Job Results:
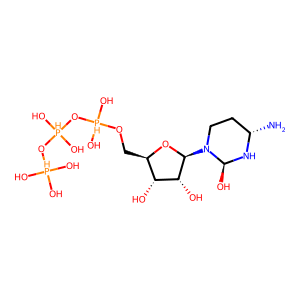
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
f782b8cc2ed803f5199da87783d483a3
Job name
Wilson_quest2
Time
2024-11-16 16:13:52
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dopamine beta-hydroxylase | 4ZEL | 6.56 | |
Target general information Gen name DBH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Copper type II ascorbate-dependent monooxygenase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Catalytic activity.Copper ion binding.Dopamine beta-monooxygenase activity.L-ascorbic acid binding. Related diseases Orthostatic hypotension 1 (ORTHYP1) [MIM:223360]: A form of orthostatic hypotension due to congenital dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a finding defined as a 20-mm Hg decrease in systolic pressure or a 10-mm Hg decrease in diastolic pressure occurring 3 minutes after a person has risen from supine to standing. Symptoms include dizziness, blurred vision, and sometimes syncope. ORTHYP1 is an autosomal recessive condition apparent from infancy or early childhood and characterized by low plasma and urinary levels of norepinephrine and epinephrine, and episodic hypoglycemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11857564}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00126; DB06774; DB09130; DB05394; DB00822; DB00988; DB00968; DB00550 Interacts with P00352; P63010-2; Q04656; Q8WUW1; Q9UNS2; Q71DI3; P61978; Q9Y2M5; Q92876; P08727; Q14693; P0DPK4; Q6GQQ9-2; P27986-2; Q9ULX5; Q96D59; Q8N6K7-2; Q9GZS3; Q8IUW3; Q86WT6-2 EC number 1.14.17.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Catecholamine biosynthesis; Copper; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal-anchor; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Vitamin C Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 123694 Length 1094 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 51.85 Isoelectric point 5.84 Charge (pH=7) -24.5 3D Binding mode Sequence PLPYHIPLDPEGSLELSWNVSYTQEAIHFQLLVRRLKAGVLFGMSDRGELENADLVVLWTDGDAYFADAWSDQKGQIHLDPQQDYQLLQVQRTPEGLTLLFKRPFGTCDPKDYLIEDGTVHLVYGILEEPFRSLEAINGSGLQMGLQRVQLLKPNIPEPELPSDACTMEVQAPNIQIPSQETTYWCYIKELPKGFSRHHIIKYEPIVTKGNEALVHHMEVFQCAPEMDSVPHFSGPCDSKMKPDRLNYCRHVLAAWALGAKAFYYPEEAGLAFGGPGSSRYLRLEVHYHNPLVIEGRNDSSGIRLYYTAKLRRFNAGIMELGLVYTPVMAIPPRETAFILTGYCTDKCTQLALPPSGIHIFASQLHTHLTGRKVVTVLVRDGREWEIVNQDNHYSPHFQEIRMLKKVVSVHPGDVLITSCTYNTEDRELATVGGFGILEEMCVNYVHYYPQTQLELCKSAVDAGFLQKYFHLINRFNNEDVCTCPQASVSQQFTSVPWNSFNRDVLKALYSFAPISMHCNKSSAVRFQGEWNLQPLPKVISTLEEPTVVSPLPYHIPLDPEGSLELSWNVSYTQEAIHFQLLVRRLKAGVLFGMSDRGELENADLVVLAYFADAWSDQKGQIHLDPQQDYQLLQVQRTPEGLTLLFKRPFGTCDPKDYLIEDGTVHLVYGILEEPFRSLEAINGSGLQMGLQRVQLLKPNIPEPELPSDACTMEVQAPNIQIPSQETTYWCYIKELPKGFSRHHIIKYEPIVTKGNEALVHHMEVFQCAPEVPHFSGPCDSKMLNYCRHVLAAWALGAKAFYYPEEAGLAFGGPGSSRYLRLEVHYHNPLVIEGRNDSSGIRLYYTAKLRRFNAGIMELGLVYTPVMAIPPRETAFILTGYCTDKCTQLALPPSGIHIFASQLHTHLTGRKVVTVLVRDGREWEIVNQDNHYSPHFQEIRMLKKVVSVHPGDVLITSCTYNTEDRELATVGGFGILEEMCVNYVHYYPQTQLELCKSAVDAGFLQKYFHLINRFNNEDVCTCPQASVSQQFTSVPWNSFNRDVLKALYSFAPISMHCNKSSAVRFQGEWNLQPLPKVISTLEEPTPQCVVSIGG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 2 | DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit A | 1ZVT | 6.49 | |
Target general information Gen name parC Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b3019;JW2987 Protein family Type II topoisomerase GyrA/ParC subunit family, ParC type 1 subfamily Biochemical class Isomerase Function ATP binding.DNA binding.DNA topoisomerase type II (ATP-hydrolyzing) activity. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB11943; DB12924; DB00817 Interacts with P22523; P0A7K2 EC number 5.6.2.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; DNA-binding; Isomerase; Membrane; Reference proteome; Topoisomerase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 26490.3 Length 246 Aromaticity 0.04 Instability index 46.03 Isoelectric point 8.94 Charge (pH=7) 2.83 3D Binding mode Sequence SEPVTIVLSQMGWVRSAKGHDIDAPGLNYKAGDSFKAAVKGKSNQPVVFVDSTGRSYAIDPITLPSARGQGEPLTGKLTLPPGATVDHMLMESDDQKLLMASDAGYGFVCTFNDLVARNRAGKALITLPENAHVMPPVVIEDASDMLLAITQAGRMLMFPVSDLPQLSKGKGNKIINIPSAEAARGEDGLAQLYVLPPQSTLTIHVGKRKIKLRPEELQKVTGERGRRGTLMRGLQRIDRVEIDSP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 3 | Platelet glycoprotein VI (GP6) | 5OU7 | 6.48 | |
Target general information Gen name GP6 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Glycoprotein 6; GPVI Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Collagen receptor involved in collagen-induced platelet adhesion and activation. Plays a key role in platelet procoagulant activity and subsequent thrombin and fibrin formation. This procoagulant function may contribute to arterial and venous thrombus formation. The signaling pathway involves the FcR gamma-chain, the Src kinases (likely FYN or LYN) and SYK, the adapter protein LAT and leads to the activation of PLCG2. Related diseases Bleeding disorder, platelet-type, 11 (BDPLT11) [MIM:614201]: A mild to moderate bleeding disorder caused by defective platelet activation and aggregation in response to collagen. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19549989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19552682}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P06241; P07948; P06241; P07948 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Blood coagulation; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hemostasis; Immunoglobulin domain; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 19027.4 Length 173 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.14 Isoelectric point 8.68 Charge (pH=7) 2.52 3D Binding mode Sequence SGPLPKPSLQALPSSLVPLEKPVTLRCQGPPGVDLYRLEKLSSSRYQDQAVLFIPAMKRSLAGRYRCSYQNGSLWSLPSDQLELVATGVFAKPSLSAQPGSGGDVTLQCQTRYGFDQFALYKEGDPERWYRASFPIITVTAAHSGTYRCYSFSSRDPYLWSAPSDPLELVVTG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 4 | Prothrombin | 4UD9 | 6.45 | |
