Job Results:
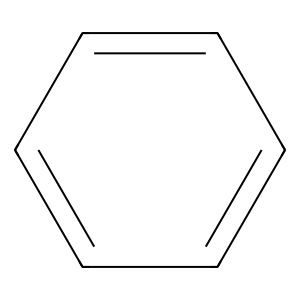
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
423f7e40872011e00644af2c38b678af
Job name
NA
Time
2025-03-13 15:35:05
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61 | HTH-type transcriptional regulator QacR | 1JT6 | 5.05 | |
Target general information Gen name qacR Organism Staphylococcus aureus Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms SAP104C_022;SAP100B_005 Protein family NA Biochemical class Transcription Function DNA binding.Transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04209; DB03608; DB03808; DB01123 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; DNA-binding; Plasmid; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,D,E Molecular weight (Da) 43715 Length 372 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 34.92 Isoelectric point 8.24 Charge (pH=7) 2.33 3D Binding mode Sequence NLKDKILGVAKELFIKNGYNATTTGEIVKLSESSKGNLYYHFKTKENLFLEILNIEESKWQEQWKKEQIKAKTNREKFYLYNELSLTTEYYYPLQNAIIEFYTEYYKTNSINEKMNKLENKYIDAYHVIFKEGNLNGEWSINDVNAVSKIAANAVNGIVTFTHEQNINERIKLMNKFSQIFLNGLSNLKDKILGVAKELFIKNGYNATTTGEIVKLSESSKGNLYYHFKTKENLFLEILNIEESKWQEQWKKEQIKAKTNREKFYLYNELSLTTEYYYPLQNAIIEFYTEYYKTNSINEKMNKLENKYIDAYHVIFKEGNLNGEWSINDVNAVSKIAANAVNGIVTFTHEQNINERIKLMNKFSQIFLNGLS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 62 | 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase | 3ISQ | 5.05 | |
Target general information Gen name HPD Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms PPD Protein family 4HPPD family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase activity.Metal ion binding. Related diseases Tyrosinemia 3 (TYRSN3) [MIM:276710]: An inborn error of metabolism characterized by elevations of tyrosine in the blood and urine, seizures and mild intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10942115, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11073718}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Hawkinsinuria (HWKS) [MIM:140350]: An inborn error of tyrosine metabolism characterized by failure to thrive, persistent metabolic acidosis, fine and sparse hair, and excretion of the unusual cyclic amino acid metabolite, hawkinsin, in the urine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11073718}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02850; DB00348 Interacts with NA EC number 1.13.11.27 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Dioxygenase; Disease variant; Endoplasmic reticulum; Golgi apparatus; Intellectual disability; Iron; Membrane; Metal-binding; Oxidoreductase; Phenylalanine catabolism; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Tyrosine catabolism Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 43164.8 Length 376 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 32.38 Isoelectric point 6.73 Charge (pH=7) -1.04 3D Binding mode Sequence AKPERGRFLHFHSVTFWVGNAKQAASFYCSKMGFEPLAYRGLETGSREVVSHVIKQGKIVFVLSSALNPWNKEMGDHLVKHGDGVKDIAFEVEDCDYIVQKARERGAKIMREPWVEQDKFGKVKFAVLQTYGDTTHTLVEKMNYIGQFLPGYEAPAFMDPLLPKLPKCSLEMIDHIVGNQPDQEMVSASEWYLKNLQFHRFWSVDDTQVHTEYSSLRSIVVANYEESIKMPINEPAPGKKKSQIQEYVDYNGGAGVQHIALKTEDIITAIRHLRERGLEFLSVPSTYYKQLREKLKTAKIKVKENIDALEELKILVDYDEKGYLLQIFTKPVQDRPTLFLEVIQRHNHQGFGAGNFNSLFKAFEEEQNLRGNLTNM Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 63 | p53-binding protein Mdm4 (MDM4) | 6Q9Y | 5.05 | |
Target general information Gen name MDM4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein Mdmx; Mdm2-like p53-binding protein; Double minute 4 protein Protein family MDM2/MDM4 family Biochemical class MDM2/MDM4 family Function Inhibits p53/TP53- and TP73/p73-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by binding its transcriptional activation domain. Inhibits degradation of MDM2. Can reverse MDM2-targeted degradation of TP53 while maintaining suppression of TP53 transactivation and apoptotic functions. Related diseases Bone marrow failure syndrome 6 (BMFS6) [MIM:618849]: A form of bone marrow failure syndrome, a heterogeneous group of life-threatening disorders characterized by hematopoietic defects in association with a range of variable extra-hematopoietic manifestations. BMFS6 is an autosomal dominant form characterized by intermittent neutropenia, lymphopenia, or anemia associated with hypocellular bone marrow, and increased susceptibility to cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32300648}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9NX04; P10415; Q7Z479; O95971; P48729; Q00987; Q13064; P41227; P06400; Q9Y4L5; P23297; P29034; P33763; P04271; P31947; P04637; P62837; Q93009; O14972; P61964; P62258; P61981; P63104; Q9BRR0; A0A0S2Z6X0; Q3YBA8; P03255-2 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Disease variant; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 19722 Length 173 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 50.78 Isoelectric point 8.48 Charge (pH=7) 2.27 3D Binding mode Sequence QVRPKLPLLKILHAAGAQGEMFTVKEVMHYLGQYIMVKQLYDQQEQHMVYCGGDLLGELLGRQSFSVKDPSPLYDMLRKNLVTLAQINQVRPKLPLLKILHAAGAQGEMFTVKEVMHYLGQYIMVKQLYDQQEQHMVYCGGDLLGELLGRQSFSVKDPSPLYDMLRKNLVTLA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 64 | ERK activator kinase 1 (MEK1) | 7M0U | 5.05 | |
Target general information Gen name MAP2K1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PRKMK1; Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1; MKK1; MEK 1; MAPKK 1; MAPK/ERKkinase 1; MAPK/ERK kinase 1; MAP kinase kinase 1; Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family, MAP kinase kinase subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Binding of extracellular ligands such as growth factors, cytokines and hormones to their cell-surface receptors activates RAS and this initiates RAF1 activation. RAF1 then further activates the dual-specificity protein kinases MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2. Both MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2 function specifically in the MAPK/ERK cascade, and catalyze the concomitant phosphorylation of a threonine and a tyrosine residue in a Thr-Glu-Tyr sequence located in the extracellular signal-regulated kinases MAPK3/ERK1 and MAPK1/ERK2, leading to their activation and further transduction of the signal within the MAPK/ERK cascade. Depending on the cellular context, this pathway mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation, predominantly through the regulation of transcription, metabolism and cytoskeletal rearrangements. One target of the MAPK/ERK cascade is peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG), a nuclear receptor that promotes differentiation and apoptosis. MAP2K1/MEK1 has been shown to export PPARG from the nucleus. The MAPK/ERK cascade is also involved in the regulation of endosomal dynamics, including lysosome processing and endosome cycling through the perinuclear recycling compartment (PNRC), as well as in the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. Dual specificity protein kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. Related diseases Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome 3 (CFC3) [MIM:615279]: