Job Results:
Ligand
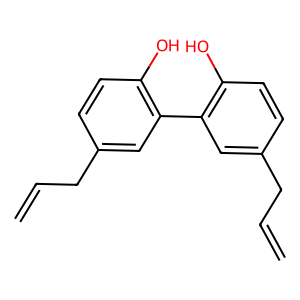
Structure
Job ID
0fdb6be2dae96620ab05e05b4d1adc2b
Job name
NA
Time
2025-04-03 17:50:26
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61 | Sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) | 3VZB | 6.99 | |
Target general information Gen name SPHK1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms SPK 1; SPK; SPHK1; SK 1; Acetyltransferase SPHK1 Protein family NA Biochemical class Kinase Function Acts on D-erythro-sphingosine and to a lesser extent sphinganine, but not other lipids, such as D,L-threo-dihydrosphingosine, N,N-dimethylsphingosine, diacylglycerol, ceramide, or phosphatidylinositol. In contrast to proapoptotic SPHK2, has a negative effect on intracellular ceramide levels, enhances cell growth and inhibits apoptosis. Involved in the regulation of inflammatory response and neuroinflammation. Via the product sphingosine 1-phosphate, stimulates TRAF2 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, and promotes activation of NF-kappa-B in response to TNF signaling leading to IL17 secretion. In response to TNF and in parallel to NF-kappa-B activation, negatively regulates RANTES inducion through p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Involved in endocytic membrane trafficking induced by sphingosine, recruited to dilate endosomes, also plays a role on later stages of endosomal maturation and membrane fusion independently of its kinase activity. In Purkinje cells, seems to be also involved in the regulation of autophagosome-lysosome fusion upon VEGFA. Catalyzes the phosphorylation of sphingosine to form sphingosine 1-phosphate (SPP), a lipid mediator with both intra- and extracellular functions. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked, syndromic, Claes-Jensen type (MRXSCJ) [MIM:300534]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRXSCJ patients manifest intellectual disability associated with variable features such as slowly progressive spastic paraplegia, seizures, facial dysmorphism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15586325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16538222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16541399, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17320160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17468742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23356856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25666439}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08868 Interacts with P07858; P68104; Q14192; Q2M3C7; Q9Y4K3; P13473-2; Q9Y371 EC number EC 2.7.1.91 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Calmodulin-binding; Cell membrane; Coated pit; Cytoplasm; Endosome; Kinase; Lipid metabolism; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Synapse; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 39813 Length 360 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 43.79 Isoelectric point 7.34 Charge (pH=7) 0.84 3D Binding mode Sequence AMGSGVLPRPCRVLVLLNPRGGKGKALQLFRSHVQPLLAEAEISFTLMLTERRNHARELVRSEELGRWDALVVMSGDGLMHEVVNGLMERPDWETAIQKPLCSLPAGSGNALAASLNHYAGYEQVTNEDLLTNCTLLLCRRLLSPMNLLSLHTASGLRLFSVLSLAWGFIADVDLESEKYRRLGEMRFTLGTFLRLAALRTYRGRLAYLPVGRVGSKTPASPVVVQQGPVDAHLVPLEEPVPSHWTVVPDEDFVLVLALLHSHLGSEMFAAPMGRCAAGVMHLFYVRAGVSRAMLLRLFLAMEKGRHMEYECPYLVYVPVVAFRLEPKDGKGVFAVDGELMVSEAVQGQVHPNYFWMVSG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 62 | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) | 5J89 | 6.99 | |
Target general information Gen name CD274 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hPD-L1; Programmed death ligand 1; PDL1; PDCD1LG1; PDCD1L1; PDCD1 ligand 1; B7H1; B7-H1; B7 homolog 1 Protein family Immunoglobulin superfamily, BTN/MOG family Biochemical class Immunoglobulin Function As a ligand for the inhibitory receptor PDCD1/PD-1, modulates the activation threshold of T-cells and limits T-cell effector response. Through a yet unknown activating receptor, may costimulate T-cell subsets that predominantly produce interleukin-10 (IL10). Plays a critical role in induction and maintenance of immune tolerance to self. Related diseases Truncation of the 3'-untranslated (3'-UTR) region of CD274 transcripts leads to elevated expression of CD274 in multiple cancers including T-cell leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and stomach adenocarcinoma (PubMed:27281199). Disruption of 3'-UTR region is caused by structural variants that stabilize CD274 transcripts, leading to overexpression (PubMed:27281199). Increased expression in tumors promotes immune evasion and tumor cell growth by allowing malignant cells to escape destruction by the immune system (PubMed:27281199). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27281199}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB15773; DB11595; DB15771; DB11945; DB15772; DB14776; DB15770; DB11714; DB15769; DB09035; DB09037; DB00203; DB00313 Interacts with P33681; Q8IZR5; Q9NX76; Q15116; Q15116 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Endosome; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Immunoglobulin domain; Membrane; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C,D Molecular weight (Da) 28335.2 Length 249 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 35.39 Isoelectric point 6.15 Charge (pH=7) -3.43 3D Binding mode Sequence AFTVTVPKDLYVVEYGSNMTIECKFPVEKQLDLAALIVYWEMEDKNIIQFVHGEEDLKVQHSSYRQRARLLKDQLSLGNAALQITDVKLQDAGVYRCMISYGGADYKRITVKVNAPYAAALEHHHAFTVTVPKDLYVVEYGSNMTIECKFPVEKQLDLAALIVYWEMEDKNIIQFVHGEEDLKVQHSSYRQRARLLKDQLSLGNAALQITDVKLQDAGVYRCMISYGGADYKRITVKVNAPYAAALEHH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 63 | 2-iminobutanoate/2-iminopropanoate deaminase | 1ONI | 6.98 | |
Target general information Gen name RIDA Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms HRSP12 Protein family RutC family Biochemical class Translation Function Deaminase activity.Endoribonuclease activity, producing 3'-phosphomonoesters.Long-chain fatty acid binding.Platinum binding.Protein homodimerization activity.RNA binding.Transition metal ion binding.Xenon atom binding. Related diseases Congenital bile acid synthesis defect 2 (CBAS2) [MIM:235555]: A condition characterized by jaundice, intrahepatic cholestasis and hepatic failure. Patients with this liver disease show absence or low levels of chenodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid in plasma and urine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12970144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15030995, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19175828, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20522910}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q8N9N5-2 EC number 3.5.99.10 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Hydrolase; Lipid metabolism; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Peroxisome; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; RNA-binding Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I Molecular weight (Da) 42624.3 Length 404 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 36.76 Isoelectric point 8.99 Charge (pH=7) 5.46 3D Binding mode Sequence SSLIRRVISTAKAPGAIGPYSQAVLVDRTIYISGQIGMDPSSGQLVSGGVAEEAKQALKNMGEILKAAGCDFTNVVKTTVLLADINDFNTVNEIYKQYFKSNFPARAAYQVAALPKGSRIEIEAVAIQGPLTTASSSLIRRVISTAKAPGAIGPYSQAVLVDRTIYISGQIGMDPSSGQLVSGGVAEEAKQALKNMGEILKAAGCDFTNVVKTTVLLADINDFNTVNEIYKQYFKSNFPARAAYQVAALPKGSRIEIEAVAIQGPLTTASSSLIRRVISTAKAPGAIGPYSQAVLVDRTIYISGQIGMDPSSGQLVSGGVAEEAKQALKNMGEILKAAGCDFTNVVKTTVLLADINDFNTVNEIYKQYFKSNFPARAAYQVAALPKGSRIEIEAVAIQGPLTTA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 64 | Receptor-type protein-tyrosine phosphatase zeta (PTPRZ1) | 5H08 | 6.98 | |
