Job Results:
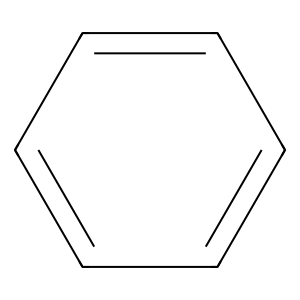
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
58348cd3352a846e4892d1c9736d3b26
Job name
NA
Time
2025-03-05 10:03:15
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | Oxygen-insensitive NADPH nitroreductase | 1F5V | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name nfsA Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms mda18;b0851;mdaA;ybjB;JW0835 Protein family Flavin oxidoreductase frp family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Chromate reductase activity.FMN binding.Oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, nitrogenous group as acceptor. Related diseases Multiple fibroadenomas of the breast (MFAB) [MIM:615554]: A benign breast disease marked by lobuloalveolar growth with abnormally high proliferation of the epithelium, and characterized by the presence of more than 3 fibroadenomas in one breast. Fibroadenomas are adenomas containing fibrous tissue. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18779591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Hyperprolactinemia (HPRL) [MIM:615555]: A disorder characterized by increased levels of prolactin in the blood not associated with gestation or the puerperium. HPRL may result in infertility, hypogonadism, and galactorrhea. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24195502}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03247; DB00698 Interacts with P28630 EC number 1.-.-.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Flavoprotein; FMN; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 53582.7 Length 480 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 45.43 Isoelectric point 6.47 Charge (pH=7) -3.13 3D Binding mode Sequence MTPTIELICGHRSIRHFTDEPISEAQREAIINSARATSSSSFLQCSSIIRITDKALREELVTLTGGQKHVAQAAEFWVFCADFNRHLQICPDAQLGLAEQLLLGVVDTAMMAQNALIAAESLGLGGVYIGGLRNNIEAVTKLLKLPQHVLPLFGLCLGWPADNPDLKPRLPASILVHENSYQPLDKGALAQYDEQLAEYYLTRGSNNRRDTWSDHIRRTIIKESRPFILDYLHKQGWATRMTPTIELICGHRSIRHFTDEPISEAQREAIINSARATSSSSFLQCSSIIRITDKALREELVTLTGGQKHVAQAAEFWVFCADFNRHLQICPDAQLGLAEQLLLGVVDTAMMAQNALIAAESLGLGGVYIGGLRNNIEAVTKLLKLPQHVLPLFGLCLGWPADNPDLKPRLPASILVHENSYQPLDKGALAQYDEQLAEYYLTRGSNNRRDTWSDHIRRTIIKESRPFILDYLHKQGWATR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 42 | Argininosuccinate lyase | 1K62 | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name ASL Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Lyase 1 family, Argininosuccinate lyase subfamily Biochemical class Lyase Function Argininosuccinate lyase activity.Identical protein binding. Related diseases Argininosuccinic aciduria (ARGINSA) [MIM:207900]: An autosomal recessive disorder of the urea cycle. The disease is characterized by mental and physical retardation, liver enlargement, skin lesions, dry and brittle hair showing trichorrhexis nodosa microscopically and fluorescing red, convulsions, and episodic unconsciousness. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11747432, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11747433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12408190, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1705937, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17326097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19703900, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22081021, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2263616, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24166829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9045711}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The phenotype heterogeneity among patients is associated with interallelic complementation resulting in either complete loss of activity or partial regeneration of functional active sites in the heterotetrameric mutant protein. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11747433}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03814; DB00125; DB02267 Interacts with P04424; Q9BTE3-2; Q96HA8; O75382 EC number 4.3.2.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Amino-acid biosynthesis; Arginine biosynthesis; Disease variant; Lyase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Urea cycle Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 51364.1 Length 459 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 35.82 Isoelectric point 6.66 Charge (pH=7) -1.25 3D Binding mode Sequence GKLWGGRFVGAVDPIMEKFNASIAYDRHLWEVDVQGSKAYSRGLEKAGLLTKAEMDQILHGLDKVAEEWAQGTFKLNSNDEDIHTANERRLKELIGATAGKLHTGRSRNDQVVTDLRLWMRQTCSTLSGLLWELIRTMVDRAEAERDVLFPGYTHLQRAQPIRWSHWILSHAVALTRDSERLLEVRKRINVLPLGSGAIAGNPLGVDRELLRAELNFGAITLNSMDATSERDFVAEFLFWRSLCMTHLSRMAEDLILYCTKEFSFVQLSDAYSTGSSLMPRKKNPDSLELIRSKAGRVFGRCAGLLMTLKGLPSTYNKDLQEDKEAVFEVSDTMSAVLQVATGVISTLQIHQENMGQALSPDMLATDLAYYLVRKGMPFRQAHEASGKAVFMAETKGVALNQLSLQELQTISPLFSGDVICVWDYRHSVEQYGALGGTARSSVDWQIRQVRALLQAQQA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 43 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 | 2W96 | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name CDK4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CDC2/CDKX subfamily Biochemical class Cell cycle Function ATP binding.Cyclin binding.Cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity.Cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity.Protein complex binding. Related diseases Melanoma, cutaneous malignant 3 (CMM3) [MIM:609048]: A malignant neoplasm of melanocytes, arising de novo or from a pre-existing benign nevus, which occurs most often in the skin but may also involve other sites. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7652577, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8528263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9311594, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9425228}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12001; DB03496; DB12010; DB09073; DB02733; DB11730; DB15442 Interacts with Q9UH17; P24385; P30279; P30281; Q16543; P50613; P38936; P46527; P49918; P42771; P42772; P42773; P55273; Q9UJC3; P08238; Q9UKT9; Q0VD86; P01106; Q9ULD0; P28749; Q08999; P09936; Q8N720 EC number 2.7.11.