A form of cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, a multiple congenital anomaly disorder characterized by a distinctive facial appearance, heart defects and intellectual disability. Heart defects include pulmonic stenosis, atrial septal defects and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Some affected individuals present with ectodermal abnormalities such as sparse, friable hair, hyperkeratotic skin lesions and a generalized ichthyosis-like condition. Typical facial features are similar to Noonan syndrome. They include high forehead with bitemporal constriction, hypoplastic supraorbital ridges, downslanting palpebral fissures, a depressed nasal bridge, and posteriorly angulated ears with prominent helices. Distinctive features of CFC3 include macrostomia and horizontal shape of palpebral fissures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16439621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18042262}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Melorheostosis, isolated (MEL) [MIM:155950]: A sclerosing bone disorder characterized by hyperostosis of the cortex of tubular bones, frequently involving one limb. The lesions may be accompanied by abnormalities of adjacent soft tissue, joint contractures, sclerodermatous skin lesions, muscle atrophy, or hemangioma. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29643386}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06892; DB07046; DB08208; DB03115; DB11967; DB06616; DB05239; DB02152; DB07101; DB08130; DB14904; DB11689; DB08911 Interacts with Q8N9N5; Q8N9N5-2; Q9NR09; P15056; Q9Y297; O15519-1; P28482; P27361; Q13526; Q9H8W4; P04049; Q8WWU5-7; Q86Y07; Q86Y07-1; P46937 EC number EC 2.7.12.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cardiomyopathy; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Ectodermal dysplasia; Intellectual disability; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Tyrosine-protein kinase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B Molecular weight (Da) 34785.9 Length 311 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 46.58 Isoelectric point 6.29 Charge (pH=7) -2.54 3D Binding mode Sequence DEQQRKRLEAFLTQKQKVGELKDDDFEKISELGAGNGGVVFKVSHKPSGLVMARKLIHLEIKPAIRNQIIRELQVLHECNSPYIVGFYGAFYSDGEISICMEHMDGGSLDQVLKKAGRIPEQILGKVSIAVIKGLTYLREKHKIMHRDVKPSNILVNSRGEIKLCDFGVSGQLIDAMANAFVGTRSYMSPERLQGTHYSVQSDIWSMGLSLVEMAVGRYPIPPPDAKELELMPMAIFELLDYIVNEPPPKLPSGVFSLEFQDFVNKCLIKNPAERADLKQLMVHAFIKRSDAEEVDFAGWLCSTIGLNQPS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 65 | Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 1 (EPCAM) | 4MZV | 5.05 | |
Target general information Gen name EPCAM Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hEGP314; TROP1; TACSTD1; Major gastrointestinal tumor-associated protein GA733-2; MIC18; M4S1; M1S2; KSA; KS 1/4 antigen; Gastrointestinal carcinoma antigen GA733; GA733-2; Epithelial glycoprotein 314 Protein family EPCAM family Biochemical class NA Function Plays a role in embryonic stem cells proliferation and differentiation. Up-regulates the expression of FABP5, MYC and cyclins A and E. May act as a physical homophilic interaction molecule between intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) and intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) at the mucosal epithelium for providing immunological barrier as a first line of defense against mucosal infection. Related diseases Diarrhea 5, with tufting enteropathy, congenital (DIAR5) [MIM:613217]: An intractable diarrhea of infancy characterized by villous atrophy and absence of inflammation, with intestinal epithelial cell dysplasia manifesting as focal epithelial tufts in the duodenum and jejunum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18572020, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24142340}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lynch syndrome 8 (LYNCH8) [MIM:613244]: A form of Lynch syndrome, an autosomal dominant disease associated with marked increase in cancer susceptibility. It is characterized by a familial predisposition to early-onset colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and extra-colonic tumors of the gastrointestinal, urological and female reproductive tracts. Lynch syndrome is reported to be the most common form of inherited colorectal cancer in the Western world. Clinically, it is often divided into two subgroups. Type I is characterized by hereditary predisposition to colorectal cancer, a young age of onset, and carcinoma observed in the proximal colon. Type II is characterized by increased risk for cancers in certain tissues such as the uterus, ovary, breast, stomach, small intestine, skin, and larynx in addition to the colon. Diagnosis of classical Lynch syndrome is based on the Amsterdam criteria: 3 or more relatives affected by colorectal cancer, one a first degree relative of the other two; 2 or more generation affected; 1 or more colorectal cancers presenting before 50 years of age; exclusion of hereditary polyposis syndromes. The term 'suspected Lynch syndrome' or 'incomplete Lynch syndrome' can be used to describe families who do not or only partially fulfill the Amsterdam criteria, but in whom a genetic basis for colon cancer is strongly suspected. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19098912}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. LYNCH8 results from heterozygous deletion of 3-prime exons of EPCAM and intergenic regions directly upstream of MSH2, resulting in transcriptional read-through and epigenetic silencing of MSH2 in tissues expressing EPCAM. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06607; DB11075; DB05831; DB05319; DB09336 Interacts with P27797; P12830; Q15078; P36957; Q8TDX7 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell junction; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Tight junction; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tumor antigen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 27439.8 Length 243 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 33.77 Isoelectric point 6.03 Charge (pH=7) -1.99 3D Binding mode Sequence XEECVCENYKLAVNCFVNNNRQCQCTSVGAQNTVICSKLAAKCLVMKAEMQGSKLGRRAKPEGALQNNDGLYDPDCDESGLFKAKQCQGTSTCWCVNTAGVRRTDKDTEITCSERVRTYWIIIELKHKAREKPYDSKSLRTALQKEITTRYQLDPKFITSILYENNVITIDLVQQSSQKTQNDVDIADVAYYFEKDVKGESLFHSKKMDLTVNGEQLDLDPGQTLIYYVDEKAPEFSMQGLKH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 66 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor alpha-3/beta-4 (CHRNA3/B4) | 6PV7 | 5.05 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA3-CHRNB4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Neuronal acetylcholine receptor Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-3/CHRNA3 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function A type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting of 3 and 4 subunits. Related diseases Bladder dysfunction, autonomic, with impaired pupillary reflex and secondary CAKUT (BAIPRCK) [MIM:191800]: An autosomal recessive disease characterized by impaired innervation and autonomic