Job Results:
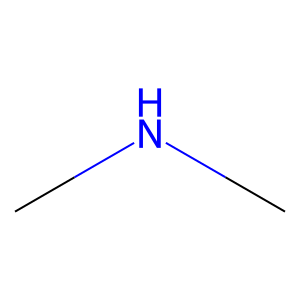
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
c3579b2488a0044c00296f575f551b42
Job name
NA
Time
2025-02-13 15:23:33
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 81 | N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE) | 4ZHT | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name GNE Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms UDPGlcNAc2epimerase/ManAc kinase; GNE; Bifunctional UDPNacetylglucosamine 2epimerase/Nacetylmannosamine kinase Protein family UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase family; ROK (NagC/XylR) family Biochemical class Kinase Function Regulates and initiates biosynthesis of N- acetylneuraminic acid (NeuAc), a precursor of sialic acids. Plays an essential role in early development. Required for normal sialylation in hematopoietic cells. Sialylation is implicated in cell adhesion, signal transduction, tumorigenicity and metastatic behavior of malignant cells. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10334995}. Related diseases Sialuria (SIALURIA) [MIM:269921]: In sialuria, free sialic acid accumulates in the cytoplasm and gram quantities of neuraminic acid are secreted in the urine. The metabolic defect involves lack of feedback inhibition of UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase by CMP-Neu5Ac, resulting in constitutive overproduction of free Neu5Ac. Clinical features include variable degrees of developmental delay, coarse facial features and hepatomegaly. Sialuria inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10330343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10356312, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11326336, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2808337}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Nonaka myopathy (NM) [MIM:605820]: An autosomal recessive myopathy characterized by early adult onset and progressive distal muscle weakness that preferentially affects the anterior tibial muscles, usually sparing the quadriceps femoris. Some individuals may have involvement of the upper limbs or proximal muscles. Muscle biopsy reveals presence of rimmed vacuoles. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11528398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11916006, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12177386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12325084, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12409274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12473753, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12473769, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12473780, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12497639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12811782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12913203, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14707127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15146476, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16503651}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thrombocytopenia 12 with or without myopathy (THC12) [MIM:620757]: A form of thrombocytopenia, a hematologic disorder defined by a decrease in the number of platelets in circulating blood, resulting in the potential for increased bleeding and decreased ability for clotting. THC12 is an autosomal recessive form manifesting from infancy or early childhood with bleeding episodes. Clinical features include petechiae, easy bruising, epistaxis, hematomas, menorrhagia, and increased bleeding after trauma or surgery. Rare patients may have thrombocytopenia without bleeding. Some affected individuals have myopathic features, usually apparent in the second or third decades of life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25257349, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30171045, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33198675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34788986, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34858435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35052006, ECO:0000269|PubMed:38237079}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P12814; Q6UY14-3; Q969Y2; Q15323; P60370; P60409; P60410; P60411; Q9BQ66; P26371; Q9BYQ4; Q7Z3S9; O43597; Q6UY14-3; Q6P5X5; P27918; A8MQ03; Q16610; Q9UHF1; P28799; P49639; Q5T749; Q15323; O76011; Q6A162; P78385; P78386; O43790; Q07627; Q8IUG1; P60409; P60410; Q8IUC1; P60328; Q52LG2; Q3SY46; Q9BYP8; Q3LHN2; Q3SYF9; Q9BYR8; Q9BYR6; Q9BYQ7; Q9BYQ6; Q9BYR3; P26371; Q3LI64; Q3LI66; Q3LI67; Q9BYQ4; Q9BYQ3; Q9BYQ0; Q99750; Q8IV28; P0DPK4; O15496; O43609; O43610; P14373; Q8IWZ5; Q15654; O14817; Q2TAL6; Q9BRX9; O76024; Q9NZC7-5 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Allosteric enzyme; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Kinase; Metal-binding; Multifunctional enzyme; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 41589.2 Length 384 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 35.07 Isoelectric point 7.05 Charge (pH=7) 0.19 3D Binding mode Sequence NRKLRVCVATCNRADYSKLAPIXFGIKTEPEFFELDVVVLGSHLIDDYGNTYRXIEQDDFDINTRLHTIVRGEDEAAXVESVGLALVKLPDVLNRLKPDIXIVHGDRFDALALATSAALXNIRILHIEGGEVSGTIDDSIRHAITKLAHYHVCCTRSAEQHLISXCEDHDRILLAGCPSYDKLLSAKNKDYXSIIRXWLGDDVKSKDYIVALQHPVTTDIKHSIKXFELTLDALISFNKRTLVLFPNIDAGSKEXVRVXRKKGIEHHPNFRAVKHVPFDQFIQLVAHAGCXIGNSSCGVREVGAFGTPVINLGTRQIGRETGENVLHVRDADTQDKILQALHLQFGKQYPCSKIYGDGNAVPRILKFLKSIDLQEPLQKKFCFP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 82 | Scavenger decapping enzyme DcpS (DCPS) | 1ST4 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name DCPS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Scavenger mRNA-decapping enzyme DcpS; Histidine triad protein member5; Hint-related 7meGMP-directed hydrolase; HINT-5; DCS-1; DCPS Protein family HIT family Biochemical class Acid anhydrides hydrolase Function Decapping scavenger enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of a residual cap structure following the degradation of mRNAs by the 3'->5' exosome-mediated mRNA decay pathway. Hydrolyzes cap analog structures like 7-methylguanosine nucleoside triphosphate (m7GpppG) with up to 10 nucleotide substrates (small capped oligoribonucleotides) and specifically releases 5'-phosphorylated RNA