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cell cycle; Cell division; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B Molecular weight (Da) 30138.4 Length 267 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 36.2 Isoelectric point 5.78 Charge (pH=7) -5.83 3D Binding mode Sequence SRYEPVAEIGVGAYGTVYKARDPHSGHFVALKSVRVPNGEEGLPISTVREVALLRRLEAFEHPNVVRLMDVCATSRTDREIKVTLVFEHVDQDLRTYLDKAPPPGLPAETIKDLMRQFLRGLDFLHANCIVHRDLKPENILVTSGGTVKLADFGLARIYSYQMALDPVVVTLWYRAPEVLLQSTYATPVDMWSVGCIFAEMFRRKPLFCGNSEADQLGKIFDLIGLPPEDDWVPEMEESGAQLLLEMLTFNPHKRISAFRALQHSYL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 44 | Retinoic acid receptor beta (RARB) | 4DM6 | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name RARB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms RAR-epsilon; RAR-beta; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 2; NR1B2; HBV-activated protein; HAP Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily Biochemical class Nuclear hormone receptor Function Retinoic acid receptors bind as heterodimers to their target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, and regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RXR/RAR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5. In the absence or presence of hormone ligand, acts mainly as an activator of gene expression due to weak binding to corepressors. In concert with RARG, required for skeletal growth, matrix homeostasis and growth plate function. Receptor for retinoic acid. Related diseases Microphthalmia, syndromic, 12 (MCOPS12) [MIM:615524]: A form of microphthalmia, a disorder of eye formation, ranging from small size of a single eye to complete bilateral absence of ocular tissues (anophthalmia). In many cases, microphthalmia/anophthalmia occurs in association with syndromes that include non-ocular abnormalities. MCOPS12 patients manifest variable features, including diaphragmatic hernia, pulmonary hypoplasia, and cardiac abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24075189, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27120018}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00459; DB00210; DB00523; DB02877; DB00926; DB05785; DB04942; DB00799; DB00755; DB12808 Interacts with O95273; P50222; Q9UBK2; P62195; P28702; P28702-3; P48443; P03255 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; DNA-binding; Metal-binding; Microphthalmia; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proto-oncogene; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 25904.1 Length 229 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 44.34 Isoelectric point 7.55 Charge (pH=7) 0.73 3D Binding mode Sequence TEKIRKAHQETFPSLCQLGKYTTNSSADHRVRLDLGLWDKFSELATKCIIKIVEFAKRLPGFTGLTIADQITLLKAACLDILILRICTRYTPEQDTMTFSDGLTLNRTQMHNAGFGPLTDLVFTFANQLLPLEMDDTETGLLSAICLICGDRQDLEEPTKVDKLQEPLLEALKIYIRKRRPSKPHMFPKILMKITDLRSISAKGAERVITLKMEIPGSMPPLIQEMLEN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 45 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 2 | 3VRJ | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name MT-CO2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms MTCO2;COXII;COII;COX2 Protein family Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 2 family Biochemical class Immune system Function Copper ion binding.Cytochrome-c oxidase activity. Related diseases Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency (MT-C4D) [MIM:220110]: A disorder of the mitochondrial respiratory chain with heterogeneous clinical manifestations, ranging from isolated myopathy to severe multisystem disease affecting several tissues and organs. Features include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, hepatomegaly and liver dysfunction, hypotonia, muscle weakness, exercise intolerance, developmental delay, delayed motor development and intellectual disability. Some affected individuals manifest a fatal hypertrophic cardiomyopathy resulting in neonatal death. A subset of patients manifest Leigh syndrome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10486321}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02659; DB04464; DB05412 Interacts with Q9NZ94-2; P49281-3 EC number 7.1.1.9 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Copper; Disease variant; Electron transport; Magnesium; Membrane; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Primary mitochondrial disease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Respiratory chain; Translocase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C Molecular weight (Da) 21687.9 Length 189 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 38 Isoelectric point 5.68 Charge (pH=7) -3.26 3D Binding mode Sequence SHSMRYFYTAMSRPGRGEPRFIAVGYVDDTQFVRFDSDAASPRMAPRAPWIEQEGPEYWDGETRNMKASAQTYRENLRIALRYYNQSEAGSHIIQVMYGCDVGPDGRLLRGHDQSAYDGKDYIALNEDLSSWTAADTAAQITQRKWEAARVAEQLRAYLEGLCVEWLRRYLENGKETLQLTTKLTNTNI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 46 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-3 | 4ZK4 | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NACHRA3 Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-3/CHRNA3 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Acetylcholine binding protein Function Acetylcholine binding.Acetylcholine-gated cation-selective channel activity.Acetylcholine receptor activity.Ligand-gated ion channel activity.Serotonin-gated cation-selective channel activity. Related diseases Bladder dysfunction, autonomic, with impaired pupillary reflex and secondary CAKUT (BAIPRCK) [MIM:191800]: An autosomal recessive disease characterized by impaired innervation and autonomic dysfunction of the urinary bladder, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, small kidneys, recurrent urinary tract infections, and progressive renal insufficiency. Additional autonomic features are impaired pupillary reflex and orthostatic hypotension. The disease manifests in utero or early childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31708116}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00915; DB01156; DB00237; DB00565; DB09028; DB00514; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB05710; DB01227; DB00848; DB00333; DB00184; DB01090; DB00202; DB01273 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E Molecular weight (Da) 46391.5 Length 408 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 30.23 Isoelectric point 4.6 Charge (pH=7) -22.73 3D Binding mode Sequence LHSQANLMRLKSDLFYPGPTKDDPLTVTLGFTLQDIVKADSSTNEVDLVYWEQQRWKLNSLMWDPNEYGNITDFRTSAADIWTPDITAYSSTRPVQVLSPQIAVVTHDGSVMFIPAQRLSFMCDPTGVDSEEGATCAVKFGSWVYSGFEIDLKTDTDQVDLSSYYASSKYEILSATQYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDVVLVVKFRERRLHSQANLMRLKSDLFNRYPGPTKDDPLTVTLGFTLQDIVKADSSTNEVDLVYWEQQRWKLNSLMWDPNEYGNITDFRTSAADIWTPDITAYSSTRPVQVLSPQIAVVTHDGSVMFIPAQRLSFMCDPTGVDSEEGATCAVKFGSWVYSGFEIDLKTDTDQVDLSSYYASSKYEILSATQYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDVVLVVKFRE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 47 | T-cell-specific kinase (ITK) | 4HCU | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name ITK Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tyrosine kinase ITK; Inducible T cell kinase; EMT Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, TEC subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Regulates the development, function and differentiation of conventional T-cells and nonconventional NKT-cells. When antigen presenting cells (APC) activate T-cell receptor (TCR), a series of phosphorylation lead to the recruitment of ITK to the cell membrane, in the vicinity of the stimulated TCR receptor, where it is phosphorylated by LCK. Phosphorylation leads to ITK autophosphorylation and full activation. Once activated, phosphorylates PLCG1, leading to the activation of this lipase and subsequent cleavage of its substrates. In turn, the endoplasmic reticulum releases calcium in the cytoplasm and the nuclear activator of activated T-cells (NFAT) translocates into the nucleus to perform its transcriptional duty. Phosphorylates 2 essential adapter proteins: the linker for activation of T-cells/LAT protein and LCP2. Then, a large number of signaling molecules such as VAV1 are recruited and ultimately lead to lymphokine production, T-cell proliferation and differentiation. Phosphorylates TBX21 at 'Tyr-530' and mediates its interaction with GATA3. Tyrosine kinase that plays an essential role in regulation of the adaptive immune response. Related diseases Lymphoproliferative syndrome 1 (LPFS1) [MIM:613011]: A rare immunodeficiency characterized by extreme susceptibility to infection with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Inadequate immune response to EBV can have a fatal outcome. Clinical features include splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, recurrent infections. There is an increased risk for lymphoma. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19425169}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12010; DB06589; DB14924; DB02010; DB15035 Interacts with P04626; P48023; P08238; Q13094; P31947; P62258; P10686 EC number EC 2.7.10.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Immunity; Kinase; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; SH2 domain; SH3 domain; Transferase; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 30116.1 Length 263 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.47 Isoelectric point 5.03 Charge (pH=7) -11.73 3D Binding mode Sequence WVIDPSELTFVQEIGSGQFGLVHLGYWLNKDKVAIKTIREGAMSEEDFIEEAEVMMKLSHPKLVQLYGVCLEQAPICLVFEFMEHGCLSDYLRTQRGLFAAETLLGMCLDVCEGMAYLEEACVIHRDLAARNCLVGENQVIKVSDFGMTRFVLDDQYTSSTGTKFPVKWASPEVFSFSRYSSKSDVWSFGVLMWEVFSEGKIPYENRSNSEVVEDISTGFRLYKPRLASTHVYQIMNHCWRERPEDRPAFSRLLRQLAEIAES Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 48 | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 | 2YL2 | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name ACACA Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms ACAC;ACCA;ACC1 Protein family NA Biochemical class Ligase Function Acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity.ATP binding.Biotin carboxylase activity.Identical protein binding.Metal ion binding. Related diseases Acetyl-CoA carboxylase-alpha deficiency (ACACAD) [MIM:613933]: An autosomal recessive inborn error of de novo fatty acid synthesis associated with severe brain damage, persistent myopathy and poor growth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:6114432}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00121 Interacts with Q13085; O60218; P38398; Q96EB6; Q9CQ20; P02654; Q92915-2; Q6NTF9-3 EC number 6.4.1.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Allosteric enzyme; Alternative promoter usage; ATP-binding; Biotin; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Fatty acid biosynthesis; Fatty acid metabolism; Ligase; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Magnesium; Manganese; Metal-binding; Multifunctional enzyme; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 54237.7 Length 486 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 39.18 Isoelectric point 6.37 Charge (pH=7) -2.46 3D Binding mode Sequence VASPAEFVTRFGGNKVIEKVLIANNGIAAVKCMRSIRRWSYEMFRNERAIRFVVMVTPEDLKANAEYIKMADHYVPVPGGPNNNNYANVELILDIAKRIPVQAVWAGWGHASENPKLPELLLKNGIAFMGPPSQAMWALGDKIASSIVAQTAGIPTLPWSGSGLRVDWSKRILNVPQELYEKGYVKDVDDGLQAAEEVGYPVMIKASEGGGGKGIRKVNNADDFPNLFRQVQAEVPGSPIFVMRLAKQSRHLEVQILADQYGNAISLFGRDCSVQRRHQKIIEEAPATIATPAVFEHMEQCAVKLAKMVGYVSAGTVEYLYSQDGSFYFLELNPRLQVEHPCTEMVADVNLPAAQLQIAMGIPLYRIKDIRMMYGVSPWGDSPIDFEDSAHVPCPRGHVIAARITGTVQELNFRSNKNVWGYFSVQFGHCFSWGENREEAISNMVVALKELSIRGDFRTTVEYLIKLLETESFQMNRIDTGWLDRL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 49 | Cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase | 2JIS | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name CSAD Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CSD Protein family Group II decarboxylase family Biochemical class Lyase Function Pyridoxal phosphate binding.Sulfinoalanine decarboxylase activity. Related diseases Myopathy with lactic acidosis and sideroblastic anemia 2 (MLASA2) [MIM:613561]: A rare oxidative phosphorylation disorder specific to skeletal muscle and bone marrow. Affected individuals manifest sideroblastic anemia, progressive lethargy, muscle weakness, and exercise intolerance associated with persistent lactic acidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20598274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22504945}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00151; DB00114 Interacts with NA EC number 4.1.1.11; 4.1.1.29 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Decarboxylase; Lyase; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 107737 Length 965 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 39.32 Isoelectric point 6.39 Charge (pH=7) -5.38 3D Binding mode Sequence LPSLAGDPVAVEALLRAVFGVVVDEAIQKGTSVSQKVCEWKEPEELKQLLDLELRSQGESQKQILERCRAVIRYSVKTGHPRFFNQLFSGLDPHALAGRIITESLNTSQYTYEIAPVFVLMEEEVLRKLRALVGWSSGDGIFCPGGSISNMYAVNLARYQRYPDCKQRGLRTLPPLALFTSKECHYSIQKGAAFLGLGTDSVRVVKADERGKMVPEDLERQIGMAEAEGAVPFLVSATSGTTVLGAFDPLEAIADVCQRHGLWLHVDAAWGGSVLLSQTHRHLLDGIQRADSVAWNPHKLLAAGLQCSALLLQDTSNLLKRCHGSKFYDVALDTGDKVVQCGRRVDCLKLWLMWKAQGDQGLERRIDQAFVLARYLVEEMKKREGFELVMEPEFVNVCFWFVPPSLRGKQESPDYHERLSKVAPVLKERMVKEGSMMIGYQPHGTRGNFFRVVVANSALTCADMDFLLNELERLGQDLLPSLAGDPVAVEALLRAVFGVVVDEAIQKGTSVSQKVCEWKEPEELKQLLDLELRSQGESQKQILERCRAVIRYSVKTGHPRFFNQLFSGLDPHALAGRIITESLNTSQYTYEIAPVFVLMEEEVLRKLRALVGWSSGDGIFCPGGSISNMYAVNLARYQRYPDCKQRGLRTLPPLALFTSKECHYSIQKGAAFLGLGTDSVRVVKADERGKMVPEDLERQIGMAEAEGAVPFLVSATSGTTVLGAFDPLEAIADVCQRHGLWLHVDAAWGGSVLLSQTHRHLLDGIQRADSVAWNPHKLLAAGLQCSALLLQDTSNLLKRCHGSQASYLFQQDKFYDVALDTGDKVVQCGRRVDCLKLWLMWKAQGDQGLERRIDQAFVLARYLVEEMKKREGFELVMEPEFVNVCFWFVPPSLRGKQESPDYHERLSKVAPVLKERMVKEGSMMIGYQPHGTRGNFFRVVVANSALTCADMDFLLNELERLGQDL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 50 | Protein-tyrosine-phosphatase | 2Z72 | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name PPI Organism Shewanella sp Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family NA Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Metal ion binding.Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity. Related diseases Brugada syndrome 7 (BRGDA7) [MIM:613120]: A tachyarrhythmia characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs, the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20031595}. The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Atrial fibrillation, familial, 16 (ATFB16) [MIM:613120]: A familial form of atrial fibrillation, a common sustained cardiac rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity and ineffective atrial contraction promoting blood stasis in the atria and reduces ventricular filling. It can result in palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20558140, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21051419}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 3.1.3.48 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Calcium; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Signal; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 38399.1 Length 338 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 29.48 Isoelectric point 5.85 Charge (pH=7) -7.13 3D Binding mode Sequence ATEFDGPYVITPISGQSTAYWICDNRLKTTSIEKLQVNRPEHCGDLPETKLSSEIKQIMPDTYLGIKKVVALSDVHGQYDVLLTLLKKQKIIDSDGNWAFGEGHMVMTGDIFDRGHQVNEVLWFMYQLDQQARDAGGMVHLLMGNHEQMVLGGDLRYVHQRYDIATTLINRPYNKLYSADTEIGQWLRSKNTIIKINDVLYMHGGISSEWISRELTLDKANALYRANVDASKKSLKADDLLNFLFFGNGPTWYRGYFSETFTEAELDTILQHFNVNHIVVGHTSQERVLGLFHNKVIAVDSSIKVGKSGELLLLENNRLIRGLYDGTRETLQENSLNQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 51 | Adrenergic receptor alpha-2A (ADRA2A) | 7EJ8 | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name ADRA2A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Alpha-2AAR; Alpha-2A adrenoreceptor; Alpha-2A adrenoceptor; Alpha-2A adrenergic receptor; Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtype C10; ADRAR; ADRA2R Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, Adrenergic receptor subfamily, ADRA2A sub-subfamily Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function The rank order of potency for agonists of this receptor is oxymetazoline > clonidine > epinephrine > norepinephrine > phenylephrine > dopamine > p-synephrine > p-tyramine > serotonin = p-octopamine. For antagonists, the rank order is yohimbine > phentolamine = mianserine > chlorpromazine = spiperone = prazosin > propanolol > alprenolol = pindolol. Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. Related diseases Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 8 (FPLD8) [MIM:620679]: An autosomal dominant form of partial lipodystrophy, a disorder characterized by abnormal subcutaneous fat distribution. FPLD8 patients show selective loss of subcutaneous adipose tissue from the limbs, beginning around 13 to 15 years of age, and abnormal accumulation of subcutaneous adipose tissue in the dorsal neck and face, as well as in the posterior thoracic and abdominal regions. The disorder is associated with metabolic abnormalities, including diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27376152}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01472; DB00321; DB00543; DB00182; DB00714; DB00964; DB09229; DB01238; DB14185; DB06216; DB00865; DB00217; DB00484; DB01200; DB00248; DB01136; DB04846; DB00477; DB09202; DB00575; DB00363; DB01151; DB00633; DB01576; DB11273; DB13345; DB00320; DB00449; DB11278; DB09167; DB04855; DB06262; DB01363; DB05492; DB00751; DB00668; DB01049; DB00696; DB01175; DB06678; DB09194; DB00800; DB06623; DB00629; DB01018; DB00502; DB11577; DB00555; DB06707; DB00589; DB04948; DB09195; DB00408; DB08815; DB00934; DB01365; DB01577; DB01403; DB00968; DB06148; DB00370; DB09205; DB09242; DB06711; DB01149; DB00368; DB00540; DB06229; DB00935; DB01267; DB00715; DB01186; DB01608; DB00925; DB00692; DB00397; DB09286; DB09244; DB06153; DB00413; DB00457; DB00433; DB01069; DB00852; DB01224; DB11124; DB11738; DB00268; DB09304; DB06764; DB13025; DB00697; DB00797; DB00193; DB00656; DB00726; DB11477; DB06694; DB01392; DB00246; DB01624 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Methylation; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 30303.9 Length 263 Aromaticity 0.16 Instability index 35.08 Isoelectric point 9.66 Charge (pH=7) 16.82 3D Binding mode Sequence YSLQVTLTLVCLAGLLMLLTVFGNVLVIIAVFTSRALKAPQNLFLVSLASADILVATLVIPFSLANEVMGYWYFGKAWCEIYLALDVLFCTSSIVHLCAISLDRYWSITQAIEYNLKRTPRRIKAIIITVWVISAVISFPPRCEINDQKWYVISSCIGSFFAPCLIMILVYVRIYQIAKRRTRRGRQNREKRFTFVLAVVIGVFVVCWFPFFFTYTLTAVGCSVPRTLFKFFFWFGYCNSSLNPVIYTIFNHDFRRAFKKILC Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 52 | Phosphatidylinositol-4-kinase beta (PI4KB) | 4WAE | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name PI4KB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PtdIns 4-kinase beta; Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta; PIK4CB; PI4Kbeta; PI4K92; PI4K-beta; NPIK Protein family PI3/PI4-kinase family, Type III PI4K subfamily Biochemical class NA Function Phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol (PI) in the first committed step in the production of the second messenger inositol-1,4,5,-trisphosphate (PIP). May regulate Golgi disintegration/reorganization during mitosis, possibly via its phosphorylation. Involved in Golgi-to-plasma membrane trafficking (By similarity). Related diseases Deafness, autosomal dominant, 87 (DFNA87) [MIM:620281]: A form of non-syndromic, sensorineural hearing loss. Sensorineural hearing loss results from damage to the neural receptors of the inner ear, the nerve pathways to the brain, or the area of the brain that receives sound information. DFNA87 is characterized by prelingual, profound sensorineural hearing loss with inner ear anomalies, including cochlear maldevelopment, absence of the osseous spiral lamina, and/or an enlarged vestibular aqueduct. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33358777}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12010 Interacts with Q9H3P7; P27348; P03495; PRO_0000424692 [P03300]; P62491 EC number EC 2.7.1.67 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Deafness; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Endoplasmic reticulum; Golgi apparatus; Host-virus interaction; Kinase; Lipid metabolism; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion outer membrane; Non-syndromic deafness; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 53130 Length 463 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 49.16 Isoelectric point 6.78 Charge (pH=7) -0.96 3D Binding mode Sequence LLRLFESKLFDISMAISYLYNSKEPGVQAYIGNRLFCFRNEDVDFYLPQLLNMYIHMDEDVGDAIKPYIVHRCRQSINFSLQCALLLGAYSSDMNSFSSPVRLAPEREFIKSLMAIGKRLATLPTKEQKTQRLISELSLLNHKLPARVWLPTAGFDHHVVRVPHTQAVVLNSKDKAPYLIYVEVLECENFDTTSVPARIPEWQEKVRRIREGSPYGHLPNWRLLSVIVKCGDDLRQELLAFQVLKQLQSIWEQERVPLWIKPYKILVISADSGMIEPVVNAVSIHQVKKQSQLSLLDYFLQEHGSYTTEAFLSAQRNFVQSCAGYCLVCYLLQVKDRHNGNILLDAEGHIIHIDFGFILSSSPRNLGFETSAFKLTTEFVDVMGGLDGDMFNYYKMLMLQGLIAARKHMDKVVQIVEIMQQGSQLPCFHGSSTIRNLKERFHMSMTEEQLQLLVEQMVDGSMR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 