Job Results:
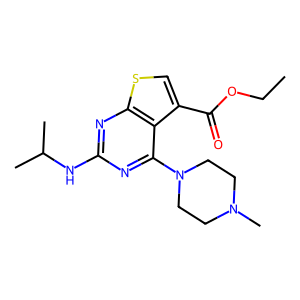
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
8adf9aabe9fa12b13024fa8d07ca9b9b
Job name
NA
Time
2026-01-21 12:38:59
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 81 | Bacterial Cystathionine beta-lyase (Bact metC) | 4ITX | 6.42 | |
Target general information Gen name Bact metC Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Cysteine-S-conjugate beta-lyase MetC; Cysteine lyase MetC; Cysteine desulfhydrase MetC; Cystathionine beta-lyase MetC; CL; CBL; Beta-cystathionase MetC; Bacterial CD Protein family Trans-sulfuration enzymes family Biochemical class Carbon-sulfur lyases Function Primarily catalyzes the cleavage of cystathionine to homocysteine, pyruvate and ammonia during methionine biosynthesis. Also exhibits cysteine desulfhydrase activity, producing sulfide from cysteine. In addition, under certain growth conditions, exhibits significant alanine racemase coactivity. Related diseases Coronary artery disease, autosomal dominant, 2 (ADCAD2) [MIM:610947]: A common heart disease characterized by reduced or absent blood flow in one or more of the arteries that encircle and supply the heart. Its most important complication is acute myocardial infarction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17332414, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23703864}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Tooth agenesis, selective, 7 (STHAG7) [MIM:616724]: An autosomal dominant form of selective tooth agenesis, a common anomaly characterized by the congenital absence of one or more teeth. Selective tooth agenesis without associated systemic disorders has sometimes been divided into 2 types: oligodontia, defined as agenesis of 6 or more permanent teeth, and hypodontia, defined as agenesis of less than 6 teeth. The number in both cases does not include absence of third molars (wisdom teeth). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26387593}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 4.4.1.13 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Amino-acid biosynthesis; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Lyase; Methionine biosynthesis; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 42756.3 Length 391 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 27.11 Isoelectric point 6.01 Charge (pH=7) -6.11 3D Binding mode Sequence KLDTQLVNAGRSKKYTLGAVNSVIQRASSLVFDSVEAKKHATRNRANGELFYGRRGTLTHFSLQQAMCELEGGAGCVLFPCGAAAVANSILAFIEQGDHVLMTNTAYESSQDFCSKILSKLGVTTSWFDPLIGADIVKHLQPNTKIVFLESPGSITMEVHDVPAIVAAVRSVVPDAIIMIDNTWAAGVLFKALDFGIDVSIQAATKYLVGHSDAMIGTAVCNARCWEQLRENAYLMGQMVDADTAYITSRGLRTLGVRLRQHHESSLKVAEWLAEHPQVARVNHPALPGSKGHEFWKRDFTGSSGLFSFVLKKKLNNEELANYLDNFSLFSMAYSWGGYESLILANQPEHIAAIRPQGEIDFSGTLIRLHIGLEDVDDLIADLDAGFARIV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 82 | Cholesterol oxidase | 4REK | 6.41 | |
Target general information Gen name choA Organism Streptomyces sp. (strain SA-COO) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family GMC oxidoreductase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Cholesterol oxidase activity.Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.Steroid delta-isomerase activity. Related diseases Bothnia retinal dystrophy (BRD) [MIM:607475]: A type of retinitis punctata albescens. Affected individuals show night blindness from early childhood with features consistent with retinitis punctata albescens and macular degeneration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10102298}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Rod-cone dystrophy Newfoundland (NFRCD) [MIM:607476]: A rod-cone dystrophy reminiscent of retinitis punctata albescens but with a substantially lower age at onset and more-rapid and distinctive progression. Rod-cone dystrophies results from initial loss of rod photoreceptors, later followed by cone photoreceptors loss. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11868161}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Retinitis punctata albescens (RPA) [MIM:136880]: A form of fleck retina disease characterized by aggregation of white flecks posteriorly in the retina, causing night blindness and delayed dark adaptation. It differs from fundus albipunctatus in being progressive and evolving to generalized atrophy of the retina. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10102299, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11453974, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9326942}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147; DB02332 Interacts with NA EC number 1.1.3.6; 5.3.3.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cholesterol metabolism; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Isomerase; Lipid metabolism; Oxidoreductase; Secreted; Signal; Steroid metabolism; Sterol metabolism Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 54367.8 Length 498 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 30.62 Isoelectric point 6.69 Charge (pH=7) -0.71 3D Binding mode Sequence GYVPAVVIGTGYGAAVSALRLGEAGVQTLMLEMGQLWNQPGPDGNIFCGMLNPDKRSSWFKNRTEAPLGSFLWLDVVNRNIDPYAGVLDRVNYDQMSVYVGRGVGGGSLVNGGMAVEPKRSYFEEILPRVDSSEMYDRYFPRANSMLRVNHIDTKWFEDTEWYKFARVSREQAGKAGLGTVFVPNVYDFGYMQREAAGEVPKSALATEVIYGNNHGKQSLDKTYLAAALGTGKVTIQTLHQVKTIRQTKDGGYALTVEQKDTDGKLLATKEISCRYLFLGAGSLGSTELLVRARDTGTLPNLNSEVGAGWGPNGNIMTARANHMWNPTGAHQSSIPALGIDAWDNSDSSVFAEIAPMPAGLETWVSLYLAITKNPQRGTFVYDAATDRAKLNWTRDQNAPAVNAAKALFDRINKANGTIYRYDLFGTQLKAFADDFCYHPLGGCVLGKATDDYGRVAGYKNLYVTDGSLIPGSVGVNPFVTITALAERNVERIIKQDV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 83 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase cot (COT) | 4Y85 | 6.41 | |
Target general information Gen name MAP3K8 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tumor progression locus 2; TPL-2; Proto-oncogene c-Cot; Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 8; ESTF; Cancer Osaka thyroid oncogene; COT Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family, MAP kinase kinase kinase subfamily Biochemical class NA Function Required for lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced, TLR4-mediated activation of the MAPK/ERK pathway in macrophages, thus being critical for production of the proinflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha (TNF) during immune responses. Involved in the regulation of T-helper cell differentiation and IFNG expression in T-cells. Involved in mediating host resistance to bacterial infection through negative regulation of type I interferon (IFN) production. In vitro, activates MAPK/ERK pathway in response to IL1 in an IRAK1-independent manner, leading to up-regulation of IL8 and CCL4. Transduces CD40 and TNFRSF1A signals that activate ERK in B-cells and macrophages, and thus may play a role in the regulation of immunoglobulin production. May also play a role in the transduction of TNF signals that activate JNK and NF-kappa-B in some cell types. In adipocytes, activates MAPK/ERK pathway in an IKBKB-dependent manner in response to IL1B and TNF, but not insulin, leading to induction of lipolysis. Plays a role in the cell cycle. Isoform 1 shows some transforming activity, although it is much weaker than that of the activated oncogenic variant. Related diseases Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, familial, 2 (HHF2) [MIM:601820]: A form of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous disorder characterized by inappropriate insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta-cells in the presence of low blood glucose levels. HHF2 is a common cause of persistent hypoglycemia in