Job Results:
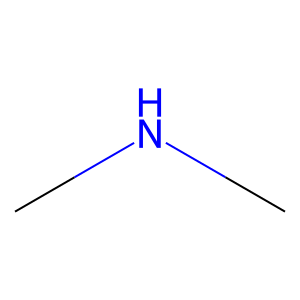
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
8da1e79bf3c5af0a1c99e2e2a8101bb5
Job name
NA
Time
2025-02-13 15:08:06
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 81 | Glutathione S-transferase LANCL1 (LANCL1) | 3E73 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name LANCL1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms p40; LanC-like protein 1; GPR69A; 40 kDa erythrocyte membrane protein Protein family LanC-like protein family Biochemical class NA Function Functions as glutathione transferase. Catalyzes conjugation of the glutathione (GSH) to artificial substrates 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB) and p-nitrophenyl acetate. Mitigates neuronal oxidative stress during normal postnatal development and in response to oxidative stresses probably through GSH antioxidant defense mechanism (By similarity). May play a role in EPS8 signaling. Binds glutathione. Related diseases Spermatogenic failure 5 (SPGF5) [MIM:243060]: An infertility disorder caused by spermatogenesis defects. Semen from affected men show close to 100% morphologically abnormal multiflagellar spermatozoa with low motility, oversized irregular heads, and abnormal midpiece and acrosome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17435757, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21733974}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9UHR4; P42858; Q08509 EC number EC 2.5.1.18 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Membrane; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 46005.4 Length 405 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 33.7 Isoelectric point 7.13 Charge (pH=7) 0.4 3D Binding mode Sequence SMDIEFMAQRAFPNPYADYNKSLAEGYFDAAGRLTPEFSQRLTNKIRELLQQMERGLKSADPRDGTGYTGWAGIAVLYLHLYDVFGDPAYLQLAHGYVKQSLNCLTKRSITFLCGDAGPLAVAAVLYHKMNNEKQAEDCITRLIHLNKIDPHAPNEMLYGRIGYIYALLFVNKNFGVEKIPQSHIQQICETILTSGENLARKRNFTAKSPLMYEWYQEYYVGAAHGLAGIYYYLMQPSLQVSQGKLHSLVKPSVDYVCQLKFPSGNYPPCIGDNRDLLVHWCHGAPGVIYMLIQAYKVFREEKYLCDAYQCADVIWQYGLLKKGYGLCHGSAGNAYAFLTLYNLTQDMKYLYRACKFAEWCLEYGEHGCRTPDTPFSLFEGMAGTIYFLADLLVPTKARFPAFEL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 82 | Bifunctional protein PutA | 3E2Q | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name putA Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b1014;poaA;JW0999 Protein family Proline dehydrogenase family; Aldehyde dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase activity.Bacterial-type RNA polymerase core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding.DNA binding.Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.Identical protein binding.Proline dehydrogenase activity.Sequence-specific DNA binding.Transcriptional repressor activity, bacterial-type RNA polymerase core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding. Related diseases Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency (FBP1D) [MIM:229700]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by impaired gluconeogenesis, and episodes of hypoglycemia and metabolic acidosis that can be lethal in newborn infants or young children. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12126934, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25601412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9382095}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03051; DB03147; DB04398 Interacts with P09546 EC number 1.2.1.88; 1.5.5.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; DNA-binding; FAD; Flavoprotein; Multifunctional enzyme; NAD; Oxidoreductase; Proline metabolism; Reference proteome; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 45567.7 Length 407 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 33.2 Isoelectric point 7.22 Charge (pH=7) 0.47 3D Binding mode Sequence QSVSRAAITAAYRRPETEAVSMLLEQARLPQPVAEQAHKLAYQLADKLRRLMGEQFVTGETIAEALANARKLEEKGFRYSYDMLGEAALTAADAQAYMVSYQQAIHAIGKASNGRGIYEGPGISIKLSALHPRYSRAQYDRVMEELYPRLKSLTLLARQYDIGINIDAEESDRLEISLDLLEKLCFEPELAGWNGIGFVIQAYQKRCPLVIDYLIDLATRSRRRLMIRLVKGAYWDSEIKRAQMDGLEGYPVYTRKVYTDVSYLACAKKLLAVPNLIYPQFATHNAHTLAAIYQLAGQNYYPGQYEFQCLHGMGEPLYEQVTGKVADGKLNRPCRISAPVGTHETLLAYLVRRLLENGANTSFVNRIADTSLPLDELVADPVTAVEKLAQQEGQTGLPHPKIPLPRD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 83 | Transferrin (TF) | 1RYO | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name TF Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Siderophilin; Serotransferrin; PRO1400; Beta-1 metal-binding globulin Protein family Transferrin family Biochemical class Transferrin Function It is responsible for the transport of iron from sites of absorption and heme degradation to those of storage and utilization. Serum transferrin may also have a further role in stimulating cell proliferation. Transferrins are iron binding transport proteins which can bind two Fe(3+) ions in association with the binding of an anion, usually bicarbonate. Related diseases Atransferrinemia (ATRAF) [MIM:209300]: A rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by abnormal synthesis of transferrin leading to iron overload and microcytic hypochromic anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11110675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15466165}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01370; DB14517; DB14518; DB01294; DB14526; DB14527; DB11136; DB14528; DB14529; DB14530; DB00515; DB09130; DB11397; DB13949; DB14490; DB14491; DB14488; DB14501; DB14489; DB13257; DB06215; DB06784; DB05260; DB01592; DB00893; DB00677; DB06757; DB11182; DB14520; DB01593; DB14487; DB14533; DB14548 Interacts with O43315; O00501; Q7Z7G2; Q9GZR5; Q9Y282; Q96KR6; P01350; P08034; Q8NBJ4; O15529; Q8TED1; Q7Z5P4; A8MZ59; O15173; Q96TC7; Q3KNW5; Q9BXS9-3; Q99523; O43278-2; Q8N9I0; P02786; Q4KMG9; Q9K0U9; Q09057; Q9K0V0; P02786 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Ion transport; Iron; Iron transport; Metal-binding; Methylation; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35854.5 Length 324 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 34.17 Isoelectric point 7.58 Charge (pH=7) 1.42 3D Binding mode Sequence KTVRWCAVSEHEATKCQSFRDHMKSVIPSDGPSVACVKKASYLDCIRAIAANEADAVTLDAGLVYDAYLAPNNLKPVVAEFYGSKEDPQTFYYAVAVVKKDSGFQMNQLRGKKSCHTGLGRSAGWNIPIGLLYCDLPEPRKPLEKAVANFFSGSCAPCADGTDFPQLCQLCPGCGCSTLNQYFGYSGAFKCLKDGAGDVAFVKHSTIFENLANKADRDQYELLCLDNTRKPVDEYKDCHLAQVPSHTVVARSMGGKEDLIWELLNQAQEHFGKDKSKEFQLFSSPHGKDLLFKDSAHGFLKVPPRMDAKMYLGYEYVTAIRNLR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 84 | Endolysin | 1AM7 | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name R Organism Escherichia phage lambda (Bacteriophage lambda) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Glycosyl hydrolase 24 family Biochemical class Glycosidase Function Lyase activity.Lysozyme activity.Lytic transglycosylase activity. Related diseases Estrogen resistance (ESTRR) [MIM:615363]: A disorder characterized by partial or complete resistance to estrogens, in the presence of elevated estrogen serum levels. Clinical features include absence of the pubertal growth spurt, delayed bone maturation, unfused epiphyses, reduced bone mineral density, osteoporosis, continued growth into adulthood and very tall adult stature. Glucose intolerance, hyperinsulinemia and lipid abnormalities may also be present. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23841731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27754803}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04206 Interacts with NA EC number 4.2.2.n2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Antimicrobial; Bacteriolytic enzyme; Cytolysis; Direct protein sequencing; Host cell lysis by virus; Host cytoplasm; Lyase; Reference proteome; Viral release from host cell Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 49834.9 Length 462 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 18.78 Isoelectric point 9.6 Charge (pH=7) 18.29 3D Binding mode Sequence MVEINNQRKAFLDMLAXSEGTDNGRQKTRNHGYDVIVGGELFTDYSDHPRKLVTLNPKLKSTGAGRYQLLSRXXDAYRKQLGLKDFSPKSQDAVALQQIKERGALPMIDRGDIRQAIDRCSNIXASLPGAGYGQFEHKADSLIAKFKEAGGTVRMVEINNQRKAFLDMLAXSEGTDNGRQKTRNHGYDVIVGGELFTDYSDHPRKLVTLNPKLKSTGAGRYQLLSRXXDAYRKQLGLKDFSPKSQDAVALQQIKERGALPMIDRGDIRQAIDRCSNIXASLPGAGYGQFEHKADSLIAKFKEAGGTVRMVEINNQRKAFLDMLAXSEGTDNGRQKTRNHGYDVIVGGELFTDYSDHPRKLVTLNPKLKSTGAGRYQLLSRXXDAYRKQLGLKDFSPKSQDAVALQQIKERGALPMIDRGDIRQAIDRCSNIXASLPGAGYGQFEHKADSLIAKFKEAGGTVR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 85 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP1) | 5WS1 | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name PARP1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP1; Poly[ADP-ribose] synthetase-1; Poly[ADP-ribose] synthase 1; Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1; PPOL; PARP-1; NAD(+)Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase-1 ADP-ribosyltrans Protein family ARTD/PARP family Biochemical class Glycosyltransferases Function Mainly mediates glutamate and aspartate ADP-ribosylation of target proteins: the ADP-D-ribosyl group of NAD(+) is transferred to the acceptor carboxyl group of glutamate and aspartate residues and further ADP-ribosyl groups are transferred to the 2'-position of the terminal adenosine moiety, building up a polymer with an average chain length of 20-30 units. Mediates the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of a number of proteins, including itself, APLF and CHFR. Also mediates serine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins following interaction with HPF1; HPF1 conferring serine specificity. Probably also catalyzes tyrosine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins following interaction with HPF1. Catalyzes the poly-ADP-ribosylation of histones in a HPF1-dependent manner. Involved in the base excision repair (BER) pathway by catalyzing the poly-ADP-ribosylation of a limited number of acceptor proteins involved in chromatin architecture and in DNA metabolism. ADP-ribosylation follows DNA damage and appears as an obligatory step in a detection/signaling pathway leading to the reparation of DNA strand breaks. In addition to base excision repair (BER) pathway, also involved in double-strand breaks (DSBs) repair: together with TIMELESS, accumulates at DNA damage sites and promotes homologous recombination repair by mediating poly-ADP-ribosylation. In addition to proteins, also able to ADP-ribosylate DNA: catalyzes ADP-ribosylation of DNA strand break termini containing terminal phosphates and a 2'-OH group in single- and double-stranded DNA, respectively. Required for PARP9 and DTX3L recruitment to DNA damage sites. PARP1-dependent PARP9-DTX3L-mediated ubiquitination promotes the rapid and specific recruitment of 53BP1/TP53BP1, UIMC1/RAP80, and BRCA1 to DNA damage sites. Acts as a regulator of transcription: positively regulates the transcription of MTUS1 and negatively regulates the transcription of MTUS2/TIP150. With EEF1A1 and TXK, forms a complex that acts as a T-helper 1 (Th1) cell-specific transcription factor and binds the promoter of IFN-gamma to directly regulate its transcription, and is thus involved importantly in Th1 cytokine production. Involved in the synthesis of ATP in the nucleus, together with NMNAT1, PARG and NUDT5. Nuclear ATP generation is required for extensive chromatin remodeling events that are energy-consuming. Poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase that mediates poly-ADP-ribosylation of proteins and plays a key role in DNA repair. Related diseases Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency (DLDD) [MIM:246900]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized biochemically by a combined deficiency of the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC), pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC), and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (KGDC). Clinically, affected individuals have lactic acidosis and neurologic deterioration due to sensitivity of the central nervous system to defects in oxidative metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10448086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11687750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12925875, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15712224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16442803, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16770810, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17404228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20160912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8506365, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8968745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9540846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9934985}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04010; DB03509; DB03072; DB03722; DB03073; DB07787; DB07096; DB07330; DB02498; DB13877; DB02701; DB11793; DB02690; DB09074; DB12332; DB11760; DB00277; DB07232; DB01593; DB14487; DB14533; DB14548 Interacts with Q8IW19; Q7Z2E3; P42574; P49715; Q86WJ1-1; P26358; Q01094; Q96L91; P11308; O60741; P09429; Q13007; Q9BQ69; P08651; Q9Y530; P09874; Q8N2W9; P46063; Q9NTX7; Q14684-1; O95863; P63165; P04637; P0CG48; Q14191; P18887; P54577; Q2M1K9; Q02085 