fragments and 7-methylguanosine monophosphate (m7GMP). Cleaves cap analog structures like tri-methyl guanosine nucleoside triphosphate (m3(2,2,7)GpppG) with very poor efficiency. Does not hydrolyze unmethylated cap analog (GpppG) and shows no decapping activity on intact m7GpppG-capped mRNA molecules longer than 25 nucleotides. Does not hydrolyze 7-methylguanosine diphosphate (m7GDP) to m7GMP (PubMed:22985415). May also play a role in the 5'->3 mRNA decay pathway; m7GDP, the downstream product released by the 5'->3' mRNA mediated decapping activity, may be also converted by DCPS to m7GMP (PubMed:14523240). Binds to m7GpppG and strongly to m7GDP. Plays a role in first intron splicing of pre- mRNAs. Inhibits activation-induced cell death. Related diseases Al-Raqad syndrome (ARS) [MIM:616459]: A syndrome characterized by delayed psychomotor development, moderate to severe intellectual disability, poor or absent speech, microcephaly, congenital hypotonia, and severe growth delay. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25701870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25712129}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07644; DB07643; DB07642; DB03593; DB01960; DB01649; DB03958 Interacts with Q96C86; P52292; O15131; O60684 EC number EC 3.6.1.59 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Intellectual disability; mRNA processing; mRNA splicing; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B,A Molecular weight (Da) 69192.9 Length 597 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 54.62 Isoelectric point 6.12 Charge (pH=7) -9.94 3D Binding mode Sequence VRLPFSGFRLQKVLRESARDKIIFLHGKVNEASGDGDGEDAVVILEKTPFQVEQVAQLLTGSPELQLQFSNDIYSTYHLFPPRQLNDVKTTVVYPATEKHLQKYLRQDLRLIRETGDDYRNITLPHLESQSLSIQWVYNILDKKAEADRIVFENPDPSDGFVLIPDLKWNQQQLDDLYLIAICHRRGIRSLRDLTPEHLPLLRNILHQGQEAILQRYRMKGDHLRVYLHYLPSYYHLNVHFTALGFEAPGSGVERAHLLAEVIENLECDPRHYQQRTLTFALRADDPLLKLLQEAQQAPVRLPFSGFRLQKVLRESARDKIIFLHGKVNEASGDGDGEDAVVILEKTPFQVEQVAQLLTGSPELQLQFSNDIYSTYHLFPPRQLNDVKTTVVYPATEKHLQKYLRQDLRLIRETGDDYRNITLPHLESQSLSIQWVYNILDKKAEADRIVFENPDPSDGFVLIPDLKWNQQQLDDLYLIAICHRRGIRSLRDLTPEHLPLLRNILHQGQEAILQRYRMKGDHLRVYLHYLPSYYHLNVHFTALGFEAPGSGVERAHLLAEVIENLECDPRHYQQRTLTFALRADDPLLKLLQEAQQS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 83 | Mannoside acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 (MGAT2) | 5VCM | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name MGAT2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms N-glycosyl-oligosaccharide-glycoprotein N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase II; GlcNAc-T II; GNT-II; Beta-1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase II; Alpha-1,6-mannosyl-glycoprotein 2-beta-N-acetylglucosaminy Protein family Glycosyltransferase 16 (GT16) protein family Biochemical class Glycosyltransferases Function Catalyzes the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) onto the free terminal mannose moiety in the core structure of the nascent N-linked glycan chain, giving rise to the second branch in complex glycans. Plays an essential role in protein N-glycosylation. Related diseases Congenital disorder of glycosylation 2A (CDG2A) [MIM:212066]: A multisystem disorder caused by a defect in glycoprotein biosynthesis and characterized by under-glycosylated serum glycoproteins. Congenital disorders of glycosylation result in a wide variety of clinical features, such as defects in the nervous system development, psychomotor retardation, dysmorphic features, hypotonia, coagulation disorders, and immunodeficiency. The broad spectrum of features reflects the critical role of N-glycoproteins during embryonic development, differentiation, and maintenance of cell functions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11228641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8808595}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 2.4.1.143 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Congenital disorder of glycosylation; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Glycosyltransferase; Golgi apparatus; Manganese; Membrane; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal-anchor; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 83308.6 Length 709 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 52.42 Isoelectric point 8.1 Charge (pH=7) 5.7 3D Binding mode Sequence NLTLRYRSLVYQLNFDQTLRNVDWAPRELVLVVQVHNRPEYLRLLLDSLRKAQGIDNVLVIFSHDFWSTEINQLIAGVNFCPVLQVFFPFSIQLYPNEFPGSDPRDCPRDLPKNAALKLGCINAEYPDSFGHYREAKFSQTKHHWWWKLHFVWERVKILRDYAGLILFLEEDHYLAPDFYHVFKKMWKLKQQECPECDVLSLGTYSSRSFYGMADKVDVKTWKSTEHNMGLALTRNAYQKLIECTDTFCTYDDYNWDWTLQYLTVSCLPKFWKVLVPQIPRIFHAGDCGCRPSTQSAQIESLLNNNKQYMFPETLTISEKFTVVAISPPRKNGGWGDIRDHELCKSYRRLQAVPQPEADNLTLRYRSLVYQLNFDQTLRNVDKAGTWAPRELVLVVQVHNRPEYLRLLLDSLRKAQGIDNVLVIFSHDFWSTEINQLIAGVNFCPVLQVFFPFSIQLYPNEFPGSDPRDCPRDLPKNAALKLGCINAEYPDSFGHYREAKFSQTKHHWWWKLHFVWERVKILRDYAGLILFLEEDHYLAPDFYHVFKKMWKLKQQECPECDVLSLGTYSRSFYGMADKVDVKTWKSTEHNMGLALTRNAYQKLIECTDTFCTYDDYNWDWTLQYLTVSCLPKFWKVLVPQIPRIFHAGDCGMHHKKTCRPSTQSAQIESLLMFPETLTISFTVVAISPPRKNGGWGDIRDHELCKSYRR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 84 | Pseudomonas UDP-3-O-acyl-GlcNAc deacetylase (Pseudo lpxC) | 6MOO | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name Pseudo lpxC Organism Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Pseudo UDP-3-O-acyl-GlcNAc deacetylase; EnvA protein Protein family LpxC family Biochemical class Carbon-nitrogen hydrolase Function Involved in the biosynthesis of lipid A, a phosphorylated glycolipid that anchors the lipopolysaccharide to the outer membrane of the cell. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked, syndromic, Claes-Jensen type (MRXSCJ) [MIM:300534]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRXSCJ patients manifest intellectual disability associated with variable features such as slowly progressive spastic paraplegia, seizures, facial dysmorphism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15586325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16538222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16541399, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17320160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17468742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23356856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25666439}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07861 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.5.1.108 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Hydrolase; Lipid A biosynthesis; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Metal-binding; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33194.2 Length 301 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 31.41 Isoelectric point 5.12 Charge (pH=7) -11.56 3D Binding mode Sequence HHEGAGTIKQRTLKNIIRATGVGLHSGEKVYLTLKPAPVDTGIVFSRTDLDPVVEIPARAENVGETTMSTTLVKGDVKVDTVEHLLSAMAGLGIDNAYVELSASEVPIMDGSAGPFVFLIQSAGLQEQEAAKKFIRIKREVSVEEGDKRAVFVPFDGFKVSFEIDFDHPVFQQASVDFSSTSFVKEVSRARTFGFMRDIEYLRSQNLALGGSVENAIVVDENRVLNEDGLRYEDEFVKHKILDAIGDLYLLGNSLIGEFRGFKSGHALNNQLLRTLIADKDAWEVVTFEDARTAPISYMRP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 85 | Neuropeptide Y receptor type 1 (NPY1R) | 5ZBQ | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name NPY1R Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Neuropeptide Y-Y1 receptor; Neuropeptide Y receptor Y1; Neuropeptide Y Y(1) receptor; NPY1R; NPY1-R Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Receptor for neuropeptide Y and peptide YY. The rank order of affinity of this receptor for pancreatic polypeptides is NPY > [Pro-34] PYY, PYY and [Leu-31, Pro-34] NPY > NPY (2-36) > [Ile-31, Gln-34] PP and PYY (3-36) > PP > NPY free acid. Related diseases 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase-2 deficiency (HMGCS2D) [MIM:605911]: A metabolic disorder characterized by severe hypoketotic hypoglycemia, encephalopathy, and hepatomegaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11228257, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11479731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12647205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16601895, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23751782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25511235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29597274}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05004 Interacts with P10082 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 53153.7 Length 463 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 34 Isoelectric point 8.93 Charge (pH=7) 9.46 3D Binding mode Sequence FSEKNAQLLAFENDDCHLPLAMIFTLALAYGAVIILGVSGNLALIIIILKQKEMRNVTNILIVNLSFSDLLVAIMCLPFTFVYTLMDHWVFGEAMCKLNPFVQCVSITVSIWSLVLIAVERHQLIINPRGWRPNNRHAYVGIAVIWVLAVASSLPFLIYQVMTDEPFQNVTLDAYKDKYVCFDQFPSDSHRLSYTTLLLVLQYFGPLCFIFICYFKIYIRLKRRSETKRINIMLLSIVVAFAVCWLPLTIFNTVFDWNHQIIATCNHNLLFLLCHLTAMISTCVNPIFYGFLNKNFQRDLQFFFNFNIFEMLRIDEGLRLKIYKDTEGYYTIGIGHLLTKSPSLNAAKSELDKAIGRNTNGVITKDEAEKLFNQDVDAAVRGILRNAKLKPVYDSLDAVRRAALINMVFQMGETGVAGFTNSLRMLQQKRWDEAAVNSRWYNQTPNRAKRVITTFRTGTWDAY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 86 | Glutathione S-transferase LANCL1 (LANCL1) | 3E73 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name LANCL1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms p40; LanC-like protein 1; GPR69A; 40 kDa erythrocyte membrane protein Protein family LanC-like protein family Biochemical class NA Function Functions as glutathione transferase. Catalyzes conjugation of the glutathione (GSH) to artificial substrates 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB) and p-nitrophenyl acetate. Mitigates neuronal oxidative stress during normal postnatal development and in response to oxidative stresses probably through GSH antioxidant defense mechanism (By similarity). May play a role in EPS8 signaling. Binds glutathione. Related diseases Spermatogenic failure 5 (SPGF5) [MIM:243060]: An infertility disorder caused by spermatogenesis defects. Semen from affected men show close to 100% morphologically abnormal multiflagellar spermatozoa with low motility, oversized irregular heads, and abnormal midpiece and acrosome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17435757, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21733974}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9UHR4; P42858; Q08509 EC number EC 2.5.1.18 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Membrane; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 46005.4 Length 405 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 33.7 Isoelectric point 7.13 Charge (pH=7) 0.4 3D Binding mode Sequence SMDIEFMAQRAFPNPYADYNKSLAEGYFDAAGRLTPEFSQRLTNKIRELLQQMERGLKSADPRDGTGYTGWAGIAVLYLHLYDVFGDPAYLQLAHGYVKQSLNCLTKRSITFLCGDAGPLAVAAVLYHKMNNEKQAEDCITRLIHLNKIDPHAPNEMLYGRIGYIYALLFVNKNFGVEKIPQSHIQQICETILTSGENLARKRNFTAKSPLMYEWYQEYYVGAAHGLAGIYYYLMQPSLQVSQGKLHSLVKPSVDYVCQLKFPSGNYPPCIGDNRDLLVHWCHGAPGVIYMLIQAYKVFREEKYLCDAYQCADVIWQYGLLKKGYGLCHGSAGNAYAFLTLYNLTQDMKYLYRACKFAEWCLEYGEHGCRTPDTPFSLFEGMAGTIYFLADLLVPTKARFPAFEL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 87 | Aldehyde oxidase (AOX1) | 7OPN | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name AOX1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms AOX1 Protein family Xanthine dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Aldehyde/oxo donor oxidoreductase Function Oxidase with broad substrate specificity, oxidizing aromatic azaheterocycles, such as N1-methylnicotinamide and N- methylphthalazinium, as well as aldehydes, such as benzaldehyde, retinal, pyridoxal, and vanillin. Plays a key role in the metabolism of xenobiotics and drugs containing aromatic azaheterocyclic substituents. Participates in the bioactivation of prodrugs such as famciclovir, catalyzing the oxidation step from 6-deoxypenciclovir topenciclovir, which is a potent antiviral agent. Is probably involved in the regulation of reactive oxygen species homeostasis. May be a prominent source of superoxide generation via the one-electron reduction of molecular oxygen. Also may catalyze nitric oxide (NO) production via the reduction of nitrite to NO with NADH or aldehyde as electron donor. May play a role in adipogenesis. Related diseases Progressive familial heart block 1B (PFHB1B) [MIM:604559]: A cardiac bundle branch disorder characterized by progressive alteration of cardiac conduction through the His-Purkinje system, with a pattern of a right bundle-branch block and/or left anterior hemiblock occurring individually or together. It leads to complete atrio-ventricular block causing syncope and sudden