Target general information Gen name PTPRZ1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase zeta; R-PTP-zeta; PTPRZ1 Protein family Protein-tyrosine phosphatase family, Receptor class 5 subfamily Biochemical class Phosphoric monoester hydrolase Function Protein tyrosine phosphatase that negatively regulates oligodendrocyte precursor proliferation in the embryonic spinal cord. Required for normal differentiation of the precursor cells into mature, fully myelinating oligodendrocytes. May play a role in protecting oligondendrocytes against apoptosis. May play a role in the establishment of contextual memory, probably via the dephosphorylation of proteins that are part of important signaling cascades. Related diseases Optic atrophy 1 (OPA1) [MIM:165500]: A condition that features progressive visual loss in association with optic atrophy. Atrophy of the optic disk indicates a deficiency in the number of nerve fibers which arise in the retina and converge to form the optic disk, optic nerve, optic chiasm and optic tracts. OPA1 is characterized by an insidious onset of visual impairment in early childhood with moderate to severe loss of visual acuity, temporal optic disk pallor, color vision deficits, and centrocecal scotoma of variable density. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11017079, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11017080, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11440988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11440989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11810270, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12036970, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12566046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14961560, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15948788, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16513463, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16617242, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18204809, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18360822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19319978, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19325939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19969356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20185555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22382025, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22857269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23401657}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Dominant optic atrophy plus syndrome (DOA+) [MIM:125250]: A neurologic disorder characterized most commonly by an insidious onset of visual loss and sensorineural hearing loss in childhood with variable presentation of other clinical manifestations including progressive external ophthalmoplegia, muscle cramps, hyperreflexia, and ataxia. There appears to be a wide range of intermediate phenotypes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15531309, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16240368, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18065439, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18158317, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18195150, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20185555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21112924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23387428}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Behr syndrome (BEHRS) [MIM:210000]: An autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by optic atrophy beginning in early childhood associated with ataxia, pyramidal signs, spasticity, intellectual disability, and posterior column sensory loss. The ataxia, spasticity, and muscle contractures, mainly of the hip adductors, hamstrings, and soleus, are progressive and become more prominent in the second decade. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21636302, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25012220, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25146916}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome 14, cardioencephalomyopathic type (MTDPS14) [MIM:616896]: An autosomal recessive mitochondrial disorder characterized by lethal infantile encephalopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and optic atrophy. Skeletal muscle biopsies show significant mtDNA depletion and abnormal mitochondria. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26561570}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9UM73; Q12860 EC number EC 3.1.3.48 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Protein phosphatase; Proteoglycan; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32208.1 Length 282 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 38.98 Isoelectric point 7.35 Charge (pH=7) 0.89 3D Binding mode Sequence GPAIPIKHFPKHVADLHASSGFTEEFEEVQSCTVDLGITADSSNHPDNKHKNRYINIVAYDHSRVKLAQLAEKDGKLTDYINANYVDGYNRPKAYIAAQGPLKSTAEDFWRMIWEHNVEVIVMITNLVEKGRRKCDQYWPADGSEEYGNFLVTQKSVQVLAYYTVRNFTLRNTKIRVVTQYHYTQWPDMGVPEYSLPVLTFVRKAAYAKRHAVGPVVVHCSAGVGRTGTYIVLDSMLQQIQHEGTVNIFGFLKHIRSQRNYLVQTEEQYVFIHDTLVEAILS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 65 | Gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit 1 | 4MS4 | 6.97 | |
Target general information Gen name GABBR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms GPRC3B;GPR51 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 3 family, GABA-B receptor subfamily Biochemical class Signaling protein / antagonist Function G-protein coupled GABA receptor activity. Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder with poor language and loss of hand skills (NDPLHS) [MIM:617903]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by psychomotor developmental stagnation or regression. NDPLHS manifest in the first years of life as loss of purposeful hand movements, loss of language, and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26740508, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28856709, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29369404}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 59 (DEE59) [MIM:617904]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of severe early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE59 is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by onset of refractory seizures in early infancy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28856709, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29100083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29369404}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08891; DB08892; DB00181; DB00363; DB02530; DB05010; DB09072 Interacts with Q9UBS5; Q9UBS5-2; P46459; Q86UR5 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Coiled coil; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Epilepsy; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Intellectual disability; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 46502.1 Length 408 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 50.05 Isoelectric point 5.78 Charge (pH=7) -5.62 3D Binding mode Sequence RRAVYIGALFPMSGGWPGGQACQPAVEMALEDVNSRRDILPDYELKLIHHDSKCDPGQATKYLYELLYNDPIKIILMPGCSSVSTLVAEAARMWNLIVLSYGSSSPALSNRQRFPTFFRTHPSATLHNPTRVKLFEKWGWKKIATIQQTTEVFTSTLDDLEERVKEAGIEITFRQSFFSDPAVPVKNLKRQDARIIVGLFYETEARKVFCEVYKERLFGKKYVWFLIGWYADNWFKIYDPSINCTVDEMTEAVEGHITTEIVMLNPANTRSISNMTSQEFVEKLTKRLKRHPEETGGFQEAPLAYDAIWALALALNKTSRLEDFNYNNQTITDQIYRAMNSSSFEGVSGHVVFDASGSRMAWTLIEQLQGGSYKKIGYYDSTKDDLSWSKTDKWIGGSPPADDYKDDD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 66 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EHMT2 (EHMT2) | 5VSC | 6.97 | |