dysfunction of the urinary bladder, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, small kidneys, recurrent urinary tract infections, and progressive renal insufficiency. Additional autonomic features are impaired pupillary reflex and orthostatic hypotension. The disease manifests in utero or early childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31708116}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00915; DB01156; DB00237; DB00565; DB09028; DB00514; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB05710; DB01227; DB00848; DB00333; DB00184; DB01090; DB00202; DB01273 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 89661.2 Length 775 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 35.11 Isoelectric point 6.07 Charge (pH=7) -5.67 3D Binding mode Sequence SEAEHRLFERLFEDYNEIIRPVANVSDPVIIHFEVSMSQLVKVDEVNQIMETNLWLKQIWNDYKLKWNPSDYGGAEFMRVPAQKIWKPDIVLYNNAVGDFQVDDKTKALLKYTGEVTWIPPAIFKSSCKIDVTYFPFDYQNCTMKFGSWSYDKAKIDLVLIGSSMNLKDYWESGEWAIIKAPGYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDITYSLYIRRLPLFYTINLIIPCLLISFLTVLVFYLPSDCGEKVTLCISVLLSLTVFLLVITETIPSTSLVIPLIGEYLLFTMIFVTLSIVITVFVLNVHYRTPTTHTMPSWVKTVFLNLLPRVMFMTRIKEAIQSVKYIAENMKAQNEAKEIQDDWKYVAMVIDRIFLWVFTLVCILGTAGLFLQPLMRVANAEEKLMDDLLNKTRYNNLIRPATSSSQLISIKLQLSLAQLISVNEREQIMTTNVWLKQEWTDYRLTWNSSRYEGVNILRIPAKRIWLPDIVLYNNADGTYEVSVYTNLIVRSNGSVLWLPPAIYKSACKIEVKYFPFDQQNCTLKFRSWTYDHTEIDMVLMTPTASMDDFTPSGEWDIVALPGRRTVNPQDPSYVDVTYDFIIKRKPLFYTINLIIPCVLTTLLAILVFYLPSDCGEKMTLCISVLLALTFFLLLISKIVPPTSLDVPLIGKYLMFTMVLVTFSIVTSVCVLNVHHRSPSTHTMAPWVKRCFLHKLPTFLFMKRRQDVQEALEGVSFIAQHMKNDDEDQSVVEDWKYVAMVVDRLFLWVFMFVCVLGTVGLFLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 67 | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) | 5J89 | 5.05 | |
Target general information Gen name CD274 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hPD-L1; Programmed death ligand 1; PDL1; PDCD1LG1; PDCD1L1; PDCD1 ligand 1; B7H1; B7-H1; B7 homolog 1 Protein family Immunoglobulin superfamily, BTN/MOG family Biochemical class Immunoglobulin Function As a ligand for the inhibitory receptor PDCD1/PD-1, modulates the activation threshold of T-cells and limits T-cell effector response. Through a yet unknown activating receptor, may costimulate T-cell subsets that predominantly produce interleukin-10 (IL10). Plays a critical role in induction and maintenance of immune tolerance to self. Related diseases Truncation of the 3'-untranslated (3'-UTR) region of CD274 transcripts leads to elevated expression of CD274 in multiple cancers including T-cell leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and stomach adenocarcinoma (PubMed:27281199). Disruption of 3'-UTR region is caused by structural variants that stabilize CD274 transcripts, leading to overexpression (PubMed:27281199). Increased expression in tumors promotes immune evasion and tumor cell growth by allowing malignant cells to escape destruction by the immune system (PubMed:27281199). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27281199}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB15773; DB11595; DB15771; DB11945; DB15772; DB14776; DB15770; DB11714; DB15769; DB09035; DB09037; DB00203; DB00313 Interacts with P33681; Q8IZR5; Q9NX76; Q15116; Q15116 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Endosome; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Immunoglobulin domain; Membrane; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C,D Molecular weight (Da) 28335.2 Length 249 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 35.39 Isoelectric point 6.15 Charge (pH=7) -3.43 3D Binding mode Sequence AFTVTVPKDLYVVEYGSNMTIECKFPVEKQLDLAALIVYWEMEDKNIIQFVHGEEDLKVQHSSYRQRARLLKDQLSLGNAALQITDVKLQDAGVYRCMISYGGADYKRITVKVNAPYAAALEHHHAFTVTVPKDLYVVEYGSNMTIECKFPVEKQLDLAALIVYWEMEDKNIIQFVHGEEDLKVQHSSYRQRARLLKDQLSLGNAALQITDVKLQDAGVYRCMISYGGADYKRITVKVNAPYAAALEHH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 68 | "Periplasmic trehalase (EC 3.2.1.28) (Alpha,alpha-trehalase) (Alpha,alpha-trehalose glucohydrolase) (Tre37A)" | 2JG0 | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name treA Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms JW1186;osmA;b1197 Protein family Glycosyl hydrolase 37 family Biochemical class NA Function Provides the cells with the ability to utilize trehalose at high osmolarity by splitting it into glucose molecules that can subsequently be taken up by the phosphotransferase-mediated uptake system. Related diseases SRC kinase activity has been shown to be increased in several tumor tissues and tumor cell lines such as colon carcinoma cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2498394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3093483}.; DISEASE: Thrombocytopenia 6 (THC6) [MIM:616937]: A form of thrombocytopenia, a hematologic disorder defined by a decrease in the number of platelets in circulating blood, resulting in the potential for increased bleeding and decreased ability for clotting. THC6 is an autosomal dominant form. Affected individuals may also have bone abnormalities and an increased risk for myelofibrosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26936507}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 3.2.1.28 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Glycosidase; Hydrolase; Periplasm; Reference proteome; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 57508.9 Length 507 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 48.32 Isoelectric point 5.48 Charge (pH=7) -10.13 3D Binding mode Sequence PQPPDILLGPLFNDVQNAKLFPDQKTFADAVPNSDPLMILADYRMQQNQSGFDLRHFVNVNFTLPKYVPPEGQSLREHIDGLWPVLTRSTENTEKWDSLLPLPEPYVVPGGRFREVYYWDSYFTMLGLAESGHWDKVADMVANFAHEIDTYGHIPNGNRSYYLSRSQPPFFALMVELLAQHEGDAALKQYLPQMQKEYAYWMDGVENLQAGQQEKRVVKLQDGTLLNRYWDDRDTPRPESWVEDIATAKSNPNRPATEIYRDLRSAAASGWDFSSRWMDNPQQLNTLRTTSIVPVDLNSLMFKMEKILARASKAAGDNAMANQYETLANARQKGIEKYLWNDQQGWYADYDLKSHKVRNQLTAAALFPLYVNAAAKDRANKMATATKTHLLQPGGLNTTSVKSGQQWDAPNGWAPLQWVATEGLQNYGQKEVAMDISWHFLTNVQHTYDREKKLVEKYDVSTTGTGGGGGEYPLQDGFGWTNGVTLKMLDLICPKEQPCDNVPATRP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 69 | Retinoic acid receptor gamma (RARG) | 1FCY | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name RARG Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms RAR-gamma; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 3; NR1B3 Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily Biochemical class Nuclear hormone receptor Function Receptor for retinoic acid. Retinoic acid receptors bind as heterodimers to their target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, and regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RAR/RXR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5. In the absence of ligand, acts mainly as an activator of gene expression due to weak binding to corepressors. Required for limb bud development. In concert with RARA or RARB, required for skeletal growth, matrix homeostasis and growth plate function (By similarity). Related diseases Cystic fibrosis (CF) [MIM:219700]: A common generalized disorder of the exocrine glands which impairs clearance of secretions in a variety of organs. It is characterized by the triad of chronic bronchopulmonary disease (with recurrent respiratory infections), pancreatic insufficiency (which leads to malabsorption and growth retardation) and elevated sweat electrolytes. It is the most common genetic disease in Caucasians, with a prevalence of about 1 in 2'000 live births. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10094564, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10869121, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10923036, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11242048, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12167682, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12394343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12529365, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1284466, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1284468, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1284529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1284530, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1284548, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1379210, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15528182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15716351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16822950, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1695717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1699669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17098864, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1710600, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1712898, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17182731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20008117, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20150177, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20691141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21884936, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2236053, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23818989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25330774, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26846474, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27241308, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28001373, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28067262, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28087700, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32026723, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33572515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7504969, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7505694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7505767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7508414, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7513296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7517264, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7520022, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7522211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7524909, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7524913, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7525450, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7537150, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7541273, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7541510, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7543567, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7544319, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7581407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7606851, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7680525, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7683628, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7683954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8081395, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8406518, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8522333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8723693, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8723695, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8800923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8829633, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8910473, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8956039, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9101301, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9222768, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9375855, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9401006, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9443874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452048, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452073, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9482579, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9507391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9521595, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9554753, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9736778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9804160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9921909}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. There is some evidence that the functional defect caused by the most common variant Phe-508 DEL can be corrected by the binding to the snake phospholipase A2 crotoxin basic subunit CB. This toxin both disrupts the Phe-508 DEL-cytokeratin 8 complex, allowing for the escape from degradation, and increases the chloride channel current (PubMed:27241308). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27241308}.; DISEASE: Congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD) [MIM:277180]: An autosomal recessive disease characterized by vas deferens aplasia resulting in azoospermia and male infertility. CBAVD may occur in isolation or as a manifestation of cystic fibrosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10066035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10651488, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17329263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7529962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7539342, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9067761, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9736778, ECO:0000269|Ref.117}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07294; DB07031; DB00459; DB00210; DB00523; DB02466; DB03466; DB02741; DB03279; DB00926; DB00982; DB05785; DB05467; DB02258; DB00799; DB00755; DB12808 Interacts with Q96RK4; P13349; P31321; P28702; P48443; O60504-2 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; DNA-binding; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Methylation; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 26574.9 Length 236 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 49.98 Isoelectric point 5.76 Charge (pH=7) -2.95 3D Binding mode Sequence ASPQLEELITKVSKAHQETFPSLCQLGKYTTNSSADHRVQLDLGLWDKFSELATKCIIKIVEFAKRLPGFTGLSIADQITLLKAACLDILMLRICTRYTPEQDTMTFSDGLTLNRTQMHNAGFGPLTDLVFAFAGQLLPLEMDDTETGLLSAICLICGDRMDLEEPEKVDKLQEPLLEALRLYARRRRPSQPYMFPRMLMKITDLRGISTKGAERAITLKMEIPGPMPPLIREMLE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 70 | Angiotensin II receptor type-1 (AGTR1) | 4ZUD | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name AGTR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Type-1 angiotensin II receptor; Angiotensin II type-1 receptor; Angiotensin II receptor 1; Angiotensin 1 receptor; AT2R1B; AT2R1; AT1BR; AT1AR; AT1; AGTR1B; AGTR1A Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Receptor for angiotensin II. Related diseases Renal tubular dysgenesis (RTD) [MIM:267430]: Autosomal recessive severe disorder of renal tubular development characterized by persistent fetal anuria and perinatal death, probably due to pulmonary hypoplasia from early-onset oligohydramnios (the Potter phenotype). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16116425}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB11842; DB08822; DB13919; DB00796; DB05739; DB00876; DB09279; DB01342; DB01029; DB00678; DB00275; DB01347; DB01349; DB00966; DB00177 Interacts with PRO_0000032458 [P01019]; P35414; P05026; Q6ZMG9; O75937; P54368 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Host-virus interaction; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 30770.7 Length 271 Aromaticity 0.16 Instability index 28.86 Isoelectric point 8.09 Charge (pH=7) 2.1 3D Binding mode Sequence ILNSSDCPKAGRHNYIFVMIPTLYSIIFVVGIFGNSLVVIVIYFYMKLKTVASVFLLNLALADLCFLLTLPLWAVYTAMEYRWPFGNYLCKIASASVSFNLYASVFLLTCLSIDRYLAIVHPTMLVAKVTCIIIWLLAGLASLPAIIHRNVFFIENTNITVCAFHYESTLPIGLGLTKNILGFLFPFLIILTSYTLIWKALNDDIFKIIMAIVLFFFFSWIPHQIFTFLDVLIQLGIIRDCRIADIVDTAMPITICIAYFNNCLNPLFYGF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 71 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | 3EQC | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name MAP2K1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms PRKMK1;MEK1 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family, MAP kinase kinase subfamily Biochemical class Transferase Function ATP binding.MAP kinase kinase activity.Protein C-terminus binding.Protein kinase activity.Protein N-terminus binding.Protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity.Protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity.Protein serine/threonine kinase activity.Protein tyrosine kinase activity.Signal transducer, downstream of receptor, with protein tyrosine phosphatase activity. Related diseases Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome 3 (CFC3) [MIM:615279]: A form of cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, a multiple congenital anomaly disorder characterized by a distinctive facial appearance, heart defects and intellectual disability. Heart defects include pulmonic stenosis, atrial septal defects and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Some affected individuals present with ectodermal abnormalities such as sparse, friable hair, hyperkeratotic skin lesions and a generalized ichthyosis-like condition. Typical facial features are similar to Noonan syndrome. They include high forehead with bitemporal constriction, hypoplastic supraorbital ridges, downslanting palpebral fissures, a depressed nasal bridge, and posteriorly angulated ears with prominent helices. Distinctive features of CFC3 include macrostomia and horizontal shape of palpebral fissures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16439621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18042262}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Melorheostosis, isolated (MEL) [MIM:155950]: A sclerosing bone disorder characterized by hyperostosis of the cortex of tubular bones, frequently involving one limb. The lesions may be accompanied by abnormalities of adjacent soft tissue, joint contractures, sclerodermatous skin lesions, muscle atrophy, or hemangioma. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29643386}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06892; DB07046; DB08208; DB03115; DB11967; DB06616; DB05239; DB02152; DB07101; DB08130; DB14904; DB11689; DB08911 Interacts with Q8N9N5; Q8N9N5-2; Q9NR09; P15056; Q9Y297; O15519-1; P28482; P27361; Q13526; Q9H8W4; P04049; Q8WWU5-7; Q86Y07; Q86Y07-1; P46937 EC number 2.7.12.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cardiomyopathy; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Ectodermal dysplasia; Intellectual disability; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Tyrosine-protein kinase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34949.2 Length 312 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 45.3 Isoelectric point 5.96 Charge (pH=7) -4.47 3D Binding mode Sequence ELELDEQQRKRLEAFLTQKQKVGELKDDDFEKISELGAGNGGVVFKVSHKPSGLVMARKLIHLEIKPAIRNQIIRELQVLHECNSPYIVGFYGAFYSDGEISICMEHMDGGSLDQVLKKAGRIPEQILGKVSIAVIKGLTYLREKHKIMHRDVKPSNILVNSRGEIKLCDFGVSGQLIDSMAVGTRSYMSPERLQGTHYSVQSDIWSMGLSLVEMAVGRYPIPPPDAKELELMFGCPMAIFELLDYIVNEPPPKLPSGVFSLEFQDFVNKCLIKNPAERADLKQLMVHAFIKRSDAEEVDFAGWLCSTIGLN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 72 | cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4C | 2QYM | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name PDE4C Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms DPDE1 Protein family Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family, PDE4 subfamily Biochemical class Hydrolase Function 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity.Metal ion binding. Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 33 (COXPD33) [MIM:617713]: An autosomal recessive disorder caused by multiple mitochondrial respiratory chain defects and impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism. Clinical manifestations are highly variable. Affected infants present with cardiomyopathy accompanied by multisystemic features involving liver, kidney, and brain. Death in infancy is observed in some patients. Children and adults present with myopathy and progressive external ophthalmoplegia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28942965}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01427; DB00201; DB05219; DB00651; DB06246; DB05266; DB01088; DB01791; DB01656; DB01954; DB09283 Interacts with Q96D03; O15499; P26718; P50221; Q6FHY5; Q9UJX0; P26367; P30626; P59817; P30626 EC number 3.1.4.53 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; cAMP; Cell projection; Cilium; Hydrolase; Manganese; Metal-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33042.2 Length 291 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 23.45 Isoelectric point 4.91 Charge (pH=7) -18.1 3D Binding mode Sequence VPRFGVQTDQEEQLAKELEDTNKWGLDVFKVAELSGNRPLTAIIFSIFQERDLLKTFQIPADTLATYLLMLEGHYHANVAYHNSLHAADVAQSTHVLLATPALEAVFTDLEILAALFASAIHDVDHPGVSNQNDASVLENHHLAVGFKLLQAENCDIFQNLSAKQRLSLRRMVIDMVLATDMSKHMNLLADLKTMVETKKVTSLGVLLLDNYSDRIQVLQNLVHCADLSNPTKPLPLYRQWTDRIMAEFFQQQVGFIDYIAHPLWETWADLVHPDAQDLLDTLEDNREWYQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 73 | Phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B) | 4KP6 | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name PDE4B Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4B; Type 4B cAMP phosphodiesterase; Type 4 cyclic adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase (type 4 PDE); PDE32; DPDE4 Protein family Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family, PDE4 subfamily Biochemical class Phosphoric diester hydrolase Function May be involved in mediating central nervous system effects of therapeutic agents ranging from antidepressants to antiasthmatic and anti-inflammatory agents. Hydrolyzes the second messenger cAMP, which is a key regulator of many important physiological processes. Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 33 (COXPD33) [MIM:617713]: An autosomal recessive disorder caused by multiple mitochondrial respiratory chain defects and impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism. Clinical manifestations are highly variable. Affected infants present with cardiomyopathy accompanied by multisystemic features involving liver, kidney, and brain. Death in infancy is observed in some patients. Children and adults present with myopathy and progressive external ophthalmoplegia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28942965}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04149; DB03606; DB03807; DB06909; DB01959; DB08299; DB03349; DB00131; DB01427; DB00201; DB03849; DB05219; DB01647; DB00651; DB00824; DB02660; DB05266; DB01088; DB01113; DB01791; DB01656; DB01954; DB04530; DB01412; DB00277; DB09283 Interacts with Q13936; Q08499 EC number EC 3.1.4.53 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; cAMP; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Hydrolase; Membrane; Metal-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 37367.1 Length 324 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 36.36 Isoelectric point 5 Charge (pH=7) -20.82 3D Binding mode Sequence NEDHLAKELEDLNKWGLNIFNVAGYSHNRPLTCIMYAIFQERDLLKTFRISSDTFITYMMTLEDHYHSDVAYHNSLHAADVAQSTHVLLSTPALDAVFTDLEILAAIFAAAIHDVDHPGVSNQFLINTNSELALMYNDESVLENHHLAVGFKLLQEEHCDIFMNLTKKQRQTLRKMVIDMVLATDMSKHMSLLADLKTMVETKKVTSSGVLLLDNYTDRIQVLRNMVHCADLSNPTKSLELYRQWTDRIMEEFFQQGDKERERGMEISPMCDKHTASVEKSQVGFIDYIVHPLWETWADLVQPDAQDILDTLEDNRNWYQSMIP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 74 | Glycolipid transfer protein | 3RZN | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name GLTP Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family GLTP family Biochemical class Lipid transport Function Glycolipid binding.Glycolipid transporter activity.Identical protein binding.Intermembrane lipid transfer activity.Lipid binding. Related diseases Brugada syndrome 7 (BRGDA7) [MIM:613120]: A tachyarrhythmia characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs, the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20031595}. The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Atrial fibrillation, familial, 16 (ATFB16) [MIM:613120]: A familial form of atrial fibrillation, a common sustained cardiac rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity and ineffective atrial contraction promoting blood stasis in the atria and reduces ventricular filling. It can result in palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20558140, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21051419}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03600; DB04465; DB03017; DB03203 Interacts with Q96DZ9; Q9NZD2 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Lipid transport; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23534.1 Length 206 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 36.45 Isoelectric point 7.08 Charge (pH=7) 0.1 3D Binding mode Sequence LAEHLLKPLPADKQIETGPFLEAVSHLPPFFDCLGSPVFTPIKADISGNITKIKAVYDTNPAKFRTLQNILEVEKEMYGAEWPKVGATLALMWLKRGLRFIQVFLQSICDGERDENHPNLIRVNATKAYEMALKKYHGWIVQKIFQAALYAAPYKSDFLKALSKGQNVTEEECLEKIRLFLVNYTATIDVIYEMYTQMNAELNYKV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 75 | Pseudomonas Transcriptional activator protein LasR (Pseudo LasR) | 3IX3 | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name Pseudo LasR Organism Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NA Protein family Autoinducer-regulated transcriptional regulatory protein family Biochemical class NA Function Transcriptional activator of elastase structural gene (LasB). Binds to the PAI autoinducer. Related diseases Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1A (IGHD1A) [MIM:262400]: An autosomal recessive, severe deficiency of growth hormone leading to dwarfism. Patients often develop antibodies to administered growth hormone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8364549}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1B (IGHD1B) [MIM:612781]: An autosomal recessive deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Patients have low but detectable levels of growth hormone, significantly retarded bone age, and a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655557}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Kowarski syndrome (KWKS) [MIM:262650]: A syndrome clinically characterized by short stature associated with bioinactive growth hormone, normal or slightly increased growth hormone secretion, pathologically low insulin-like growth factor 1 levels, and normal catch-up growth on growth hormone replacement therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17519310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8552145, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9276733}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 2 (IGHD2) [MIM:173100]: An autosomal dominant deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Clinical severity is variable. Patients have a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11502836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9152628}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08324 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; DNA-binding; Quorum sensing; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 18305.5 Length 163 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.52 Isoelectric point 5.19 Charge (pH=7) -6.78 3D Binding mode Sequence FLELERSSGKLEWSAILQKMASDLGFSKILFGLLPKDSQDYENAFIVGNYPAAWREHYDRAGYARVDPTVSHCTQSVLPIFWEPSIYQTRKQHEFFEEASAAGLVYGLTMPLHGARGELGALSLSVEAENRAEANRFMESVLPTLWMLKDYALQSGAGLAFEH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 76 | Monoglyceride lipase (MAGL) | 3PE6 | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name MGLL Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Monoacylglycerol lipase; MGL; Lysophospholipaselike; Lysophospholipase-like; Lysophospholipase homolog; HUK5; HU-K5 Protein family AB hydrolase superfamily, Monoacylglycerol lipase family Biochemical class Carboxylic ester hydrolase Function Hydrolyzes the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol, and thereby contributes to the regulation of endocannabinoid signaling, nociperception and perception of pain. Regulates the levels of fatty acids that serve as signaling molecules and promote cancer cell migration, invasion and tumor growth. Converts monoacylglycerides to free fatty acids and glycerol. Related diseases Systemic lupus erythematosus 9 (SLEB9) [MIM:610927]: A chronic, relapsing, inflammatory, and often febrile multisystemic disorder of connective tissue, characterized principally by involvement of the skin, joints, kidneys and serosal membranes. It is of unknown etiology, but is thought to represent a failure of the regulatory mechanisms of the autoimmune system. The disease is marked by a wide range of system dysfunctions, an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and the formation of LE cells in the blood or bone marrow. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17360460}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Immunodeficiency, common variable, 7 (CVID7) [MIM:614699]: A primary immunodeficiency characterized by antibody deficiency, hypogammaglobulinemia, recurrent bacterial infections and an inability to mount an antibody response to antigen. The defect results from a failure of B-cell differentiation and impaired secretion of immunoglobulins; the numbers of circulating B-cells is usually in the normal range, but can be low. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22035880}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P07550; P37235 EC number EC 3.1.1.23 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Fatty acid biosynthesis; Fatty acid metabolism; Hydrolase; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid degradation; Lipid metabolism; Membrane; Nitration; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine esterase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 31808.4 Length 289 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 29.7 Isoelectric point 6.73 Charge (pH=7) -0.91 3D Binding mode Sequence PRRTPQSIPYQDLPHLVNADGQYLFCRYWAPTGTPKALIFVSHGAGEHSGRYEELARMLMGLDLLVFAHDHVGHGQSEGERMVVSDFHVFVRDVLQHVDSMQKDYPGLPVFLLGHSMGGAIAILTAAERPGHFAGMVLISPLVLANPESATTFKVLAAKVLNSVLPNLSSGPIDSSVLSRNKTEVDIYNSDPLICRAGLKVCFGIQLLNAVSRVERALPKLTVPFLLLQGSADRLCDSKGAYLLMELAKSQDKTLKIYEGAYHVLHKELPEVTNSVFHEINMWVSQRTA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 77 | Euchromatic histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 1 (EHMT1) | 5TTG | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name EHMT1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms EHMT1 Protein family Class V-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily Biochemical class NA Function Histone methyltransferase that specifically mono- and dimethylates 'Lys-9' of histone H3 (H3K9me1 and H3K9me2, respectively) in euchromatin. H3K9me represents a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional repression by recruiting HP1 proteins to methylated histones. Also weakly methylates 'Lys-27' of histone H3 (H3K27me). Also required for DNA methylation, the histone methyltransferase activity is not required for DNA methylation, suggesting that these 2 activities function independently. Probably targeted to histone H3 by different DNA-binding proteins like E2F6, MGA, MAX and/or DP1. During G0 phase, it probably contributes to silencing of MYC- and E2F-responsive genes, suggesting a role in G0/G1 transition in cell cycle. In addition to the histone methyltransferase activity, also methylates non-histone proteins: mediates dimethylation of 'Lys-373' of p53/TP53. Related diseases Kleefstra syndrome 1 (KLEFS1) [MIM:610253]: A form of Kleefstra syndrome, an autosomal dominant disease characterized by variable intellectual disability, psychomotor developmental delay, seizures, behavioral abnormalities, and facial dysmorphisms. KLEFS1 patients additionally manifest brachy(micro)cephaly, congenital heart defects, and urogenital defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16826528, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19264732}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The syndrome can be either caused by intragenic EHMT1 mutations leading to haploinsufficiency of the EHMT1 gene or by a submicroscopic 9q34.3 deletion. Although it is not known if and to what extent other genes in the 9q34.3 region contribute to the syndrome observed in deletion cases, EHMT1 seems to be the major determinant of the core disease phenotype (PubMed:19264732). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16826528, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19264732}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q99549; Q04206; Q04207 EC number EC 2.1.1.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ANK repeat; Chromatin regulator; Chromosome; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Methyltransferase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 30066.9 Length 260 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 49.19 Isoelectric point 5.73 Charge (pH=7) -4.88 3D Binding mode Sequence VERIVSRDIARGYERIPIPCVNAVDSEPCPSNYKYVSQNCVTSPMNIDRNITHLQYCVCIDDCSSSNCMCGQLSMRCWYDKDGRLLPEFNMAEPPLIFECNHACSCWRNCRNRVVQNGLRARLQLYRTRDMGWGVRSLQDIPPGTFVCEYVGELISDSEADVREEDSYLFDLDNDGEVYCIDARFYGNVSRFINHHCEPNLVPVRVFMAHQDLRFPRIAFFSTRLIEAGEQLGFDYGERFWDIKGKLFSCRCGSPKCRHS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 78 | Organic cation transporter 3 (OCT3) | 7ZH6 | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name SLC22A3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Solute carrier family 22 member 3; Extraneuronal monoamine transporter; EMTH Protein family Major facilitator (TC 2.A.1) superfamily, Organic cation transporter (TC 2.A.1.19) family Biochemical class NA Function Mediates potential-dependent transport of a variety of organic cations. May play a significant role in the disposition of cationic neurotoxins and neurotransmitters in the brain. Related diseases Deafness, autosomal dominant, 2A (DFNA2A) [MIM:600101]: A form of non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss. Sensorineural deafness results from damage to the neural receptors of the inner ear, the nerve pathways to the brain, or the area of the brain that receives sound information. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10025409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10369879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10571947, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10925378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21242547}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00718; DB08838; DB00182; DB00122; DB14006; DB00501; DB00575; DB00363; DB01151; DB00988; DB00783; DB13952; DB13953; DB13954; DB13955; DB13956; DB00983; DB00536; DB05381; DB00458; DB00762; DB00709; DB00448; DB08882; DB01042; DB01577; DB00331; DB08893; DB00184; DB00368; DB00526; DB00925; DB00413; DB00457; DB01035; DB00396; DB00938; DB00391; DB13943; DB13944; DB08837; DB08841; DB00541 Interacts with P00519 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Glycoprotein; Ion transport; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 53067.4 Length 478 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 38.82 Isoelectric point 9.07 Charge (pH=7) 10.54 3D Binding mode Sequence