death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19726882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20562447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21887725}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva 6 (EKVP6) [MIM:618531]: A form of erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva, a genodermatosis characterized by the coexistence of two independent skin lesions: transient erythema and hyperkeratosis that is usually localized but occasionally occurs in its generalized form. Clinical presentation varies significantly within a family and from one family to another. Palmoplantar keratoderma is present in around 50% of cases. EKVP6 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30528822}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00437; DB00513; DB00484; DB11791; DB00215; DB00924; DB03516; DB01175; DB00426; DB12466; DB09054; DB09078; DB00170; DB01033; DB00563; DB08840; DB00157; DB00339; DB00481; DB04827; DB00962; DB00246; DB00909 Interacts with Q06278 EC number EC 1.2.3.1 Uniprot keywords 2Fe-2S; 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; FAD; Flavoprotein; Iron; Iron-sulfur; Lipid metabolism; Metal-binding; Molybdenum; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 286845 Length 2590 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 42.7 Isoelectric point 6.92 Charge (pH=7) -1.62 3D Binding mode Sequence ASELLFYVNGRKVIEKNVDPETMLLPYLRKKLRLTGTKYGCGGGGCGACTVMISRYNPITKRIRHHPANACLIPICSLYGAAVTTVEGIGSTHTRIHPVQERIAKCHGTQCGFCTPGMVMSIYTLLRNHPEPTLDQLTDALGGNLCRCTGYRPIIDACKTFCKPKLFAEEEFLPLDPTQELIFPPELMIMAEKQSQRTRVFGSERMMWFSPVTLKELLEFKFKYPQAPVIMGNTSVGPEVKFKGVFHPVIISPDRIEELSVVNHAYNGLTLGAGLSLAQVKDILADVVQKLPEEKTQMYHALLKHLGTLAGSQIRNMASLGGHIISRHPDSDLNPILAVGNCTLNLLSKEGKRQIPLNEQFLSKCPNADLKPQEILVSVNIPYSRKWEFVSAFRQAQRQENALAIVNSGMRVFFGEGDGIIRELCISYGGVGPATICAKNSCQKLIGRHWNEQMLDIACRLILNEVSLLGSAPGGKVEFKRTLIISFLFKFYLEVSQILKKMDPVHYPSLADKYESALEDLHSKHHCSTLKYQNQHPEDPIGHPIMHLSGVKHATGEAIYCDDMPLVDQELFLTFVTSSRAHAKIVSIDLSEALSMPGVVDIMTAEHLSDVNSFCFFTEAEKFLATDKVFCVGQLVCAVLADSEVQAKRAAKRVKIVYQDLEPLILTIEESIQHNSSFKPERKLEYGNVDEAFKVVDQILEGEIHMGGQEHFYMETQSMLVVPKGEDQEMDVYVSTQFPKYIQDIVASTLKLPANKVMCHVRRVGGAFGGKVLKTGIIAAVTAFAANKHGRAVRCVLERGEDMLITGGRHPYLGKYKAGFMNDGRILALDMEHYSNAGASLDESLFVIEMGLLKMDNAYKFPNLRCRGWACRTNLPSNTAFRGFGFPQAALITESCITEVAAKCGLSPEKVRIINMYKEIDQTPYKQEINAKNLIQCWRECMAMSSYSLRKVAVEKFNAENYWKKKGLAMVPLKFPVGLGSRAAGQAAALVHIYLDGSVLVTHGGIEMGQGVHTKMIQVVSRELRMPMSNVHLRGTSTETVPNANISGGSVVADLNGLAVKDACQTLLKRLEPIISKNPKGTWKDWAQTAFDESINLSAVGYFRGYESDMNWEKGEGQPFEYFVYGAACSEVEIDCLTGDHKNIRTDIVMDVGCSINPAIDIGQIEGAFIQGMGLYTIEELNYSPQGILHTHGPDQYKIPAICDMPTELHIALLPPSQNSNTLYSSKGLGESGVFLGCSVFFAIHDAVSAARQERGLHLTLNSPLTPEKIRMACEDKFTKMIPRDEPGSYVPWNVASELLFYVNGRKVIEKNVDPETMLLPYLRKKLRLTGTKYGCGGGGCGACTVMISRYNPITKRIRHHPANACLIPICSLYGAAVTTVEGIGSTHTRIHPVQERIAKCHGTQCGFCTPGMVMSIYTLLRNHPEPTLDQLTDALGGNLCRCTGYRPIIDACKTFCKPKLFAEEEFLPLDPTQELIFPPELMIMAEKQSQRTRVFGSERMMWFSPVTLKELLEFKFKYPQAPVIMGNTSVGPEVKFKGVFHPVIISPDRIEELSVVNHAYNGLTLGAGLSLAQVKDILADVVQKLPEEKTQMYHALLKHLGTLAGSQIRNMASLGGHIISRHPDSDLNPILAVGNCTLNLLSKEGKRQIPLNEQFLSKCPNADLKPQEILVSVNIPYSRKWEFVSAFRQAQRQENALAIVNSGMRVFFGEGDGIIRELCISYGGVGPATICAKNSCQKLIGRHWNEQMLDIACRLILNEVSLLGSAPGGKVEFKRTLIISFLFKFYLEVSQILKKMDPVHYPSLADKYESALEDLHSKHHCSTLKYQNQHPEDPIGHPIMHLSGVKHATGEAIYCDDMPLVDQELFLTFVTSSRAHAKIVSIDLSEALSMPGVVDIMTAEHLSDVNSFCFFTEAEKFLATDKVFCVGQLVCAVLADSEVQAKRAAKRVKIVYQDLEPLILTIEESIQHNSSFKPERKLEYGNVDEAFKVVDQILEGEIHMGGQEHFYMETQSMLVVPKGEDQEMDVYVSTQFPKYIQDIVASTLKLPANKVMCHVRRVGGAFGGKVLKTGIIAAVTAFAANKHGRAVRCVLERGEDMLITGGRHPYLGKYKAGFMNDGRILALDMEHYSNAGASLDESLFVIEMGLLKMDNAYKFPNLRCRGWACRTNLPSNTAFRGFGFPQAALITESCITEVAAKCGLSPEKVRIINMYKEIDQTPYKQEINAKNLIQCWRECMAMSSYSLRKVAVEKFNAENYWKKKGLAMVPLKFPVGLGSRAAGQAAALVHIYLDGSVLVTHGGIEMGQGVHTKMIQVVSRELRMPMSNVHLRGTSTETVPNANISGGSVVADLNGLAVKDACQTLLKRLEPIISKNPKGTWKDWAQTAFDESINLSAVGYFRGYESDMNWEKGEGQPFEYFVYGAACSEVEIDCLTGDHKNIRTDIVMDVGCSINPAIDIGQIEGAFIQGMGLYTIEELNYSPQGILHTHGPDQYKIPAICDMPTELHIALLPPSQNSNTLYSSKGLGESGVFLGCSVFFAIHDAVSAARQERGLHLTLNSPLTPEKIRMACEDKFTKMIPRDEPGSYVPWNV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 88 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-6 (RSK6) | 6G77 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name RPS6KA6 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms pp90RSK4; p90RSK6; p90-RSK 6; S6K-alpha-6; Ribosomal S6 kinase 4; RSK4; RSK-4; 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase 6 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, S6 kinase subfamily Biochemical class NA Function Constitutively active serine/threonine-protein kinase that exhibits growth-factor-independent kinase activity and that may participate in p53/TP53-dependent cell growth arrest signaling and play an inhibitory role during embryogenesis. Related diseases Symptomatic deficiency in lactate transport (SDLT) [MIM:245340]: Deficiency of lactate transporter may result in an acidic intracellular environment created by muscle activity with consequent degeneration of muscle and release of myoglobin and creatine kinase. This defect might compromise extreme performance in otherwise healthy individuals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10590411}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, familial, 7 (HHF7) [MIM:610021]: A form of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous disorder characterized by inappropriate insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta-cells in the presence of low blood glucose levels. HHF7 features include exercise-induced hyperinsulinism, loss of consciousness due to hypoglycemia, and hypoglycemic seizures. HHF7 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17701893}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Monocarboxylate transporter 1 deficiency (MCT1D) [MIM:616095]: A metabolic disorder characterized by recurrent ketoacidosis, a pathologic state due to ketone formation exceeding ketone utilization. The clinical consequences of ketoacidosis are vomiting, osmotic diuresis, dehydration, and Kussmaul breathing. The condition may progress to decreased consciousness and, ultimately, death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25390740}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12010 Interacts with Q7Z698 EC number EC 2.7.11.