Target general information Gen name EHMT2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein G9a; NG36; Lysine N-methyltransferase 1C; KMT1C; Histone H3-K9 methyltransferase 3; HLA-B-associated transcript 8; H3-K9-HMTase 3; G9A; Euchromatic histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2; C6orf3 Protein family Class V-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, Histone-lysine methyltransferase family, Suvar3-9 subfamily Biochemical class Methyltransferase Function H3K9me represents a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional repression by recruiting HP1 proteins to methylated histones. Also mediates monomethylation of 'Lys-56' of histone H3 (H3K56me1) in G1 phase, leading to promote interaction between histone H3 and PCNA and regulating DNA replication. Also weakly methylates 'Lys-27' of histone H3 (H3K27me). Also required for DNA methylation, the histone methyltransferase activity is not required for DNA methylation, suggesting that these 2 activities function independently. Probably targeted to histone H3 by different DNA-binding proteins like E2F6, MGA, MAX and/or DP1. May also methylate histone H1. In addition to the histone methyltransferase activity, also methylates non-histone proteins: mediates dimethylation of 'Lys-373' of p53/TP53. Also methylates CDYL, WIZ, ACIN1, DNMT1, HDAC1, ERCC6, KLF12 and itself. Histone methyltransferase that specifically mono- and dimethylates 'Lys-9' of histone H3 (H3K9me1 and H3K9me2, respectively) in euchromatin. Related diseases Pseudohypoaldosteronism 2C (PHA2C) [MIM:614492]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by severe hypertension, hyperkalemia, hyperchloremia, mild hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis in some cases, and correction of physiologic abnormalities by thiazide diuretics. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11498583}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Neuropathy, hereditary sensory and autonomic, 2A (HSAN2A) [MIM:201300]: A form of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy, a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by degeneration of dorsal root and autonomic ganglion cells, and by sensory and/or autonomic abnormalities. HSAN2A is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by impairment of pain, temperature and touch sensation, onset of symptoms in infancy or early childhood, occurrence of distal extremity pathologies (paronychia, whitlows, ulcers, and Charcot joints), frequent amputations, sensory loss that affects all modalities of sensation (lower and upper limbs and perhaps the trunk as well), absence or diminution of tendon reflexes (usually in all limbs), minimal autonomic dysfunction, absence of sensory nerve action potentials, and virtual absence of myelinated fibers with decreased numbers of unmyelinated fibers in sural nerves. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15060842, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15911806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18521183}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q6VMQ6-2; Q6P1J9; Q9UBC3; P38919; Q9UM22; P23771; Q99684; Q13547; Q96JB3; Q92831; O60341-1; Q9Y4X4; P57682; Q13330; O94776; Q9BTC8; P20592; Q9BSU3; Q99801-1; O60568; Q9NQX1; Q5JSZ5; Q7Z3Z2; Q9P2R6; Q14119; Q96GT9; O60315; Q9NWS9-2; Q96JM2; A0A0S2Z5X4; Q96BV0; Q96EG3; Q07120; O60341-1 EC number EC 2.1.1.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ANK repeat; Chromatin regulator; Chromosome; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Methylation; Methyltransferase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 31010.9 Length 269 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 47.49 Isoelectric point 5.16 Charge (pH=7) -9.31 3D Binding mode Sequence TEKIICRDVARGYENVPIPCVNGVDGEPCPEDYKYISENCETSTMNIDRNITHLQHCTCVDDCSSSNCLCGQLSIRCWYDKDGRLLQEFNKIEPPLIFECNQACSCWRNCKNRVVQSGIKVRLQLYRTAKMGWGVRALQTIPQGTFICEYVGELISDAEADVREDDSYLFDLDEVYCIDARYYGNISRFINHLCDPNIIPVRVFMLHQDLRFPRIAFFSSRDIRTGEELGFDYGDRFWDIKSKYFTCQCGSEKCKHSAEAIALEQSRLA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 67 | Plasma retinol-binding protein (RBP4) | 5NU7 | 6.97 | |
Target general information Gen name RBP4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Retinol-binding protein 4; RBP4; RBP; Plasma retinol-binding protein(1-176); PRBP Protein family Calycin superfamily, Lipocalin family Biochemical class Calycin family Function Delivers retinol from the liver stores to the peripheral tissues. In plasma, the RBP-retinol complex interacts with transthyretin, this prevents its loss by filtration through the kidney glomeruli. Related diseases Retinal dystrophy, iris coloboma, and comedogenic acne syndrome (RDCCAS) [MIM:615147]: A disease characterized by retinal degeneration, ocular colobomas involving both the anterior and posterior segment, impaired night vision and loss of visual acuity. Additional characteristic features include developmental abnormalities and severe acne. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10232633, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23189188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9888420}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Loss of functional RBP4 protein results in serum retinol deficiency. Lack of normal levels of retinol impairs the visual cycle leading to night blindness at early stages; prolonged deficiency may lead to retinal degeneration. Additionally, retinol deficiency may result in dry skin, increased susceptibility to infection and acne (PubMed:23189188). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23189188}.; DISEASE: Microphthalmia/Coloboma 10 (MCOPCB10) [MIM:616428]: A disorder of eye formation, ranging from small size of a single eye to complete bilateral absence of ocular tissues. Ocular abnormalities like opacities of the cornea and lens, scaring of the retina and choroid, and other abnormalities may also be present. Ocular colobomas are a set of malformations resulting from abnormal morphogenesis of the optic cup and stalk, and the fusion of the fetal fissure (optic fissure). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25910211}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06985; DB06755; DB05076; DB03917; DB00755; DB00162 Interacts with Q9UBX0; P02766; O55245 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Methylation; Microphthalmia; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Retinol-binding; Secreted; Sensory transduction; Signal; Transport; Vision; Vitamin A Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 20030.2 Length 174 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 28.54 Isoelectric point 5.24 Charge (pH=7) -4.02 3D Binding mode Sequence ERDCRVSSFRVKENFDKARFSGTWYAMAKKDPEGLFLQDNIVAEFSVDETGQMSATAKGRVRLLNNWDVCADMVGTFTDTEDPAKFKMKYWGVASFLQKGNDDHWIVDTDYDTYAVQYSCRLLNLDGTCADSYSFVFSRDPNGLPPEAQKIVRQRQEELCLARQYRLIVHNGYC Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 68 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor alpha-2 (CHRNA2) | 5FJV | 6.97 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CHRNA2 Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-2/CHRNA2 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. Related diseases Epilepsy, nocturnal frontal lobe, 4 (ENFL4) [MIM:610353]: An autosomal dominant focal epilepsy characterized by nocturnal seizures associated with fear sensation, tongue movements, and nocturnal wandering, closely resembling nightmares and sleep walking. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16826524}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Seizures, benign familial infantile, 6 (BFIS6) [MIM:610353]: A form of benign familial infantile epilepsy, a neurologic disorder characterized by afebrile seizures occurring in clusters during the first year of life, without neurologic sequelae. BFIS6 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25847220}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00732; DB00237; DB00411; DB00565; DB01245; DB00514; DB01135; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB00483; DB08960; DB00657; DB01336; DB00416; DB01226; DB00184; DB01337; DB01338; DB00721; DB00728; DB05740; DB00202; DB01199; DB01339 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Epilepsy; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 48323.4 Length 413 Aromaticity 0.15 Instability index 32 Isoelectric point 5.69 Charge (pH=7) -6.58 3D Binding mode Sequence DRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLPEDRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 69 | Diamine oxidase (AOC1) | 3HII | 6.97 | |
