Job Results:
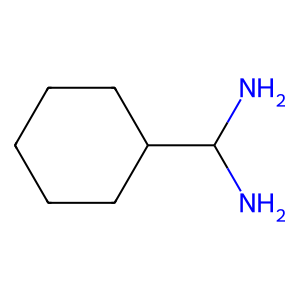
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
4bf9c02e58aa46f37e9fcadaa19f4c3b
Job name
White_task31
Time
2024-08-21 06:26:39
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mucin-1 (MUC1) | 6KX1 | 7.00 | |
Target general information Gen name MUC1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tumour-associated antigen mucin 1; Tumor-associated mucin; Tumor-associated epithelial membraneantigen; Tumor-associated epithelial membrane antigen; Polymorphic epithelial mucin; Peanut-reactive urin Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Can act both as an adhesion and an anti-adhesion protein. May provide a protective layer on epithelial cells against bacterial and enzyme attack. The alpha subunit has cell adhesive properties. Related diseases MUC1/CA 15-3 is used as a serological clinical marker of breast cancer to monitor response to breast cancer treatment and disease recurrence (PubMed:20816948). Decreased levels over time may be indicative of a positive response to treatment. Conversely, increased levels may indicate disease progression. At an early stage disease, only 21% of patients exhibit high MUC1/CA 15-3 levels, that is why CA 15-3 is not a useful screening test. Most antibodies target the highly immunodominant core peptide domain of 20 amino acid (APDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTS) tandem repeats. Some antibodies recognize glycosylated epitopes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20816948}.; DISEASE: Tubulointerstitial kidney disease, autosomal dominant, 2 (ADTKD2) [MIM:174000]: A form of autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease, a genetically heterogeneous disorder characterized by slowly progressive loss of kidney function, bland urinary sediment, hyperuricemia, absent or mildly increased albuminuria, lack of severe hypertension during the early stages, and normal or small kidneys on ultrasound. Renal histology shows variable abnormalities including interstitial fibrosis with tubular atrophy, microcystic dilatation of the tubules, thickening of tubular basement membranes, medullary cysts, and secondary glomerulosclerotic or glomerulocystic changes with abnormal glomerular tufting. There is significant variability, as well as incomplete penetrance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23396133}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB11090; DB06584 Interacts with P00519; P00533; P08581; P15941-7; Q08AM2; O60242; Q15848; Q86W74-2; P02652; P05067-2; P29972; P41181; Q92482; Q9H2C2; Q92843; Q6PL45-2; Q8WVV5; P06681; O14523; Q06432; Q9P0B6; Q08722-3; P19397; P34810; Q8N6F1-2; P56747; Q8NHS1; Q96FZ5; Q4VAQ0; Q8N6G5; Q07325; O43169; P78329; P56851; Q9BV81; P54852; O75355-2; Q9UKR5; P01350; P39905-3; Q9Y3E0; Q9NPR9; Q9HCP6; O60725; Q9Y5U4; P11215; Q969L2; Q13021; Q9P0N8; Q6N075; P30301; Q96S97; O95167; Q99519; Q92982; Q9NZG7; Q16617; Q8N912; Q8NH19; Q6TCH4; P26678; P60201-2; Q8IY26; P54315; Q59EV6; P30405; Q96AA3; Q02161-2; Q8TAC9; Q9Y6D0; Q8N6R1; P11686; Q8IWU4; Q969S0; Q6ICL7; Q9NVC3; Q9NRQ5; B2RUZ4; Q9NZ01; P07204; Q9BZW4; P17152; A0PK00; Q9BTD3; Q5BJH2-2; Q9BVK8; Q9Y6G1; Q9P0S9; Q14656; Q8NBD8; Q9BU79; Q8N2M4; Q8N661; Q5BJF2; Q9Y2Y6; O14763; Q8N609; Q5BVD1; Q53HI1; O95183; Q9BQB6; Q8IVQ6; P00519; P17676 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Autocatalytic cleavage; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Nucleus; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tumor suppressor Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B,C Molecular weight (Da) 25132.6 Length 230 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 44.8 Isoelectric point 7.12 Charge (pH=7) 0.18 3D Binding mode Sequence DVVMTQTPLSLPVSLGDQASISCRSSQSLVHSNGNTYLHWYLQKPGQSPKLLIYKVSNRFSGVPDRFSGSGSGTDFTLKISRVEAEDLGVYFCSQSTHVPPWTFGGGTKLEIKRADAAPTVSIFPPSSEQLTSGGASVVCFLNNFYPKDINVKWKIDGSERQNGVLNSWTDQDSKDSTYSMSSTLTLTKDEYERHNSYTCEATHKTSTSPIVKSFNRNEXVTSAPDTRPA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 2 | Oxygen-insensitive NADPH nitroreductase | 3QDL | 6.94 | |
Target general information Gen name rdxA Organism Helicobacter pylori (strain ATCC 700392 / 26695) (Campylobacter pylori) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms HP_0954 Protein family Nitroreductase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Oxidoreductase activity. Related diseases Hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia (HVLI) [MIM:618850]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by highly elevated plasma concentrations of valine and leucine/isoleucine. Affected individuals suffer from headache and mild memory impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. A patient with hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia was identified as compound heterozygote for Gln-170 (inherited from his father) and Lys-264 (inherited from his mother), both variants reduced the catalytic activity of the enzyme. After treatment with vitamin B6, a precursor of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, a BCAT2 cofactor, the blood levels of branched chain amino acids, especially valine, were decreased and brain lesions were improved. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00916 Interacts with NA EC number 1.-.-.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Antibiotic resistance; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 40094.3 Length 352 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 55.15 Isoelectric point 6.72 Charge (pH=7) -0.86 3D Binding mode Sequence MQRLESYILMKFLDQEKRRQLLNERHSCKMFDSHYEFSSTELEEIAEIARLSPSSYNTQPWHFVMVTDKDLKKQIAAHSYFNEEMIKSASALMVVCSLSYILEQCYIAVGQICMGVSLMGLDSCIIGGFDPLKVGEVLEERINPKIACLIALGKRVAEASQKSRKSKVDAITWLMKFLDQEKRRQLLNERHSCKMFDSHYEFSSTELEEIAEIARLSPSSYNTQPWHFVMVTDKDLKKQIAAHSYFNEEMIKSASALMVVCSLRPSELLPMQRLESYILEQCYIAVGQICMGVSLMGLDSCIIGGFDPLKVGEVLEERINKPKIACLIALGKRVAEASQKSRKSKVDAITWL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 3 | HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 2 (HPH-2) | 6ZBO | 6.90 | |
Target general information Gen name EGLN1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms SM-20; Prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein 2; PHD2; Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase 2; HPH-2; HIF-PH2; Egl nine homolog 1; C1orf12 Protein family NA Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Cellular oxygen sensor that catalyzes, under normoxic conditions, the post-translational formation of 4-hydroxyproline in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) alpha proteins. Hydroxylates a specific proline found in each of the oxygen-dependent degradation (ODD) domains (N-terminal, NODD, and C-terminal, CODD) of HIF1A. Also hydroxylates HIF2A. Has a preference for the CODD site for both HIF1A and HIF1B. Hydroxylated HIFs are then targeted for proteasomal degradation via the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitination complex. Under hypoxic conditions, the hydroxylation reaction is attenuated allowing HIFs to escape degradation resulting in their translocation to the nucleus, heterodimerization with HIF1B, and increased