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Kinase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33406.4 Length 291 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 38.08 Isoelectric point 8.4 Charge (pH=7) 2.55 3D Binding mode Sequence VVKEIPITHHVKEGYEKADPAQFELLKVLGQGSFGKVFLVRKKTGPDAGQLYAMKVLKKASLKVRDDILVEVNHPFIVKLHYAFQTEGKLYLILDFLRGGDVFTRLSKEVLFTEEDVKFYLAELALALDHLHQLGIVYRDLKPENILLDEIGHIKLTDFGLSKESVDQEKKAYSFCGTVEYMAPEVVNRRGHSQSADWWSYGVLMFEMLTGTLPFQGKDRNETMNMILKAKLGMPQFLSAEAQSLLRMLFKRNPANRLGSEGVEEIKRHLFFANIDWDKLYKREVQPPFKP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 89 | Cholinesterase (BCHE) | 1P0I | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name BCHE Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Pseudocholinesterase; Choline esterase II; CHE1; Butyrylcholine esterase; Acylcholine acylhydrolase Protein family Type-B carboxylesterase/lipase family Biochemical class Type-B carboxylesterase/lipase Function Esterase with broad substrate specificity. Contributes to the inactivation of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Can degrade neurotoxic organophosphate esters. Related diseases Butyrylcholinesterase deficiency (BCHED) [MIM:617936]: An autosomal recessive metabolic condition characterized by increased sensitivity to certain anesthetic drugs, including the muscle relaxants succinylcholine or mivacurium. BCHED results in slower hydrolysis of these drugs and, consequently, a prolonged neuromuscular block, leading to apnea. The duration of the prolonged apnea varies significantly depending on the extent of the enzyme deficiency. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10404729, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11928765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12881446, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1306123, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1349196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1415224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15563885, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15781196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1611188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16788378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17700357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18075469, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18300943, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25054547, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25264279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2915989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7634491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8554068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8680411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9110359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9191541, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9388484, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9543549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9694584}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08200; DB08201; DB03814; DB07940; DB03672; DB03128; DB08897; DB01122; DB06692; DB01408; DB00868; DB06756; DB11148; DB03568; DB04250; DB06774; DB01161; DB00856; DB00477; DB00122; DB14006; DB00527; DB00515; DB04920; DB00907; DB00979; DB01245; DB00944; DB11397; DB02811; DB00711; DB00449; DB07681; DB00843; DB01135; DB01057; DB01010; DB01364; DB03822; DB08658; DB00674; DB00941; DB00762; DB06636; DB00677; DB01064; DB01221; DB00772; DB00888; DB00358; DB02845; DB08893; DB01226; DB09205; DB01400; DB00585; DB00892; DB01337; DB00082; DB00183; DB00790; DB04892; DB03976; DB01338; DB00733; DB01035; DB00721; DB00392; DB09288; DB00545; DB00178; DB05386; DB00989; DB05875; DB00202; DB00391; DB00382; DB00871; DB04572; DB14031; DB00620; DB00508; DB01116; DB01199 Interacts with P54252; P46379-2; P06276; P55212; O75190-2; O14901; P13473-2; O75400-2; P62826; P67812; P02814 EC number EC 3.1.1.8 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Serine esterase; Sialic acid; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 58935.5 Length 523 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 38.71 Isoelectric point 8.63 Charge (pH=7) 5.36 3D Binding mode Sequence IIIATKNGKVRGMQLTVFGGTVTAFLGIPYAQPPLGRLRFKKPQSLTKWSDIWNATKYANSCCQNIDQSFPGFHGSEMWNPNTDLSEDCLYLNVWIPAPKPKNATVLIWIYGGGFQTGTSSLHVYDGKFLARVERVIVVSMNYRVGALGFLALPGNPEAPGNMGLFDQQLALQWVQKNIAAFGGNPKSVTLFGESAGAASVSLHLLSPGSHSLFTRAILQSGSFNAPWAVTSLYEARNRTLNLAKLTGCSRENETEIIKCLRNKDPQEILLNEAFVVPYGTPLSVNFGPTVDGDFLTDMPDILLELGQFKKTQILVGVNKDEGTAFLVYGAPGFSKDNNSIITRKEFQEGLKIFFPGVSEFGKESILFHYTDWVQRPENYREALGDVVGDYNFICPALEFTKKFSEWGNNAFFYYFEHRSSKLPWPEWMGVMHGYEIEFVFGLPLERRDYTKAEEILSRSIVKRWANFAKYGNPQETQNQSTSWPVFKSTEQKYLTLNTESTRIMTKLRAQQCRFWTSFFPKV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 90 | DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit A | 1ZVT | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name parC Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b3019;JW2987 Protein family Type II topoisomerase GyrA/ParC subunit family, ParC type 1 subfamily Biochemical class Isomerase Function ATP binding.DNA binding.DNA topoisomerase type II (ATP-hydrolyzing) activity. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB11943; DB12924; DB00817 Interacts with P22523; P0A7K2 EC number 5.6.2.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; DNA-binding; Isomerase; Membrane; Reference proteome; Topoisomerase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 26490.3 Length 246 Aromaticity 0.04 Instability index 46.03 Isoelectric point 8.94 Charge (pH=7) 2.83 3D Binding mode Sequence SEPVTIVLSQMGWVRSAKGHDIDAPGLNYKAGDSFKAAVKGKSNQPVVFVDSTGRSYAIDPITLPSARGQGEPLTGKLTLPPGATVDHMLMESDDQKLLMASDAGYGFVCTFNDLVARNRAGKALITLPENAHVMPPVVIEDASDMLLAITQAGRMLMFPVSDLPQLSKGKGNKIINIPSAEAARGEDGLAQLYVLPPQSTLTIHVGKRKIKLRPEELQKVTGERGRRGTLMRGLQRIDRVEIDSP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 91 | Deoxyribodipyrimidine photo-lyase | 1OWL | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name phr Organism Synechococcus sp. (strain ATCC 27144 / PCC 6301 / SAUG 1402/1) (Anacystis nidulans) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms phrA;syc1392_c Protein family DNA photolyase class-1 family Biochemical class Lyase Function Deoxyribodipyrimidine photo-lyase activity.DNA binding.Nucleotide binding. Related diseases Myeloperoxidase deficiency (MPOD) [MIM:254600]: A disorder characterized by decreased myeloperoxidase activity in