clinically characterized by short stature associated with bioinactive growth hormone, normal or slightly increased growth hormone secretion, pathologically low insulin-like growth factor 1 levels, and normal catch-up growth on growth hormone replacement therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17519310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8552145, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9276733}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 2 (IGHD2) [MIM:173100]: An autosomal dominant deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Clinical severity is variable. Patients have a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11502836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9152628}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08324 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; DNA-binding; Quorum sensing; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 18305.5 Length 163 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.52 Isoelectric point 5.19 Charge (pH=7) -6.78 3D Binding mode Sequence FLELERSSGKLEWSAILQKMASDLGFSKILFGLLPKDSQDYENAFIVGNYPAAWREHYDRAGYARVDPTVSHCTQSVLPIFWEPSIYQTRKQHEFFEEASAAGLVYGLTMPLHGARGELGALSLSVEAENRAEANRFMESVLPTLWMLKDYALQSGAGLAFEH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 5 | Pseudomonas Transcriptional activator protein LasR (Pseudo LasR) | 3IX3 | 7.50 | |
Target general information Gen name Pseudo LasR Organism Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NA Protein family Autoinducer-regulated transcriptional regulatory protein family Biochemical class NA Function Transcriptional activator of elastase structural gene (LasB). Binds to the PAI autoinducer. Related diseases Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1A (IGHD1A) [MIM:262400]: An autosomal recessive, severe deficiency of growth hormone leading to dwarfism. Patients often develop antibodies to administered growth hormone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8364549}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1B (IGHD1B) [MIM:612781]: An autosomal recessive deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Patients have low but detectable levels of growth hormone, significantly retarded bone age, and a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655557}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Kowarski syndrome (KWKS) [MIM:262650]: A syndrome clinically characterized by short stature associated with bioinactive growth hormone, normal or slightly increased growth hormone secretion, pathologically low insulin-like growth factor 1 levels, and normal catch-up growth on growth hormone replacement therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17519310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8552145, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9276733}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 2 (IGHD2) [MIM:173100]: An autosomal dominant deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Clinical severity is variable. Patients have a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11502836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9152628}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08324 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; DNA-binding; Quorum sensing; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 18305.5 Length 163 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.52 Isoelectric point 5.19 Charge (pH=7) -6.78 3D Binding mode Sequence FLELERSSGKLEWSAILQKMASDLGFSKILFGLLPKDSQDYENAFIVGNYPAAWREHYDRAGYARVDPTVSHCTQSVLPIFWEPSIYQTRKQHEFFEEASAAGLVYGLTMPLHGARGELGALSLSVEAENRAEANRFMESVLPTLWMLKDYALQSGAGLAFEH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 6 | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor (GPR119) | 7XZ6 | 7.48 | |