EC number EC 2.4.2.30 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; ADP-ribosylation; Allosteric enzyme; Apoptosis; Chromosome; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; DNA damage; DNA repair; DNA-binding; Glycosyltransferase; Immunity; Innate immunity; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; NAD; Nucleotidyltransferase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 36904 Length 329 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 35.9 Isoelectric point 6.83 Charge (pH=7) -0.44 3D Binding mode Sequence DLIKMIFDVESMKKAMVEYEIDLQKMPLGKLSKRQIQAAYSILSEVQQAVSQGSDSQILDLSNRFYTLIPHDFGMKKPPLLNNADSVQAKAEMLDNLLDIEVAYSLPIDVNYEKLKTDIKVVDRDSEEAEIIRKYVKNTHATTHNAYDLEVIDIFKIEREGECQRYKPFKQLHNRRLLWHGSRTTNFAGILSQGLRIAPPEAPVTGYMFGKGIYFADMVSKSANYCHTSQGDPIGLILLGEVALGNMYELKHASHISKLPKGKHSVKGLGKTTPDPSANISLDGVDVPLGTGISSGVNDTSLLYNEYIVYDIAQVNLKYLLKLKFNFKT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 86 | Penicillin-binding protein 2B | 2WAD | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name penA Organism Streptococcus pneumoniae (strain ATCC BAA-255 / R6) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms spr1517;pbp2b Protein family Transpeptidase family Biochemical class Peptide binding protein Function Penicillin binding. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01163; DB00415; DB08795; DB01140; DB00456; DB01066; DB00493; DB01331; DB01212; DB00567; DB03313; DB00485; DB00739; DB01603; DB00607; DB00713; DB00319 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Antibiotic resistance; Cell membrane; Cell shape; Cell wall biogenesis/degradation; Membrane; Peptidoglycan synthesis; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 65444.4 Length 607 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 30.15 Isoelectric point 4.95 Charge (pH=7) -20.68 3D Binding mode Sequence SQTKVTTSSARGEIYDASGKPLVENTLKQVVSFTRSNKMTATDLKEIAKKLLTYVSISSPNLTERQLADYYLADPEIYKKTVEALPSESELYNNAVDSVPTSQLNYTEDEKKEIYLFSQLNAVGNFATGTIATDPLNDSQVAVIASISKEMPGISISTSWDRKILETSLSSIVGSVSSEKAGLPAEEAESYLKKGYSLNDRVGTSYLEKQYEEVLQGKRPVKEIHLDKHGDMESVENIEEGSKGKNIKLTIDLAFQDSVDALLKSYFNSELGNGGAKYSEGVYAVALNPQTGAVLSMSGLKHDLKTGELTPDSLGTVTNVFVPGSVVKAATISSGWENGVLSGNQTLTDQPIVFQGSAPIYSWYKLAYGSFPITAVEALEYSSNAYVVQTALGIMGQTYQPNMFVGTSNLESAMGKLRSTFGEYGLGSATGIDLPDESTGLVPKEYNFANFITNAFGQFDNYTPMQLAQYVATIANNGVRLAPHIVEGIYDNNDKGGLGELIQAIDTKEINKVNISESDMAILHQGFYQVSHGTSPLTTGRAFSDGATVSISGKTGTNTNAVAYAPTENPQIAVAVVFPHNTNLTKNVGPAIARDIINLYNQHHPMN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 87 | Pancreatic alpha-amylase (AMY2A) | 4GQR | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name AMY2A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PA; 1,4-alpha-D-glucan glucanohydrolase Protein family Glycosyl hydrolase 13 family Biochemical class Glycosylase Function Hydrolyses alpha bonds of large, alpha-linked polysaccharides, such as starch and glycogen, yielding glucose and maltose. Related diseases Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA) [MIM:256800]: Characterized by a congenital insensitivity to pain, anhidrosis (absence of sweating), absence of reaction to noxious stimuli, self-mutilating behavior, and intellectual disability. This rare autosomal recessive disorder is also known as congenital sensory neuropathy with anhidrosis or hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type IV or familial dysautonomia type II. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10090906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10233776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10330344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10567924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10861667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10982191, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11159935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11310631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18077166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22302274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27676246, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28177573, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28328124, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8696348}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Chromosomal aberrations involving NTRK1 are found in papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) (PubMed:1532241, PubMed:2869410, PubMed:7565764). Translocation t(1;3)(q21;q11) with TFG generates the TRKT3 (TRK-T3) transcript by fusing TFG to the 3'-end of NTRK1 (PubMed:7565764). A rearrangement with TPM3 generates the TRK transcript by fusing TPM3 to the 3'-end of NTRK1 (PubMed:2869410). An intrachromosomal rearrangement that links the protein kinase domain of NTRK1 to the 5'-end of the TPR gene forms the fusion protein TRK-T1. TRK-T1 is a 55 kDa protein reacting with antibodies against the C-terminus of the NTRK1 protein (PubMed:1532241). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1532241, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2869410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7565764}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03439; DB03495; DB04618; DB02889; DB04453; DB03092; DB00284; DB03971; DB03773; DB02379; DB00702; DB01922; DB00491; DB02218; DB03088 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.2.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Carbohydrate metabolism; Chloride; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Glycosidase; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 55758.8 Length 496 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 23.97 Isoelectric point 6.45 Charge (pH=7) -2.34 3D Binding mode Sequence XYSPNTQQGRTSIVHLFEWRWVDIALECERYLAPKGFGGVQVSPPNENVAIYNPFRPWWERYQPVSYKLCTRSGNEDEFRNMVTRCNNVGVRIYVDAVINHMCGNAVSAGTSSTCGSYFNPGSRDFPAVPYSGWDFNDGKCKTGSGDIENYNDATQVRDCRLTGLLDLALEKDYVRSKIAEYMNHLIDIGVAGFRLDASKHMWPGDIKAILDKLHNLNSNWFPAGSKPFIYQEVIDLGGEPIKSSDYFGNGRVTEFKYGAKLGTVIRKWNGEKMSYLKNWGEGWGFVPSDRALVFVDNHDNQRGHGAGGASILTFWDARLYKMAVGFMLAHPYGFTRVMSSYRWPRQFQNGNDVNDWVGPPNNNGVIKEVTINPDTTCGNDWVCEHRWRQIRNMVIFRNVVDGQPFTNWYDNGSNQVAFGRGNRGFIVFNNDDWSFSLTLQTGLPAGTYCDVISGDKINGNCTGIKIYVSDDGKAHFSISNSAEDPFIAIHAESKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 88 | Riboflavin synthase | 1PKV | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name ribC Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms JW1654;ribE;b1662 Protein family NA Biochemical class Transferase Function Riboflavin synthase activity. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00140 Interacts with NA EC number 2.5.1.9 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Reference proteome; Repeat; Riboflavin biosynthesis; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 19023.5 Length 174 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 2.85 Isoelectric point 5.13 Charge (pH=7) -9.8 3D Binding mode Sequence MFTGIVQGTAKLVSIDEKPNFRTHVVELPDHMLDGLETGASVAHNGCCLTVTEINGNHVSFDLMKETLRITNLGDLKVGDWVNVERAMFTGIVQGTAKLVSIDEKPNFRTHVVELPDHMLDGLETGASVAHNGCCLTVTEINGNHVSFDLMKETLRITNLGDLKVGDWVNVERA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 89 | Fumarate reductase flavoprotein subunit | 1KF6 | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name frdA Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms JW4115;b4154 Protein family FAD-dependent oxidoreductase 2 family, FRD/SDH subfamily Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Electron carrier activity.FAD binding.Fumarate reductase (menaquinone).Succinate dehydrogenase activity. Related diseases Glycogen storage disease 11 (GSD11) [MIM:612933]: A metabolic disorder that results in exertional myoglobinuria, pain, cramps and easy fatigue. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2334430}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07490; DB07918; DB00730 Interacts with P0AC47; P0ACB4; P76111 EC number 1.3.5.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell inner membrane; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Electron transport; FAD; Flavoprotein; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,M Molecular weight (Da) 90370.7 Length 820 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 28.88 Isoelectric point 5.86 Charge (pH=7) -16.21 3D Binding mode Sequence MQTFQADLAIVGAGGAGLRAAIAAAQANPNAKIALISKVYPMRSHTVAAEGGSAAVAQDHDSFEYHFHDTVAGGDWLCEQDVVDYFVHHCPTEMTQLELWGCPWSRRPDGSVNVRRFGGMKIERTWFAADKTGFHMLHTLFQTSLQFPQIQRFDEHFVLDILVDDGHVRGLVAMNMMEGTLVQIRANAVVMATGGAGRVYRYNTNGGIVTGDGMGMALSHGVPLRDMEFVQYHPTGLPGSGILMTEGCRGEGGILVNKNGYRYLQDYGMGPETPLGEPKNKYMELGPRDKVSQAFWHEWRKGNTISTPRGDVVYLDLRHLGEKKLHERLPFICELAKAYVGVDPVKEPIPVRPTAHYTMGGIETDQNCETRIKGLFAVGECSSVGLHGANRLGSNSLAELVVFGRLAGEQATERAATAGNGNEAAIEAQAAGVEQRLKDLVNQDGGENWAKIRDEMGLAMEEGCGIYRTPELMQKTIDKLAELQERFKRVRITDTSSVFNTDLLYTIELGHGLNVAECMAHSAMARKESRGAHQRLDEGCTERDDVNFLKHTLAFRDADGTTRLEYSDVKITTLPPAAEMKNLKIEVVRYNPEVDTAPHSAFYEVPYDATTSLLDALGYIKDNLAPDLSYRWSCRMAICGSCGMMVNNVPKLACKTFLRDYTDGMKVEALANFPIERDLVVDMTHFIESLEAIKPYIIGNSRTADQGTNIQTPAQMAKYHQFSGCINCGLCYAACPQFGLNPEFIGPAAITLAHRYNEDSRDHGKKERMAQLNSQNGVWSCTFVGYCSEVCPKHVDPAAAIQQGKVESSKDFLIATLKPR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 90 | Bifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase, mitochondrial | 5TC4 | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name MTHFD2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NMDMC Protein family Tetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Magnesium ion binding.Methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase activity.Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity.Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity.Phosphate ion binding. Related diseases Acute hepatic porphyria (AHEPP) [MIM:612740]: A form of porphyria. Porphyrias are inherited defects in the biosynthesis of heme, resulting in the accumulation and increased excretion of porphyrins or porphyrin precursors. They are classified as erythropoietic or hepatic, depending on whether the enzyme deficiency occurs in red blood cells or in the liver. AHP is characterized by attacks of gastrointestinal disturbances, abdominal colic, paralyses and peripheral neuropathy. Most attacks are precipitated by drugs, alcohol, caloric deprivation, infections, or endocrine factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10706561, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1309003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1569184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17236137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2063868}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00157; DB00116 Interacts with Q9UJ70-2 EC number 1.5.1.15; 3.5.4.9 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Hydrolase; Isopeptide bond; Magnesium; Mitochondrion; Multifunctional enzyme; NAD; NADP; One-carbon metabolism; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transit peptide; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 31600.3 Length 292 Aromaticity 0.03 Instability index 27.9 Isoelectric point 8 Charge (pH=7) 1.64 3D Binding mode Sequence EAVVISGRKLAQQIKQEVRQEVEEWVASGNKRPHLSVILVGENPASHSYVLNKTRAAAVVGINSETIMKPASISEEELLNLINKLNNDDNVDGLLVQLPLPEHIDERRICNAVSPDKDVDGFHVINVGRMCLDQYSMLPATPWGVWEIIKRTGIPTLGKNVVVAGRSKNVGMPIAMLLHTDGAHERPGGDATVTISHRYTPKEQLKKHTILADIVISAAGIPNLITADMIKEGAAVIDVGINRVHKPKLVGDVDFEGVRQKAGYITPVPGGVGPMTVAMLMKNTIIAAKKVL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 91 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] | 3EYA | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name poxB Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b0871;JW0855 Protein family TPP enzyme family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.Identical protein binding.Lipid binding.Magnesium ion binding.Pyruvate dehydrogenase (quinone) activity.Thiamine pyrophosphate binding. Related diseases Glycogen storage disease 6 (GSD6) [MIM:232700]: A metabolic disorder characterized by mild to moderate hypoglycemia, mild ketosis, growth retardation, and prominent hepatomegaly. Heart and skeletal muscle are not affected. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9529348}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P07003 EC number 1.2.5.