expression of hypoxy-inducible genes. EGLN1 is the most important isozyme under normoxia and, through regulating the stability of HIF1, involved in various hypoxia-influenced processes such as angiogenesis in retinal and cardiac functionality. Target proteins are preferentially recognized via a LXXLAP motif. Related diseases Erythrocytosis, familial, 3 (ECYT3) [MIM:609820]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by elevated serum hemoglobin and hematocrit, and normal serum erythropoietin levels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16407130, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17579185}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00126; DB11682; DB14490; DB14491; DB14488; DB14501; DB14489; DB08687; DB01592; DB07112; DB04847; DB12255 Interacts with Q99814; Q14318; Q16665; Q13438; PRO_0000037551 [Q9WMX2] EC number EC 1.14.11.29 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Congenital erythrocytosis; Cytoplasm; Dioxygenase; Disease variant; Iron; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation; Vitamin C; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,D Molecular weight (Da) 45717.8 Length 406 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 24.41 Isoelectric point 7.59 Charge (pH=7) 1.54 3D Binding mode Sequence LPALKLALEYIVPCMNKHGICVVDDFLGKETGQQIGDEVRALHDTGKFTGDKITWIEGKEPGCETIGLLMSSMDDLIRHCNGKLGSYKINGRTKAMVACYPGNGTGYVRHVDNPNGDGRCVTCIYYLNKDWDAKVSGGILRIFPEGKAQFADIEPKFDRLLFFWSDRRNPHEVQPAYATRYAITVWYFDADERARAKVKYLTGELPALKLALEYIVPCMNKHGICVVDDFLGKETGQQIGDEVRALHDTGKFTGDKITWIEGKEPGCETIGLLMSSMDDLIRHCNGKLGSYKINGRTKAMVACYPGNGTGYVRHVDNPNGDGRCVTCIYYLNKDWDAKVSGGILRIFPEGKAQFADIEPKFDRLLFFWSDRRNPHEVQPAYATRYAITVWYFDADERARAKVKYLT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 4 | Lysine-specific demethylase 4E (KDM4E) | 2W2I | 6.81 | |
Target general information Gen name KDM4E Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Lysine-specific demethylase 4D-like; KDM4DL; KDM4D-like protein Protein family JHDM3 histone demethylase family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Histone demethylase that specifically demethylates 'Lys-9' of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code. Related diseases Defects in KAT2B has been found in a patient with isolated coloboma, a defect of the eye characterized by the absence of ocular structures due to abnormal morphogenesis of the optic cup and stalk, and the fusion of the fetal fissure (optic fissure). Isolated colobomas may be associated with an abnormally small eye (microphthalmia) or small cornea. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28493397}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.14.11.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Chromatin regulator; Dioxygenase; Iron; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35131.5 Length 305 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 39.34 Isoelectric point 6 Charge (pH=7) -6.1 3D Binding mode Sequence HTIMTFYPTMEEFADFNTYVAYMESQGAHQAGLAKVIPPKEWKARQMYDDIEDILIATPLQQVTSGQGGVFTQYHKKKKAMRVGQYRRLANSKKYQTPPHQNFADLEQRYWKSHPGNPPIYGADISGSLFEESTKQWNLGHLGTILDLLEQECGVVIEGVNTPYLYFGMWKTTFAWHTEDMDLYSINYLHFGEPKTWYVVPPEHGQHLERLARELFPDISAFLRHKVALISPTVLKENGIPFNCMTQEAGEFMVTFPYGYHAGFNHGFNCAEAINFATPRWIDYGKMAVTFSMDPFVRIVQPESY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 5 | Organic cation transporter 3 (OCT3) | 7ZH6 | 6.80 | |
Target general information Gen name SLC22A3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Solute carrier family 22 member 3; Extraneuronal monoamine transporter; EMTH Protein family Major facilitator (TC 2.A.1) superfamily, Organic cation transporter (TC 2.A.1.19) family Biochemical class NA Function Mediates potential-dependent transport of a variety of organic cations. May play a significant role in the disposition of cationic neurotoxins and neurotransmitters in the brain. Related diseases Deafness, autosomal dominant, 2A (DFNA2A) [MIM:600101]: A form of non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss. Sensorineural deafness results from damage to the neural receptors of the inner ear, the nerve pathways to the brain, or the area of the brain that receives sound information. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10025409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10369879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10571947, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10925378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21242547}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00718; DB08838; DB00182; DB00122; DB14006; DB00501; DB00575; DB00363; DB01151; DB00988; DB00783; DB13952; DB13953; DB13954; DB13955; DB13956; DB00983; DB00536; DB05381; DB00458; DB00762; DB00709; DB00448; DB08882; DB01042; DB01577; DB00331; DB08893; DB00184; DB00368; DB00526; DB00925; DB00413; DB00457; DB01035; DB00396; DB00938; DB00391; DB13943; DB13944; DB08837; DB08841; DB00541 Interacts with P00519 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Glycoprotein; Ion transport; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 53067.4 Length 478 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 38.82 Isoelectric point 9.07 Charge (pH=7) 10.54 3D Binding mode Sequence SFDEALQRVGEFGRFQRRVFLLLCLTGVTFAFLFVGVVFLGTQPDHYWCRGPSAAALAERCGWSPEEEWNRTAPASRGRCQRYLLSAPLVPCRGGWRYAQAHSTIVSEFDLVCVNAWMLDLTQAILNLGFLTGAFTLGYAADRYGRIVIYLLSCLGVGVTGVVVAFAPNFPVFVIFRFLQGVFGKGTWMTCYVIVTEIVGSKQRRIVGIVIQMFFTLGIIILPGIAYFIPNWQGIQLAITLPSFLFLLYYWVVPESPRWLITRKKGDKALQILRRIAKCNVSNPSFLDLVRTPQMRKCTLILMFAWFTSAVVYQGLVMRLGNLYIDFFISGVVELPGALLILLTIERLGRRLPFAASNIVAGVACLVTAFLPEGIAWLRTTVATLGRLGITMAFEIVYLVNSELYPTTLRNFGVSLCSGLCDFGGIIAPFLLFRLAAVWLELPLIIFGILASICGGLVMLLPETKGIALPETVDDVEK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 6 | Carbonic anhydrase IV (CA-IV) | 3FW3 | 6.80 | |
Target general information Gen name CA4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Carbonic anhydrase 4; Carbonate dehydratase IV; CAIV Protein family Alpha-carbonic anhydrase family Biochemical class Alpha-carbonic anhydrase Function May stimulate the sodium/bicarbonate transporter activity of SLC4A4 that acts in pH homeostasis. It is essential for acid overload removal from the retina and retina epithelium, and acid release in the choriocapillaris in the choroid. Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. Related diseases Retinitis pigmentosa 17 (RP17) [MIM:600852]: A retinal dystrophy belonging to the group of pigmentary retinopathies. Retinitis pigmentosa is characterized by retinal pigment deposits visible on fundus examination and primary loss of rod photoreceptor cells followed by secondary loss of cone photoreceptors. Patients typically have night vision blindness and loss of midperipheral visual field. As their condition progresses, they lose their far peripheral visual field and eventually central vision as well. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15563508, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17652713, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20450258}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Defective acid overload removal from retina and retinal epithelium, due to mutant CA4, is responsible for photoreceptor degeneration, indicating that impaired pH homeostasis is the most likely cause underlying the RP17 phenotype. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00819; DB00436; DB00562; DB01194; DB00606; DB01144; DB00869; DB08846; DB00311; DB00774; DB00703; DB00232; DB09460; DB00273; DB01021; DB00909 Interacts with NA EC number EC 4.2.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; GPI-anchor; Lipoprotein; Lyase; Membrane; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Retinitis pigmentosa; Signal; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 27055.7 Length 235 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 44.3 Isoelectric point 6.87 Charge (pH=7) -0.36 3D Binding mode Sequence HWCYEVQLVPVKWGGNCQKDRQSPINIVTTKAKVDKKLGRFFFGYDKKQTWTVQNNGHSVMMLLENKASISGGGLPAPYQAKQLHLHWSDLPYKGSEHSLDGEHFAMEMHIVHEKEEIAVLAFLVEATQVNEGFQPLVEALSNIPKPEMSTTMAESSLLDLLPEEKRHYFRYLGSLTTPTCDEKVVWTVFREPIQLHREQILAFQKLYYDKEQTVSMKDNVRPLQQLGQRTVIKS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 7 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 (mGluR3) | 4XAR | 6.79 | |
Target general information Gen name GRM3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms mGLUR3; Group III metabotropic glutamate receptor; GPRC1C Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 3 family Biochemical class GPCR glutamate Function Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity. G-protein coupled receptor for glutamate. Related diseases Paramyotonia congenita (PMC) [MIM:168300]: An autosomal dominant channelopathy characterized by myotonia, increased by exposure to cold, intermittent flaccid paresis, not necessarily dependent on cold or myotonia, lability of serum potassium, non-progressive nature and lack of atrophy or hypertrophy of muscles. In some patients, myotonia is not increased by cold exposure (paramyotonia without cold paralysis). Patients may have a combination phenotype of PMC and HYPP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10369308, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10727489, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1310898, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1316765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1338909, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15318338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15790667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786525, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18166706, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18690054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19077043, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20076800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8242056, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8308722, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8388676, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8580427}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Periodic paralysis hypokalemic 2 (HOKPP2) [MIM:613345]: An autosomal dominant disorder manifested by episodic flaccid generalized muscle weakness associated with falls of serum potassium levels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10599760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10944223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11558801, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11591859, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16890191, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17898326, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18162704, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19118277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20522878, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21043388, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24549961}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Periodic paralysis hyperkalemic (HYPP) [MIM:170500]: An autosomal dominant channelopathy characterized by episodic flaccid generalized muscle weakness associated with high levels of serum potassium. Concurrence of myotonia is found in HYPP patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1659668, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1659948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20076800}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Periodic paralysis normokalemic (NKPP) [MIM:170500]: A disorder closely related to hyperkalemic periodic paralysis, but marked by a lack of alterations in potassium levels during attacks of muscle weakness. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15596759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18046642, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20522878}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Myotonia SCN4A-related (MYOSCN4A) [MIM:608390]: A phenotypically highly variable myotonia aggravated by potassium loading, and sometimes by cold. Myotonia is characterized by sustained muscle tensing that prevents muscles from relaxing normally. It causes muscle stiffness that can interfere with movement. In some people the stiffness is very mild, while in other cases it may be severe enough to interfere with walking, running, and other activities of daily life. Myotonia SCN4A-related includes myotonia permanens and myotonia fluctuans. In myotonia permanens, the myotonia is generalized and there is a hypertrophy of the muscle, particularly in the neck and the shoulder. Attacks of severe muscle stiffness of the thoracic muscles may be life threatening due to impaired ventilation. In myotonia fluctuans, the muscle stiffness may fluctuate from day to day, provoked by exercise. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10218481, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786525, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16832098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17212350, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17998485, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18203179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18337100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19015483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19347921, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20076800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27653901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8058156, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9392583}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 16 (CMS16) [MIM:614198]: A form of congenital myasthenic syndrome, a group of disorders characterized by failure of neuromuscular transmission, including pre-synaptic, synaptic, and post-synaptic disorders that are not of autoimmune origin. Clinical features are easy fatigability and muscle weakness. CMS16 is characterized by fatigable generalized weakness and recurrent attacks of respiratory and bulbar paralysis since birth. The fatigable weakness involves lid-elevator, external ocular, facial, limb and truncal muscles and an decremental response of the compound muscle action potential