Target general information Gen name GPR119 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms GPR119; G-protein coupled receptor 119 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Receptor for the endogenous fatty-acid ethanolamide oleoylethanolamide (OEA) and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC). Functions as a glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylate cyclase. Seems to act through a G(s) mediated pathway. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 24 (DEE24) [MIM:615871]: A disease characterized by early-onset seizures, intellectual disability of varying degrees, and behavioral disturbances or autistic features in most individuals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24747641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27864847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 10 (GEFSP10) [MIM:618482]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder with incomplete penetrance, characterized by variable types of seizures including absence, tonic-clonic, febrile, focal, and eyelid myoclonia. Some patients have normal neurologic development. Others have mild-to-moderate intellectual disability or autism spectrum disorder. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29936235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05166 Interacts with Q12797-6 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; G-protein coupled receptor; Lipid-binding; Membrane; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 32134.1 Length 292 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 34.96 Isoelectric point 9.12 Charge (pH=7) 8.03 3D Binding mode Sequence MESSFSFGVILAVLASLIIATNTLVAVAVLLLIHKNDGVSLCFTLNLAVADTLIGVAISGLLTDQLSSPSRPTQKTLCSLRMAFVTSSAAASVLTVMLITFDRYLAIKQPFRYLKIMSGFVAGACIAGLWLVSYLIGFLPLGIPMFQQTAYKGQCSFFAVFHPHFVLTLSCVGFFPAMLLFVFFYCDMLKIASMHSQQIRKMEHAGAMAGSDFKALRTVSVLIGSFALSWTPFLITGIVQVACQECHLYLVLERYLWLLGVGNSLLNPLIYAYWQKEVRLQLYHMALGVKKV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 7 | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor (GPR119) | 7XZ6 | 7.48 | |
Target general information Gen name GPR119 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms GPR119; G-protein coupled receptor 119 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Receptor for the endogenous fatty-acid ethanolamide oleoylethanolamide (OEA) and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC). Functions as a glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylate cyclase. Seems to act through a G(s) mediated pathway. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 24 (DEE24) [MIM:615871]: A disease characterized by early-onset seizures, intellectual disability of varying degrees, and behavioral disturbances or autistic features in most individuals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24747641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27864847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 10 (GEFSP10) [MIM:618482]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder with incomplete penetrance, characterized by variable types of seizures including absence, tonic-clonic, febrile, focal, and eyelid myoclonia. Some patients have normal neurologic development. Others have mild-to-moderate intellectual disability or autism spectrum disorder. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29936235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05166 Interacts with Q12797-6 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; G-protein coupled receptor; Lipid-binding; Membrane; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 32134.1 Length 292 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 34.96 Isoelectric point 9.12 Charge (pH=7) 8.03 3D Binding mode Sequence MESSFSFGVILAVLASLIIATNTLVAVAVLLLIHKNDGVSLCFTLNLAVADTLIGVAISGLLTDQLSSPSRPTQKTLCSLRMAFVTSSAAASVLTVMLITFDRYLAIKQPFRYLKIMSGFVAGACIAGLWLVSYLIGFLPLGIPMFQQTAYKGQCSFFAVFHPHFVLTLSCVGFFPAMLLFVFFYCDMLKIASMHSQQIRKMEHAGAMAGSDFKALRTVSVLIGSFALSWTPFLITGIVQVACQECHLYLVLERYLWLLGVGNSLLNPLIYAYWQKEVRLQLYHMALGVKKV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 8 | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor (GPR119) | 7XZ6 | 7.48 | |
