Job Results:
Ligand
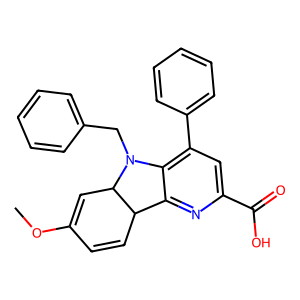
Structure
Job ID
195891f0cd6db7cda8666dbe4295d47d
Job name
NA
Time
2025-09-26 08:49:45
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 81 | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) | 5FY9 | 7.65 | |
Target general information Gen name KDM5B Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Retinoblastomabinding protein 2 homolog 1; Retinoblastoma-binding protein 2 homolog 1; RBP2H1; RBP2-H1; RBBP2H1; PLU1; PLU-1; Lysinespecific demethylase 5B; Jumonji/ARID domaincontaining protein 1B; J Protein family JARID1 histone demethylase family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Does not demethylate histone H3 'Lys-9' or H3 'Lys-27'. Demethylates trimethylated, dimethylated and monomethylated H3 'Lys-4'. Acts as a transcriptional corepressor for FOXG1B and PAX9. Favors the proliferation of breast cancer cells by repressing tumor suppressor genes such as BRCA1 and HOXA5. In contrast, may act as a tumor suppressor for melanoma. Represses the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer-mediated transcriptional activation of the core clock component PER2. Histone demethylase that demethylates 'Lys-4' of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 65 (MRT65) [MIM:618109]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRT65 patients have moderate to severe intellectual disability, developmental delay, and facial dysmorphism. Camptodactyly is present in some patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29276005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30409806}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P49711 EC number EC 1.14.11.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Biological rhythms; Chromatin regulator; Dioxygenase; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Iron; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 53020.6 Length 460 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 44.23 Isoelectric point 5.28 Charge (pH=7) -18.32 3D Binding mode Sequence SMFLPPPECPVFEPSWEEFADPFAFIHKIRPIAEQTGICKVRPPPDWQPPFACDVDKLHFTPRIQRLNELEAQTRVKLGGGGARDYTLRTFGEMADAFKSDYFNMPVHMVPTELVEKEFWRLVSTIEEDVTVEYGADIASKEFGSGFPVRDIKLSPEEEEYLDSGWNLNNMPVMEQSVLAHITADICGMKLPWLYVGMCFSSFCWHIEDHWSYSINYLHWGEPKTWYGVPGYAAEQLENVMKKLAPELFVSQPDLLHQLVTIMNPNTLMTHEVPVYRTNQCAGEFVITFPRAYHSGFNQGFNFAEAVNFCTVDWLPLGRQCVEHYRLLHRYCVFSHDEMICKMASKADVLDVVVASTVQKDMAIMIEDEKALRETVRKLGVIDSERMDFELLPDDERQCVKCKTTCFMSAISCSCKPGLLVCLHHVKELCSCPPYKYKLRYRYTLDDLYPMMNALKLRAE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 82 | GABA(A) receptor gamma-2 (GABRG2) | 6X3X | 7.64 | |
Target general information Gen name GABRG2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit gamma-2; GABA(A) receptor subunit gamma-2 Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor (TC 1.A.9.5) subfamily, GABRG2 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function Plays an important role in the formation of functional inhibitory GABAergic synapses in addition to mediating synaptic inhibition as a GABA-gated ion channel. The gamma2 subunit is necessary but not sufficient for a rapid formation of active synaptic contacts and the synaptogenic effect of this subunit is influenced by the type of alpha and beta subunits present in the receptor pentamer. The alpha1/beta2/gamma2 receptor and the alpha1/beta3/gamma2 receptor exhibit synaptogenic activity. The alpha2/beta2/gamma2 receptor exhibits synatogenic activity whereas the alpha2/beta3/gamma2 receptor shows very little or no synaptogenic activity. Functions also as histamine receptor and mediates cellular responses to histamine. Ligand-gated chloride channel which is a component of the heteropentameric receptor for GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 74 (DEE74) [MIM:618396]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of severe early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE74 is an autosomal dominant form with onset in the first year of life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27864268}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Epilepsy, childhood absence 2 (ECA2) [MIM:607681]: A subtype of idiopathic generalized epilepsy characterized by an onset at age 6-7 years, frequent absence seizures (several per day) and bilateral, synchronous, symmetric 3-Hz spike waves on EEG. Tonic-clonic seizures often develop in adolescence. Some individuals manifest febrile seizures. Absence seizures may either remit or persist into adulthood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11326275}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Febrile seizures, familial, 8 (FEB8) [MIM:607681]: Seizures associated with febrile episodes in childhood without any evidence of intracranial infection or defined pathologic or traumatic cause. It is a common condition, affecting 2-5% of children aged 3 months to 5 years. The majority are simple febrile seizures (generally defined as generalized onset, single seizures with a duration of less than 30 minutes). Complex febrile seizures are characterized by focal onset, duration greater than 30 minutes, and/or more than one seizure in a 24 hour period. The likelihood of developing epilepsy following simple febrile seizures is low. Complex febrile seizures are associated with a moderately increased incidence of epilepsy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16924025}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 3 (GEFSP3) [MIM:607681]: A rare autosomal dominant, familial condition with incomplete penetrance and large intrafamilial variability. Patients display febrile seizures persisting sometimes beyond the age of 6 years and/or a variety of afebrile seizure types. This disease combines febrile seizures, generalized seizures often precipitated by fever at age 6 years or more, and partial seizures, with a variable degree of severity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11326274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23708187}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12537; DB00546; DB06579; DB00404; DB00543; DB11901; DB14719; DB11859; DB01558; DB09017; DB00237; DB00241; DB01489; DB00395; DB00475; DB14715; DB01594; DB00349; DB01068; DB00628; DB01559; DB01553; DB01511; DB01189; DB00829; DB13837; DB00228; DB01215; DB00402; DB00189; DB01545; DB09166; DB00292; DB01567; DB01205; DB01544; DB00690; DB05087; DB01381; DB01437; DB00801; DB01159; DB00753; DB01587; DB00555; DB13643; DB00186; DB13872; DB13437; DB00603; DB01043; DB00371; DB00463; DB01028; DB01107; DB15489; DB00683; DB12458; DB01595; DB14028; DB00334; DB00842; DB14672; DB00312; DB00252; DB13335; DB01708; DB01588; DB00794; DB00818; DB01589; DB12404; DB01236; DB09118; DB00306; DB01956; DB00231; DB11582; DB00897; DB00425; DB00909; DB15490 Interacts with P51513; O95166 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Chloride; Chloride channel; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Epilepsy; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Palmitate; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 77460 Length 672 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 35.95 Isoelectric point 8.75 Charge (pH=7) 7.31 3D Binding mode Sequence SNMSLVKETVDRLLKGYDIRLRPDFGGPPVAVGMNIDIASIDMVSEVNMDYTLTMYFQQAWRDKRLSYNVIPLNLTLDNRVADQLWVPDTYFLNDKKSFVHGVTVKNRMIRLHPDGTVLYGLRITTTAACMMDLRRYPLDEQNCTLEIESYGYTTDDIEFYWRGDDNAVTGVTKIELPQFSIVDYKLITKKVVFSTGSYPRLSLSFKLKRNIGYFILQTYMPSILITILSWVSFWINYDASAARVALGITTVLTMTTINTHLRETLPKIPYVKAIDMYLMGCFVFVFMALLEYALVNYIFFSQPARAAAIDRWSRIFFPVVFSFFNIVYWLYYVDNTTVFTRILDRLLDGYDNRLRPGLGERVTEVKTDIFVTSFGPVSDHDMEYTIDVFFRQSWKDERLKFKGPMTVLRLNNLMASKIWTPDTFFHNGKKSVAHNMTMPNKLLRITEDGTLLYTMRLTVRAECPMHLEDFPMDAHACPLKFGSYAYTRAEVVYEWTREPARSVVVAEDGSRLNQYDLLGQTVDSGIVQSSTGEYVVMTTHFHLKRKIGYFVIQTYLPCIMTVILSQVSFWLNRESVPARTVFGVTTVLTMTTLSISARNSLPKVAYATAMDWFIAVCYAFVFSALIEFATVNYFTKSQPARAAKIDRLSRIAFPLLFGIFNLVYWATYLNR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 83 | Thyrotropin receptor (TSHR) | 7XW6 | 7.64 | |