on repetitive stimulation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12766226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25707578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26659129}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Congenital myopathy 22A, classic (CMYO22A) [MIM:620351]: A form of congenital myopathy, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of muscle disorders characterized by hypotonia and muscle weakness apparent at birth, and specific pathological features on muscle biopsy. CMYO22A is an autosomal recessive form characterized by fetal hypokinesia, polyhydramnios, and severe neonatal hypotonia associated with respiratory insufficiency. Affected individuals who survive the neonatal period have delayed motor development, difficulty walking, proximal muscle weakness of the upper and lower limbs, facial and neck muscle weakness, easy fatigability, and mild limb contractures or foot deformities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26700687, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28262468, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36090556}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Congenital myopathy 22B, severe fetal (CMYO22B) [MIM:620369]: A severe congenital myopathy, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of muscle disorders characterized by hypotonia and muscle weakness apparent at birth, and specific pathological features on muscle biopsy. CMYO22B is an autosomal recessive form characterized by onset in utero. Affected individuals show fetal akinesia, and develop fetal hydrops with pulmonary hypoplasia, severe joint contractures, and generalized muscle hypoplasia. Death occurs in utero or soon after birth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26700687}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05096 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 50355.5 Length 445 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 38.26 Isoelectric point 6.52 Charge (pH=7) -1.53 3D Binding mode Sequence RREIKIEGDLVLGGLFPINEKGTGTEECGRINEDRGIQRLEAMLFAIDEINKDDYLLPGVKLGVHILDTCSRDTYALEQSLEFVRASLLLIAGVIGGSYSSVSIQVANLLRLFQIPQISYASTSAKLSDKSRYDYFARTVPPDFYQAKAMAEILRFFNWTYVSTVASEGDYGETGIEAFEQEARLRNISIATAEKVGRSNIRKSYDSVIRELLQKPNARVVVLFMRSDDSRELIAAASRANASFTWVASDGWGAQESIIKGSEHVAYGAITLELASQPVRQFDRYFQSLNPYNNHRNPWFRDFWEQKFQCSLRVCDKHLAIDSSNYEQESKIMFVVNAVYAMAHALHKMQRTLCPNTTKLCDAMKILDGKKLYKDYLLKINFTAPDADSIVKFDTFGDGMGRYNVFNFQNVGGKYSYLKVGHWAETLSLDVNSIHWSRNSVPTSE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 8 | Interleukin 21 receptor (IL21R) | 6PLH | 6.74 | |
Target general information Gen name IL21R Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms UNQ3121/PRO10273; Novel interleukin receptor; NILR; Interleukin-21 receptor; IL21 receptor; IL-21R; IL-21 receptor; CD360 Protein family Type I cytokine receptor family, Type 4 subfamily Biochemical class Cytokine receptor Function This is a receptor for interleukin-21. Related diseases Immunodeficiency 56 (IMD56) [MIM:615207]: An autosomal recessive primary immunodeficiency characterized by B- and T-cell defects and variable dysfunction of NK cells. Patients tend to have normal numbers of lymphocytes, but show defective class-switched B-cells, low IgG, defective antibody response, and defective T-cell responses to certain antigens. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23440042}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Chromosomal aberrations involving IL21R is a cause of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (B-cell NHL). Translocation t(3;16)(q27;p11), with BCL6. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P29972 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Chromosomal rearrangement; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C,B Molecular weight (Da) 48376.5 Length 446 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.94 Isoelectric point 8.24 Charge (pH=7) 3.56 3D Binding mode Sequence DVVMTHTPLSLPVSLGDQASISCRSSQSLVHSNGNTYLHWYLQKPGQSPKLLIYKVSNRFSGVPDRFSGSGSGADFTLKISRVEAEDLGVYFCSQSTHVPRTFGGGTKLEIKRADAAPTVSIFPPSSEQLTSGGASVVCFLNNFYPKDINVKWKIDGSERQNGVLNSWTDQDSKDSTYSMSSTLTLTKDEYERHNSYTCEATHKTSTSPIVKSFNRNECXVHLQQPGADLVKPGASVKMSCKASGYTFTSYWITWVKLRPGQGLEWIGDIYPGSGSTNFIEKFKSKATLTVDTSSSTAYMQLRSLTSEDSAVYYCARRGHGNYEDYWGQGTTLIVSSAKTTAPSVYPLAPVCGTGSSVTLGCLVKGYFPEPVTLTWNSGSLSSGVHTFPAVLQSDLYTLSSSVTVTSSTWPSQSITCNVAHPASSTKVDKKIEPRGPTTWSEWSDP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 9 | Aspartate carbamoyltransferase (CAD) | 4C6E | 6.68 | |
Target general information Gen name CAD Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CAD Protein family CarA family; CarB family; Metallo-dependent hydrolases superfamily, DHOase family, CAD subfamily; Aspartate/ornithine carbamoyltransferase superfamily, ATCase family Biochemical class Carbon-nitrogen ligase Function This protein is a "fusion" protein encoding four enzymatic activities of the pyrimidine pathway (GATase, CPSase, ATCase and DHOase). Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 50 (DEE50) [MIM:616457]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of severe early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE50 is an autosomal recessive, progressive disease with onset in infancy and favorable response to treatment with oral uridine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25678555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28087732}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00128; DB00130; DB03459 Interacts with P27708; Q8N137; P63104 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Allosteric enzyme; ATP-binding; Congenital disorder of glycosylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Epilepsy; Hydrolase; Ligase; Magnesium; Manganese; Metal-binding; Multifunctional enzyme; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Pyrimidine biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transferase; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 38268.4 Length 351 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 41.29 Isoelectric point 5.86 Charge (pH=7) -10.56 3D Binding mode Sequence KLVRLPGLIDVHVHLREPGGTHKEDFASGTAAALAGGITMVCAMPNTRPPIIDAPALALAQKLAEAGARCDFALFLGASSENAGTLGTVAGSAAGLXLYLNETFSELRLDSVVQWMEHFETWPSHLPIVAHAEQQTVAAVLMVAQLTQRSVHICHVARKEEILLIKAAKARGLPVTCEVAPHHLFLSHDDLERLGPGKGEVRPELGSRQDVEALWENMAVIDCFASDHAPHTLEEKCGSRPPPGFPGLETMLPLLLTAVSEGRLSLDDLLQRLHHNPRRIFHLPPQEDTYVEVDLEHEWTIPSHMPFSKAHWTPFEGQKVKGTVRRVVLRGEVAYIDGQVLVPPGYGQDVR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 10 | Carbonic anhydrase VII (CA-VII) | 3ML5 | 6.64 | |