Target general information Gen name GPR119 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms GPR119; G-protein coupled receptor 119 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Receptor for the endogenous fatty-acid ethanolamide oleoylethanolamide (OEA) and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC). Functions as a glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylate cyclase. Seems to act through a G(s) mediated pathway. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 24 (DEE24) [MIM:615871]: A disease characterized by early-onset seizures, intellectual disability of varying degrees, and behavioral disturbances or autistic features in most individuals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24747641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27864847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 10 (GEFSP10) [MIM:618482]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder with incomplete penetrance, characterized by variable types of seizures including absence, tonic-clonic, febrile, focal, and eyelid myoclonia. Some patients have normal neurologic development. Others have mild-to-moderate intellectual disability or autism spectrum disorder. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29936235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05166 Interacts with Q12797-6 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; G-protein coupled receptor; Lipid-binding; Membrane; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 32134.1 Length 292 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 34.96 Isoelectric point 9.12 Charge (pH=7) 8.03 3D Binding mode Sequence MESSFSFGVILAVLASLIIATNTLVAVAVLLLIHKNDGVSLCFTLNLAVADTLIGVAISGLLTDQLSSPSRPTQKTLCSLRMAFVTSSAAASVLTVMLITFDRYLAIKQPFRYLKIMSGFVAGACIAGLWLVSYLIGFLPLGIPMFQQTAYKGQCSFFAVFHPHFVLTLSCVGFFPAMLLFVFFYCDMLKIASMHSQQIRKMEHAGAMAGSDFKALRTVSVLIGSFALSWTPFLITGIVQVACQECHLYLVLERYLWLLGVGNSLLNPLIYAYWQKEVRLQLYHMALGVKKV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 9 | Folate receptor beta (FOLR2) | 4KN0 | 7.43 | |
Target general information Gen name FOLR2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Placental folate-binding protein; Folate receptor, fetal/placental; Folate receptor type-beta; Folate receptor 2; FR-beta; FOLR2 Protein family Folate receptor family Biochemical class Folate receptor Function Binds to folate and reduced folic acid derivatives and mediates delivery of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and folate analogs into the interior of cells. Has high affinity for folate and folic acid analogs at neutral pH. Exposure to slightly acidic pH after receptor endocytosis triggers a conformation change that strongly reduces its affinity for folates and mediates their release. Related diseases Acute hepatic porphyria (AHEPP) [MIM:612740]: A form of porphyria. Porphyrias are inherited defects in the biosynthesis of heme, resulting in the accumulation and increased excretion of porphyrins or porphyrin precursors. They are classified as erythropoietic or hepatic, depending on whether the enzyme deficiency occurs in red blood cells or in the liver. AHP is characterized by attacks of gastrointestinal disturbances, abdominal colic, paralyses and peripheral neuropathy. Most attacks are precipitated by drugs, alcohol, caloric deprivation, infections, or endocrine factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10706561, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1309003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1569184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17236137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2063868}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00158; DB00563; DB05168 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Folate-binding; Glycoprotein; GPI-anchor; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23841.6 Length 205 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 56.78 Isoelectric point 7.92 Charge (pH=7) 2.58 3D Binding mode Sequence RTDLLNVCMDAKHHKTKPGPEDKLHDQCSPWKKNACCTASTSQELHKDTSRLYNFNWDHCGKMEPACKRHFIQDTCLYECSPNLGPWIQQVNQSWRKERFLDVPLCKEDCQRWWEDCHTSHTCKSNWHRGWDWTSGVNKCPAGALCRTFESYFPTPAALCEGLWSHSYKVSNYSRGSGRCIQMWFDSAQGNPNEEVARFYAAAMH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 10 | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | 2IIP | 7.43 | |
