Job Results:
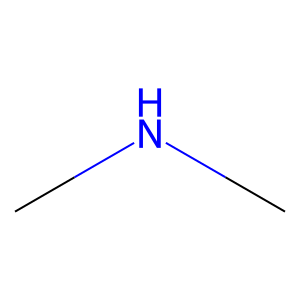
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
0d2a0cc2796a5efce48fb403877956df
Job name
NA
Time
2025-02-13 15:27:50
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61 | Hydrogen peroxide-inducible genes activator | 1I69 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name oxyR Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b3961;mor;momR;JW3933 Protein family LysR transcriptional regulatory family Biochemical class Transcription Function Bacterial-type RNA polymerase core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding.Transcription factor activity, bacterial-type RNA polymerase core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; DNA-binding; Glutathionylation; Oxidation; Reference proteome; Repressor; S-nitrosylation; Stress response; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 46013 Length 412 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 44.76 Isoelectric point 5.57 Charge (pH=7) -14.52 3D Binding mode Sequence ETMSGPLHIGLIPTVGPYLLPHIIPMLHQTFPKLEMYLHEAQTHQLLAQLDSGKLDAVILALVKESEAFIEVPLFDEPMLLAIYEDHPWANREAVPMADLAGEKLLMLEDGHSLRDQAMGFCFDTHFRATSLETLRNMVAAGSGITLLPALAVPPERKRDGVVYLPAIKPEPRRTIGLVYRPGSPLRSRYEQLAEAIRARMDGHFDETMSGPLHIGLIPTVGPYLLPHIIPMLHQTFPKLEMYLHEAQTHQLLAQLDSGKLDAVILALVKESEAFIEVPLFDEPMLLAIYEDHPWANREAVPMADLAGEKLLMLEDGHSLRDQAMGFCFETHFRATSLETLRNMVAAGSGITLLPALAVPPERKRDGVVYLPAIKPEPRRTIGLVYRPGSPLRSRYEQLAEAIRARMDGHFD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 62 | S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase proenzyme (AMD1) | 1JL0 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name AMD1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms SamDC; S-adenosylmethioninedecarboxylase; AdoMetDC; AMD Protein family Eukaryotic AdoMetDC family Biochemical class Carbon-carbon lyase Function Promotes maintenance and self-renewal of embryonic stem cells, by maintaining spermine levels. Essential for biosynthesis of the polyamines spermidine and spermine. Related diseases Niemann-Pick disease A (NPDA) [MIM:257200]: An early-onset lysosomal storage disorder caused by failure to hydrolyze sphingomyelin to ceramide. It results in the accumulation of sphingomyelin and other metabolically related lipids in reticuloendothelial and other cell types throughout the body, leading to cell death. Niemann-Pick disease type A is a primarily neurodegenerative disorder characterized by onset within the first year of life, intellectual disability, digestive disorders, failure to thrive, major hepatosplenomegaly, and severe neurologic symptoms. The severe neurological disorders and pulmonary infections lead to an early death, often around the age of four. Clinical features are variable. A phenotypic continuum exists between type A (basic neurovisceral) and type B (purely visceral) forms of Niemann-Pick disease, and the intermediate types encompass a cluster of variants combining clinical features of both types A and B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12556236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1391960, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15221801, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15877209, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1618760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1718266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18815062, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19405096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2023926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20386867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22818240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23252888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23430884, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26499107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27338287, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8680412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8693491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9266408, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9660788}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Niemann-Pick disease B (NPDB) [MIM:607616]: A late-onset lysosomal storage disorder caused by failure to hydrolyze sphingomyelin to ceramide. It results in the accumulation of sphingomyelin and other metabolically related lipids in reticuloendothelial and other cell types throughout the body, leading to cell death. Clinical signs involve only visceral organs. The most constant sign is hepatosplenomegaly which can be associated with pulmonary symptoms. Patients remain free of neurologic manifestations. However, a phenotypic continuum exists between type A (basic neurovisceral) and type B (purely visceral) forms of Niemann-Pick disease, and the intermediate types encompass a cluster of variants combining clinical features of both types A and B. In Niemann-Pick disease type B, onset of the first symptoms occurs in early childhood and patients can survive into adulthood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12369017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12556236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1301192, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15241805, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16010684, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1618760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16472269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18815062, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1885770, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19050888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19405096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20386867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21098024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21621718, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22613662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22818240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23252888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23430512, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25920558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26084044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26499107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27338287, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27659707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8051942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8664904}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08163; DB00118; DB01917 Interacts with P17707; Q96A98; Q8WY91 EC number EC 4.1.1.50 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Autocatalytic cleavage; Decarboxylase; Direct protein sequencing; Lyase; Phosphoprotein; Polyamine biosynthesis; Proteomics identification; Pyruvate; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Schiff base; Spermidine biosynthesis; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 35790.5 Length 311 