Target general information Gen name F2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Peptidase S1 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Calcium ion binding.Growth factor activity.Heparin binding.Lipopolysaccharide binding.Receptor binding.Serine-type endopeptidase activity.Thrombospondin receptor activity. Related diseases Factor II deficiency (FA2D) [MIM:613679]: A very rare blood coagulation disorder characterized by mucocutaneous bleeding symptoms. The severity of the bleeding manifestations correlates with blood factor II levels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1349838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1354985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1421398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14962227, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2719946, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3242619, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3567158, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3771562, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3801671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:6405779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7792730, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7865694}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Ischemic stroke (ISCHSTR) [MIM:601367]: A stroke is an acute neurologic event leading to death of neural tissue of the brain and resulting in loss of motor, sensory and/or cognitive function. Ischemic strokes, resulting from vascular occlusion, is considered to be a highly complex disease consisting of a group of heterogeneous disorders with multiple genetic and environmental risk factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15534175}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thrombophilia due to thrombin defect (THPH1) [MIM:188050]: A multifactorial disorder of hemostasis characterized by abnormal platelet aggregation in response to various agents and recurrent thrombi formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2825773}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. A common genetic variation in the 3-prime untranslated region of the prothrombin gene is associated with elevated plasma prothrombin levels and an increased risk of venous thrombosis.; DISEASE: Pregnancy loss, recurrent, 2 (RPRGL2) [MIM:614390]: A common complication of pregnancy, resulting in spontaneous abortion before the fetus has reached viability. The term includes all miscarriages from the time of conception until 24 weeks of gestation. Recurrent pregnancy loss is defined as 3 or more consecutive spontaneous abortions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11506076}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07211; DB07796; DB07016; DB07521; DB06850; DB07091; DB06845; DB07088; DB07131; DB07095; DB07515; DB07897; DB06878; DB06947; DB08624; DB06869; DB06929; DB07400; DB04771; DB04772; DB02287; DB07277; DB07550; DB07549; DB07548; DB07105; DB04722; DB07366; DB08254; DB01725; DB08062; DB07639; DB07461; DB07120; DB07190; DB07741; DB07353; DB07508; DB07809; DB08546; DB08061; DB07718; DB03136; DB02723; DB07440; DB07376; DB06861; DB06866; DB06865; DB03865; DB06841; DB07934; DB08422; DB07659; DB07660; DB07658; DB13151; DB00025; DB11166; DB00278; DB01766; DB07083; DB00006; DB00100; DB13152; DB09228; DB09130; DB03159; DB06911; DB06996; DB06919; DB07027; DB07133; DB07143; DB07005; DB06695; DB00055; DB01225; DB05714; DB12831; DB03847; DB07278; DB01767; DB06404; DB09332; DB00001; DB13998; DB04136; DB00170; DB06838; DB13999; DB06868; DB06942; DB06936; DB07165; DB07527; DB07522; DB07665; DB07946; DB06859; DB06853; DB06858; DB07279; DB08187; DB04591; DB07944; DB07128; DB12598; DB01123; DB04786; DB05777; DB04697; DB09109; DB14738; DB04898; DB01593; DB14487; DB08152 Interacts with P05067; P07204; Q846V4; PRO_0000032489 [P01008] EC number 3.4.21.5 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acute phase; Blood coagulation; Calcium; Cleavage on pair of basic residues; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Gamma-carboxyglutamic acid; Glycoprotein; Hemostasis; Hydrolase; Kringle; Pharmaceutical; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Serine protease; Signal; Thrombophilia; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID H Molecular weight (Da) 29321.6 Length 254 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 39.57 Isoelectric point 8.56 Charge (pH=7) 4.16 3D Binding mode Sequence IVEGSDAEIGMSPWQVMLFRSPQELLCGASLISDRWVLTAAHCLLTENDLLVRIGKHSRTRYRNIEKISMLEKIYIHPRYNWENLDRDIALMKLKKPVAFSDYIHPVCLPDRETLLQAGYKGRVTGWGNLKETWGQPSVLQVVNLPIVERPVCKDSTRIRITDNMFCAYKKRGDACEGDSGGPFVMKSNNRWYQMGIVSWGEGCRDGKYGFYTHVFRLKKWIQKVIDQFGGDFEEIPEELQCGLRPLFEKKSLE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 5 | C1 esterase inhibitor (SERPING1) | 5DUQ | 6.43 | |
Target general information Gen name SERPING1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Serpin G1; SERPING1; Plasma protease C1 inhibitor; C1inhibiting factor; C1Inh; C1 Inh Protein family Serpin family Biochemical class Serpin protein Function Activation of the C1 complex is under control of the C1- inhibitor. It forms a proteolytically inactive stoichiometric complex with the C1r or C1s proteases. May play a potentially crucial role in regulating important physiological pathways including complement activation, blood coagulation, fibrinolysis and the generation of kinins. Very efficient inhibitor of FXIIa. Inhibits chymotrypsin and kallikrein. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8495195}. Related diseases Angioedema, hereditary, 1 (HAE1) [MIM:106100]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by episodic local swelling involving subcutaneous or submucous tissue of the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts, face, extremities, and genitalia. Hereditary angioedema due to C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency is comprised of two clinically indistinguishable forms. In hereditary angioedema type 1, serum levels of C1 esterase inhibitor are decreased, while in type 2, the levels are normal or elevated, but the protein is non-functional. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12773530, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1363816, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1451784, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14635117, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16409206, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2118657, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2296585, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22994404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2365061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24456027, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3178731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7814636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7883978, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8172583, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8529136, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8755917, ECO:0000269|Ref.41}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09130; DB05961 Interacts with P00736; P09871; O43889-2; O00187; P00750; A0A7D5SLD3; PRO_0000037310 [P0C6X7]; PRO_0000037320 [P0C6X7]; O82882; Q79GN7 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Blood coagulation; Complement pathway; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Fibrinolysis; Glycoprotein; Hemostasis; Immunity; Innate immunity; Protease inhibitor; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Serine protease inhibitor; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 40705.7 Length 362 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 29.5 Isoelectric point 7.75 Charge (pH=7) 1.26 3D Binding mode Sequence STEAVLGDALVDFSLKLYHAFSAMKKVETNMAFSPFSIASLLTQVLLGAGENTKTNLESILSYPKDFTCVHQALKGFTTKGVTSVSQIFHSPDLAIRDTFVNASRTLYSSSPRVLSNNSDANLELINTWVAKNTNNKISRLLDSLPSDTRLVLLNAIYLSAKWKTTFDPKKTRMEPFHFKNSVIKVPMMNSKKYPVAHFIDQTLKAKVGQLQLSHNLSLVILVPQNLKHRLEDMEQALSPSVFKAIMEKLEMSKFQPTLLTLPRIKVTTSQDMLSIMEKLEFFDFSYDLNLCGLTEDPDLQVSAMQHQTVLELTETGVEAAAASAISVARTLLVFEVQQPFLFMLWDQQHKFPVFMGRVYDP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 6 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase C | 2ESL | 6.42 | |
