Job Results:
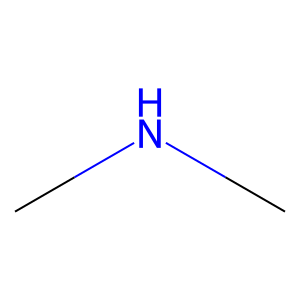
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
0d2a0cc2796a5efce48fb403877956df
Job name
NA
Time
2025-02-13 15:27:50
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | Monomeric sarcosine oxidase | 2GF3 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name soxA Organism Bacillus sp. (strain B-0618) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms sox Protein family MSOX/MTOX family, MSOX subfamily Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Sarcosine oxidase activity. Related diseases Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10394368}.; DISEASE: Obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]: A condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753710}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]: A form of lipodystrophy characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous fat from the extremities. Facial adipose tissue may be increased, decreased or normal. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12453919}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Glioma 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851250}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03098; DB01918; DB03517; DB03147; DB03366; DB02083; DB02543 Interacts with NA EC number 1.5.3.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Oxidoreductase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 42606.4 Length 385 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 26.97 Isoelectric point 5.27 Charge (pH=7) -17.18 3D Binding mode Sequence STHFDVIVVGAGSMGMAAGYQLAKQGVKTLLVDAFDPPHTNGSHHGDTRIIRHAYGEGREYVPLALRSQELWYELEKETHHKIFTKTGVLVFGPKGESAFVAETMEAAKEHSLTVDLLEGDEINKRWPGITVPENYNAIFEPNSGVLFSENCIRAYRELAEARGAKVLTHTRVEDFDISPDSVKIETANGSYTADKLIVSMGAWNSKLLSKLNLDIPLQPYRQVVGFFESDESKYSNDIDFPGFMVEVPNGIYYGFPSFGGCGLKLGYHTFGQKIDPDTINREFGVYPEDESNLRAFLEEYMPGANGELKRGAVCMYTKTLDEHFIIDLHPEHSNVVIAAGFSGHGFKFSSGVGEVLSQLALTGKTEHDISIFSINRPALKESLQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 42 | Angiopoietin 1 receptor (TEK) | 3BEA | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name TEK Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hTIE2; VMCM1; VMCM; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TIE-2; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TEK; Tyrosine kinase with Ig and EGF homology domains-2; Tunica interna endothelial cell kinase; TIE2; P140 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, Tie subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Has anti-inflammatory effects by preventing the leakage of proinflammatory plasma proteins and leukocytes from blood vessels. Required for normal angiogenesis and heart development during embryogenesis. Required for post-natal hematopoiesis. After birth, activates or inhibits angiogenesis, depending on the context. Inhibits angiogenesis and promotes vascular stability in quiescent vessels, where endothelial cells have tight contacts. In quiescent vessels, ANGPT1 oligomers recruit TEK to cell-cell contacts, forming complexes with TEK molecules from adjoining cells, and this leads to preferential activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and the AKT1 signaling cascades. In migrating endothelial cells that lack cell-cell adhesions, ANGT1 recruits TEK to contacts with the extracellular matrix, leading to the formation of focal adhesion complexes, activation of PTK2/FAK and of the downstream kinases MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1, and ultimately to the stimulation of sprouting angiogenesis. ANGPT1 signaling triggers receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation at specific tyrosine residues that then serve as binding sites for scaffold proteins and effectors. Signaling is modulated by ANGPT2 that has lower affinity for TEK, can promote TEK autophosphorylation in the absence of ANGPT1, but inhibits ANGPT1-mediated signaling by competing for the same binding site. Signaling is also modulated by formation of heterodimers with TIE1, and by proteolytic processing that gives rise to a soluble TEK extracellular domain. The soluble extracellular domain modulates signaling by functioning as decoy receptor for angiopoietins. TEK phosphorylates DOK2, GRB7, GRB14, PIK3R1; SHC1 and TIE1. Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for ANGPT1, ANGPT2 and ANGPT4 and regulates angiogenesis, endothelial cell survival, proliferation, migration, adhesion and cell spreading, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, but also maintenance of vascular quiescence. Related diseases Dominantly inherited venous malformations (VMCM) [MIM:600195]: An error of vascular morphogenesis characterized by dilated, serpiginous channels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10369874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19079259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19888299, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8980225}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Somatic mutations of TEK are associated with solitary and multiple sporadic venous malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19079259}.; DISEASE: May play a role in a range of diseases with a vascular component, including neovascularization of tumors, psoriasis and inflammation.; DISEASE: Glaucoma 3, primary congenital, E (GLC3E) [MIM:617272]: An autosomal dominant form of primary congenital glaucoma (PCG). PCG is characterized by marked increase of intraocular pressure at birth or early childhood, large ocular globes (buphthalmos) and corneal edema. It results from developmental defects of the trabecular meshwork and anterior chamber angle of the eye that prevent adequate drainage of aqueous humor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27270174}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00415; DB12010; DB08221; DB08901; DB08896; DB14840; DB11800; DB05294 Interacts with Q15389; O15123; O15123-1; Q16678; Q05209; P23467; P08575; Q12913; Q15262; Q16827 EC number EC 2.7.10.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Angiogenesis; ATP-binding; Cell junction; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; EGF-like domain; Glaucoma; Glycoprotein; Immunoglobulin domain; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34965.9 Length 310 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 43.57 Isoelectric point 8.39 Charge (pH=7) 3.42 3D Binding mode Sequence QVRWKIIESYEGNSYTFIDPTQLPYNEKWEFPRNNLQFGKTLGAGAFGKVVEATAFGLGKEDAVLKVAVKMLKSTAHADEKEALMSELKIMSHLGQHENIVNLLGACTHGGPVLVITEYCCYGDLLNFLRRKSRVLSTLSTRDLLHFSSQVAQGMAFLASKNCIHRDVAARNVLLTNGHVAKIGDFGLARDIMNDSNYIVKGNARLPVKWMAPESIFDCVYTVQSDVWSYGILLWEIFSLGLNPYPGILVNSKFYKLVKDGYQMAQPAFAPKNIYSIMQACWALEPTHRPTFQQICSFLQEQAQEDRRER Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 43 | Kynureninase (KYNU) | 3E9K | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name KYNU Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms L-kynurenine hydrolase; KYNU Protein family Kynureninase family Biochemical class Carbon-carbon bonds hydrolase Function Catalyzes the cleavage of L-kynurenine (L-Kyn) and L-3- hydroxykynurenine (L-3OHKyn) into anthranilic acid (AA) and 3- hydroxyanthranilic acid (3-OHAA), respectively. Has a preference for the L-3-hydroxy form. Also has cysteine-conjugate-beta-lyase activity. Related diseases Hydroxykynureninuria (HYXKY) [MIM:236800]: An inborn error of amino acid metabolism characterized by massive urinary excretion of large amounts of kynurenine, 3-hydroxykynurenine and xanthurenic acid. Affected individuals manifest renal tubular dysfunction, metabolic acidosis, psychomotor retardation, non-progressive encephalopathy, and muscular hypertonia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17334708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28792876}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Vertebral, cardiac, renal, and limb defects syndrome 2 (VCRL2) [MIM:617661]: An autosomal recessive congenital malformation syndrome characterized by vertebral segmentation abnormalities, congenital cardiac defects, renal defects, and distal mild limb defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28792876}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00160; DB07069; DB00114 Interacts with Q8WUE5; P56545-3; Q9NVL1-2; P61968; P59942; Q8TDC0; P78356-2; Q86WH2 EC number EC 3.7.1.3 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Proteomics identification; Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 50204.5 Length 446 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 39.91 Isoelectric point 6.36 Charge (pH=7) -4.59 3D Binding mode Sequence LELPADTVQRIAAELKCHPTDERVALHLDEEDKLRHFREXFYIPKIQDLPPVDLSLVNKDENAIYFLGNSLGLQPKMVKTYLEEELDKWAKIAAYGHEVGKRPWITGDESIVGLMKDIVGANEKEIALMNALTVNLHLLMLSFFKPTPKRYKILLEAKAFPSDHYAIESQLQLHGLNIEESMRMIKPREGEETLRIEDILEVIEKEGDSIAVILFSGVHFYTGQHFNIPAITKAGQAKGCYVGFDLAHAVGNVELYLHDWGVDFACWCSYKYLNAGAGGIAGAFIHEKHAHTIKPALVGWFGHELSTRFKMDNKLQLIPGVCGFRISNPPILLVCSLHASLEIFKQATMKALRKKSVLLTGYLEYLIKHNYGVVNIITPSHVEERGCQLTITFSVPNKDVFQELEKRGVVCDKRNPNGIRVAPVPLYNSFHDVYKFTNLLTSILDS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 44 | Lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase (EC 1.14.13.70) | 4G3J | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name Tb11.02.4080 Organism Trypanosoma brucei brucei (strain 927/4 GUTat10.1) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Cytochrome P450 family Biochemical class NA Function NA Related diseases LTC4 synthase deficiency is associated with a neurometabolic developmental disorder characterized by muscular hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, and microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10896305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9820300}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 1.14.13.70 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Heme; Iron; Metal-binding; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID D Molecular weight (Da) 50691.4 Length 448 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 54.09 Isoelectric point 6.99 Charge (pH=7) -0.03 3D Binding mode Sequence GKLPPVYPVTVPILGHIIQFGKSPLGFMQECKRQLKSGIFTINIVGKRVTIVGDPHEHSRFFLPRNEVLSPREVYSFMVPVFGEGVAYAAPYPRMREQLNFLAEELTIAKFQNFVPAIQHEVRKFMAANWDKDEGEINLLEDCSTMIINTACQCLFGEDLRKRLDARRFAQLLAKMESSLIPAAVFLPILLKLPLPQSARCHEARTELQKILSEIIIARKEEEVNKDSSTSDLLSGLLSAVYRDGTPMSLHEVCGMIVAAMFAGQHTSSITTTWSMLHLMHPANVKHLEALRKEIEEFPAQLNYNNVMDEMPFAERCARESIRRDPPLLMLMRKVMADVKVGSYVVPKGDIIACSPLLSHHDEEAFPEPRRWDPERDEKVEGAFIGFGAGVHKCIGQKFGLLQVKTILATAFRSYDFQLLRDEVPDPDYHTMVVGPTASQCRVKYIRR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 45 | Alr1529 protein | 1Z8H | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name alr1529 Organism Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family NA Biochemical class Hydrolase Function NA Related diseases Desbuquois dysplasia 1 (DBQD1) [MIM:251450]: A chondrodysplasia characterized by severe prenatal and postnatal growth retardation (less than -5 SD), joint laxity, short extremities, progressive scoliosis, round face, midface hypoplasia, prominent bulging eyes. The main radiologic features are short long bones with metaphyseal splay, a 'Swedish key' appearance of the proximal femur (exaggerated trochanter), and advance carpal and tarsal bone age. Two forms of Desbuquois dysplasia are distinguished on the basis of the presence or absence of characteristic hand anomalies: an extra ossification center distal to the second metacarpal, delta phalanx, bifid distal thumb phalanx, and phalangeal dislocations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19853239, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20425819, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21037275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21412251, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21654728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22539336}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epiphyseal dysplasia, multiple, 7 (EDM7) [MIM:617719]: A form of multiple epiphyseal dysplasia, a generalized skeletal dysplasia associated with significant morbidity. Joint pain, joint deformity, waddling gait, and short stature are the main clinical signs and symptoms. Radiological examination of the skeleton shows delayed, irregular mineralization of the epiphyseal ossification centers and of the centers of the carpal and tarsal bones. Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia is broadly categorized into the more severe Fairbank and the milder Ribbing types. The Fairbank type is characterized by shortness of stature, short and stubby fingers, small epiphyses in several joints, including the knee, ankle, hand, and hip. The Ribbing type is confined predominantly to the hip joints and is characterized by hands that are normal and stature that is normal or near-normal. EDM7 inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28742282}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 45603.2 Length 401 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 49.26 Isoelectric point 7.67 Charge (pH=7) 1.26 3D Binding mode Sequence KTQIRICFVGDSFVNGTGDPECLGWTGRVCVNANKKGYDVTYYNLGIRRDTSSDIAKRWLQEVSLRLHKEYNSLVVFSFGLNDTTLENGKPRVSIAETIKNTREILTQAKKLYPVLXISPAPYIEQQDPGRRRRTIDLSQQLALVCQDLDVPYLDVFPLLEKPSVWLHEAKANDGVHPQAGGYTEFARIVENWDAWLNWFRKTQIRICFVGDSFVNGTGDPECLGWTGRVCVNANKKGYDVTYYNLGIRRDTSSDIAKRWLQEVSLRLHKEYNSLVVFSFGLNDTTLENGKPRVSIAETIKNTREILTQAKKLYPVLXISPAPYIEQQDPGRRRRTIDLSQQLALVCQDLDVPYLDVFPLLEKPSVWLHEAKANDGVHPQAGGYTEFARIVENWDAWLNWF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 46 | Protein cereblon (CRBN) | 5FQD | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name CRBN Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein cereblon Protein family CRBN family Biochemical class NA Function Substrate recognition component of a DCX (DDB1-CUL4-X-box) E3 protein ligase complex that mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins, such as MEIS2. Normal degradation of key regulatory proteins is required for normal limb outgrowth and expression of the fibroblast growth factor FGF8. May play a role in memory and learning by regulating the assembly and neuronal surface expression of large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in brain regions involved in memory and learning via its interaction with KCNT1. Binding of pomalidomide and other thalidomide-related drugs changes the substrate specificity of the human protein, leading to decreased degradation of MEIS2 and other target proteins and increased degradation of MYC, IRF4, IKZF1 and IKZF3. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 2 (MRT2) [MIM:607417]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRT2 patients display mild intellectual disability with a standard IQ ranged from 50 to 70. IQ scores are lower in males than females. Developmental milestones are mildly delayed. There are no dysmorphic or autistic features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15557513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28143899}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00480; DB08910; DB01041 Interacts with Q96A83-2; P48729; Q16531; O14901; Q8IVT2; Q9P286; A0A6Q8PF08; Q93062; Q16531; Q13422-7 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation; Ubl conjugation pathway; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B,E Molecular weight (Da) 38245.7 Length 337 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 40.62 Isoelectric point 5.7 Charge (pH=7) -6.53 3D Binding mode Sequence EFIVGGKYKLNITNGEEVAVINFDTSLPTSHTYLGADMEEFHGRTLHDDDSCQVIPVLPQVMMILIPGQTLPLQLFHPQEVSMVRNLIQKDRTFAVLAYSNVQEREAQFGTTAEIYAYREEIVKVKAIGRQRFKVLEQQAKVQILPECVLAETLMDRIKKQLREWDENLKDDSLPSNPIDFSYRVAACLPIDDVLRIQLLKIGSAIQRLRCELDIMNKCTSLCCKQCQETEITTKNEIFSLSLCGPMAAYVNPHGYVHETLTVYKACNLNLIGRPSTEHSWFPGYAWTVAQCKICASHIGWKFTATKKDMSPQKFWGLTRSALLPTIPDTEDEISPD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 47 | Haemophilus influenzae NadR protein (Hae-influ nadR) | 1LW7 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name Hae-influ nadR Organism Haemophilus influenzae (strain ATCC 51907 / DSM 11121 / KW20 / Rd) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms nadR; Transcriptional regulator nadR Protein family Bacterial NMN adenylyltransferase family; Bacterial RNK family Biochemical class Nicotinamide ribonucleoside uptake permease Function This enzyme has twoactivities: nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) adenylyltransferase and ribosylnicotinamide (RN) kinase. The RN kinase activity catalyzes the phosphorylation of RN to form nicotinamide ribonucleotide. The NMN adenylyltransferase activity catalyzes the transfer of the AMP moiety of ATP to nicotinamide ribonucleotide to form NAD(+). Related diseases Involved in the epigenetic regulation of ESR1 expression in breast cancer in a TFAP2C, IFI16 and HDAC4/5/6-dependent manner. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24413532}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative initiation; ATP-binding; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Kinase; Membrane; Multifunctional enzyme; NAD; Nucleotide-binding; Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 39581.5 Length 344 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 41.39 Isoelectric point 6.94 Charge (pH=7) -0.18 3D Binding mode Sequence EKKVGVIFGKFYPVHTGHINXIYEAFSKVDELHVIVCSDTVRDLKLFYDSKXKRXPTVQDRLRWXQQIFKYQKNQIFIHHLVEDGIPSYPNGWQSWSEAVKTLFHEKHFEPSIVFSSEPQDKAPYEKYLGLEVSLVDPDRTFFNVSATKIRTTPFQYWKFIPKEARPFFAKTVAILGGESSGKSVLVNKLAAVFNTTSAWEYGREFVFEKLGGDEQAMQYSDYPQXALGHQRYIDYAVRHSHKIAFIDTDFITTQAFCIQYEGKAHPFLDSXIKEYPFDVTILLKNNTEQKQRQQFQQLLKKLLDKYKVPYIEIESPSYLDRYNQVKAVIEKVLNEEEISELQN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 48 | N-acetylgalactosamine 6 sulfatase (GALNS) | 4FDJ | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name GALNS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase; N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase; Galactose-6-sulfate sulfatase; GalNAc6S sulfatase; GalN6S; Chondroitinsulfatase; Chondroitinase Protein family Sulfatase family Biochemical class Sulfuric ester hydrolase Function Catalyzes the chemical reaction of cleaving off the 6-sulfate groups of the N-acetyl-D-galactosamine 6-sulfate units of the macromolecule chondroitin sulfate and, similarly, of the D-galactose 6-sulfate units of the macromolecule keratan sulfate. Related diseases Mucopolysaccharidosis 4A (MPS4A) [MIM:253000]: A form of mucopolysaccharidosis type 4, an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease characterized by intracellular accumulation of keratan sulfate and chondroitin-6-sulfate. Key clinical features include short stature, skeletal dysplasia, dental anomalies, and corneal clouding. Intelligence is normal and there is no direct central nervous system involvement, although the skeletal changes may result in neurologic complications. There is variable severity, but patients with the severe phenotype usually do not survive past the second or third decade of life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1522213, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16287098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24726177, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7581409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7633425, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7668283, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7795586, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8651279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8826435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9298823, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9375852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9521421}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09301 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.1.6.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Calcium; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Dwarfism; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lysosome; Metal-binding; Mucopolysaccharidosis; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 55013.8 Length 493 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 35.46 Isoelectric point 6.14 Charge (pH=7) -6.48 3D Binding mode Sequence PQPPNILLLLMDDMGWGDLGVYGEPSRETPNLDRMAAEGLLFPNFYSANPLXSPSRAALLTGRLPIRNGFYTTNAHARNAYTPQEIVGGIPDSEQLLPELLKKAGYVSKIVGKWHLGHRPQFHPLKHGFDEWFGSPNCHFGPYDNKARPNIPVYRDWEMVGRYYEEFPINLKTGEANLTQIYLQEALDFIKRQARHHPFFLYWAVDATHAPVYASKPFLGTSQRGRYGDAVREIDDSIGKILELLQDLHVADNTFVFFTSDNGAALISAPEQGGSNGPFLCGKQTTFEGGMREPALAWWPGHVTAGQVSHQLGSIMDLFTTSLALAGLTPPSDRAIDGLNLLPTLLQGRLMDRPIFYYRGDTLMAATLGQHKAHFWTWTNSWENFRQGIDFCPGQNVSGVTTHNLEDHTKLPLIFHLGRDPGERFPLSFASAEYQEALSRITSVVQQHQEALVPAQPQLNVCNWAVMNWAPPGCEKLGKCLTPPESIPKKCLW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 49 | Soluble epoxide hydrolase (EPHX2) | 1ZD3 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name EPHX2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Bifunctional epoxide hydrolase 2 Protein family AB hydrolase superfamily, Epoxide hydrolase family Biochemical class Ether bond hydrolase Function Bifunctional enzyme. The C-terminal domain has epoxide hydrolase activity and acts on epoxides (alkene oxides, oxiranes) and arene oxides. Plays a role in xenobiotic metabolism by degrading potentially toxic epoxides (By similarity). Also determines steady-state levels of physiological mediators. The N-terminal domain has lipid phosphatase activity, with the highest activity towards threo-9,10-phosphonooxy-hydroxy-octadecanoic acid, followed by erythro-9,10-phosphonooxy-hydroxy-octadecanoic acid, 12-phosphonooxy-octadec-9Z-enoic acid and 12-phosphonooxy-octadec-9E-enoic acid. Related diseases Leukemia, juvenile myelomonocytic (JMML) [MIM:607785]: An aggressive pediatric myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative disorder characterized by malignant transformation in the hematopoietic stem cell compartment with proliferation of differentiated progeny. Patients have splenomegaly, enlarged lymph nodes, rashes, and hemorrhages. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17332249}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Noonan syndrome 6 (NS6) [MIM:613224]: A form of Noonan syndrome, a disease characterized by short stature, facial dysmorphic features such as hypertelorism, a downward eyeslant and low-set posteriorly rotated ears, and a high incidence of congenital heart defects and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Other features can include a short neck with webbing or redundancy of skin, deafness, motor delay, variable intellectual deficits, multiple skeletal defects, cryptorchidism, and bleeding diathesis. Individuals with Noonan syndrome are at risk of juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, a myeloproliferative disorder characterized by excessive production of myelomonocytic cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19966803}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: RAS-associated autoimmune leukoproliferative disorder (RALD) [MIM:614470]: A disorder of apoptosis, characterized by chronic accumulation of non-malignant lymphocytes, defective lymphocyte apoptosis, and an increased risk for the development of hematologic malignancies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17517660}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Melanocytic nevus syndrome, congenital (CMNS) [MIM:137550]: A syndrome characterized by congenital pigmentary skin lesions which can occur at any site and can cover most of the body surface. These lesions may or may not be hairy. Congenital melanocytic nevi are associated with neuromelanosis (the presence of melanin-producing cells within the brain parenchyma or leptomeninges). Less commonly they are associated with malignant melanoma in childhood, both in the skin and the central nervous system. CMNS patients also tend to have a characteristic facial appearance, including wide or prominent forehead, periorbital fullness, small short nose with narrow nasal bridge, round face, full cheeks, prominent premaxilla, and everted lower lip. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18633438, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23392294}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Melanosis, neurocutaneous (NCMS) [MIM:249400]: A rare congenital disease characterized by the presence of giant or multiple melanocytic nevi on the skin, foci of melanin-producing cells within the brain parenchyma, and infiltration of leptomeninges by abnormal melanin deposits. Neurologic abnormalities include seizures, hydrocephalus, arachnoid cysts, tumors, and syringomyelia. Some patients may develop malignant melanoma. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23392294}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Keratinocytic non-epidermolytic nevus (KNEN) [MIM:162900]: Epidermal nevi of the common, non-organoid and non-epidermolytic type are benign skin lesions and may vary in their extent from a single (usually linear) lesion to widespread and systematized involvement. They may be present at birth or develop early during childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22499344}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thyroid cancer, non-medullary, 2 (NMTC2) [MIM:188470]: A form of non-medullary thyroid cancer (NMTC), a cancer characterized by tumors originating from the thyroid follicular cells. NMTCs represent approximately 95% of all cases of thyroid cancer and are classified into papillary, follicular, Hurthle cell, and anaplastic neoplasms. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12727991}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08257; DB08258; DB08259; DB06345; DB12610; DB08256; DB02029; DB04213; DB03677 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Aromatic hydrocarbons catabolism; Cytoplasm; Detoxification; Direct protein sequencing; Hydrolase; Lipid metabolism; Lipoprotein; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Multifunctional enzyme; Peroxisome; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 61744.9 Length 547 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 43.97 Isoelectric point 5.81 Charge (pH=7) -7.76 3D Binding mode Sequence TLRAAVFDLDGVLALPAVFGVLGRTEEALALPRGLLNDAFQKGGPEGATTRLMKGEITLSQWIPLMEENCRKCSETAKVCLPKNFSIKEIFDKAISARKINRPMLQAALMLRKKGFTTAILTNTWLDDRAERDGLAQLMCELKMHFDFLIESCQVGMVKPEPQIYKFLLDTLKASPSEVVFLDDIGANLKPARDLGMVTILVQDTDTALKELEKVTGIQLLNTPAPLPTSCNPSDMSHGYVTVKPRVRLHFVELGSGPAVCLCHGFPESWYSWRYQIPALAQAGYRVLAMDMKGYGESSAPPEIEEYCMEVLCKEMVTFLDKLGLSQAVFIGHDWGGMLVWYMALFYPERVRAVASLNTPFIPANPNMSPLESIKANPVFDYQLYFQEPGVAEAELEQNLSRTFKSLFRASDESVLSMHKVCEAGGLFVNSPEEPSLSRMVTEEEIQFYVQQFKKSGFRGPLNWYRNMERNWKWACKSLGRKILIPALMVTAEKDFVLVPQMSQHMEDWIPHLKRGHIEDCGHWTQMDKPTEVNQILIKWLDSDARN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 50 | Bacterial Pyruvate decarboxylase (Bact aceE) | 1L8A | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name Bact aceE Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms aceE; Pyruvate decarboxylase E1 component Protein family NA Biochemical class Aldehyde/oxo donor oxidoreductase Function The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-coa and co(2). It contains multiple copies of three enzymatic components: pyruvate dehydrogenase (e1), dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (e2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase. Related diseases Pseudovaginal perineoscrotal hypospadias (PPSH) [MIM:264600]: A form of male pseudohermaphroditism in which 46,XY males show ambiguous genitalia at birth, including perineal hypospadias and a blind perineal pouch, and develop masculinization at puberty. The name of the disorder stems from the finding of a blind-ending perineal opening resembling a vagina and a severely hypospadiac penis with the urethra opening onto the perineum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10718838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10898110, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10999800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12843198, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15064320, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1522235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15528927, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15770495, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16098368, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16181229, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7554313, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8626825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8768837, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9208814, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9745434, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9843052}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01987 