infancy. Unless early and aggressive intervention is undertaken, brain damage from recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia may occur. HHF2 inheritance can be autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10204114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12364426, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15562009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15579781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15807877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15998776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16332676, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16357843, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18596924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19357197, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7847376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8923010}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Diabetes mellitus, permanent neonatal, 2 (PNDM2) [MIM:618856]: A form of permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus, a type of diabetes characterized by onset of persistent hyperglycemia within the first six months of life. Initial clinical manifestations include intrauterine growth retardation, hyperglycemia, glycosuria, osmotic polyuria, severe dehydration, and failure to thrive. Some PNDM2 patients may also have developmental delay, muscle weakness, epilepsy and dysmorphic features. PNDM2 transmission pattern is consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15115830, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15292329, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15448106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15448107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15580558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15583126, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16609879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16731833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17213273, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17652641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17855752, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20022885, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842488}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus 3 (TNDM3) [MIM:610582]: Neonatal diabetes mellitus, defined as insulin-requiring hyperglycemia within the first month of life, is a rare entity. In about half of the neonates, diabetes is transient and resolves at a median age of 3 months, whereas the rest have a permanent form of diabetes. In a significant number of patients with transient neonatal diabetes mellitus, diabetes type 2 appears later in life. The onset and severity of TNDM3 is variable with childhood-onset diabetes, gestational diabetes or adult-onset diabetes described. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15718250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15784703}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Defects in KCNJ11 may contribute to non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), also known as diabetes mellitus type 2.; DISEASE: Maturity-onset diabetes of the young 13 (MODY13) [MIM:616329]: A form of diabetes that is characterized by an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance, onset in childhood or early adulthood (usually before 25 years of age), a primary defect in insulin secretion and frequent insulin-independence at the beginning of the disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22701567}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P08238; P19838; Q00653; Q13526; Q8NFZ5 EC number EC 2.7.11.25 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative initiation; ATP-binding; Cell cycle; Cytoplasm; Immunity; Kinase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Proto-oncogene; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34773.8 Length 307 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 39.24 Isoelectric point 6.68 Charge (pH=7) -1.2 3D Binding mode Sequence LSSVRYGTVEDLLAFANHISNTPQESGILLNMVITPQNGRYQIDSDVLLIPWKLTYRNIFIPRGAFGKVYLAQDIKTKKRMACKLIPVDQFKPSDVEIQACFRHENIAELYGAVLWGETVHLFMEAGEGGSVLEKLESCGPMREFEIIWVTKHVLKGLDFLHSKKVIHHDIKPSNIVFMSTKAVLVDFGLSVQMTEDVYFPKDLRGTEIYMSPEVILCRGHSTKADIYSLGATLIHMQTGTPPWVKRYPRSAYPSYLYIIHKQAPPLEDIADDCSPGMRELIEASLERNPNHRPRAADLLKHEALNP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 84 | Glutathione S-transferase kappa 1 | 3RPN | 6.41 | |
Target general information Gen name GSTK1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms HDCMD47P Protein family GST superfamily, Kappa family Biochemical class Transferase / transferase inhibitor Function Glutathione peroxidase activity.Glutathione transferase activity.Protein disulfide oxidoreductase activity.Receptor binding. Related diseases Dyskinesia, limb and orofacial, infantile-onset (IOLOD) [MIM:616921]: An autosomal recessive, early-onset hyperkinetic movement disorder characterized by axial hypotonia, dyskinesia of the limbs and trunk, orofacial dyskinesia, drooling, and dysarthria. The severity of the hyperkinesis is variable. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27058446}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Striatal degeneration, autosomal dominant 2 (ADSD2) [MIM:616922]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by striatal degeneration and dysfunction of basal ganglia, resulting in hyperkinesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27058447}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00143; DB04700 Interacts with O95273; Q8IZU0; Q60994; Q7Z3Y8 EC number 2.5.1.18 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Peroxisome; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F Molecular weight (Da) 24811.7 Length 220 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 47.17 Isoelectric point 7.96 Charge (pH=7) 1.39 3D Binding mode Sequence GPLPRTVELFYDVLSPYSWLGFEILCRYQNIWNINLQLRPSLITGIMKDSGNKPPGLLPRKGLYMANDLKLLRHHLQIPIHFPKDFLSVMLEKGSLSAMRFLTAVNLEHPEMLEKASRELWMRVWSRNEDITEPQSILAAAEKAGMSAEQAQGLLEKIATPKVKNQLKETTEAACRYGAFGLPITVAHVDGQTHMLFGSDRMELLAHLLGEKWMGPIPPA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 85 | Notch-1 receptor (NOTCH1) | 5L0R | 6.41 | |
Target general information Gen name NOTCH1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hN1; Translocationassociated notch protein TAN1; Translocation-associated notch protein TAN-1; TAN1; Notch 1 intracellular domain; Notch 1; Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1; NICD Protein family NOTCH family Biochemical class Notch protein Function Upon ligand activation through the released notch intracellular domain (NICD) it forms a transcriptional activator complex with RBPJ/RBPSUH and activates genes of the enhancer of split locus. Affects the implementation of differentiation, proliferation and apoptotic programs. Involved in angiogenesis; negatively regulates endothelial cell proliferation and migration and angiogenic sprouting. Involved in the maturation of both CD4(+) and CD8(+) cells in the thymus. Important for follicular differentiation and possibly cell fate selection within the follicle. During cerebellar development, functions as a receptor for neuronal DNER and is involved in the differentiation of Bergmann glia. Represses neuronal and myogenic differentiation. May play an essential role in postimplantation development, probably in some aspect of cell specification and/or differentiation. May be involved in mesoderm development, somite formation and neurogenesis. May enhance