Target general information Gen name TSHR Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Thyroid stimulating hormone receptor; TSHR; TSH-R; TSH receptor Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, FSH/LSH/TSH subfamily Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Receptor for thyrothropin. Plays a central role in controlling thyroid cell metabolism. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylate cyclase. Also acts as a receptor for thyrostimulin (gpa2+gpb5). Related diseases Defects in TSHR are found in patients affected by hyperthyroidism with different etiologies. Somatic, constitutively activating TSHR mutations and/or constitutively activating G(s)alpha mutations have been identified in toxic thyroid nodules (TTNs) that are the predominant cause of hyperthyroidism in iodine deficient areas. These mutations lead to TSH independent activation of the cAMP cascade resulting in thyroid growth and hormone production. TSHR mutations are found in autonomously functioning thyroid nodules (AFTN), toxic multinodular goiter (TMNG) and hyperfunctioning thyroid adenomas (HTA). TMNG encompasses a spectrum of different clinical entities, ranging from a single hyperfunctioning nodule within an enlarged thyroid, to multiple hyperfunctioning areas scattered throughout the gland. HTA are discrete encapsulated neoplasms characterized by TSH-independent autonomous growth, hypersecretion of thyroid hormones, and TSH suppression. Defects in TSHR are also a cause of thyroid neoplasms (papillary and follicular cancers).; DISEASE: Autoantibodies against TSHR are directly responsible for the pathogenesis and hyperthyroidism of Graves disease. Antibody interaction with TSHR results in an uncontrolled receptor stimulation.; DISEASE: Hypothyroidism, congenital, non-goitrous, 1 (CHNG1) [MIM:275200]: A non-autoimmune condition characterized by resistance to thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) leading to increased levels of plasma TSH and low levels of thyroid hormone. It presents variable severity depending on the completeness of the defect. Most patients are euthyroid and asymptomatic, with a normal sized thyroid gland. Only a subset of patients develop hypothyroidism and present a hypoplastic thyroid gland. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10720030, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11095460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11442002, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12050212, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14725684, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15531543, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25978107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7528344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8954020, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9100579, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9185526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9329388}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Familial gestational hyperthyroidism (HTFG) [MIM:603373]: A condition characterized by abnormally high levels of serum thyroid hormones occurring during early pregnancy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9854118}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Hyperthyroidism, non-autoimmune (HTNA) [MIM:609152]: A condition characterized by abnormally high levels of serum thyroid hormones, thyroid hyperplasia, goiter and lack of anti-thyroid antibodies. Typical features of Graves disease such as exophthalmia, myxedema, antibodies anti-TSH receptor and lymphocytic infiltration of the thyroid gland are absent. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10199795, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10852462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11081252, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11127522, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11201847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11517004, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11549687, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15163335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7800007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7920658, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8636266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8964822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9349581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9360555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9398746, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9589634}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00024 Interacts with P30542; Q9NPA3; Q14160; P21579 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Congenital hypothyroidism; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Leucine-rich repeat; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Sulfation; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 63643.2 Length 562 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 33.57 Isoelectric point 8.41 Charge (pH=7) 6.83 3D Binding mode Sequence PCECHQEEDFRVTCKDIQRIPSLPPSTQTLKLIETHLRTIPSHAFSNLPNISRIYVSIDVTLQQLESHSFYNLSKVTHIEIRNTRNLTYIDPDALKELPLLKFLGIFNTGLKMFPDLTKVYSTDIFFILEITDNPYMTSIPVNAFQGLCNETLTLKLYNNGFTSVQGYAFNGTKLDAVYLNKNKYLTVIDKDAFGGVYSGPSLLDVSQTSVTALPSKGLEHLKELIARNTWTLKKLPLSLSFLHLTRADLSYPIHCCAFKNQKEDMVCTPKSDEFNPCEDIMGYKFLRIVVWFVSLLALLGNVFVLLILLTSHYKLNVPRFLMCNLAFADFCMGMYLLLIASVDLYTHSEYYNHAIDWQTGPGCNTAGFFTVFASELSVYTLTVITLERWYAITFAMRLDRKIRLRHACAIMVGGWVCCFLLALLPLVGISSYAKVSICLPMDTETPLALAYIVFVLTLNIVAFVIVCCCYVKIYITVRNPDKDTKIAKRMAVLIFTDFICMAPISFYALSAILNKPLITVSNSKILLVLFYPLNSCANPFLYAIFTKAFQRDVFILLSKFG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 84 | Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM) | 3GR4 | 7.63 | |
Target general information Gen name PKM Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms p58; Tumor M2-PK; Thyroid hormone-binding protein 1; THBP1; Pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme; Pyruvate kinase isozymes M1/M2; Pyruvate kinase PKM; Pyruvate kinase 2/3; PKM2; PK3; PK2; Opa-interacting pr Protein family Pyruvate kinase family Biochemical class Kinase Function Stimulates POU5F1-mediated transcriptional activation. Plays a general role in caspase independent cell death of tumor cells. The ratio between the highly active tetrameric form and nearly inactive dimeric form determines whether glucose carbons are channeled to biosynthetic processes or used for glycolytic ATP production. The transition between the 2 forms contributes to the control of glycolysis and is important for tumor cell proliferation and survival. Promotes in a STAT1-dependent manner, the expression of the immune checkpoint protein CD274 in ARNTL/BMAL1-deficient macrophages. Glycolytic enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to ADP, generating ATP. Related diseases Congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency (CSID) [MIM:222900]: Autosomal recessive intestinal disorder that is clinically characterized by fermentative diarrhea, abdominal pain, and cramps upon ingestion of sugar. The symptoms are the consequence of absent or drastically reduced enzymatic activities of sucrase and isomaltase. The prevalence of CSID is 0.02 % in individuals of European descent and appears to be much higher in Greenland, Alaskan, and Canadian native people. CSID arises due to post-translational perturbations in the intracellular transport, polarized sorting, aberrant processing, and defective function of SI. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10903344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11340066, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14724820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16329100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8609217}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07697; DB07692; DB02726; DB07628; DB00787; DB11638; DB09130; DB08951; DB01733; DB11263; DB00119 Interacts with P49407; P32121; Q96IK1-2; P35222; P53355; P22607; P42858; P04049; Q8N488; Q7Z699; Q9BSI4; Q9UMX0; Q9Y649; Q9WMX2; P35222; P53355; Q9H6Z9; P68431; Q16665; P27361 EC number EC 2.7.1.40 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Allosteric enzyme; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Glycolysis; Hydroxylation; Isopeptide bond; Kinase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Methylation; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Potassium; Proteomics identification; Pyruvate; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation; Transferase; Translation regulation; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 112053 Length 1024 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 27.06 Isoelectric point 7.34 Charge (pH=7) 1.66 3D Binding mode Sequence IQTQQLHAAMADTFLEHMCRLDIDSPPITARNTGIICTIGPASRSVETLKEMIKSGMNVARLNFSHGTHEYHAETIKNVRTATESFASDPILYRPVAVALDTKGPEIRTGLIKGSGTAEVELKKGATLKITLDNAYMEKCDENILWLDYKNICKVVEVGSKIYVDDGLISLQVKQKGADFLVTEVENGGSLGSKKGVNLPGAAVDLPAVSEKDIQDLKFGVEQDVDMVFASFIRKASDVHEVRKVLGEKGKNIKIISKIENHEGVRRFDEILEASDGIMVARGDLGIEIPAEKVFLAQKMMIGRCNRAGKPVICATQMLESMIKKPRPTRAEGSDVANAVLDGADCIMLSGETAKGDYPLEAVRMQHLIAREAEAAIYHLQLFEELRRLAPITSDPTEATAVGAVEASFKCCSGAIIVLTKSGRSAHQVARYRPRAPIIAVTRNPQTARQAHLYRGIFPVLCKDPVQEAWAEDVDLRVNFAMNVGKARGFFKKGDVVIVLTGWRPGSGFTNTMRVVPVPIQTQQLHAAMADTFLEHMCRLDIDSPPITARNTGIICTIGPASRSVETLKEMIKSGMNVARLNFSHGTHEYHAETIKNVRTATESFASDPILYRPVAVALDTKGPEIRTGLIKEVEATLKITLDNAYMEKCDENILWLDYKNICKVVEVGSKIYVDDGLISLQVDFLVTEVENGGSLGSKKGVNLPGAAVDLPAVSEKDIQDLKFGVEQDVDMVFASFIRKASDVHEVRKVLGEKGKNIKIISKIENHEGVRRFDEILEASDGIMVARGDLGIEIPAEKVFLAQKMMIGRCNRAGKPVICATQMLESMIKKPRPTRAEGSDVANAVLDGADCIMLSGETAKGDYPLEAVRMQHLIAREAEAAIYHLQLFEELRRLAPITSDPTEATAVGAVEASFKCCSGAIIVLTKSGRSAHQVARYRPRAPIIAVTRNPQTARQAHLYRGIFPVLCKDPVQEAWAEDVDLRVNFAMNVGKARGFFKKGDVVIVLTGWRPGSGFTNTMRVVPVP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 85 | Nitric-oxide synthase inducible (NOS2) | 3E7G | 7.63 | |