neutrophils and monocytes that results in disseminated candidiasis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:37198333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7904599, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8142659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8621627, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9354683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9637725}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147 Interacts with NA EC number 4.1.99.3 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Chromophore; Direct protein sequencing; DNA damage; DNA repair; DNA-binding; FAD; Flavoprotein; Lyase; Nucleotide-binding Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 53346.9 Length 473 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 53.22 Isoelectric point 6.92 Charge (pH=7) -0.23 3D Binding mode Sequence APILFWHRRDLRLSDNIGLAAARAQSAQLIGLFCLDPQILQSADMAPARVAYLQGCLQELQQRYQQAGSRLLLLQGDPQHLIPQLAQQLQAEAVYWNQDIEPYGRDRDGQVAAALKTAGIRAVQLWDQLLHSPDQILSGSGNPYSVYGPFWKNWQAQPKPTPVATPTELVDLSPEQLTAIAPLLLSELPTLKQLGFDWDGGFPVEPGETAAIARLQEFCDRAIADYDPQRNFPAEAGTSGLSPALKFGAIGIRQAWQAASAAHALSRSDEARNSIRVWQQELAWREFYQHALYHFPSLADGPYRSLWQQFPWENREALFTAWTQAQTGYPIVDAAMRQLTETGWMHNRCRMIVASFLTKDLIIDWRRGEQFFMQHLVDGDLAANNGGWQWSASSGMDPKPLRIFNPASQAKKFDATATYIKRWLPELRHVHPKDLISGEITPIERRGYPAPIVNHNLRQKQFKALYNQLKAAI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 92 | Glutamate dehydrogenase 1, mitochondrial | 1L1F | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name GLUD1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms GLUD Protein family Glu/Leu/Phe/Val dehydrogenases family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function ADP binding.ATP binding.Glutamate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity.Glutamate dehydrogenase [NAD(P)+] activity.GTP binding.Identical protein binding.Leucine binding.NAD+ binding. Related diseases Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, familial, 6 (HHF6) [MIM:606762]: A form of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous disorder characterized by inappropriate insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta-cells in the presence of low blood glucose levels. HHF6 is an autosomal dominant form characterized by hypoglycemia due to congenital hyperinsulinism combined with persistent hyperammonemia. Clinical features include loss of consciousness due to hypoglycemia, hypoglycemic seizures, and mental retardation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10636977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11214910, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11297618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9571255}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB11081; DB00142; DB04137; DB00756; DB00157 Interacts with P49448 EC number 1.4.1.3 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; ADP-ribosylation; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Endoplasmic reticulum; GTP-binding; Hydroxylation; Mitochondrion; NADP; Nucleotide-binding; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F Molecular weight (Da) 49471.9 Length 447 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 27.17 Isoelectric point 7.3 Charge (pH=7) 0.81 3D Binding mode Sequence DPNFFKMVEGFFDRGASIVEDKLVEDLRTRESEEQKRNRVRGILRIIKPCNHVLSLSFPIRRDDGSWEVIEGYRAQHSQHRTPCKGGIRYSTDVSVDEVKALASLMTYKCAVVDVPFGGAKAGVKINPKNYTDNELEKITRRFTMELAKKGFIGPGIDVPAPDMSTGEREMSWIADTYASTIGHYDINAHACVTGKPISQGGIHGRISATGRGVFHGIENFINEASYMSILGMTPGFGDKTFVVQGFGNVGLHSMRYLHRFGAKCIAVGESDGSIWNPDGIDPKELEDFKLQHGSILGFPKAKPYEGSILEADCDILIPAASEKQLTKSNAPRVKAKIIAEGANGPTTPEADKIFLERNIMVIPDLYLNAGGVTVSYFEWLKNLNHVSYSEKDIVHSGLAYTMERSARQIMRTAMKYNLGLDLRTAAYVNAIEKVFKVYNEAGVTFT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 93 | Gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit 1 | 4MS4 | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name GABBR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms GPRC3B;GPR51 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 3 family, GABA-B receptor subfamily Biochemical class Signaling protein / antagonist Function G-protein coupled GABA receptor activity. Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder with poor language and loss of hand skills (NDPLHS) [MIM:617903]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by psychomotor developmental stagnation or regression. NDPLHS manifest in the first years of life as loss of purposeful hand movements, loss of language, and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26740508, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28856709, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29369404}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 59 (DEE59) [MIM:617904]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of severe early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE59 is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by onset of refractory seizures in early infancy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28856709, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29100083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29369404}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08891; DB08892; DB00181; DB00363; DB02530; DB05010; DB09072 Interacts with Q9UBS5; Q9UBS5-2; P46459; Q86UR5 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Coiled coil; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Epilepsy; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Intellectual disability; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 46502.1 Length 408 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 50.05 Isoelectric point 5.78 Charge (pH=7) -5.62 3D Binding mode Sequence RRAVYIGALFPMSGGWPGGQACQPAVEMALEDVNSRRDILPDYELKLIHHDSKCDPGQATKYLYELLYNDPIKIILMPGCSSVSTLVAEAARMWNLIVLSYGSSSPALSNRQRFPTFFRTHPSATLHNPTRVKLFEKWGWKKIATIQQTTEVFTSTLDDLEERVKEAGIEITFRQSFFSDPAVPVKNLKRQDARIIVGLFYETEARKVFCEVYKERLFGKKYVWFLIGWYADNWFKIYDPSINCTVDEMTEAVEGHITTEIVMLNPANTRSISNMTSQEFVEKLTKRLKRHPEETGGFQEAPLAYDAIWALALALNKTSRLEDFNYNNQTITDQIYRAMNSSSFEGVSGHVVFDASGSRMAWTLIEQLQGGSYKKIGYYDSTKDDLSWSKTDKWIGGSPPADDYKDDD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 94 | Aldose reductase (AKR1B1) | 1US0 | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name AKR1B1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Aldehyde reductase; AKR1B1 Protein family Aldo/keto reductase family Biochemical class Short-chain dehydrogenases reductase Function Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a wide variety of carbonyl-containing compounds to their corresponding alcohols with a broad range of catalytic efficiencies. Related diseases Glutamine deficiency, congenital (GLND) [MIM:610015]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by variable brain malformations, encephalopathy, severe developmental delay, seizures, and decreased glutamine levels in bodily fluids. Death in early infancy may occur. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16267323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26711351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 116 (DEE116) [MIM:620806]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE116 is autosomal dominant form characterized by severe developmental delay, seizures, and white matter abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. DEE116 is caused by variants that disrupt the canonical translation start codon in GLUL resulting in initiation of translation at Met-18 (PubMed:38579670). The resulting protein is enzymatically competent but insensitive to negative feedback regulation via glutamine-induced degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07028; DB07030; DB07450; DB02101; DB08449; DB08000; DB07139; DB07498; DB02007; DB02020; DB11859; DB02994; DB04272; DB07187; DB00694; DB00997; DB06246; DB01039; DB02021; DB16707; DB00143; DB02834; DB08084; DB01689; DB07063; DB06077; DB02518; DB00157; DB03461; DB05383; DB05533; DB05327; DB02712; DB00605; DB02383; DB02132; DB08772; DB07093; DB07999; DB08098 Interacts with Q9BUY7 EC number EC 1.1.1.300 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Lipid metabolism; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35447.6 Length 313 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 36.41 Isoelectric point 7.1 Charge (pH=7) 0.26 3D Binding mode Sequence MASRILLNNGAKMPILGLGTWKSPPGQVTEAVKVAIDVGYRHIDCAHVYQNENEVGVAIQEKLREQVVKREELFIVSKLWCTYHEKGLVKGACQKTLSDLKLDYLDLYLIHWPTGFKPGKEFFPLDESGNVVPSDTNILDTWAAMEELVDEGLVKAIGISNFNHLQVEMILNKPGLKYKPAVNQIECHPYLTQEKLIQYCQSKGIVVTAYSPLGSPDRPWAKPEDPSLLEDPRIKAIAAKHNKTTAQVLIRFPMQRNLVVIPKSVTPERIAENFKVFDFELSSQDMTTLLSYNRNWRVCALLSCTSHKDYPFH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 95 | Neprilysin | 1R1H | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name MME Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms EPN Protein family Peptidase M13 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Endopeptidase activity.Exopeptidase activity.Metalloendopeptidase activity.Metallopeptidase activity.Peptide binding.Zinc ion binding. Related diseases Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, 2T (CMT2T) [MIM:617017]: An axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal degeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26991897, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27588448}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spinocerebellar ataxia 43 (SCA43) [MIM:617018]: A form of spinocerebellar ataxia, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of cerebellar disorders. Patients show progressive incoordination of gait and often poor coordination of hands, speech and eye movements, due to degeneration of the cerebellum with variable involvement of the brainstem and spinal cord. SCA43 is a slowly progressive, autosomal dominant form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27583304}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08575; DB02597; DB00616; DB11623; DB05796; DB06655; DB02558; DB02062; DB00886; DB02557; DB09292; DB13928; DB08626 Interacts with P05067; P21926; Q06787-7; P08107; P04792 EC number 3.4.24.11 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Myristate; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathy; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal-anchor; Spinocerebellar ataxia; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 79435.8 Length 696 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.5 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -11.46 3D Binding mode Sequence GICKSSDCIKSAARLIQNMDATTEPCTDFFKYACGGWLKRNVIPETSSRYGNFDILRDELEVVLKDVLQEPKTEDIVAVQKAKALYRSCINESAIDSRGGEPLLKLLPDIYGWPVATENWEQKYGASWTAEKAIAQLNSKYGKKVLINLFVGTDDKNSVNHVIHIDQPRLGLPSRDYYECTGIYKEACTAYVDFMISVARLIRQEERLPIDENQLALEMNKVMELEKEIANATAKPEDRNDPMLLYNKMTLAQIQNNFSLEINGKPFSWLNFTNEIMSTVNISITNEEDVVVYAPEYLTKLKPILTKYSARDLQNLMSWRFIMDLVSSLSRTYKESRNAFRKALYGTTSETATWRRCANYVNGNMENAVGRLYVEAAFAGESKHVVEDLIAQIREVFIQTLDDLTWMDAETKKRAEEKALAIKERIGYPDDIVSNDNKLNNEYLELNYKEDEYFENIIQNLKFSQSKQLKKLREKVDKDEWISGAAVVNAFYSSGRNQIVFPAGILQPPFFSAQQSNSLNYGGIGMVIGHEITHGFDDNGRNFNKDGDLVDWWTQQSASNFKEQSQCMVYQYGNFSWDLAGGQHLNGINTLGENIADNGGLGQAYRAYQNYIKKNGEEKLLPGLDLNHKQLFFLNFAQVWCGTYRPEYAVNSIKTDVHSPGNFRIIGTLQNSAEFSEAFHCRKNSYMNPEKKCRVW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 96 | Transferrin (TF) | 1RYO | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name TF Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Siderophilin; Serotransferrin; PRO1400; Beta-1 metal-binding globulin Protein family Transferrin family Biochemical class Transferrin Function It is responsible for the transport of iron from sites of absorption and heme degradation to those of storage and utilization. Serum transferrin may also have a further role in stimulating cell proliferation. Transferrins are iron binding transport proteins which can bind two Fe(3+) ions in association with the binding of an anion, usually bicarbonate. Related diseases Atransferrinemia (ATRAF) [MIM:209300]: A rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by abnormal synthesis of transferrin leading to iron overload and microcytic hypochromic anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11110675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15466165}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01370; DB14517; DB14518; DB01294; DB14526; DB14527; DB11136; DB14528; DB14529; DB14530; DB00515; DB09130; DB11397; DB13949; DB14490; DB14491; DB14488; DB14501; DB14489; DB13257; DB06215; DB06784; DB05260; DB01592; DB00893; DB00677; DB06757; DB11182; DB14520; DB01593; DB14487; DB14533; DB14548 Interacts with