Job Results:
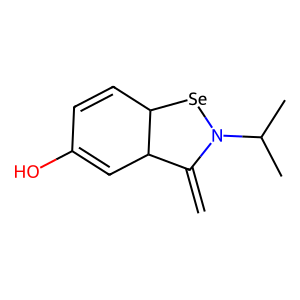
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
6035497cf04470e01d5d7dbbed13b512
Job name
NA
Time
2025-10-13 17:35:32
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 81 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) | 4EAR | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name PNP Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PNP; Inosine phosphorylase Protein family PNP/MTAP phosphorylase family Biochemical class Pentosyltransferase Function The purine nucleoside phosphorylases catalyze the phosphorolytic breakdown of the N-glycosidic bond in the beta- (deoxy)ribonucleoside molecules, with the formation of the corresponding free purine bases and pentose-1-phosphate. Related diseases Purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency (PNPD) [MIM:613179]: A disorder that interrupts both the catabolism of inosine into hypoxanthine and guanosine into guanine, and leads to the accumulation of guanosine, inosine, and their deoxified by-products. The main clinical presentation is recurrent infections due to severe T-cell immunodeficiency. Some patients also have neurologic impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1384322, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3029074, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8931706}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03881; DB03551; DB02222; DB02391; DB03609; DB01667; DB04260; DB02796; DB04753; DB00640; DB00242; DB00900; DB06185; DB02377; DB02857; DB04754; DB04757; DB04076; DB02230; DB04335; DB02568; DB03101 Interacts with P05067; Q9UQM7; O14576-2; P06241; P14136; Q92993-2; Q9BXM7; P00491; P17612; P63000; Q92673; Q15583 EC number EC 2.4.2.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Glycosyltransferase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Purine salvage; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 31849.2 Length 288 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 34.77 Isoelectric point 6.42 Charge (pH=7) -1.63 3D Binding mode Sequence GYTYEDYKNTAEYLLSHTKHRPQVAIICGSGLGGLTDKLTQAQIFDYSEIPNFPRSTVPGHAGRLVFGFLNGRACVMMQGRFHMYEGYPLYKVTFPVRVFHLLGVDTLVVTNAAGGLNPKFEVGDIMLIRDHINLPGFSGQNPLRGPNDERFGDRFPAMSDAYDRTMRQRALSTYKQMGEQRELQEGTYVMVAGPSFETVAECRVLQKLGADAVGMSTVPEVIVARHCGLRVFGFSLITNKVIMDYESLEKANXEEVLAAGKQAAQKLEQFVSILMASIDRFPAMSDA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 82 | 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (4HPPD) (HPD) (HPPDase) (EC 1.13.11.27) | 1T47 | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name hpd Organism Streptomyces avermitilis (strain ATCC 31267 / DSM 46492 / JCM 5070 / NBRC 14893 / NCIMB 12804 / NRRL 8165 / MA-4680) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms SAV_5149 Protein family 4HPPD family Biochemical class NA Function NA Related diseases LTC4 synthase deficiency is associated with a neurometabolic developmental disorder characterized by muscular hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, and microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10896305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9820300}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08307 Interacts with NA EC number 1.13.11.27 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Dioxygenase; Iron; Metal-binding; Oxidoreductase; Phenylalanine catabolism; Reference proteome; Repeat; Tyrosine catabolism Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B Molecular weight (Da) 39744.4 Length 362 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 22.41 Isoelectric point 5.19 Charge (pH=7) -15.14 3D Binding mode Sequence DPFPVKGMDAVVFAVGNAKQAAHYYSTAFGMQLVAYSGPENGSRETASYVLTNGSARFVLTSVIKPATPWGHFLADHVAEHGDGVVDLAIEVPDARAAHAYAIEHGARSVAEPYELKDEHGTVVLAAIATYGKTRHTLVDRTGYDGPYLPGYVAAAPIVEPPAHRTFQAIDHCVGNVELGRMNEWVGFYNKVMGFTNMKEFVGDDIATEYSALMSKVVADGTLKVKFPINEPALAKKKSQIDEYLEFYGGAGVQHIALNTGDIVETVRTMRAAGVQFLDTPDSYYDTLGEWVGDTRVPVDTLRELKILADRDEDGYLLQIFTKPVQDRPTVFFEIIERHGSMGFGKGNFKALFEAIEREQEK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 83 | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1A) | 5L9B | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name HIF1A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms bHLHe78; Transcription factor HIF-1; PASD8; PAS domain-containing protein 8; Member of PAS protein 1; MOP1; Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor (HIF)-1; Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; Hypoxia-in Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Under hypoxic conditions, activates the transcription of over 40 genes, including erythropoietin, glucose transporters, glycolytic enzymes, vascular endothelial growth factor, HILPDA, and other genes whose protein products increase oxygen delivery or facilitate metabolic adaptation to hypoxia. Plays an essential role in embryonic vascularization, tumor angiogenesis and pathophysiology of ischemic disease. Heterodimerizes with ARNT; heterodimer binds to core DNA sequence 5'-TACGTG-3' within the hypoxia response element (HRE) of target gene promoters. Activation requires recruitment of transcriptional coactivators such as CREBBP and EP300. Activity is enhanced by interaction with both, NCOA1 or NCOA2. Interaction with redox regulatory protein APEX seems to activate CTAD and potentiates activation by NCOA1 and CREBBP. Involved in the axonal distribution and transport of mitochondria in neurons during hypoxia. Functions as a master transcriptional regulator of the adaptive response to hypoxia. Related diseases Essential hypertension (EHT) [MIM:145500]: A condition in which blood pressure is consistently higher than normal with no identifiable cause. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12372404}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02342; DB01136; DB05959; DB08687; DB01275; DB06082; DB12255 Interacts with P10275; P27540; P49407; Q9C0J9; O00257; Q92793; P35222; Q96CJ1; Q9GZT9; Q96KS0; Q9H6Z9; Q09472; P11474; P49327; P09467; Q8N461; P23771; Q9NWT6; Q9Y2N7-4; Q92831; Q13330; P46531; Q13438; Q8N2W9; P14618-1; P25789; Q9UHD8-1; P84022; P08047; O60224; P63165; O94888; P40818; P40337; P17861; Q99PV5; Q5RIX9; Q6S7F2; Q61539; Q8BIF2; P51450-2 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Activator; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; DNA-binding; Glycoprotein; Host-virus interaction; Hydroxylation; Isopeptide bond; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; S-nitrosylation; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C,D Molecular weight (Da) 26523.9 Length 236 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 24.97 Isoelectric point 5.58 Charge (pH=7) -4.83 3D Binding mode Sequence LDLEMLAPYIPMDDDFQLLPALKLALEYIVPAMNKHGICVVDDFLGKETGQQIGDEVRALHDTGKFTDGQLVSQKSDSSKDIRGDKITWIEGKEPGCETIGLLMSSMDDLIRHCNGKLGSYKINGRTKAMVACYPGNGTGYVRHVDNPNGDGRCVTCIYYLNKDWDAKVSGGILRIFPEGKAQFADIEPKFDRLLFFWSDRRNPHEVQPAYATRYAITVWYFDADERAAAKVKYLT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 84 | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | 4A9K | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name CREBBP Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CREBbinding protein; CBP Protein family NA Biochemical class Acyltransferase Function Acetylates non-histone proteins, like NCOA3 and FOXO1. Binds specifically to phosphorylated CREB and enhances its transcriptional activity toward cAMP-responsive