Target general information Gen name PPIC Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CYPC Protein family Cyclophilin-type PPIase family Biochemical class Isomerase / immunosuppressant Function Cyclosporin A binding.Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity. Related diseases Canavan disease (CAND) [MIM:271900]: A rare neurodegenerative condition of infancy or childhood characterized by white matter vacuolization and demyelination that gives rise to a spongy appearance. The clinical features are onset in early infancy, atonia of neck muscles, hypotonia, hyperextension of legs and flexion of arms, blindness, severe mental defect, megalocephaly, and death by 18 months on the average. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10407784, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10564886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10909858, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12205125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12638939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12706335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24036223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28101991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7599639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7668285, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8023850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8252036, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8659549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452117}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00172 Interacts with Q8N9N5; Q8N9N5-2; Q96L46; B3EWG5; O43765; Q96EQ0; Q9NZ09; Q9UMX0; Q9UMX0-2; Q9UHD9 EC number 5.2.1.8 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Isomerase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Rotamase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F Molecular weight (Da) 19625.2 Length 181 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 4.3 Isoelectric point 7.14 Charge (pH=7) 0.2 3D Binding mode Sequence RGPSVTAKVFFDVRIGDKDVGRIVIGLFGKVVPKTVENFVALATGEKGYGYKGSKFHRVIKDFMIQGGDITTGDGTGGVSIYGETFPDENFKLKHYGIGWVSMANAGPDTNGSQFFITLTKPTWLDGKHVVFGKVIDGMTVVHSIELQATDGHDRPLTNCSIINSGKIDVKTPFVVEIADW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 7 | Complement C1s component (C1S) | 1ELV | 6.42 | |
Target general information Gen name C1S Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Complement component 1 subcomponent s; Complement C1s subcomponent; C1-esterase; C1 esterase Protein family Peptidase S1 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function C1r activates C1s so that it can, in turn, activate C2 and C4. C1s B chain is a serine protease that combines with C1q and C1r to form C1, the first component of the classical pathway of the complement system. Related diseases Complement component C1s deficiency (C1SD) [MIM:613783]: A rare defect resulting in C1 deficiency and impaired activation of the complement classical pathway. C1 deficiency generally leads to severe immune complex disease with features of systemic lupus erythematosus and glomerulonephritis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11390518}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, periodontal type, 2 (EDSPD2) [MIM:617174]: A form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, a connective tissue disorder characterized by hyperextensible skin, atrophic cutaneous scars due to tissue fragility and joint hyperlaxity. EDSPD2 is characterized by the association of typical features of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with gingival recession and severe early-onset periodontal disease, leading to premature loss of permanent teeth. EDSPD2 transmission pattern is consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27745832}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02371; DB09228; DB09130; DB12831; DB06404; DB14996; DB01593; DB14487; DB14533; DB14548 Interacts with P00736; P09871; P06681; O43889-2; Q9H6H4; P05155 EC number EC 3.4.21.42 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Calcium; Complement pathway; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; EGF-like domain; Ehlers-Danlos syndrome; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Hydroxylation; Immunity; Innate immunity; Metal-binding; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Serine protease; Signal; Sushi Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33278.6 Length 303 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 33.69 Isoelectric point 5.16 Charge (pH=7) -7.95 3D Binding mode Sequence LDCGIPESIENGKVEDPESTLFGSVIRYTCEEPYYYMEGGGEYHCAGNGSWVNEVLGPELPKCVPVCGVPREPFIIGGSDADIKNFPWQVFFDNPWAGGALINEYWVLTAAHVVEGNREPTMYVGSTSVQKMLTPEHVFIHPGWKLLAVPEGRTNFDNDIALVRLKDPVKMGPTVSPICLPGTSSDYNLMDGDLGLISGWGRTEKRDRAVRLKAARLPVAPLRKCKEVAYVFTPNMICAGGEKGMDSCKGDSGGAFAVQDPNDKTKFYAAGLVSWGPQCGTYGLYTRVKNYVDWIMKTMQENS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 8 | Bacterial Elongation factor Tu (Bact EFTu) | 2HCJ | 6.40 | |
Target general information Gen name Bact EFTu Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms tufA; P43; Elongation factor Tu 1; EFTu 1 Protein family TRAFAC class translation factor GTPase superfamily, Classic translation factor GTPase family, EF-Tu/EF-1A subfamily Biochemical class GTP-binding elongation factor family Function May play an important regulatory rolein cell growth and in the bacterial response to nutrient deprivation. Related diseases Spermatogenic failure 21 (SPGF21) [MIM:617644]: An infertility disorder caused by spermatogenesis defects and characterized by acephalic spermatozoa in the semen of affected individuals. SPGF21 inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28199965}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P61517; P76251; P15038; P0A6Y5; P00956; P04951; P10441; P22634; P23909; P33590; P0A6Z6; P77756; P0AG30; P0ADX9; P0A6P1; P0A8J4; P63389; P39408; Q06259; P14647 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Antibiotic resistance; Cell inner membrane; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Elongation factor; GTP-binding; Membrane; Methylation; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Protein biosynthesis; Reference proteome; RNA-binding Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 40202.6 Length 368 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 26.38 Isoelectric point 5.26 Charge (pH=7) -14.58 3D Binding mode Sequence TKPHVNVGTIGHVDHGKTTLTAAITTVLAKTYGGITINTSHVEYDTPTRHYAHVDXPGHADYVKNMITGAAQMDGAILVVAATDGPMPQTREHILLGRQVGVPYIIVFLNKCDMVDDEELLELVEMEVRELLSQYDFPGDDTPIVRGSALKALEGDAEWEAKILELAGFLDSYIPEPERAIDKPFLLPIEDVFSISGRGTVVTGRVERGIIKVGEEVEIVGIKETQKSTCTGVEMFRKLLDEGRAGENVGVLLRGIKREEIERGQVLAKPGTIKPHTKFESEVYILSKDEGGRHTPFFKGYRPQFYFRTTDVTGTIELPEGVEMVMPGDNIKMVVTLIHPIAMDDGLRFAIREGGRTVGAGVVAKVLG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 9 | Prothrombin | 4UD9 | 6.40 | |