Target general information Gen name NNMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, NNMT/PNMT/TEMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase activity.Pyridine N-methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00627 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Citrullination; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 27886.8 Length 251 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.66 Isoelectric point 5.23 Charge (pH=7) -5.11 3D Binding mode Sequence GFTSKDTYLSHFNPRDYLEKYYSAESQILKHLLKNLFKIFCLDGVKGDLLIDIGSGPTIYQLLSACESFKEIVVTDYSDQNLQELEKWLKAAPAAFDWSPVVTYVCDLEGNRVKGPEKEEKLRQAVKQVLKCDVTQSQPLGAVPLPPADCVLSTLCLDAACPDLPTYCRALRNLGSLLKPGGFLVIMDALKSSYYMIGEQKFSSLPLGREAVEAAVKEAGYTIEWFEVISQSYSSTMANNEGLFSLVARKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 11 | Folate receptor beta (FOLR2) | 4KN0 | 7.43 | |
Target general information Gen name FOLR2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Placental folate-binding protein; Folate receptor, fetal/placental; Folate receptor type-beta; Folate receptor 2; FR-beta; FOLR2 Protein family Folate receptor family Biochemical class Folate receptor Function Binds to folate and reduced folic acid derivatives and mediates delivery of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and folate analogs into the interior of cells. Has high affinity for folate and folic acid analogs at neutral pH. Exposure to slightly acidic pH after receptor endocytosis triggers a conformation change that strongly reduces its affinity for folates and mediates their release. Related diseases Acute hepatic porphyria (AHEPP) [MIM:612740]: A form of porphyria. Porphyrias are inherited defects in the biosynthesis of heme, resulting in the accumulation and increased excretion of porphyrins or porphyrin precursors. They are classified as erythropoietic or hepatic, depending on whether the enzyme deficiency occurs in red blood cells or in the liver. AHP is characterized by attacks of gastrointestinal disturbances, abdominal colic, paralyses and peripheral neuropathy. Most attacks are precipitated by drugs, alcohol, caloric deprivation, infections, or endocrine factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10706561, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1309003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1569184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17236137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2063868}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00158; DB00563; DB05168 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Folate-binding; Glycoprotein; GPI-anchor; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23841.6 Length 205 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 56.78 Isoelectric point 7.92 Charge (pH=7) 2.58 3D Binding mode Sequence RTDLLNVCMDAKHHKTKPGPEDKLHDQCSPWKKNACCTASTSQELHKDTSRLYNFNWDHCGKMEPACKRHFIQDTCLYECSPNLGPWIQQVNQSWRKERFLDVPLCKEDCQRWWEDCHTSHTCKSNWHRGWDWTSGVNKCPAGALCRTFESYFPTPAALCEGLWSHSYKVSNYSRGSGRCIQMWFDSAQGNPNEEVARFYAAAMH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 12 | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | 2IIP | 7.43 | |
Target general information Gen name NNMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, NNMT/PNMT/TEMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase activity.Pyridine N-methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00627 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Citrullination; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 27886.8 Length 251 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.66 Isoelectric point 5.23 Charge (pH=7) -5.11 3D Binding mode Sequence GFTSKDTYLSHFNPRDYLEKYYSAESQILKHLLKNLFKIFCLDGVKGDLLIDIGSGPTIYQLLSACESFKEIVVTDYSDQNLQELEKWLKAAPAAFDWSPVVTYVCDLEGNRVKGPEKEEKLRQAVKQVLKCDVTQSQPLGAVPLPPADCVLSTLCLDAACPDLPTYCRALRNLGSLLKPGGFLVIMDALKSSYYMIGEQKFSSLPLGREAVEAAVKEAGYTIEWFEVISQSYSSTMANNEGLFSLVARKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 13 | Folate receptor beta (FOLR2) | 4KN0 | 7.43 | |