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell inner membrane; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Lipid-binding; Magnesium; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Oxidoreductase; Pyruvate; Reference proteome; Thiamine pyrophosphate; Ubiquinone Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I,J,K,L Molecular weight (Da) 113027 Length 1046 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 35.99 Isoelectric point 5.75 Charge (pH=7) -24.38 3D Binding mode Sequence MKQTVAAYIAKTLESAGVKRIWGVTGDSLNGLSDSLNRMGTIEWMSTRHEEVAAFAAGAEAQLSGELAVCAGSCGPGNLHLINGLFDCHRNHVPVLAIAAHIPSSEIGSGYFQETHPQELFRECSHYCELVSSPEQIPQVLAIAMRKAVLNRGVSVVVLPGDVALKPAPEGATMHWYHAPQPVVTPEEEELRKLAQLLRYSSNIALMCGSGCAGAHKELVEFAGKIKAPIVHALRGKEHVEYDNPYDVGMTGLIGFSSGFHTMMNADTLVLLGTQFPYRAFYPTDAKIIQIDINPASIGAHSKVDMALVGDIKSTLRALLPLVEEKADRKFLDKALEDYRDARKGLDDLAKPSEKAIHPQYLAQQISHFAADDAIFTCDVGTPTVWAARYLKMNGKRRLLGSFNHGSMANAMPQALGAQATEPERQVVAMCGDGGFSMLMGDFLSVVQMKLPVKIVVFNNSVLGFDGTELHDTNFARIAEACGITGIRVEKASEVDEALQRAFSIDGPVLVDVVVAKEELAIPMKQTVAAYIAKTLESAGVKRIWGVTGDSLNGLSDSLNRMGTIEWMSTRHEEVAAFAAGAEAQLSGELAVCAGSCGPGNLHLINGLFDCHRNHVPVLAIAAHIPSSEIGSGYFQETHPQELFRECSHYCELVSSPEQIPQVLAIAMRKAVLNRGVSVVVLPGDVALKPAPEGATMHWYHAPQPVVTPEEEELRKLAQLLRYSSNIALMCGSGCAGAHKELVEFAGKIKAPIVHALRGKEHVEYDNPYDVGMTGLIGFSSGFHTMMNADTLVLLGTQFPYRAFYPTDAKIIQIDINPASIGAHSKVDMALVGDIKSTLRALLPLVEEKADRKFLDKALEDYRDARKGLDDLAKPSEKAIHPQYLAQQISHFAADDAIFTCDVGTPTVWAARYLKMNGKRRLLGSFNHGSMANAMPQALGAQATEPERQVVAMCGDGGFSMLMGDFLSVVQMKLPVKIVVFNNSVLGFVGTELHDTNFARIAEACGITGIRVEKASEVDEALQRAFSIDGPVLVDVVVAKEELAIP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 92 | Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase | 5I85 | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name SMPD1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms ASM Protein family Acid sphingomyelinase family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Acid sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase activity.Hydrolase activity, acting on glycosyl bonds.Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase activity.Zinc ion binding. Related diseases Niemann-Pick disease A (NPDA) [MIM:257200]: An early-onset lysosomal storage disorder caused by failure to hydrolyze sphingomyelin to ceramide. It results in the accumulation of sphingomyelin and other metabolically related lipids in reticuloendothelial and other cell types throughout the body, leading to cell death. Niemann-Pick disease type A is a primarily neurodegenerative disorder characterized by onset within the first year of life, intellectual disability, digestive disorders, failure to thrive, major hepatosplenomegaly, and severe neurologic symptoms. The severe neurological disorders and pulmonary infections lead to an early death, often around the age of four. Clinical features are variable. A phenotypic continuum exists between type A (basic neurovisceral) and type B (purely visceral) forms of Niemann-Pick disease, and the intermediate types encompass a cluster of variants combining clinical features of both types A and B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12556236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1391960, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15221801, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15877209, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1618760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1718266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18815062, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19405096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2023926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20386867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22818240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23252888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23430884, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26499107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27338287, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8680412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8693491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9266408, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9660788}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Niemann-Pick disease B (NPDB) [MIM:607616]: A late-onset lysosomal storage disorder caused by failure to hydrolyze sphingomyelin to ceramide. It results in the accumulation of sphingomyelin and other metabolically related lipids in reticuloendothelial and other cell types throughout the body, leading to cell death. Clinical signs involve only visceral organs. The most constant sign is hepatosplenomegaly which can be associated with pulmonary symptoms. Patients remain free of neurologic manifestations. However, a phenotypic continuum exists between type A (basic neurovisceral) and type B (purely visceral) forms of Niemann-Pick disease, and the intermediate types encompass a cluster of variants combining clinical features of both types A and B. In Niemann-Pick disease type B, onset of the first symptoms occurs in early childhood and patients can survive into adulthood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12369017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12556236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1301192, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15241805, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16010684, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1618760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16472269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18815062, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1885770, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19050888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19405096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20386867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21098024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21621718, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22613662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22818240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23252888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23430512, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25920558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26084044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26499107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27338287, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27659707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8051942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8664904}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00381; DB12151; DB00477; DB01151; DB14009 Interacts with P55210 EC number 3.1.4.12; 3.1.4.3 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Glycosidase; Host-virus interaction; Hydrolase; Lipid droplet; Lipid metabolism; Lysosome; Metal-binding; Neurodegeneration; Niemann-Pick disease; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 58913.8 Length 528 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 46.93 Isoelectric point 6.48 Charge (pH=7) -3.6 3D Binding mode Sequence WGNLTCPICKGLFTAINLGLKKEPNVARVGSVAIKLCNLLKIAPPAVCQSIVHLFEDDMVEVWRRSVLSPSEACGLLLGSTCGHWDIFSSWNISLPTVPKPPPKPPSPPAPGAPVSRILFLTDLHWDHDYLEGTDPDCADPLCCRRGSGLPPASRPGAGYWGEYSKCDLPLRTLESLLSGLGPAGPFDMVYWTGDIPAHDVWHQTRQDQLRALTTVTALVRKFLGPVPVYPAVGNHESTPVNSFPPPFIEGNHSSRWLYEAMAKAWEPWLPAEALRTLRIGGFYALSPYPGLRLISLNMNFCSRENFWLLINSTDPAGQLQWLVGELQAAEDRGDKVHIIGHIPPGHCLKSWSWNYYRIVARYENTLAAQFFGHTHVDEFEVFYDEETLSRPLAVAFLAPSATTYIGLNPGYRVYQIDGNYSGSSHVVLDHETYILNLTQANIPGAIPHWQLLYRARETYGLPNTLPTAWHNLVYRMRGDMQLFQTFWFLYHKGHPPSEPCGTPCRLATLCAQLSARADSPALCRHLM Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 93 | Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase subunit M2 | 3OLJ | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name RRM2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms RR2 Protein family Ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase small chain family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Metal ion binding.Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase activity, thioredoxin disulfide as acceptor. Related diseases Pyruvate kinase hyperactivity (PKHYP) [MIM:102900]: Autosomal dominant phenotype characterized by increase of red blood cell ATP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9090535}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Pyruvate kinase deficiency of red cells (PKRD) [MIM:266200]: A frequent cause of hereditary non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia. Clinically, pyruvate kinase-deficient patients suffer from a highly variable degree of chronic hemolysis, ranging from severe neonatal jaundice and fatal anemia at birth, severe transfusion-dependent chronic hemolysis, moderate hemolysis with exacerbation during infection, to a fully compensated hemolysis without apparent anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10087985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10772876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11328279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11960989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1536957, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1896471, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19085939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2018831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21794208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7706479, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8161798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8180378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8476433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8481523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8483951, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8664896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8807089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9075576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9482576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9827908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9886305, ECO:0000269|Ref.24}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00242; DB05260; DB05801; DB05003; DB05428 Interacts with P41002; Q9UM11; P23921; O00560 EC number 1.17.4.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Deoxyribonucleotide synthesis; Iron; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 33579.4 Length 286 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 43.7 Isoelectric point 5.12 Charge (pH=7) -12.86 3D Binding mode Sequence MGVEDEPLLRENPRRFVIFPIEYHDIWQMYKKAEASFWTAEEVDLSKDIQHWESLKPEERYFISHVLAFFAASDGIVNENLVERFSQEVQITEARCFYGFQIAMENIHSEMYSLLIDTYIKDPKEREFLFNAIETMPCVKKKADWALRWIGDKEATYGERVVAFAAVEGIFFSGSFASIFWLKKRGLMPGLTFSNELISRDEGLHCDFACLMFKHLVHKPSEERVREIIINAVRIEQEFLTEALPVKLIGMNCTLMKQYIEFVADRLMLELGFSKVFRVENPFDFM Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 94 | Nitric-oxide synthase brain (NOS1) | 5ADF | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name NOS1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylase NOS1; Nitric oxide synthase, brain; Neuronal NOS; NOS, type I; NOS type I; NNOS; NC-NOS; N-NOS; BNOS Protein family NOS family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function In the brain and peripheral nervous system, NO displays many properties of a neurotransmitter. Probably has nitrosylase activity and mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of cytoplasmic target proteins such SRR. Produces nitric oxide (NO) which is a messenger molecule with diverse functions throughout the body. Related diseases Variation Asp-298 in NOS3 may be associated with susceptibility to coronary spasm. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11740345, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9737779}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02143; DB02727; DB01997; DB03892; DB02207; DB03710; DB00155; DB00843; DB00997; DB03147; DB03247; DB01942; DB01221; DB02077; DB01821; DB09241; DB03144; DB03449; DB02044; DB02644; DB08019; DB08018; DB02027; DB03461; DB04223; DB06096; DB02991; DB03707 Interacts with Q08AM6 EC number EC 1.14.13.39 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calmodulin-binding; Cell membrane; Cell projection; FAD; Flavoprotein; FMN; Heme; Iron; Membrane; Metal-binding; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Synapse; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 34875.7 Length 299 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 42.94 Isoelectric point 5.96 Charge (pH=7) -6.25 3D Binding mode Sequence CPRFLKVKNWETEVVLTDTLHLKSTLETGCTEYICMGSIMHPRDYCDNSRYNILEEVAKKMNLDMRKTSSLWKDQALVEINIAVLYSFQSDKVTIVDHHSATESFIKHMENEYRCRGGCPADWVWIVPPMSGSITPVFHQEMLNYRLRFLKVKNWETEVVLTDTLHLKSTLETGCTEYICMGSIMHPRDYCDNSRYNILEEVAKKMNLDMRKTSSLWKDQALVEINIAVLYSFQSDKVTIVDHHSATESFIKHMENEYRCRGGCPADWVWIVPPMSGSITPVFHQEMLNYRLTPSFEYQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 95 | Glycine amidinotransferase, mitochondrial | 7JDW | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name GATM Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms AGAT Protein family Amidinotransferase family Biochemical class Transferase Function Glycine amidinotransferase activity. Related diseases Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 3 (CCDS3) [MIM:612718]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by developmental delay/regression, intellectual disability, severe disturbance of expressive and cognitive speech, and severe depletion of creatine/phosphocreatine in the brain. Most patients develop a myopathy characterized by muscle weakness and atrophy later in