Target general information Gen name F2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Peptidase S1 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Calcium ion binding.Growth factor activity.Heparin binding.Lipopolysaccharide binding.Receptor binding.Serine-type endopeptidase activity.Thrombospondin receptor activity. Related diseases Factor II deficiency (FA2D) [MIM:613679]: A very rare blood coagulation disorder characterized by mucocutaneous bleeding symptoms. The severity of the bleeding manifestations correlates with blood factor II levels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1349838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1354985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1421398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14962227, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2719946, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3242619, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3567158, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3771562, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3801671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:6405779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7792730, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7865694}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Ischemic stroke (ISCHSTR) [MIM:601367]: A stroke is an acute neurologic event leading to death of neural tissue of the brain and resulting in loss of motor, sensory and/or cognitive function. Ischemic strokes, resulting from vascular occlusion, is considered to be a highly complex disease consisting of a group of heterogeneous disorders with multiple genetic and environmental risk factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15534175}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thrombophilia due to thrombin defect (THPH1) [MIM:188050]: A multifactorial disorder of hemostasis characterized by abnormal platelet aggregation in response to various agents and recurrent thrombi formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2825773}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. A common genetic variation in the 3-prime untranslated region of the prothrombin gene is associated with elevated plasma prothrombin levels and an increased risk of venous thrombosis.; DISEASE: Pregnancy loss, recurrent, 2 (RPRGL2) [MIM:614390]: A common complication of pregnancy, resulting in spontaneous abortion before the fetus has reached viability. The term includes all miscarriages from the time of conception until 24 weeks of gestation. Recurrent pregnancy loss is defined as 3 or more consecutive spontaneous abortions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11506076}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07211; DB07796; DB07016; DB07521; DB06850; DB07091; DB06845; DB07088; DB07131; DB07095; DB07515; DB07897; DB06878; DB06947; DB08624; DB06869; DB06929; DB07400; DB04771; DB04772; DB02287; DB07277; DB07550; DB07549; DB07548; DB07105; DB04722; DB07366; DB08254; DB01725; DB08062; DB07639; DB07461; DB07120; DB07190; DB07741; DB07353; DB07508; DB07809; DB08546; DB08061; DB07718; DB03136; DB02723; DB07440; DB07376; DB06861; DB06866; DB06865; DB03865; DB06841; DB07934; DB08422; DB07659; DB07660; DB07658; DB13151; DB00025; DB11166; DB00278; DB01766; DB07083; DB00006; DB00100; DB13152; DB09228; DB09130; DB03159; DB06911; DB06996; DB06919; DB07027; DB07133; DB07143; DB07005; DB06695; DB00055; DB01225; DB05714; DB12831; DB03847; DB07278; DB01767; DB06404; DB09332; DB00001; DB13998; DB04136; DB00170; DB06838; DB13999; DB06868; DB06942; DB06936; DB07165; DB07527; DB07522; DB07665; DB07946; DB06859; DB06853; DB06858; DB07279; DB08187; DB04591; DB07944; DB07128; DB12598; DB01123; DB04786; DB05777; DB04697; DB09109; DB14738; DB04898; DB01593; DB14487; DB08152 Interacts with P05067; P07204; Q846V4; PRO_0000032489 [P01008] EC number 3.4.21.5 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acute phase; Blood coagulation; Calcium; Cleavage on pair of basic residues; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Gamma-carboxyglutamic acid; Glycoprotein; Hemostasis; Hydrolase; Kringle; Pharmaceutical; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Serine protease; Signal; Thrombophilia; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID H Molecular weight (Da) 29321.6 Length 254 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 39.57 Isoelectric point 8.56 Charge (pH=7) 4.16 3D Binding mode Sequence IVEGSDAEIGMSPWQVMLFRSPQELLCGASLISDRWVLTAAHCLLTENDLLVRIGKHSRTRYRNIEKISMLEKIYIHPRYNWENLDRDIALMKLKKPVAFSDYIHPVCLPDRETLLQAGYKGRVTGWGNLKETWGQPSVLQVVNLPIVERPVCKDSTRIRITDNMFCAYKKRGDACEGDSGGPFVMKSNNRWYQMGIVSWGEGCRDGKYGFYTHVFRLKKWIQKVIDQFGGDFEEIPEELQCGLRPLFEKKSLE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 10 | DNA [cytosine-5]-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | 3EPZ | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name DNMT1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms MCMT; M.HsaI; Dnmt1; DNMT; DNA methyltransferase HsaI; DNA MTase HsaI; DNA (cytosine5)methyltransferase 1; DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1; CXXCtype zinc finger protein 9; CXXC9; CXXC-type zinc f Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, C5-methyltransferase family Biochemical class Methyltransferase Function Preferentially methylates hemimethylated DNA. Associates with DNA replication sites in S phase maintaining the methylation pattern in the newly synthesized strand, that is essential for epigenetic inheritance. Associates with chromatin during G2 and M phases to maintain DNA methylation independently of replication. It is responsible for maintaining methylation patterns established in development. DNA methylation is coordinated with methylation of histones. Mediates transcriptional repression by direct binding to HDAC2. In association with DNMT3B and via the recruitment of CTCFL/BORIS, involved in activation of BAG1 gene expression by modulating dimethylation of promoter histone H3 at H3K4 and H3K9. Probably forms a corepressor complex required for activated KRAS-mediated promoter hypermethylation and transcriptional silencing of tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) or other tumor-related genes in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. Also required to maintain a transcriptionally repressive state of genes in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells (ESCs). Associates at promoter regions of tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) leading to their gene silencing. Promotes tumor growth. Methylates CpG residues. Related diseases Neuropathy, hereditary sensory, 1E (HSN1E) [MIM:614116]: A neurodegenerative disorder characterized by adult onset of progressive peripheral sensory loss associated with progressive hearing impairment and early-onset dementia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21532572}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Cerebellar ataxia, deafness, and narcolepsy, autosomal dominant (ADCADN) [MIM:604121]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder characterized by adult onset of progressive cerebellar ataxia, narcolepsy, cataplexy, sensorineural deafness, and dementia. More variable features include optic atrophy, sensory neuropathy, psychosis, and depression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22328086}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00928; DB01262; DB12116; DB01099; DB05668; DB01035; DB00721 Interacts with P31749; P35222; Q96JK2; O75530; Q15910; Q96JM7; P48552; P09874; Q9NRD5; Q8WTS6; Q96EB6; Q96T88; P63104; Q77UV9; Q9QR71 EC number EC 2.1.1.37 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Activator; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Deafness; Disease variant; DNA-binding; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Methylation; Methyltransferase; Neuropathy; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Repressor; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 23471.3 Length 215 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 42.93 Isoelectric point 4.83 Charge (pH=7) -10.83 3D Binding mode Sequence GPKCIQCGQYLDDPDLKYGQHPPDAVDEPQALPQHKLTCFSVYCKHGHLCPIDTGLIEKNIELFFSGSAKPIGGVNGKNLGPINEWWITGGEKALIGFSTSFAEYILXDPSPEYAPIFGLXQEKIYISKIVVEFLQSNSDSTYEDLINKIETTVPPSGLNLNRFTEDSLLRHAQFVVEQVESYDEAGDQPIFLTPCXRDLIKLAGVTLGQRRAQA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 11 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase C | 2ESL | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name PPIC Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CYPC Protein family Cyclophilin-type PPIase family Biochemical class Isomerase / immunosuppressant Function Cyclosporin A binding.Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity. Related diseases Canavan disease (CAND) [MIM:271900]: A rare neurodegenerative condition of infancy or childhood characterized by white matter vacuolization and demyelination that gives rise to a spongy appearance. The clinical features are onset in early infancy, atonia of neck muscles, hypotonia, hyperextension of legs and flexion of arms, blindness, severe mental defect, megalocephaly, and death by 18 months on the average. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10407784, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10564886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10909858, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12205125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12638939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12706335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24036223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28101991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7599639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7668285, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8023850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8252036, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8659549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452117}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00172 Interacts with Q8N9N5; Q8N9N5-2; Q96L46; B3EWG5; O43765; Q96EQ0; Q9NZ09; Q9UMX0; Q9UMX0-2; Q9UHD9 EC number 5.2.1.8 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Isomerase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Rotamase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F Molecular weight (Da) 19625.2 Length 181 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 4.3 Isoelectric point 7.14 Charge (pH=7) 0.2 3D Binding mode Sequence RGPSVTAKVFFDVRIGDKDVGRIVIGLFGKVVPKTVENFVALATGEKGYGYKGSKFHRVIKDFMIQGGDITTGDGTGGVSIYGETFPDENFKLKHYGIGWVSMANAGPDTNGSQFFITLTKPTWLDGKHVVFGKVIDGMTVVHSIELQATDGHDRPLTNCSIINSGKIDVKTPFVVEIADW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 12 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase C | 2ESL | 6.38 | |
Target general information Gen name PPIC Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CYPC Protein family Cyclophilin-type PPIase family Biochemical class Isomerase / immunosuppressant Function Cyclosporin A binding.Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity. Related diseases Canavan disease (CAND) [MIM:271900]: A rare neurodegenerative condition of infancy or childhood characterized by white matter vacuolization and demyelination that gives rise to a spongy appearance. The clinical features are onset in early infancy, atonia of neck muscles, hypotonia, hyperextension of legs and flexion of arms, blindness, severe mental defect, megalocephaly, and death by 18 months on the average. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10407784, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10564886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10909858, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12205125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12638939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12706335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24036223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28101991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7599639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7668285, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8023850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8252036, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8659549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452117}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00172 Interacts with Q8N9N5; Q8N9N5-2; Q96L46; B3EWG5; O43765; Q96EQ0; Q9NZ09; Q9UMX0; Q9UMX0-2; Q9UHD9 EC number 5.2.1.8 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Isomerase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Rotamase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F Molecular weight (Da) 19625.2 Length 181 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 4.3 Isoelectric point 7.14 Charge (pH=7) 0.2 3D Binding mode Sequence RGPSVTAKVFFDVRIGDKDVGRIVIGLFGKVVPKTVENFVALATGEKGYGYKGSKFHRVIKDFMIQGGDITTGDGTGGVSIYGETFPDENFKLKHYGIGWVSMANAGPDTNGSQFFITLTKPTWLDGKHVVFGKVIDGMTVVHSIELQATDGHDRPLTNCSIINSGKIDVKTPFVVEIADW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 13 | Caspase-3 (CASP3) | 2XYG | 6.36 | |