Target general information Gen name NOS2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms iNOS; Peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylase NOS2; Nitric oxide synthase, inducible; NOS2A; NOS type II; Inducible NOS; Inducible NO synthase; Hepatocyte NOS; HEP-NOS Protein family NOS family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Produces nitric oxide (NO) which is a messenger molecule with diverse functions throughout the body. In macrophages, NO mediates tumoricidal and bactericidal actions. Also has nitrosylase activity and mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of cytoplasmic target proteins such PTGS2/COX2 (By similarity). As component of the iNOS-S100A8/9 transnitrosylase complex involved in the selective inflammatory stimulus-dependent S-nitrosylation of GAPDH on 'Cys-247' implicated in regulation of the GAIT complex activity and probably multiple targets including ANXA5, EZR, MSN and VIM. Involved in inflammation, enhances the synthesis of proinflammatory mediators such as IL6 and IL8. Related diseases Cerebellar ataxia, impaired intellectual development, and dysequilibrium syndrome 3 (CAMRQ3) [MIM:613227]: An autosomal recessive, congenital cerebellar ataxia associated with dysarthia, quadrupedal gait and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19461874}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07003; DB07007; DB07011; DB07405; DB08750; DB01997; DB07029; DB07008; DB08214; DB07002; DB01835; DB06879; DB04534; DB03100; DB02207; DB00125; DB00155; DB01234; DB14649; DB11327; DB00997; DB07306; DB07388; DB05252; DB01381; DB03366; DB05214; DB04400; DB09237; DB00244; DB01110; DB01017; DB03144; DB01686; DB03449; DB06916; DB07318; DB07389; DB02044; DB02644; DB05383; DB02234; DB03953; DB02462; DB08814 Interacts with P04406 EC number EC 1.14.13.39 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Calmodulin-binding; Cytoplasm; FAD; Flavoprotein; FMN; Heme; Iron; Metal-binding; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 48633 Length 421 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.5 Isoelectric point 6.75 Charge (pH=7) -1.04 3D Binding mode Sequence RHVRIKNWGSGMTFQDTLHHKAKGILTCRSKSCLGSIMTPKSLTRGPRDKPTPPDELLPQAIEFVNQYYGSFKEAKIEEHLARVEAVTKEIETTGTYQLTGDELIFATKQAWRNAPRCIGRIQWSNLQVFDARSCSTAREMFEHICRHVRYSTNNGNIRSAITVFPQRSDGKHDFRVWNAQLIRYAGYQMPDGSIRGDPANVEFTQLCIDLGWKPKYGRFDVVPLVLQANGRDPELFEIPPDLVLEVAMEHPKYEWFRELELKWYALPAVANMLLEVGGLEFPGCPFNGWYMGTEIGVRDFCDVQRYNILEEVGRRMGLETHKLASLWKDQAVVEINIAVLHSFQKQNVTIMDHHSAAESFMKYMQNEYRSRGGCPADWIWLVPPMSGSITPVFHQEMLNYVLSPFYYYQVEAWKTHVWQD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 86 | Dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation regulated kinase 2 (DYRK2) | 6HDR | 7.63 | |
Target general information Gen name DYRK2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, MNB/DYRK subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Functions in part via its role in ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal protein degradation. Functions downstream of ATM and phosphorylates p53/TP53 at 'Ser-46', and thereby contributes to the induction of apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Phosphorylates NFATC1, and thereby inhibits its accumulation in the nucleus and its transcription factor activity. Phosphorylates EIF2B5 at 'Ser-544', enabling its subsequent phosphorylation and inhibition by GSK3B. Likewise, phosphorylation of NFATC1, CRMP2/DPYSL2 and CRMP4/DPYSL3 promotes their subsequent phosphorylation by GSK3B. May play a general role in the priming of GSK3 substrates. Inactivates GYS1 by phosphorylation at 'Ser-641', and potentially also a second phosphorylation site, thus regulating glycogen synthesis. Mediates EDVP E3 ligase complex formation and is required for the phosphorylation and subsequent degradation of KATNA1. Phosphorylates TERT at 'Ser-457', promoting TERT ubiquitination by the EDVP complex. Phosphorylates SIAH2, and thereby increases its ubiquitin ligase activity. Promotes the proteasomal degradation of MYC and JUN, and thereby regulates progress through the mitotic cell cycle and cell proliferation. Promotes proteasomal degradation of GLI2 and GLI3, and thereby plays a role in smoothened and sonic hedgehog signaling. Plays a role in cytoskeleton organization and neurite outgrowth via its phosphorylation of DCX and DPYSL2. Phosphorylates CRMP2/DPYSL2, CRMP4/DPYSL3, DCX, EIF2B5, EIF4EBP1, GLI2, GLI3, GYS1, JUN, MDM2, MYC, NFATC1, p53/TP53, TAU/MAPT and KATNA1. Can phosphorylate histone H1, histone H3 and histone H2B (in vitro). Can phosphorylate CARHSP1 (in vitro). Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in the regulation of the mitotic cell cycle, cell proliferation, apoptosis, organization of the cytoskeleton and neurite outgrowth. Related diseases Bone marrow failure and diabetes mellitus syndrome (BMFDMS) [MIM:620044]: A form of bone marrow failure syndrome, a heterogeneous group of life-threatening disorders characterized by hematopoietic defects in association with a range of variable extra-hematopoietic manifestations. BMFDMS is an autosomal recessive form characterized by various degrees of bone marrow failure, ranging from dyserythropoiesis to bone marrow aplasia, with onset in infancy or early childhood, and non-autoimmune insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus appearing in the first or second decades. Many patients show pigmentary skin abnormalities and short stature. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28073829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35611808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35931051}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9NR20; Q13422; Q9BQD3; Q9BRK4; P23497; O43379; P62258; Q96C00 EC number EC 2.7.12.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Apoptosis; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Kinase; Magnesium; Manganese; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation; Ubl conjugation pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 46422.1 Length 407 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 44.91 Isoelectric point 9.09 Charge (pH=7) 12.37 3D Binding mode Sequence HHHSXGVDLGTENLYFQSMGKVKATPMTPEQAMKQYMQKLTAFEHHEIFSYPEIYFLGLNAKKRQGMTGGPNNGGYDDDQGSYVQVPHDHVAYRYEVLKVIGKGSFGQVVKAYDHKVHQHVALKMVRNEKRFHRQAAEEIRILEHLRKQDKDNTMNVIHMLENFTFRNHICMTFELLSMNLYELIKKNKFQGFSLPLVRKFAHSILQCLDALHKNRIIHCDLKPENILLKQQGRSGIKVIDFGSSCYEHQRVYTXIQSRFYRAPEVILGARYGMPIDMWSLGCILAELLTGYPLLPGEDEGDQLACMIELLGMPSQKLLDASKRAKNFVSXKGYPRYCTVTTLSDVVLNGGRSRRGKLRGPPESREWGNALKGCDDPLFLDFLKQCLEWDPAVRMTPGQALRHPWLR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 87 | Matrix metalloproteinase-10 (MMP-10) | 1Q3A | 7.62 | |
Target general information Gen name MMP10 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Transin-2; Stromelysin-2; STMY2; SL-2 Protein family Peptidase M10A family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Activates procollagenase. Can degrade fibronectin, gelatins of type I, III, IV, and V; weakly collagens III, IV, and V. Related diseases Orthostatic hypotension 1 (ORTHYP1) [MIM:223360]: A form of orthostatic hypotension due to congenital dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a finding defined as a 20-mm Hg decrease in systolic pressure or a 10-mm Hg decrease in diastolic pressure occurring 3 minutes after a person has risen from supine to standing. Symptoms include dizziness, blurred vision, and sometimes syncope. ORTHYP1 is an autosomal recessive condition apparent from infancy or early childhood and characterized by low plasma and urinary levels of norepinephrine and epinephrine, and episodic hypoglycemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11857564}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00786; DB08271 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.4.24.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Calcium; Collagen degradation; Disulfide bond; Extracellular matrix; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Zinc; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 52822 Length 471 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 21.13 Isoelectric point 4.83 Charge (pH=7) -35.32 3D Binding mode Sequence MPKWRKTHLTYRIVNYTPDLPRDAVDSAIEKALKVWEEVTPLTFSRLYEGEADIMISFAVKEHGDNYSFDGPGHSLAHAYPPGPGLYGDIHFDDDEKWTEDASGTNLFLVAAHELGHSLGLFHSANTEALMYPLYNSLAQFRLSQDDVNGIQSLYGPKWRKTHLTYRIVNYTPDLPRDAVDSAIEKALKVWEEVTPLTFSRLYEGEADIMISFAVKEHGDNYSFDGPGHSLAHAYPPGPGLYGDIHFDDDEKWTEDASGTNLFLVAAHELGHSLGLFHSANTEALMYPLYNSLAQFRLSQDDVNGIQSLYGGMPKWRKTHLTYRIVNYTPDLPRDAVDSAIEKALKVWEEVTPLTFSRLYEGEADIMISFAVKEHGDNYSFDGPGHSLAHAYPPGPGLYGDIHFDDDEKWTEDASGTNLFLVAAHELGHSLGLFHSANTEALMYPLYNSFTELAQFRLSQDDVNGIQSLYG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 88 | Glycine oxidase | 1RYI | 7.62 | |