HIF1A function by sequestering HIF1AN away from HIF1A. Required for the THBS4 function in regulating protective astrogenesis from the subventricular zone (SVZ) niche after injury. Involved in determination of left/right symmetry by modulating the balance between motile and immotile (sensory) cilia at the left-right organiser (LRO). Functions as a receptor for membrane-bound ligands Jagged-1 (JAG1), Jagged-2 (JAG2) and Delta-1 (DLL1) to regulate cell-fate determination. Related diseases Aortic valve disease 1 (AOVD1) [MIM:109730]: A common defect in the aortic valve in which two rather than three leaflets are present. It is often associated with aortic valve calcification, stenosis and insufficiency. In extreme cases, the blood flow may be so restricted that the left ventricle fails to grow, resulting in hypoplastic left heart syndrome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16025100}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Adams-Oliver syndrome 5 (AOS5) [MIM:616028]: A form of Adams-Oliver syndrome, a disorder characterized by the congenital absence of skin (aplasia cutis congenita) in combination with transverse limb defects. Aplasia cutis congenita can be located anywhere on the body, but in the vast majority of the cases, it is present on the posterior parietal region where it is often associated with an underlying defect of the parietal bones. Limb abnormalities are typically limb truncation defects affecting the distal phalanges or entire digits (true ectrodactyly). Only rarely, metatarsals/metacarpals or more proximal limb structures are also affected. Apart from transverse limb defects, syndactyly, most commonly of second and third toes, can also be observed. The clinical features are highly variable and can also include cardiovascular malformations, brain abnormalities and vascular defects such as cutis marmorata and dilated scalp veins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25132448}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q13315; Q969H0; Q16665; P78504; O60341; Q8N423; Q92585; P19838; P46531; Q13153; Q13526; Q06330; Q06330-6; Q13573; P98170; Q8IZL2; Q96JK9 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; Angiogenesis; ANK repeat; Calcium; Cell membrane; Developmental protein; Differentiation; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; EGF-like domain; Endosome; Glycoprotein; Hydroxylation; Isopeptide bond; Membrane; Metal-binding; Notch signaling pathway; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 46121.2 Length 394 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 39.95 Isoelectric point 7.22 Charge (pH=7) 0.63 3D Binding mode Sequence KWKVFIDQINRSLENYEPCSSQNCSCYHGVIEEDLTPFRGGISRKMMAEVVRRKLGTHYQITKNRLYRENDCMFPSRCSGVEHFILEVIGRLPDMEMVINVRDYPQVPKWMEPAIPVFSFSKTSEYHDIMYPAWTFWEGGPAVWPIYPTGLGRWDLFREDLVRSAAQWPWKKKNSTAYFRGSRTSPERDPLILLSRKNPKLVDAEYTKNQAWKSMKDTLGKPAAKDVHLVDHCKYKYLFNFRGVAASFRFKHLFLCGSLVFHVGDEWLEFFYPQLKPWVHYIPVKTDLSNVQELLQFVKANDDVAQEIAERGSQFIRNHLQMDDITCYWENLLSEYSKFLSYNVTRRKGYDQIIPVNECVSNPCQNDATCLDQIGEFQCICMPGYEGVHCEVNT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 86 | MEK kinase kinase 3 (MAP4K3) | 5J5T | 6.41 | |
Target general information Gen name MAP4K3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms RAB8IPL1; Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 3; MEKKK 3; MAPK/ERK kinase kinase kinase 3; Germinal center kinase-related protein kinase; GLK Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family, STE20 subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Appears to act upstream of the JUN N-terminal pathway. May play a role in the response to environmental stress. Related diseases A chromosomal aberration involving NPM1 is found in a form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Translocation t(2;5)(p23;q35) with ALK. The resulting chimeric NPM1-ALK protein homodimerize and the kinase becomes constitutively activated. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8122112, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8633037}.; DISEASE: A chromosomal aberration involving NPM1 is found in a form of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Translocation t(5;17)(q32;q11) with RARA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8562957}.; DISEASE: A chromosomal aberration involving NPM1 is a cause of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Translocation t(3;5)(q25.1;q34) with MLF1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8570204}.; DISEASE: Defects in NPM1 are associated with acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Mutations in exon 12 affecting the C-terminus of the protein are associated with an aberrant cytoplasmic location. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15659725}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12010 Interacts with P62993; Q13094; Q9Y4K4; Q04759; Q02111 EC number EC 2.7.11.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Kinase; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33570.4 Length 298 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 40.61 Isoelectric point 6.85 Charge (pH=7) -0.5 3D Binding mode Sequence SQEDFELIQRIGSGTYGDVYKARNVNTGELAAIKVIKLEPGEDFAVVQQEIIMMKDCKHPNIVAYFGSYLRRDKLWICMEFCGGGSLQDIYHVTGPLSELQIAYVSRETLQGLYYLHSKGKMHRDIKGANILLXDNGHVKLADFGVSAQITATIAAFIGTPYWMAPEVAAVERKGGYNQLCDLWAVGITAIELAELQPPMFDLHPMRALFLMTKSNFQPPKLKDKMKWSNSFHHFVKMALTKNPKKRPTAEKLLQHPFVTQHLTRSLAIELLDKVNNPSTYHDFDDDDPEPLVAVPHR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 87 | UDP-glucose 4-epimerase (GALE) | 1EK6 | 6.41 | |
Target general information Gen name GALE Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms UDP-galactose4-epimerase; UDP-galactose4'-epimerase; UDP-galactose 4-epimerase; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4-epimerase; UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine 4-epimerase; UDP-GlcNAc 4-epimerase; UDP-GalNAc 4-epimera Protein family NAD(P)-dependent epimerase/dehydratase family Biochemical class Racemases and epimerase Function The reaction with UDP-Gal plays a critical role in the Leloir pathway of galactose catabolism in which galactose is converted to the glycolytic intermediate glucose 6-phosphate. It contributes to the catabolism of dietary galactose and enables the endogenous biosynthesis of both UDP-Gal and UDP-GalNAc when exogenous sources are limited. Both UDP-sugar interconversions are important in the synthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids. Catalyzes two distinct but analogous reactions: the reversible epimerization of UDP-glucose to UDP-galactose and the reversible epimerization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine. Related diseases Galactosemia 3 (GALAC3) [MIM:230350]: A form of galactosemia, an inborn error of galactose metabolism typically manifesting in the neonatal period, after ingestion of galactose, with jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, hepatocellular insufficiency, food intolerance, hypoglycemia, renal tubular dysfunction, muscle hypotonia, sepsis and cataract. GALAC3 is an autosomal recessive form caused by galactose epimerase deficiency. It can manifest as benign, peripheral form with mild symptoms and enzymatic deficiency in circulating blood cells only. A second form, known as generalized epimerase deficiency, is characterized by undetectable levels of enzyme activity in all tissues and severe clinical features, including restricted growth