Target general information Gen name AOC1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Kidney amine oxidase; KAO; Histaminase; Amiloride-binding protein; AOC1; ABP Protein family Copper/topaquinone oxidase family Biochemical class CH-NH(2) donor oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the degradation of compounds such as putrescine, histamine, spermine, and spermidine, substances involved in allergic and immune responses, cell proliferation, tissue differentiation, tumor formation, and possibly apoptosis. Placental DAO is thought to play a role in the regulation of the female reproductive function. Related diseases Lichtenstein-Knorr syndrome (LIKNS) [MIM:616291]: An autosomal recessive neurologic disorder characterized by progressive cerebellar ataxia and severe progressive sensorineural hearing loss. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25205112, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30237576}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00594; DB01373; DB09130; DB03608; DB05383 Interacts with Q15038; O75593; Q8IUC2; Q96HA8; Q7Z3K3; Q6ZRY4; Q01085-2; O43711; Q96K80 EC number EC 1.4.3.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Cell membrane; Copper; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Heparin-binding; Membrane; Metal-binding; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; TPQ Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 162607 Length 1425 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 45.72 Isoelectric point 6.76 Charge (pH=7) -4.07 3D Binding mode Sequence PRKAGVFSDLSNQELKAVHSFLWSKKELRLQPSSTTTMAKNTVFLIEMLLPKKYHVLRFLDKGERHPVREARAVIFFGDQEHPNVTEFAVGPLPGPCYMRALSPRPGYQSSWASRPISTAEYALLYHTLQEATKPLHQFFLNTTGFSFQDCHDRCLAFTDVAPRGVASGQRRSWLIIQRYVEGYFLHPTGLELLVDHGSTDAGHWAVEQVWYNGKFYGSPEELARKYADGEVDVVVLEDPLEPPLFSSHKPRGDFPSPIHVSGPRLVQPHGPRFRLEGNAVLYGGWSFAFRLRSSSGLQVLNVHFGGERIAYEVSVQEAVALYGGHTPAGMQTKYLDVGWGLGSVTHELAPGIDCPETATFLDTFHYYDADDPVHYPRALCLFEMPTGVPLRRHFNSNFKGGFNFYAGLKGQVLVLRTTSTVYNXDYIWDFIFYPNGVMEAKMHATGYVHATFYTPEGLRHGTRLHTHLIGNIHTHLVHYRVDLDVAGTKNSFQTLQMKLENITNPWSPRHRVVQPTLEQTQYSWERQAAFRFKRKLPKYLLFTSPQENPWGHKRSYRLQIHSMADQVLPPGWQEEQAITWARYPLAVTKYRESELCSSSIYHQNDPWDPPVVFEQFLHNNENIENEDLVAWVTVGFLHIPHSEDIPNTATPGNSVGFLLRPFNFFPEDPSLASRDTVIVWPRDNGPNYVQRWIPEDRDCSMPPPFSYNGTYRPVRKAGVFSDLSNQELKAVHSFLWSKKELRLQPSSTTTMAKNTVFLIEMLLPKKYHVLRFLDKGERHPVREARAVIFFGDQEHPNVTEFAVGPLPGPCYMRALSPRPGYQSSWASRPISTAEYALLYHTLQEATKPLHQFFLNTTGFSFQDCHDRCLAFTDVAPRGVASGQRRSWLIIQRYVEGYFLHPTGLELLVDHGSTDAGHWAVEQVWYNGKFYGSPEELARKYADGEVDVVVLEPPLFSSHKPRGDFPSPIHVSGPRLVQPHGPRFRLEGNAVLYGGWSFAFRLRSSSGLQVLNVHFGGERIAYEVSVQEAVALYGGHTPAGMQTKYLDVGWGLGSVTHELAPGIDCPETATFLDTFHYYDADDPVHYPRALCLFEMPTGVPLRRHFNSNFKGGFNFYAGLKGQVLVLRTTSTVYNXDYIWDFIFYPNGVMEAKMHATGYVHATFYTPEGLRHGTRLHTHLIGNIHTHLVHYRVDLDVAGTKNSFQTLQMKLENITNPWSPRHRVVQPTLEQTQYSWERQAAFRFKRKLPKYLLFTSPQENPWGHKRSYRLQIHSMADQVLPPGWQEEQAITWARYPLAVTKYRESELCSSSIYHQNDPWDPPVVFEQFLHNNENIENEDLVAWVTVGFLHIPHSEDIPNTATPGNSVGFLLRPFNFFPEDPSLASRDTVIVWPRDNGPNYVQRWIPEDRDCSMPPPFSYNGTYRPV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 70 | Hepatitis B virus Capsid protein (HBV C) | 7PZL | 6.97 | |
Target general information Gen name HBV C Organism Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate France/Tiollais/1979) (HBV-D) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Core antigen; Core protein; HBcAg; p21.5 Protein family Orthohepadnavirus core antigen family Biochemical class NA Function Self assembles to form an icosahedral capsid. Most capsid appear to be large particles with an icosahedral symmetry of T=4 and consist of 240 copies of capsid protein, though a fraction forms smaller T=3 particles consisting of 180 capsid proteins. Entering capsid are transported along microtubules to the nucleus. Phosphorylation of the capsid is thought to induce exposure of nuclear localization signal in the C-terminal portion of the capsid protein that allows binding to the nuclear pore complex via the importin (karyopherin-) alpha and beta. Capsids are imported in intact form through the nuclear pore into the nuclear basket, where it probably binds NUP153. Only capsids that contain the mature viral genome can release the viral DNA and capsid protein into the nucleoplasm. Immature capsids get stucked in the basket. Capsids encapsulate the pre-genomic RNA and the P protein. Pre-genomic RNA is reverse transcribed into DNA while the capsid is still in the cytoplasm. The capsid can then either be directed to the nucleus, providing more genome for transcription, or bud through the endoplasmic reticulum to provide new virions. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 14 (OZEMA14) [MIM:620276]: An autosomal recessive female infertility disorder characterized by oocyte maturation arrest, fertilization failure, and/or early embryonic arrest. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32666501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33683667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33898437, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34218387}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative initiation; Capsid protein; Cytoplasmic inwards viral transport; DNA-binding; Host cytoplasm; Host-virus interaction; Microtubular inwards viral transport; Phosphoprotein; Reference proteome; Repeat; RNA-binding; T=4 icosahedral capsid protein; Viral penetration into host nucleus; Virion; Virus entry into host cell Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 32388.9 Length 286 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 42.05 Isoelectric point 5.06 Charge (pH=7) -11.81 3D Binding mode Sequence MDIDPYKEFGATVELLSFLPSDFFPSVRDLLDTASALYREALESPEHCSPHHTALRQAIVCWGELMTLATWVGVNLEDPASRDLVVSYVNTNMGLKFRQLLWFHISCLTFGRETVIEYLVSFGVWIRTPPAYRPPNAPILSTLMDIDPYKEFGATVELLSFLPSDFFPSVRDLLDTASALYREALESPEHCSPHHTALRQAIVCWGELMTLATWVGVNLEDPASRDLVVSYVNTNMGLKFRQLLWFHISCLTFGRETVIEYLVSFGVWIRTPPAYRPPNAPILSTL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 71 | Squalene synthetase (FDFT1) | 3WCM | 6.97 | |
Target general information Gen name FDFT1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Squalene synthase; SS; SQS; Farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase; FPP:FPP farnesyltransferase Protein family Phytoene/squalene synthase family Biochemical class Alkyl aryl transferase Function Participates in the isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway, catalyzing a two-step reaction in which two identical molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) are converted into squalene, with the consumption of NADPH. Related diseases Squalene synthase deficiency (SQSD) [MIM:618156]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by profound developmental delay, brain abnormalities, 2/3 syndactyly of the toes, facial dysmorphisms, low total and LDL-cholesterol, and abnormal urine organic acids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29909962}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05317 Interacts with Q13520; Q3SXY8; P04233-2; P11912; O75503; O43889-2; Q9GZR5; Q5JX71; P48165; Q8TDT2; Q8N5M9; Q6IBW4-4; Q96RD7; Q14973; Q9NQQ7-3; Q96MV1; Q9Y320 EC number EC 2.5.1.21 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cholesterol biosynthesis; Cholesterol metabolism; Endoplasmic reticulum; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Magnesium; Membrane; Metal-binding; Multifunctional enzyme; NAD; NADP; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Steroid biosynthesis; Steroid metabolism; Sterol biosynthesis; Sterol metabolism; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 37860 Length 329 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.19 Isoelectric point 5.47 Charge (pH=7) -7.65 3D Binding mode Sequence LSSSLKTCYKYLNQTSRSFAAVIQALDGEMRNAVCIFYLVLRALDTLEDDMTISVEKKVPLLHNFHSFLYQPDWRFMESKEKDRQVLEDFPTISLEFRNLAEKYQTVIADICRRMGIGMAEFLDKHVTSEQEWDKYCHYVAGLVGIGLSRLFSASEFEDPLVGEDTERANSMGLFLQKTNIIRDYLEDQQGGREFWPQEVWSRYVKKLGDFALPENIDLAVQCLNELITNALHHIPDVITYLSRLRNQSVFNFCAIPQVMAIATLAACYNNQQVFKGAVLIVTLMMDATNMPAVKAIIYQYMEEIYHRIPDSNPSSSKTRQIISTIRTQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 72 | T-cell receptor beta constant 1 (TRBC1) | 4LCC | 6.97 | |