Target general information Gen name CASP3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Yama protein; SREBP cleavage activity 1; SCA-1; Protein Yama; Cysteine protease CPP32; Caspase 3; CPP32; CPP-32; CASP-3; Apopain Protein family Peptidase C14A family Biochemical class Peptidase Function At the onset of apoptosis it proteolytically cleaves poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) at a '216-Asp-|-Gly-217' bond. Cleaves and activates sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) between the basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper domain and the membrane attachment domain. Cleaves and activates caspase-6, -7 and -9. Involved in the cleavage of huntingtin. Triggers cell adhesion in sympathetic neurons through RET cleavage. Involved in the activation cascade of caspases responsible for apoptosis execution. Related diseases Smith-Kingsmore syndrome (SKS) [MIM:616638]: An autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by intellectual disability, macrocephaly, seizures, umbilical hernia, and facial dysmorphic features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25851998, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26542245, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27830187}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Focal cortical dysplasia 2 (FCORD2) [MIM:607341]: A form of focal cortical dysplasia, a malformation of cortical development that results in medically refractory epilepsy in the pediatric population and in adults. FCORD2 is a severe form, with onset usually in childhood, characterized by disrupted cortical lamination and specific cytological abnormalities. It is classified in 2 subtypes: type IIA characterized by dysmorphic neurons and lack of balloon cells; type IIB with dysmorphic neurons and balloon cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25799227, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25878179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26018084, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27830187}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08498; DB08497; DB08213; DB06862; DB08251; DB03124; DB08229; DB00945; DB05408; DB13751; DB06255; DB07696; DB01017; DB08499; DB12843; DB13048; DB00282; DB12709 Interacts with O43823; Q9Y243; P05067; P54252; P55212; P55211; Q14203-5; P42858; Q00987; O60551; P09874; Q5JUK2; P10599; Q9BYP7; P98170 EC number EC 3.4.22.56 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Apoptosis; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Hydrolase; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation; Thiol protease; Ubl conjugation; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 27483.1 Length 239 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 38.09 Isoelectric point 8.39 Charge (pH=7) 3.03 3D Binding mode Sequence SGISLDNSYKMDYPEMGLCIIINNKNFHKSTGMTSRSGTDVDAANLRETFRNLKYEVRNKNDLTREEIVELMRDVSKEDHSKRSSFVCVLLSHGEEGIIFGTNGPVDLKKITNFFRGDRCRSLTGKPKLFIIQACRGTELDCGIETHKIPVEADFLYAYSTAPGYYSWRNSKDGSWFIQSLCAMLKQYADKLEFMHILTRVNRKVATEFESFSFDATFHAKKQIPCIVSMLTKELYFYH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 14 | Adrenergic receptor beta-2 (ADRB2) | 2RH1 | 6.34 | |
Target general information Gen name ADRB2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Beta-2 adrenoreceptor; Beta-2 adrenoceptor; Beta-2 adrenergic receptor; B2AR; ADRB2R Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, Adrenergic receptor subfamily, ADRB2 sub-subfamily Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function The beta-2-adrenergic receptor binds epinephrine with an approximately 30-fold greater affinity than it does norepinephrine. Beta-adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced activation of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. Related diseases Cortical dysplasia, complex, with other brain malformations 6 (CDCBM6) [MIM:615771]: A disorder of aberrant neuronal migration and disturbed axonal guidance. Affected individuals have microcephaly, ataxia, and severe delayed psychomotor development. Brain imaging shows variable malformations of cortical development, including white matter streaks, dysmorphic basal ganglia, corpus callosum abnormalities, brainstem and cerebellar hypoplasia, cortical dysplasia, polymicrogyria. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23246003}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Skin creases, congenital symmetric circumferential, 1 (CSCSC1) [MIM:156610]: An autosomal dominant disease characterized by multiple, symmetric, circumferential rings of folded skin, affecting primarily the limbs. Affected individuals also exhibit intellectual disability, cleft palate, and dysmorphic features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26637975}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07543; DB01193; DB00866; DB01118; DB00182; DB01102; DB01274; DB01238; DB09204; DB06216; DB00335; DB01408; DB05590; DB09013; DB00195; DB00217; DB01295; DB00612; DB00901; DB08807; DB06726; DB08808; DB00248; DB00521; DB01136; DB04846; DB01407; DB00785; DB01151; DB11273; DB13345; DB00449; DB11278; DB00841; DB09273; DB06262; DB01363; DB01364; DB00668; DB01049; DB11587; DB01288; DB00983; DB05039; DB00221; DB01064; DB00598; DB01210; DB13139; DB01365; DB13624; DB01214; DB00264; DB01203; DB05849; DB04861; DB00368; DB00540; DB00334; DB09080; DB00816; DB01580; DB00715; DB01359; DB00925; DB00397; DB00960; DB01291; DB01366; DB01182; DB00571; DB06814; DB00852; DB01917; DB11124; DB00867; DB01001; DB00938; DB00489; DB03566; DB00127; DB00871; DB00373; DB00726; DB12248; DB09082; DB09185 Interacts with P30542; P07550; P32121; Q96B67; Q9UII2; Q9ULD4-2; Q9NSI6-4; Q5M9N0-2; A0AVK6; Q658K8; O00472; Q15910-2; Q15486; P61978; Q5TCQ9; Q99685; O14745; Q9NR21-5; Q8WVD3; Q9H0X6; Q13573; P12931; Q5T0J7-2; Q8N0U2 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Endosome; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; Hydroxylation; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32266.1 Length 282 Aromaticity 0.15 Instability index 36.1 Isoelectric point 8.02 Charge (pH=7) 2.1 3D Binding mode Sequence DEVWVVGMGIVMSLIVLAIVFGNVLVITAIAKFERLQTVTNYFITSLACADLVMGLAVVPFGAAHILMKMWTFGNFWCEFWTSIDVLCVTASIETLCVIAVDRYFAITSPFKYQSLLTKNKARVIILMVWIVSGLTSFLPIQMHWYRATHQEAINCYAEETCCDFFTNQAYAIASSIVSFYVPLVIMVFVYSRVFQEAKRQLKFCLKEHKALKTLGIIMGTFTLCWLPFFIVNIVHVIQDNLIRKEVYILLNWIGYVNSGFNPLIYCRSPDFRIAFQELLCL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 15 | Retinal rod rhodopsin-sensitive cGMP 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit gamma | 3JWR | 6.32 | |
