Job Results:
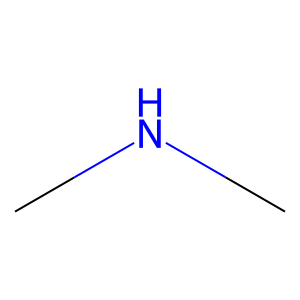
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
43b2a7cfabc12f2b0137afb38036989c
Job name
NA
Time
2025-03-05 09:37:27
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | Glutamic acid decarboxylase 1 (GAD1) | 3VP6 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name GAD1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Glutamate decarboxylase 67 kDa isoform; Glutamate decarboxylase 1; GAD67; GAD-67; GAD; 67 kDa glutamic acid decarboxylase Protein family Group II decarboxylase family Biochemical class NA Function Catalyzes the production of GABA. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 89 (DEE89) [MIM:619124]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE89 is an autosomal recessive severe form characterized by profound global developmental delay with impaired intellectual development, absent speech, inability to sit or walk due to axial hypotonia and spastic quadriparesis, and onset of seizures in the first days or months of life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32282878}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00142; DB00114 Interacts with Q6RW13; Q6RW13-2; Q96DZ9; Q96DZ9-2; P46952; Q969L2; P16333; Q13188 EC number EC 4.1.1.15 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Decarboxylase; Disease variant; Epilepsy; Intellectual disability; Lyase; Neurotransmitter biosynthesis; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 112173 Length 991 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 35.6 Isoelectric point 6.46 Charge (pH=7) -6.01 3D Binding mode Sequence TDFSNLFARDLLPAKNGEEQTVQFLLEVVDILLNYVRKTFDRSTKVLDFHHPHQLLEGMEGFNLELSDHPESLEQILVDCRDTLKYGVRTGHPRFFNQLSTGLDIIGLAGEWLTSTANTNMFTYEIAPVFVLMEQITLKKMREIVGWSSKDGDGIFSPGGAISNMYSIMAARYKYFPEVKTKGMAAVPKLVLFTSEQSHYSIKKAGAALGFGTDNVILIKCNERGKIIPADFEAKILEAKQKGYVPFYVNATAGTTVYGAFDPIQEIADICEKYNLWLHVDAAWGGGLLMSRKHRHKLNGIERANSVTWNPHXMMGVLLQCSAILVKEKGILQGCNQMHASYLFQQDKHYDVSYDTGDKAIQCGRHVDIFKFWLMWKAKGTVGFENQINKCLELAEYLYAKIKNREEFEMVFNGEPEHTNVCFWYIPQSLRGVPDSPQRREKLHKVAPKIKALMMESGTTMVGYQPQGDKANFFRMVISNPAATQSDIDFLIEEIERLGQFSNLFARDLLPAKNGEEQTVQFLLEVVDILLNYVRKTFDRSTKVLDFHHPHQLLEGMEGFNLELSDHPESLEQILVDCRDTLKYGVRTGHPRFFNQLSTGLDIIGLAGEWLTSTANTNMFTYEIAPVFVLMEQITLKKMREIVGWSSKDGDGIFSPGGAISNMYSIMAARYKYFPEVKTKGMAAVPKLVLFTSEQSHYSIKKAGAALGFGTDNVILIKCNERGKIIPADFEAKILEAKQKGYVPFYVNATAGTTVYGAFDPIQEIADICEKYNLWLHVDAAWGGGLLMSRKHRHKLNGIERANSVTWNPHXMMGVLLQCSAILVKEKGILQGCNQMHASYLFQQDKHYDVSYDTGDKAIQCGRHVDIFKFWLMWKAKGTVGFENQINKCLELAEYLYAKIKNREEFEMVFNGEPEHTNVCFWYIPQSDSPQRREKLHKVAPKIKALMMESGTTMVGYQPQGDKANFFRMVISNPAATQSDIDFLIEEIERL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 42 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) | 6YND | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name GAPDH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylase GAPDH; OK/SW-cl.12; GAPD; D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; CDABP0047 Protein family Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Aldehyde/oxo donor oxidoreductase Function Participates in nuclear events including transcription, RNA transport, DNA replication and apoptosis. Nuclear functions are probably due to the nitrosylase activity that mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of nuclear target proteins such as SIRT1, HDAC2 and PRKDC. Modulates the organization and assembly of the cytoskeleton. Facilitates the CHP1-dependent microtubule and membrane associations through its ability to stimulate the binding of CHP1 to microtubules. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is a key enzyme in glycolysis that catalyzes the first step of the pathway by converting D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) into 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate. Component of the GAIT (gamma interferon-activated inhibitor of translation) complex which mediates interferon-gamma-induced transcript-selective translation inhibition in inflammation processes. Upon interferon-gamma treatment assembles into the GAIT complex which binds to stem loop-containing GAIT elements in the 3'-UTR of diverse inflammatory mRNAs (such as ceruplasmin) and suppresses their translation. Has both glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and nitrosylase activities, thereby playing a role in glycolysis and nuclear functions, respectively. Related diseases Bone marrow failure and diabetes mellitus syndrome (BMFDMS) [MIM:620044]: A form of bone marrow failure syndrome, a heterogeneous group of life-threatening disorders characterized by hematopoietic defects in association with a range of variable extra-hematopoietic manifestations. BMFDMS is an autosomal recessive form characterized by various degrees of bone marrow failure, ranging from dyserythropoiesis to bone marrow aplasia, with onset in infancy or early childhood, and non-autoimmune insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus appearing in the first or second decades. Many patients show pigmentary skin abnormalities and short stature. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28073829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35611808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35931051}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07347; DB02059; DB11638; DB09130; DB00157; DB03893; DB09092 Interacts with Q6UY14-3; Q9UIJ7; P05067; Q9UQM7; Q14194; P35222; Q9BPW9-4; P00533; O00471; O75344; P06241; P04406; O14556; Q8NEA9; P42858; Q92993-2; P42695; P35228; P12004; P00558; P48147; P17612; Q8WUY3; Q9UHX1-2; P15927; P05109; Q96GZ6; P00441; Q9BSI4; P10599 EC number EC 1.2.1.12 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; ADP-ribosylation; Alternative splicing; Apoptosis; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; Glycolysis; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Innate immunity; Isopeptide bond; Membrane; Methylation; NAD; Nucleus; Oxidation; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation; Transferase; Translation regulation; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35818.4 Length 333 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 13.69 Isoelectric point 8.64 Charge (pH=7) 3.64 3D Binding mode Sequence GKVKVGVNGFGRIGRLVTRAAFNSGKVDIVAINDPFIDLNYMVYMFQYDSTHGKFHGTVKAENGKLVINGNPITIFQERDPSKIKWGDAGAEYVVESTGVFTTMEKAGAHLQGGAKRVIISAPSADAPMFVMGVNHEKYDNSLKIISNASTTNCLAPLAKVIHDNFGIVEGLMTTVHAITATQKTVDGPSGKLWRDGRGALQNIIPASTGAAKAVGKVIPELNGKLTGMAFRVPTANVSVVDLTCRLEKPAKYDDIKKVVKQASEGPLKGILGYTEHQVVSSDFNSDTHSSTFDAGAGIALNDHFVKLISWYDNEFGYSNRVVDLMAHMASKE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 43 | Aspartyl aminopeptidase (DNPEP) | 4DYO | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name DNPEP Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms DAP; ASPEP Protein family Peptidase M18 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Likely to play an important role in intracellular protein and peptide metabolism. Aminopeptidase with specificity towards an acidic amino acid at the N-terminus. Related diseases Cohen-Gibson syndrome (COGIS) [MIM:617561]: An autosomal dominant overgrowth disorder characterized by