Target general information Gen name TRBC1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms TCRBC1; BV05S1J2.2 Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Alpha-beta T cell receptors are antigen specific receptors which are essential to the immune response and are present on the cell surface of T lymphocytes. Recognize peptide-major histocompatibility (MH) (pMH) complexes that are displayed by antigen presenting cells (APC), a prerequisite for efficient T cell adaptive immunity against pathogens. Binding of alpha-beta TR to pMH complex initiates TR-CD3 clustering on the cell surface and intracellular activation of LCK that phosphorylates the ITAM motifs of CD3G, CD3D, CD3E and CD247 enabling the recruitment of ZAP70. In turn, ZAP70 phosphorylates LAT, which recruits numerous signaling molecules to form the LAT signalosome. The LAT signalosome propagates signal branching to three major signaling pathways, the calcium, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase and the nuclear factor NF-kappa-B (NF-kB) pathways, leading to the mobilization of transcription factors that are critical for gene expression and essential for T cell growth and differentiation. The T cell repertoire is generated in the thymus, by V-(D)-J rearrangement. This repertoire is then shaped by intrathymic selection events to generate a peripheral T cell pool of self-MH restricted, non-autoaggressive T cells. Post-thymic interaction of alpha-beta TR with the pMH complexes shapes TR structural and functional avidity. Constant region of T cell receptor (TR) alpha chain. Related diseases Immunodeficiency 57 with autoinflammation (IMD57) [MIM:618108]: An autosomal recessive primary immunodeficiency characterized by lymphopenia and recurrent viral, bacterial, and fungal infections. Patients exhibit early-onset inflammatory bowel disease involving the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract, and develop progressive polyarthritis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30026316}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. RIPK1-deficient immune cells from IMD57 patients have impaired proinflammatory signaling leading to dysregulated cytokine secretion and are prone to necroptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30026316}.; DISEASE: Autoinflammation with episodic fever and lymphadenopathy (AIEFL) [MIM:618852]: An autosomal dominant immunologic disorder characterized by early onset of recurrent episodes of unexplained fever, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and increased levels of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in patient serum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31827280, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31827281}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02740 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Immunoglobulin domain; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; T cell receptor; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C,B,A Molecular weight (Da) 84668.2 Length 736 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 39.96 Isoelectric point 5.8 Charge (pH=7) -14.36 3D Binding mode Sequence IQRPPKIQVYSRHPPNYLNCYVYGFHPPQIEIDLLKIKSEQSDLSFSKDWSFYLLSHATPNSKDQYSCRVKHVTLEQPRIVKWDRTHSLRYFRLGISEIPEFISAGYVDSHPITMYNSVSQLKEPRALWMEENLAPDHWERYTQLLRGWQQMFKVELKQLQHHYNHSGFHTYQRMIGCELLEDGSITGFLQYAYDGQDFLIFNKDTLSWMAMDNVADIIRRVWEANQHELLYQKNWLEEECIAWLKRFLEYGKDALQRTEPPKVRVNHKTTLYCRAYGFYPPEISINWMKNGEEIFQDTDYGGILPSGDGTYQTWVSVELGDIYSCHVEHGGVHMVLQGFQQNIDQPTEMTATEGAIVQINCTYQTSGFNGLFWYQQHAGEAPTFLSYNVLDGLEEKGRFSSFLSRSKGYSYLLLKELQMKDSASYLCAVKDSNYQLIWGAGTKLIIKPNIQNPDPAVYQLRDSKSSDKSVCLFTDFDKDSDVYITDKKSNSAVAWSNAGVTQTPKFQVLKTGQSMTLQCAQDMNHNSMYWYRQDPGMGLRLIYYSASEGTTDKGEVPNGYNVSRLNKREFSLRLESAAPSQTSVYFCASSVWTGEGSGELFFGEGSRLTVLEDLKNVFPPEVAVFEPSEAEISHTQKATLVCLATGFYPDHVELSWWVNGKEVHSGVCTDPQPLKEQPALNDSRYALSSRLRVSATFWQNPRNHFRCQVQFYGLSENDEWKPVTQIVSAEAWGRA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 73 | Janus kinase 2 (JAK-2) | 3UGC | 6.96 | |
Target general information Gen name JAK2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, JAK subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Mediates essential signaling events in both innate and adaptive immunity. In the cytoplasm, plays a pivotal role in signal transduction via its association with type I receptors such as growth hormone (GHR), prolactin (PRLR), leptin (LEPR), erythropoietin (EPOR), thrombopoietin (THPO); or type II receptors including IFN-alpha, IFN-beta, IFN-gamma and multiple interleukins. Following ligand-binding to cell surface receptors, phosphorylates specific tyrosine residues on the cytoplasmic tails of the receptor, creating docking sites for STATs proteins. Subsequently, phosphorylates the STATs proteins once they are recruited to the receptor. Phosphorylated STATs then form homodimer or heterodimers and translocate to the nucleus to activate gene transcription. For example, cell stimulation with erythropoietin (EPO) during erythropoiesis leads to JAK2 autophosphorylation, activation, and its association with erythropoietin receptor (EPOR) that becomes phosphorylated in its cytoplasmic domain. Then, STAT5 (STAT5A or STAT5B) is recruited, phosphorylated and activated by JAK2. Once activated, dimerized STAT5 translocates into the nucleus and promotes the transcription of several essential genes involved in the modulation of erythropoiesis. Part of a signaling cascade that is activated by increased cellular retinol and that leads to the activation of STAT5 (STAT5A or STAT5B). In addition, JAK2 mediates angiotensin-2-induced ARHGEF1 phosphorylation. Plays a role in cell cycle by phosphorylating CDKN1B. Cooperates with TEC through reciprocal phosphorylation to mediate cytokine-driven activation of FOS transcription. In the nucleus, plays a key role in chromatin by specifically mediating phosphorylation of 'Tyr-41' of histone H3 (H3Y41ph), a specific tag that promotes exclusion of CBX5 (HP1 alpha) from chromatin. Non-receptor tyrosine kinase involved in various processes such as cell growth, development, differentiation or histone modifications. Related diseases Chromosomal aberrations involving JAK2 are found in both chronic and acute forms of eosinophilic, lymphoblastic and myeloid leukemia. Translocation t(8;9)(p22;p24) with PCM1 links the protein kinase domain of JAK2 to the major portion of PCM1. Translocation t(9;12)(p24;p13) with ETV6.; DISEASE: Budd-Chiari syndrome (BDCHS) [MIM:600880]: A syndrome caused by obstruction of hepatic venous outflow involving either the hepatic veins or the terminal segment of the inferior vena cava. Obstructions are generally caused by thrombosis and lead to hepatic congestion and ischemic necrosis. Clinical manifestations observed in the majority of patients include hepatomegaly, right upper quadrant pain and abdominal ascites. Budd-Chiari syndrome is associated with a combination of disease states including primary myeloproliferative syndromes and thrombophilia due to factor V Leiden, protein C deficiency and antithrombin III deficiency. Budd-Chiari syndrome is a rare but typical complication in patients with polycythemia vera. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16707754}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Polycythemia vera (PV) [MIM:263300]: A myeloproliferative disorder characterized by abnormal proliferation of all hematopoietic bone marrow elements, erythroid hyperplasia, an absolute increase in total blood volume, but also by myeloid leukocytosis, thrombocytosis and splenomegaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15781101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15793561, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15858187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16603627, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25644777}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thrombocythemia 3 (THCYT3) [MIM:614521]: A myeloproliferative disorder characterized by excessive platelet production, resulting in increased numbers of circulating platelets. It can be associated with spontaneous hemorrhages and thrombotic episodes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16325696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22397670}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Myelofibrosis (MYELOF) [MIM:254450]: A disorder characterized by replacement of the bone marrow by fibrous tissue, occurring in association with a myeloproliferative disorder. Clinical manifestations may include anemia, pallor, splenomegaly, hypermetabolic state, petechiae, ecchymosis, bleeding, lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, portal hypertension. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML) [MIM:601626]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. AML is a malignant disease of bone marrow characterized by maturational arrest of hematopoietic precursors at an early stage of development. Clonal expansion of myeloid blasts occurs in bone marrow, blood, and other tissue. Myelogenous leukemias develop from changes in cells that normally produce neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils and monocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16247455}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04716; DB07162; DB08067; DB07161; DB14973; DB11817; DB11986; DB12500; DB12010; DB11763; DB11697; DB15822; DB08877; DB08895; DB05243; DB15035 Interacts with P32927; Q01344; P23458; O60674; P40238; P16333; P18031; O75116; P29597; Q9JHI9 EC number EC 2.7.10.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; ATP-binding; Chromatin regulator; Chromosomal rearrangement; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Immunity; Innate immunity; Kinase; Magnesium; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Proto-oncogene; Reference proteome; Repeat; SH2 domain; Transferase; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32174.5 Length 274 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 50.94 Isoelectric point 7.78 Charge (pH=7) 1.46 3D Binding mode Sequence QFEERHLKFLQQLGKGNFGSVEMCRYDPLQDNTGEVVAVKKLQHSTEEHLRDFEREIEILKSLQHDNIVKYKGVCYSAGRRNLKLIMEYLPYGSLRDYLQKHKERIDHIKLLQYTSQICKGMEYLGTKRYIHRDLATRNILVENENRVKIGDFGLTKPGESPIFWYAPESLTESKFSVASDVWSFGVVLYELFTYIEKSKSPPAEFMRMIGNDKQGQMIVFHLIELLKNNGRLPRPDGCPDEIYMIMTECWNNNVNQRPSFRDLALRVDQIRDN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 74 | Pregnane X receptor (NR1I2) | 1NRL | 6.96 | |
Target general information Gen name NR1I2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Steroid and xenobiotic receptor; SXR; PXR; Orphan nuclear receptor PXR; Orphan nuclear receptor PAR1; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 2 Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily Biochemical class Nuclear hormone receptor Function Transcription factor that activates the transcription of multiple genes involved in the metabolism and secretion of potentially harmful xenobiotics, drugs and endogenous compounds. Activated by the antibiotic rifampicin and various plant metabolites, such as hyperforin, guggulipid, colupulone, and isoflavones. Response to specific ligands is species-specific. Activated by naturally occurring steroids, such as pregnenolone and progesterone. Binds to a response element in the promoters of the CYP3A4 and ABCB1/MDR1 genes. Nuclear receptor that binds and is activated by variety of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. Related diseases Atrial fibrillation, familial, 14 (ATFB14) [MIM:615378]: A familial form of atrial fibrillation, a common sustained cardiac rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity and ineffective atrial contraction promoting blood stasis in the atria and reduces ventricular filling. It can result in palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19808477}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Genetic variations in SCN2B may be involved in Brugada syndrome (PubMed:23559163). This tachyarrhythmia is characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs, the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23559163}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04468; DB14001; DB01393; DB00564; DB06777; DB01068; DB00257; DB00531; DB14002; DB01234; DB14649; DB00255; DB01248; DB05928; DB01127; DB00530; DB00783; DB13952; DB13953; DB13954; DB13955; DB13956; DB00977; DB00754; DB01039; DB13873; DB00499; DB01645; DB07931; DB01892; DB01181; DB01026; DB00431; DB00532; DB00849; DB01110; DB00834; DB11605; DB01115; DB00239; DB01229; DB00312; DB04930; DB01174; DB04824; DB00252; DB12582; DB01708; DB02789; DB11087; DB04216; DB02709; DB01045; DB01220; DB08864; DB00503; DB00421; DB04466; DB01138; DB00675; DB07080; DB08604; DB13179; DB00163; DB00682 Interacts with P08238; Q15788 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; Alternative splicing; DNA-binding; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 31908.8 Length 275 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 46.37 Isoelectric point 6.78 Charge (pH=7) -0.54 3D Binding mode Sequence GLTEEQRMMIRELMDAQMKTFDTTFSHFKNFRLPGVREEAAKWSQVRKDLCSLKVSLQLRGEDGSVWNYKPPADSGGKEIFSLLPHMADMSTYMFKGIISFAKVISYFRDLPIEDQISLLKGAAFELCQLRFNTVFNAETGTWECGRLSYCLEDTAGGFQQLLLEPMLKFHYMLKKLQLHEEEYVLMQAISLFSPDRPGVLQHRVVDQLQEQFAITLKSYIECNRPQPAHRFLFLKIMAMLTELRSINAQHTQRLLRIQDIHPFATPLMQELFGI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 75 | Monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) | 2V5Z | 6.96 | |
Target general information Gen name MAOB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms MAO-B; Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] B Protein family Flavin monoamine oxidase family Biochemical class CH-NH(2) donor oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the oxidative deamination of biogenic and xenobiotic amines and has important functions in the metabolism of neuroactive and vasoactive amines in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. MAOB preferentially degrades benzylamine and phenylethylamine. Related diseases Microvascular complications of diabetes 5 (MVCD5) [MIM:612633]: Pathological conditions that develop in numerous tissues and organs as a consequence of diabetes mellitus. They include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy leading to end-stage renal disease, and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic retinopathy remains the major cause of new-onset blindness among diabetic adults. It is characterized by vascular permeability and increased tissue ischemia and angiogenesis. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Homozygosity for the Leu-55 allele is strongly associated with the development of retinal disease in diabetic patients. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08176; DB02211; DB08516; DB08480; DB01472; DB04307; DB07512; DB07513; DB00915; DB00182; DB06698; DB04889; DB00215; DB09130; DB04147; DB00988; DB01363; DB00668; DB01175; DB02509; DB03147; DB14914; DB00614; DB04818; DB02095; DB01247; DB00601; DB01577; DB01442; DB01171; DB08082; DB02643; DB04677; DB03894; DB08804; DB04820; DB00184; DB04821; DB12612; DB01626; DB00780; DB00191; DB00388; DB01132; DB00721; DB01168; DB01367; DB09363; DB06654; DB01037; DB01104; DB14569; DB09042; DB00752; DB16446; DB09185; DB04832; DB00909 Interacts with P55212; P28329-3; Q8NI60; Q5RI15; Q92915-2; P22607; Q53GS7; P06396; P01112; O14901; P13473-2; P21397; Q9BVL2; O75400-2; P62826; Q6NTF9-3; Q9Y371; Q7Z699; Q9UMX0; Q9Y649 EC number EC 1.4.3.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion outer membrane; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 56019.9 Length 494 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 34.81 Isoelectric point 6.51 Charge (pH=7) -2.2 3D Binding mode Sequence NKCDVVVVGGGISGMAAAKLLHDSGLNVVVLEARDRVGGRTYTLRNQKVKYVDLGGSYVGPTQNRILRLAKELGLETYKVNEVERLIHHVKGKSYPFRGPFPPVWNPITYLDHNNFWRTMDDMGREIPSDAPWKAPLAEEWDNMTMKELLDKLCWTESAKQLATLFVNLCVTAETHEVSALWFLWYVKQCGGTTRIISTTNGGQERKFVGGSGQVSERIMDLLGDRVKLERPVIYIDQTRENVLVETLNHEMYEAKYVISAIPPTLGMKIHFNPPLPMMRNQMITRVPLGSVIKCIVYYKEPFWRKKDYCGTMIIDGEEAPVAYTLDDTKPEGNYAAIMGFILAHKARKLARLTKEERLKKLCELYAKVLGSLEALEPVHYEEKNWCEEQYSGGCYTTYFPPGILTQYGRVLRQPVDRIYFAGTETATHWSGYMEGAVEAGERAAREILHAMGKIPEDEIWQSEPESVDVPAQPITTTFLERHLPSVPGLLRLI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 76 | Cyclopropane mycolic acid synthase MmaA2 | 1TPY | 6.96 | |