53 | Acyloxyacyl hydrolase (neutrophil) | 5W7C | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name AOAH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Acyloxyacyl hydrolase Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Removes the secondary (acyloxyacyl-linked) fatty acyl chains from the lipid A region of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. By breaking down LPS, terminates the host response to bacterial infection and prevents prolonged and damaging inflammatory responses (By similarity). In peritoneal macrophages, seems to be important for recovery from a state of immune tolerance following infection by Gram-negative bacteria (By similarity). Related diseases Major depressive disorder (MDD) [MIM:608516]: A common psychiatric disorder. It is a complex trait characterized by one or more major depressive episodes without a history of manic, mixed, or hypomanic episodes. A major depressive episode is characterized by at least 2 weeks during which there is a new onset or clear worsening of either depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure in nearly all activities. Four additional symptoms must also be present including changes in appetite, weight, sleep, and psychomotor activity; decreased energy; feelings of worthlessness or guilt; difficulty thinking, concentrating, or making decisions; or recurrent thoughts of death or suicidal ideation, plans, or attempts. The episode must be accompanied by distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15229186}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q15700 EC number EC 3.1.1.77 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lipid metabolism; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C Molecular weight (Da) 47779.7 Length 420 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.45 Isoelectric point 7.72 Charge (pH=7) 2.1 3D Binding mode Sequence GSDICSLPVLAKICQKIKLAMEQSVPFKDVDSDKYSVFPTLRGYHWRGRDCNDSDESVYPGRRPNNWDVHQDSNCNGIWGVDPKDGVPYEKKFCEGSQPRGIILLGDAAGAHFHISPEWITASQMSLNSFINLPTALTNELDWPQLSGATGFLDSTVGIKEKSIYLRLWKRNHCNHRDYQNISRNGASSRNLKKFIESLSRNKVLDYPAIVIYAMIGNDVCSGKSDPVPAMTTPEKLYSNVMQTLKHLNSHLPNGSHVILYGLPDGTFLWDNLHNRYHPLGQLNKDMTYAQLYSFLNCLQVSPCHGWMSSNKTLRTLTSERAEQLSNTLKKIAASEKFTNFNLFYMDFAFHEIIQEWQKRGGQPWQLIEPVDGFHPNEVALLLLADHFWKKVQLQWPQILGKENPFNPQIKQVFGDQGGH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 54 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor alpha-2 (CHRNA2) | 5FJV | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CHRNA2 Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-2/CHRNA2 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. Related diseases Epilepsy, nocturnal frontal lobe, 4 (ENFL4) [MIM:610353]: An autosomal dominant focal epilepsy characterized by nocturnal seizures associated with fear sensation, tongue movements, and nocturnal wandering, closely resembling nightmares and sleep walking. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16826524}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Seizures, benign familial infantile, 6 (BFIS6) [MIM:610353]: A form of benign familial infantile epilepsy, a neurologic disorder characterized by afebrile seizures occurring in clusters during the first year of life, without neurologic sequelae. BFIS6 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25847220}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00732; DB00237; DB00411; DB00565; DB01245; DB00514; DB01135; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB00483; DB08960; DB00657; DB01336; DB00416; DB01226; DB00184; DB01337; DB01338; DB00721; DB00728; DB05740; DB00202; DB01199; DB01339 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Epilepsy; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 48323.4 Length 413 Aromaticity 0.15 Instability index 32 Isoelectric point 5.69 Charge (pH=7) -6.58 3D Binding mode Sequence DRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLPEDRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 55 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor beta-4 (CHRNB4) | 6PV7 | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNB4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CHRNB4; Beta-4 nAChR Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Beta-4/CHRNB4 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. Related diseases Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) [MIM:144700]: Renal cell carcinoma is a heterogeneous group of sporadic or hereditary carcinoma derived from cells of the proximal renal tubular epithelium. It is subclassified into clear cell renal carcinoma (non-papillary carcinoma), papillary renal cell carcinoma, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, collecting duct carcinoma with medullary carcinoma of the kidney, and unclassified renal cell carcinoma. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma is the most common subtype. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20054297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23622243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23792563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25728682}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Defects of SETD2 are associated with loss of DNA methylation at non-promoter regions (PubMed:23792563). SETD2 defects lead to aberrant and reduced nucleosome compaction and chromatin association of key replication proteins, such as MCM7 and DNA polymerase delta, leading to hinder replication fork progression and prevent loading of RAD51 homologous recombination repair factor at DNA breaks (PubMed:25728682). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23792563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25728682}.; DISEASE: Luscan-Lumish syndrome (LLS) [MIM:616831]: An autosomal dominant syndrome with a variable phenotype. Clinical features include macrocephaly, distinctive facial appearance, postnatal overgrowth, various degrees of learning difficulties, autism spectrum disorder, and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23160955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24852293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26084711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27317772}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute lymphoblastic (ALL) [MIM:613065]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. ALL is a malignant disease of bone marrow and the most common malignancy diagnosed in children. The malignant cells are lymphoid precursor cells (lymphoblasts) that are arrested in an early stage of development. The lymphoblasts replace the normal marrow elements, resulting in