life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11555793, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20682460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22386973, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23660394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23770102, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26490222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27233232}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Fanconi renotubular syndrome 1 (FRTS1) [MIM:134600]: A form of Fanconi renotubular syndrome, a disease due to a generalized dysfunction of the proximal kidney tubule resulting in decreased solute and water reabsorption. Patients have polydipsia and polyuria with phosphaturia, glycosuria and aminoaciduria. They may develop hypophosphatemic rickets or osteomalacia, acidosis and a tendency toward dehydration. Some eventually develop renal insufficiency. FRTS1 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29654216}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04454; DB02068; DB02530; DB00145; DB04185; DB00129 Interacts with Q6UY14-3; Q14457; Q9Y6G5; Q9UI10; Q13322-4; Q13352; Q14693; Q96CM3; P11684; Q9P1W8; Q8NFB2; Q13829; Q6ZMY6-2 EC number 2.1.4.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 41665.3 Length 360 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 52.78 Isoelectric point 6.64 Charge (pH=7) -1.3 3D Binding mode Sequence CPVSSYNEWDPLEEVIVGRAENACVPPFTIEVKANTYEKYWPFYQKQGGHYFPKDHLKKAVAEIEEMCNILKTEGVTVRRPDPIDWSLKYKTPDFESTGLYSAMPRDILIVVGNEIIEAPMAWRSRFFEYRAYRSIIKDYFHRGAKWTTAPKPTMADELYNQDYPIHSVEDRHKLAAQGKFVTTEFEPCFDAADFIRAGRDIFAQRSQVTNYLGIEWMRRHLAPDYRVHIISFKDPNPMHIDATFNIIGPGIVLSNPDRPCHQIDLFKKAGWTIITPPTPIIPDDHPLWMSSKWLSMNVLMLDEKRVMVDANEVPIQKMFEKLGITTIKVNIRNANSLGGGFHCWTCDVRRRGTLQSYLD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 96 | Thiopurine S-methyltransferase | 2BZG | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name TPMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, TPMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Thiopurine S-methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 3 (CCDS3) [MIM:612718]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by developmental delay/regression, intellectual disability, severe disturbance of expressive and cognitive speech, and severe depletion of creatine/phosphocreatine in the brain. Most patients develop a myopathy characterized by muscle weakness and atrophy later in life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11555793, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20682460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22386973, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23660394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23770102, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26490222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27233232}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Fanconi renotubular syndrome 1 (FRTS1) [MIM:134600]: A form of Fanconi renotubular syndrome, a disease due to a generalized dysfunction of the proximal kidney tubule resulting in decreased solute and water reabsorption. Patients have polydipsia and polyuria with phosphaturia, glycosuria and aminoaciduria. They may develop hypophosphatemic rickets or osteomalacia, acidosis and a tendency toward dehydration. Some eventually develop renal insufficiency. FRTS1 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29654216}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00993; DB00436; DB01327; DB01033; DB01250; DB01021 Interacts with Q8TAP4-4; Q15047-2; P61981 EC number 2.1.1.67 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Methyltransferase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 25971.5 Length 229 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 32.58 Isoelectric point 6.74 Charge (pH=7) -0.6 3D Binding mode Sequence EVQKNQVLTLEEWQDKWVNGKTAFHQEQGHQLLKKHLDTFLKGKSGLRVFFPLCGKAVEXKWFADRGHSVVGVEISELGIQEFFTEQNLSYSEEPITEIPGTKVFKSSSGNISLYCCSIFDLPRTNIGKFDXIWDRGALVAINPGDRKCYADTXFSLLGKKFQYLLCVLSYDPTKHPGPPFYVPHAEIERLFGKICNIRCLEKVDAFEERHKSWGIDCLFEKLYLLTEK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 97 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | 3EQC | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name MAP2K1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms PRKMK1;MEK1 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family, MAP kinase kinase subfamily Biochemical class Transferase Function ATP binding.MAP kinase kinase activity.Protein C-terminus binding.Protein kinase activity.Protein N-terminus binding.Protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity.Protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity.Protein serine/threonine kinase activity.Protein tyrosine kinase activity.Signal transducer, downstream of receptor, with protein tyrosine phosphatase activity. Related diseases Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome 3 (CFC3) [MIM:615279]: A form of cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, a multiple congenital anomaly disorder characterized by a distinctive facial appearance, heart defects and intellectual disability. Heart defects include pulmonic stenosis, atrial septal defects and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Some affected individuals present with ectodermal abnormalities such as sparse, friable hair, hyperkeratotic skin lesions and a generalized ichthyosis-like condition. Typical facial features are similar to Noonan syndrome. They include high forehead with bitemporal constriction, hypoplastic supraorbital ridges, downslanting palpebral fissures, a depressed nasal bridge, and posteriorly angulated ears with prominent helices. Distinctive features of CFC3 include macrostomia and horizontal shape of palpebral fissures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16439621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18042262}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Melorheostosis, isolated (MEL) [MIM:155950]: A sclerosing bone disorder characterized by hyperostosis of the cortex of tubular bones, frequently involving one limb. The lesions may be accompanied by abnormalities of adjacent soft tissue, joint contractures, sclerodermatous skin lesions, muscle atrophy, or hemangioma. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29643386}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06892; DB07046; DB08208; DB03115; DB11967; DB06616; DB05239; DB02152; DB07101; DB08130; DB14904; DB11689; DB08911 Interacts with Q8N9N5; Q8N9N5-2; Q9NR09; P15056; Q9Y297; O15519-1; P28482; P27361; Q13526; Q9H8W4; P04049; Q8WWU5-7; Q86Y07; Q86Y07-1; P46937 EC number 2.7.12.