Target general information Gen name thiO Organism Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms goxB;yjbR;BSU11670 Protein family DAO family, ThiO subfamily Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function FAD binding.Glycine oxidase activity.Oxidoreductase activity. Related diseases Hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia (HVLI) [MIM:618850]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by highly elevated plasma concentrations of valine and leucine/isoleucine. Affected individuals suffer from headache and mild memory impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. A patient with hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia was identified as compound heterozygote for Gln-170 (inherited from his father) and Lys-264 (inherited from his mother), both variants reduced the catalytic activity of the enzyme. After treatment with vitamin B6, a precursor of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, a BCAT2 cofactor, the blood levels of branched chain amino acids, especially valine, were decreased and brain lesions were improved. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02713; DB03147 Interacts with NA EC number 1.4.3.19 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; FAD; Flavoprotein; Herbicide resistance; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome; Thiamine biosynthesis Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 40395.8 Length 364 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 36.07 Isoelectric point 6.02 Charge (pH=7) -6.35 3D Binding mode Sequence MKRHYEAVVIGGGIIGSAIAYYLAKENKNTALFESGTMGGRTTSAAAGMLGAHAECEERDAFFDFAMHSQRLYKGLGEELYALSGVDIRQHNGGMFKLAFSEEDVLQLRQMDDLDSVSWYSKEEVLEKEPYASGDIFGASFIQDDVHVEPYFVCKAYVKAAKMLGAEIFEHTPVLHVERDGEALFIKTPSGDVWANHVVVASGVWSGMFFKQLGLNNAFLPVKGECLSVWNDDIPLTKTLYHDHCYIVPRKSGRLVVGATMKPGDWSETPDLGGLESVMKKAKTMLPAIQNMKVDRFWAGLRPGTKDGKPYIGRHPEDSRILFAAGHFRNGILLAPATGALISDLIMNKEVNQDWLHAFRIDRK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 89 | TWIK-related acid-sensitive potassium channel 1 (TASK1) | 6RV3 | 7.62 | |
Target general information Gen name KCNK3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Two pore potassium channel KT3.1; Two pore K(+) channel KT3.1; TWIK-related acid-sensitive K(+) channel 1; Acid-sensitive potassium channel protein TASK-1 Protein family Two pore domain potassium channel (TC 1.A.1.8) family Biochemical class NA Function pH-dependent, voltage-insensitive, background potassium channel protein. Rectification direction results from potassium ion concentration on either side of the membrane. Acts as an outward rectifier when external potassium concentration is low. When external potassium concentration is high, current is inward. Related diseases Pulmonary hypertension, primary, 4 (PPH4) [MIM:615344]: A rare disorder characterized by plexiform lesions of proliferating endothelial cells in pulmonary arterioles. The lesions lead to elevated pulmonary arterial pression, right ventricular failure, and death. The disease can occur from infancy throughout life and it has a mean age at onset of 36 years. Penetrance is reduced. Although familial pulmonary hypertension is rare, cases secondary to known etiologies are more common and include those associated with the appetite-suppressant drugs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23883380}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Defects in this gene may cause developmental delay with sleep apnea (DDSA). A disorder characterized by developmental neurologic, skeletal and respiratory anomalies including microcephaly, arthrogryposis, scoliosis, cleft palate, facial dysmorphology, bilateral talipes, feeding difficulties and central and/or obstructive sleep apnea. Malformations are detected as early as 21 weeks post gestation. Severely affected patients require ongoing treatment with nocturnal O2 or pressure-controlled ventilation. The disease is associated with recurrent de novo gain of function variants. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:36195757}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00561; DB01159 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Membrane; Metal-binding; Potassium; Potassium channel; Potassium transport; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Sodium; Sodium channel; Sodium transport; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 58522.5 Length 517 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 39.16 Isoelectric point 8.4 Charge (pH=7) 4.32 3D Binding mode Sequence MKRQNVRTLALIVCTFTYLLVGAAVFDALESEPELIERQRLELRQQELRARYNLSQGGYEELERVVLRLKPHKAGVQWRFAGSFYFAITVITTIGYGHAAPSTDGGKVFCMFYALLGIPLTLVMFQSLGERINTLVRYLLHRAKKGLGADVSMANMVLIGFFSCISTLCIGAAAFSHYEHWTFFQAYYYCFITLTTIGFGDYVALQKDQALQTQPQYVAFSFVYILTGLTVIGAFLNLVVLRFMTMNAEDEKRDAENLMKRQNVRTLALIVCTFTYLLVGAAVFDALESEPELIERQRLELRQQELRARYNLSQGGYEELERVVLRLKPHKAGVQWRFAGSFYFAITVITTIGYGHAAPSTDGGKVFCMFYALLGIPLTLVMFQSLGERINTLVRYLLHRAKKGLGMADVSMANMVLIGFFSCISTLCIGAAAFSHYEHWTFFQAYYYCFITLTTIGFGDYVALQKDQALQTQPQYVAFSFVYILTGLTVIGAFLNLVVLRFMTMNAEDEKRDAENL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 90 | Cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2) | 6PT0 | 7.62 | |
Target general information Gen name CNR2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hCB2; Cannabinoid CB2 receptor; CX5; CB2B; CB2A; CB-2 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function May function in inflammatory response, nociceptive transmission and bone homeostasis. Heterotrimeric G protein-coupled receptor for endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol mediating inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Related diseases Factor V deficiency (FA5D) [MIM:227400]: A blood coagulation disorder leading to a hemorrhagic diathesis known as parahemophilia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10942390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12393490}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thrombophilia due to activated protein C resistance (THPH2) [MIM:188055]: A hemostatic disorder due to defective degradation of factor V by activated protein C. It is characterized by a poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C resulting in tendency to thrombosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10391209, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10942390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11435304, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11858490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14617013, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14695241, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16710414, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8164741, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9454742}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Budd-Chiari syndrome (BDCHS) [MIM:600880]: A syndrome caused by obstruction of hepatic venous outflow involving either the hepatic veins or the terminal segment of the inferior vena cava. Obstructions are generally caused by thrombosis and lead to hepatic congestion and ischemic necrosis. Clinical manifestations observed in the majority of patients include hepatomegaly, right upper quadrant pain and abdominal ascites. Budd-Chiari syndrome is associated with a combination of disease states including primary myeloproliferative syndromes and thrombophilia due to factor V Leiden, protein C deficiency and antithrombin III deficiency. Budd-Chiari syndrome is a rare but typical complication in patients with polycythemia vera. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9245936}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Ischemic stroke (ISCHSTR) [MIM:601367]: A stroke is an acute neurologic event leading to death of neural tissue of the brain and resulting in loss of motor, sensory and/or cognitive function. Ischemic strokes, resulting from vascular occlusion, is considered to be a highly complex disease consisting of a group of heterogeneous disorders with multiple genetic and environmental risk factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15534175}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Pregnancy loss, recurrent, 1 (RPRGL1) [MIM:614389]: A common complication of pregnancy, resulting in spontaneous abortion before the fetus has reached viability. The term includes all miscarriages from the time of conception until 24 weeks of gestation. Recurrent pregnancy loss is defined as 3 or more consecutive spontaneous abortions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11018168}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09061; DB00470; DB06202; DB14009; DB00486; DB14011; DB02955; DB16321; DB11755 Interacts with Q9UKJ8; Q15848; Q9NRZ5; P13236; P21964; Q14802-3; Q8N387; Q8IXM6; I3L0A0; Q96AA3; Q9Y6D0; Q6ICL7; Q9NP94; Q13501; Q96HH6; Q969S6; Q9NWH2; Q9H2L4; Q8N2M4; Q6ZT21; Q5TGU0; Q9Y548; Q9BSR8; Q96EC8 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Cell projection; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Inflammatory response; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 32999.2 Length 298 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 30.98 Isoelectric point 9.49 Charge (pH=7) 14.35 3D Binding mode Sequence MKDYMILSGPQKTAVAVLCTLLGLLSALENVAVLYLILSSHQLRRKPSYLFIGSLAGADFLASVVFACSFVNFHVFHGVDSKAVFLLKIGSVTMTFTASVGSLLLTAIDRYLCLRYPPSYKALLTRGRALVTLGIMWVLSALVSYLPLMGWTCCPRPCSELFPLIPNDYLLSWLLFIAFLFSGIIYTYGHVLWKAHQHVASLSGHQDRQVPGMARMRLDVRLAKTLGLVLAVLLICWFPVLALMAHSLATTLSDQVKKAFAFCSMLCLINSMVNPVIYALRSGEIRSSAHHCLAHWKK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 91 | Trypanosoma Trypanothione reductase (Trypano TPR) | 2WBA | 7.62 | |