and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11279193, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11903335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15639193, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16301867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16302980, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9326324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9538513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9973283}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thrombocytopenia 13, syndromic (THC13) [MIM:620776]: An autosomal recessive form of thrombocytopenia, a hematologic disorder defined by a decrease in the number of platelets in circulating blood, resulting in the potential for increased bleeding and decreased ability for clotting. THC13 patients have enlarged, gray platelets with defective function. Some affected individuals have leukopenia or anemia and pancytopenia. Additional variable features include mitral valve malformations, pyloric stenosis, and impaired intellectual development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30247636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33510604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34159722, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36395340}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03501; DB03095; DB03041; DB01861; DB02196; DB03397 Interacts with Q14376 EC number EC 5.1.3.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Carbohydrate metabolism; Disease variant; Galactose metabolism; Isomerase; NAD; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 38082 Length 346 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 33.02 Isoelectric point 6.26 Charge (pH=7) -2.83 3D Binding mode Sequence MAEKVLVTGGAGYIGSHTVLELLEAGYLPVVIDNFHNAFRGGGSLPESLRRVQELTGRSVEFEEMDILDQGALQRLFKKYSFMAVIHFAGLKAVGESVQKPLDYYRVNLTGTIQLLEIMKAHGVKNLVFSSSATVYGNPQYLPLDEAHPTGGCTNPYGKSKFFIEEMIRDLCQADKTWNAVLLRYFNPTGAHASGCIGEDPQGIPNNLMPYVSQVAIGRREALNVFGNDYDTEDGTGVRDYIHVVDLAKGHIAALRKLKEQCGCRIYNLGTGTGYSVLQMVQAMEKASGKKIPYKVVARREGDVAACYANPSLAQEELGWTAALGLDRMCEDLWRWQKQNPSGFGT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 88 | Oxalosuccinate decarboxylase (IDH1) | 6ADG | 6.40 | |
Target general information Gen name IDH1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PICD; NADP(+)-specific ICDH; Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP] cytoplasmic; IDP; IDH; Cytosolic NADP-isocitrate dehydrogenase Protein family Isocitrate and isopropylmalate dehydrogenases family Biochemical class Short-chain dehydrogenases reductase Function Catalyses the NADPH-dependent reduction of alpha-ketoglutarate to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG). Related diseases Glioma (GLM) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19117336, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. Mutations affecting Arg-132 are tissue-specific, and suggest that this residue plays a unique role in the development of high-grade gliomas. Mutations of Arg-132 to Cys, His, Leu or Ser abolish magnesium binding and abolish the conversion of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate. Instead, alpha-ketoglutarate is converted to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate. Elevated levels of R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate are correlated with an elevated risk of malignant brain tumors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646}.; DISEASE: Genetic variations are associated with cartilaginous tumors such as enchondroma or chondrosarcoma. Mutations of Arg-132 to Cys, Gly or His abolish the conversion of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate. Instead, alpha-ketoglutarate is converted to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26161668}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09374; DB01727; DB14568; DB03461; DB16267 Interacts with P0DP23; P27797; P36957; O75874; Q8TDX7; P16284; P17612; P50454; P37173; Q05086-3 EC number EC 1.1.1.42 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Glyoxylate bypass; Magnesium; Manganese; Metal-binding; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Peroxisome; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Tricarboxylic acid cycle Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 92711.7 Length 823 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 26.74 Isoelectric point 6.42 Charge (pH=7) -4.48 3D Binding mode Sequence KKISGGSVVEMQGDEMTRIIWELIKEKLIFPYVELDLHSYDLGIENRDATNDQVTKDAAEAIKKHNVGVKCATITPDEKRVEEFKLKQMWKSPNGTIRNILGGTVFREAIICKNIPRLVSGWVKPIIIGHHAYGDQYRATDFVVPGPGKVEITYTPSDGTQKVTYLVHNFEEGGGVAMGMYNQDKSIEDFAHSSFQMALSKGWPLYLSTKNTILKKYDGRFKDIFQEIYDKQYKSQFEAQKIWYEHRLIDDMVAQAMKSEGGFIWACKNYDGDVQSDSVAQGYGSLGMMTSVLVCPDGKTVEAEAAHGTVTRHYRMYQKGQETSTNPIASIFAWTRGLAHRAKLDNNKELAFFANALEEVSIETIEAGFMTKDLAACIKGLPNVQRSDYLNTFEFMDKLGENLKIKLAQAKLKKISGGSVVEMQGDEMTRIIWELIKEKLIFPYVELDLHSYDLGIENRDATNDQVTKDAAEAIKKHNVGVKCATITPDEKRVEEFKLKQMWKSPNGTIRNILGGTVFREAIICKNIPRLVSGWVKPIIIGHHAYGDQYRATDFVVPGPGKVEITYTPSDGTQKVTYLVHNFEEGGGVAMGMYNQDKSIEDFAHSSFQMALSKGWPLYLSTKNTILKKYDGRFKDIFQEIYDKQYKSQFEAQKIWYEHRLIDDMVAQAMKSEGGFIWACKNYDGDVQSDSVAQGYGSLGMMTSVLVCPDGKTVEAEAAHGTVTRHYRMYQKGQETSTNPIASIFAWTRGLAHRAKLDNNKELAFFANALEEVSIETIEAGFMTKDLAACIKGLPNVQRSDYLNTFEFMDKLGENLKIKLAQAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 89 | Transferrin (TF) | 1RYO | 6.40 | |
Target general information Gen name TF Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Siderophilin; Serotransferrin; PRO1400; Beta-1 metal-binding globulin Protein family Transferrin family Biochemical class Transferrin Function It is responsible for the transport of iron from sites of absorption and heme degradation to those of storage and utilization. Serum transferrin may also have a further role in stimulating cell proliferation. Transferrins are iron binding transport proteins which can bind two Fe(3+) ions in association with the binding of an anion, usually bicarbonate. Related diseases Atransferrinemia (ATRAF) [MIM:209300]: A rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by abnormal synthesis of transferrin leading to iron overload and microcytic hypochromic anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11110675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15466165}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01370; DB14517; DB14518; DB01294; DB14526; DB14527; DB11136; DB14528; DB14529; DB14530; DB00515; DB09130; DB11397; DB13949; DB14490; DB14491; DB14488; DB14501; DB14489; DB13257; DB06215; DB06784; DB05260; DB01592; DB00893; DB00677; DB06757; DB11182; DB14520; DB01593; DB14487; DB14533; DB14548 Interacts with O43315; O00501; Q7Z7G2; Q9GZR5; Q9Y282; Q96KR6; P01350; P08034; Q8NBJ4; O15529; Q8TED1; Q7Z5P4; A8MZ59; O15173; Q96TC7; Q3KNW5; Q9BXS9-3; Q99523; O43278-2; Q8N9I0; P02786; Q4KMG9; Q9K0U9; Q09057; Q9K0V0; P02786 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Ion transport; Iron; Iron transport; Metal-binding; Methylation; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35854.5 Length 324 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 34.17 Isoelectric point 7.58 Charge (pH=7) 1.42 3D Binding mode Sequence KTVRWCAVSEHEATKCQSFRDHMKSVIPSDGPSVACVKKASYLDCIRAIAANEADAVTLDAGLVYDAYLAPNNLKPVVAEFYGSKEDPQTFYYAVAVVKKDSGFQMNQLRGKKSCHTGLGRSAGWNIPIGLLYCDLPEPRKPLEKAVANFFSGSCAPCADGTDFPQLCQLCPGCGCSTLNQYFGYSGAFKCLKDGAGDVAFVKHSTIFENLANKADRDQYELLCLDNTRKPVDEYKDCHLAQVPSHTVVARSMGGKEDLIWELLNQAQEHFGKDKSKEFQLFSSPHGKDLLFKDSAHGFLKVPPRMDAKMYLGYEYVTAIRNLR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 90 | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) | 5FY9 | 6.40 | |