genes. Acts as a coactivator of ALX1. Acts as a circadian transcriptional coactivator which enhances the activity of the circadian transcriptional activators: NPAS2-ARNTL/BMAL1 and CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimers. Acetylates PCNA; acetylation promotes removal of chromatin-bound PCNA and its degradation during nucleotide excision repair (NER). Functions as a transcriptional coactivator for SMAD4 in the TGF-beta signaling pathway. Acetylates histones, giving a specific tag for transcriptional activation. Related diseases Chromosomal aberrations involving CREBBP may be a cause of acute myeloid leukemias. Translocation t(8;16)(p11;p13) with KAT6A; translocation t(11;16)(q23;p13.3) with KMT2A/MLL1; translocation t(10;16)(q22;p13) with KAT6B. KAT6A-CREBBP may induce leukemia by inhibiting RUNX1-mediated transcription.; DISEASE: Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 1 (RSTS1) [MIM:180849]: A disorder characterized by craniofacial abnormalities, postnatal growth deficiency, broad thumbs, broad big toes, intellectual disability and a propensity for development of malignancies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11331617, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12114483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12566391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15706485, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20684013, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24616510, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25388907}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Menke-Hennekam syndrome 1 (MKHK1) [MIM:618332]: A form of Menke-Hennekam syndrome, a congenital autosomal dominant disease characterized by developmental delay, growth retardation, and craniofacial dysmorphism. Patients have intellectual disability of variable severity, speech delay, autistic behavior, short stature and microcephaly. Main facial characteristics include short palpebral fissures, telecanthi, depressed nasal ridge, short nose, anteverted nares, short columella and long philtrum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27311832, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29460469, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30737887}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08655; DB02587 Interacts with P31749; P10275; P61201; P16220; P35222; Q9UER7; Q12778; O43524; P23769; P62805; Q16665; P42858; P48551; Q14653; Q13568; Q92831; Q13351; O00629; Q86UE4; P55209; Q14686; Q04206; P36956-1; P36956-3; Q12772; Q9UL17; P04637; P0DTC9; P04608; P03070; P03255; P03259; P03259-2 EC number EC 2.3.1.48 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Activator; Acyltransferase; Alternative splicing; Biological rhythms; Bromodomain; Chromosomal rearrangement; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Host-virus interaction; Intellectual disability; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Methylation; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 13704.6 Length 115 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 42.15 Isoelectric point 4.94 Charge (pH=7) -3.23 3D Binding mode Sequence KIFKPEELRQALMPTLEALYRQDPESLPFRQPVDPQLLGIPDYFDIVKNPMDLSTIKRKLDTGQYQEPWQYVDDVWLMFNNAWLYNRKTSRVYKFCSKLAEVFEQEIDPVMQSLG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 85 | Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) | 6VP0 | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name DGAT1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Retinol O-fatty-acyltransferase; Diglyceride acyltransferase; Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1; DGAT; Acyl-CoA retinol O-fatty-acyltransferase; ARAT; AGRP1; ACAT-related gene product 1 Protein family Membrane-bound acyltransferase family, Sterol o-acyltransferase subfamily Biochemical class Acyltransferase Function Catalyzes the terminal and only committed step in triacylglycerol synthesis by using diacylglycerol and fatty acyl CoA as substrates. In contrast to DGAT2 it is not essential for survival. May be involved in VLDL (very low density lipoprotein) assembly. In liver, plays a role in esterifying exogenous fatty acids to glycerol. Functions as the major acyl-CoA retinol acyltransferase (ARAT) in the skin, where it acts to maintain retinoid homeostasis and prevent retinoid toxicity leading to skin and hair disorders. Related diseases Diarrhea 7, protein-losing enteropathy type (DIAR7) [MIM:615863]: A life-threatening disease characterized by severe, intractable, watery diarrhea. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23114594, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30237576}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with O75907; PRO_0000045602 [Q99IB8] EC number EC 2.3.1.20 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acyltransferase; Disease variant; Endoplasmic reticulum; Lipid metabolism; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C Molecular weight (Da) 47494.5 Length 404 Aromaticity 0.17 Instability index 37.65 Isoelectric point 9.51 Charge (pH=7) 15.57 3D Binding mode Sequence WELRCHRLQDSLFSSDSGFSNYRGILNWCVVMLILSNARLFLENLIKYGILVDPIQVVSLFLKDPYSWPAPCLVIAANVFAVAAFQVEKRLAVGALTEQAGLLLHVANLATILCFPAAVVLLVESITPVGSLLALMAHTILFLKLFSYRDVNSWCRRARAKHTVSYPDNLTYRDLYYFLFAPTLCYELNFPRSPRIRKRFLLRRILEMLFFTQLQVGLIQQWMVPTIQNSMKPFKDMDYSRIIERLLKLAVPNHLIWLIFFYWLFHSCLNAVAELMQFGDREFYRDWWNSESVTYFWQNWNIPVHKWCIRHFYKPMLRRGSSKWMARTGVFLASAFFHEYLVSVPLRMFRLWAFTGMMAQIPLAWFVGRFFQGNYGNAAVWLSLIIGQPIAVLMYVHDYYVLNY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 86 | Dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation regulated kinase 2 (DYRK2) | 6HDR | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name DYRK2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, MNB/DYRK subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Functions in part via its role in ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal protein degradation. Functions downstream of ATM and phosphorylates p53/TP53 at 'Ser-46', and thereby contributes to the induction of apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Phosphorylates NFATC1, and thereby inhibits its accumulation in the nucleus and its transcription factor activity. Phosphorylates EIF2B5 at 'Ser-544', enabling its subsequent phosphorylation and inhibition by GSK3B. Likewise, phosphorylation of NFATC1, CRMP2/DPYSL2 and CRMP4/DPYSL3 promotes their subsequent phosphorylation by GSK3B. May play a general role in the priming of GSK3 substrates. Inactivates GYS1 by phosphorylation at 'Ser-641', and potentially also a second phosphorylation site, thus regulating glycogen synthesis. Mediates EDVP E3 ligase complex formation and is required for the phosphorylation and subsequent degradation of KATNA1. Phosphorylates TERT at 'Ser-457', promoting TERT ubiquitination by the EDVP complex. Phosphorylates SIAH2, and thereby increases its ubiquitin ligase activity. Promotes the proteasomal degradation of MYC and JUN, and thereby regulates progress through the mitotic cell cycle and cell proliferation. Promotes proteasomal degradation of GLI2 and GLI3, and thereby plays a role in smoothened and sonic hedgehog signaling. Plays a role in cytoskeleton organization and neurite outgrowth via its phosphorylation of DCX and DPYSL2. Phosphorylates CRMP2/DPYSL2, CRMP4/DPYSL3, DCX, EIF2B5, EIF4EBP1, GLI2, GLI3, GYS1, JUN, MDM2, MYC, NFATC1, p53/TP53, TAU/MAPT and KATNA1. Can phosphorylate histone H1, histone H3 and histone H2B (in vitro). Can phosphorylate CARHSP1 (in vitro). Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in the regulation of the mitotic cell cycle, cell proliferation, apoptosis, organization of the cytoskeleton and neurite outgrowth. Related diseases Bone marrow failure and diabetes mellitus syndrome (BMFDMS) [MIM:620044]: A form of bone marrow failure syndrome, a heterogeneous group of life-threatening disorders characterized by hematopoietic defects in association with a range of variable extra-hematopoietic manifestations. BMFDMS is an autosomal recessive form characterized by various degrees of bone marrow failure, ranging from dyserythropoiesis to bone marrow aplasia, with onset in infancy or early childhood, and non-autoimmune insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus appearing in the first or second decades. Many patients show pigmentary skin abnormalities and short stature. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28073829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35611808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35931051}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9NR20; Q13422; Q9BQD3; Q9BRK4; P23497; O43379; P62258; Q96C00 EC number EC 2.7.12.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Apoptosis; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Kinase; Magnesium; Manganese; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation; Ubl conjugation pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 46422.1 Length 407 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 44.91 Isoelectric point 9.09 Charge (pH=7) 12.37 3D Binding mode Sequence HHHSXGVDLGTENLYFQSMGKVKATPMTPEQAMKQYMQKLTAFEHHEIFSYPEIYFLGLNAKKRQGMTGGPNNGGYDDDQGSYVQVPHDHVAYRYEVLKVIGKGSFGQVVKAYDHKVHQHVALKMVRNEKRFHRQAAEEIRILEHLRKQDKDNTMNVIHMLENFTFRNHICMTFELLSMNLYELIKKNKFQGFSLPLVRKFAHSILQCLDALHKNRIIHCDLKPENILLKQQGRSGIKVIDFGSSCYEHQRVYTXIQSRFYRAPEVILGARYGMPIDMWSLGCILAELLTGYPLLPGEDEGDQLACMIELLGMPSQKLLDASKRAKNFVSXKGYPRYCTVTTLSDVVLNGGRSRRGKLRGPPESREWGNALKGCDDPLFLDFLKQCLEWDPAVRMTPGQALRHPWLR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 87 | Cyclin A2 (CCNA2) | 2C5V | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name CCNA2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Cyclin-A2; Cyclin-A; Cyclin A; CCNA Protein family Cyclin family, Cyclin AB subfamily Biochemical class NA Function Functions through the formation of specific serine/threonine protein kinase holoenzyme complexes with the cyclin-dependent protein kinases CDK1 or CDK2. The cyclin subunit confers the substrate specificity of these complexes and differentially interacts with and activates CDK1 and CDK2 throughout the cell cycle. Cyclin which controls both the G1/S and the G2/M transition phases of the cell cycle. Related diseases Crouzon syndrome (CS) [MIM:123500]: An autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by craniosynostosis, hypertelorism, exophthalmos and external strabismus, parrot-beaked nose, short upper lip, hypoplastic maxilla, and a relative mandibular prognathism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10574673, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11173845, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11380921, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11781872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17803937, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7581378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7655462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7874170, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7987400, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8528214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8644708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8946174, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8956050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9152842, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9521581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9677057, ECO:0000269|Ref.10}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Jackson-Weiss syndrome (JWS) [MIM:123150]: An autosomal dominant craniosynostosis syndrome characterized by craniofacial abnormalities and abnormality of the feet: broad great toes with medial deviation and tarsal-metatarsal coalescence. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7874170, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8528214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8644708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9385368, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9677057}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Apert syndrome (APRS) [MIM:101200]: A syndrome characterized by facio-cranio-synostosis, osseous and membranous syndactyly of the four extremities, and midface hypoplasia. The craniosynostosis is bicoronal and results in acrocephaly of brachysphenocephalic type. Syndactyly of the fingers and toes may be total (mitten hands and sock feet) or partial affecting the second, third, and fourth digits. Intellectual deficit is frequent and often severe, usually being associated with cerebral malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11390973, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11781872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15190072, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7668257, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7719344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9002682, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452027, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9677057}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Pfeiffer syndrome (PS) [MIM:101600]: A syndrome characterized by the association of craniosynostosis, broad and deviated thumbs and big toes, and partial syndactyly of the fingers and toes. Three subtypes are known: mild autosomal dominant form (type 1); cloverleaf skull, elbow ankylosis, early death, sporadic (type 2); craniosynostosis, early demise, sporadic (type 3). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394936, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10945669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11173845, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11781872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16844695, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17803937, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7719333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7719345, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8644708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9002682, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9150725, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9693549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9719378}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Beare-Stevenson cutis gyrata syndrome (BSTVS) [MIM:123790]: An autosomal dominant disease characterized by craniofacial anomalies, particularly craniosynostosis, and ear defects, cutis gyrata, acanthosis nigricans, anogenital anomalies, skin tags, and prominent umbilical stump. The skin furrows have a corrugated appearance and are widespread. Cutis gyrata variably affects the scalp, forehead, face, preauricular area, neck, trunk, hands, and feet. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12000365, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8696350}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Familial scaphocephaly syndrome (FSPC) [MIM:609579]: An autosomal dominant craniosynostosis syndrome characterized by scaphocephaly, macrocephaly, hypertelorism, maxillary retrusion, and mild intellectual disability. Scaphocephaly is the most common of the craniosynostosis conditions and is characterized by a long, narrow head. It is due to premature fusion of the sagittal suture or from external deformation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16061565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17803937}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lacrimo-auriculo-dento-digital syndrome 1 (LADD1) [MIM:149730]: A form of lacrimo-auriculo-dento-digital syndrome, an autosomal dominant disease characterized by aplastic/hypoplastic lacrimal and salivary glands and ducts, cup-shaped ears, hearing loss, hypodontia and enamel hypoplasia, and distal limb segments anomalies. In addition to these cardinal features, facial dysmorphism, malformations of the kidney and respiratory system and abnormal genitalia have been reported. Craniosynostosis and severe syndactyly are not observed. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16501574, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18056630}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Antley-Bixler syndrome, without genital anomalies or disordered steroidogenesis (ABS2) [MIM:207410]: A rare syndrome characterized by craniosynostosis, radiohumeral synostosis present from the perinatal period, midface hypoplasia, choanal stenosis or atresia, femoral bowing and multiple joint contractures. Arachnodactyly and/or camptodactyly have also been reported. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10633130}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Bent bone dysplasia syndrome 1 (BBDS1) [MIM:614592]: A perinatal lethal skeletal dysplasia characterized by poor mineralization of the calvarium, craniosynostosis, dysmorphic facial features, prenatal teeth, hypoplastic pubis and clavicles, osteopenia, and bent long bones. Dysmorphic facial features included low-set ears, hypertelorism, midface hypoplasia, prematurely erupted fetal teeth, and micrognathia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22387015}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Saethre-Chotzen syndrome (SCS) [MIM:101400]: A craniosynostosis syndrome characterized by coronal synostosis, brachycephaly, low frontal hairline, facial asymmetry, hypertelorism, broad halluces, and clinodactyly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9585583}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08463; DB08285; DB07137; DB07852; DB08527; DB08355; DB06948; DB08248; DB08309; DB02915; DB02091; DB08178; DB08182; DB08241; DB06844; DB08219; DB07533; DB07538; DB07534; DB07539; DB08572; DB07688; DB07471; DB07203; DB08233; DB02407; DB02833; DB08218; DB06944; DB07562; DB07164; DB07126; DB08694 Interacts with P31749; P24941; P38936; P46527; Q96PU4; P03129; P03070 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cell cycle; Cell division; Cyclin; Cytoplasm; Host-virus interaction; Mitosis; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33659.8 Length 296 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 32.75 Isoelectric point 8.6 Charge (pH=7) 3.38 3D Binding mode Sequence MENFQKVEKIGEGTYGVVYKARNKLTGEVVALKKIRLDTETEGVPSTAIREISLLKELNHPNIVKLLDVIHTENKLYLVFEFLHQDLKKFMDASALTGIPLPLIKSYLFQLLQGLAFCHSHRVLHRDLKPQNLLINTEGAIKLADFGLARAFGVPVRTYTHEVVTLWYRAPEILLGCKYYSTAVDIWSLGCIFAEMVTRRALFPGDSEIDQLFRIFRTLGTPDEVVWPGVTSMPDYKPSFPKWARQDFSKVVPPLDEDGRSLLSQMLHYDPNKRISAKAALAHPFFQDVTKPVPHL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 88 | Zinc finger protein Helios (IKZF2) | 7LPS | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name IKZF2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Ikaros family zinc finger protein 2 Protein family Ikaros C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family Biochemical class NA Function Associates with Ikaros at centromeric heterochromatin. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 25, with amelogenesis imperfecta (DEE25) [MIM:615905]: An autosomal recessive disease characterized by subclinical seizures appearing in the first days of life, evolving to severe epileptic disease. Affected individuals have profound or severe delayed development with lack of speech, and most patients do not acquire the ability to sit. Additional variable features include axial hypotonia, peripheral hypertonia, and abnormal involuntary movements such as dystonia and choreoathetosis. Dental abnormalities, including delayed eruption, hypodontia, tooth hypoplasia, yellow discoloration, thin enamel, and enamel chipping are observed in most patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24995870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26384929, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30054523}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P29972; P56545; P56545-3; Q17RB8; P09022; Q8N8B7-2 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Activator; Alternative splicing; DNA-binding; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B,C Molecular weight (Da) 47006.6 Length 410 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 44.28 Isoelectric point 7.23 Charge (pH=7) 0.69 3D Binding mode Sequence INFDTSLPTSHTYLGADMEEFHGRTLHDDDSCQVIPVLPQVMMILIPGQTLPLQLFHPQEVSMVRNLIQKDRTFAVLAYSNVQEREAQFGTTAEIYAYREEQDFGIEIVKVKAIGRQRFKVLELRTQSDGIQQAKVQILPECVLPSTMSAVQLESLNKCQIFPCSYKWWQKYQKRKFHCANLTSWPRWLYSLYDAETLMDRIKKQLREWDENLKDDSLPSNPIDFSYRVAACLPIDDVLRIQLLKIGSAIQRLRCELDIMNKCTSLCCKQCQETEITTKNEIFSLSLCGPMAAYVNPHGYVHETLTVYKACNLNLIGRPSTEHSWFPGYAWTVAQCKICASHIGWKFTATKKDMSPQKFWGLTRSALLPTIPDTEDEISPDGERPFHCNQCGASFTQKGNLLRHIKLHSG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 89 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor beta-2 (CHRNB2) | 6CNJ | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNB2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor beta2; Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor beta 2-subunit protein; CHRNB2; Beta-2 nAChR; Alpha-4/beta-2 nicotinic receptor Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Beta-2/CHRNB2 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane permeable to sodiun ions. Related diseases Epilepsy, nocturnal frontal lobe, 3 (ENFL3) [MIM:605375]: An autosomal dominant focal epilepsy characterized by nocturnal seizures with hyperkinetic automatisms and poorly organized stereotyped movements. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11062464, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11104662}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00572; DB00237; DB00565; DB09028; DB01245; DB00514; DB07720; DB00898; DB00753; DB00657; DB00333; DB00184; DB00981; DB05458; DB05855; DB05740; DB00747; DB00202; DB01273 Interacts with P43681-1; P30532 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Epilepsy; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 84601.2 Length 728 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 39.72 Isoelectric point 5.86 Charge (pH=7) -9.84 3D Binding mode Sequence ETRAHAEERLLKKLFSGYNKWSRPVANISDVVLVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWVKQEWHDYKLRWDPADYENVTSIRIPSELIWRPDIVLYNNADGDFAVTHLTKAHLFHDGRVQWTPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCTMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLVNMHSRVDQLDFWESGEWVIVDAVGTYNTRKYECCAEIYPDITYAFVIRRLPLFYTINLIIPCLLISCLTVLVFYLPSECGEKITLCISVLLSLTVFLLLITEIIPSTSLVIPLIGEYLLFTMIFVTLSIVITVFVLNVHHRSPRTHTMPTWVRRVFLDIVPRLLLMKRFERSVKEDWKYVAMVIDRIFLWMFIIVCLLGTVGLFLPPWDTEERLVEHLLDPSRYNKLIRPATNGSELVTVQLMVSLAQLISVHEREQIMTTNVWLTQEWEDYRLTWKPEEFDNMKKVRLPSKHIWLPDVVLYNNADGMYEVSFYSNAVVSYDGSIFWLPPAIYKSACKIEVKHFPFDQQNCTMKFRSWTYDRTEIDLVLKSEVASLDDFTPSGEWDIVALPGRRNENPDDSTYVDITYDFIIRRKPLFYTINLIIPCVLITSLAILVFYLPSDCGEKMTLCISVLLALTVFLLLISKIVPPTSLDVPLVGKYLMFTMVLVTFSIVTSVCVLNVHHRSPTTHTMAPWVKVVFLEKLPALLFMQQSVSEDWKYVAMVIDRLFLWIFVFVCVFGTIGMF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 90 | Hyperpolarization cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1 (HCN1) | 6UQF | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name HCN1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1; Brain cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1; BCNG1; BCNG-1 Protein family Potassium channel HCN family Biochemical class Voltage-gated ion channel Function Contributes to the native pacemaker currents in heart (If) and in neurons (Ih). May mediate responses to sour stimuli. Hyperpolarization-activated ion channel exhibiting weak selectivity for potassium over sodium ions. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 24 (DEE24) [MIM:615871]: A disease characterized by early-onset seizures, intellectual disability of varying degrees, and behavioral disturbances or autistic features in most individuals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24747641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27864847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 10 (GEFSP10) [MIM:618482]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder with incomplete penetrance, characterized by variable types of seizures including absence, tonic-clonic, febrile, focal, and eyelid myoclonia. Some patients have normal neurologic development. Others have mild-to-moderate intellectual disability or autism spectrum disorder. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29936235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30351409}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9UKA4; Q8IVW6; P01024; Q06787; Q9Y3Q4; P22626; Q16352; P27448; P09874; Q9Y5H9; P11216; Q9C0C4; P78362; Q96PV0; Q4ACU6-1 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; cAMP; cAMP-binding; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Epilepsy; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Potassium; Potassium channel; Potassium transport; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Sodium; Sodium channel; Sodium transport; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Voltage-gated channel Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 61946.7 Length 531 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 38.45 Isoelectric point 7.94 Charge (pH=7) 2.42 3D Binding mode Sequence MQRQFTSMLQPGVNKFSLRMFGSQKAVEKEQERVKTAGFWIIHPYSDFRFYWDLIMLIMMVGNLVIIPVGITFFTEQTTTPWIIFNVASDTVCLLDLIMNFRTGTVNEDSSEIILDPKVIKMNYLKSWFVVDFISSIPVDYIFLIVERALRIVRFTKILCLLRLLRLSRLIRYIHQWEEIFHMTYDLASAVVRIFNLIGMMLLLCHWDGCLQFLVPLLQDFPPDCWVSLNEMVNDSWGKQYSYALFKAMSHMLCIGYGAQAPVSMSDLWITMLSMIVGATCYAMFVGHATALIQSLDSSRRQYQEKYKQVEQYMSFHKLPADMRQKIHDYYEHRYQGKIFDEENILNELNDPLREEIVNFNCRKLVATMPLFANADPNFVTAMLSKLRFEVFQPGDYIIREGAVGKKMYFIQHGVAGVITKSSKEMKLTDGSYFGEICLLTKGRRTASVRADTYCRLYSLSVDNFNEVLEEYPMMRRAFETVAIDRLDRIGKKNSILLQKFQKDLNTGVFNNQENEILKQIVKHDREMVQA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 91 | Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 (HMGCS2) | 2WYA | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name HMGCS2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms HMGCS2; HMG-CoAsynthase; 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A synthase 2 Protein family Thiolase-like superfamily, HMG-CoA synthase family Biochemical class Acyltransferase Function This enzyme condenses acetyl-CoA with acetoacetyl-CoA to form HMG-CoA, which is the substrate for HMG-CoA reductase. Related diseases 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase-2 deficiency (HMGCS2D) [MIM:605911]: A metabolic disorder characterized by severe hypoketotic hypoglycemia, encephalopathy, and hepatomegaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11228257, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11479731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12647205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16601895, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23751782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25511235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29597274}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 2.3.3.10 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cholesterol biosynthesis; Cholesterol metabolism; Disease variant; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Mitochondrion; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Steroid biosynthesis; Steroid metabolism; Sterol biosynthesis; Sterol metabolism; Transferase; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,D Molecular weight (Da) 102499 Length 920 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 33.48 Isoelectric point 6.72 Charge (pH=7) -1.41 3D Binding mode Sequence SMPKDVGILALEVYFPAQYVDQTDLEKYNNVEAGKYTVGLGQTRMGFCSVQEDINSLCLTVVQRLMERIQLPWDSVGRLEVGTETIIDKSKAVKTVLMELFQDSGNTDIEGIDTTNACYGGTASLFNAANWMESSSWDGRYAMVVCGDIAVYPSGNARPTGGAGAVAMLIGPKAPLALERGLRGTHMENVYDFYKPNLASEYPIVDGKLSIQCYLRALDRCYTSYRKKIQNQWKQAGSDRPFTLDDLQYMIFHTPFCKMVQKSLARLMFNDFLSASSDTQTSLYKGLEAFGGLKLEDTYTNKDLDKALLKASQDMFDKKTKASLYLSTHNGNMYTSSLYGCLASLLSHHSAQELAGSRIGAFSYGSGLAASFFSFRVSQDAAPGSPLDKLVSSTSDLPKRLASRKCVSPEEFTEIMNQREQFYHKVNFSPPGDTNSLFPGTWYLERVDEQHRRKYARRPVSMPKDVGILALEVYFPAQYVDQTDLEKYNNVEAGKYTVGLGQTRMGFCSVQEDINSLCLTVVQRLMERIQLPWDSVGRLEVGTETIIDKSKAVKTVLMELFQDSGNTDIEGIDTTNACYGGTASLFNAANWMESSSWDGRYAMVVCGDIAVYPSGNARPTGGAGAVAMLIGPKAPLALERGLRGTHMENVYDFYKPNLASEYPIVDGKLSIQCYLRALDRCYTSYRKKIQNQWKQAGSDRPFTLDDLQYMIFHTPFCKMVQKSLARLMFNDFLSASSDTQTSLYKGLEAFGGLKLEDTYTNKDLDKALLKASQDMFDKKTKASLYLSTHNGNMYTSSLYGCLASLLSHHSAQELAGSRIGAFSYGSGLAASFFSFRVSQDAAPGSPLDKLVSSTSDLPKRLASRKCVSPEEFTEIMNQREQFYHKVNFSPPGDTNSLFPGTWYLERVDEQHRRKYARRPV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 92 | Aggrecanase (ADAMTS5) | 3HY7 | 5.70 | |