a marked decrease in the production of normal blood cells. Consequently, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia occur to varying degrees. The lymphoblasts also proliferate in organs other than the marrow, particularly the liver, spleen, and lymphnodes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24509477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24662245}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML) [MIM:601626]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. AML is a malignant disease of bone marrow characterized by maturational arrest of hematopoietic precursors at an early stage of development. Clonal expansion of myeloid blasts occurs in bone marrow, blood, and other tissue. Myelogenous leukemias develop from changes in cells that normally produce neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils and monocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16314571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24509477}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 70 (MRD70) [MIM:620157]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by mild global developmental delay, moderately impaired intellectual disability with speech difficulties, and behavioral abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32710489}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Rabin-Pappas syndrome (RAPAS) [MIM:620155]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by severely impaired global development, intellectual disability, microcephaly, facial dysmorphism, and variable congenital anomalies affecting the skeletal, genitourinary, cardiac, and other organ systems. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32710489}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00237; DB00565; DB00514; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB01227; DB00184; DB01090; DB00202 Interacts with Q6FHY5 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 89661.2 Length 775 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 35.11 Isoelectric point 6.07 Charge (pH=7) -5.67 3D Binding mode Sequence SEAEHRLFERLFEDYNEIIRPVANVSDPVIIHFEVSMSQLVKVDEVNQIMETNLWLKQIWNDYKLKWNPSDYGGAEFMRVPAQKIWKPDIVLYNNAVGDFQVDDKTKALLKYTGEVTWIPPAIFKSSCKIDVTYFPFDYQNCTMKFGSWSYDKAKIDLVLIGSSMNLKDYWESGEWAIIKAPGYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDITYSLYIRRLPLFYTINLIIPCLLISFLTVLVFYLPSDCGEKVTLCISVLLSLTVFLLVITETIPSTSLVIPLIGEYLLFTMIFVTLSIVITVFVLNVHYRTPTTHTMPSWVKTVFLNLLPRVMFMTRIKEAIQSVKYIAENMKAQNEAKEIQDDWKYVAMVIDRIFLWVFTLVCILGTAGLFLQPLMRVANAEEKLMDDLLNKTRYNNLIRPATSSSQLISIKLQLSLAQLISVNEREQIMTTNVWLKQEWTDYRLTWNSSRYEGVNILRIPAKRIWLPDIVLYNNADGTYEVSVYTNLIVRSNGSVLWLPPAIYKSACKIEVKYFPFDQQNCTLKFRSWTYDHTEIDMVLMTPTASMDDFTPSGEWDIVALPGRRTVNPQDPSYVDVTYDFIIKRKPLFYTINLIIPCVLTTLLAILVFYLPSDCGEKMTLCISVLLALTFFLLLISKIVPPTSLDVPLIGKYLMFTMVLVTFSIVTSVCVLNVHHRSPSTHTMAPWVKRCFLHKLPTFLFMKRRQDVQEALEGVSFIAQHMKNDDEDQSVVEDWKYVAMVVDRLFLWVFMFVCVLGTVGLFLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 56 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor alpha-3/beta-4 (CHRNA3/B4) | 6PV7 | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA3-CHRNB4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Neuronal acetylcholine receptor Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-3/CHRNA3 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function A type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting of 3 and 4 subunits. Related diseases Bladder dysfunction, autonomic, with impaired pupillary reflex and secondary CAKUT (BAIPRCK) [MIM:191800]: An autosomal recessive disease characterized by impaired innervation and autonomic dysfunction of the urinary bladder, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, small kidneys, recurrent urinary tract infections, and progressive renal insufficiency. Additional autonomic features are impaired pupillary reflex and orthostatic hypotension. The disease manifests in utero or early childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31708116}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00915; DB01156; DB00237; DB00565; DB09028; DB00514; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB05710; DB01227; DB00848; DB00333; DB00184; DB01090; DB00202; DB01273 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 89661.2 Length 775 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 35.11 Isoelectric point 6.07 Charge (pH=7) -5.67 3D Binding mode Sequence SEAEHRLFERLFEDYNEIIRPVANVSDPVIIHFEVSMSQLVKVDEVNQIMETNLWLKQIWNDYKLKWNPSDYGGAEFMRVPAQKIWKPDIVLYNNAVGDFQVDDKTKALLKYTGEVTWIPPAIFKSSCKIDVTYFPFDYQNCTMKFGSWSYDKAKIDLVLIGSSMNLKDYWESGEWAIIKAPGYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDITYSLYIRRLPLFYTINLIIPCLLISFLTVLVFYLPSDCGEKVTLCISVLLSLTVFLLVITETIPSTSLVIPLIGEYLLFTMIFVTLSIVITVFVLNVHYRTPTTHTMPSWVKTVFLNLLPRVMFMTRIKEAIQSVKYIAENMKAQNEAKEIQDDWKYVAMVIDRIFLWVFTLVCILGTAGLFLQPLMRVANAEEKLMDDLLNKTRYNNLIRPATSSSQLISIKLQLSLAQLISVNEREQIMTTNVWLKQEWTDYRLTWNSSRYEGVNILRIPAKRIWLPDIVLYNNADGTYEVSVYTNLIVRSNGSVLWLPPAIYKSACKIEVKYFPFDQQNCTLKFRSWTYDHTEIDMVLMTPTASMDDFTPSGEWDIVALPGRRTVNPQDPSYVDVTYDFIIKRKPLFYTINLIIPCVLTTLLAILVFYLPSDCGEKMTLCISVLLALTFFLLLISKIVPPTSLDVPLIGKYLMFTMVLVTFSIVTSVCVLNVHHRSPSTHTMAPWVKRCFLHKLPTFLFMKRRQDVQEALEGVSFIAQHMKNDDEDQSVVEDWKYVAMVVDRLFLWVFMFVCVLGTVGLFLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 57 | RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT2) | 3D0E | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name AKT2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms RAC-PK-beta; Protein kinase B beta; Protein kinase Akt-2; PKB beta Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, RAC subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function AKT2 is one of 3 closely related serine/threonine-protein kinases (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3) called the AKT kinase, and which regulate many processes including metabolism, proliferation, cell survival, growth and angiogenesis. This is mediated through serine and/or threonine phosphorylation of a range of downstream substrates. Over 100 substrate candidates have been reported so far, but for most of them, no isoform specificity has been reported. AKT is responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake by mediating insulin-induced translocation of the SLC2A4/GLUT4 glucose transporter to the cell surface. Phosphorylation of PTPN1 at 'Ser-50' negatively modulates its phosphatase activity preventing dephosphorylation of the insulin receptor and the attenuation of insulin signaling. Phosphorylation of TBC1D4 triggers the binding of this effector to inhibitory 14-3-3 proteins, which is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. AKT regulates also the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen by phosphorylating GSK3A at 'Ser-21' and GSK3B at 'Ser-9', resulting in inhibition of its kinase activity. Phosphorylation of GSK3 isoforms by AKT is also thought to be one mechanism by which cell proliferation is driven. AKT regulates also cell survival via the phosphorylation of MAP3K5 (apoptosis signal-related kinase). Phosphorylation of 'Ser-83' decreases MAP3K5 kinase activity stimulated by oxidative stress and thereby prevents apoptosis. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 at 'Ser-939' and 'Thr-1462', thereby activating mTORC1 signaling and leading to both phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and in activation of RPS6KB1. AKT is involved in the phosphorylation of members of the FOXO factors (Forkhead family of transcription factors), leading to binding of 14-3-3 proteins and cytoplasmic localization. In particular, FOXO1 is phosphorylated at 'Thr-24', 'Ser-256' and 'Ser-319'. FOXO3 and FOXO4 are phosphorylated on equivalent sites. AKT has an important role in the regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription and positively regulates the activity of CREB1 (cyclic AMP (cAMP)-response element binding protein). The phosphorylation of CREB1 induces the binding of accessory proteins that are necessary for the transcription of pro-survival genes such as BCL2 and MCL1. AKT phosphorylates 'Ser-454' on ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), thereby potentially regulating ACLY activity and fatty acid synthesis. Activates the 3B isoform of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE3B) via phosphorylation of 'Ser-273', resulting in reduced cyclic AMP levels and inhibition of lipolysis. Phosphorylates PIKFYVE on 'Ser-318', which results in increased PI(3)P-5 activity. The Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC1 is another substrate and its phosphorylation is implicated in the regulation cell proliferation and cell growth. AKT plays a role as key modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway controlling the tempo of the process of newborn neurons integration during adult neurogenesis, including correct neuron positioning, dendritic development and synapse formation. Signals downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI(3)K) to mediate the effects of various growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). AKT mediates the antiapoptotic effects of IGF-I. Essential for the SPATA13-mediated regulation of cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly. May be involved in the regulation of the placental development. Related diseases Defects in AKT2 are a cause of susceptibility to breast cancer (BC). AKT2 promotes metastasis of tumor cells without affecting the latency of tumor development. May play a role in glioblastoma cell survival (PubMed:20167810). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20167810}.; DISEASE: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) [MIM:125853]: A multifactorial disorder of glucose homeostasis caused by a lack of sensitivity to insulin. Affected individuals usually have an obese body habitus and manifestations of a metabolic syndrome characterized by diabetes, insulin resistance, hypertension and hypertriglyceridemia. The disease results in long-term complications that affect the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and blood vessels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15166380, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19164855}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Hypoinsulinemic hypoglycemia with hemihypertrophy (HIHGHH) [MIM:240900]: A disorder characterized by hypoglycemia, low insulin levels, low serum levels of ketone bodies and branched-chain amino acids, left-sided hemihypertrophy, neonatal macrosomia, reduced consciousness and hypoglycemic seizures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21979934}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08073; DB07859; DB12218; DB07947; DB07812 Interacts with P31749; P49841; P08238; Q6FHY5; Q9NRD5; Q04864-2; O60504; P53804; Q9C0C9; P08670; Q15118-1 EC number EC 2.7.11.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Apoptosis; ATP-binding; Carbohydrate metabolism; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Developmental protein; Diabetes mellitus; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endosome; Glucose metabolism; Glycogen biosynthesis; Glycogen metabolism; Glycoprotein; Kinase; Manganese; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Proto-oncogene; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Sugar transport; Transferase; Translation regulation; Transport; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 37380.5 Length 324 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 29.68 Isoelectric point 6.19 Charge (pH=7) -3.43 3D Binding mode Sequence KVTMNDFDYLKLLGKGTFGKVILVREKATGRYYAMKILRKEVIIAKDEVAHTVTESRVLQNTRHPFLTALKYAFQTHDRLCFVMEYANGGELFFHLSRERVFTEERARFYGAEIVSALEYLHSRDVVYRDIKLENLMLDKDGHIKITDFGLCKEGISDGATMKXFCGTPEYLAPEVLEDNDYGRAVDWWGLGVVMYEMMCGRLPFYNQDHERLFELILMEEIRFPRTLSPEAKSLLAGLLKKDPKQRLGGGPSDAKEVMEHRFFLSINWQDVVQKKLLPPFKPQVTSEVDTRYFDDEFTAQSITIXPPDQRTHFPQFDYSASIR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 58 | MAPK signal-integrating kinase 1 (MKNK1) | 5WVD | 5.06 | |
Target general information Gen name MKNK1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Mnk1; MAP kinase signal-integrating kinase 1 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family Biochemical class Protein kinase superfamily. CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family Function May play a role in the response to environmental stress and cytokines. Appears to regulate translation by phosphorylating EIF4E, thus increasing the affinity of this protein for the 7-methylguanosine-containing mRNA cap. Related diseases Defects in MELK are associated with some cancers, such as brain or breast cancers. Expression is dramatically increased in aggressive undifferentiated tumors, correlating with poor patient outcome in breast and brain cancers, suggesting a role in tumor-initiating cells and proliferation via its function in cell proliferation regulation. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12010 Interacts with P54253; Q03060-25; P42858; P28482; Q16539; Q96CV9 EC number EC 2.7.11.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Kinase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Translation regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 27536.2 Length 241 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 50.42 Isoelectric point 6.02 Charge (pH=7) -3.43 3D Binding mode Sequence PGKFEDMYKLTSELLGEGAYAKVQGAVSLQNGKEYAVKIIEKQAGHSRSRVFREVETLYQCQGNKNILELIEFFEDDTRFYLVFEKLQGGSILAHIQKQKHFNEREASRVVRDVAAALDFLHTKGIAHRDLKPENILCESPEKVSPVKICDFDLGSGYMAPEVVEVFTDQATFYDKRCDLWSLGVVLYIMLSGYPPFKYEFPDKDWAHISSEAKDLISKLLVRDAKQRLSAAQVLQHPWVQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 59 | "Periplasmic trehalase (EC 3.2.1.28) (Alpha,alpha-trehalase) (Alpha,alpha-trehalose glucohydrolase) (Tre37A)" | 2JG0 | 5.05 | |