Target general information Gen name KDM5B Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Retinoblastomabinding protein 2 homolog 1; Retinoblastoma-binding protein 2 homolog 1; RBP2H1; RBP2-H1; RBBP2H1; PLU1; PLU-1; Lysinespecific demethylase 5B; Jumonji/ARID domaincontaining protein 1B; J Protein family JARID1 histone demethylase family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Does not demethylate histone H3 'Lys-9' or H3 'Lys-27'. Demethylates trimethylated, dimethylated and monomethylated H3 'Lys-4'. Acts as a transcriptional corepressor for FOXG1B and PAX9. Favors the proliferation of breast cancer cells by repressing tumor suppressor genes such as BRCA1 and HOXA5. In contrast, may act as a tumor suppressor for melanoma. Represses the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer-mediated transcriptional activation of the core clock component PER2. Histone demethylase that demethylates 'Lys-4' of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 65 (MRT65) [MIM:618109]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRT65 patients have moderate to severe intellectual disability, developmental delay, and facial dysmorphism. Camptodactyly is present in some patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29276005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30409806}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P49711 EC number EC 1.14.11.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Biological rhythms; Chromatin regulator; Dioxygenase; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Iron; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 53020.6 Length 460 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 44.23 Isoelectric point 5.28 Charge (pH=7) -18.32 3D Binding mode Sequence SMFLPPPECPVFEPSWEEFADPFAFIHKIRPIAEQTGICKVRPPPDWQPPFACDVDKLHFTPRIQRLNELEAQTRVKLGGGGARDYTLRTFGEMADAFKSDYFNMPVHMVPTELVEKEFWRLVSTIEEDVTVEYGADIASKEFGSGFPVRDIKLSPEEEEYLDSGWNLNNMPVMEQSVLAHITADICGMKLPWLYVGMCFSSFCWHIEDHWSYSINYLHWGEPKTWYGVPGYAAEQLENVMKKLAPELFVSQPDLLHQLVTIMNPNTLMTHEVPVYRTNQCAGEFVITFPRAYHSGFNQGFNFAEAVNFCTVDWLPLGRQCVEHYRLLHRYCVFSHDEMICKMASKADVLDVVVASTVQKDMAIMIEDEKALRETVRKLGVIDSERMDFELLPDDERQCVKCKTTCFMSAISCSCKPGLLVCLHHVKELCSCPPYKYKLRYRYTLDDLYPMMNALKLRAE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 91 | Glucarate dehydratase | 1EC8 | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name gudD Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b2787;ygcX;JW2758 Protein family Mandelate racemase/muconate lactonizing enzyme family, GlucD subfamily Biochemical class Lyase Function Glucarate dehydratase activity.Magnesium ion binding. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03237; DB03212; DB03603; DB03734 Interacts with NA EC number 4.2.1.40 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Lyase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 48707 Length 442 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 26.98 Isoelectric point 5.69 Charge (pH=7) -10.89 3D Binding mode Sequence FTTPVVTEMQVIPVAGHDSMLMNLSGAHAPFFTRNIVIIKDNSGHTGVGEIPGGEKIRKTLEDAIPLVVGKTLGEYKNVLTLVRNTFADRDAGGRGLQTFDLRTTIHVVTGIEAAMLDLLGQHLGVNVASLLGDGQQRSEVEMLGYLFFVGNRKATPLPYQSQPDDSCDWYRLRHEEAMTPDAVVRLAEAAYEKYGFNDFKLKGGVLAGEEEAESIVALAQRFPQARITLDPNGAWSLNEAIKIGKYLKGSLAYAEDPCGAEQGFSGREVMAEFRRATGLPTATNMIATDWRQMGHTLSLQSVDIPLADPHFWTMQGSVRVAQMCHEFGLTWGSHSNNHFDISLAMFTHVAAAAPGKITAIDTHWIWQEGNQRLTKEPFEIKGGLVQVPEKPGLGVEIDMDQVMKAHELYQKHGLGARDDAMGMQYLIPGWTFDNKRPCMVR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 92 | Medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 4P13 | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name ACADM Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity.Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.Identical protein binding.Medium-chain-acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity. Related diseases Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase medium-chain deficiency (ACADMD) [MIM:201450]: An inborn error of mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation which causes fasting hypoglycemia, hepatic dysfunction and encephalopathy, often resulting in death in infancy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10767181, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11349232, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11409868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11486912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1363805, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1671131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1684086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1902818, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2251268, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2393404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2394825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7603790, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7929823, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8198141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9158144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9882619}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03415; DB03147; DB02910 Interacts with PRO_0000000502 [P11310] EC number 1.3.8.7 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; FAD; Fatty acid metabolism; Flavoprotein; Lipid metabolism; Mitochondrion; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 85080.3 Length 773 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 30.55 Isoelectric point 5.71 Charge (pH=7) -7.7 3D Binding mode Sequence LGFSFEFTEQQKEFQATARKFAREEIIPVAAEYDKTGEYPVPLIRRAWELGLMNTHIPENCGGLGLGTFDACLISEELAYGCTGVQTAIEGNSLGQMPIIIAGNDQQKKKYLGRMTEEPLMCAYCVTEPGAGSDVAGIKTKAEKKGDEYIINGQKMWITNGGKANWYFLLARSDPDPKAPANKAFTGFIVEADTPGIQIGRKELNMGQRCSDTRGIVFEDVKVPKENVLIGDGAGFKVAMGAFDKTRPVVAAGAVGLAQRALDEATKYALERKTFGKLLVEHQAISFMLAEMAMEVELARMSYQRAAWEVDSGRRNTYYASIAKAFAGDIANQLATDAVQILGGNGFNTEYPVEKLMRDAKIYQIYEGTSQIQRLIVAREHIDKYKLGFSFEFTEQQKEFQATARKFAREEIIPVAAEYDKTGEYPVPLIRRAWELGLMNTHIPENCGGLGLGTFDACLISEELAYGCTGVQTAIEGNSLGQMPIIIAGNDQQKKKYLGRMTEEPLMCAYCVTEPGAGSDVAGIKTKAEKKGDEYIINGQKMWITNGGKANWYFLLARSDPDPKAPANKAFTGFIVEADTPGIQIGRKELNMGQRCSDTRGIVFEDVKVPKENVLIGDGAGFKVAMGAFDKTRPVVAAGAVGLAQRALDEATKYALERKTFGKLLVEHQAISFMLAEMAMEVELARMSYQRAAWEVDSGRRNTYYASIAKAFAGDIANQLATDAVQILGGNGFNTEYPVEKLMRDAKIYQIYEGTSQIQRLIVAREHIDKYKN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 93 | Ferredoxin reductase | 2GQW | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name bphA4 Organism Pseudomonas sp. (strain KKS102) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family NA Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.Oxidoreductase activity. Related diseases LTC4 synthase deficiency is associated with a neurometabolic developmental disorder characterized by muscular hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, and microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10896305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9820300}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; FAD; Flavoprotein; Nucleotide-binding Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 42484 Length 401 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 32.45 Isoelectric point 6.13 Charge (pH=7) -2.69 3D Binding mode Sequence LKAPVVVLGAGLASVSFVAELRQAGYQGLITVVGDEAERPYDRPPLSKDFMAHGDAEKIRLDCKRAPEVEWLLGVTAQSFDPQAHTVALSDGRTLPYGTLVLATGAAPRALPTLQGATMPVHTLRTLEDARRIQAGLRPQSRLLIVGGGVIGLELAATARTAGVHVSLVETQPRLMSRAAPATLADFVARYHAAQGVDLRFERSVTGSVDGVVLLDDGTRIAADMVVVGIGVLANDALARAAGLACDDGIFVDAYGRTTCPDVYALGDVTRQRNPLSGRFERIETWSNAQNQGIAVARHLVDPTAPGYAELPWYWSDQGALRIQVAGLASGDEEIVRGEVSLDAPKFTLIELQKGRIVGATCVNNARDFAPLRRLLAVGAKPDRAALADPATDLRKLAAAV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 