Target general information Gen name ADAMTS5 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Aggrecanase-2; ADMP-2; ADAMTS5; ADAMTS-5; ADAM-TS5; ADAM-TS 5; ADAM-TS 11; A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondinmotifs 5 Protein family NA Biochemical class Peptidase Function Cleaves aggrecan, a cartilage proteoglycan, and may be involved in its turnover. May play an important role in the destruction of aggrecan in arthritic diseases. May play a role in proteolytic processing mostly during the peri-implantation period. Related diseases Mucopolysaccharidosis 1H (MPS1H) [MIM:607014]: A severe form of mucopolysaccharidosis type 1, a rare lysosomal storage disease characterized by progressive physical deterioration with urinary excretion of dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate. Patients with MPS1H usually present, within the first year of life, a combination of hepatosplenomegaly, skeletal deformities, corneal clouding and severe intellectual disability. Obstructive airways disease, respiratory infection and cardiac complications usually result in death before 10 years of age. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10466419, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10735634, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12559846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1301941, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15300847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19396826, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21394825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24036510, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31194252, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7550232, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7550242, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7951228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8019563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8328452, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8401515, ECO:0000269|Ref.20}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Mucopolysaccharidosis 1H/S (MPS1H/S) [MIM:607015]: A form of mucopolysaccharidosis type 1, a rare lysosomal storage disease characterized by progressive physical deterioration with urinary excretion of dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate. MPS1H/S represents an intermediate phenotype of the MPS1 clinical spectrum. It is characterized by relatively little neurological involvement, but most of the somatic symptoms described for severe MPS1 develop in the early to mid-teens, causing considerable loss of mobility. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10466419, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10735634, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12559846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15300847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21394825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7550232, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7550242, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8401515}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Mucopolysaccharidosis 1S (MPS1S) [MIM:607016]: A mild form of mucopolysaccharidosis type 1, a rare lysosomal storage disease characterized by progressive physical deterioration with urinary excretion of dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate. Patients with MPS1S may have little or no neurological involvement, normal stature and life span, but present development of joints stiffness, mild hepatosplenomegaly, aortic valve disease and corneal clouding. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12559846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15300847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19396826, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21394825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25256405, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7550232, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7550242, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8213840}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06837; DB03880; DB06945 Interacts with P13608 EC number EC 3.4.24.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cleavage on pair of basic residues; Disulfide bond; Extracellular matrix; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Zinc; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23997.8 Length 217 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 46.68 Isoelectric point 5.82 Charge (pH=7) -8.36 3D Binding mode Sequence SRARQVELLLVADASMARKYGRGLQHYLLTLASIANRLYSHASIENHIRLAVVKVVVLGDKDKSLEVSKNAATTLKNFCKWQHQHNQLGDDHEEHYDAAILFTREDLCGHHSCDTLGMADVGTICSPERSCAVIEDDGLHAAFTVAHEIGHLLGLSHDDSKFCEETFGSTEDKRLMSSILTSIDASKPWSKCTSATITEFLDDGHGNCLLDLPRKQI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 93 | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1 (CHRM1) | 5CXV | 5.69 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRM1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms M1 receptor Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subfamily, CHRM1 sub-subfamily Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Primary transducing effect is Pi turnover. The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Related diseases Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-beta deficiency (PDHBD) [MIM:614111]: An enzymatic defect causing primary lactic acidosis in children. It is associated with a broad clinical spectrum ranging from fatal lactic acidosis in the newborn to chronic neurologic dysfunction with structural abnormalities in the central nervous system without systemic acidosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15138885}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03128; DB08897; DB05752; DB00321; DB00543; DB00517; DB04365; DB01238; DB14185; DB00572; DB00245; DB00767; DB01019; DB00810; DB09128; DB00835; DB00354; DB00411; DB00185; DB00477; DB01239; DB00568; DB00771; DB00363; DB00907; DB00979; DB00942; DB00434; DB00496; DB01151; DB00804; DB01231; DB00280; DB09167; DB01142; DB00366; DB01175; DB09194; DB06702; DB01148; DB00875; DB00483; DB00986; DB06787; DB11181; DB00725; DB00424; DB09262; DB00458; DB00332; DB01221; DB00408; DB00934; DB04843; DB00454; DB06709; DB00940; DB01403; DB00462; DB00340; DB01233; DB00805; DB01618; DB05152; DB00622; DB05766; DB00540; DB00334; DB01062; DB00383; DB00219; DB00715; DB01085; DB00670; DB06153; DB00387; DB00392; DB00420; DB01069; DB00782; DB00777; DB12278; DB11156; DB01224; DB11855; DB13581; DB00747; DB01591; DB02010; DB00342; DB11235; DB01409; DB01036; DB00193; DB00505; DB00508; DB00376; DB09089; DB00726; DB00809; DB00209; DB09076; DB09185; DB00246 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Synapse; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33337 Length 291 Aromaticity 0.15 Instability index 26.7 Isoelectric point 8.75 Charge (pH=7) 5.76 3D Binding mode Sequence KGPWQVAFIGITTGLLSLATVTGNLLVLISFKVNTELKTVNNYFLLSLACADLIIGTFSMNLYTTYLLMGHWALGTLACDLWLALDYVASQASVMNLLLISFDRYFSVTRPLSYRAKRTPRRAALMIGLAWLVSFVLWAPAILFWQYLVGERTVLAGQCYIQFLSQPIITFGTAMAAFYLPVTVMCTLYWRIYRETENRFSLVKEKKAARTLSAILLAFILTWTPYNIMVLVSTFCKDCVPETLWELGYWLCYVNSTINPMCYALCNKAFRDTFRLLLLCRWDKDYKDDDD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 94 | Thymidine kinase | 1E2K | 5.69 | |
Target general information Gen name TK Organism Human herpesvirus 1 (strain 17) (HHV-1) (Human herpes simplex virus 1) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms UL23 Protein family Herpesviridae thymidine kinase family Biochemical class Transferase Function ATP binding.Thymidine kinase activity. Related diseases Atransferrinemia (ATRAF) [MIM:209300]: A rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by abnormal synthesis of transferrin leading to iron overload and microcytic hypochromic anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11110675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15466165}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 2.7.1.21 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ATP-binding; DNA synthesis; Early protein; Kinase; Nucleotide-binding; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 67808.8 Length 624 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 43.94 Isoelectric point 6.1 Charge (pH=7) -7.02 3D Binding mode Sequence MPTLLRVYIDGPHGMGKTTTTQLLVADDIVYVPEPMTYWRVLGASETIANIYTTQHRLDQGEISAGDAAVVMTSAQITMGMPYAVTDAVLAPHIGGEAGPPPALTLIFDRHPIAALLCYPAARYLMGSMTPQAVLAFVALIPPTLPGTNIVLGALPEDRHIDRLAKRQRPGERLDLAMLAAIRRVYGLLANTVRYLQCGGSWREDWGQLSGTGPRPHIGDTLFTLFRAPELLAPNGDLYNVFAWALDVLAKRLRSMHVFILDYDQSPAGCRDALLQLTSGMVQTHVTTPGSIPTICDLARTFAREMGEMPTLLRVYIDGPHGMGKTTTTQLLVALGSRDDIVYVPEPMTYWRVLGASETIANIYTTQHRLDQGEISAGDAAVVMTSAQITMGMPYAVTDAVLAPHIGGEAHAPPPALTLIFDRHPIAALLCYPAARYLMGSMTPQAVLAFVALIPPTLPGTNIVLGALPEDRHIDRLAKRERLDLAMLAAIRRVYGLLANTVRYLQCGGSWREDWGQLSGTAVPQSNAGPRPHIGDTLFTLFRAPELLAPNGDLYNVFAWALDVLAKRLRSMHVFILDYDQSPAGCRDALLQLTSGMVQTHVTTPGSIPTICDLARTFAREMGE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 95 | Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C1 | 1MRQ | 5.69 | |