Target general information Gen name PDE6G Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms PDEG Protein family Rod/cone cGMP-PDE gamma subunit family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function 3',5'-cyclic-GMP phosphodiesterase activity.CGMP binding.Enzyme inhibitor activity.Spectrin binding. Related diseases Retinitis pigmentosa 57 (RP57) [MIM:613582]: A retinal dystrophy belonging to the group of pigmentary retinopathies. Retinitis pigmentosa is characterized by retinal pigment deposits visible on fundus examination and primary loss of rod photoreceptor cells followed by secondary loss of cone photoreceptors. Patients typically have night vision blindness and loss of midperipheral visual field. As their condition progresses, they lose their far peripheral visual field and eventually central vision as well. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20655036}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07954; DB00203; DB00820; DB00862 Interacts with O14503; Q96JM7; A0A6Q8PF08; O43741; Q8R511; P62994; Q9QY17; Q63787 EC number 3.1.4.35 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; cGMP; Hydrolase; Reference proteome; Retinitis pigmentosa; Sensory transduction; Vision Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C,D Molecular weight (Da) 40027.7 Length 345 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 37.44 Isoelectric point 6.02 Charge (pH=7) -6.88 3D Binding mode Sequence EAFNHLELHELAQYGIISHMEETRELQSLAAAVVPSAQTLKITDFSFSDFELSDLETALCTIRMFTDLNLVQNFQMKHEVLCRWILSVKKNYRKNVAYHNWRHAFNTAQCMFAALKAGKIQNKLTDLEILALLIAALSHDLDHRGVNNSYIQRSEHPLAQLYCHSIMEHHHFDQCLMILNSPGNQILSGLSIEEYKTTLKIIKQAILATDLALYIKRRGEFFELIRKNQFNLEDPHQKELFLAMLMTACDLSAITKPWPIQQRIAELVATEFWEQGDLERTVLQQQPIPMMDRNKRDELPKLQVGFIDFVCTQLYEALTHVSEDCFPLLDGCRKNRQKWQALAEQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 16 | Suppressor of tumorigenicity 14 protein (ST14) | 3P8G | 6.31 | |
Target general information Gen name ST14 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tumor-associated differentially-expressed gene 15 protein; Tumor associated differentially-expressed gene-15 protein; TADG15; Serine protease TADG-15; Serine protease 14; SNC19; Prostamin; PRSS14; Mem Protein family Peptidase S1 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Proposed to play a role in breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Exhibits trypsin-like activity as defined by cleavage of synthetic substrates with Arg or Lys as the P1 site. Involved in the terminal differentiation of keratinocytes through prostasin (PRSS8) activation and filaggrin (FLG) processing. Degrades extracellular matrix. Related diseases Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive 11 (ARCI11) [MIM:602400]: A form of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis, a disorder of keratinization with abnormal differentiation and desquamation of the epidermis, resulting in abnormal skin scaling over the whole body. The main skin phenotypes are lamellar ichthyosis (LI) and non-bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (NCIE), although phenotypic overlap within the same patient or among patients from the same family can occur. Lamellar ichthyosis is a condition often associated with an embedment in a collodion-like membrane at birth; skin scales later develop, covering the entire body surface. Non-bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma characterized by fine whitish scaling on an erythrodermal background; larger brownish scales are present on the buttocks, neck and legs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17273967, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18843291}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03127; DB13729; DB00013 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.4.21.109 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Hypotrichosis; Ichthyosis; Membrane; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Serine protease; Signal-anchor; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 26451.5 Length 241 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 30.45 Isoelectric point 5.6 Charge (pH=7) -5.69 3D Binding mode Sequence VVGGTDADEGEWPWQVSLHALGQGHICGASLISPNWLVSAAHCYIDDRGFRYSDPTQWTAFLGLHDQSQRSAPGVQERRLKRIISHPFFNDFTFDYDIALLELEKPAEYSSMVRPICLPDASHVFPAGKAIWVTGWGHTQYGGTGALILQKGEIRVIQQTTCENLLPQQITPRMMCVGFLSGGVDSCQGDSGGPLSSVEADGRIFQAGVVSWGDGCAQRNKPGVYTRLPLFRDWIKENTGV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 17 | Dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS) (EC 2.5.1.15) (Dihydropteroate pyrophosphorylase) | 4NIR | 6.26 | |
Target general information Gen name folP Organism Bacillus anthracis Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms GBAA_0071 Protein family DHPS family Biochemical class NA Function Catalyzes the condensation of para-aminobenzoate (pABA) with 6-hydroxymethyl-7,8-dihydropterin diphosphate (DHPt-PP) to form 7,8-dihydropteroate (H2Pte), the immediate precursor of folate derivatives. {ECO:0000256|RuleBase:RU361205}." Related diseases Pentosuria (PNTSU) [MIM:260800]: An inborn error of metabolism characterized by excessive urinary excretion of L-xylulose. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11882650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22042873, ECO:0000269|PubMed:4392213}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04047; DB03705; DB03592; DB04196 Interacts with NA EC number 2.5.1.15 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Folate biosynthesis; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 59575.9 Length 538 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 41.43 Isoelectric point 5.08 Charge (pH=7) -24.21 3D Binding mode Sequence MKWDYDLRCGEYTLNLNEKTLIMGILNVTPDSFSDGGSYNEVDAAVRHAKEMRDEGAHIIDIGGESTRPGFAKVSVEEEIKRVVPMIQAVSKEVKLPISIDTYKAEVAKQAIEAGAHIINDIWGAKAEPKIAEVAAHYDVPIILMHNRDNMNYRNLMADMIADLYDSIKIAKDAGVRDENIILDPGIGFAKTPEQNLEAMRNLEQLNVLGYPVLLGTSRKSFIGHVLDLPVEERLEGTGATVCLGIEKGCEFVRVHDVKEMSRMAKMMDAMIGKMKWDYDLRCGEYTLNLNEKTLIMGILNVTPSDGGSYNEVDAAVRHAKEMRDEGAHIIDIGGESVSVEEEIKRVVPMIQAVSKEVKLPISIDTYKAEVAKQAIEAGAHIINDIWGAKAEPKIAEVAAHYDVPIILMHNRDNMNYRNLADMIADLYDSIKIAKDAGVRDENIILDPGIGFAKTPEQNLEAMRNLEQLNVLGYPVLLGTSRKSFIGHVLDLPVEERLEGTGATVCLGIEKGCEFVRVHDVKEMSRMAKMMDAMIGKG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 18 | Pol polyprotein | 5KAO | 6.20 | |