94 | TetR family transcriptional regulator | 2V57 | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name lfrR Organism Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (Mycobacterium smegmatis) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family NA Biochemical class Transcription Function DNA binding. Related diseases LTC4 synthase deficiency is associated with a neurometabolic developmental disorder characterized by muscular hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, and microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10896305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9820300}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01123 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 37947.8 Length 348 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 36.27 Isoelectric point 5.5 Charge (pH=7) -9.3 3D Binding mode Sequence GARERTRRAILDAAMLVLADHPTAALGDIAAAAGVGRSTVHRYYPERTDLLRALARHVHDLSNAAIERADPTSGPVDAALRRVVESQLDLGPIVLFVYYEPSILADPELAAYFDIGDEAIVEVLNRASTERYPPGWARRVFWALMQAGYEAAKDGMPRHQIVDAIMTSLTSGIITLARERTRRAILDAAMLVLADHPTAALGDIAAAAGVGRSTVHRYYPERTDLLRALARHVHDLSNAAIERADPTSGPVDAALRRVVESQLDLGPIVLFVYYEPSILADPELAAYFDIGDEAIVEVLNRASYPPGWARRVFWALMQAGYEAAKDGMPRHQIVDAIMTSLTSGIITL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 95 | Smoothened homolog (SMO) | 4JKV | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name SMO Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Smo-D473H; SMOH; Protein Gx Protein family G-protein coupled receptor Fz/Smo family Biochemical class GPCR frizzled Function Binding of sonic hedgehog (SHH) to its receptor patched is thought to prevent normal inhibition by patched of smoothened (SMO). Required for the accumulation of KIF7, GLI2 and GLI3 in the cilia. Interacts with DLG5 at the ciliary base to induce the accumulation of KIF7 and GLI2 at the ciliary tip for GLI2 activation. G protein-coupled receptor that probably associates with the patched protein (PTCH) to transduce the hedgehog's proteins signal. Related diseases Curry-Jones syndrome (CRJS) [MIM:601707]: A multisystem disorder characterized by patchy skin lesions, polysyndactyly, diverse cerebral malformations, unicoronal craniosynostosis, iris colobomas, microphthalmia, and intestinal malrotation with myofibromas or hamartomas. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24859340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27236920}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. 8 individuals have been identified with the disease-causing mutation Phe-412 and all were mosaic. The mutation could not be reliably detected in blood, greatest success rates were obtained with affected tissues obtained by invasive procedures. It is thought that the mutation has arisen postzygotically early during embryonic development (PubMed:27236920). This mutation has also been identified in ameloblastoma, medulloblastoma, meningioma, and basal cell carcinoma, and has been reported as the oncogenic driver in some of these tumors (PubMed:24859340). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24859340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27236920}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01047; DB11978; DB06786; DB09143; DB08828 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Developmental protein; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 37420.1 Length 333 Aromaticity 0.16 Instability index 25.17 Isoelectric point 6.65 Charge (pH=7) -0.76 3D Binding mode Sequence AYIQKYLSGQCEVPLVRTDNPKSWYEDVEGCGIQCQNPLFTEAEHQDMHSYIAAFGAVTGLCTLFTLATFVADWRNSNRYPAVILFYVNACFFVGSIGWLAQFMDGARREIVCRADGTMRLGEPTSNETLSCVIIFVIVYYALMAGVVWFVVLTYAWHTSFKALGKTSYFHLLTWSLPFVLTVAILAVAQVDGDSVSGICFVGYKNYRYRAGFVLAPIGLVLIVGGYFLIRGVMTLFSIKSNHPGLLSEKAASKINETMLRLGIFGFLAFGFVLITFSCHFYDFFNQAEWERSFRDYVLCQANDCEIKNRPSLLVEKINLFAMFGTGIAMSTW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 96 | P2Y purinoceptor 12 | 4PXZ | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name P2RY12 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms HORK3 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class Membrane protein Function ADP receptor activity.G-protein coupled adenosine receptor activity.Guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Related diseases Bleeding disorder, platelet-type, 8 (BDPLT8) [MIM:609821]: A condition characterized by mild to moderate mucocutaneous bleeding, and excessive bleeding after surgery or trauma. The defect is due to severe impairment of platelet response to ADP resulting in defective platelet aggregation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11196645, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12578987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25428217}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06441; DB00758; DB06350; DB01240; DB06209; DB01069; DB05553; DB15163; DB08816; DB00208; DB00374; DB16349 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Blood coagulation; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Hemostasis; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 28830.4 Length 248 Aromaticity 0.17 Instability index 24.19 Isoelectric point 9.39 Charge (pH=7) 10.55 3D Binding mode Sequence SLCTRDYKITQVLFPLLYTVLFFVGLITNGLAMRIFFQIRSKSNFIIFLKNTVISDLLMILTFPFKILSDAKLGTGPLRTFVCQVTSVIFYFTMYISISFLGLITIDPKNLLGAKILSVVIWAFMFLLSLPNMILTNRQPRDKNVKKCSFLKSEFGLVWHEIVNYICQVIFWINFLIVVKVFIIIAVFFICFVPFHFARIPYTLSQTRDVFDCTAENTLFYVKESTLWLTSLNACLNPFIYFFLCKSF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 97 | Protein-cysteine N-palmitoyltransferase HHAT (HHAT) | 7MHY | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name HHAT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Skinny hedgehog protein 1; Melanoma antigen recognized by T-cells 2; MART-2; Hedgehog acyltransferase; HHAT Protein family Membrane-bound acyltransferase family, HHAT subfamily Biochemical class Acyltransferase Function Catalyzes N-terminal palmitoylation of SHH; which is required for SHH signaling. May bind GTP. . Related diseases Nivelon-Nivelon-Mabille syndrome (NNMS) [MIM:600092]: An autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by progressive microcephaly, cerebellar vermis hypoplasia, and skeletal dysplasia. Additional variable features include early infantile-onset seizures, intrauterine and postnatal growth retardation, generalized chondrodysplasia, and micromelia. 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis may be present. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24784881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30912300}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with O00560 EC number EC 2.3.1.