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 39.47 Isoelectric point 6.03 Charge (pH=7) -2.01 3D Binding mode Sequence HFFEGTEKLLEVWFSRQGSGDLRTIPRSEWDILLKDVQCSIISVTKTDKQEAYVLSESSMFVSKRRFILKTCGTTLLLKALVPLLKLARDYSGFDSIQSFFYSRKNFMKPSHQGYPHRNFQEEIEFLNAIFPNGAGYCMGRMNSDCWYLYTLDFRVISQPDQTLEILMSELDPAVMDQFYMKDGVTAKDVTRESGIRDLIPGSVIDATMFNPCGYSMNGMKSDGTYWTIAITPEPEFSYVSFETNLSQTSYDDLIRKVVEVFKPGKFVTTLFVNQSSKCPQKIEGFKRLDCQSAMFNDYNFVFTSFAKKQQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 63 | Deoxycytidine kinase (DCK) | 1P5Z | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name DCK Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms dCK Protein family DCK/DGK family Biochemical class Kinase Function Required for the phosphorylation of the deoxyribonucleosides deoxycytidine (dC), deoxyguanosine (dG) and deoxyadenosine (dA). Has broad substrate specificity, and does not display selectivity based on the chirality of the substrate. It is also an essential enzyme for the phosphorylation of numerous nucleoside analogs widely employed as antiviral and chemotherapeutic agents. Related diseases Microvascular complications of diabetes 5 (MVCD5) [MIM:612633]: Pathological conditions that develop in numerous tissues and organs as a consequence of diabetes mellitus. They include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy leading to end-stage renal disease, and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic retinopathy remains the major cause of new-onset blindness among diabetic adults. It is characterized by vascular permeability and increased tissue ischemia and angiogenesis. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Homozygosity for the Leu-55 allele is strongly associated with the development of retinal disease in diabetic patients. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02594; DB00242; DB00631; DB00987; DB01262; DB05494; DB00879; DB01073; DB00441; DB00709; DB01280; DB00642; DB04961; DB00943 Interacts with Q16854 EC number EC 2.7.1.74 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ATP-binding; Direct protein sequencing; Kinase; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B Molecular weight (Da) 27128.5 Length 229 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 52.5 Isoelectric point 5.26 Charge (pH=7) -7.8 3D Binding mode Sequence RIKKISIEGNIAAGKSTFVNILKQLCEDWEVVPEPVARWCNVQSTNGGNVLQMMYEKPERWSFTFQTYACLSRIRAQLASLNGKLKDAEKPVLFFERSVYSDRYIFASNLYESECMNETEWTIYQDWHDWMNNQFGQSLELDGIIYLQATPETCLHRIYLRGRNEEQGIPLEYLEKLHYKHESWLLHRTLKTNFDYLQEVPILTLDVNEDFKDKYESLVEKVKEFLSTL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 64 | Cystathionine gamma-lyase (CTH) | 3COG | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name CTH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Gamma-cystathionase; Cysteine-protein sulfhydrase Protein family Trans-sulfuration enzymes family Biochemical class NA Function Catalyzes the last step in the trans-sulfuration pathway from methionine to cysteine. Has broad substrate specificity. Converts cystathionine to cysteine, ammonia and 2-oxobutanoate. Converts two cysteine molecules to lanthionine and hydrogen sulfide. Can also accept homocysteine as substrate. Specificity depends on the levels of the endogenous substrates. Generates the endogenous signaling molecule hydrogen sulfide (H2S), and so contributes to the regulation of blood pressure. Acts as a cysteine-protein sulfhydrase by mediating sulfhydration of target proteins: sulfhydration consists of converting -SH groups into -SSH on specific cysteine residues of target proteins such as GAPDH, PTPN1 and NF-kappa-B subunit RELA, thereby regulating their function. Related diseases Cystathioninuria (CSTNU) [MIM:219500]: Autosomal recessive phenotype characterized by abnormal accumulation of plasma cystathionine, leading to increased urinary excretion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12574942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18476726}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02328; DB03928; DB00151; DB04217; DB00114 Interacts with P32929; Q96NT3; Q96NT3-2; Q96HA8; Q6P9E2 EC number EC 4.4.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Amino-acid biosynthesis; Calmodulin-binding; Cysteine biosynthesis; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Lipid metabolism; Lyase; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 86026 Length 782 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 32.4 Isoelectric point 6.27 Charge (pH=7) -9.46 3D Binding mode Sequence GFLPHFQHFATQAIHVGQDPEQWTSRAVVPPISLSTTFKQGAPGQHSGFEYSRSGNPTRNCLEKAVAALDGAKYCLAFASGLAATVTITHLLKAGDQIICMDDVYGGTNRYFRQVASEFGLKISFVDCSKIKLLEAAITPETKLVWIETPTNPTQKVIDIEGCAHIVHKHGDIILVVDNTFMSPYFQRPLALGADISMYSATKYMNGHSDVVMGLVSVNCESLHNRLRFLQNSLGAVPSPIDCYLCNRGLKTLHVRMEKHFKNGMAVAQFLESNPWVEKVIYPGLPSHPQHELVKRQCTGCTGMVTFYIKGTLQHAEIFLKNLKLFTLAESLGGFESLAELPAIMTHASVLKNDRDVLGISDTLIRLSVGLEDEEDLLEDLDQALKAAHPPSGFLPHFQHFATQAIHVGQDPEQWTSRAVVPPISLSTTFKQGAPGQGFEYSRSGNPTRNCLEKAVAALDGAKYCLAFASGLAATVTITHLLKAGDQIICMDDVYGGTNRYFRQVASEFGLKISFVDCSKIKLLEAAITPETKLVWIETPTNPTQKVIDIEGCAHIVHKHGDIILVVDNTFMSPYFQRPLALGADISMYSATKYMNGHSDVVMGLVSVNCESLHNRLRFLQNSLGAVPSPIDCYLCNRGLKTLHVRMEKHFKNGMAVAQFLESNPWVEKVIYPGLPSHPQHELVKRQCTGCTGMVTFYIKGTLQHAEIFLKNLKLFTLAESLGGFESLAELPAIMTHASVLKNDRDVLGISDTLIRLSVGLEDEEDLLEDLDQALKAAHPPS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 65 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | 4H3Q | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name MAP2K2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms MEK2;MKK2;PRKMK2 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family, MAP kinase kinase subfamily Biochemical class Transferase Function ATP binding.MAP kinase kinase activity.Metal ion binding.PDZ domain binding.Protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity.Protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity.Protein serine/threonine kinase activity.Protein tyrosine kinase activity.Scaffold protein binding. Related diseases Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome 4 (CFC4) [MIM:615280]: A form of cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, a multiple congenital anomaly disorder characterized by a distinctive facial appearance, heart defects and intellectual disability. Heart defects include pulmonic stenosis, atrial septal defects and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Some affected individuals present with ectodermal abnormalities such as sparse, friable hair, hyperkeratotic skin lesions and a generalized ichthyosis-like condition. Typical facial features are similar to Noonan syndrome. They include high forehead with bitemporal constriction, hypoplastic supraorbital ridges, downslanting palpebral fissures, a depressed nasal bridge, and posteriorly angulated ears with prominent helices. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16439621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18042262, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20358587}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB11967; DB06616; DB12010; DB14904; DB11689; DB08911 Interacts with P05067; P10398; Q96II5; P15056; O95273; Q12959; P61978-2; Q8IVT5; P00540; P04049 EC number 2.7.12.