Target general information Gen name Trypano TPR Organism Trypanosoma brucei brucei Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms TRYR; TPR; Parasite-specific trypanothione reductase; N(1),N(8)-bis(glutathionyl)spermidine reductase Protein family Class-I pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductase family Biochemical class Sulfur donor oxidoreductase Function Trypanothione is the parasite analog of glutathione; this enzyme is the equivalent of glutathione reductase. Related diseases Immunodeficiency 57 with autoinflammation (IMD57) [MIM:618108]: An autosomal recessive primary immunodeficiency characterized by lymphopenia and recurrent viral, bacterial, and fungal infections. Patients exhibit early-onset inflammatory bowel disease involving the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract, and develop progressive polyarthritis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30026316}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. RIPK1-deficient immune cells from IMD57 patients have impaired proinflammatory signaling leading to dysregulated cytokine secretion and are prone to necroptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30026316}.; DISEASE: Autoinflammation with episodic fever and lymphadenopathy (AIEFL) [MIM:618852]: An autosomal dominant immunologic disorder characterized by early onset of recurrent episodes of unexplained fever, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and increased levels of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in patient serum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31827280, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31827281}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.8.1.12 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Disulfide bond; FAD; Flavoprotein; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Redox-active center Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 105578 Length 978 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 33.76 Isoelectric point 6.25 Charge (pH=7) -6.81 3D Binding mode Sequence SKAFDLVVIGAGSGGLEAGWNAATLYGKRVAVVDVQTSHGPPFYAALGGTCVNVGCVPKKLMVTGAQYMDHLRESAGFGWEFDGSSVKANWKKLIAAKNEAVLDINKSYEGMFNDTEGLDFFLGWGSLESKNVVVVRETADPKSAVKERLQADHILLATGSWPQMPAIPGIEHCISSNEAFYLPEPPRRVLTVGGGFISVEFAGIFNAYKPPGGKVTLCYRNNLILRGFDETIREEVTKQLTANGIEIMTNENPAKVSLNTDGSKHVTFESGKTLDVDVVMMAIGRIPRTNDLQLGNVGVKLTPKGGVQVDEFSRTNVPNIYAIGDITDRLMLTPVAINEGAALVDTVFGNKPRKTDHTRVASAVFSIPPIGTCGLIEEVAAKEFEKVAVYMSSFTPLMHNISGSKYKKFVAKIVTNHSDGTVLGVHLLGDGAPEIIQAVGVCLRLNAKISDFYNTIGVHPTSAEELCSMRTPSYYYVKGEKMEKLPDSSKAFDLVVIGAGSGGLEAGWNAATLYGKRVAVVDVQTSHGPPFYAALGGTCVNVGCVPKKLMVTGAQYMDHLRESAGFGWEFDGSSVKANWKKLIAAKNEAVLDINKSYEGMFNDTEGLDFFLGWGSLESKNVVVVRETADPKSAVKERLQADHILLATGSWPQMPAIPGIEHCISSNEAFYLPEPPRRVLTVGGGFISVEFAGIFNAYKPPGGKVTLCYRNNLILRGFDETIREEVTKQLTANGIEIMTNENPAKVSLNTDGSKHVTFESGKTLDVDVVMMAIGRIPRTNDLQLGNVGVKLTPKGGVQVDEFSRTNVPNIYAIGDITDRLMLTPVAINEGAALVDTVFGNKPRKTDHTRVASAVFSIPPIGTCGLIEEVAAKEFEKVAVYMSSFTPLMHNISGSKYKKFVAKIVTNHSDGTVLGVHLLGDGAPEIIQAVGVCLRLNAKISDFYNTIGVHPTSAEELCSMRTPSYYYVKGEKMEKLPDS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 92 | Ecdysone receptor (20-hydroxy-ecdysone receptor) (EcRH) (Ecdysteroid receptor) (Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group H member 1) | 3IXP | 7.61 | |
Target general information Gen name NA Organism Helicoverpa armigera (Cotton bollworm) (Heliothis armigera) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily Biochemical class NA Function NA Related diseases NA Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; DNA-binding; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Receptor; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,D Molecular weight (Da) 52799.1 Length 462 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 51.97 Isoelectric point 8.09 Charge (pH=7) 2.37 3D Binding mode Sequence QELSIERLLEMESLVADPSEEFQFLRVGPDSNVPPKFRAPVSSLCQIGNKQIAALVVWARDIPHFSQLEMEDQILLIKGSWNELLLFAIAWRSMEFLTSPPQLMCLMPGMTLHRNSALQAGVGQIFDRVLSELSLKMRTLRVDQAEYVALKAIILLNPDVKGLKNRQEVEVLREKMFLCLDEYCRRSRSSEEGRFAALLLRLPALRSISLKSFEHLFFFHLVADTSIAGYIRDALRNHAPPIVPPLTANQKSLIARLVYYQEGYEQMPFRQITEMTILTVQLIVEFAKGLPGFSKISQSDQITLLKACSSEVMMLRVARRYDAATDSVLFANNQAYTRDNYRKAGMAYVIEDLLHFCRCMYSMMMDNVHYALLTAIVIFSDRPGLEQPSLVEEIQRYYLNTLRVYILNQNSASPRSAVIFGKILGILTEIRTLGMQNSNMCISLKLKNRKLPPFLEEIWDVA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 93 | Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1 (LSD) | 6W4K | 7.61 | |
Target general information Gen name KDM1A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A; LSD1; KIAA0601; KDM1; Flavin-containing amine oxidase domain-containing protein 2; BRAF35-HDAC complex protein BHC110; AOF2 Protein family Flavin monoamine oxidase family Biochemical class CH-NH(2) donor oxidoreductase Function Histone demethylase that can demethylate both 'Lys-4' (H3K4me) and 'Lys-9' (H3K9me) of histone H3, thereby acting as a coactivator or a corepressor, depending on the context. Acts by oxidizing the substrate by FAD to generate the corresponding imine that is subsequently hydrolyzed. Acts as a corepressor by mediating demethylation of H3K4me, a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional activation. Demethylates both mono- (H3K4me1) and di-methylated (H3K4me2) H3K4me. May play a role in the repression of neuronal genes. Alone, it is unable to demethylate H3K4me on nucleosomes and requires the presence of RCOR1/CoREST to achieve such activity. Also acts as a coactivator of androgen receptor (ANDR)-dependent transcription, by being recruited to ANDR target genes and mediating demethylation of H3K9me, a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional repression. The presence of PRKCB in ANDR-containing complexes, which mediates phosphorylation of 'Thr-6' of histone H3 (H3T6ph), a specific tag that prevents demethylation H3K4me, prevents H3K4me demethylase activity of KDM1A. Demethylates di-methylated 'Lys-370' of p53/TP53 which prevents interaction of p53/TP53 with TP53BP1 and represses p53/TP53-mediated transcriptional activation. Demethylates and stabilizes the DNA methylase DNMT1. Required for gastrulation during embryogenesis. Component of a RCOR/GFI/KDM1A/HDAC complex that suppresses, via histone deacetylase (HDAC) recruitment, a number of genes implicated in multilineage blood cell development. Effector of SNAI1-mediated transcription repression of E-cadherin/CDH1, CDN7 and KRT8. Required for the maintenance of the silenced state of the SNAI1 target genes E-cadherin/CDH1 and CDN7. Related diseases Cleft palate, psychomotor retardation, and distinctive facial features (CPRF) [MIM:616728]: A syndrome characterized by cleft palate, developmental delay, psychomotor retardation, and facial dysmorphic features including a prominent forehead, slightly arched eyebrows, elongated palpebral fissures, a wide nasal bridge, thin lips, and widely spaced teeth. Cleft palate is a congenital fissure of the soft and/or hard palate, due to faulty fusion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23020937, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24838796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26656649}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB16446 Interacts with Q9BYF1; Q99996; Q86SG2; Q13490; Q6P047; Q8TC20-4; Q9BWT7; Q49A88-3; Q99459; Q9BXL8; Q86XR8-3; Q8NHQ1; Q8TAP6; Q12873; P38432; Q96EY1; P26378-2; Q9UPT5-1; Q3B820; Q9H8W3; Q8IZU1; Q9BQS8; O95995; Q96CN9; Q08379; Q9NYA3; Q8NEC7; Q9BX10; Q16695; Q96CS2; O15379; Q9UBX0; Q9NSC5; Q16891; O75564-2; O60341; Q9BVG8-5; Q8TBB5; P19012; Q15323; Q14525; Q92764; Q6A163; Q6A162; Q96JB6; Q9Y250; O95983; P01106; Q3BBV0; Q7Z6G3-2; P35240; Q16236; P46531; Q13133; Q9Y466; Q96F24; A5D8V7; Q8IZS5; Q9BYU1; Q8IZL8; Q99471; Q5T6S3; Q03181; P62191; Q9NS23; P50749; Q86WH2; Q06330; Q9UKL0; Q8IZ40; Q9P2K3-2; Q96P16-3; Q8N6K7; Q9UGK8; Q13435; O15198; O95863; Q96H20; Q8N0Z3; Q96BD6; Q8N4C7; Q8N6V9; Q9UBB9; Q08117-2; Q2M3C6; P45379-11; Q05BL1; Q9BUZ4; Q5W5X9-3; Q8TF42; Q9H9H4; Q9Y3C0; O96006; O15060; Q92618; O14646; Q96KQ7; Q96KQ7-1; P05771-1; Q9UKL0; P17542; P04637; P22091 EC number EC 1.