Target general information Gen name CA7 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Carbonic anhydrase 7; Carbonate dehydratase VII Protein family Alpha-carbonic anhydrase family Biochemical class Alpha-carbonic anhydrase Function Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. Related diseases Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 8 (NBIA8) [MIM:617917]: A neurodegenerative disorder associated with iron accumulation, primarily in the basal ganglia. Disease onset is in early childhood. Clinical features include speech delay, progressive cerebellar ataxia, unbalanced gait, and loss of ambulation. NBIA8 transmission pattern is consistent with autosomal recessive inheritance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29395073}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00819; DB00562; DB00606; DB01144; DB08846; DB00311; DB00774; DB00703; DB00909 Interacts with NA EC number EC 4.2.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Lyase; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 29393.6 Length 262 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 40.14 Isoelectric point 7 Charge (pH=7) -0.01 3D Binding mode Sequence GHHGWGYGQDDGPSHWHKLYPIAQGDRQSPINIISSQAVYSPSLQPLELSYEACMSLSITNNGHSVQVDFNDSDDRTVVTGGPLEGPYRLKQFHFHWGKKHDVGSEHTVDGKSFPSELHLVHWNAKKYSTFGEAASAPDGLAVVGVFLETGDEHPSMNRLTDALYMVRFKGTKAQFSCFNPKSLLPASRHYWTYPGSLTTPPLSESVTWIVLREPISISERQMGKFRSLLFTSEDDERIHMVNNFRPPQPLKGRVVKASFRA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 11 | Embryonic ectoderm development protein (EED) | 7QK4 | 6.62 | |
Target general information Gen name EED Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hEED; WD protein associating with integrin cytoplasmic tails 1; WAIT-1 Protein family WD repeat ESC family Biochemical class NA Function Polycomb group (PcG) protein. Component of the PRC2/EED-EZH2 complex, which methylates 'Lys-9' and 'Lys-27' of histone H3, leading to transcriptional repression of the affected target gene. Also recognizes 'Lys-26' trimethylated histone H1 with the effect of inhibiting PRC2 complex methyltransferase activity on nucleosomal histone H3 'Lys-27', whereas H3 'Lys-27' recognition has the opposite effect, enabling the propagation of this repressive mark. The PRC2/EED-EZH2 complex may also serve as a recruiting platform for DNA methyltransferases, thereby linking two epigenetic repression systems. Genes repressed by the PRC2/EED-EZH2 complex include HOXC8, HOXA9, MYT1 and CDKN2A. Related diseases Cohen-Gibson syndrome (COGIS) [MIM:617561]: An autosomal dominant overgrowth disorder characterized by accelerated osseous maturation, advanced bone age, skeletal abnormalities including flaring of the metaphyses of the long bones, large hands with long fingers and camptodactyly, scoliosis, cervical spine anomalies, dysmorphic facial features, and variable intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25787343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27193220, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27868325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28229514, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28475857}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q8IXJ9; P49368; Q16531; P26358; Q9Y6K1; Q9UBC3; O75530; Q92800; Q15910; Q92833-1; Q15156; P63244; Q9NY59; Q15022; Q9JJY3; G5E9A7; Q92800-2; Q15910-2; P28799; Q8WXH2; O60333-2; P35240; O60260-5; Q9Y3C5; P37840; Q7Z699; Q13148; P40337-2 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative initiation; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Chromosome; Disease variant; Host-virus interaction; Methylation; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation; WD repeat Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 40324.5 Length 350 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.7 Isoelectric point 6.16 Charge (pH=7) -5.11 3D Binding mode Sequence CKYSFKCVNSLKEDHNQPLFGVQFNWHSKEGDPLVFATVGSNRVTLYECHSQGEIRLLQSYVDADADENFYTCAWTYDSNTSHPLLAVAGSRGIIRIINPITMQCIKHYVGHGNAINELKFHPRDPNLLLSVSKDHALRLWNIQTDTLVAIFGGVEGHRDEVLSADYDLLGEKIMSCGMDHSLKLWRINSKRMMNAIKESYDYPFISQKIHFPDFSTRDIHRNYVDCVRWLGDLILSKSCENAIVCWKPGKMEDDIDKIKPSESNVTILGRFDYSQCDIWYMRFSMDFWQKMLALGNQVGKLYVWDLEVECTTLTHHKCGAAIRQTSFSRDSSILIAVCDDASIWRWDRL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 12 | Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA-IX) | 5FL4 | 6.57 | |
Target general information Gen name CA9 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Renal cell carcinoma-associated antigen G250; RCC-associated antigen G250; PMW1; P54/58N; Membrane antigen MN; MN; G250 antigen (MN/CA IX/G250); G250; Carbonic anhydrase 9; Carbonate dehydratase IX; C Protein family Alpha-carbonic anhydrase family Biochemical class Alpha-carbonic anhydrase Function Participates in pH regulation. May be involved in the control of cell proliferation and transformation. Appears to be a novel specific biomarker for a cervical neoplasia. Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. Related diseases Hydroxykynureninuria (HYXKY) [MIM:236800]: An inborn error of amino acid metabolism characterized by massive urinary excretion of large amounts of kynurenine, 3-hydroxykynurenine and xanthurenic acid. Affected individuals manifest renal tubular dysfunction, metabolic acidosis, psychomotor retardation, non-progressive encephalopathy, and muscular hypertonia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17334708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28792876}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Vertebral, cardiac, renal, and limb defects syndrome 2 (VCRL2) [MIM:617661]: An autosomal recessive congenital malformation syndrome characterized by vertebral segmentation abnormalities, congenital cardiac defects, renal defects, and distal mild limb defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28792876}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00562; DB00606; DB12741; DB08846; DB05304; DB00774; DB09460; DB00909 Interacts with P21291; O76003 EC number EC 4.2.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Lyase; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 27522.8 Length 251 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 48.97 Isoelectric point 5.48 Charge (pH=7) -7.5 3D Binding mode Sequence WRYGGDPPWPRVSPACAGRFQSPVDIRPQLAAFSPALRPLELLGFQLPPLPELRLRNNGHSVQLTLPPGLEMALGPGREYRALQLHLHWGAAGRPGSEHTVEGHRFPAEIHVVHLSTAFARVDEALGRPGGLAVLAAFLEEGPEENSAYEQLLSRLEEIAEEGSETQVPGLDISALLPSDFSRYFQYEGSLTTPPCAQGVIWTVFNQTVMLSAKQLHTLSDTLWGPGDSRLQLNFRATQPLNGRVIEASFP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 13 | Solute carrier family 19 member 1 (SLC19A1) | 8GOF | 6.56 | |