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; ATP-binding; Cardiomyopathy; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Ectodermal dysplasia; Intellectual disability; Kinase; Magnesium; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Tyrosine-protein kinase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B Molecular weight (Da) 41918.9 Length 364 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 40.94 Isoelectric point 7.34 Charge (pH=7) 0.91 3D Binding mode Sequence AGPEMVRGQVFDVGPRYTNLSYIGEGAYGMVCSAYDNVNKVRVAIKKISPFEHQTYCQRTLREIKILLAFRHENIIGINDIIRAPTIEQMKDVYIVQDLMETDLYKLLKTQHLSNDHICYFLYQILRGLKYIHSANVLHRDLKPSNLLLNTTSDLKICDFGLARVADPDHDHTGFLTEYVATRWYRAPEIMLNSKGYTKSIDIWSVGCILAEMLSNRPIFPGKHYLDQLNHILGILGSPSQEDLNCGINLKARNYLLSLPHKNKVPWNRLFPNADSKALDLLDKMLTFNPHKRIEVEQALAHPYLAQYYDPSDEPIAEAPFKFDMELDDLPKEKLKELIFEETARFQPGYRSRRKPVLPALTIN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 66 | Cytosolic purine 5'-nucleotidase | 2JC9 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name NT5C2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms PNT5;NT5B;NT5CP Protein family 5'(3')-deoxyribonucleotidase family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function 5'-nucleotidase activity.Metal ion binding.Nucleoside phosphotransferase activity.Nucleotide binding. Related diseases Spastic paraplegia 45, autosomal recessive (SPG45) [MIM:613162]: A form of spastic paraplegia, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs. Rate of progression and the severity of symptoms are quite variable. Initial symptoms may include difficulty with balance, weakness and stiffness in the legs, muscle spasms, and dragging the toes when walking. In some forms of the disorder, bladder symptoms (such as incontinence) may appear, or the weakness and stiffness may spread to other parts of the body. Some SPG45 patients manifest intellectual disability, contractures and learning disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24482476, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28884889}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00171; DB00811; DB06408 Interacts with P48047; P51116; Q8IVS8; Q7L9L4; Q86TA1; Q70IA8; Q9Y5B8; Q6ZVK8; O00560; Q9NRS6 EC number 2.7.1.77; 3.1.3.5; 3.1.3.99 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Allosteric enzyme; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hereditary spastic paraplegia; Hydrolase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Neurodegeneration; Nucleotide metabolism; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 53978.4 Length 467 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 30.87 Isoelectric point 8.25 Charge (pH=7) 3.41 3D Binding mode Sequence TSWSDRLQNAADMPANMDKHALKKYRREAYHRVFVNRSLAMEKIKCFGFDMDYTLAVYKSPEYESLGFELTVERLVSIGYPQELLSFAYDSTFPTRGLVFDTLYGNLLKVDAYGNLLVCAHGFNFIRGPETREQYPNKFIQRDDTERFYILNTLFNLPETYLLACLVDFFTNCPRYTSCETGFKDGDLFMSYRSMFQDVRDAVDWVHYKGSLKEKTVENLEKYVVKDGKLPLLLSRMKEVGKVFLATNSDYKYTDKIMTYLFDFPHGPKPGSSHRPWQSYFDLILVDARKPLFFGEGTVLRQVDTKTGKLKIGTYTGPLQHGIVYSGGSSDTICDLLGAKGKDILYIGDHIFGDILKSKKRQGWRTFLVIPELAQELHVWTDKSSLFEELQSLDIFLAQRRIKKVTHDMDMCYGMMGSLFRSGSRQTLFASQVMRYADLYAASFINLLYYPFSYLFRAAHVLMPHES Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 67 | Alanine aminotransferase 2 | 3IHJ | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name GPT2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms AAT2;ALT2 Protein family Class-I pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent aminotransferase family, Alanine aminotransferase subfamily Biochemical class Transferase Function L-alanine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity.Pyridoxal phosphate binding. Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder with spastic paraplegia and microcephaly (NEDSPM) [MIM:616281]: An autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by severe psychomotor developmental delay, dysarthria, walking difficulties, moderately to severely impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and progressive microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25758935}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00160; DB00142; DB00780; DB00114 Interacts with NA EC number 2.6.1.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Aminotransferase; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 48717.7 Length 436 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 47.17 Isoelectric point 6.07 Charge (pH=7) -4.32 3D Binding mode Sequence PIVLKAGEIELELQRGIKKPFTEVIRANPITFLRQVMALCTYPNLLDSPSFPEDAKKRARRILQACSQGVNCIREDVAAYITRRDGGVPADPDNIYLTTGASDGISTILKILVSGGGKSRTGVMIPIPQYPLYSAVISELDAIQVNYYLDEENCWALNVNELRRAVQEAKDHCDPKVLCIINPGNPTGQVQSRKCIEDVIHFAWEEKLFLLADEVYQDNVYSPDCRFHSFKKVLYEMGPEYSSNVELASFHSTSKGYMGECGYRGGYMEVINLHPEIKGQLVKLLSVRLCPPVSGQAAMDIVVNPPVAGEESFEQFSREKESVLGNLAKKAKLTEDLFNQVPGIHCNPLQGAMYAFPRIFIPAKAVEAAQAHQMAPDMFYCMKLLEETGICVVPGSGFGQREGTYHFRMTILPPVEKLKTVLQKVKDFHINFLEKY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 68 | Smoothened homolog (SMO) | 4JKV | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name SMO Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Smo-D473H; SMOH; Protein Gx Protein family G-protein coupled receptor Fz/Smo family Biochemical class GPCR frizzled Function Binding of sonic hedgehog (SHH) to its receptor patched is thought to prevent normal inhibition by patched of smoothened (SMO). Required for the accumulation of KIF7, GLI2 and GLI3 in the cilia. Interacts with DLG5 at the ciliary base to induce the accumulation of KIF7 and GLI2 at the ciliary tip for GLI2 activation. G protein-coupled receptor that probably associates with the patched protein (PTCH) to transduce the hedgehog's proteins signal. Related diseases Curry-Jones syndrome (CRJS) [MIM:601707]: A multisystem disorder characterized by patchy skin lesions, polysyndactyly, diverse cerebral malformations, unicoronal craniosynostosis, iris colobomas, microphthalmia, and intestinal malrotation with myofibromas or hamartomas. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24859340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27236920}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. 8 individuals have been identified with the disease-causing mutation Phe-412 and all were mosaic. The mutation could not be reliably detected in blood, greatest success rates were obtained with affected tissues obtained by invasive procedures. It is thought that the mutation has arisen postzygotically early during embryonic development (PubMed:27236920). This mutation has also been identified in ameloblastoma, medulloblastoma, meningioma, and basal cell carcinoma, and has been reported as the oncogenic driver in some of these tumors (PubMed:24859340). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24859340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27236920}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01047; DB11978; DB06786; DB09143; DB08828 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Developmental protein; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 37420.1 Length 333 Aromaticity 0.16 Instability index 25.17 Isoelectric point 6.65 Charge (pH=7) -0.76 3D Binding mode Sequence AYIQKYLSGQCEVPLVRTDNPKSWYEDVEGCGIQCQNPLFTEAEHQDMHSYIAAFGAVTGLCTLFTLATFVADWRNSNRYPAVILFYVNACFFVGSIGWLAQFMDGARREIVCRADGTMRLGEPTSNETLSCVIIFVIVYYALMAGVVWFVVLTYAWHTSFKALGKTSYFHLLTWSLPFVLTVAILAVAQVDGDSVSGICFVGYKNYRYRAGFVLAPIGLVLIVGGYFLIRGVMTLFSIKSNHPGLLSEKAASKINETMLRLGIFGFLAFGFVLITFSCHFYDFFNQAEWERSFRDYVLCQANDCEIKNRPSLLVEKINLFAMFGTGIAMSTW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 69 | Phospholipase D2 (PLD2) | 6OHP | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name PLD2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hPLD2; Phosphatidylcholine-hydrolyzing phospholipase D2; PLD1C; PLD 2; Choline phosphatase 2 Protein family Phospholipase D family Biochemical class Phosphoric diester hydrolase Function May have a role in signal-induced cytoskeletal regulation and/or endocytosis. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 80, with variant lissencephaly (MRT80) [MIM:620653]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by global developmental delay, mildly to moderately impaired intellectual development, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder, hypotonia, seizure, poor social skills, and autistic traits. Brain imaging shows fronto-temporal lissencephaly and pachygyria. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:37880421}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00122; DB14006 Interacts with P05067; P23528; P62993; P15153; P13051-2 EC number EC 3.1.4.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Hydrolase; Lipid degradation; Lipid metabolism; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 66788.7 Length 586 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 41.26 Isoelectric point 6.54 Charge (pH=7) -3.31 3D Binding mode Sequence FLQLHRHDSYAPPRPGTLARWFVNGAGYFAAVADAILRAQEEIFITDWWLSPEVYLKRPAHSDDWRLDIMLKRKAEEGVRVSILLFKEVELALGINSGYSKRALMLLHPNIKVMRHPDQVTLWAHHEKLLVVDQVVAFLGGLDLAYGRWDDLHYRLTDLGDLSHNQFFWLGKDYSNLITKDWVQLDRPFEDFIDRETTPRMPWRDVGVVVHGLPARDLARHFIQRWNFTKTTKAKXKTPTYPYLLPKSTSTFTLPGGQCTTVQVLRSVDRWSAGTLENSILNAYLHTIRESQHFLYIENQFFISCSDGRTVLNKVGDEIVDRILKAHKQGWCYRVYVLLPLLPGFEGDISTGGGNSIQAILHFTYRTLCRGEYSILHRLKAAMGTAWRDYISICGLRTHGELGGHPVSELIYIHSKVLIADDRTVIIGSANINDRSLLGKRDSELAVLIEDTETEPSLMNGAEYQAGRFALSLRKHCFGVILGANTRPDLDLRDPICDDFFQLWQDMAESNANIYEQIFRCLPSNATRSLRTLREYVAVEPLATVSPPLARSELTQVQGHLVHFPLKFLEDESLLPPGMIPLEVWT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 70 | Thymidine kinase 1 (TK1) | 1W4R | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name TK1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Thymidine kinase, cytosolic Protein family Thymidine kinase family Biochemical class Kinase Function cytosol, identical protein binding, thymidine kinase activity, zinc ion binding, DNA metabolic process, nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process, protein homotetramerization, pyrimidine nucleoside salvage, thymidine metabolic process Related diseases Seizures, benign familial infantile, 3 (BFIS3) [MIM:607745]: A form of benign familial infantile epilepsy, a neurologic disorder characterized by afebrile seizures occurring in clusters during the first year of life, without neurologic sequelae. BFIS3 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11371648, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12243921, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15048894, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16417554, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17021166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17386050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18479388, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20371507, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22612257, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23360469, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23758435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982755, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26291284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29844171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30144217}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 11 (DEE11) [MIM:613721]: An autosomal dominant seizure disorder characterized by neonatal or infantile onset of refractory seizures with resultant delayed neurologic development and persistent neurologic abnormalities. Patients may progress to West syndrome, which is characterized by tonic spasms with clustering, arrest of psychomotor development, and hypsarrhythmia on EEG. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19783390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19786696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20956790, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22677033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23033978, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23195492, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23550958, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23662938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23708187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23935176, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23988467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24463883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24579881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24659627, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24710820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25457084, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25459969, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25772804, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25818041, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26138355, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26291284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26993267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27864847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29625812, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29844171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30144217, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30415926}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Defects in SCN2A are associated with genetic epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+), a familial autosomal dominant epilepsy syndrome, a clinical subset of febrile seizures, characterized by frequent episodes after 6 years of age and various types of subsequent epilepsy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29635106}.; DISEASE: Defects in SCN2A are associated with autism spectrum disorders (ASD). It seems that mutations resulting in sodium channel gain of function and increased neuron excitability lead to infantile seizures, whereas variants resulting in sodium channel loss of function and decrease neuron excitability are associated with ASD. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28256214}.; DISEASE: Episodic ataxia 9 (EA9) [MIM:618924]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder characterized by episodic ataxia manifesting in the first years of life, early-onset seizures, difficulty walking, dizziness, slurred speech, headache, vomiting, and pain. The duration of ataxic episodes is heterogeneous. Most patients show episodes lasting minutes to maximum several hours, but periods lasting days up to weeks have been reported. Some patients have mildly delayed development with speech delay and/or autistic features or mildly impaired intellectual development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26645390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27159988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27328862, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28065826}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01692; DB04485; DB02452; DB00432; DB00495 Interacts with P05067; A0A087WZT3; Q92993; Q1RN33; P04183 EC number EC 2.7.1.21 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; DNA synthesis; Kinase; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 19373.5 Length 174 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 36.21 Isoelectric point 8.63 Charge (pH=7) 3.88 3D Binding mode Sequence RGQIQVILGPMFSGKSTELMRRVRRFQIAQYKCLVIKYAKDTRYSSSFCTHDRNTMEALPACLLRDVAQEALGVAVIGIDEGQFFPDIVEFCEAMANAGKTVIVAALDGTFQRKPFGAILNLVPLAESVVKLTAVCMECFREAAYTKRLGTEKEVEVIGGADKYHSVCRLCYFK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 71 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) | 6YND | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name GAPDH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylase GAPDH; OK/SW-cl.12; GAPD; D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; CDABP0047 Protein family Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Aldehyde/oxo donor oxidoreductase Function Participates in nuclear events including transcription, RNA transport, DNA replication and apoptosis. Nuclear functions are probably due to the nitrosylase activity that mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of nuclear target proteins such as SIRT1, HDAC2 and PRKDC. Modulates the organization and assembly of the cytoskeleton. Facilitates the CHP1-dependent microtubule and membrane associations through its ability to stimulate the binding of CHP1 to microtubules. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is a key enzyme in glycolysis that catalyzes the first step of the pathway by converting D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) into 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate. Component of the GAIT (gamma interferon-activated inhibitor of translation) complex which mediates interferon-gamma-induced transcript-selective translation inhibition in inflammation processes. Upon interferon-gamma treatment assembles into the GAIT complex which binds to stem loop-containing GAIT elements in the 3'-UTR of diverse inflammatory mRNAs (such as ceruplasmin) and suppresses their translation. Has both glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and nitrosylase activities, thereby playing a role in glycolysis and nuclear functions, respectively. Related diseases Bone marrow failure and diabetes mellitus syndrome (BMFDMS) [MIM:620044]: A form of bone marrow failure syndrome, a heterogeneous group of life-threatening disorders characterized by hematopoietic defects in association with a range of variable extra-hematopoietic manifestations. BMFDMS is an autosomal recessive form characterized by various degrees of bone marrow failure, ranging from dyserythropoiesis to bone marrow aplasia, with onset in infancy or early childhood, and non-autoimmune insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus appearing in the first or second decades. Many patients show pigmentary skin abnormalities and short stature. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28073829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35611808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35931051}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07347; DB02059; DB11638; DB09130; DB00157; DB03893; DB09092 Interacts with Q6UY14-3; Q9UIJ7; P05067; Q9UQM7; Q14194; P35222; Q9BPW9-4; P00533; O00471; O75344; P06241; P04406; O14556; Q8NEA9; P42858; Q92993-2; P42695; P35228; P12004; P00558; P48147; P17612; Q8WUY3; Q9UHX1-2; P15927; P05109; Q96GZ6; P00441; Q9BSI4; P10599 EC number EC 1.2.1.12 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; ADP-ribosylation; Alternative splicing; Apoptosis; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; Glycolysis; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Innate immunity; Isopeptide bond; Membrane; Methylation; NAD; Nucleus; Oxidation; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation; Transferase; Translation regulation; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35818.4 Length 333 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 13.69 Isoelectric point 8.64 Charge (pH=7) 3.64 3D Binding mode Sequence GKVKVGVNGFGRIGRLVTRAAFNSGKVDIVAINDPFIDLNYMVYMFQYDSTHGKFHGTVKAENGKLVINGNPITIFQERDPSKIKWGDAGAEYVVESTGVFTTMEKAGAHLQGGAKRVIISAPSADAPMFVMGVNHEKYDNSLKIISNASTTNCLAPLAKVIHDNFGIVEGLMTTVHAITATQKTVDGPSGKLWRDGRGALQNIIPASTGAAKAVGKVIPELNGKLTGMAFRVPTANVSVVDLTCRLEKPAKYDDIKKVVKQASEGPLKGILGYTEHQVVSSDFNSDTHSSTFDAGAGIALNDHFVKLISWYDNEFGYSNRVVDLMAHMASKE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 72 | Cathepsin L (CTSL) | 3BC3 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name CTSL Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Major excreted protein; MEP; Cathepsin L1; CTSL1 Protein family Peptidase C1 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Important for the overall degradation of proteins in lysosomes. Related diseases Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, 2DD (CMT2DD) [MIM:618036]: A dominant axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal degeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29499166}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Hypomagnesemia, seizures, and impaired intellectual development 2 (HOMGSMR2) [MIM:618314]: An autosomal dominant disease characterized by generalized seizures in infancy, severe hypomagnesemia, and renal magnesium wasting. Seizures persist despite magnesium supplementation and are associated with significant intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30388404}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07477; DB12010; DB03661; DB14962 Interacts with O60911; O43765; P0DTC2; P59594; G5EFH4 EC number EC 3.4.22.15 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative initiation; Cell membrane; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Host-virus interaction; Hydrolase; Lysosome; Membrane; Nucleus; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Thiol protease; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23519.9 Length 214 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 