Interacts with P0AFG8; P0A8N7; P77439; P46889; P0A6F5; P0AEV9; P0AB83; P0AB89; P0AG40; P05100; P26602; P0A9U1; P0A8L7; P76049; P76170 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Direct protein sequencing; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Oxidoreductase; Pyruvate; Reference proteome; Thiamine pyrophosphate Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 179825 Length 1602 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.46 Isoelectric point 5.51 Charge (pH=7) -42.23 3D Binding mode Sequence ISNYINTIPVEEQPEYPGNLELERRIRSAIRWNAIMTVLRASKKDLELGGHMASFQSSATIYDVCFNHFFRARNEQDGGDLVYFQGHISPGVYARAFLEGRLTQEQLDNFRQEVHGNGLSSYPHPKLMPEFWQFPTVSMGLGPIGAIYQAKFLKYLEHRGLKDTSKQTVYAFLGDGEMDEPESKGAITIATREKLDNLVFVINCNLQRLDGPVTGNGKIINELEGIFEGAGWNVIKVMWGSRWDELLRKDTSGKLIQLMNETVDGDYQTFKSKDGAYVREHFFGKYPETAALVADWTDEQIWALNRGGHDPKKIYAAFKKAQETKGKATVILAHTIKGYGMGDAAMDGVRHIRDRFNVPVSDADIEKLPYITFPEGSEEHTYLHAQRQKLHGYLPSRQPNFTEKLELPSLQDFGALLEEQSKEISTTIAFVRALNVMLKNKSIKDRLVPIIADEARTFGMEGLFRQIGIYSPEDEKGQILQEGINELGAGCSWLAAATSYSTNNLPMIPFYIYYSMFGFQRIGDLCWAAGDQQARGFLIGGTSGRTTLNGEGLQHEDGHSHIQSLTIPNCISYDPAYAYEVAVIMHDGLERMYGEKQENVYYYITTLNENYHMPAMPEGAEEGIRKGIYKLETIEGSKGKVQLLGSGSILRHVREAAEILAKDYGVGSDVYSVTSFTELARDGQDCERWNMLHPLETPRVPYIAQVMNDAPAVASTDYMKLFAEQVRTYVPADDYRVLGTDGFGRSDSRENLRHHFEVDASYVVVAALGELAKRGEIDKKVVADAIAKFNIDADKVNPRLAISNYINTIPVEEQPEYPGNLELERRIRSAIRWNAIMTVLRASKKDLELGGHMASFQSSATIYDVCFNHFFRARNEQDGGDLVYFQGHISPGVYARAFLEGRLTQEQLDNFRQEVHGNGLSSYPHPKLMPEFWQFPTVSMGLGPIGAIYQAKFLKYLEHRGLKDTSKQTVYAFLGDGEMDEPESKGAITIATREKLDNLVFVINCNLQRLDGPVTGNGKIINELEGIFEGAGWNVIKVMWGSRWDELLRKDTSGKLIQLMNETVDGDYQTFKSKDGAYVREHFFGKYPETAALVADWTDEQIWALNRGGHDPKKIYAAFKKAQETKGKATVILAHTIKGYGMGDAAMDGVRHIRDRFNVPVSDADIEKLPYITFPEGSEEHTYLHAQRQKLHGYLPSRQPNFTEKLELPSLQDFGALLEEQSKEISTTIAFVRALNVMLKNKSIKDRLVPIIADEARTFGMEGLFRQIGIYSPEDEKGQILQEGINELGAGCSWLAAATSYSTNNLPMIPFYIYYSMFGFQRIGDLCWAAGDQQARGFLIGGTSGRTTLNGEGLQHEDGHSHIQSLTIPNCISYDPAYAYEVAVIMHDGLERMYGEKQENVYYYITTLNENYHMPAMPEGAEEGIRKGIYKLETIEGSKGKVQLLGSGSILRHVREAAEILAKDYGVGSDVYSVTSFTELARDGQDCERWNMLHPLETPRVPYIAQVMNDAPAVASTDYMKLFAEQVRTYVPADDYRVLGTDGFGRSDSRENLRHHFEVDASYVVVAALGELAKRGEIDKKVVADAIAKFNIDADKVNPRLA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 51 | Glutamate carboxypeptidase III (NAALAD2) | 3FED | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name NAALAD2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NAALADase II; NAALAD2 Protein family Peptidase M28 family, M28B subfamily Biochemical class Peptidase Function Has N-acetylated-alpha-linked-acidic dipeptidase (NAALADase) activity. Also exhibits a dipeptidyl-peptidase IV type activity. Inactivate the peptide neurotransmitter N- acetylaspartylglutamate. Related diseases Dystonia 1, torsion, autosomal dominant (DYT1) [MIM:128100]: A primary torsion dystonia, and the most common and severe form. Dystonia is defined by the presence of sustained involuntary muscle contractions, often leading to abnormal postures. Dystonia type 1 is characterized by involuntary, repetitive, sustained muscle contractions or postures involving one or more sites of the body, in the absence of other neurological symptoms. Typically, symptoms develop first in an arm or leg in middle to late childhood and progress in approximately 30% of patients to other body regions (generalized dystonia) within about five years. 'Torsion' refers to the twisting nature of body movements observed in DYT1, often affecting the trunk. Distribution and severity of symptoms vary widely between affected individuals, ranging from mild focal dystonia to severe generalized dystonia, even within families. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14970196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15505207, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16361107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17428918, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18167355, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18477710, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18827015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19955557, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20169475, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21102408, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24930953, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27490483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9288096}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita 5 (AMC5) [MIM:618947]: A form of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita, a developmental condition characterized by multiple joint contractures resulting from reduced or absent fetal movements. AMC5 is an autosomal recessive form characterized by severe congenital contractures, developmental delay, strabismus and tremor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28516161, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29053766, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30244176}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9UHD4; Q6NTF9-3; B2RUZ4; O76024 EC number EC 3.4.17.21 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Carboxypeptidase; Cell membrane; Dipeptidase; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Membrane; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Multifunctional enzyme; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal-anchor; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 77761.6 Length 690 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 39.42 Isoelectric point 8.48 Charge (pH=7) 4.65 3D Binding mode Sequence SIRWKLVSEMKAENIKSFLRSFTKLPHLAGTEQNFLLAKKIQTQWKKFGLDSAKLVHYDVLLSYPNETNANYISIVDEHETEIFKTSPPPDGYENVTNIVPPYNAFSAQGMPEGDLVYVNYARTEDFFKLEREMGINCTGKIVIARYGKIFRGNKVKNAMLAGAIGIILYSDPADYFAPEVQPYPKGWNLPGTAAQRGNVLNLNGAGDPLTPGYPAKEYTFRLDVEEGVGIPRIPVHPIGYNDAEILLRYLGGIAPPDKSWKGALNVSYSIGPGFTGSSFRKVRMHVYNINKITRIYNVVGTIRGSVEPDRYVILGGHRDSWVFGAIDPTSGVAVLQEIARSFGKLMSKGWRPRRTIIFASWDAEEFGLLGSTEWAEENVKILQERSIAYINSDSSIEGNYTLRVDCTPLLYQLVYKLTKEIPSPDDGFESKSLYESWLEKDPSPENKNLPRINKLGSGSDFEAYFQRLGIASGRARYTKNKKTDKYSSYPVYHTIYETFELVEKFYDPTFKKQLSVAQLRGALVYELVDSKIIPFNIQDYAEALKNYAASIYNLSKKHDQQLTDHGVSFDSLFSAVKNFSEAASDFHKRLIQVDLNNPIAVRMMNDQLMLLERAFIDPLGLPGKLFYRHIIFAPSSHNKYAGESFPGIYDAIFDIENKANSRLAWKEVKKHISIAAFTIQAAAGTLKEV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 52 | Triggering receptor expressed on monocytes 1 (TREM1) | 1Q8M | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name Trem1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Trem1; TREM-1 Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Stimulates neutrophil and monocyte-mediated inflammatory responses. Triggers release of pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines, as well as increased surface expression of cell activation markers. Amplifier of inflammatory responses that are triggered by bacterial and fungal infections and is a crucial mediator of septic shock. Related diseases GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 1 (GLUT1DS1) [MIM:606777]: A neurologic disorder showing wide phenotypic variability. The most severe 'classic' phenotype comprises infantile-onset epileptic encephalopathy associated