SFDEALQRVGEFGRFQRRVFLLLCLTGVTFAFLFVGVVFLGTQPDHYWCRGPSAAALAERCGWSPEEEWNRTAPASRGRCQRYLLSAPLVPCRGGWRYAQAHSTIVSEFDLVCVNAWMLDLTQAILNLGFLTGAFTLGYAADRYGRIVIYLLSCLGVGVTGVVVAFAPNFPVFVIFRFLQGVFGKGTWMTCYVIVTEIVGSKQRRIVGIVIQMFFTLGIIILPGIAYFIPNWQGIQLAITLPSFLFLLYYWVVPESPRWLITRKKGDKALQILRRIAKCNVSNPSFLDLVRTPQMRKCTLILMFAWFTSAVVYQGLVMRLGNLYIDFFISGVVELPGALLILLTIERLGRRLPFAASNIVAGVACLVTAFLPEGIAWLRTTVATLGRLGITMAFEIVYLVNSELYPTTLRNFGVSLCSGLCDFGGIIAPFLLFRLAAVWLELPLIIFGILASICGGLVMLLPETKGIALPETVDDVEK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 79 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase KMT5C (KMT5C) | 3RQ4 | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name KMT5C Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Lysine N-methyltransferase 5C; Lysine-specific methyltransferase 5C; Suppressor of variegation 4-20 homolog 2; Su(var)4-20 homolog 2; Suv4-20h2; [histone H4]-N-methyl-L-lysine20 N-methyltransferase KM Protein family Class V-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, Histone-lysine methyltransferase family, Suvar4-20 subfamily Biochemical class NA Function Histone methyltransferase that specifically methylates monomethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me1) and dimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me2) of histone H4 to produce respectively dimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me2) and trimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me3) and thus regulates transcription and maintenance of genome integrity. In vitro also methylates unmodified 'Lys-20' (H4K20me0) of histone H4 and nucleosomes. H4 'Lys-20' trimethylation represents a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional repression. Mainly functions in pericentric heterochromatin regions, thereby playing a central role in the establishment of constitutive heterochromatin in these regions. KMT5C is targeted to histone H3 via its interaction with RB1 family proteins (RB1, RBL1 and RBL2) (By similarity). Facilitates TP53BP1 foci formation upon DNA damage and proficient non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ)-directed DNA repair by catalyzing the di- and trimethylation of 'Lys-20' of histone H4. May play a role in class switch reconbination by catalyzing the di- and trimethylation of 'Lys-20' of histone H4 (By similarity). Related diseases Brachydactyly A2 (BDA2) [MIM:112600]: A form of brachydactyly. Brachydactyly defines a group of inherited malformations characterized by shortening of the digits due to abnormal development of the phalanges and/or the metacarpals. In brachydactyly type A2 shortening of the middle phalanges is confined to the index finger and the second toe, all other digits being more or less normal. Because of a rhomboid or triangular shape of the affected middle phalanx, the end of the second finger usually deviates radially. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19327734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357617}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. Duplications of a cis-regulatory element located approximately 110 kb downstream of BMP2 have been found in BDA2 families. They likely cause altered BMP2 expression with pathological consequences. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19327734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357617}.; DISEASE: Short stature, facial dysmorphism, and skeletal anomalies with or without cardiac anomalies 1 (SSFSC1) [MIM:617877]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by short stature, facial dysmorphism, skeletal anomalies, and variable cardiac defects. Distinctive facial features include midface retrusion, short upturned nose, long philtrum, high-arched or cleft palate, and variable degrees of micrognathia and dental crowding. Skeletal anomalies include patterning defects of the axial skeleton, characterized by 11 pairs of ribs and brachydactyly of the fifth ray. Congenital heart defects are variably observed and appear to involve primarily the cardiac outflow tract. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29198724}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q13185 EC number EC 2.1.1.361 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Chromosome; Metal-binding; Methyltransferase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repressor; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 27285.8 Length 240 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 42.74 Isoelectric point 8.32 Charge (pH=7) 3.24 3D Binding mode Sequence DRVTARELCENDDLATSLVLDPYLGFRTHKMNVSPVPPLRRQQHLRSALETFLRQRDLEAAYRALTLGGWTARYFQSRGPRQEAALKTHVYRYLRAFLPESGFTILPCTRYSMETNGAKIVSTRAWKKNEKLELLVGCIAELREADEGLLRAGENDFSIMYSTRKRSAQLWLGPAAFINHDCKPNCKFVPADGNAACVKVLRDIEPGDEVTCFYGEGFFGEKNEHCECHTCERKGEGAFR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 80 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor alpha-3/beta-4 (CHRNA3/B4) | 6PV7 | 5.04 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA3-CHRNB4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Neuronal acetylcholine receptor Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-3/CHRNA3 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function A type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting of 3 and 4 subunits. Related diseases Bladder dysfunction, autonomic, with impaired pupillary reflex and secondary CAKUT (BAIPRCK) [MIM:191800]: An autosomal recessive disease characterized by impaired innervation and autonomic dysfunction of the urinary bladder, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, small kidneys, recurrent urinary tract infections, and progressive renal insufficiency. Additional autonomic features are impaired pupillary reflex and orthostatic hypotension. The disease manifests in utero or early childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31708116}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00915; DB01156; DB00237; DB00565; DB09028; DB00514; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB05710; DB01227; DB00848; DB00333; DB00184; DB01090; DB00202; DB01273 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 89661.2 Length 775 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 35.11 Isoelectric point 6.07 Charge (pH=7) -5.67 3D Binding mode Sequence SEAEHRLFERLFEDYNEIIRPVANVSDPVIIHFEVSMSQLVKVDEVNQIMETNLWLKQIWNDYKLKWNPSDYGGAEFMRVPAQKIWKPDIVLYNNAVGDFQVDDKTKALLKYTGEVTWIPPAIFKSSCKIDVTYFPFDYQNCTMKFGSWSYDKAKIDLVLIGSSMNLKDYWESGEWAIIKAPGYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDITYSLYIRRLPLFYTINLIIPCLLISFLTVLVFYLPSDCGEKVTLCISVLLSLTVFLLVITETIPSTSLVIPLIGEYLLFTMIFVTLSIVITVFVLNVHYRTPTTHTMPSWVKTVFLNLLPRVMFMTRIKEAIQSVKYIAENMKAQNEAKEIQDDWKYVAMVIDRIFLWVFTLVCILGTAGLFLQPLMRVANAEEKLMDDLLNKTRYNNLIRPATSSSQLISIKLQLSLAQLISVNEREQIMTTNVWLKQEWTDYRLTWNSSRYEGVNILRIPAKRIWLPDIVLYNNADGTYEVSVYTNLIVRSNGSVLWLPPAIYKSACKIEVKYFPFDQQNCTLKFRSWTYDHTEIDMVLMTPTASMDDFTPSGEWDIVALPGRRTVNPQDPSYVDVTYDFIIKRKPLFYTINLIIPCVLTTLLAILVFYLPSDCGEKMTLCISVLLALTFFLLLISKIVPPTSLDVPLIGKYLMFTMVLVTFSIVTSVCVLNVHHRSPSTHTMAPWVKRCFLHKLPTFLFMKRRQDVQEALEGVSFIAQHMKNDDEDQSVVEDWKYVAMVVDRLFLWVFMFVCVLGTVGLFLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||