Target general information Gen name mmaA2 Organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms Rv0644c;mma2 Protein family CFA/CMAS family Biochemical class Transferase Function Cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase activity.Methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 16 (OZEMA16) [MIM:617234]: A rare cause of female primary infertility. In affected women, ovulation and fertilization proceed normally but embryos are arrested at early stages of development. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27545678}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01718; DB01752 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.79 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Methyltransferase; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32493.6 Length 285 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.61 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -10.17 3D Binding mode Sequence NDLTPHFEDVQAHYDLSDDFFRLFLDPTQTYSCAHFEREDMTLEEAQIAKIDLALGKLGLQPGMTLLDIGCGWGATMRRAIAQYDVNVVGLTLSKNQAAHVQKSFDEMDTPRDRRVLLAGWEQFNEPVDRIVSIGAFEHFGHDRHADFFARAHKILPPDGVLLLHTITGLTRQQMVDHGLPLTLWLARFLKFIATEIFPGGQPPTIEMVEEQSAKTGFTLTRRQSLQPHYARTLDLWAEALQEHKSEAIAIQSEEVYERYMKYLTGCAKLFRVGYIDVNQFTLAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 77 | ABL T315I mutant (ABL T315I) | 4TWP | 6.96 | |
Target general information Gen name ABL1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms p150 T315I; T315I Abl; Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 T315I; Proto-oncogene c-Abl T315I; JTK7 T315I; C-ABL T315I; Abl T315I; Abelson tyrosine-protein kinase 1 T315I; Abelson murine leukem Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, ABL subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Coordinates actin remodeling through tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins controlling cytoskeleton dynamics like WASF3 (involved in branch formation); ANXA1 (involved in membrane anchoring); DBN1, DBNL, CTTN, RAPH1 and ENAH (involved in signaling); or MAPT and PXN (microtubule-binding proteins). Phosphorylation of WASF3 is critical for the stimulation of lamellipodia formation and cell migration. Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion and motility through phosphorylation of key regulators of these processes such as BCAR1, CRK, CRKL, DOK1, EFS or NEDD9. Phosphorylates multiple receptor tyrosine kinases and more particularly promotes endocytosis of EGFR, facilitates the formation of neuromuscular synapses through MUSK, inhibits PDGFRB-mediated chemotaxis and modulates the endocytosis of activated B-cell receptor complexes. Other substrates which are involved in endocytosis regulation are the caveolin (CAV1) and RIN1. Moreover, ABL1 regulates the CBL family of ubiquitin ligases that drive receptor down-regulation and actin remodeling. Phosphorylation of CBL leads to increased EGFR stability. Involved in late-stage autophagy by regulating positively the trafficking and function of lysosomal components. ABL1 targets to mitochondria in response to oxidative stress and thereby mediates mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death. In response to oxidative stress, phosphorylates serine/threonine kinase PRKD2 at 'Tyr-717'. ABL1 is also translocated in the nucleus where it has DNA-binding activity and is involved in DNA-damage response and apoptosis. Many substrates are known mediators of DNA repair: DDB1, DDB2, ERCC3, ERCC6, RAD9A, RAD51, RAD52 or WRN. Activates the proapoptotic pathway when the DNA damage is too severe to be repaired. Phosphorylates TP73, a primary regulator for this type of damage-induced apoptosis. Phosphorylates the caspase CASP9 on 'Tyr-153' and regulates its processing in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. Phosphorylates PSMA7 that leads to an inhibition of proteasomal activity and cell cycle transition blocks. ABL1 acts also as a regulator of multiple pathological signaling cascades during infection. Several known tyrosine-phosphorylated microbial proteins have been identified as ABL1 substrates. This is the case of A36R of Vaccinia virus, Tir (translocated intimin receptor) of pathogenic E. coli and possibly Citrobacter, CagA (cytotoxin-associated gene A) of H. pylori, or AnkA (ankyrin repeat-containing protein A) of A. phagocytophilum. Pathogens can highjack ABL1 kinase signaling to reorganize the host actin cytoskeleton for multiple purposes, like facilitating intracellular movement and host cell exit. Finally, functions as its own regulator through autocatalytic activity as well as through phosphorylation of its inhibitor, ABI1. Regulates T-cell differentiation in a TBX21-dependent manner. Phosphorylates TBX21 on tyrosine residues leading to an enhancement of its transcriptional activator activity. Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase that plays a role in many key processes linked to cell growth and survival such as cytoskeleton remodeling in response to extracellular stimuli, cell motility and adhesion, receptor endocytosis, autophagy, DNA damage response and apoptosis. Related diseases Leukemia, chronic myeloid (CML) [MIM:608232]: A clonal myeloproliferative disorder of a pluripotent stem cell with a specific cytogenetic abnormality, the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph), involving myeloid, erythroid, megakaryocytic, B-lymphoid, and sometimes T-lymphoid cells, but not marrow fibroblasts. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: A chromosomal aberration involving ABL1 has been found in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Translocation t(9;22)(q34;q11) with BCR. The translocation produces a BCR-ABL found also in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:3021337}.; DISEASE: A chromosomal aberration involving ABL1 is found in a form of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (PubMed:15361874). Translocation t(9;9)(q34;q34) with NUP214 (PubMed:15361874). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15361874}.; DISEASE: Congenital heart defects and skeletal malformations syndrome (CHDSKM) [MIM:617602]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by congenital heart disease with atrial and ventricular septal defects, variable skeletal abnormalities, and failure to thrive. Skeletal defects include pectus excavatum, scoliosis, and finger contractures. Some patient exhibit joint laxity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28288113}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08043; DB08583; DB07831; DB08350; DB12597; DB00171; DB06616; DB12267; DB01254; DB12010; DB00619; DB13749; DB08231; DB03878; DB04868; DB08339; DB08901; DB12323; DB08896; DB14989; DB05184 Interacts with Q8IZP0; Q9NYB9; O14672; P10275; Q13315; Q4KMG0; P46108; P46109; P35222; P00533; P04626; Q03468; Q14315; P36888; P05107; P10721; Q38SD2; Q92918; Q7Z434; O43196; P15941; P15941-12; P16333; O43900; Q13905; Q86UR5; Q13671; P31947; Q15464; O75751; P37840; Q9BX66; O60504-2; Q07890; P12931; P51692; Q9Y4G6; P11387; P04637; P15498; Q9Y6W5; P62258; P61981; P63104; O35158; P37840; P48165; Q15323; P37840 EC number EC 2.7.10.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Apoptosis; ATP-binding; Autophagy; Cell adhesion; Chromosomal rearrangement; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Disease variant; DNA damage; DNA repair; DNA-binding; Endocytosis; Kinase; Lipoprotein; Magnesium; Manganese; Membrane; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Myristate; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Proto-oncogene; Reference proteome; SH2 domain; SH3 domain; Transferase; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 30776.1 Length 266 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 36.47 Isoelectric point 5.39 Charge (pH=7) -7.71 3D Binding mode Sequence DKWEMERTDITMKHKLGGGQYGEVYEGVWKKYSLTVAVKTLEVEEFLKEAAVMKEIKHPNLVQLLGVCTREPPFYIIIEFMTYGNLLDYLRECNRQEVNAVVLLYMATQISSAMEYLEKKNFIHRDLAARNCLVGENHLVKVADFGLSRLMTGDTYTAHAGAKFPIKWTAPESLAYNKFSIKSDVWAFGVLLWEIATYGMSPYPGIDLSQVYELLEKDYRMERPEGCPEKVYELMRACWQWNPSDRPSFAEIHQAFETMFQESSIS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 78 | Wnt-7a protein (WNT7A) | 4UZQ | 6.96 | |