Target general information Gen name FOLR2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Placental folate-binding protein; Folate receptor, fetal/placental; Folate receptor type-beta; Folate receptor 2; FR-beta; FOLR2 Protein family Folate receptor family Biochemical class Folate receptor Function Binds to folate and reduced folic acid derivatives and mediates delivery of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and folate analogs into the interior of cells. Has high affinity for folate and folic acid analogs at neutral pH. Exposure to slightly acidic pH after receptor endocytosis triggers a conformation change that strongly reduces its affinity for folates and mediates their release. Related diseases Acute hepatic porphyria (AHEPP) [MIM:612740]: A form of porphyria. Porphyrias are inherited defects in the biosynthesis of heme, resulting in the accumulation and increased excretion of porphyrins or porphyrin precursors. They are classified as erythropoietic or hepatic, depending on whether the enzyme deficiency occurs in red blood cells or in the liver. AHP is characterized by attacks of gastrointestinal disturbances, abdominal colic, paralyses and peripheral neuropathy. Most attacks are precipitated by drugs, alcohol, caloric deprivation, infections, or endocrine factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10706561, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1309003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1569184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17236137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2063868}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00158; DB00563; DB05168 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Folate-binding; Glycoprotein; GPI-anchor; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23841.6 Length 205 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 56.78 Isoelectric point 7.92 Charge (pH=7) 2.58 3D Binding mode Sequence RTDLLNVCMDAKHHKTKPGPEDKLHDQCSPWKKNACCTASTSQELHKDTSRLYNFNWDHCGKMEPACKRHFIQDTCLYECSPNLGPWIQQVNQSWRKERFLDVPLCKEDCQRWWEDCHTSHTCKSNWHRGWDWTSGVNKCPAGALCRTFESYFPTPAALCEGLWSHSYKVSNYSRGSGRCIQMWFDSAQGNPNEEVARFYAAAMH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 14 | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | 2IIP | 7.43 | |
Target general information Gen name NNMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, NNMT/PNMT/TEMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase activity.Pyridine N-methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00627 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Citrullination; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 27886.8 Length 251 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.66 Isoelectric point 5.23 Charge (pH=7) -5.11 3D Binding mode Sequence GFTSKDTYLSHFNPRDYLEKYYSAESQILKHLLKNLFKIFCLDGVKGDLLIDIGSGPTIYQLLSACESFKEIVVTDYSDQNLQELEKWLKAAPAAFDWSPVVTYVCDLEGNRVKGPEKEEKLRQAVKQVLKCDVTQSQPLGAVPLPPADCVLSTLCLDAACPDLPTYCRALRNLGSLLKPGGFLVIMDALKSSYYMIGEQKFSSLPLGREAVEAAVKEAGYTIEWFEVISQSYSSTMANNEGLFSLVARKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 15 | Cyclopropane mycolic acid synthase MmaA2 | 1TPY | 7.42 | |
Target general information Gen name mmaA2 Organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms Rv0644c;mma2 Protein family CFA/CMAS family Biochemical class Transferase Function Cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase activity.Methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 16 (OZEMA16) [MIM:617234]: A rare cause of female primary infertility. In affected women, ovulation and fertilization proceed normally but embryos are arrested at early stages of development. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27545678}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01718; DB01752 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.79 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Methyltransferase; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32493.6 Length 285 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.61 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -10.17 3D Binding mode Sequence NDLTPHFEDVQAHYDLSDDFFRLFLDPTQTYSCAHFEREDMTLEEAQIAKIDLALGKLGLQPGMTLLDIGCGWGATMRRAIAQYDVNVVGLTLSKNQAAHVQKSFDEMDTPRDRRVLLAGWEQFNEPVDRIVSIGAFEHFGHDRHADFFARAHKILPPDGVLLLHTITGLTRQQMVDHGLPLTLWLARFLKFIATEIFPGGQPPTIEMVEEQSAKTGFTLTRRQSLQPHYARTLDLWAEALQEHKSEAIAIQSEEVYERYMKYLTGCAKLFRVGYIDVNQFTLAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 16 | Cyclopropane mycolic acid synthase MmaA2 | 1TPY | 7.42 | |