Target general information Gen name AKR1C1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms DDH1;DDH Protein family Aldo/keto reductase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function 17-alpha,20-alpha-dihydroxypregn-4-en-3-one dehydrogenase activity.Alditol:NADP+ 1-oxidoreductase activity.Aldo-keto reductase (NADP) activity.Androsterone dehydrogenase (B-specific) activity.Bile acid binding.Carboxylic acid binding.Indanol dehydrogenase activity.Ketosteroid monooxygenase activity.Oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, quinone or similar compound as acceptor.Phenanthrene 9,10-monooxygenase activity.Trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol dehydrogenase activity. Related diseases Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) [MIM:135100]: A rare autosomal dominant connective tissue disorder resulting in skeletal malformations and progressive extraskeletal ossification. Heterotopic ossification begins in childhood and can be induced by trauma or may occur without warning. Bone formation is episodic and progressive, leading to a debilitating ankylosis of all major joints of the axial and appendicular skeleton, rendering movement impossible. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16642017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19085907, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19330033}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04674; DB00945; DB07768; DB01039; DB07931; DB06077; DB00959; DB00461; DB00157; DB03467; DB03461; DB00776; DB12612; DB00936 Interacts with P51857; P26045; Q7Z699 EC number 1.1.1.-; 1.1.1.112; 1.1.1.149; 1.1.1.209; 1.1.1.210; 1.1.1.357; 1.1.1.51; 1.1.1.53; 1.1.1.62; 1.3.1.20 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Lipid metabolism; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 36784.9 Length 323 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 42.07 Isoelectric point 8.06 Charge (pH=7) 2.42 3D Binding mode Sequence QDSKYQCVKLNDGHFMPVLGFGTYAPAEVPKSKALEATKLAIEAGFRHIDSAHLYNNEEQVGLAIRSKIADGSVKREDIFYTSKLWCNSHRPELVRPALERSLKNLQLDYVDLYLIHFPVSVKPGEEVIPKDENGKILFDTVDLCATWEAVEKCKDAGLAKSIGVSNFNRRQLEMILNKPGLKYKPVCNQVECHPYFNQRKLLDFCKSKDIVLVAYSALGSHREEPWVDPNSPVLLEDPVLCALAKKHKRTPALIALRYQLQRGVVVLAKSYNEQRIRQNVQVFEFQLTSEEMKAIDGLNRNVRYLTLDIFAGPPNYPFSDEY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 96 | Glycolipid transfer protein | 3RZN | 5.69 | |
Target general information Gen name GLTP Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family GLTP family Biochemical class Lipid transport Function Glycolipid binding.Glycolipid transporter activity.Identical protein binding.Intermembrane lipid transfer activity.Lipid binding. Related diseases Brugada syndrome 7 (BRGDA7) [MIM:613120]: A tachyarrhythmia characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs, the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20031595}. The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Atrial fibrillation, familial, 16 (ATFB16) [MIM:613120]: A familial form of atrial fibrillation, a common sustained cardiac rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity and ineffective atrial contraction promoting blood stasis in the atria and reduces ventricular filling. It can result in palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20558140, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21051419}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03600; DB04465; DB03017; DB03203 Interacts with Q96DZ9; Q9NZD2 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Lipid transport; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23534.1 Length 206 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 36.45 Isoelectric point 7.08 Charge (pH=7) 0.1 3D Binding mode Sequence LAEHLLKPLPADKQIETGPFLEAVSHLPPFFDCLGSPVFTPIKADISGNITKIKAVYDTNPAKFRTLQNILEVEKEMYGAEWPKVGATLALMWLKRGLRFIQVFLQSICDGERDENHPNLIRVNATKAYEMALKKYHGWIVQKIFQAALYAAPYKSDFLKALSKGQNVTEEECLEKIRLFLVNYTATIDVIYEMYTQMNAELNYKV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 97 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 8 (CDK8) | 3RGF | 5.69 | |
Target general information Gen name CDK8 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein kinase K35; Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit CDK8; Mediator complex subunit CDK8; Cell division protein kinase 8 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CDC2/CDKX subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Mediator functions as a bridge to convey information from gene-specific regulatory proteins to the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Mediator is recruited to promoters by direct interactions with regulatory proteins and serves as a scaffold for the assembly of a functional preinitiation complex with RNA polymerase II and the general transcription factors. Phosphorylates the CTD (C-terminal domain) of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAp II), which may inhibit the formation of a transcription initiation complex. Phosphorylates CCNH leading to down-regulation of the TFIIH complex and transcriptional repression. Recruited through interaction with MAML1 to hyperphosphorylate the intracellular domain of NOTCH, leading to its degradation. Component of the Mediator complex, a coactivator involved in regulated gene transcription of nearly all RNA polymerase II-dependent genes. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder with hypotonia and behavioral abnormalities (IDDHBA) [MIM:618748]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder with onset in infancy. IDDHBA is characterized by hypotonia, global developmental delay, learning disability, and behavioral abnormalities, such as autistic features and attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Additional variable features may include non-specific facial dysmorphism, congenital heart defects, ocular anomalies, and poor feeding. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30905399}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03496 Interacts with P24863; Q01094; P02489; Q14204; Q92876 EC number EC 2.7.11.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Autism spectrum disorder; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Kinase; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repressor; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 37655.2 Length 321 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.04 Isoelectric point 8.56 Charge (pH=7) 5.13 3D Binding mode Sequence DKMDYDFKVKLSSERERVEDLFEYEGCKVGHVYKAKRKDGKDDKDYALKQIEGTGISMSACREIALLRELKHPNVISLQKVFLSHADRKVWLLFDYAEHDLWHIIKFHRASKLPRGMVKSLLYQILDGIHYLHANWVLHRDLKPANILVMGEGPERGRVKIADMGFARVTFWYRAPELLLGARHYTKAIDIWAIGCIFAELLTSEPIFHCRQNPYHHDQLDRIFNVMGFPADKDWEDIKKMPEHSTLMKDFRRNTYTNCSLIKYMEKHKVKPDSKAFHLLQKLLTMDPIKRITSEQAMQDPYFLEDPLPTSDVFAGCQIPY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 98 | Cerebron E3 ubiquitin ligase complex (CRL4-CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase) | 4CI1 | 5.69 | |