Target general information Gen name WNT7A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein Wnt-7a Protein family Wnt family Biochemical class NA Function Plays an important role in embryonic development, including dorsal versus ventral patterning during limb development, skeleton development and urogenital tract development. Required for central nervous system (CNS) angiogenesis and blood-brain barrier regulation. Required for normal, sexually dimorphic development of the Mullerian ducts, and for normal fertility in both sexes. Required for normal neural stem cell proliferation in the hippocampus dentate gyrus. Required for normal progress through the cell cycle in neural progenitor cells, for self-renewal of neural stem cells, and for normal neuronal differentiation and maturation. Promotes formation of synapses via its interaction with FZD5. Ligand for members of the frizzled family of seven transmembrane receptors that functions in the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Related diseases Limb pelvis hypoplasia aplasia syndrome (LPHAS) [MIM:276820]: A syndrome of severe deficiency of the extremities due to hypo- or aplasia of one or more long bones of one or more limbs. Pelvic manifestations include hip dislocation, hypoplastic iliac bone and aplastic pubic bones. Thoracic deformity, unusual facies and genitourinary anomalies can be present. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16826533, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17431918, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20949531, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21271649, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27638328}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Fuhrmann syndrome (FUHRS) [MIM:228930]: Distinct limb-malformation disorder characterized also by various degrees of limb aplasia/hypoplasia and joint dysplasia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16826533}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P55212; P22607; P06396; P13473-2; Q9UMX0; Q9Y5W5; Q5T9L3; Q9Z0J1 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Developmental protein; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Extracellular matrix; Glycoprotein; Lipoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Wnt signaling pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 40475.5 Length 356 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 50.49 Isoelectric point 7.67 Charge (pH=7) 1.62 3D Binding mode Sequence EDLRLHLLLNTSVTCNDGSPAGYYLKESRGSRRWLLFLEGGWYCFNRENCDSRYDTMRRLMSSRDWPRTRTGTGILSSQPEENPYWWNANMVFIPYCSSDVWSGASSKSEKNEYAFMGALIIQEVVRELLGRGLSGAKVLLLAGSAAGGTGVLLNVDRVAEQLEKLGYPAIQVRGLADSGWFLDNKQYRHTDCVDTITCAPTEAIRRGIRYWNGVVPERCRRQFQEGEEWNCFFGYKVYPTLRSPVFVVQWLFDEAQLTVDNVHLTGQPVQEGLRLYIQNLGRELRHTLKDVPASFAPACLSHEIIIRSHWTDVQVKGTSLPRALHCWDRSLHKGCPVHLVDSCPWPHCNPSCPTS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 79 | Retinoic acid receptor beta (RARB) | 4DM6 | 6.95 | |
Target general information Gen name RARB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms RAR-epsilon; RAR-beta; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 2; NR1B2; HBV-activated protein; HAP Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily Biochemical class Nuclear hormone receptor Function Retinoic acid receptors bind as heterodimers to their target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, and regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RXR/RAR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5. In the absence or presence of hormone ligand, acts mainly as an activator of gene expression due to weak binding to corepressors. In concert with RARG, required for skeletal growth, matrix homeostasis and growth plate function. Receptor for retinoic acid. Related diseases Microphthalmia, syndromic, 12 (MCOPS12) [MIM:615524]: A form of microphthalmia, a disorder of eye formation, ranging from small size of a single eye to complete bilateral absence of ocular tissues (anophthalmia). In many cases, microphthalmia/anophthalmia occurs in association with syndromes that include non-ocular abnormalities. MCOPS12 patients manifest variable features, including diaphragmatic hernia, pulmonary hypoplasia, and cardiac abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24075189, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27120018}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00459; DB00210; DB00523; DB02877; DB00926; DB05785; DB04942; DB00799; DB00755; DB12808 Interacts with O95273; P50222; Q9UBK2; P62195; P28702; P28702-3; P48443; P03255 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; DNA-binding; Metal-binding; Microphthalmia; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proto-oncogene; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 25904.1 Length 229 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 44.34 Isoelectric point 7.55 Charge (pH=7) 0.73 3D Binding mode Sequence TEKIRKAHQETFPSLCQLGKYTTNSSADHRVRLDLGLWDKFSELATKCIIKIVEFAKRLPGFTGLTIADQITLLKAACLDILILRICTRYTPEQDTMTFSDGLTLNRTQMHNAGFGPLTDLVFTFANQLLPLEMDDTETGLLSAICLICGDRQDLEEPTKVDKLQEPLLEALKIYIRKRRPSKPHMFPKILMKITDLRSISAKGAERVITLKMEIPGSMPPLIQEMLEN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 80 | Monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) | 2V5Z | 6.95 | |
Target general information Gen name MAOB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms MAO-B; Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] B Protein family Flavin monoamine oxidase family Biochemical class CH-NH(2) donor oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the oxidative deamination of biogenic and xenobiotic amines and has important functions in the metabolism of neuroactive and vasoactive amines in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. MAOB preferentially degrades benzylamine and phenylethylamine. Related diseases Microvascular complications of diabetes 5 (MVCD5) [MIM:612633]: Pathological conditions that develop in numerous tissues and organs as a consequence of diabetes mellitus. They include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy leading to end-stage renal disease, and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic retinopathy remains the major cause of new-onset blindness among diabetic adults. It is characterized by vascular permeability and increased tissue ischemia and angiogenesis. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Homozygosity for the Leu-55 allele is strongly associated with the development of retinal disease in diabetic patients. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08176; DB02211; DB08516; DB08480; DB01472; DB04307; DB07512; DB07513; DB00915; DB00182; DB06698; DB04889; DB00215; DB09130; DB04147; DB00988; DB01363; DB00668; DB01175; DB02509; DB03147; DB14914; DB00614; DB04818; DB02095; DB01247; DB00601; DB01577; DB01442; DB01171; DB08082; DB02643; DB04677; DB03894; DB08804; DB04820; DB00184; DB04821; DB12612; DB01626; DB00780; DB00191; DB00388; DB01132; DB00721; DB01168; DB01367; DB09363; DB06654; DB01037; DB01104; DB14569; DB09042; DB00752; DB16446; DB09185; DB04832; DB00909 Interacts with P55212; P28329-3; Q8NI60; Q5RI15; Q92915-2; P22607; Q53GS7; P06396; P01112; O14901; P13473-2; P21397; Q9BVL2; O75400-2; P62826; Q6NTF9-3; Q9Y371; Q7Z699; Q9UMX0; Q9Y649 EC number EC 1.4.3.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion outer membrane; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 56019.9 Length 494 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 34.81 Isoelectric point 6.51 Charge (pH=7) -2.2 3D Binding mode Sequence NKCDVVVVGGGISGMAAAKLLHDSGLNVVVLEARDRVGGRTYTLRNQKVKYVDLGGSYVGPTQNRILRLAKELGLETYKVNEVERLIHHVKGKSYPFRGPFPPVWNPITYLDHNNFWRTMDDMGREIPSDAPWKAPLAEEWDNMTMKELLDKLCWTESAKQLATLFVNLCVTAETHEVSALWFLWYVKQCGGTTRIISTTNGGQERKFVGGSGQVSERIMDLLGDRVKLERPVIYIDQTRENVLVETLNHEMYEAKYVISAIPPTLGMKIHFNPPLPMMRNQMITRVPLGSVIKCIVYYKEPFWRKKDYCGTMIIDGEEAPVAYTLDDTKPEGNYAAIMGFILAHKARKLARLTKEERLKKLCELYAKVLGSLEALEPVHYEEKNWCEEQYSGGCYTTYFPPGILTQYGRVLRQPVDRIYFAGTETATHWSGYMEGAVEAGERAAREILHAMGKIPEDEIWQSEPESVDVPAQPITTTFLERHLPSVPGLLRLI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||