-.-.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Chromosome; Coiled coil; Developmental protein; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; FAD; Flavoprotein; Isopeptide bond; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 72462.2 Length 651 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 32.07 Isoelectric point 7.01 Charge (pH=7) 0.05 3D Binding mode Sequence VEGAAFQSRLPHDRMTSQEAACFPDIISGPQQTQKVFLFIRNRTLQLWLDNPKIQLTFEATLQQLEAPYNSDTVLVHRVHSYLERHGLINFGIYKRIKPLPTKKTGKVIIIGSGVSGLAAARQLQSFGMDVTLLEARDRVGGRVATFRKGNYVADLGAMVVTGLGGNPMMELAKIKQKCPLYEANGQAVPKEKDEMVEQEFNRLLEATSYLSHQLDFNVLNNKPVSLGQALEVVIQLQEKHVKDEQIEHWKKIVKTQEELKELLNKMVNLKEKIKELHQQYKEASEVKPPRDITAEFLVKSKHRDLTALCKEYDELAETQGKLEEKLQELEANPPSDVYLSSRDRQILDWHFANLEFANATPLSTLSLKHWDQDDDFEFTGSHLTVRNGYSCVPVALAEGLDIKLNTAVRQVRYTASGCEVIAVNTRSTSQTFIYKCDAVLCTLPLGVLKQQPPAVQFVPPLPEWKTSAVQRMGFGNLNKVVLCFDRVFWDPSVNLFGHVGSTTASRGELFLFWNLYKAPILLALVAGEAAGIMENISDDVIVGRCLAILKGIFGSSAVPQPKETVVSRWRADPWARGSYSYVAAGSSGNDYDLMAQPITPGPSIPGAPQPIPRLFFAGEHTIRNYPATVHGALLSGLREAGRIADQFLGA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 94 | G-protein coupled bile acid receptor 1 (GPBAR1) | 7CFM | 7.61 | |
Target general information Gen name GPBAR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hGPCR19; hBG37; TGR5; Membrane-type receptor for bile acids; M-BAR; G-protein coupled receptor GPCR19; BG37 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Bile acid-binding induces its internalization, activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and intracellular cAMP production. May be involved in the suppression of macrophage functions by bile acids. Receptor for bile acid. Related diseases Dystonia 34, myoclonic (DYT34) [MIM:619724]: A form of dystonia, a disorder defined by the presence of sustained involuntary muscle contraction, often leading to abnormal postures. DYT34 is an autosomal dominant form characterized by childhood-onset dystonia predominantly affecting hands and neck, with a fast tremor with superimposed myoclonus and, in some individuals, subtle cerebellar signs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32212350}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Neurodevelopmental disorder with or without variable movement or behavioral abnormalities (NEDMAB) [MIM:619725]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by motor and language developmental delay, intellectual disability often associated with early-onset movement disorders comprising cerebellar ataxia and/or extrapyramidal symptoms. Other variable features include autism spectrum disorder or autistic features and epilepsy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33242881}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06777; DB02659; DB03619 Interacts with P38646 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 29418.5 Length 273 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.15 Isoelectric point 9.83 Charge (pH=7) 9.97 3D Binding mode Sequence LSLALASLIITANLLLALGIAWDRRLRSPPAGCFFLSLLLAGLLTGLALPTLPGLWNQSRRGYWSCLLVYLAPNFSFLSLLANLLLVHGERYMAVLRPLQPPGSIRLALLLTWAGPLLFASLPALGWNHWTPGANCSSQAIFPAPYLYLEVYGLLLPAVGAAAFLSVRVLATAHRQLQDICRLERAVCRDEPSALARALTWRQARAQAGAMLLFGLCWGPYVATLLLSVLAYEQRPPLGPGTLLSLLSLGSASAAAVPVAMGLGDQRYTAPWR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 95 | Sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) | 3VZB | 7.61 | |
Target general information Gen name SPHK1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms SPK 1; SPK; SPHK1; SK 1; Acetyltransferase SPHK1 Protein family NA Biochemical class Kinase Function Acts on D-erythro-sphingosine and to a lesser extent sphinganine, but not other lipids, such as D,L-threo-dihydrosphingosine, N,N-dimethylsphingosine, diacylglycerol, ceramide, or phosphatidylinositol. In contrast to proapoptotic SPHK2, has a negative effect on intracellular ceramide levels, enhances cell growth and inhibits apoptosis. Involved in the regulation of inflammatory response and neuroinflammation. Via the product sphingosine 1-phosphate, stimulates TRAF2 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, and promotes activation of NF-kappa-B in response to TNF signaling leading to IL17 secretion. In response to TNF and in parallel to NF-kappa-B activation, negatively regulates RANTES inducion through p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Involved in endocytic membrane trafficking induced by sphingosine, recruited to dilate endosomes, also plays a role on later stages of endosomal maturation and membrane fusion independently of its kinase activity. In Purkinje cells, seems to be also involved in the regulation of autophagosome-lysosome fusion upon VEGFA. Catalyzes the phosphorylation of sphingosine to form sphingosine 1-phosphate (SPP), a lipid mediator with both intra- and extracellular functions. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked, syndromic, Claes-Jensen type (MRXSCJ) [MIM:300534]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRXSCJ patients manifest intellectual disability associated with variable features such as slowly progressive spastic paraplegia, seizures, facial dysmorphism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15586325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16538222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16541399, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17320160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17468742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23356856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25666439}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08868 Interacts with P07858; P68104; Q14192; Q2M3C7; Q9Y4K3; P13473-2; Q9Y371 EC number EC 2.7.1.91 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Calmodulin-binding; Cell membrane; Coated pit; Cytoplasm; Endosome; Kinase; Lipid metabolism; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Synapse; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 39813 Length 360 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 43.79 Isoelectric point 7.34 Charge (pH=7) 0.84 3D Binding mode Sequence AMGSGVLPRPCRVLVLLNPRGGKGKALQLFRSHVQPLLAEAEISFTLMLTERRNHARELVRSEELGRWDALVVMSGDGLMHEVVNGLMERPDWETAIQKPLCSLPAGSGNALAASLNHYAGYEQVTNEDLLTNCTLLLCRRLLSPMNLLSLHTASGLRLFSVLSLAWGFIADVDLESEKYRRLGEMRFTLGTFLRLAALRTYRGRLAYLPVGRVGSKTPASPVVVQQGPVDAHLVPLEEPVPSHWTVVPDEDFVLVLALLHSHLGSEMFAAPMGRCAAGVMHLFYVRAGVSRAMLLRLFLAMEKGRHMEYECPYLVYVPVVAFRLEPKDGKGVFAVDGELMVSEAVQGQVHPNYFWMVSG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 96 | "Periplasmic trehalase (EC 3.2.1.28) (Alpha,alpha-trehalase) (Alpha,alpha-trehalose glucohydrolase) (Tre37A)" | 2JG0 | 7.60 | |
Target general information Gen name treA Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms JW1186;osmA;b1197 Protein family Glycosyl hydrolase 37 family Biochemical class NA Function Provides the cells with the ability to utilize trehalose at high osmolarity by splitting it into glucose molecules that can subsequently be taken up by the phosphotransferase-mediated uptake system. Related diseases SRC kinase activity has been shown to be increased in several tumor tissues and tumor cell lines such as colon carcinoma cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2498394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3093483}.; DISEASE: Thrombocytopenia 6 (THC6) [MIM:616937]: A form of thrombocytopenia, a hematologic disorder defined by a decrease in the number of platelets in circulating blood, resulting in the potential for increased bleeding and decreased ability for clotting. THC6 is an autosomal dominant form. Affected individuals may also have bone abnormalities and an increased risk for myelofibrosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26936507}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 3.2.1.28 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Glycosidase; Hydrolase; Periplasm; Reference proteome; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 57508.9 Length 507 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 48.32 Isoelectric point 5.48 Charge (pH=7) -10.13 3D Binding mode Sequence PQPPDILLGPLFNDVQNAKLFPDQKTFADAVPNSDPLMILADYRMQQNQSGFDLRHFVNVNFTLPKYVPPEGQSLREHIDGLWPVLTRSTENTEKWDSLLPLPEPYVVPGGRFREVYYWDSYFTMLGLAESGHWDKVADMVANFAHEIDTYGHIPNGNRSYYLSRSQPPFFALMVELLAQHEGDAALKQYLPQMQKEYAYWMDGVENLQAGQQEKRVVKLQDGTLLNRYWDDRDTPRPESWVEDIATAKSNPNRPATEIYRDLRSAAASGWDFSSRWMDNPQQLNTLRTTSIVPVDLNSLMFKMEKILARASKAAGDNAMANQYETLANARQKGIEKYLWNDQQGWYADYDLKSHKVRNQLTAAALFPLYVNAAAKDRANKMATATKTHLLQPGGLNTTSVKSGQQWDAPNGWAPLQWVATEGLQNYGQKEVAMDISWHFLTNVQHTYDREKKLVEKYDVSTTGTGGGGGEYPLQDGFGWTNGVTLKMLDLICPKEQPCDNVPATRP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 97 | S-mephenytoin 4-hydroxylase (CYP2C9) | 1R9O | 7.60 | |