Target general information Gen name CUL4A/CUL4B-DDB1-CRBN Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NA Protein family Cullin family Biochemical class NA Function NA Related diseases Orotic aciduria 1 (ORAC1) [MIM:258900]: A disorder of pyrimidine metabolism resulting in megaloblastic anemia and orotic acid crystalluria that is frequently associated with some degree of physical and intellectual disability. A minority of cases have additional features, particularly congenital malformations and immune deficiencies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9042911}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P54253; Q86VP6; Q16531; Q92466; P08238; O94888; P55072 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Biological rhythms; DNA damage; DNA repair; Host-virus interaction; Isopeptide bond; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation; Ubl conjugation pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B Molecular weight (Da) 42669.7 Length 368 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 44.94 Isoelectric point 8.72 Charge (pH=7) 6.58 3D Binding mode Sequence MINFDTSLPTSHMYLGSDMEEFHGRTLHDDDSCQVIPVLPHVMVMLIPGQTLPLQLFHPQEVSMVRNLIQKDRTFAVLAYSNVREREAHFGTTAEIYAYREEQEYGIETVKVKAIGRQRFKVLEIRTQSDGIQQAKVQILPERVLPSTMSAVQLQSLSRRHIRAFRQWWQKYQKRKFHCASLTSWPPWLYSLYDAETLMERVKRQLHEWDENLKDESLPTNPIDFSYRVAACLPIDDALRIQLLKIGSAIQRLRELDIMNKTSLCCKQCQDTEITTKNEIFSLSLCGPMAAYVNPHGYIHETLTVYKACNLNLSGRPSTEHSWFPGYAWTIAQCRICGNHMGWKFTATKKDMSPQKFWGLTRSALLPR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 99 | Pseudomonas Transcriptional activator protein LasR (Pseudo LasR) | 3IX3 | 5.69 | |
Target general information Gen name Pseudo LasR Organism Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NA Protein family Autoinducer-regulated transcriptional regulatory protein family Biochemical class NA Function Transcriptional activator of elastase structural gene (LasB). Binds to the PAI autoinducer. Related diseases Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1A (IGHD1A) [MIM:262400]: An autosomal recessive, severe deficiency of growth hormone leading to dwarfism. Patients often develop antibodies to administered growth hormone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8364549}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1B (IGHD1B) [MIM:612781]: An autosomal recessive deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Patients have low but detectable levels of growth hormone, significantly retarded bone age, and a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655557}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Kowarski syndrome (KWKS) [MIM:262650]: A syndrome clinically characterized by short stature associated with bioinactive growth hormone, normal or slightly increased growth hormone secretion, pathologically low insulin-like growth factor 1 levels, and normal catch-up growth on growth hormone replacement therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17519310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8552145, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9276733}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 2 (IGHD2) [MIM:173100]: An autosomal dominant deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Clinical severity is variable. Patients have a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11502836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9152628}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08324 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; DNA-binding; Quorum sensing; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 18305.5 Length 163 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.52 Isoelectric point 5.19 Charge (pH=7) -6.78 3D Binding mode Sequence FLELERSSGKLEWSAILQKMASDLGFSKILFGLLPKDSQDYENAFIVGNYPAAWREHYDRAGYARVDPTVSHCTQSVLPIFWEPSIYQTRKQHEFFEEASAAGLVYGLTMPLHGARGELGALSLSVEAENRAEANRFMESVLPTLWMLKDYALQSGAGLAFEH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 100 | TWIK-related acid-sensitive potassium channel 1 (TASK1) | 6RV3 | 5.69 | |
Target general information Gen name KCNK3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Two pore potassium channel KT3.1; Two pore K(+) channel KT3.1; TWIK-related acid-sensitive K(+) channel 1; Acid-sensitive potassium channel protein TASK-1 Protein family Two pore domain potassium channel (TC 1.A.1.8) family Biochemical class NA Function pH-dependent, voltage-insensitive, background potassium channel protein. Rectification direction results from potassium ion concentration on either side of the membrane. Acts as an outward rectifier when external potassium concentration is low. When external potassium concentration is high, current is inward. Related diseases Pulmonary hypertension, primary, 4 (PPH4) [MIM:615344]: A rare disorder characterized by plexiform lesions of proliferating endothelial cells in pulmonary arterioles. The lesions lead to elevated pulmonary arterial pression, right ventricular failure, and death. The disease can occur from infancy throughout life and it has a mean age at onset of 36 years. Penetrance is reduced. Although familial pulmonary hypertension is rare, cases secondary to known etiologies are more common and include those associated with the appetite-suppressant drugs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23883380}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Defects in this gene may cause developmental delay with sleep apnea (DDSA). A disorder characterized by developmental neurologic, skeletal and respiratory anomalies including microcephaly, arthrogryposis, scoliosis, cleft palate, facial dysmorphology, bilateral talipes, feeding difficulties and central and/or obstructive sleep apnea. Malformations are detected as early as 21 weeks post gestation. Severely affected patients require ongoing treatment with nocturnal O2 or pressure-controlled ventilation. The disease is associated with recurrent de novo gain of function variants. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:36195757}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00561; DB01159 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Membrane; Metal-binding; Potassium; Potassium channel; Potassium transport; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Sodium; Sodium channel; Sodium transport; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 58522.5 Length 517 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 39.16 Isoelectric point 8.4 Charge (pH=7) 4.32 3D Binding mode Sequence MKRQNVRTLALIVCTFTYLLVGAAVFDALESEPELIERQRLELRQQELRARYNLSQGGYEELERVVLRLKPHKAGVQWRFAGSFYFAITVITTIGYGHAAPSTDGGKVFCMFYALLGIPLTLVMFQSLGERINTLVRYLLHRAKKGLGADVSMANMVLIGFFSCISTLCIGAAAFSHYEHWTFFQAYYYCFITLTTIGFGDYVALQKDQALQTQPQYVAFSFVYILTGLTVIGAFLNLVVLRFMTMNAEDEKRDAENLMKRQNVRTLALIVCTFTYLLVGAAVFDALESEPELIERQRLELRQQELRARYNLSQGGYEELERVVLRLKPHKAGVQWRFAGSFYFAITVITTIGYGHAAPSTDGGKVFCMFYALLGIPLTLVMFQSLGERINTLVRYLLHRAKKGLGMADVSMANMVLIGFFSCISTLCIGAAAFSHYEHWTFFQAYYYCFITLTTIGFGDYVALQKDQALQTQPQYVAFSFVYILTGLTVIGAFLNLVVLRFMTMNAEDEKRDAENL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||