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cardiomyopathy; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Ectodermal dysplasia; Intellectual disability; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Tyrosine-protein kinase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34949.2 Length 312 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 45.3 Isoelectric point 5.96 Charge (pH=7) -4.47 3D Binding mode Sequence ELELDEQQRKRLEAFLTQKQKVGELKDDDFEKISELGAGNGGVVFKVSHKPSGLVMARKLIHLEIKPAIRNQIIRELQVLHECNSPYIVGFYGAFYSDGEISICMEHMDGGSLDQVLKKAGRIPEQILGKVSIAVIKGLTYLREKHKIMHRDVKPSNILVNSRGEIKLCDFGVSGQLIDSMAVGTRSYMSPERLQGTHYSVQSDIWSMGLSLVEMAVGRYPIPPPDAKELELMFGCPMAIFELLDYIVNEPPPKLPSGVFSLEFQDFVNKCLIKNPAERADLKQLMVHAFIKRSDAEEVDFAGWLCSTIGLN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 98 | TRANSPORT INHIBITOR RESPONSE 1 protein | 2P1Q | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name IAA7 Organism Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms AXR2;At3g23050;MXC7.8 Protein family Aux/IAA family Biochemical class Signaling protein Function DNA binding transcription factor activity. Related diseases LTC4 synthase deficiency is associated with a neurometabolic developmental disorder characterized by muscular hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, and microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10896305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9820300}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9LW29; Q9C5W9; Q8RYC8; Q94AH6; Q9ZR12; P49677; Q38828; Q38829; Q38830; Q38831; O24407; O24408; O24409; P49678; O24410; Q8LAL2; Q9XFM0; Q38822; Q9M1R4; Q9C5X0; Q9C8Y3; Q39255; Q570C0 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Auxin signaling pathway; Nucleus; Reference proteome; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B,C Molecular weight (Da) 65385.2 Length 581 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 47.83 Isoelectric point 7.46 Charge (pH=7) 1.23 3D Binding mode Sequence QVVGWPPVRNYRKFPEEVLEHVFSFIQLDKDRNSVSLVCKSWYEIERWCRRKVFIGNCYAVSPATVIRRFPKVRSVELKGKPHFADFNLVPDGWGGYVYPWIEAMSSSYTWLEEIRLKRMVVTDDCLELIAKSFKNFKVLVLSSCEGFSTDGLAAIAATCRNLKELDLRESDVDDVSGHWLSHFPDTYTSLVSLNISCLASEVSFSALERLVTRCPNLKSLKLNRAVPLEKLATLLQRAPQLEELGTGGYTAEVRPDVYSGLSVALSGCKELRCLSGFWDAVPAYLPAVYSVCSRLTTLNLSYATVQSYDLVKLLCQCPKLQRLWVLDYIEDAGLEVLASTCKDLRELRVFPSEPFVMEPNVALTEQGLVSVSMGCPKLESVLYFCRQMTNAALITIARNRPNMTRFRLCIIEPKAPDYLTLEPLDIGFGAIVEHCKDLRRLSLSGLLTDKVFEYIGTYAKKMEMLSVAFAGDSDLGMHHVLSGCDSLRKLEIRDCPFGDKALLANASKLETMRSLWMSSCSVSFGACKLLGQKMPKLNVEVIDERGAPDSRPESCPVERVFIYRTVAGPRFDMPGFVWNM Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 99 | Alanine aminotransferase 2 | 3IHJ | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name GPT2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms AAT2;ALT2 Protein family Class-I pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent aminotransferase family, Alanine aminotransferase subfamily Biochemical class Transferase Function L-alanine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity.Pyridoxal phosphate binding. Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder with spastic paraplegia and microcephaly (NEDSPM) [MIM:616281]: An autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by severe psychomotor developmental delay, dysarthria, walking difficulties, moderately to severely impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and progressive microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25758935}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00160; DB00142; DB00780; DB00114 Interacts with NA EC number 2.6.1.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Aminotransferase; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 48717.7 Length 436 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 47.17 Isoelectric point 6.07 Charge (pH=7) -4.32 3D Binding mode Sequence PIVLKAGEIELELQRGIKKPFTEVIRANPITFLRQVMALCTYPNLLDSPSFPEDAKKRARRILQACSQGVNCIREDVAAYITRRDGGVPADPDNIYLTTGASDGISTILKILVSGGGKSRTGVMIPIPQYPLYSAVISELDAIQVNYYLDEENCWALNVNELRRAVQEAKDHCDPKVLCIINPGNPTGQVQSRKCIEDVIHFAWEEKLFLLADEVYQDNVYSPDCRFHSFKKVLYEMGPEYSSNVELASFHSTSKGYMGECGYRGGYMEVINLHPEIKGQLVKLLSVRLCPPVSGQAAMDIVVNPPVAGEESFEQFSREKESVLGNLAKKAKLTEDLFNQVPGIHCNPLQGAMYAFPRIFIPAKAVEAAQAHQMAPDMFYCMKLLEETGICVVPGSGFGQREGTYHFRMTILPPVEKLKTVLQKVKDFHINFLEKY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 100 | DNA protection during starvation protein | 1O9R | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name dps Organism Agrobacterium fabrum (strain C58 / ATCC 33970) (Agrobacterium tumefaciens (strain C58)) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms Atu2477;AGR_C_4495 Protein family Dps family Biochemical class Iron-binding protein Function Ferric iron binding.Oxidoreductase activity, oxidizing metal ions. Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder with spastic paraplegia and microcephaly (NEDSPM) [MIM:616281]: An autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by severe psychomotor developmental delay, dysarthria, walking difficulties, moderately to severely impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and progressive microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25758935}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 1.16.-.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Iron; Iron storage; Metal-binding; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F Molecular weight (Da) 106227 Length 967 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 22.32 Isoelectric point 5.52 Charge (pH=7) -34.69 3D Binding mode Sequence MKTHKTKNDLPSNAKSTVIGILNESLASVIDLALVTKQAHWNLKGPQFIAVHELLDTFRTQLDNHGDTIAERVVQLGGTALGSLQAVSSTTKLKAYPTDIYKIHDHLDALIERYGEVANMIRKAIDDSDEAGDPTTADIFTAASRDLDKSLWFLEAHVQEKSMKTHKTKNDLPSNAKSTVIGILNESLASVIDLALVTKQAHWNLKGPQFIAVHELLDTFRTQLDNHGDTIAERVVQLGGTALGSLQAVSSTTKLKAYPTDIYKIHDHLDALIERYGEVANMIRKAIDDSDEAGDPTTADIFTAASRDLDKSLWFLEAHVQEKSTHKTKNDLPSNAKSTVIGILNESLASVIDLALVTKQAHWNLKGPQFIAVHELLDTFRTQLDNHGDTIAERVVQLGGTALGSLQAVSSTTKLKAYPTDIYKIHDHLDALIERYGEVANMIRKAIDDSDEAGDPTTADIFTAASRDLDKSLWFLEAHVQEKSHKTKNDLPSNAKSTVIGILNESLASVIDLALVTKQAHWNLKGPQFIAVHELLDTFRTQLDNHGDTIAERVVQLGGTALGSLQAVSSTTKLKAYPTDIYKIHDHLDALIERYGEVANMIRKAIDDSDEAGDPTTADIFTAASRDLDKSLWFLEAHVQEKSMKTHKTKNDLPSNAKSTVIGILNESLASVIDLALVTKQAHWNLKGPQFIAVHELLDTFRTQLDNHGDTIAERVVQLGGTALGSLQAVSSTTKLKAYPTDIYKIHDHLDALIERYGEVANMIRKAIDDSDEAGDPTTADIFTAASRDLDKSLWFLEAHVQEKSMKTHKTKNDLPSNAKSTVIGILNESLASVIDLALVTKQAHWNLKGPQFIAVHELLDTFRTQLDNHGDTIAERVVQLGGTALGSLQAVSSTTKLKAYPTDIYKIHDHLDALIERYGEVANMIRKAIDDSDEAGDPTTADIFTAASRDLDKSLWFLEAHVQEKS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||