Target general information Gen name CYP2C9 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Cytochrome P450 PB-1; Cytochrome P450 MP-8; Cytochrome P450 MP-4; Cytochrome P450 2C9; Cytochrome P-450MP; Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase; CYPIIC9; CYP2C10; (S)-limonene 7-monooxygenase; (S)-limonene 6-mo Protein family Cytochrome P450 family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. This enzyme contributes to the wide pharmacokinetics variability of the metabolism of drugs such as S-warfarin, diclofenac, phenytoin, tolbutamide and losartan. Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. Related diseases MUC1/CA 15-3 is used as a serological clinical marker of breast cancer to monitor response to breast cancer treatment and disease recurrence (PubMed:20816948). Decreased levels over time may be indicative of a positive response to treatment. Conversely, increased levels may indicate disease progression. At an early stage disease, only 21% of patients exhibit high MUC1/CA 15-3 levels, that is why CA 15-3 is not a useful screening test. Most antibodies target the highly immunodominant core peptide domain of 20 amino acid (APDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTS) tandem repeats. Some antibodies recognize glycosylated epitopes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20816948}.; DISEASE: Tubulointerstitial kidney disease, autosomal dominant, 2 (ADTKD2) [MIM:174000]: A form of autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease, a genetically heterogeneous disorder characterized by slowly progressive loss of kidney function, bland urinary sediment, hyperuricemia, absent or mildly increased albuminuria, lack of severe hypertension during the early stages, and normal or small kidneys on ultrasound. Renal histology shows variable abnormalities including interstitial fibrosis with tubular atrophy, microcystic dilatation of the tubules, thickening of tubular basement membranes, medullary cysts, and secondary glomerulosclerotic or glomerulocystic changes with abnormal glomerular tufting. There is significant variability, as well as incomplete penetrance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23396133}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08496; DB14055; DB12001; DB05812; DB14973; DB06736; DB01418; DB00414; DB14033; DB00945; DB15568; DB06594; DB00969; DB12015; DB00404; DB01424; DB01118; DB00321; DB00381; DB00613; DB00701; DB17449; DB01217; DB01435; DB11901; DB06605; DB00673; DB04557; DB01274; DB06413; DB06697; DB12597; DB11586; DB01072; DB01076; DB01117; DB15011; DB06237; DB15233; DB06442; DB11995; DB00972; DB08822; DB05015; DB12319; DB00443; DB01128; DB13746; DB13975; DB00188; DB00559; DB12151; DB01194; DB05541; DB01222; DB00921; DB01156; DB08875; DB00201; DB13919; DB00796; DB09061; DB14737; DB01101; DB08502; DB00564; DB13406; DB06016; DB01136; DB14984; DB00482; DB09063; DB00439; DB00672; DB00501; DB00568; DB00604; DB00515; DB12499; DB04920; DB14025; DB00349; DB00758; DB00257; DB00363; DB04665; DB05219; DB11672; DB14635; DB01176; DB00531; DB08912; DB11963; DB06292; DB00250; DB11943; DB00705; DB00304; DB09213; DB04856; DB00514; DB11994; DB00829; DB00586; DB00266; DB00255; DB08995; DB01075; DB03756; DB00757; DB00843; DB00869; DB09167; DB00590; DB01142; DB00470; DB00476; DB00625; DB06374; DB00216; DB15444; DB13874; DB11718; DB08899; DB00668; DB12147; DB11823; DB00783; DB13952; DB13953; DB13954; DB13955; DB13956; DB00655; DB04574; DB00330; DB00898; DB00977; DB00749; DB01628; DB14766; DB06414; DB04854; DB00949; DB01023; DB00574; DB01039; DB03317; DB15669; DB01195; DB00322; DB00196; DB13136; DB04841; DB01544; DB00544; DB00472; DB00712; DB01095; DB00176; DB00983; DB06717; DB01320; DB11679; DB15149; DB00317; DB01241; DB01645; DB01381; DB08962; DB01120; DB00222; DB01067; DB01251; DB01289; DB01016; DB00986; DB00502; DB01159; DB01355; DB00741; DB00327; DB01050; DB01177; DB01181; DB00619; DB06370; DB00328; DB04818; DB01029; DB11633; DB06636; DB00951; DB11757; DB08820; DB14568; DB09570; DB01221; DB06738; DB01026; DB01009; DB00465; DB06218; DB00448; DB01097; DB09078; DB11560; DB12070; DB01137; DB04725; DB00281; DB11611; DB17083; DB09198; DB06448; DB01601; DB00455; DB06725; DB00678; DB09280; DB01283; DB12474; DB08932; DB09238; DB14921; DB14009; DB00603; DB00784; DB01065; DB00814; DB00170; DB00532; DB01357; DB13675; DB00333; DB00763; DB01028; DB09241; DB00959; DB00916; DB01110; DB06595; DB00834; DB16236; DB01171; DB00745; DB11763; DB00471; DB00486; DB14011; DB00461; DB00788; DB00731; DB00220; DB09048; DB00238; DB00622; DB06803; DB00184; DB01115; DB04868; DB12005; DB00957; DB06174; DB00334; DB14881; DB09080; DB16267; DB00338; DB00904; DB11632; DB04911; DB04938; DB00621; DB00617; DB08439; DB00715; DB00022; DB00850; DB12978; DB03783; DB01174; DB00946; DB00812; DB00252; DB13941; DB04951; DB00554; DB17472; DB08860; DB15822; DB01411; DB06209; DB14631; DB00635; DB00794; DB01032; DB00396; DB01131; DB00420; DB01069; DB09288; DB00818; DB01589; DB04216; DB00908; DB00468; DB01129; DB00980; DB08896; DB16826; DB02709; DB13174; DB00615; DB01045; DB11753; DB01201; DB08864; DB12457; DB14924; DB00503; DB00533; DB00412; DB01098; DB12332; DB11614; DB08877; DB00936; DB00418; DB01037; DB11689; DB06731; DB06739; DB01104; DB00203; DB00641; DB12371; DB06268; DB00398; DB15569; DB12548; DB09118; DB06820; DB00359; DB06150; DB00576; DB01015; DB08798; DB06729; DB00891; DB01138; DB00263; DB00870; DB00675; DB06204; DB06083; DB12095; DB00231; DB00444; DB00469; DB15133; DB00857; DB00624; DB13943; DB13944; DB13946; DB11712; DB01041; DB01154; DB08816; DB00208; DB04831; DB06137; DB00839; DB01124; DB00323; DB01036; DB01685; DB00214; DB05109; DB07615; DB00752; DB00374; DB00755; DB12245; DB12808; DB00347; DB00440; DB00726; DB00197; DB15328; DB14989; DB13609; DB12255; DB00580; DB00313; DB00177; DB00862; DB08881; DB00285; DB00661; DB06652; DB01080; DB08828; DB11739; DB00582; DB09068; DB14975; DB00682; DB04898; DB00549; DB06737; DB00495; DB00744; DB00425; DB01198; DB09120 Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.14.14.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Direct protein sequencing; Endoplasmic reticulum; Heme; Iron; Lipid metabolism; Membrane; Metal-binding; Microsome; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Steroid metabolism; Sterol metabolism Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 51880.7 Length 455 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 41.03 Isoelectric point 8.23 Charge (pH=7) 3.95 3D Binding mode Sequence RGKLPPGPTPLPLQIGIKDISKSLTNLSKVYGPVFTLYFGLKPIVVLHGYEAVKEALIDLGEEFSGRGIFPLAERANRGFGIVFSNGKKWKEIRRFSLMTLRNFGMGKRSIEDRVQEEARCLVEELRKTKASPCDPTFILGCAPCNVICSIIFHKRFDYKDQQFLNLMEKLNENIKILSSPWIPIIDYFPGTHNKLLKNVAFMKSYILEKVKEHQESMDMNNPQDFIDCFLMKMEKEKHNQPSEFTIESLENTAVDLFGAGTETTSTTLRYALLLLLKHPEVTAKVQEEIERVIGRNRSPCMQDRSHMPYTDAVVHEVQRYIDLLPTSLPHAVTCDIKFRNYLIPKGTTILISLTSVLHDNKEFPNPEMFDPHHFLDEGGNFKKSKYFMPFSAGKRICVGEALAGMELFLFLTSILQNFNLKSLVDPKNLDTTPVVNGFASVPPFYQLCFIPIHH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 98 | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase beta (IKKB) | 4KIK | 7.59 | |