accelerated osseous maturation, advanced bone age, skeletal abnormalities including flaring of the metaphyses of the long bones, large hands with long fingers and camptodactyly, scoliosis, cervical spine anomalies, dysmorphic facial features, and variable intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25787343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27193220, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27868325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28229514, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28475857}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00142 Interacts with Q9ULA0; Q8TBB1; Q00013; Q9UPN6 EC number EC 3.4.11.21 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative initiation; Aminopeptidase; Cytoplasm; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 50574.6 Length 457 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 55.73 Isoelectric point 7.73 Charge (pH=7) 2.3 3D Binding mode Sequence GKARKEAVQTAAKELLKFVNRSPSPFHAVAECRNRLLQAGFSELKETEKWNIKPESKYFMTRNSSTIIAFAVGGQYVPGNGFSLIGAHTDSPCLRVKRRSRRSQVGFQQVGVETYGGGIWSTWFDRDLTLAGRVIVKCPTSGRLEQQLVHVERPILRIPHLAIHLQRNINENFGPNTEMHLVPILATAIQEELEKGTERHHSVLMSLLCAHLGLSPKDIVEMELCLADTQPAVLGGAYDEFIFAPRLDNLHSCFCALQALIDSCAGPGSLATEPHVRMVTLYDNEEVGSESAQGAQSLLTELVLRRISASCQHPTAFEEAIPKSFMISADMAHAVHPNYLDKHEENHRPLFHKGPVIKVNSKQRYASNAVSEALIREVANKVKVPLQDLMVRNDTPCGTTIGPILASRLGLRVLDLGSPQLAMHSIREMACTTGVLQTLTLFKGFFELFPSLAENLY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 44 | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B) | 5FY9 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name KDM5B Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Retinoblastomabinding protein 2 homolog 1; Retinoblastoma-binding protein 2 homolog 1; RBP2H1; RBP2-H1; RBBP2H1; PLU1; PLU-1; Lysinespecific demethylase 5B; Jumonji/ARID domaincontaining protein 1B; J Protein family JARID1 histone demethylase family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Does not demethylate histone H3 'Lys-9' or H3 'Lys-27'. Demethylates trimethylated, dimethylated and monomethylated H3 'Lys-4'. Acts as a transcriptional corepressor for FOXG1B and PAX9. Favors the proliferation of breast cancer cells by repressing tumor suppressor genes such as BRCA1 and HOXA5. In contrast, may act as a tumor suppressor for melanoma. Represses the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer-mediated transcriptional activation of the core clock component PER2. Histone demethylase that demethylates 'Lys-4' of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 65 (MRT65) [MIM:618109]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRT65 patients have moderate to severe intellectual disability, developmental delay, and facial dysmorphism. Camptodactyly is present in some patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29276005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30409806}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P49711 EC number EC 1.14.11.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Biological rhythms; Chromatin regulator; Dioxygenase; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Iron; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 53020.6 Length 460 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 44.23 Isoelectric point 5.28 Charge (pH=7) -18.32 3D Binding mode Sequence SMFLPPPECPVFEPSWEEFADPFAFIHKIRPIAEQTGICKVRPPPDWQPPFACDVDKLHFTPRIQRLNELEAQTRVKLGGGGARDYTLRTFGEMADAFKSDYFNMPVHMVPTELVEKEFWRLVSTIEEDVTVEYGADIASKEFGSGFPVRDIKLSPEEEEYLDSGWNLNNMPVMEQSVLAHITADICGMKLPWLYVGMCFSSFCWHIEDHWSYSINYLHWGEPKTWYGVPGYAAEQLENVMKKLAPELFVSQPDLLHQLVTIMNPNTLMTHEVPVYRTNQCAGEFVITFPRAYHSGFNQGFNFAEAVNFCTVDWLPLGRQCVEHYRLLHRYCVFSHDEMICKMASKADVLDVVVASTVQKDMAIMIEDEKALRETVRKLGVIDSERMDFELLPDDERQCVKCKTTCFMSAISCSCKPGLLVCLHHVKELCSCPPYKYKLRYRYTLDDLYPMMNALKLRAE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 45 | Staphylococcus Peptide deformylase (Stap-coc def) | 1Q1Y | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name Stap-coc def Organism Staphylococcus aureus Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms def; Stap-coc Polypeptide deformylase Protein family Polypeptide deformylase family Biochemical class Carbon-nitrogen hydrolase Function Removes the formyl group from the N-terminal Met of newly synthesized proteins. Requires at least a dipeptide for an efficient rate of reaction. N-terminal L-methionine is a prerequisite for activity but the enzyme has broad specificity at other positions. Related diseases Immunodeficiency 43 (IMD43) [MIM:241600]: A disorder characterized by marked reduction in serum concentrations of immunoglobulins and albumin, and hypoproteinemia due to hypercatabolism. Patients may suffer from recurrent respiratory tract infections and severe skin disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16549777}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Amyloidosis, hereditary systemic 6 (AMYLD6) [MIM:620659]: A form of hereditary systemic amyloidosis, a disorder characterized by amyloid deposition in multiple tissues resulting in a wide clinical spectrum. AMYLD6 is mainly characterized by gastrointestinal and cardiac symptoms. Neurologic involvement, sicca syndrome, and carpal tunnel syndrome may also be present. Inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22693999}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Apart from the presence of causative mutations, beta-2-microglobulin may adopt the fibrillar configuration of amyloid, resulting in amyloidosis, when its serum levels are persistently high, as seen in patients on long-term hemodialysis (PubMed:7918443). In contrast to patients with dialysis-related amyloidosis, patients with hereditary amyloidosis have normal circulating concentrations of beta2-microglobulin (PubMed:22693999). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22693999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7918443}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04310 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Hydrolase; Iron; Metal-binding; Protein biosynthesis Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 20835.6 Length 186 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 42.9 Isoelectric point 5.65 Charge (pH=7) -7.59 3D Binding mode Sequence MLTMKDIIRDGHPTLRQKAAELELPLTKEEKETLIAMREFLVNSQDEEIAKRYGLRSGVGLAAPQINISKRMIAVLIPDDGSGKSYDYMLVNPKIVSHSVQEAYLPTGEGXLSVDDNVAGLVHRHNRITIKAKDIEGNDIQLRLKGYPAIVFQHEIDHLNGVMFYDHIDKDHPLQPHTDAVEVLEH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 46 | Triggering receptor expressed on monocytes 1 (TREM1) | 1Q8M | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name Trem1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Trem1; TREM-1 Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Stimulates neutrophil and monocyte-mediated inflammatory responses. Triggers release of pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines, as well as increased surface expression of cell activation markers. Amplifier of inflammatory responses that are triggered by bacterial and fungal infections and is a crucial mediator of septic shock. Related diseases GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 1 (GLUT1DS1) [MIM:606777]: A neurologic disorder showing wide phenotypic variability. The most severe 'classic' phenotype comprises infantile-onset epileptic encephalopathy associated with delayed development, acquired microcephaly, motor incoordination, and spasticity. Onset of seizures, usually characterized by apneic episodes, staring spells, and episodic eye movements, occurs within the first 4 months of life. Other paroxysmal findings include intermittent ataxia, confusion, lethargy, sleep disturbance, and headache. Varying degrees of cognitive impairment can occur, ranging from learning disabilities to severe intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10227690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10980529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11136715, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11603379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12325075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15622525, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19901175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20129935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20221955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20574033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24847886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30197081}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 2 (GLUT1DS2) [MIM:612126]: A clinically variable disorder characterized primarily by onset in childhood of paroxysmal exercise-induced dyskinesia. The dyskinesia involves transient abnormal involuntary movements, such as dystonia and choreoathetosis, induced by exercise or exertion, and affecting the exercised limbs. Some patients may also have epilepsy, most commonly childhood absence epilepsy. Mild intellectual disability may also occur. In some patients involuntary exertion-induced dystonic, choreoathetotic, and ballistic movements may be associated with macrocytic hemolytic anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14605501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18451999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19630075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19798636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20129935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20574033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20621801, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20830593, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21204808}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epilepsy, idiopathic generalized 12 (EIG12) [MIM:614847]: A disorder characterized by recurring generalized seizures in the absence of detectable brain lesions and/or metabolic abnormalities. Generalized seizures arise diffusely and simultaneously from both hemispheres of the brain. Seizure types include juvenile myoclonic seizures, absence seizures, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. In some EIG12 patients seizures may remit with age. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19798636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22282645, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23280796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Dystonia 9 (DYT9) [MIM:601042]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder characterized by childhood onset of paroxysmal choreoathetosis and progressive spastic paraplegia. Most patients show some degree of cognitive impairment. Other variable features may include seizures, migraine headaches, and ataxia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21832227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Stomatin-deficient cryohydrocytosis with neurologic defects (SDCHCN) [MIM:608885]: A rare form of stomatocytosis characterized by episodic hemolytic anemia, cold-induced red cells cation leak, erratic hyperkalemia, neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, hepatosplenomegaly, cataracts, seizures, intellectual disability, and movement disorder. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21791420, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22492876}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01694 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Immunoglobulin domain; Innate immunity; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 28186.2 Length 242 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 45.2 Isoelectric point 6.1 Charge (pH=7) -3.8 3D Binding mode Sequence MELRAATKLTEEKYELKEGQTLDVKCDYTLEKFASSQKAWQIIRDGEMPKTLACTERPSKNSHPVQVGRIILEDYHDHGLLRVRMVNLQVEDSGLYQCVIYQPPKEPHMLFDRIRLVVTLEMELRAATKLTEEKYELKEGQTLDVKCDYTLEKFASSQKAWQIIRDGEMPKTLACTERPSKNSHPVQVGRIILEDYHDHGLLRVRMVNLQVEDSGLYQCVIYQPPKEPHMLFDRIRLVVTLE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 47 | NAPE-hydrolyzing phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD) | 4QN9 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name NAPEPLD Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NAPE-PLD; N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolyzing phospholipase D; N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D; C7orf18 Protein family NAPE-PLD family Biochemical class NA Function Hydrolyzes N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamines (NAPEs) to produce N-acylethanolamines (NAEs) and phosphatidic acid. Responsible for the generation of these bioactive fatty acid ethanolamides (FAEs), including anandamide (N-arachidonoylethanolamine), the ligand of cannabinoid and vanilloid receptors. As a regulator of lipid metabolism in the adipose tissue, mediates the crosstalk between adipocytes, gut microbiota and immune cells to control body temperature and weight. In particular, regulates energy homeostasis by promoting cold-induced brown or beige adipocyte differentiation program to generate heat from fatty acids and glucose (By similarity). Related diseases Glioma (GLM) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539269}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. H3F3A mutations affecting residues involved in post-translational modifications of histone H3.3 are recurrent in malignant, aggressive gliomas including glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) (PubMed:22286061, PubMed:22286216). The mechanism through which mutations lead to tumorigenesis involves altered histones methylation, impaired regulation of Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) activity, and aberrant epigenetic regulation of gene expression (PubMed:23539183, PubMed:23539269, PubMed:23603901). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23603901}.; DISEASE: Bryant-Li-Bhoj neurodevelopmental syndrome 1 (BRYLIB1) [MIM:619720]: An autosomal dominant disorder predominantly characterized by global developmental delay, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and delayed motor milestones. Clinical manifestations are highly variable, including abnormal head shape, dysmorphic facial features, oculomotor abnormalities, feeding problems, and non-specific brain imaging abnormalities. Additional features may include hearing loss, seizures, short stature, and mild skeletal defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BRYLIB1 is caused by variants in H3-3A. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}.; DISEASE: Bryant-Li-Bhoj neurodevelopmental syndrome 2 (BRYLIB2) [MIM:619721]: An autosomal dominant disorder predominantly characterized by global developmental delay, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and delayed motor milestones. Clinical manifestations are highly variable, including abnormal head shape, dysmorphic facial features, oculomotor abnormalities, feeding problems, and non-specific brain imaging abnormalities. Additional features may include hearing loss, seizures, short stature, and mild skeletal defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BRYLIB2 is caused by variants in H3-3B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}.; DISEASE: H3F3A and H3F3B mutations affecting residues involved in post-translational modifications of histone H3.3 are implicated in the pathogenesis of some bone and cartilage neoplasms. Mutations have been found with high prevalence in chondroblastoma and giant cell tumors of bone, and with low frequency in osteosarcoma, conventional chondrosarcoma and clear cell chondrosarcoma. Chondroblastoma samples frequently carry a H3F3B mutation affecting residue Lys-37 (H3K36), although H3F3A is mutated in some cases. Most giant cell tumors of bone harbor H3F3A mutations affecting residue Gly-35 (H3G34). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24162739}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB14009 Interacts with Q6IQ20 EC number EC 3.1.4.54 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Endosome; Golgi apparatus; Hydrolase; Lipid degradation; Lipid metabolism; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phospholipid degradation; Phospholipid metabolism; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 74256.5 Length 643 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 48.34 Isoelectric point 5.65 Charge (pH=7) -17.61 3D Binding mode Sequence SKKGKDGRFVNPWPTWKNPSIPNSSVPSSKEELDKELPVLKPYFITNPEEAGVREAGLRVTWLGHATVMVEMDELIFLTDPIFSSRASPSQYMGPKRFRRSPCTISELPPIDAVLISHNHYDHLDYNSVIALNERFGNELRWFVPLGLLDWMQKCGCENVIELDWWEENCVPGHDKVTFVFTPSQHWCKRTLMDDNKVLWGSWSVLGPWNRFFFAGDTGYCPAFEEIGKRFGPFDLAAIPIGAYEPRWFMKYQHVDPEEAVRIHTDVQTKKSMAIHWGTFALANEHYLEPPVKLNEALERYGLNAEDFFVLKHGESRYLNNSKKGKDGRFVNPWPTWKNPSIPNSSVPSSKEELDKELPVLKPYFITNPEEAGVREAGLRVTWLGHATVMVEMDELIFLTDPIFSSRASPSQYMGPKRFRRSPCTISELPPIDAVLISHNHYDHLDYNSVIALNERFGNELRWFVPLGLLDWMQKCGCENVIELDWWEENCVPGHDKVTFVFTPSQHWCKRTLMDDNKVLWGSWSVLGPWNRFFFAGDTGYCPAFEEIGKRFGPFDLAAIPIGAYEPRWFMKYQHVDPEEAVRIHTDVQTKKSMAIHWGTFALANEHYLEPPVKLNEALERYGLNAEDFFVLKHGESRYLNND Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 48 | Aldehyde oxidase (AOX1) | 7OPN | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name AOX1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms AOX1 Protein family Xanthine dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Aldehyde/oxo donor oxidoreductase Function Oxidase with broad substrate specificity, oxidizing aromatic azaheterocycles, such as N1-methylnicotinamide and N- methylphthalazinium, as well as aldehydes, such as benzaldehyde, retinal, pyridoxal, and vanillin. Plays a key role in the metabolism of xenobiotics and drugs containing aromatic azaheterocyclic substituents. Participates in the bioactivation of prodrugs such as famciclovir, catalyzing the oxidation step from 6-deoxypenciclovir topenciclovir, which is a potent antiviral agent. Is probably involved in the regulation of reactive oxygen species homeostasis. May be a prominent source of superoxide generation via the one-electron reduction of molecular oxygen. Also may catalyze nitric oxide (NO) production via the reduction of nitrite to NO with NADH or aldehyde as electron donor. May play a role in adipogenesis. Related diseases Progressive familial heart block 1B (PFHB1B) [MIM:604559]: A cardiac bundle branch disorder characterized by progressive alteration of cardiac conduction through the His-Purkinje system, with a pattern of a right bundle-branch block and/or left anterior hemiblock occurring individually or together. It leads to complete atrio-ventricular block causing syncope and sudden death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19726882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20562447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21887725}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva 6 (EKVP6) [MIM:618531]: A form of erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva, a genodermatosis characterized by the coexistence of two independent skin lesions: transient erythema and hyperkeratosis that is usually localized but occasionally occurs in its generalized form. Clinical presentation varies significantly within a family and from one family to another. Palmoplantar keratoderma is present in around 50% of cases. EKVP6 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30528822}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00437; DB00513; DB00484; DB11791; DB00215; DB00924; DB03516; DB01175; DB00426; DB12466; DB09054; DB09078; DB00170; DB01033; DB00563; DB08840; DB00157; DB00339; DB00481; DB04827; DB00962; DB00246; DB00909 Interacts with Q06278 EC number EC 1.2.3.1 Uniprot keywords 2Fe-2S; 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; FAD; Flavoprotein; Iron; Iron-sulfur; Lipid metabolism; Metal-binding; Molybdenum; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 286845 Length 2590 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 42.7 Isoelectric point 6.92 Charge (pH=7) -1.62 3D Binding mode Sequence ASELLFYVNGRKVIEKNVDPETMLLPYLRKKLRLTGTKYGCGGGGCGACTVMISRYNPITKRIRHHPANACLIPICSLYGAAVTTVEGIGSTHTRIHPVQERIAKCHGTQCGFCTPGMVMSIYTLLRNHPEPTLDQLTDALGGNLCRCTGYRPIIDACKTFCKPKLFAEEEFLPLDPTQELIFPPELMIMAEKQSQRTRVFGSERMMWFSPVTLKELLEFKFKYPQAPVIMGNTSVGPEVKFKGVFHPVIISPDRIEELSVVNHAYNGLTLGAGLSLAQVKDILADVVQKLPEEKTQMYHALLKHLGTLAGSQIRNMASLGGHIISRHPDSDLNPILAVGNCTLNLLSKEGKRQIPLNEQFLSKCPNADLKPQEILVSVNIPYSRKWEFVSAFRQAQRQENALAIVNSGMRVFFGEGDGIIRELCISYGGVGPATICAKNSCQKLIGRHWNEQMLDIACRLILNEVSLLGSAPGGKVEFKRTLIISFLFKFYLEVSQILKKMDPVHYPSLADKYESALEDLHSKHHCSTLKYQNQHPEDPIGHPIMHLSGVKHATGEAIYCDDMPLVDQELFLTFVTSSRAHAKIVSIDLSEALSMPGVVDIMTAEHLSDVNSFCFFTEAEKFLATDKVFCVGQLVCAVLADSEVQAKRAAKRVKIVYQDLEPLILTIEESIQHNSSFKPERKLEYGNVDEAFKVVDQILEGEIHMGGQEHFYMETQSMLVVPKGEDQEMDVYVSTQFPKYIQDIVASTLKLPANKVMCHVRRVGGAFGGKVLKTGIIAAVTAFAANKHGRAVRCVLERGEDMLITGGRHPYLGKYKAGFMNDGRILALDMEHYSNAGASLDESLFVIEMGLLKMDNAYKFPNLRCRGWACRTNLPSNTAFRGFGFPQAALITESCITEVAAKCGLSPEKVRIINMYKEIDQTPYKQEINAKNLIQCWRECMAMSSYSLRKVAVEKFNAENYWKKKGLAMVPLKFPVGLGSRAAGQAAALVHIYLDGSVLVTHGGIEMGQGVHTKMIQVVSRELRMPMSNVHLRGTSTETVPNANISGGSVVADLNGLAVKDACQTLLKRLEPIISKNPKGTWKDWAQTAFDESINLSAVGYFRGYESDMNWEKGEGQPFEYFVYGAACSEVEIDCLTGDHKNIRTDIVMDVGCSINPAIDIGQIEGAFIQGMGLYTIEELNYSPQGILHTHGPDQYKIPAICDMPTELHIALLPPSQNSNTLYSSKGLGESGVFLGCSVFFAIHDAVSAARQERGLHLTLNSPLTPEKIRMACEDKFTKMIPRDEPGSYVPWNVASELLFYVNGRKVIEKNVDPETMLLPYLRKKLRLTGTKYGCGGGGCGACTVMISRYNPITKRIRHHPANACLIPICSLYGAAVTTVEGIGSTHTRIHPVQERIAKCHGTQCGFCTPGMVMSIYTLLRNHPEPTLDQLTDALGGNLCRCTGYRPIIDACKTFCKPKLFAEEEFLPLDPTQELIFPPELMIMAEKQSQRTRVFGSERMMWFSPVTLKELLEFKFKYPQAPVIMGNTSVGPEVKFKGVFHPVIISPDRIEELSVVNHAYNGLTLGAGLSLAQVKDILADVVQKLPEEKTQMYHALLKHLGTLAGSQIRNMASLGGHIISRHPDSDLNPILAVGNCTLNLLSKEGKRQIPLNEQFLSKCPNADLKPQEILVSVNIPYSRKWEFVSAFRQAQRQENALAIVNSGMRVFFGEGDGIIRELCISYGGVGPATICAKNSCQKLIGRHWNEQMLDIACRLILNEVSLLGSAPGGKVEFKRTLIISFLFKFYLEVSQILKKMDPVHYPSLADKYESALEDLHSKHHCSTLKYQNQHPEDPIGHPIMHLSGVKHATGEAIYCDDMPLVDQELFLTFVTSSRAHAKIVSIDLSEALSMPGVVDIMTAEHLSDVNSFCFFTEAEKFLATDKVFCVGQLVCAVLADSEVQAKRAAKRVKIVYQDLEPLILTIEESIQHNSSFKPERKLEYGNVDEAFKVVDQILEGEIHMGGQEHFYMETQSMLVVPKGEDQEMDVYVSTQFPKYIQDIVASTLKLPANKVMCHVRRVGGAFGGKVLKTGIIAAVTAFAANKHGRAVRCVLERGEDMLITGGRHPYLGKYKAGFMNDGRILALDMEHYSNAGASLDESLFVIEMGLLKMDNAYKFPNLRCRGWACRTNLPSNTAFRGFGFPQAALITESCITEVAAKCGLSPEKVRIINMYKEIDQTPYKQEINAKNLIQCWRECMAMSSYSLRKVAVEKFNAENYWKKKGLAMVPLKFPVGLGSRAAGQAAALVHIYLDGSVLVTHGGIEMGQGVHTKMIQVVSRELRMPMSNVHLRGTSTETVPNANISGGSVVADLNGLAVKDACQTLLKRLEPIISKNPKGTWKDWAQTAFDESINLSAVGYFRGYESDMNWEKGEGQPFEYFVYGAACSEVEIDCLTGDHKNIRTDIVMDVGCSINPAIDIGQIEGAFIQGMGLYTIEELNYSPQGILHTHGPDQYKIPAICDMPTELHIALLPPSQNSNTLYSSKGLGESGVFLGCSVFFAIHDAVSAARQERGLHLTLNSPLTPEKIRMACEDKFTKMIPRDEPGSYVPWNV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 49 | N(G),N(G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1 | 3I4A | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name DDAH1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms DDAH Protein family DDAH family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Amino acid binding.Catalytic activity.Dimethylargininase activity.Metal ion binding. Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder with poor language and loss of hand skills (NDPLHS) [MIM:617903]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by psychomotor developmental stagnation or regression. NDPLHS manifest in the first years of life as loss of purposeful hand movements, loss of language, and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26740508, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28856709, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29369404}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 59 (DEE59) [MIM:617904]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of severe early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE59 is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by onset of refractory seizures in early infancy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28856709, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29100083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29369404}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00155; DB05351; DB00736; DB00213 Interacts with NA EC number 3.5.3.18 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Direct protein sequencing; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 30156.3 Length 275 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 38.25 Isoelectric point 5.56 Charge (pH=7) -7.51 3D Binding mode Sequence AAFGRATHAVVRALPESLGQHALRSAKGEEVDVARAERQHQLYVGVLGSKLGLQVVELPADESLPDCVFVEDVAVVCEETALITRPGAPSRRKEVDMMKEALEKLQLNIVEMKDENATLDGGDVLFTGREFFVGLSKRTNQRGAEILADTFKDYAVSTVPVADGLHLKSFCSMAGPNLIAIGSSESAQKALKIMQQMSDHRYDKLTVPDDIAANCIYLNIPNKGHVLLHRTPEEYPESAKVYEKLKDHMLIPVSMSELEKVDGLLTCCSVLINKK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 50 | Quinone-dependent D-lactate dehydrogenase | 1F0X | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name dld Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms JW2121;b2133 Protein family Quinone-dependent D-lactate dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase activity.D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome) activity.Electron carrier activity.FAD binding.Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.NAD binding.Oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, quinone or similar compound as acceptor.Quinone binding. Related diseases Myeloperoxidase deficiency (MPOD) [MIM:254600]: A disorder characterized by decreased myeloperoxidase activity in neutrophils and monocytes that results in disseminated candidiasis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:37198333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7904599, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8142659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8621627, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9354683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9637725}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147; DB00756 Interacts with NA EC number 1.1.5.12 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell inner membrane; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Membrane; Oxidoreductase; Quinone; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 56475.2 Length 502 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 32.5 Isoelectric point 5.97 Charge (pH=7) -10.38 3D Binding mode Sequence NKAFLNELARLVGSSHLLTDPAKTARYRKGFRSGQGDALAVVFPGSLLELWRVLKACVTADKIILMQAANTGLTEGSTPNGNDYDRDVVIISTLRLDKLHVLGKGEQVLAYPGTTLYSLEKALKPLGREPHSVIGSSCIGASVIGGICNNSGGSLVQRGPAYTEMSLFARINEDGKLTLVNHLGIDLGETPEQILSKLDDDRIKDDDVRHDGRHAHDYDYVHRVRDIEADTPARYNADPDRLFESSGCAGKLAVFAVRLDTFEAEKNQQVFYIGTNQPEVLTEIRRHILANFENLPVAGEYMHRDIYDIAELPPRMKNWRDKYEHHLLLKMAGDGVGEAKSWLVDYFKQAEGDFFVCTPEEGSKAFLHRFAAAGAAIRYQAVHSDEVEDILALDIALRRNDTEWYEHLPPEIDSQLVHKLYYGHFMCYVFHQDYIVKKGVDVHALKEQMLELLQQRGAQYPAEHNVGHLYKAPETLQKFYRENDPTNSMNPGIGKTSKRKNW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 51 | Monomeric sarcosine oxidase | 2GF3 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name soxA Organism Bacillus sp. (strain B-0618) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms sox Protein family MSOX/MTOX family, MSOX subfamily Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Sarcosine oxidase activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03098; DB01918; DB03517; DB03147; DB03366; DB02083; DB02543 Interacts with NA EC number 1.5.3.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Oxidoreductase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 42606.4 Length 385 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 26.97 Isoelectric point 5.27 Charge (pH=7) -17.18 3D Binding mode Sequence STHFDVIVVGAGSMGMAAGYQLAKQGVKTLLVDAFDPPHTNGSHHGDTRIIRHAYGEGREYVPLALRSQELWYELEKETHHKIFTKTGVLVFGPKGESAFVAETMEAAKEHSLTVDLLEGDEINKRWPGITVPENYNAIFEPNSGVLFSENCIRAYRELAEARGAKVLTHTRVEDFDISPDSVKIETANGSYTADKLIVSMGAWNSKLLSKLNLDIPLQPYRQVVGFFESDESKYSNDIDFPGFMVEVPNGIYYGFPSFGGCGLKLGYHTFGQKIDPDTINREFGVYPEDESNLRAFLEEYMPGANGELKRGAVCMYTKTLDEHFIIDLHPEHSNVVIAAGFSGHGFKFSSGVGEVLSQLALTGKTEHDISIFSINRPALKESLQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 52 | Aminoacylase-1 | 1Q7L | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name ACY1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Peptidase M20A family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Aminoacylase activity.Identical protein binding.Metal ion binding.Metallopeptidase activity. Related diseases Aminoacylase-1 deficiency (ACY1D) [MIM:609924]: An enzymatic deficiency resulting in encephalopathy, unspecific psychomotor delay, psychomotor