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acyltransferase; Alternative splicing; Developmental protein; Disease variant; Dwarfism; Endoplasmic reticulum; Golgi apparatus; GTP-binding; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Palmitate; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 57096.2 Length 491 Aromaticity 0.17 Instability index 42.88 Isoelectric point 7.18 Charge (pH=7) 0.62 3D Binding mode Sequence MLPRWELALYLLASLGFHFYSFYEVYKVSREHEEELDQEFELETDTLFGGLKKDATDFEWSFWMEWGKQWLVWLLLGHMVVSQMATLLARKHRPWILMLYGMWACWCVLGTPGVAMVLLHTTISFCVAQFRSQLLTWLCSLLLLSTLRLQGVEEVKRRWYKTENEYYLLQFTLTVRCLYYTSFSLELCWQQLPAASTSYSFPWMLAYVFYYPVLHNGPILSFSEFIKQMQQQEHDSLKASLCVLALGLGRLLCWWWLAELMAHLMYMHAIYSSIPLLETVSCWTLGGLALAQVLFFYVKYLVLFGVPALLMRLDGLTPPALPRCVSTMFSFTGMWRYFDVGLHNFLIRYVYIPVGGSQHGLLGTLFSTAMTFAFVSYWHGGYDYLWCWAALNWLGVTVENGVRRLVETPCIQDSLARYFSPQARRRFHAALASCSTSMLILSNLVFLGGNEVGKTYWNRIFIQGWPWVTLSVLGFLYCYSHVGIAWAQTYA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 98 | Protein kinase C epsilon (PRKCE) | 5LIH | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name PRKCE Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein kinase C epsilon type; PKCE; PKC epsilon; NPKC-epsilon Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, PKC subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Mediates cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix via integrin-dependent signaling, by mediating angiotensin-2-induced activation of integrin beta-1 (ITGB1) in cardiac fibroblasts. Phosphorylates MARCKS, which phosphorylates and activates PTK2/FAK, leading to the spread of cardiomyocytes. Involved in the control of the directional transport of ITGB1 in mesenchymal cells by phosphorylating vimentin (VIM), an intermediate filament (IF) protein. In epithelial cells, associates with and phosphorylates keratin-8 (KRT8), which induces targeting of desmoplakin at desmosomes and regulates cell-cell contact. Phosphorylates IQGAP1, which binds to CDC42, mediating epithelial cell-cell detachment prior to migration. In HeLa cells, contributes to hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced cell migration, and in human corneal epithelial cells, plays a critical role in wound healing after activation by HGF. During cytokinesis, forms a complex with YWHAB, which is crucial for daughter cell separation, and facilitates abscission by a mechanism which may implicate the regulation of RHOA. In cardiac myocytes, regulates myofilament function and excitation coupling at the Z-lines, where it is indirectly associated with F-actin via interaction with COPB1. During endothelin-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, mediates activation of PTK2/FAK, which is critical for cardiomyocyte survival and regulation of sarcomere length. Plays a role in the pathogenesis of dilated cardiomyopathy via persistent phosphorylation of troponin I (TNNI3). Involved in nerve growth factor (NFG)-induced neurite outgrowth and neuron morphological change independently of its kinase activity, by inhibition of RHOA pathway, activation of CDC42 and cytoskeletal rearrangement. May be involved in presynaptic facilitation by mediating phorbol ester-induced synaptic potentiation. Phosphorylates gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit gamma-2 (GABRG2), which reduces the response of GABA receptors to ethanol and benzodiazepines and may mediate acute tolerance to the intoxicating effects of ethanol. Upon PMA treatment, phosphorylates the capsaicin- and heat-activated cation channel TRPV1, which is required for bradykinin-induced sensitization of the heat response in nociceptive neurons. Is able to form a complex with PDLIM5 and N-type calcium channel, and may enhance channel activities and potentiates fast synaptic transmission by phosphorylating the pore-forming alpha subunit CACNA1B (CaV2. 2). In prostate cancer cells, interacts with and phosphorylates STAT3, which increases DNA-binding and transcriptional activity of STAT3 and seems to be essential for prostate cancer cell invasion. Downstream of TLR4, plays an important role in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced immune response by phosphorylating and activating TICAM2/TRAM, which in turn activates the transcription factor IRF3 and subsequent cytokines production. In differentiating erythroid progenitors, is regulated by EPO and controls the protection against the TNFSF10/TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, via BCL2. May be involved in the regulation of the insulin-induced phosphorylation and activation of AKT1. Calcium-independent, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that plays essential roles in the regulation of multiple cellular processes linked to cytoskeletal proteins, such as cell adhesion, motility, migration and cell cycle, functions in neuron growth and ion channel regulation, and is involved in immune response, cancer cell invasion and regulation of apoptosis. Related diseases Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, familial, 2 (HHF2) [MIM:601820]: A form of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous disorder characterized by inappropriate insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta-cells in the presence of low blood glucose levels. HHF2 is a common cause of persistent hypoglycemia in infancy. Unless early and aggressive intervention is undertaken, brain damage from recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia may occur. HHF2 inheritance can be autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10204114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12364426, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15562009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15579781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15807877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15998776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16332676, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16357843, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18596924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19357197, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7847376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8923010}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Diabetes mellitus, permanent neonatal, 2 (PNDM2) [MIM:618856]: A form of permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus, a type of diabetes characterized by onset of persistent hyperglycemia within the first six months of life. Initial clinical manifestations include intrauterine growth retardation, hyperglycemia, glycosuria, osmotic polyuria, severe dehydration, and failure to thrive. Some PNDM2 patients may also have developmental delay, muscle weakness, epilepsy and dysmorphic features. PNDM2 transmission pattern is consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15115830, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15292329, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15448106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15448107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15580558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15583126, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16609879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16731833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17213273, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17652641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17855752, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20022885, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842488}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus 3 (TNDM3) [MIM:610582]: Neonatal diabetes mellitus, defined as insulin-requiring hyperglycemia within the first month of life, is a rare entity. In about half of the neonates, diabetes is transient and resolves at a median age of 3 months, whereas the rest have a permanent form of diabetes. In a significant number of patients with transient neonatal diabetes mellitus, diabetes type 2 appears later in life. The onset and severity of TNDM3 is variable with childhood-onset diabetes, gestational diabetes or adult-onset diabetes described. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15718250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15784703}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Defects in KCNJ11 may contribute to non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), also known as diabetes mellitus type 2.; DISEASE: Maturity-onset diabetes of the young 13 (MODY13) [MIM:616329]: A form of diabetes that is characterized by an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance, onset in childhood or early adulthood (usually before 25 years of age), a primary defect in insulin secretion and frequent insulin-independence at the beginning of the disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22701567}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09096; DB11752; DB04209; DB12010; DB06064; DB02010; DB00675 Interacts with P05067; P15056; P08238; C6GKH1; Q9BPZ7; P17252; Q15349; P31947; P37840; P62258; P63104 EC number EC 2.7.11.13 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ATP-binding; Cell adhesion; Cell cycle; Cell division; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Immunity; Kinase; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,F Molecular weight (Da) 39129.4 Length 339 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 42.21 Isoelectric point 6.17 Charge (pH=7) -3.73 3D Binding mode Sequence SLGLQDFDLLRVIGRGSYAKVLLVRLKKTDRIYAMKVVKKELVWVQTEKHVFEQASNHPFLVGLHSCFQTESRLFFVIEYVNGGDLMFHMQRQRKLPEEHARFYSAEISLALNYLHERGIIYRDLKLDNVLLDSEGHIKLTDYGMCKEGLRPGDTTSXFCGTPNYIAPEILRGEDYGFSVDWWALGVLMFEMMAGRSPFDIQNTEDYLFQVILEKQIRIPRSLSVKAASVLKSFLNKDPKERLGCHPQTGFADIQGHPFFRNVDWDMMEQKQVVPPFKPNISGEFGLDNFDSQFTNEPVQLXPDDDDIVRKIDQSEFEGFEYINPLRMRPFKRQGSVRR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 99 | Guanylate cyclase soluble beta-1 (GUCY1B1) | 7D9R | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name GUCY1B1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Soluble guanylate cyclase small subunit; Guanylate cyclase soluble subunit beta-3; Guanylate cyclase soluble subunit beta-1; GUCY1B3; GUCSB3; GUC1B3; GCS-beta-3; GCS-beta-1 Protein family Adenylyl cyclase class-4/guanylyl cyclase family Biochemical class Phosphorus-oxygen lyase Function Mediates responses to nitric oxide (NO) by catalyzing the biosynthesis of the signaling molecule cGMP. Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder with seizures, hypotonia, and brain imaging abnormalities (NEDSHBA) [MIM:618922]: An autosomal recessive neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by global developmental delay, hypotonia, severe to profound intellectual disability, early-onset epilepsy, and microcephaly. Neuroimaging shows cerebral atrophy, thin corpus callosum and hypomyelination in a majority of cases. Death in childhood may occur. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27435318, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28097321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32286009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33476302, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33500274}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09401; DB15456 Interacts with Q02108; Q02108-1 EC number EC 4.6.1.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; cGMP biosynthesis; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; GTP-binding; Heme; Iron; Lyase; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 121177 Length 1071 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 42.35 Isoelectric point 6.18 Charge (pH=7) -11.86 3D Binding mode Sequence SRVYLHTLAESICKLIFPEFERLNVALQRTLAKHKFEKTIAEQAVAAGVPVEVIKESLGEEVFKICYEEDENILGVVGGTLKDFLNSFSTLLKQASILCLLHVYYFTTSLILPGIIKAAAHVLYETEVEVSLYLLYSVHSLVIPTSLFCKTFPFHFMFDKDMTILQFGNGIRRLMNRRDKPNFEEYFEILTPKINQTFSGIMTMLNMQFVVRVRRVMDLKGQMIYIVESSAILFLGSPCVLYLSDIPIHNALRDVVLIGEQARAQDGLKKRLGKLKATLEQAHQALEEEKKKTVDLLCSIFPCEVAQQLWQGQVVQAKKFSNVTMLFSDIVGFTAICSQCSPLQVITMLNALYTRFDQQCGELDVYKVETIGDAYCVAGGLHKESDTHAVQIALMAVKMMELSDEVMSPHGEPIKMRIGLHSGSVFAGVVGVKMPRYCLFGNNVTLANKFESCSVPRKINVSPTTYRLLKDCPGFVFTPRSREELPPNFPSEIPGICHFLDAMYGFVNHALELLVIRNYGPEVWEDIKKEAQLDEEGQFLVRIIYDDSKTYDLVAAASKVLNLNAGEILQMFGKMFFVFCQESGYDTILRVLGSNVREFLQNLDALHDHLATIYPGMRAPSFRCTDAEKGKGLILHYYSEREGLQDIVIGIIKTVAQQIHGTEIDMKVIQQRNEECDHTQFLIEEKEESRISPYTFCKAFPFHIIFDRDLVVTQCGNAIYRVLPQLQPGNCSLLSVFSLVRPHIDISFHGILSHINTVFVLRSKEGLLDSCLRLKGQMIYLPEADSILFLCSPSVMNLDDLTRRGLYLSDIPLHDATRDLVLLGEQFREEYKLTQELEILTDRLQLTLRALEDEKKKTDTLLYSVLPPSVANELRHKRPVPAKRYDNVTILFSGIVGFNAFCSKHAGAMKIVNLLNDLYTRFDTLTDSRKNPFVYKVETVGDKYMTVSGLPEPCIHHARSICHLALDMMEIAGQVQVDGESVQITIGIHTGEVVTGVIGQRMPRYCLFGNTVNLTSRTETTGEKGKINVSEYTYRCLMSPENSDPQFHLEHRGPVSMKGKKEPMQVWFLSR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 100 | Mutated oxalosuccinate decarboxylase (mIDH1) | 6ADG | 6.39 | |
Target general information Gen name IDH1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PICD (mutated); Oxalosuccinate decarboxylase (mutated); NADP(+)-specific ICDH (mutated); Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP] cytoplasmic (mutated); IDP (mutated); IDH (mutated); Cytosolic NADP-isocitrate Protein family Isocitrate and isopropylmalate dehydrogenases family Biochemical class Short-chain dehydrogenases reductase Function Catalyses the NADPH-dependent reduction of alpha-ketoglutarate to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG). Related diseases Glioma (GLM) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19117336, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. Mutations affecting Arg-132 are tissue-specific, and suggest that this residue plays a unique role in the development of high-grade gliomas. Mutations of Arg-132 to Cys, His, Leu or Ser abolish magnesium binding and abolish the conversion of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate. Instead, alpha-ketoglutarate is converted to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate. Elevated levels of R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate are correlated with an elevated risk of malignant brain tumors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646}.; DISEASE: Genetic variations are associated with cartilaginous tumors such as enchondroma or chondrosarcoma. Mutations of Arg-132 to Cys, Gly or His abolish the conversion of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate. Instead, alpha-ketoglutarate is converted to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26161668}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09374; DB01727; DB14568; DB03461; DB16267 Interacts with P0DP23; P27797; P36957; O75874; Q8TDX7; P16284; P17612; P50454; P37173; Q05086-3 EC number EC 1.1.1.42 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Glyoxylate bypass; Magnesium; Manganese; Metal-binding; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Peroxisome; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Tricarboxylic acid cycle Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 92711.7 Length 823 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 26.74 Isoelectric point 6.42 Charge (pH=7) -4.48 3D Binding mode Sequence KKISGGSVVEMQGDEMTRIIWELIKEKLIFPYVELDLHSYDLGIENRDATNDQVTKDAAEAIKKHNVGVKCATITPDEKRVEEFKLKQMWKSPNGTIRNILGGTVFREAIICKNIPRLVSGWVKPIIIGHHAYGDQYRATDFVVPGPGKVEITYTPSDGTQKVTYLVHNFEEGGGVAMGMYNQDKSIEDFAHSSFQMALSKGWPLYLSTKNTILKKYDGRFKDIFQEIYDKQYKSQFEAQKIWYEHRLIDDMVAQAMKSEGGFIWACKNYDGDVQSDSVAQGYGSLGMMTSVLVCPDGKTVEAEAAHGTVTRHYRMYQKGQETSTNPIASIFAWTRGLAHRAKLDNNKELAFFANALEEVSIETIEAGFMTKDLAACIKGLPNVQRSDYLNTFEFMDKLGENLKIKLAQAKLKKISGGSVVEMQGDEMTRIIWELIKEKLIFPYVELDLHSYDLGIENRDATNDQVTKDAAEAIKKHNVGVKCATITPDEKRVEEFKLKQMWKSPNGTIRNILGGTVFREAIICKNIPRLVSGWVKPIIIGHHAYGDQYRATDFVVPGPGKVEITYTPSDGTQKVTYLVHNFEEGGGVAMGMYNQDKSIEDFAHSSFQMALSKGWPLYLSTKNTILKKYDGRFKDIFQEIYDKQYKSQFEAQKIWYEHRLIDDMVAQAMKSEGGFIWACKNYDGDVQSDSVAQGYGSLGMMTSVLVCPDGKTVEAEAAHGTVTRHYRMYQKGQETSTNPIASIFAWTRGLAHRAKLDNNKELAFFANALEEVSIETIEAGFMTKDLAACIKGLPNVQRSDYLNTFEFMDKLGENLKIKLAQAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||