Target general information Gen name IKBKB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B inhibitor kinase beta; NFKBIKB; Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta; IkBKB; IKKB; IKK2; IKK-beta; IKK-B; I-kappa-B-kinase beta; I-kappa-B kinase 2 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Ser/Thr protein kinase family, I-kappa-B kinase subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Serine kinase that plays an essential role in the NF-kappa-B signaling pathway which is activated by multiple stimuli such as inflammatory cytokines, bacterial or viral products, DNA damages or other cellular stresses. Acts as part of the canonical IKK complex in the conventional pathway of NF-kappa-B activation. Phosphorylates inhibitors of NF-kappa-B on 2 critical serine residues. These modifications allow polyubiquitination of the inhibitors and subsequent degradation by the proteasome. In turn, free NF-kappa-B is translocated into the nucleus and activates the transcription of hundreds of genes involved in immune response, growth control, or protection against apoptosis. In addition to the NF-kappa-B inhibitors, phosphorylates several other components of the signaling pathway including NEMO/IKBKG, NF-kappa-B subunits RELA and NFKB1, as well as IKK-related kinases TBK1 and IKBKE. IKK-related kinase phosphorylations may prevent the overproduction of inflammatory mediators since they exert a negative regulation on canonical IKKs. Phosphorylates FOXO3, mediating the TNF-dependent inactivation of this pro-apoptotic transcription factor. Also phosphorylates other substrates including NCOA3, BCL10 and IRS1. Within the nucleus, acts as an adapter protein for NFKBIA degradation in UV-induced NF-kappa-B activation. Related diseases Immunodeficiency 15B (IMD15B) [MIM:615592]: An autosomal recessive primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by onset in infancy of life-threatening bacterial, fungal, and viral infections and failure to thrive. Laboratory studies show hypo- or agammaglobulinemia with relatively normal numbers of B and T-cells, and impaired differentiation and activation of immune cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24369075}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Immunodeficiency 15A (IMD15A) [MIM:618204]: An autosomal dominant primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by lymphopenia, inflammation and immune activation of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Patients suffer from recurrent respiratory tract infections, oral candidiasis, and otitis media. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30337470}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06151; DB00945; DB01169; DB00995; DB06521; DB12010; DB00244; DB05183; DB00795 Interacts with O14965; Q16543; O15111; O14920; Q9Y6K9; Q14145; Q99558; O43318; Q9Y6Q9; P19838; P25963; Q15653; P67775; Q04206; P23396; Q9UGK3; Q9UKE5; P04637; Q92574; P03230; P0DTC9; P24772; P03409; Q5D1E7; Q8WXH2 EC number EC 2.7.11.10 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Host-virus interaction; Hydroxylation; Isopeptide bond; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation; SCID; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 32710.2 Length 285 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 43.69 Isoelectric point 6.73 Charge (pH=7) -0.66 3D Binding mode Sequence GAWEMKERLGTGGFGNVIRWHNQETGEQIAIKQCRQELSPRNRERWCLEIQIMRRLTHPNVVAARDVPEGMQNLAPNDLPLLAMEYCQGGDLRKYLNQFENCCGLREGAILTLLSDIASALRYLHENRIIHRDLKPENIVLQQGEQRLIHKIIDLGYAKELXLCTXFVGTLQYLAPELLEQQKYTVTVDYWSFGTLAFECITGFRPFLPNWQPVQWHSKVRQKSEVDIVVSEDLNGTVKFSSSLPYPNNLNSVLAERLEKWLQLMLMWHPRQRGTDPTYGPNGCF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 99 | Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase (TH) | 2XSN | 7.59 | |
Target general information Gen name TH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tyrosine 3-hydroxylase; TH Protein family Biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylase family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Plays an important role in the physiology of adrenergic neurones. Related diseases Segawa syndrome autosomal recessive (ARSEGS) [MIM:605407]: A form of DOPA-responsive dystonia presenting in infancy or early childhood. Dystonia is defined by the presence of sustained involuntary muscle contractions, often leading to abnormal postures. Some cases present with parkinsonian symptoms in infancy. Unlike all other forms of dystonia, it is an eminently treatable condition, due to a favorable response to L-DOPA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10585338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11196107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11246459, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15505183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15747353, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16049992, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17696123, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18058633, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18554280, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19491146, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20056467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20430833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21940685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22264700, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22815559, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23762320, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23939262, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24753243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7814018, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8528210, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8817341, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9613851, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9703425}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: May play a role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease (PD). A genome-wide copy number variation analysis has identified a 34 kilobase deletion over the TH gene in a PD patient but not in any controls. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20809526}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03552; DB04400; DB00765; DB00120; DB00360; DB00135 Interacts with P29762; P61978-2; Q99750; P08651-5; O75928-2; Q9UHX1-2; P0DJD3-2; P07101-3; Q9UJ04; C9J7I0; Q5MCW4 EC number EC 1.14.16.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Catecholamine biosynthesis; Cell projection; Cytoplasm; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Disease variant; Dystonia; Iron; Metal-binding; Monooxygenase; Neurotransmitter biosynthesis; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Parkinson disease; Parkinsonism; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Synapse Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 34997 Length 306 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 42.59 Isoelectric point 5.32 Charge (pH=7) -12.31 3D Binding mode Sequence VPWFPRKVSELDKCHHLVTKFDPDLDLDHPGFSDQVYRQRRKLIAEIAFQYRHGDPIPRVEYTAEEIATWKEVYTTLKGLYATHACGEHLEAFALLERFSGYREDNIPQLEDVSRFLKERTGFQLRPVAGLLSARDFLASLAFRVFQCTQYIRHASSPMHSPEPDCCHELLGHVPMLADRTFAQFSQDIGLASLGASDEEIEKLSTLYWFTVEFGLCKQNGEVKAYGAGLLSSYGELLHCLSEEPEIRAFDPEAAAVQPYQDQTYQSVYFVSESFSDAKDKLRSYASRIQRPFSVKFDPYTLAIDV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 100 | Fatty acid-binding protein, intestinal | 3AKM | 7.59 | |
Target general information Gen name FABP2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms FABPI Protein family Calycin superfamily, Fatty-acid binding protein (FABP) family Biochemical class Transport protein Function Fatty acid binding.Transporter activity. Related diseases Usher syndrome 3B (USH3B) [MIM:614504]: A syndrome characterized by progressive vision and hearing loss during early childhood. Some patients have the so-called 'Charles Bonnet syndrome,' involving decreased visual acuity and vivid visual hallucinations. USH is a genetically heterogeneous condition characterized by the association of retinitis pigmentosa with sensorineural deafness. Age at onset and differences in auditory and vestibular function distinguish Usher syndrome type 1 (USH1), Usher syndrome type 2 (USH2) and Usher syndrome type 3 (USH3). USH3 is characterized by postlingual, progressive hearing loss, variable vestibular dysfunction, and onset of retinitis pigmentosa symptoms, including nyctalopia, constriction of the visual fields, and loss of central visual acuity, usually by the second decade of life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22279524}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, 2W (CMT2W) [MIM:616625]: An autosomal dominant, axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal degeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. CMT2W patients manifest a peripheral neuropathy mainly affecting the lower limbs and resulting in gait difficulties and distal sensory impairment. Most patients also have upper limb involvement. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22930593, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26072516, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29235198}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04557; DB09213; DB00783; DB13952; DB13953; DB13954; DB13955; DB13956; DB01050; DB08231; DB03796; DB01138 Interacts with O95994; Q9NYB0 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Lipid-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 15075.9 Length 131 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 32.01 Isoelectric point 6.88 Charge (pH=7) -0.09 3D Binding mode Sequence AFDSTWKVDRSENYDKFMEKMGVNIVKRKLAAHDNLKLTITQEGNKFTVKESSAFRNIEVVFELGVTFNYNLADGTELRGTWSLEGNKLIGKFKRTDNGNELNTVREIIGDELVQTYVYEGVEAKRIFKKD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||