Target general information Gen name SLC19A1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Reduced folate carrier protein; RFC1; RFC; Placental folate transporter; Intestinal folate carrier 1; IFC-1; Folate transporter 1; FOLT; FLOT1 Protein family Reduced folate carrier (RFC) transporter (TC 2.A.48) family Biochemical class NA Function Transporter for the intake of folate. Uptake of folate in human placental choriocarcinoma cells occurs by a novel mechanism called potocytosis which functionally couples three components, namely the folate receptor, the folate transporter, and a V-type H(+)-pump. Related diseases Megaloblastic anemia, folate-responsive (MEGAF) [MIM:601775]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by megaloblastic anemia resulting from decreased folate transport into erythrocytes. Disease manifestations include hemolytic anemia, hyperhomocysteinemia, and low vitamin B12. Serum folate levels are normal, but erythrocyte folate levels are decreased. Treatment with oral folate corrects the anemia and normalizes homocysteine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32276275}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Immunodeficiency 114, folate-responsive (IMD114) [MIM:620603]: An autosomal recessive immunologic disorder manifesting in early infancy and characterized by recurrent skin and respiratory infections, mucosal bleeding, oral ulcers, chronic diarrhea, and poor overall growth. Affected individuals have lymphopenia, low serum immunoglobulins, and impaired T cell proliferation. Some patients have global developmental delay. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:36517554, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36745868}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB11256; DB00563; DB00642; DB06813; DB01157 Interacts with Q7Z3Y9 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Antiport; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Folate-binding; Glycoprotein; Hereditary hemolytic anemia; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 46087.7 Length 407 Aromaticity 0.15 Instability index 34.62 Isoelectric point 9.82 Charge (pH=7) 17.33 3D Binding mode Sequence DPELRSWRHLVCYLCFYGFMAQIRPGESFITPYLLGPDKNFTREQVTNEITPVLSYSYLAVLVPVFLLTDYLRYTPVLLLQGLSFVSVWLLLLLGHSVAHMQLMELFYSVTMAARIAYSSYIFSLVRPARYQRVAGYSRAAVLLGVFTSSVLGQLLVTVGRVSFSTLNYISLAFLTFSVVLALFLKRPKRSLFFNRDDSVLARMLRELGDSLRRPQLRLWSLWWVFNSAGYYLVVYYVHILWNEVDPTTNSARVYNGAADAASTLLGAITSFAAGFVKIRWARWSKLLIAGVTATQAGLVFLLAHTRHPSSIWLCYAAFVLFRGSYQFLVPIATFQIASSLSKELCALVFGVNTFFATIVKTIITFIVSDVRGLGLPVRKQFQLYSVYFLILSIIYFLGAMLDGLRH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 14 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme | 5AMC | 6.53 | |
Target general information Gen name ACE Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms DCP1;DCP Protein family Peptidase M2 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Actin binding.Bradykinin receptor binding.Carboxypeptidase activity.Chloride ion binding.Drug binding.Endopeptidase activity.Exopeptidase activity.Metallodipeptidase activity.Metallopeptidase activity.Mitogen-activated protein kinase binding.Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding.Peptidyl-dipeptidase activity.Tripeptidyl-peptidase activity.Zinc ion binding. Related diseases Ischemic stroke (ISCHSTR) [MIM:601367]: A stroke is an acute neurologic event leading to death of neural tissue of the brain and resulting in loss of motor, sensory and/or cognitive function. Ischemic strokes, resulting from vascular occlusion, is considered to be a highly complex disease consisting of a group of heterogeneous disorders with multiple genetic and environmental risk factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15534175}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Renal tubular dysgenesis (RTD) [MIM:267430]: Autosomal recessive severe disorder of renal tubular development characterized by persistent fetal anuria and perinatal death, probably due to pulmonary hypoplasia from early-onset oligohydramnios (the Potter phenotype). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16116425}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Microvascular complications of diabetes 3 (MVCD3) [MIM:612624]: Pathological conditions that develop in numerous tissues and organs as a consequence of diabetes mellitus. They include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy leading to end-stage renal disease, and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic retinopathy remains the major cause of new-onset blindness among diabetic adults. It is characterized by vascular permeability and increased tissue ischemia and angiogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10099885}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) [MIM:614519]: A pathological condition characterized by bleeding into one or both cerebral hemispheres including the basal ganglia and the cerebral cortex. It is often associated with hypertension and craniocerebral trauma. Intracerebral bleeding is a common cause of stroke. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15277638}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00542; DB00616; DB01197; DB01340; DB15565; DB00584; DB09477; DB02032; DB00492; DB00722; DB00691; DB03740; DB00886; DB00790; DB00881; DB00178; DB01180; DB01348; DB08836; DB00519; DB13166 Interacts with P05556 EC number 3.4.15.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative promoter usage; Alternative splicing; Calmodulin-binding; Carboxypeptidase; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Membrane; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 70008.2 Length 607 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 46.01 Isoelectric point 5.71 Charge (pH=7) -13.56 3D Binding mode Sequence LDPGLQPGQFSADEAGAQLFAQSYQSSAEQVLFQSVAASWAHDTNITAENARRQEEAALLSQEFAEAWGQKAKELYEPIWQQFTDPQLRRIIGAVRTLGSANLPLAKRQQYNALLSQMSRIYSTAKVCLTATCWSLDPDLTNILASSRSYAMLLFAWEGWHNAAGIPLKPLYEDFTALSNEAYKQDGFTDTGAYWRSWYNSPTFEDDLEHLYQQLEPLYLNLHAFVRRALHRRYGDRYINLRGPIPAHLLGDMWAQSWENIYDMVVPFPDKPNLDVTSTMLQQGWQATHMFRVAEEFFTSLELSPMPPEFWEGSMLEKPADGREVVCHASAWDFYNRKDFRIKQCTRVTMDQLSTVHHEMGHIQYYLQYKDLPVSLRRGANPGFHEAIGDVLALSVSTPEHLHKIGLLDRVTNDTESDINYLLKMALEKIAFLPFGYLVDQWRWGVFSGRTPPSRYNFDWWYLRTKYQGICPPVTRNETHFDAGAKFHVPNVTPYIRYFVSFVLQFQFHEALCKEAGYEGPLHQCDIYRSTKAGAKLRKVLRAGSSRPWQEVLKDMVGLDALDAQPLLKYFQLVTQWLQEQNQQNGEVLGWPEYQWHPPLPDNYPEG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 15 | Platelet glycoprotein VI (GP6) | 5OU7 | 6.53 | |
Target general information Gen name GP6 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Glycoprotein 6; GPVI Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Collagen receptor involved in collagen-induced platelet adhesion and activation. Plays a key role in platelet procoagulant activity and subsequent thrombin and fibrin formation. This procoagulant function may contribute to arterial and venous thrombus formation. The signaling pathway involves the FcR gamma-chain, the Src kinases (likely FYN or LYN) and SYK, the adapter protein LAT and leads to the activation of PLCG2. Related diseases Bleeding disorder, platelet-type, 11 (BDPLT11) [MIM:614201]: A mild to moderate bleeding disorder caused by defective platelet activation and aggregation in response to collagen. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19549989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19552682}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P06241; P07948; P06241; P07948 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Blood coagulation; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hemostasis; Immunoglobulin domain; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 19027.4 Length 173 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.14 Isoelectric point 8.68 Charge (pH=7) 2.52 3D Binding mode Sequence SGPLPKPSLQALPSSLVPLEKPVTLRCQGPPGVDLYRLEKLSSSRYQDQAVLFIPAMKRSLAGRYRCSYQNGSLWSLPSDQLELVATGVFAKPSLSAQPGSGGDVTLQCQTRYGFDQFALYKEGDPERWYRASFPIITVTAAHSGTYRCYSFSSRDPYLWSAPSDPLELVVTG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 16 | Pyruvate kinase PKLR | 4IP7 | 6.52 | |