Target general information Gen name pol Organism Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family NA Biochemical class Hydrolase / hydrolase inhibitor Function Aspartic-type endopeptidase activity. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 16 (OZEMA16) [MIM:617234]: A rare cause of female primary infertility. In affected women, ovulation and fertilization proceed normally but embryos are arrested at early stages of development. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27545678}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00701; DB01072; DB04887; DB01264; DB01319; DB00224; DB01601; DB00503; DB01232; DB00932 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Aspartyl protease; Hydrolase; Protease Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 21411 Length 198 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 42.78 Isoelectric point 9.45 Charge (pH=7) 4.15 3D Binding mode Sequence PQVTLWQRPLVTIKIGGQLKEALLDTGADDTVLEEMSLPGRWKPKMIGGIGGFIKVRQYDQILIEIAGHKAIGTVLVGPTPVNIIGRNLLTQIGATLNFPQVTLWQRPLVTIKIGGQLKEALLDTGADDTVLEEMSLPGRWKPKMIGGIGGFIKVRQYDQILIEIAGHKAIGTVLVGPTPVNIIGRNLLTQIGATLNF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 19 | Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase 1 (IMPDH1) | 1JCN | 6.20 | |
Target general information Gen name IMPDH1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Superoxide-inducible protein 12; SOI12; Probable inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase IMD1; NAD-dependent inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase; Inosine dehydrogenase; IMPDH-I; IMPDH 1; IMPDH; IMPD1; Protein family IMPDH/GMPR family Biochemical class CH-OH donor oxidoreductase Function Could also have a single-stranded nucleic acid-binding activity and could play a role in RNA and/or DNA metabolism. It may also have a role in the development of malignancy and the growth progression of some tumors. Catalyzes the conversion of inosine 5'-phosphate (IMP) to xanthosine 5'-phosphate (XMP), the first committed and rate-limiting step in the de novo synthesis of guanine nucleotides, and therefore plays an important role in the regulation of cell growth. Related diseases Retinitis pigmentosa 10 (RP10) [MIM:180105]: A retinal dystrophy belonging to the group of pigmentary retinopathies. Retinitis pigmentosa is characterized by retinal pigment deposits visible on fundus examination and primary loss of rod photoreceptor cells followed by secondary loss of cone photoreceptors. Patients typically have night vision blindness and loss of midperipheral visual field. As their condition progresses, they lose their far peripheral visual field and eventually central vision as well. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11875049, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11875050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16384941}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leber congenital amaurosis 11 (LCA11) [MIM:613837]: A severe dystrophy of the retina, typically becoming evident in the first years of life. Visual function is usually poor and often accompanied by nystagmus, sluggish or near-absent pupillary responses, photophobia, high hyperopia and keratoconus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16384941}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03948; DB00993; DB01033; DB00688; DB01024; DB00157; DB00811; DB06408; DB06103 Interacts with Q96D03; P20839-3; P12268; O75928-2; Q9Y4B4; P78317; Q7KZS0 EC number EC 1.1.1.205 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; CBS domain; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; DNA-binding; GMP biosynthesis; Leber congenital amaurosis; Metal-binding; Methylation; NAD; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Potassium; Proteomics identification; Purine biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Repeat; Retinitis pigmentosa; RNA-binding Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 42447.5 Length 395 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 33.17 Isoelectric point 5.61 Charge (pH=7) -6.1 3D Binding mode Sequence TGYVPEDGLTAQQLFASADDLTYNDFLILPGFIDFIADEVDLTSALTRKITLKTPLISSPMDTVTEADMAIAMALMGGIGFIHHNCTPEFQANEVRKVKNFEQGFITDPVVLSPGIPITEVGIVTSRDIDPRIELVVAPAGVTLKEANEILQRSKKGKLPIVNDCDELVRTDLKKNRDYPLASKDSQKQLLCGAAVGTREDDKYRLDLLTQAGVDVIVLDSSQGNSVYQIAMVHYIKQKYPHLQVIGGNVVTAAQAKNLIDAGVDGLRVGMGCGSICITQEVMACGRPQGTAVYKVAEYARRFGVPIIADGGIQTVGHVVKALALGASTVMMGSLLAATTEAPGEKGSIQKFVPYLIAGIQHGCQDIGARSLSVLRSMMYSGELKFEKRTMSAQI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 20 | Membrane-associated lectin type-C (CD209) | 2XR6 | 6.17 | |
Target general information Gen name CD209 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Surface C-type lectin DC-SIGN; Probable mannose-binding C-type lectin DC-SIGN; MDC-SIGN1A type I isoform; Dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing nonintegrin 1; Dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Pathogen-recognition receptor expressed on the surface of immature dendritic cells (DCs) and involved in initiation of primary immune response. Thought to mediate the endocytosis of pathogens which are subsequently degraded in lysosomal compartments. The receptor returns to the cell membrane surface and the pathogen-derived antigens are presented to resting T-cells via MHC class II proteins to initiate the adaptive immune response. Related diseases Olmsted syndrome 1 (OLMS1) [MIM:614594]: An autosomal dominant, rare congenital disorder characterized by bilateral mutilating palmoplantar keratoderma and periorificial keratotic plaques with severe itching at all lesions. Diffuse alopecia, constriction of digits, and onychodystrophy have also been reported. Infections and squamous cell carcinomas can arise on the keratotic areas. The digital constriction may progress to autoamputation of fingers and toes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22405088, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22835024}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Palmoplantar keratoderma, non-epidermolytic, focal 2 (FNEPPK2) [MIM:616400]: A dermatological disorder characterized by non-epidermolytic, abnormal thickening of the skin on the palms and soles. Focal palmoplantar keratoderma consists of localized areas of hyperkeratosis located mainly on pressure points and sites of recurrent friction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25285920}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q08AM6; P0DTC2; PRO_0000278734 [Q03463]; Q86V38; P55212; P02489; O75190-2; O14645; O75460-2; Q0VDC6; P54652; Q8IY31-3; O14901; P13473-2; Q9BVL2; A0A6Q8PF08; O75400-2; P62826; P50502; Q8IYN2; Q08AM6 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Cell adhesion; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Endocytosis; Glycoprotein; Host cell receptor for virus entry; Host-virus interaction; Immunity; Innate immunity; Lectin; Mannose-binding; Membrane; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal-anchor; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 14973.4 Length 130 Aromaticity 0.15 Instability index 44.12 Isoelectric point 4.91 Charge (pH=7) -3.99 3D Binding mode Sequence PCPWEWTFFQGNCYFMSNSQRNWHDSITACKEVGAQLVVIKSAEEQNFLQLQSSRSNRFTWMGLSDLNQEGTWQWVDGSPLLPSFKQYWNRGEPNNVGEEDCAEFSGNGWNDDKCNLAKFWICKKSAASS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||