Target general information Gen name mmaA2 Organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms Rv0644c;mma2 Protein family CFA/CMAS family Biochemical class Transferase Function Cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase activity.Methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 16 (OZEMA16) [MIM:617234]: A rare cause of female primary infertility. In affected women, ovulation and fertilization proceed normally but embryos are arrested at early stages of development. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27545678}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01718; DB01752 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.79 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Methyltransferase; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32493.6 Length 285 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.61 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -10.17 3D Binding mode Sequence NDLTPHFEDVQAHYDLSDDFFRLFLDPTQTYSCAHFEREDMTLEEAQIAKIDLALGKLGLQPGMTLLDIGCGWGATMRRAIAQYDVNVVGLTLSKNQAAHVQKSFDEMDTPRDRRVLLAGWEQFNEPVDRIVSIGAFEHFGHDRHADFFARAHKILPPDGVLLLHTITGLTRQQMVDHGLPLTLWLARFLKFIATEIFPGGQPPTIEMVEEQSAKTGFTLTRRQSLQPHYARTLDLWAEALQEHKSEAIAIQSEEVYERYMKYLTGCAKLFRVGYIDVNQFTLAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 17 | Cyclopropane mycolic acid synthase MmaA2 | 1TPY | 7.42 | |
Target general information Gen name mmaA2 Organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms Rv0644c;mma2 Protein family CFA/CMAS family Biochemical class Transferase Function Cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase activity.Methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 16 (OZEMA16) [MIM:617234]: A rare cause of female primary infertility. In affected women, ovulation and fertilization proceed normally but embryos are arrested at early stages of development. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27545678}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01718; DB01752 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.79 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Methyltransferase; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32493.6 Length 285 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.61 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -10.17 3D Binding mode Sequence NDLTPHFEDVQAHYDLSDDFFRLFLDPTQTYSCAHFEREDMTLEEAQIAKIDLALGKLGLQPGMTLLDIGCGWGATMRRAIAQYDVNVVGLTLSKNQAAHVQKSFDEMDTPRDRRVLLAGWEQFNEPVDRIVSIGAFEHFGHDRHADFFARAHKILPPDGVLLLHTITGLTRQQMVDHGLPLTLWLARFLKFIATEIFPGGQPPTIEMVEEQSAKTGFTLTRRQSLQPHYARTLDLWAEALQEHKSEAIAIQSEEVYERYMKYLTGCAKLFRVGYIDVNQFTLAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 18 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 8 (DPP-8) | 6EOP | 7.39 | |
Target general information Gen name DPP8 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Prolyl dipeptidase DPP8; MSTP141; MSTP135; MSTP097; Dipeptidyl peptidase VIII; Dipeptidyl peptidase IV-related protein 1; DPRP1; DPRP-1; DPP VIII; DP8 Protein family Peptidase S9B family, DPPIV subfamily Biochemical class Peptidase Function Dipeptidyl peptidase that cleaves off N-terminal dipeptides from proteins having a Pro or Ala residue at position 2. Related diseases Orotic aciduria 1 (ORAC1) [MIM:258900]: A disorder of pyrimidine metabolism resulting in megaloblastic anemia and orotic acid crystalluria that is frequently associated with some degree of physical and intellectual disability. A minority of cases have additional features, particularly congenital malformations and immune deficiencies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9042911}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.4.14.5 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Aminopeptidase; Apoptosis; Cytoplasm; Hydrolase; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine protease Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,D Molecular weight (Da) 97764.9 Length 849 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 47.71 Isoelectric point 5.69 Charge (pH=7) -21.66 3D Binding mode Sequence LEPFYVERYSWSQLKKLLADTRKYHGYMMAKAPHDFMFVKRNDPDGPHSDRIYYLAMSNRENTLFYSEIPKTINRAAVLMLSWKPLLDLFQYSREEELLRERKRIGTVGIASYDYHQGSGTFLFQAGSGIYHVKDGGPQGFTQQPLRPNLVETSCPNIRMDPKLCPADPDWIAFIHSNDIWISNIVTREERRLTYVHNELANMEEDARSAGVATFVLQEEFDRYSGYWWCPKAETTPSGGKILRILYEENDESEVEIIHVTSPMLETRRADSFRYPKTGTANPKVTFKMSEIMIDAEGRIIDVIDKELIQPFEILFEGVEYIARAGWTPEGKYAWSILLDRSQTRLQIVLISPELFIPVEDDVMERQRLIESVPDSVTPLIIYEETTDIWINIHDIFHVFPQSHEEEIEFIFASECKTGFRHLYKITSILKESKYKRSSGGLPAPSDFKCPIKEEIAITSGEWEVLGRHGSNIQVDEVRRLVYFEGTKDSPLEHHLYVVSYVNPGEVTRLTDRGYSHSCCISQHCDFFISKYSNQKNPHCVSLYKLSSPEDDPTCKTKEFWATILDSAGPLPDYTPPEIFSFESTTGFTLYGMLYKPHDLQPGKKYPTVLFIYGGPQVQLVNNRFKGVKYFRLNTLASLGYVVVVIDNRGSXHRGLKFEGAFKYKMGQIEIDDQVEGLQYLASRYDFIDLDRVGIHGWSYGGYLSLMALMQRSDIFRVAIAGAPVTLWIFYDTGYTERYMGHPDQNEQGYYLGSVAMQAEKFPSEPNRLLLLHGFLDENVHFAHTSILLSFLVRAGKPYDLQIYPQERHSIRVPESGEHYELHLLHYLQENLGSRIAALKVSLRFLYEG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 19 | Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) | 2G72 | 7.39 | |