delay with atrophy of the vermis and syringomyelia, marked muscular hypotonia or normal clinical features. Epileptic seizures are a frequent feature. All affected individuals exhibit markedly increased urinary excretion of several N-acetylated amino acids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16274666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16465618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17562838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21414403}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06151; DB00128; DB09130 Interacts with Q03154; O75934; Q96HA8; P36639; P36639-2; Q8TCT1; P0CG20; Q96A09; P54274; O43711; Q9UPN9; Q9NZC7-5 EC number 3.5.1.14 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 31172.2 Length 275 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 36.46 Isoelectric point 6 Charge (pH=7) -5.26 3D Binding mode Sequence NPWWAAFSRVCKDMNLTLEPEIMPAAGDNRYIRAVGVPALGFSPMNRTPVLLHDHDERLHEAVFLRGVDIYTRLLPALASVPALPEEHPSVTLFRQYLRIRTVQPKPDYGAAVAFFEETARQLGLGCQKVEVAPGYVVTVLTWPGTNPTLSSILLNSHTDVVPVFKEHWSHDPFEAFKDSEGYIYARGAQDMKCVSIQYLEAVRRLKVEGHRFPRTIHMTFVPDEEVGGHQGMELFVQRPEFHALRAGFALDEGIANPTDAFTVFYSERSPWWVR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 53 | Aminoacylase-1 | 1Q7L | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name ACY1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Peptidase M20A family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Aminoacylase activity.Identical protein binding.Metal ion binding.Metallopeptidase activity. Related diseases Aminoacylase-1 deficiency (ACY1D) [MIM:609924]: An enzymatic deficiency resulting in encephalopathy, unspecific psychomotor delay, psychomotor delay with atrophy of the vermis and syringomyelia, marked muscular hypotonia or normal clinical features. Epileptic seizures are a frequent feature. All affected individuals exhibit markedly increased urinary excretion of several N-acetylated amino acids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16274666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16465618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17562838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21414403}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06151; DB00128; DB09130 Interacts with Q03154; O75934; Q96HA8; P36639; P36639-2; Q8TCT1; P0CG20; Q96A09; P54274; O43711; Q9UPN9; Q9NZC7-5 EC number 3.5.1.14 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 31172.2 Length 275 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 36.46 Isoelectric point 6 Charge (pH=7) -5.26 3D Binding mode Sequence NPWWAAFSRVCKDMNLTLEPEIMPAAGDNRYIRAVGVPALGFSPMNRTPVLLHDHDERLHEAVFLRGVDIYTRLLPALASVPALPEEHPSVTLFRQYLRIRTVQPKPDYGAAVAFFEETARQLGLGCQKVEVAPGYVVTVLTWPGTNPTLSSILLNSHTDVVPVFKEHWSHDPFEAFKDSEGYIYARGAQDMKCVSIQYLEAVRRLKVEGHRFPRTIHMTFVPDEEVGGHQGMELFVQRPEFHALRAGFALDEGIANPTDAFTVFYSERSPWWVR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 54 | Leukotriene C4 synthase (LTC4S) | 3PCV | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name LTC4S Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Leukotriene-C(4)Leukotriene C4 synthase synthase; Leukotriene-C(4) synthase; LTC4 synthase Protein family MAPEG family Biochemical class Carbon-sulfur lyase Function Catalyzes the conjugation of leukotriene A4 with reduced glutathione to form leukotriene C4. Related diseases LTC4 synthase deficiency is associated with a neurometabolic developmental disorder characterized by muscular hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, and microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10896305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9820300}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00972; DB00143 Interacts with P11912; Q96BA8; Q15125; O14843; Q14802-3; Q8TDT2; O15529; Q16873; Q8TBB6; Q4KMG9 EC number EC 4.4.1.20 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Endoplasmic reticulum; Leukotriene biosynthesis; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Lyase; Membrane; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 16099 Length 146 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 38.66 Isoelectric point 10.2 Charge (pH=7) 7.66 3D Binding mode Sequence MKDEVALLAAVTLLGVLLQAYFSLQVISARRAFRVSPPLTTGPPEFERVYRAQVNCSEYFPLFLATLWVAGIFFHEGAAALCGLVYLFARLRYFQGYARSAQLRLAPLYASARALWLLVALAALGLLAHFLPAALRAALLGRLRTL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 55 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] | 3EYA | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name poxB Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b0871;JW0855 Protein family TPP enzyme family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.Identical protein binding.Lipid binding.Magnesium ion binding.Pyruvate dehydrogenase (quinone) activity.Thiamine pyrophosphate binding. Related diseases Glycogen storage disease 6 (GSD6) [MIM:232700]: A metabolic disorder characterized by mild to moderate hypoglycemia, mild ketosis, growth retardation, and prominent hepatomegaly. Heart and skeletal muscle are not affected. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9529348}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P07003 EC number 1.2.5.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell inner membrane; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Lipid-binding; Magnesium; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Oxidoreductase; Pyruvate; Reference proteome; Thiamine pyrophosphate; Ubiquinone Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I,J,K,L Molecular weight (Da) 113027 Length 1046 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 35.99 Isoelectric point 5.75 Charge (pH=7) -24.38 3D Binding mode Sequence MKQTVAAYIAKTLESAGVKRIWGVTGDSLNGLSDSLNRMGTIEWMSTRHEEVAAFAAGAEAQLSGELAVCAGSCGPGNLHLINGLFDCHRNHVPVLAIAAHIPSSEIGSGYFQETHPQELFRECSHYCELVSSPEQIPQVLAIAMRKAVLNRGVSVVVLPGDVALKPAPEGATMHWYHAPQPVVTPEEEELRKLAQLLRYSSNIALMCGSGCAGAHKELVEFAGKIKAPIVHALRGKEHVEYDNPYDVGMTGLIGFSSGFHTMMNADTLVLLGTQFPYRAFYPTDAKIIQIDINPASIGAHSKVDMALVGDIKSTLRALLPLVEEKADRKFLDKALEDYRDARKGLDDLAKPSEKAIHPQYLAQQISHFAADDAIFTCDVGTPTVWAARYLKMNGKRRLLGSFNHGSMANAMPQALGAQATEPERQVVAMCGDGGFSMLMGDFLSVVQMKLPVKIVVFNNSVLGFDGTELHDTNFARIAEACGITGIRVEKASEVDEALQRAFSIDGPVLVDVVVAKEELAIPMKQTVAAYIAKTLESAGVKRIWGVTGDSLNGLSDSLNRMGTIEWMSTRHEEVAAFAAGAEAQLSGELAVCAGSCGPGNLHLINGLFDCHRNHVPVLAIAAHIPSSEIGSGYFQETHPQELFRECSHYCELVSSPEQIPQVLAIAMRKAVLNRGVSVVVLPGDVALKPAPEGATMHWYHAPQPVVTPEEEELRKLAQLLRYSSNIALMCGSGCAGAHKELVEFAGKIKAPIVHALRGKEHVEYDNPYDVGMTGLIGFSSGFHTMMNADTLVLLGTQFPYRAFYPTDAKIIQIDINPASIGAHSKVDMALVGDIKSTLRALLPLVEEKADRKFLDKALEDYRDARKGLDDLAKPSEKAIHPQYLAQQISHFAADDAIFTCDVGTPTVWAARYLKMNGKRRLLGSFNHGSMANAMPQALGAQATEPERQVVAMCGDGGFSMLMGDFLSVVQMKLPVKIVVFNNSVLGFVGTELHDTNFARIAEACGITGIRVEKASEVDEALQRAFSIDGPVLVDVVVAKEELAIP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 56 | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 | 2JJK | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name FBP1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms FBP Protein family FBPase class 1 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function AMP binding.Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate 1-phosphatase activity.Identical protein binding.Metal ion binding.Monosaccharide binding. Related diseases Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency (FBP1D) [MIM:229700]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by impaired gluconeogenesis, and episodes of hypoglycemia and metabolic acidosis that can be lethal in newborn infants or young children. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12126934, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25601412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9382095}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02778; DB07312; DB07321; DB08484; DB00131; DB04493; DB05518; DB05053; DB04175; DB07270; DB02848 Interacts with O00499; Q99814; P09467; O00757; P51116; Q16665; P42858 EC number 3.1.3.11 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Allosteric enzyme; Carbohydrate metabolism; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Gluconeogenesis; Hydrolase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 69197.4 Length 634 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 25.2 Isoelectric point 7.84 Charge (pH=7) 2.55 3D Binding mode Sequence DVNTLTRFVMEEGRKARGTGELTQLLNSLCTAVKAISSAVRKAGIAHLYGIAGKLDVLSNDLVMNMLKSSFATCVLVSEEDKHAIIVEPEKRGKYVVCFDPLDGSSNIDCLVSVGTIFGIYRKKSTDEPSEKDALQPGRNLVAAGYALYGSATMLVLAMDCGVNCFMLDPAIGEFILVDKDVKIKKKGKIYSLNEGYAKDFDPAVTEYIQRKKFPPDNSAPYGARYVGSMVADVHRTLVYGGIFLYPANKKSPNGKLRLLYECNPMAYVMEKAGGMATTGKEAVLDVIPTDIHQRAPVILGSPDDVLEFLKVYEKHSDVNTLTRFVMEEGRKARGTGELTQLLNSLCTAVKAISSAVRKAGIAHLYGIAGKLDVLSNDLVMNMLKSSFATCVLVSEEDKHAIIVEPEKRGKYVVCFDPLDGSSNIDCLVSVGTIFGIYRKKSTDEPSEKDALQPGRNLVAAGYALYGSATMLVLAMDCGVNCFMLDPAIGEFILVDKDVKIKKKGKIYSLNEGYAKDFDPAVTEYIQRKKFPPDNSAPYGARYVGSMVADVHRTLVYGGIFLYPANKKSPNGKLRLLYECNPMAYVMEKAGGMATTGKEAVLDVIPTDIHQRAPVILGSPDDVLEFLKVYEKHS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 57 | Cytochrome b (Complex III subunit 3) (Complex III subunit III) (Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 3) (Ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase complex cytochrome b subunit) | 4G6H | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name MT-CYB Organism Bos taurus (Bovine) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CYTB;MTCYB;COB Protein family Cytochrome b family Biochemical class NA Function Component of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex (complex III or cytochrome b-c1 complex) that is part of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The b-c1 complex mediates electron transfer from ubiquinol to cytochrome c. Contributes to the generation of a proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane that is then used for ATP synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1327781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20025846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9485330, ECO:0000305|PubMed:189810}." Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 6 (COXPD6) [MIM:300816]: A mitochondrial disease resulting in a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by psychomotor delay, hypotonia, areflexia, muscle weakness and wasting. Some patients manifest prenatal ventriculomegaly and severe postnatal encephalomyopathy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20362274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22019070, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25583628, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26004228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26173962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27178839}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, X-linked recessive, 4, with or without cerebellar ataxia (CMTX4) [MIM:310490]: A neuromuscular disorder characterized by progressive sensorimotor axonal neuropathy, distal sensory impairment, difficulty walking due to peripheral neuropathy and/or cerebellar ataxia, and deafness due to auditory neuropathy. Additional features include cognitive impairment, cerebellar atrophy, dysarthria, abnormal extraocular movements, tremor, dysmetria and spasticity. The age at onset ranges from infancy to young adulthood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23217327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26004228}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Deafness, X-linked, 5, with peripheral neuropathy (DFNX5) [MIM:300614]: A form of hearing loss characterized by absent or severely abnormal auditory brainstem response, abnormal middle ear reflexes, abnormal speech discrimination, loss of outer hair cell function, and cochlear nerve hypoplasia. DFNX5 patients manifest auditory neuropathy with childhood onset, associated with distal sensory impairment affecting the peripheral nervous system. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25986071}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, X-linked, with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy (SEMDHL) [MIM:300232]: An X-linked recessive developmental disorder characterized by slowly progressive skeletal and neurologic abnormalities, including short stature, large and deformed joints, significant motor impairment, visual defects, and sometimes cognitive deficits. Affected individuals typically have normal early development in the first year or so of life, followed by development regression and the development of symptoms. Brain imaging shows white matter abnormalities consistent with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842795}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Electron transport; Heme; Iron; Membrane; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Reference proteome; Respiratory chain; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubiquinone Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 105644 Length 944 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37 Isoelectric point 9.24 Charge (pH=7) 19.42 3D Binding mode Sequence TMKVIDPQHSDKPNVLILGSGWGAISFLKHIDTKKYNVSIISPRSYFLFTPLLPSAPVGTVDEKSIIEPIVNFALKKKGNVTYYEAEATSINPDRNTVTIKSLSAVSQLYQPENHLGLHQAEPAEIKYDYLISAVGAEPNTFGIPGVTDYGHFLKEIPNSLEIRRTFAANLEKANLLPKGDPERRRLLSIVVVGGGPTGVEAAGELQDYVHQDLRKFLPALAEEVQIHLVEALPIVLNMFEKKLSSYAQSHLENTSIKVHLRTAVAKVEEKQLLAKTKHEDGKITEETIPYGTLIWATGNKARPVITDLFKKIPEQNSSKRGLAVNDFLQVKGSNNIFAIGDNAFAGLPPTAQVAHQEAEYLAKNFDKMAQIPNFQKNLSSRKDKIDLLFEENNFKPFKYNDLGALAYLGSERAIATIRSGKRTFYTGGGLMTFYLWRILYLSMILSARSRLKVFFDWIKLAFFKRDFFKGLTMKVIDPQHSDKPNVLILGSGWGAISFLKHIDTKKYNVSIISPRSYFLFTPLLPSAPVGTVDEKSIIEPIVNFALKKKGNVTYYEAEATSINPDRNTVTIKSLSAVSQLYQPENHLGLHQAEPAEIKYDYLISAVGAEPNTFGIPGVTDYGHFLKEIPNSLEIRRTFAANLEKANLLPKGDPERRRLLSIVVVGGGPTGVEAAGELQDYVHQDLRKFLPALAEEVQIHLVEALPIVLNMFEKKLSSYAQSHLENTSIKVHLRTAVAKVEEKQLLAKTKHEDGKITEETIPYGTLIWATGNKARPVITDLFKKIPEQNSSKRGLAVNDFLQVKGSNNIFAIGDNAFAGLPPTAQVAHQEAEYLAKNFDKMAQIPNFQKNLSSRKDKIDLLFEENNFKPFKYNDLGALAYLGSERAIATIRSGKRTFYTGGGLMTFYLWRILYLSMILSARSRLKVFFDWIKLAFFKRDFFKGL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 58 | Aspartate aminotransferase, mitochondrial | 5AX8 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name GOT2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms KYAT4 Protein family Class-I pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent aminotransferase family Biochemical class Transferase Function 4-hydroxyglutamate transaminase activity.Amino acid binding.Enzyme binding.Kynurenine-oxoglutarate transaminase activity.L-aspartate:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity.L-phenylalanine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity.Phospholipid binding.Protein homodimerization activity.Pyridoxal phosphate binding.RNA binding. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 82 (DEE82) [MIM:618721]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of severe early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE82 is an autosomal recessive metabolic encephalopathy characterized by epilepsy from the first year of life, global developmental delay, hypotonia and feeding difficulties apparent soon after birth, and intellectual and motor disabilities. Other features include poor overall growth, progressive microcephaly and biochemical abnormalities, including increased serum lactate and ammonia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31422819}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02783; DB00128; DB00151; DB00142; DB00114 Interacts with NA EC number 2.6.1.1; 2.6.1.7 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Aminotransferase; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Epilepsy; Lipid transport; Membrane; Methylation; Mitochondrion; Nitration; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome; Transferase; Transit peptide; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 44694.8 Length 401 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 26.15 Isoelectric point 8.98 Charge (pH=7) 8.22 3D Binding mode Sequence SSWWTHVEMGPPDPILGVTEAFKRDTNSKKMNLGVGAYRDDNGKPYVLPSVRKAEAQIAAKNLDKEYLPIGGLAEFCKASAELALGENSEVLKSGRFVTVQTISGTGALRIGASFLQRFFKFSRDVFLPKPTWGNHTPIFRDAGMQLQGYRYYDPKTCGFDFTGAVEDISKIPEQSVLLLHACAHNPTGVDPRPEQWKEIATVVKKRNLFAFFDMAYQGFASGDGDKDAWAVRHFIEQGINVCLCQSYAKNMGLYGERVGAFTMVCKDADEAKRVESQLKILIRPMYSNPPLNGARIAAAILNTPDLRKQWLQEVKGMADRIIGMRTQLVSNLKKEGSTHNWQHITDQIGMFCFTGLKPEQVERLIKEFSIYMTKDGRISVAGVTSSNVGYLAHAIHQVTK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 59 | Ornithine decarboxylase (ODC1) | 2OO0 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name ODC1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms ODC Protein family Orn/Lys/Arg decarboxylase class-II family Biochemical class Carbon-carbon lyase Function Polyamines are essential for cell proliferation and are implicated in cellular processes, ranging from DNA replication to apoptosis. Catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step of polyamine biosynthesis that converts ornithine into putrescine, which is the precursor for the polyamines, spermidine and spermine. Related diseases Bachmann-Bupp syndrome (BABS) [MIM:619075]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by global developmental delay, alopecia, absolute or relative macrocephaly, and facial dysmorphism. Neuroimaging shows white matter abnormalities, prominent Virchow-Robin spaces, periventricular cysts, and abnormalities of the corpus callosum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30239107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30475435}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BABS is due to truncating variants that lead to a gain of function. This phenomenon apparently results from truncation proximal to or involving the C-terminal region of ODC1 protein, distal enough to allow escape from nonsense-mediated decay. A gain of function is corroborated by elevated plasma levels of N-acetylputrescine, with otherwise normal polyamine levels, in affected individuals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30475435}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06243; DB04263; DB03856; DB04083; DB02824; DB01917; DB00114; DB02209; DB00203; DB00127; DB00313 Interacts with Q9H8Y8; Q92993; Q9UMX2; Q9UMX2-2 EC number EC 4.1.1.17 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Decarboxylase; Disease variant; Hypotrichosis; Lyase; Phosphoprotein; Polyamine biosynthesis; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 45682.9 Length 410 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 40.93 Isoelectric point 5.61 Charge (pH=7) -6.68 3D Binding mode Sequence LMNNFGNEEFDCHFLDEGFTAKDILDQKINEVSSSDDKDAFYVADLGDILKKHLRWLKALPRVTPFYAVKCNDSKAIVKTLAATGTGFDCASKTEIQLVQSLGVPPERIIYANPCKQVSQIKYAANNGVQMMTFDSEVELMKVARAHPKAKLVLRIATDDSKAVCRLSVKFGATLRTSRLLLERAKELNIDVVGVSFHVGSGCTDPETFVQAISDARCVFDMGAEVGFSMYLLDIGGGFPGSEDVKLKFEEITGVINPALDKYFPSDSGVRIIAEPGRYYVASAFTLAVNIIAKKIVLEQTFMYYVNDGVYGSFNCILYDHAHVKPLLQKRPKPDEKYYSSSIWGPTCDGLDRIVERCDLPEMHVGDWMLFENMGAYTVAAASTFNGFQRPTIYYVMSGPAWQLMQQFQN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 60 | Ornithine delta-aminotransferase (OAT) | 2OAT | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name OAT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Ornithine--oxo-acid aminotransferase; Ornithine aminotransferase, mitochondrial Protein family Class-III pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent aminotransferase family Biochemical class Transaminase Function Catalyzes the transfer of the delta-amino group from L-ornithine. Related diseases Hyperornithinemia with gyrate atrophy of choroid and retina (HOGA) [MIM:258870]: A disorder clinically characterized by a triad of progressive chorioretinal degeneration, early cataract formation, and type II muscle fiber atrophy. Characteristic chorioretinal atrophy with progressive constriction of the visual fields leads to blindness at the latest during the sixth decade of life. Patients generally have normal intelligence. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1612597, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1737786, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23076989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2793865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3375240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7668253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7887415}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02821; DB02054; DB00129; DB00114 Interacts with P05067 EC number EC 2.6.1.13 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Aminotransferase; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Mitochondrion; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome; Transferase; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 44807.9 Length 404 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 26.67 Isoelectric point 5.72 Charge (pH=7) -6.54 3D Binding mode Sequence GPPTSDDIFEREYKYGAHNYHPLPVALERGKGIYLWDVEGRKYFDFLSSYSAVNQGHCHPKIVNALKSQVDKLTLTSRAFYNNVLGEYEEYITKLFNYHKVLPMNTGVEAGETACKLARKWGYTVKGIQKYKAKIVFAAGNFWGRTLSAISSSTDPTSYDGFGPFMPGFDIIPYNDLPALERALQDPNVAAFMVEPIQGEAGVVVPDPGYLMGVRELCTRHQVLFIADEIQTGLARTGRWLAVDYENVRPDIVLLGKALSGGLYPVSAVLCDDDIMLTIKPGEHGSTYGGNPLGCRVAIAALEVLEEENLAENADKLGIILRNELMKLPSDVVTAVRGKGLLNAIVIKETKDWDAWKVCLRLRDNGLLAKPTHGDIIRFAPPLVIKEDELRESIEIINKTILSF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||