30.95 Isoelectric point 4.79 Charge (pH=7) -9.97 3D Binding mode Sequence APRSVDWREKGYVTPVKNQGQCGSWAFSATGALEGQMFRKTGRLISLSEQNLVDCSGPQGNEGCNGGLMDYAFQYVQDNGGLDSEESYPYEATEESCKYNPKYSVANDTGFVDIPKQEKALMKAVATVGPISVAIDAGHESFLFYKEGIYFEPDCSSEDMDHGVLVVGYGFESNKYWLVKNSWGEEWGMGGYVKMAKDRRNHCGIASAASYPTV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 73 | Dibasic-processing enzyme (Furin) | 7LCU | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name FURIN Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Paired basic amino acid residuecleaving enzyme; Paired basic amino acid residue-cleaving enzyme; PCSK3; PACE; FUR; Dibasicprocessing enzyme Protein family Peptidase S8 family, Furin subfamily Biochemical class Peptidase Function Mediates processing of TGFB1, an essential step in TGF-beta-1 activation. Ubiquitous endoprotease within constitutive secretory pathways capable of cleavage at the RX(K/R)R consensus motif. Related diseases Brachydactyly A2 (BDA2) [MIM:112600]: A form of brachydactyly. Brachydactyly defines a group of inherited malformations characterized by shortening of the digits due to abnormal development of the phalanges and/or the metacarpals. In brachydactyly type A2 shortening of the middle phalanges is confined to the index finger and the second toe, all other digits being more or less normal. Because of a rhomboid or triangular shape of the affected middle phalanx, the end of the second finger usually deviates radially. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19327734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357617}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. Duplications of a cis-regulatory element located approximately 110 kb downstream of BMP2 have been found in BDA2 families. They likely cause altered BMP2 expression with pathological consequences. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19327734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357617}.; DISEASE: Short stature, facial dysmorphism, and skeletal anomalies with or without cardiac anomalies 1 (SSFSC1) [MIM:617877]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by short stature, facial dysmorphism, skeletal anomalies, and variable cardiac defects. Distinctive facial features include midface retrusion, short upturned nose, long philtrum, high-arched or cleft palate, and variable degrees of micrognathia and dental crowding. Skeletal anomalies include patterning defects of the axial skeleton, characterized by 11 pairs of ribs and brachydactyly of the fifth ray. Congenital heart defects are variably observed and appear to involve primarily the cardiac outflow tract. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29198724}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03600 Interacts with P05067; P50281; Q9H239; O14793; K9N5Q8; P0DTC2; Q91QT1 EC number EC 3.4.21.75 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Autocatalytic cleavage; Calcium; Cell membrane; Cleavage on pair of basic residues; Disulfide bond; Endosome; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; Heparin-binding; Host-virus interaction; Hydrolase; Membrane; Metal-binding; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Serine protease; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 51029.8 Length 470 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 26.23 Isoelectric point 5.23 Charge (pH=7) -16.94 3D Binding mode Sequence YQEPTDPKFPQQWYLSGVTQRDLNVKAAWAQGYTGHGIVVSILDDGIEKNHPDLAGNYDPGASFDVNDQDPDPQPRYTQMNDNRHGTRCAGEVAAVANNGVCGVGVAYNARIGGVRMLDGEVTDAVEARSLGLNPNHIHIYSASWGPEDDGKTVDGPARLAEEAFFRGVSQGRGGLGSIFVWASGNGGREHDSCNCDGYTNSIYTLSISSATQFGNVPWYSEACSSTLATTYSSGNQNEKQIVTTDLRQKCTESHTGTSASAPLAAGIIALTLEANKDLTWRDMQHLVVQTSKPAHLNANDWATNGVGRKVSHSYGYGLLDAGAMVALAQDWTTVAPQRKCIIDILTEPKDIGKRLEVRKTVTACLGEPNHITRLEHAQARLTLSYNRRGDLAIHLVSPMGTRSTLLAARPHDYSADGFNDWAFMTTHSWDEDPSGEWVLEIENTSEANNYGTLTKFTLVLYGTAGENLY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 74 | Transketolase (TK) | 4KXV | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name TKT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms TKT1; SDDHD; HEL107; HEL-S-48 Protein family Transketolase family Biochemical class Transketolase Function Catalyzes the transfer of a two-carbon ketol group from a ketose donor to an aldose acceptor, via a covalent intermediate with the cofactor thiamine pyrophosphate. Related diseases Short stature, developmental delay, and congenital heart defects (SDDHD) [MIM:617044]: An autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by short stature, developmental delay, intellectual disability and congenital heart defects including ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect and patent foramen ovale. Cataract and uveitis are observed in some patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27259054}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09130 Interacts with P54274 EC number EC 2.2.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Dwarfism; Isopeptide bond; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Thiamine pyrophosphate; Transferase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 67546.4 Length 620 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 35.53 Isoelectric point 7.37 Charge (pH=7) 1.28 3D Binding mode Sequence ESYHKPDQQKLQALKDTANRLRISSIQATTAAGSGHPTSCCSAAEIMAVLFFHTMRYKSQDPRNPHNDRFVLSKGHAAPILYAVWAEAGFLAEAELLNLRKISSDLDGHPVPKQAFTDVATGSLGQGLGAACGMAYTGKYFDKASYRVYCLLGDGELSEGSVWEAMAFASIYKLDNLVAILDINRLGQSDPAPLQHQMDIYQKRCEAFGWHAIIVDGHSVEELCKAFGQAKHQPTAIIAKTFKGRGITGVEDKESWHGKPLPKNMAEQIIQEIYSQIQSKKKILATPPQEDAPSVDIANIRMPSLPSYKVGDKIATRKAYGQALAKLGHASDRIIALDGDTKNSTFSEIFKKEHPDRFIECYIAEQNMVSIAVGCATRNRTVPFCSTFAAFFTRAFDQIRMAAISESNINLCGSHCGVSIGEDGPSQMALEDLAMFRSVPTSTVFYPSDGVATEKAVELAANTKGICFIRTSRPENAIIYNNNEDFQVGQAKVVLKSKDDQVTVIGAGVTLHEALAAAELLKKEKINIRVLDPFTIKPLDRKLILDSARATKGRILTVEDHYYEGGIGEAVSSAVVGEPGITVTHLAVNRVPRSGKPAELLKMFGIDRDAIAQAVRGLIT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 75 | Glutathione S-transferase LANCL1 (LANCL1) | 3E73 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name LANCL1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms p40; LanC-like protein 1; GPR69A; 40 kDa erythrocyte membrane protein Protein family LanC-like protein family Biochemical class NA Function Functions as glutathione transferase. Catalyzes conjugation of the glutathione (GSH) to artificial substrates 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB) and p-nitrophenyl acetate. Mitigates neuronal oxidative stress during normal postnatal development and in response to oxidative stresses probably through GSH antioxidant defense mechanism (By similarity). May play a role in EPS8 signaling. Binds glutathione. Related diseases Spermatogenic failure 5 (SPGF5) [MIM:243060]: An infertility disorder caused by spermatogenesis defects. Semen from affected men show close to 100% morphologically abnormal multiflagellar spermatozoa with low motility, oversized irregular heads, and abnormal midpiece and