Target general information Gen name PNMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PNMTase; PENT; Noradrenaline N-methyltransferase Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, NNMT/PNMT/TEMT family Biochemical class NA Function Converts noradrenaline to adrenaline. Related diseases A chromosomal aberration involving TRIM24/TIF1 is found in papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs). Translocation t(7;10)(q32;q11) with RET. The translocation generates the TRIM24/RET (PTC6) oncogene. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10439047}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08129; DB08128; DB07739; DB07798; DB07747; DB03468; DB08550; DB03824; DB04273; DB07906; DB07597; DB09571; DB00968; DB08631; DB01752; DB08654 Interacts with Q9P2G9-2; Q8TBB1 EC number EC 2.1.1.28 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Catecholamine biosynthesis; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 29198.9 Length 264 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 54.33 Isoelectric point 5.91 Charge (pH=7) -3.69 3D Binding mode Sequence APGQAAVASAYQRFEPRAYLRNNYAPPRGDLCNPNGVGPWKLRCLAQTFATGEVSGRTLIDIGSGPTVYQLLSACSHFEDITMTDFLEVNRQELGRWLQEEPGAFNWSMYSQHACLIEGKGECWQDKERQLRARVKRVLPIDVHQPQPLGAGSPAPLPADALVSAFCLEAVSPDLASFQRALDHITTLLRPGGHLLLIGALEESWYLAGEARLTVVPVSEEEVREALVRSGYKVRDLRTYIMPAHLQTGVDDVKGVFFAWAQKV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 20 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 8 (DPP-8) | 6EOP | 7.39 | |
Target general information Gen name DPP8 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Prolyl dipeptidase DPP8; MSTP141; MSTP135; MSTP097; Dipeptidyl peptidase VIII; Dipeptidyl peptidase IV-related protein 1; DPRP1; DPRP-1; DPP VIII; DP8 Protein family Peptidase S9B family, DPPIV subfamily Biochemical class Peptidase Function Dipeptidyl peptidase that cleaves off N-terminal dipeptides from proteins having a Pro or Ala residue at position 2. Related diseases Orotic aciduria 1 (ORAC1) [MIM:258900]: A disorder of pyrimidine metabolism resulting in megaloblastic anemia and orotic acid crystalluria that is frequently associated with some degree of physical and intellectual disability. A minority of cases have additional features, particularly congenital malformations and immune deficiencies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9042911}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.4.14.5 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Aminopeptidase; Apoptosis; Cytoplasm; Hydrolase; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine protease Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,D Molecular weight (Da) 97764.9 Length 849 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 47.71 Isoelectric point 5.69 Charge (pH=7) -21.66 3D Binding mode Sequence LEPFYVERYSWSQLKKLLADTRKYHGYMMAKAPHDFMFVKRNDPDGPHSDRIYYLAMSNRENTLFYSEIPKTINRAAVLMLSWKPLLDLFQYSREEELLRERKRIGTVGIASYDYHQGSGTFLFQAGSGIYHVKDGGPQGFTQQPLRPNLVETSCPNIRMDPKLCPADPDWIAFIHSNDIWISNIVTREERRLTYVHNELANMEEDARSAGVATFVLQEEFDRYSGYWWCPKAETTPSGGKILRILYEENDESEVEIIHVTSPMLETRRADSFRYPKTGTANPKVTFKMSEIMIDAEGRIIDVIDKELIQPFEILFEGVEYIARAGWTPEGKYAWSILLDRSQTRLQIVLISPELFIPVEDDVMERQRLIESVPDSVTPLIIYEETTDIWINIHDIFHVFPQSHEEEIEFIFASECKTGFRHLYKITSILKESKYKRSSGGLPAPSDFKCPIKEEIAITSGEWEVLGRHGSNIQVDEVRRLVYFEGTKDSPLEHHLYVVSYVNPGEVTRLTDRGYSHSCCISQHCDFFISKYSNQKNPHCVSLYKLSSPEDDPTCKTKEFWATILDSAGPLPDYTPPEIFSFESTTGFTLYGMLYKPHDLQPGKKYPTVLFIYGGPQVQLVNNRFKGVKYFRLNTLASLGYVVVVIDNRGSXHRGLKFEGAFKYKMGQIEIDDQVEGLQYLASRYDFIDLDRVGIHGWSYGGYLSLMALMQRSDIFRVAIAGAPVTLWIFYDTGYTERYMGHPDQNEQGYYLGSVAMQAEKFPSEPNRLLLLHGFLDENVHFAHTSILLSFLVRAGKPYDLQIYPQERHSIRVPESGEHYELHLLHYLQENLGSRIAALKVSLRFLYEG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||