O43315; O00501; Q7Z7G2; Q9GZR5; Q9Y282; Q96KR6; P01350; P08034; Q8NBJ4; O15529; Q8TED1; Q7Z5P4; A8MZ59; O15173; Q96TC7; Q3KNW5; Q9BXS9-3; Q99523; O43278-2; Q8N9I0; P02786; Q4KMG9; Q9K0U9; Q09057; Q9K0V0; P02786 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Ion transport; Iron; Iron transport; Metal-binding; Methylation; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35854.5 Length 324 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 34.17 Isoelectric point 7.58 Charge (pH=7) 1.42 3D Binding mode Sequence KTVRWCAVSEHEATKCQSFRDHMKSVIPSDGPSVACVKKASYLDCIRAIAANEADAVTLDAGLVYDAYLAPNNLKPVVAEFYGSKEDPQTFYYAVAVVKKDSGFQMNQLRGKKSCHTGLGRSAGWNIPIGLLYCDLPEPRKPLEKAVANFFSGSCAPCADGTDFPQLCQLCPGCGCSTLNQYFGYSGAFKCLKDGAGDVAFVKHSTIFENLANKADRDQYELLCLDNTRKPVDEYKDCHLAQVPSHTVVARSMGGKEDLIWELLNQAQEHFGKDKSKEFQLFSSPHGKDLLFKDSAHGFLKVPPRMDAKMYLGYEYVTAIRNLR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 97 | Thymidine kinase | 1E2K | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name TK Organism Human herpesvirus 1 (strain 17) (HHV-1) (Human herpes simplex virus 1) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms UL23 Protein family Herpesviridae thymidine kinase family Biochemical class Transferase Function ATP binding.Thymidine kinase activity. Related diseases Atransferrinemia (ATRAF) [MIM:209300]: A rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by abnormal synthesis of transferrin leading to iron overload and microcytic hypochromic anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11110675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15466165}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 2.7.1.21 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ATP-binding; DNA synthesis; Early protein; Kinase; Nucleotide-binding; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 67808.8 Length 624 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 43.94 Isoelectric point 6.1 Charge (pH=7) -7.02 3D Binding mode Sequence MPTLLRVYIDGPHGMGKTTTTQLLVADDIVYVPEPMTYWRVLGASETIANIYTTQHRLDQGEISAGDAAVVMTSAQITMGMPYAVTDAVLAPHIGGEAGPPPALTLIFDRHPIAALLCYPAARYLMGSMTPQAVLAFVALIPPTLPGTNIVLGALPEDRHIDRLAKRQRPGERLDLAMLAAIRRVYGLLANTVRYLQCGGSWREDWGQLSGTGPRPHIGDTLFTLFRAPELLAPNGDLYNVFAWALDVLAKRLRSMHVFILDYDQSPAGCRDALLQLTSGMVQTHVTTPGSIPTICDLARTFAREMGEMPTLLRVYIDGPHGMGKTTTTQLLVALGSRDDIVYVPEPMTYWRVLGASETIANIYTTQHRLDQGEISAGDAAVVMTSAQITMGMPYAVTDAVLAPHIGGEAHAPPPALTLIFDRHPIAALLCYPAARYLMGSMTPQAVLAFVALIPPTLPGTNIVLGALPEDRHIDRLAKRERLDLAMLAAIRRVYGLLANTVRYLQCGGSWREDWGQLSGTAVPQSNAGPRPHIGDTLFTLFRAPELLAPNGDLYNVFAWALDVLAKRLRSMHVFILDYDQSPAGCRDALLQLTSGMVQTHVTTPGSIPTICDLARTFAREMGE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 98 | Penicillin-binding protein 2B | 2WAD | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name penA Organism Streptococcus pneumoniae (strain ATCC BAA-255 / R6) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms spr1517;pbp2b Protein family Transpeptidase family Biochemical class Peptide binding protein Function Penicillin binding. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01163; DB00415; DB08795; DB01140; DB00456; DB01066; DB00493; DB01331; DB01212; DB00567; DB03313; DB00485; DB00739; DB01603; DB00607; DB00713; DB00319 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Antibiotic resistance; Cell membrane; Cell shape; Cell wall biogenesis/degradation; Membrane; Peptidoglycan synthesis; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 65444.4 Length 607 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 30.15 Isoelectric point 4.95 Charge (pH=7) -20.68 3D Binding mode Sequence SQTKVTTSSARGEIYDASGKPLVENTLKQVVSFTRSNKMTATDLKEIAKKLLTYVSISSPNLTERQLADYYLADPEIYKKTVEALPSESELYNNAVDSVPTSQLNYTEDEKKEIYLFSQLNAVGNFATGTIATDPLNDSQVAVIASISKEMPGISISTSWDRKILETSLSSIVGSVSSEKAGLPAEEAESYLKKGYSLNDRVGTSYLEKQYEEVLQGKRPVKEIHLDKHGDMESVENIEEGSKGKNIKLTIDLAFQDSVDALLKSYFNSELGNGGAKYSEGVYAVALNPQTGAVLSMSGLKHDLKTGELTPDSLGTVTNVFVPGSVVKAATISSGWENGVLSGNQTLTDQPIVFQGSAPIYSWYKLAYGSFPITAVEALEYSSNAYVVQTALGIMGQTYQPNMFVGTSNLESAMGKLRSTFGEYGLGSATGIDLPDESTGLVPKEYNFANFITNAFGQFDNYTPMQLAQYVATIANNGVRLAPHIVEGIYDNNDKGGLGELIQAIDTKEINKVNISESDMAILHQGFYQVSHGTSPLTTGRAFSDGATVSISGKTGTNTNAVAYAPTENPQIAVAVVFPHNTNLTKNVGPAIARDIINLYNQHHPMN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 99 | Bacterial Dihydropteroate synthetase (Bact folP) | 1AJ0 | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name Bact folP Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms folP; H2Pte synthase; Dihydropteroate synthase; Dihydropteroate pyrophosphorylase; DHPS Protein family DHPS family Biochemical class Alkyl aryl transferase Function Dhps catalyzes the formation of the immediate precursor of folic acid. It is implicated in resistance to sulfonamide. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB14033; DB00634; DB01298; DB01581; DB06821; DB01582; DB00576; DB01015; DB00259; DB06729; DB00263 Interacts with NA EC number EC 2.5.1.15 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Folate biosynthesis; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 30614.8 Length 282 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 32.55 Isoelectric point 5.68 Charge (pH=7) -8.5 3D Binding mode Sequence MKLFAQGTSLDLSHPHVMGILNVTPDSFSDGGTHNSLIDAVKHANLMINAGATIIDVGGESTRPGAAEVSVEEELQRVIPVVEAIAQRFEVWISVDTSKPEVIRESAKVGAHIINDIRSLSEPGALEAAAETGLPVCLMHMQGNPKTMQEAPKYDDVFAEVNRYFIEQIARCEQAGIAKEKLLLDPGFGFGKNLSHNYSLLARLAEFHHFNLPLLVGMSRKSMIGQLLNVGPSERLSGSLACAVIAAMQGAHIIRVHDVKETVEAMRVVEATLSAKENKRYE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 100 | Riboflavin synthase | 1PKV | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name ribC Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms JW1654;ribE;b1662 Protein family NA Biochemical class Transferase Function Riboflavin synthase activity. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00140 Interacts with NA EC number 2.5.1.9 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Reference proteome; Repeat; Riboflavin biosynthesis; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 19023.5 Length 174 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 2.85 Isoelectric point 5.13 Charge (pH=7) -9.8 3D Binding mode Sequence MFTGIVQGTAKLVSIDEKPNFRTHVVELPDHMLDGLETGASVAHNGCCLTVTEINGNHVSFDLMKETLRITNLGDLKVGDWVNVERAMFTGIVQGTAKLVSIDEKPNFRTHVVELPDHMLDGLETGASVAHNGCCLTVTEINGNHVSFDLMKETLRITNLGDLKVGDWVNVERA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||