acrosome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17435757, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21733974}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9UHR4; P42858; Q08509 EC number EC 2.5.1.18 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Membrane; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 46005.4 Length 405 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 33.7 Isoelectric point 7.13 Charge (pH=7) 0.4 3D Binding mode Sequence SMDIEFMAQRAFPNPYADYNKSLAEGYFDAAGRLTPEFSQRLTNKIRELLQQMERGLKSADPRDGTGYTGWAGIAVLYLHLYDVFGDPAYLQLAHGYVKQSLNCLTKRSITFLCGDAGPLAVAAVLYHKMNNEKQAEDCITRLIHLNKIDPHAPNEMLYGRIGYIYALLFVNKNFGVEKIPQSHIQQICETILTSGENLARKRNFTAKSPLMYEWYQEYYVGAAHGLAGIYYYLMQPSLQVSQGKLHSLVKPSVDYVCQLKFPSGNYPPCIGDNRDLLVHWCHGAPGVIYMLIQAYKVFREEKYLCDAYQCADVIWQYGLLKKGYGLCHGSAGNAYAFLTLYNLTQDMKYLYRACKFAEWCLEYGEHGCRTPDTPFSLFEGMAGTIYFLADLLVPTKARFPAFEL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 76 | NH(3)-dependent NAD(+) synthetase | 1KQP | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name nadE Organism Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms outB;BSU03130 Protein family NAD synthetase family Biochemical class Ligase Function ATP binding.Metal ion binding.NAD+ synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity.NAD+ synthase activity. Related diseases Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, 15 (HLD15) [MIM:617951]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by hypomyelinating leukodystrophy with thinning of the corpus callosum. Clinical features include motor and cognitive impairment appearing in the first or second decade of life, dystonia, ataxia, spasticity, and dysphagia. Most patients develop severe optic atrophy, and some have hearing loss. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29576217}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02596; DB04099; DB00798 Interacts with NA EC number 6.3.1.5 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ATP-binding; Direct protein sequencing; Ligase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; NAD; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Reference proteome; Sporulation; Stress response Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 60509.3 Length 542 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 31.96 Isoelectric point 5.07 Charge (pH=7) -19.73 3D Binding mode Sequence SMQEKIMRELHVKPSIDPKQEIEDRVNFLKQYVKKTGAKGFVLGISGGQDSTLAGRLAQLAVESIREEGGDAQFIAVRLPHGTQQDEDDAQLALKFIKPDKSWKFDIKSTVSAFSDQYQQETGDQLTDFNKGNVKARTRMIAQYAIGGQEGLLVLGTDHAAEAVTGFFTKYGDGGADLLPLTGLTKRQGRTLLKELGAPERLYLKEPTADLLDEKPQQSDETELGISYDEIDDYLEGKEVSAKVSEALEKRYSMTEHKRQVPASMFDDWWKSMQEKIMRELHVKPSIDPKQEIEDRVNFLKQYVKKTGAKGFVLGISGGQDSTLAGRLAQLAVESIREEGGDAQFIAVRLPHGTQQDEDDAQLALKFIKPDKSWKFDIKSTVSAFSDQYQQETGDQLTDFNKGNVKARTRMIAQYAIGGQEGLLVLGTDHAAEAVTGFFTKYGDGGADLLPLTGLTKRQGRTLLKELGAPERLYLKEPTADLLDEKPQQSDETELGISYDEIDDYLEGKEVSAKVSEALEKRYSMTEHKRQVPASMFDDWWK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 77 | Neprilysin | 1R1H | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name MME Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms EPN Protein family Peptidase M13 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Endopeptidase activity.Exopeptidase activity.Metalloendopeptidase activity.Metallopeptidase activity.Peptide binding.Zinc ion binding. Related diseases Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, 2T (CMT2T) [MIM:617017]: An axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal degeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26991897, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27588448}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spinocerebellar ataxia 43 (SCA43) [MIM:617018]: A form of spinocerebellar ataxia, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of cerebellar disorders. Patients show progressive incoordination of gait and often poor coordination of hands, speech and eye movements, due to degeneration of the cerebellum with variable involvement of the brainstem and spinal cord. SCA43 is a slowly progressive, autosomal dominant form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27583304}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08575; DB02597; DB00616; DB11623; DB05796; DB06655; DB02558; DB02062; DB00886; DB02557; DB09292; DB13928; DB08626 Interacts with P05067; P21926; Q06787-7; P08107; P04792 EC number 3.4.24.11 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Myristate; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathy; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal-anchor; Spinocerebellar ataxia; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 79435.8 Length 696 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.5 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -11.46 3D Binding mode Sequence GICKSSDCIKSAARLIQNMDATTEPCTDFFKYACGGWLKRNVIPETSSRYGNFDILRDELEVVLKDVLQEPKTEDIVAVQKAKALYRSCINESAIDSRGGEPLLKLLPDIYGWPVATENWEQKYGASWTAEKAIAQLNSKYGKKVLINLFVGTDDKNSVNHVIHIDQPRLGLPSRDYYECTGIYKEACTAYVDFMISVARLIRQEERLPIDENQLALEMNKVMELEKEIANATAKPEDRNDPMLLYNKMTLAQIQNNFSLEINGKPFSWLNFTNEIMSTVNISITNEEDVVVYAPEYLTKLKPILTKYSARDLQNLMSWRFIMDLVSSLSRTYKESRNAFRKALYGTTSETATWRRCANYVNGNMENAVGRLYVEAAFAGESKHVVEDLIAQIREVFIQTLDDLTWMDAETKKRAEEKALAIKERIGYPDDIVSNDNKLNNEYLELNYKEDEYFENIIQNLKFSQSKQLKKLREKVDKDEWISGAAVVNAFYSSGRNQIVFPAGILQPPFFSAQQSNSLNYGGIGMVIGHEITHGFDDNGRNFNKDGDLVDWWTQQSASNFKEQSQCMVYQYGNFSWDLAGGQHLNGINTLGENIADNGGLGQAYRAYQNYIKKNGEEKLLPGLDLNHKQLFFLNFAQVWCGTYRPEYAVNSIKTDVHSPGNFRIIGTLQNSAEFSEAFHCRKNSYMNPEKKCRVW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 78 | Bifunctional protein PutA | 3E2Q | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name putA Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b1014;poaA;JW0999 Protein family Proline dehydrogenase family; Aldehyde dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase activity.Bacterial-type RNA polymerase core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding.DNA binding.Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.Identical protein binding.Proline dehydrogenase activity.Sequence-specific DNA binding.Transcriptional repressor activity, bacterial-type RNA polymerase core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding. Related diseases Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency (FBP1D) [MIM:229700]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by impaired gluconeogenesis, and episodes of hypoglycemia and metabolic acidosis that can be lethal in newborn infants or young children. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12126934, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25601412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9382095}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03051; DB03147; DB04398 Interacts with P09546 EC number 1.2.1.88; 1.5.5.