Target general information Gen name treA Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms JW1186;osmA;b1197 Protein family Glycosyl hydrolase 37 family Biochemical class NA Function Provides the cells with the ability to utilize trehalose at high osmolarity by splitting it into glucose molecules that can subsequently be taken up by the phosphotransferase-mediated uptake system. Related diseases SRC kinase activity has been shown to be increased in several tumor tissues and tumor cell lines such as colon carcinoma cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2498394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3093483}.; DISEASE: Thrombocytopenia 6 (THC6) [MIM:616937]: A form of thrombocytopenia, a hematologic disorder defined by a decrease in the number of platelets in circulating blood, resulting in the potential for increased bleeding and decreased ability for clotting. THC6 is an autosomal dominant form. Affected individuals may also have bone abnormalities and an increased risk for myelofibrosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26936507}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 3.2.1.28 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Glycosidase; Hydrolase; Periplasm; Reference proteome; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 57508.9 Length 507 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 48.32 Isoelectric point 5.48 Charge (pH=7) -10.13 3D Binding mode Sequence PQPPDILLGPLFNDVQNAKLFPDQKTFADAVPNSDPLMILADYRMQQNQSGFDLRHFVNVNFTLPKYVPPEGQSLREHIDGLWPVLTRSTENTEKWDSLLPLPEPYVVPGGRFREVYYWDSYFTMLGLAESGHWDKVADMVANFAHEIDTYGHIPNGNRSYYLSRSQPPFFALMVELLAQHEGDAALKQYLPQMQKEYAYWMDGVENLQAGQQEKRVVKLQDGTLLNRYWDDRDTPRPESWVEDIATAKSNPNRPATEIYRDLRSAAASGWDFSSRWMDNPQQLNTLRTTSIVPVDLNSLMFKMEKILARASKAAGDNAMANQYETLANARQKGIEKYLWNDQQGWYADYDLKSHKVRNQLTAAALFPLYVNAAAKDRANKMATATKTHLLQPGGLNTTSVKSGQQWDAPNGWAPLQWVATEGLQNYGQKEVAMDISWHFLTNVQHTYDREKKLVEKYDVSTTGTGGGGGEYPLQDGFGWTNGVTLKMLDLICPKEQPCDNVPATRP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 60 | Acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha | 4ZJS | 5.05 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms ACHRA;CHNRA Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-1/CHRNA1 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Immune system Function Acetylcholine binding.Acetylcholine-gated cation-selective channel activity.Acetylcholine receptor activity.Ion channel activity.Ligand-gated ion channel activity. Related diseases Multiple pterygium syndrome, lethal type (LMPS) [MIM:253290]: Multiple pterygia are found infrequently in children with arthrogryposis and in fetuses with fetal akinesia syndrome. In lethal multiple pterygium syndrome there is intrauterine growth retardation, multiple pterygia, and flexion contractures causing severe arthrogryposis and fetal akinesia. Subcutaneous edema can be severe, causing fetal hydrops with cystic hygroma and lung hypoplasia. Oligohydramnios and facial anomalies are frequent. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18252226}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: The alpha subunit is the main focus for antibody binding in myasthenia gravis. Myasthenia gravis is characterized by sporadic muscular fatigability and weakness, occurring chiefly in muscles innervated by cranial nerves, and characteristically improved by cholinesterase-inhibiting drugs.; DISEASE: Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 1A, slow-channel (CMS1A) [MIM:601462]: A common congenital myasthenic syndrome. Congenital myasthenic syndromes are characterized by muscle weakness affecting the axial and limb muscles (with hypotonia in early-onset forms), the ocular muscles (leading to ptosis and ophthalmoplegia), and the facial and bulbar musculature (affecting sucking and swallowing, and leading to dysphonia). The symptoms fluctuate and worsen with physical effort. CMS1A is a slow-channel myasthenic syndrome. It is caused by kinetic abnormalities of the AChR, resulting in prolonged AChR channel opening episodes, prolonged endplate currents, and depolarization block. This is associated with calcium overload, which may contribute to subsequent degeneration of the endplate and postsynaptic membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16685696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7619526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8872460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9158151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9221765}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 1B, fast-channel (CMS1B) [MIM:608930]: A form of congenital myasthenic syndrome, a group of disorders characterized by failure of neuromuscular transmission, including pre-synaptic, synaptic, and post-synaptic disorders that are not of autoimmune origin. Clinical features are easy fatigability and muscle weakness affecting the axial and limb muscles (with hypotonia in early-onset forms), the ocular muscles (leading to ptosis and ophthalmoplegia), and the facial and bulbar musculature (affecting sucking and swallowing, and leading to dysphonia). The symptoms fluctuate and worsen with physical effort. CMS1B is a fast-channel myasthenic syndrome. It is caused by kinetic abnormalities of the AChR, resulting in brief opening and activity of the channel, with a rapid decay in endplate current, failure to achieve threshold depolarization of the endplate and consequent failure to fire an action potential. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10195214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12588888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15079006}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08838; DB00565; DB00555 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Congenital myasthenic syndrome; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E Molecular weight (Da) 46717.8 Length 411 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 38.02 Isoelectric point 4.77 Charge (pH=7) -22.31 3D Binding mode Sequence EHETRLVAKLFKDYSSVVRPVEDHRQVVEVTLGFTLQDIVKADSSTNEVDLVYYEQQRWVDYNLKWNPDDYGGVKKIHIPAADIWTPDITAYSSTRPVQVLSPQIAVVTHDGSVMFIPAQRLSFMCDPTGVDSEEGATCAVKFGSWVYSGFEIDLKTDTDQVDLSSYYASSKYEILSATQTRQVQHYSCCPEPYIDVNLVVKFREEHETRLVAKLFKDYSSVVRPVEDHRQVVEVTLGFTLQDIVKADSSTNEVDLVYYEQQRWVDYNLKWNPDDYGGVKKIHIPAADIWTPDITAYSSTRPVQVLSPQIAVVTHDGSVMFIPAQRLSFMCDPTGVDSEEGATCAVKFGSWVYSGFEIDLKTDTDQVDLSSYYASSKYEILSATQTRQVQHYSCCPEPYIDVNLVVKFRER Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||