Target general information Gen name PKLR Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms PKL;PK1 Protein family Pyruvate kinase family Biochemical class Transferase Function ATP binding.Kinase activity.Magnesium ion binding.Potassium ion binding.Pyruvate kinase activity. Related diseases Pyruvate kinase hyperactivity (PKHYP) [MIM:102900]: Autosomal dominant phenotype characterized by increase of red blood cell ATP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9090535}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Pyruvate kinase deficiency of red cells (PKRD) [MIM:266200]: A frequent cause of hereditary non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia. Clinically, pyruvate kinase-deficient patients suffer from a highly variable degree of chronic hemolysis, ranging from severe neonatal jaundice and fatal anemia at birth, severe transfusion-dependent chronic hemolysis, moderate hemolysis with exacerbation during infection, to a fully compensated hemolysis without apparent anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10087985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10772876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11328279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11960989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1536957, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1896471, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19085939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2018831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21794208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7706479, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8161798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8180378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8476433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8481523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8483951, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8664896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8807089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9075576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9482576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9827908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9886305, ECO:0000269|Ref.24}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02726; DB00787; DB04551; DB16236; DB00119 Interacts with Q9UBL6-2 EC number 2.7.1.40 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Allosteric enzyme; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Disease variant; Glycolysis; Hereditary hemolytic anemia; Kinase; Magnesium; Manganese; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Potassium; Proteomics identification; Pyruvate; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 45695.1 Length 421 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 34.44 Isoelectric point 6.88 Charge (pH=7) -0.35 3D Binding mode Sequence GTAFFQQQQLPAAMADTFLEHLCLLDIDSEPVAARSTSIIATIGPASRSVERLKEMIKAGMNIARLNFSHGSHEYHAESIANVREAVESFSPLSYRPVAIALDTKGPEIGLSEQDVRDLRFGVEHGVDIVFASFVRKASDVAAVRAALGPEGHGIKIISKIENHEGVKRFDEILEVSDGIMVARGDLGIEIPAEKVFLAQKMMIGRCNLAGKPVVCATQMLESMITKPRPTRAETSDVANAVLDGADCIMLSGETAKGNFPVEAVKMQHAIAREAEAAVYHRQLFEELRRAAPLSRDPTEVTAIGAVEAAFKCCAAAIIVLTTTGRSAQLLSRYRPRAAVIAVTRSAQAARQVHLCRGVFPLLYREPPEAIWADDVDRRVQFGIESGKLRGFLRVGDLVIVVTGWRPGSGYTNIMRVLSIS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 17 | Carbonic anhydrase XIV (CA-XIV) | 5CJF | 6.50 | |
Target general information Gen name CA14 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms UNQ690/PRO1335; Carbonic anhydrase 14; Carbonate dehydratase XIV Protein family Alpha-carbonic anhydrase family Biochemical class Alpha-carbonic anhydrase Function Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. Related diseases Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (IBDD) [MIM:611283]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by plasma carnitine deficiency and elevated C4-acylcarnitine. Patients manifest variable clinical features including failure to thrive, seizures, anemia, muscular hypotonia and developmental delay. Some patients may be asymptomatic. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12359132, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15505379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16857760}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00819; DB00562; DB00606; DB08846; DB00909 Interacts with NA EC number EC 4.2.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Lyase; Membrane; Metal-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 29397.4 Length 260 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 59.95 Isoelectric point 5.54 Charge (pH=7) -11 3D Binding mode Sequence HWTYEGPHGQDHWPASYPECGNNAQSPIDIQTDSVTFDPDLPALQPGYDQTEPLDLHNNGHTVQLSLPSTLYLGGLPRKYVAAQLHLHWGQKGPGGSEHQINSEATFAELHIVHYDSDSYDSLSEAAERPQGLAVLGILIEVETKNIAYEHILSHLHEVRHKDQKTSVPPFNLRELLPKQGQYFRYNGSLTTPPCYQSVLWTVFYRRSQISMEQLEKLGTLFSTEEEPSKLLVQNYRALQPLNQRMVFASFIQAGSSYTT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 18 | Amylin receptor (IAPPR) | 6ZIS | 6.50 | |
Target general information Gen name CALCR-RAMP1/RAMP2/RAMP3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Complex of Calcitonin receptor and Receptor activity-modifying protein Protein family RAMP family Biochemical class NA Function Transports the calcitonin gene-related peptide type 1 receptor (CALCRL) to the plasma membrane. Acts as a receptor for calcitonin-gene-related peptide (CGRP) together with CALCRL. Related diseases Immunodeficiency 9 (IMD9) [MIM:612782]: An immune disorder characterized by recurrent infections, impaired activation and proliferative response of T-cells, decreased T-cell production of cytokines, and normal lymphocytes counts and serum immunoglobulin levels. In surviving patients ectodermal dysplasia with anhidrosis and non-progressive myopathy may be observed. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16147976, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16582901}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Myopathy, tubular aggregate, 2 (TAM2) [MIM:615883]: A rare congenital myopathy characterized by regular arrays of membrane tubules on muscle biopsies without additional histopathological hallmarks. Tubular aggregates in muscle are structures of variable appearance consisting of an outer tubule containing either one or more microtubule-like structures or amorphous material. TAM2 patients have myopathy and pupillary abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24591628, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28058752}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01278 Interacts with Q16602; P21145; Q5J8X5; Q16617 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 63832.6 Length 569 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 22.42 Isoelectric point 5.07 Charge (pH=7) -16.96 3D Binding mode Sequence SAKIEEGKLVIWINGDKGYNGLAEVGKKFEKDTGIKVTVEHPDKLEEKFPQVAATGDGPDIIFWAHDRFGGYAQSGLLAEITPDKAFQDKLYPFTWDAVRYNGKLIAYPIAVEALSLIYNKDLLPNPPKTWEEIPALDKELKAKGKSALMFNLQEPYFTWPLIAADGGYAFKYENGKYDIKDVGVDNAGAKAGLTFLVDLIKNKHMNADTDYSIAEAAFNKGETAMTINGPWAWSNIDTSKVNYGVTVLPTFKGQPSKPFVGVLSAGINAASPNKELAKEFLENYLLTDEGLEAVNKDKPLGAVALKSYEEELAKDPRIAATMENAQKGEIMPNIPQMSAFWYAVRTAVINAASGRQTVDEALKDAQTNAAAEFTTACQEANYGALLRELCLTQFQVDMEAVGETLWCDWGRTIRSYRELADCTWHMAEKLGCFWPNAEVDRFFLAVHGRYFRSCPISIQLGVTRNKIMTAQYECYQKIMQDPIQQGVYCQRTWDGWLCWNDVAAGTESMQLCPDYFQDFDPSEKVTKICDQDGNWFRHPASQRTWTDYTQCNVNTHEKVKTALNLFYL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 19 | Vasopressin V1a receptor | 1YTV | 6.49 | |