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; DNA-binding; FAD; Flavoprotein; Multifunctional enzyme; NAD; Oxidoreductase; Proline metabolism; Reference proteome; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 45567.7 Length 407 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 33.2 Isoelectric point 7.22 Charge (pH=7) 0.47 3D Binding mode Sequence QSVSRAAITAAYRRPETEAVSMLLEQARLPQPVAEQAHKLAYQLADKLRRLMGEQFVTGETIAEALANARKLEEKGFRYSYDMLGEAALTAADAQAYMVSYQQAIHAIGKASNGRGIYEGPGISIKLSALHPRYSRAQYDRVMEELYPRLKSLTLLARQYDIGINIDAEESDRLEISLDLLEKLCFEPELAGWNGIGFVIQAYQKRCPLVIDYLIDLATRSRRRLMIRLVKGAYWDSEIKRAQMDGLEGYPVYTRKVYTDVSYLACAKKLLAVPNLIYPQFATHNAHTLAAIYQLAGQNYYPGQYEFQCLHGMGEPLYEQVTGKVADGKLNRPCRISAPVGTHETLLAYLVRRLLENGANTSFVNRIADTSLPLDELVADPVTAVEKLAQQEGQTGLPHPKIPLPRD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 79 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP1) | 5WS1 | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name PARP1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP1; Poly[ADP-ribose] synthetase-1; Poly[ADP-ribose] synthase 1; Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1; PPOL; PARP-1; NAD(+)Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase-1 ADP-ribosyltrans Protein family ARTD/PARP family Biochemical class Glycosyltransferases Function Mainly mediates glutamate and aspartate ADP-ribosylation of target proteins: the ADP-D-ribosyl group of NAD(+) is transferred to the acceptor carboxyl group of glutamate and aspartate residues and further ADP-ribosyl groups are transferred to the 2'-position of the terminal adenosine moiety, building up a polymer with an average chain length of 20-30 units. Mediates the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of a number of proteins, including itself, APLF and CHFR. Also mediates serine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins following interaction with HPF1; HPF1 conferring serine specificity. Probably also catalyzes tyrosine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins following interaction with HPF1. Catalyzes the poly-ADP-ribosylation of histones in a HPF1-dependent manner. Involved in the base excision repair (BER) pathway by catalyzing the poly-ADP-ribosylation of a limited number of acceptor proteins involved in chromatin architecture and in DNA metabolism. ADP-ribosylation follows DNA damage and appears as an obligatory step in a detection/signaling pathway leading to the reparation of DNA strand breaks. In addition to base excision repair (BER) pathway, also involved in double-strand breaks (DSBs) repair: together with TIMELESS, accumulates at DNA damage sites and promotes homologous recombination repair by mediating poly-ADP-ribosylation. In addition to proteins, also able to ADP-ribosylate DNA: catalyzes ADP-ribosylation of DNA strand break termini containing terminal phosphates and a 2'-OH group in single- and double-stranded DNA, respectively. Required for PARP9 and DTX3L recruitment to DNA damage sites. PARP1-dependent PARP9-DTX3L-mediated ubiquitination promotes the rapid and specific recruitment of 53BP1/TP53BP1, UIMC1/RAP80, and BRCA1 to DNA damage sites. Acts as a regulator of transcription: positively regulates the transcription of MTUS1 and negatively regulates the transcription of MTUS2/TIP150. With EEF1A1 and TXK, forms a complex that acts as a T-helper 1 (Th1) cell-specific transcription factor and binds the promoter of IFN-gamma to directly regulate its transcription, and is thus involved importantly in Th1 cytokine production. Involved in the synthesis of ATP in the nucleus, together with NMNAT1, PARG and NUDT5. Nuclear ATP generation is required for extensive chromatin remodeling events that are energy-consuming. Poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase that mediates poly-ADP-ribosylation of proteins and plays a key role in DNA repair. Related diseases Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency (DLDD) [MIM:246900]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized biochemically by a combined deficiency of the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC), pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC), and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (KGDC). Clinically, affected individuals have lactic acidosis and neurologic deterioration due to sensitivity of the central nervous system to defects in oxidative metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10448086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11687750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12925875, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15712224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16442803, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16770810, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17404228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20160912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8506365, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8968745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9540846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9934985}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04010; DB03509; DB03072; DB03722; DB03073; DB07787; DB07096; DB07330; DB02498; DB13877; DB02701; DB11793; DB02690; DB09074; DB12332; DB11760; DB00277; DB07232; DB01593; DB14487; DB14533; DB14548 Interacts with Q8IW19; Q7Z2E3; P42574; P49715; Q86WJ1-1; P26358; Q01094; Q96L91; P11308; O60741; P09429; Q13007; Q9BQ69; P08651; Q9Y530; P09874; Q8N2W9; P46063; Q9NTX7; Q14684-1; O95863; P63165; P04637; P0CG48; Q14191; P18887; P54577; Q2M1K9; Q02085 EC number EC 2.4.2.30 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; ADP-ribosylation; Allosteric enzyme; Apoptosis; Chromosome; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; DNA damage; DNA repair; DNA-binding; Glycosyltransferase; Immunity; Innate immunity; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; NAD; Nucleotidyltransferase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 36904 Length 329 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 35.9 Isoelectric point 6.83 Charge (pH=7) -0.44 3D Binding mode Sequence DLIKMIFDVESMKKAMVEYEIDLQKMPLGKLSKRQIQAAYSILSEVQQAVSQGSDSQILDLSNRFYTLIPHDFGMKKPPLLNNADSVQAKAEMLDNLLDIEVAYSLPIDVNYEKLKTDIKVVDRDSEEAEIIRKYVKNTHATTHNAYDLEVIDIFKIEREGECQRYKPFKQLHNRRLLWHGSRTTNFAGILSQGLRIAPPEAPVTGYMFGKGIYFADMVSKSANYCHTSQGDPIGLILLGEVALGNMYELKHASHISKLPKGKHSVKGLGKTTPDPSANISLDGVDVPLGTGISSGVNDTSLLYNEYIVYDIAQVNLKYLLKLKFNFKT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 80 | Riboflavin synthase | 1PKV | 3.99 | |
Target general information Gen name ribC Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms JW1654;ribE;b1662 Protein family NA Biochemical class Transferase Function Riboflavin synthase activity. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00140 Interacts with NA EC number 2.5.1.9 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Reference proteome; Repeat; Riboflavin biosynthesis; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 19023.5 Length 174 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 2.85 Isoelectric point 5.13 Charge (pH=7) -9.8 3D Binding mode Sequence MFTGIVQGTAKLVSIDEKPNFRTHVVELPDHMLDGLETGASVAHNGCCLTVTEINGNHVSFDLMKETLRITNLGDLKVGDWVNVERAMFTGIVQGTAKLVSIDEKPNFRTHVVELPDHMLDGLETGASVAHNGCCLTVTEINGNHVSFDLMKETLRITNLGDLKVGDWVNVERA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||