Target general information Gen name AVPR1A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms AVPR1 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, Vasopressin/oxytocin receptor subfamily Biochemical class Sugar binding protein Function Peptide binding.Peptide hormone binding.Protein kinase C binding.V1A vasopressin receptor binding.Vasopressin receptor activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09059; DB00872; DB00035; DB00093; DB14642; DB16279; DB05452; DB13929; DB02638; DB06212; DB00067 Interacts with P25106 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID M,N Molecular weight (Da) 40697.6 Length 371 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 20.94 Isoelectric point 5.07 Charge (pH=7) -9.93 3D Binding mode Sequence NSSSNKIEEGKLVIWINGDKGYNGLAEVGKKFEKDTGIKVTVEHPDKLEEKFPQVAATGDGPDIIFWAHDRFGGYAQSGLLAEITPDKAFQDKLYPFTWDAVRYNGKLIAYPIAVEALSLIYNKDLLPNPPKTWEEIPALDKELKAKGKSALMFNLQEPYFTWPLIAADGGYAFKYENGKYDIKDVGVDNAGAKAGLTFLVDLIKNKHMNADTDYSIAEAAFNKGETAMTINGPWAWSNIDTSKVNYGVTVLPTFKGQPSKPFVGVLSAGINAASPNKELAKEFLENYLLTDEGLEAVNKDKPLGAVALKSYEEELAKDPRIAATMENAQKGEIMPNIPQMSAFWYAVRTAVINAASGRQTVDEALKDAQT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 20 | Lysine-specific demethylase 4C (KDM4C) | 4XDO | 6.44 | |
Target general information Gen name KDM4C Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms KIAA0780; Jumonji domain-containing protein 2C; JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 3C; JMJD2C; JHDM3C; Gene amplified in squamous cell carcinoma 1 protein; GASC1; GASC-1 protein Protein family JHDM3 histone demethylase family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Does not demethylate histone H3 'Lys-4', H3 'Lys-27' nor H4 'Lys-20'. Demethylates trimethylated H3 'Lys-9' and H3 'Lys-36' residue, while it has no activity on mono- and dimethylated residues. Demethylation of Lys residue generates formaldehyde and succinate. Histone demethylase that specifically demethylates 'Lys-9' and 'Lys-36' residues of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code. Related diseases Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) [MIM:144700]: Renal cell carcinoma is a heterogeneous group of sporadic or hereditary carcinoma derived from cells of the proximal renal tubular epithelium. It is subclassified into clear cell renal carcinoma (non-papillary carcinoma), papillary renal cell carcinoma, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, collecting duct carcinoma with medullary carcinoma of the kidney, and unclassified renal cell carcinoma. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma is the most common subtype. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20054297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23622243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23792563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25728682}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Defects of SETD2 are associated with loss of DNA methylation at non-promoter regions (PubMed:23792563). SETD2 defects lead to aberrant and reduced nucleosome compaction and chromatin association of key replication proteins, such as MCM7 and DNA polymerase delta, leading to hinder replication fork progression and prevent loading of RAD51 homologous recombination repair factor at DNA breaks (PubMed:25728682). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23792563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25728682}.; DISEASE: Luscan-Lumish syndrome (LLS) [MIM:616831]: An autosomal dominant syndrome with a variable phenotype. Clinical features include macrocephaly, distinctive facial appearance, postnatal overgrowth, various degrees of learning difficulties, autism spectrum disorder, and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23160955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24852293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26084711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27317772}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute lymphoblastic (ALL) [MIM:613065]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. ALL is a malignant disease of bone marrow and the most common malignancy diagnosed in children. The malignant cells are lymphoid precursor cells (lymphoblasts) that are arrested in an early stage of development. The lymphoblasts replace the normal marrow elements, resulting in a marked decrease in the production of normal blood cells. Consequently, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia occur to varying degrees. The lymphoblasts also proliferate in organs other than the marrow, particularly the liver, spleen, and lymphnodes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24509477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24662245}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML) [MIM:601626]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. AML is a malignant disease of bone marrow characterized by maturational arrest of hematopoietic precursors at an early stage of development. Clonal expansion of myeloid blasts occurs in bone marrow, blood, and other tissue. Myelogenous leukemias develop from changes in cells that normally produce neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils and monocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16314571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24509477}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 70 (MRD70) [MIM:620157]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by mild global developmental delay, moderately impaired intellectual disability with speech difficulties, and behavioral abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32710489}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Rabin-Pappas syndrome (RAPAS) [MIM:620155]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by severely impaired global development, intellectual disability, microcephaly, facial dysmorphism, and variable congenital anomalies affecting the skeletal, genitourinary, cardiac, and other organ systems. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32710489}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.14.11.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Dioxygenase; Iron; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 39355.6 Length 338 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 38.34 Isoelectric point 8.04 Charge (pH=7) 2.41 3D Binding mode Sequence LNPSCKIMTFRPSMEEFREFNKYLAYMESKGAHRAGLAKVIPPKEWKPRQCYDDIDNLLIPAPIQQMVTGQSGLFTQYNIQKKAMTVKEFRQLANSGKYCTPRYLDYEDLERKYWKNLTFVAPIYGADINGSIYDEGVDEWNIARLNTVLDVVEEECGISIEGVNTPYLYFGMWKTTFAWHTEDMDLYSINYLHFGEPKSWYAIPPEHGKRLERLAQGFFPSSSQGCDAFLRHKMTLISPSVLKKYGIPFDKITQEAGEFMITFPYGYHAGFNHGFNCAESTNFATVRWIDYGKVAKLCTCRKDMVKISMDIFVRKFQPDRYQLWKQGKDIYTIDHTK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||