with delayed development, acquired microcephaly, motor incoordination, and spasticity. Onset of seizures, usually characterized by apneic episodes, staring spells, and episodic eye movements, occurs within the first 4 months of life. Other paroxysmal findings include intermittent ataxia, confusion, lethargy, sleep disturbance, and headache. Varying degrees of cognitive impairment can occur, ranging from learning disabilities to severe intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10227690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10980529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11136715, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11603379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12325075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15622525, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19901175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20129935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20221955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20574033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24847886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30197081}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 2 (GLUT1DS2) [MIM:612126]: A clinically variable disorder characterized primarily by onset in childhood of paroxysmal exercise-induced dyskinesia. The dyskinesia involves transient abnormal involuntary movements, such as dystonia and choreoathetosis, induced by exercise or exertion, and affecting the exercised limbs. Some patients may also have epilepsy, most commonly childhood absence epilepsy. Mild intellectual disability may also occur. In some patients involuntary exertion-induced dystonic, choreoathetotic, and ballistic movements may be associated with macrocytic hemolytic anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14605501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18451999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19630075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19798636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20129935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20574033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20621801, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20830593, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21204808}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epilepsy, idiopathic generalized 12 (EIG12) [MIM:614847]: A disorder characterized by recurring generalized seizures in the absence of detectable brain lesions and/or metabolic abnormalities. Generalized seizures arise diffusely and simultaneously from both hemispheres of the brain. Seizure types include juvenile myoclonic seizures, absence seizures, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. In some EIG12 patients seizures may remit with age. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19798636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22282645, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23280796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Dystonia 9 (DYT9) [MIM:601042]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder characterized by childhood onset of paroxysmal choreoathetosis and progressive spastic paraplegia. Most patients show some degree of cognitive impairment. Other variable features may include seizures, migraine headaches, and ataxia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21832227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Stomatin-deficient cryohydrocytosis with neurologic defects (SDCHCN) [MIM:608885]: A rare form of stomatocytosis characterized by episodic hemolytic anemia, cold-induced red cells cation leak, erratic hyperkalemia, neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, hepatosplenomegaly, cataracts, seizures, intellectual disability, and movement disorder. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21791420, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22492876}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01694 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Immunoglobulin domain; Innate immunity; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 28186.2 Length 242 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 45.2 Isoelectric point 6.1 Charge (pH=7) -3.8 3D Binding mode Sequence MELRAATKLTEEKYELKEGQTLDVKCDYTLEKFASSQKAWQIIRDGEMPKTLACTERPSKNSHPVQVGRIILEDYHDHGLLRVRMVNLQVEDSGLYQCVIYQPPKEPHMLFDRIRLVVTLEMELRAATKLTEEKYELKEGQTLDVKCDYTLEKFASSQKAWQIIRDGEMPKTLACTERPSKNSHPVQVGRIILEDYHDHGLLRVRMVNLQVEDSGLYQCVIYQPPKEPHMLFDRIRLVVTLE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 53 | NAPE-hydrolyzing phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD) | 4QN9 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name NAPEPLD Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NAPE-PLD; N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolyzing phospholipase D; N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D; C7orf18 Protein family NAPE-PLD family Biochemical class NA Function Hydrolyzes N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamines (NAPEs) to produce N-acylethanolamines (NAEs) and phosphatidic acid. Responsible for the generation of these bioactive fatty acid ethanolamides (FAEs), including anandamide (N-arachidonoylethanolamine), the ligand of cannabinoid and vanilloid receptors. As a regulator of lipid metabolism in the adipose tissue, mediates the crosstalk between adipocytes, gut microbiota and immune cells to control body temperature and weight. In particular, regulates energy homeostasis by promoting cold-induced brown or beige adipocyte differentiation program to generate heat from fatty acids and glucose (By similarity). Related diseases Glioma (GLM) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539269}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. H3F3A mutations affecting residues involved in post-translational modifications of histone H3.3 are recurrent in malignant, aggressive gliomas including glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) (PubMed:22286061, PubMed:22286216). The mechanism through which mutations lead to tumorigenesis involves altered histones methylation, impaired regulation of Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) activity, and aberrant epigenetic regulation of gene expression (PubMed:23539183, PubMed:23539269, PubMed:23603901). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23603901}.; DISEASE: Bryant-Li-Bhoj neurodevelopmental syndrome 1 (BRYLIB1) [MIM:619720]: An autosomal dominant disorder predominantly characterized by global developmental delay, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and delayed motor milestones. Clinical manifestations are highly variable, including abnormal head shape, dysmorphic facial features, oculomotor abnormalities, feeding problems, and non-specific brain imaging abnormalities. Additional features may include hearing loss, seizures, short stature, and mild skeletal defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BRYLIB1 is caused by variants in H3-3A. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}.; DISEASE: Bryant-Li-Bhoj neurodevelopmental syndrome 2 (BRYLIB2) [MIM:619721]: An autosomal dominant disorder predominantly characterized by global developmental delay, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and delayed motor milestones. Clinical manifestations are highly variable, including abnormal head shape, dysmorphic facial features, oculomotor abnormalities, feeding problems, and non-specific brain imaging abnormalities. Additional features may include hearing loss, seizures, short stature, and mild skeletal defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BRYLIB2 is caused by variants in H3-3B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}.; DISEASE: H3F3A and H3F3B mutations affecting residues involved in post-translational modifications of histone H3.3 are implicated in the pathogenesis of some bone and cartilage neoplasms. Mutations have been found with high prevalence in chondroblastoma and giant cell tumors of bone, and with low frequency in osteosarcoma, conventional chondrosarcoma and clear cell chondrosarcoma. Chondroblastoma samples frequently carry a H3F3B mutation affecting residue Lys-37 (H3K36), although H3F3A is mutated in some cases. Most giant cell tumors of bone harbor H3F3A mutations affecting residue Gly-35 (H3G34). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24162739}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB14009 Interacts with Q6IQ20 EC number EC 3.1.4.54 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Endosome; Golgi apparatus; Hydrolase; Lipid degradation; Lipid metabolism; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phospholipid degradation; Phospholipid metabolism; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 74256.5 Length 643 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 48.34 Isoelectric point 5.65 Charge (pH=7) -17.61 3D Binding mode Sequence SKKGKDGRFVNPWPTWKNPSIPNSSVPSSKEELDKELPVLKPYFITNPEEAGVREAGLRVTWLGHATVMVEMDELIFLTDPIFSSRASPSQYMGPKRFRRSPCTISELPPIDAVLISHNHYDHLDYNSVIALNERFGNELRWFVPLGLLDWMQKCGCENVIELDWWEENCVPGHDKVTFVFTPSQHWCKRTLMDDNKVLWGSWSVLGPWNRFFFAGDTGYCPAFEEIGKRFGPFDLAAIPIGAYEPRWFMKYQHVDPEEAVRIHTDVQTKKSMAIHWGTFALANEHYLEPPVKLNEALERYGLNAEDFFVLKHGESRYLNNSKKGKDGRFVNPWPTWKNPSIPNSSVPSSKEELDKELPVLKPYFITNPEEAGVREAGLRVTWLGHATVMVEMDELIFLTDPIFSSRASPSQYMGPKRFRRSPCTISELPPIDAVLISHNHYDHLDYNSVIALNERFGNELRWFVPLGLLDWMQKCGCENVIELDWWEENCVPGHDKVTFVFTPSQHWCKRTLMDDNKVLWGSWSVLGPWNRFFFAGDTGYCPAFEEIGKRFGPFDLAAIPIGAYEPRWFMKYQHVDPEEAVRIHTDVQTKKSMAIHWGTFALANEHYLEPPVKLNEALERYGLNAEDFFVLKHGESRYLNND Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 54 | mRNA-capping enzyme | 2C46 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name RNGTT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CAP1A Protein family Non-receptor class of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase family; Eukaryotic GTase family Biochemical class Transferase Function GTP binding.MRNA guanylyltransferase activity.Polynucleotide 5'-phosphatase activity.Protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity.Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity.RNA guanylyltransferase activity.Triphosphatase activity. Related diseases Atrial fibrillation, familial, 14 (ATFB14) [MIM:615378]: A familial form of atrial fibrillation, a common sustained cardiac rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity and ineffective atrial contraction promoting blood stasis in the atria and reduces ventricular filling. It can result in palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19808477}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Genetic variations in SCN2B may be involved in Brugada syndrome (PubMed:23559163). This tachyarrhythmia is characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs, the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23559163}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q92624; P16333-1 EC number 2.7.7.50; 3.6.1.74 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; GTP-binding; Host-virus interaction; Hydrolase; mRNA capping; mRNA processing; Multifunctional enzyme; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleotidyltransferase; Nucleus; Protein phosphatase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 21849.8 Length 189 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 53.71 Isoelectric point 5.89 Charge (pH=7) -2.91 3D Binding mode Sequence NKIPPRWLNCPRRGQPVAGRFLPLKTMLGPRYDSQVAEENRFHPSMLSNYLKSVKMGLLVDLTNTSRFYDRNDIEKEGIKYIKLQCKGHGECPTTENTETFIRLCERFELIGVHCTHGFNRTGFLICAFLVEKMDWSIEAAVATFAQARPPGIYKGDYLKELFRRYGDIEEAPPPPLLPDWCFEDDEDE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 55 | Endolysin | 1AM7 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name R Organism Escherichia phage lambda (Bacteriophage lambda) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Glycosyl hydrolase 24 family Biochemical class Glycosidase Function Lyase activity.Lysozyme activity.Lytic transglycosylase activity. Related diseases Estrogen resistance (ESTRR) [MIM:615363]: A disorder characterized by partial or complete resistance to estrogens, in the presence of elevated estrogen serum levels. Clinical features include absence of the pubertal growth spurt, delayed bone maturation, unfused epiphyses, reduced bone mineral density, osteoporosis, continued growth into adulthood and very tall adult stature. Glucose intolerance, hyperinsulinemia and lipid abnormalities may also be present. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23841731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27754803}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04206 Interacts with NA EC number 4.2.2.n2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Antimicrobial; Bacteriolytic enzyme; Cytolysis; Direct protein sequencing; Host cell lysis by virus; Host cytoplasm; Lyase; Reference proteome; Viral release from host cell Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 49834.9 Length 462 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 18.78 Isoelectric point 9.6 Charge (pH=7) 18.29 3D Binding mode Sequence MVEINNQRKAFLDMLAXSEGTDNGRQKTRNHGYDVIVGGELFTDYSDHPRKLVTLNPKLKSTGAGRYQLLSRXXDAYRKQLGLKDFSPKSQDAVALQQIKERGALPMIDRGDIRQAIDRCSNIXASLPGAGYGQFEHKADSLIAKFKEAGGTVRMVEINNQRKAFLDMLAXSEGTDNGRQKTRNHGYDVIVGGELFTDYSDHPRKLVTLNPKLKSTGAGRYQLLSRXXDAYRKQLGLKDFSPKSQDAVALQQIKERGALPMIDRGDIRQAIDRCSNIXASLPGAGYGQFEHKADSLIAKFKEAGGTVRMVEINNQRKAFLDMLAXSEGTDNGRQKTRNHGYDVIVGGELFTDYSDHPRKLVTLNPKLKSTGAGRYQLLSRXXDAYRKQLGLKDFSPKSQDAVALQQIKERGALPMIDRGDIRQAIDRCSNIXASLPGAGYGQFEHKADSLIAKFKEAGGTVR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 56 | mRNA-capping enzyme | 2C46 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name RNGTT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CAP1A Protein family Non-receptor class of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase family; Eukaryotic GTase family Biochemical class Transferase Function GTP binding.MRNA guanylyltransferase activity.Polynucleotide 5'-phosphatase activity.Protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity.Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity.RNA guanylyltransferase activity.Triphosphatase activity. Related diseases Atrial fibrillation, familial, 14 (ATFB14) [MIM:615378]: A familial form of atrial fibrillation, a common sustained cardiac rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity and ineffective atrial contraction promoting blood stasis in the atria and reduces ventricular filling. It can result in palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19808477}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Genetic variations in SCN2B may be involved in Brugada syndrome (PubMed:23559163). This tachyarrhythmia is characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs, the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23559163}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q92624; P16333-1 EC number 2.7.7.50; 3.6.1.74 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; GTP-binding; Host-virus interaction; Hydrolase; mRNA capping; mRNA processing; Multifunctional enzyme; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleotidyltransferase; Nucleus; Protein phosphatase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 21849.8 Length 189 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 53.71 Isoelectric point 5.89 Charge (pH=7) -2.91 3D Binding mode Sequence NKIPPRWLNCPRRGQPVAGRFLPLKTMLGPRYDSQVAEENRFHPSMLSNYLKSVKMGLLVDLTNTSRFYDRNDIEKEGIKYIKLQCKGHGECPTTENTETFIRLCERFELIGVHCTHGFNRTGFLICAFLVEKMDWSIEAAVATFAQARPPGIYKGDYLKELFRRYGDIEEAPPPPLLPDWCFEDDEDE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 57 | Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (PLAU) | 4JNI | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name PLAU Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms UPA; U-plasminogen activator Protein family Peptidase S1 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Specifically cleaves the zymogen plasminogen to form the active enzyme plasmin. Related diseases Quebec platelet disorder (QPD) [MIM:601709]: An autosomal dominant bleeding disorder due to a gain-of-function defect in fibrinolysis. Although affected individuals do not exhibit systemic fibrinolysis, they show delayed onset bleeding after challenge, such as surgery. The hallmark of the disorder is markedly increased PLAU levels within platelets, which causes intraplatelet plasmin generation and secondary degradation of alpha-granule proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20007542}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07129; DB07122; DB01905; DB02287; DB03729; DB01725; DB08072; DB07625; DB07626; DB08697; DB03136; DB01977; DB07076; DB03082; DB02705; DB02473; DB02398; DB02551; DB03865; DB06855; DB06856; DB03046; DB04059; DB04172; DB00594; DB03127; DB02526; DB03159; DB05254; DB03782; DB06857; DB16701; DB03876; DB03476 Interacts with Q9UKQ2; P05067; Q03405-1; P05121; P55000 EC number EC 3.4.21.73 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Blood coagulation; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; EGF-like domain; Fibrinolysis; Glycoprotein; Hemostasis; Hydrolase; Kringle; Pharmaceutical; Phosphoprotein; Plasminogen activation; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Serine protease; Signal; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID U Molecular weight (Da) 25825.3 Length 229 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 47.36 Isoelectric point 8.65 Charge (pH=7) 5.38 3D Binding mode Sequence IIGGEFTTIENQPWFAAIYRRSVTYVCGGSLISPCWVISATHCFPKKEDYIVYLGRSRLNSNTQGEMKFEVENLILHKDYSALAHHNDIALLKIRRCAQPSRTIQTIALPSMYNDPQFGTSCEITGFGKEQSTDYLYPEQLKMTVVKLISHRECQQHYYGSEVTTKMLCAAQWKTDSCQGDSGGPLVCSLQGRMTLTGIVSWGRGCALDKPGVYTRVSHFLPWIRSHTK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 58 | Ornithine delta-aminotransferase (OAT) | 2OAT | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name OAT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Ornithine--oxo-acid aminotransferase; Ornithine aminotransferase, mitochondrial Protein family Class-III pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent aminotransferase family Biochemical class Transaminase Function Catalyzes the transfer of the delta-amino group from L-ornithine. Related diseases Hyperornithinemia with gyrate atrophy of choroid and retina (HOGA) [MIM:258870]: A disorder clinically characterized by a triad of progressive chorioretinal degeneration, early cataract formation, and type II muscle fiber atrophy. Characteristic chorioretinal atrophy with progressive constriction of the visual fields leads to blindness at the latest during the sixth decade of life. Patients generally have normal intelligence. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1612597, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1737786, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23076989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2793865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3375240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7668253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7887415}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02821; DB02054; DB00129; DB00114 Interacts with P05067 EC number EC 2.6.1.13 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Aminotransferase; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Mitochondrion; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome; Transferase; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 44807.9 Length 404 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 26.67 Isoelectric point 5.72 Charge (pH=7) -6.54 3D Binding mode Sequence GPPTSDDIFEREYKYGAHNYHPLPVALERGKGIYLWDVEGRKYFDFLSSYSAVNQGHCHPKIVNALKSQVDKLTLTSRAFYNNVLGEYEEYITKLFNYHKVLPMNTGVEAGETACKLARKWGYTVKGIQKYKAKIVFAAGNFWGRTLSAISSSTDPTSYDGFGPFMPGFDIIPYNDLPALERALQDPNVAAFMVEPIQGEAGVVVPDPGYLMGVRELCTRHQVLFIADEIQTGLARTGRWLAVDYENVRPDIVLLGKALSGGLYPVSAVLCDDDIMLTIKPGEHGSTYGGNPLGCRVAIAALEVLEEENLAENADKLGIILRNELMKLPSDVVTAVRGKGLLNAIVIKETKDWDAWKVCLRLRDNGLLAKPTHGDIIRFAPPLVIKEDELRESIEIINKTILSF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 59 | Ornithine decarboxylase (ODC1) | 2OO0 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name ODC1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms ODC Protein family Orn/Lys/Arg decarboxylase class-II family Biochemical class Carbon-carbon lyase Function Polyamines are essential for cell proliferation and are implicated in cellular processes, ranging from DNA replication to apoptosis. Catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step of polyamine biosynthesis that converts ornithine into putrescine, which is the precursor for the polyamines, spermidine and spermine. Related diseases Bachmann-Bupp syndrome (BABS) [MIM:619075]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by global developmental delay, alopecia, absolute or relative macrocephaly, and facial dysmorphism. Neuroimaging shows white matter abnormalities, prominent Virchow-Robin spaces, periventricular cysts, and abnormalities of the corpus callosum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30239107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30475435}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BABS is due to truncating variants that lead to a gain of function. This phenomenon apparently results from truncation proximal to or involving the C-terminal region of ODC1 protein, distal enough to allow escape from nonsense-mediated decay. A gain of function is corroborated by elevated plasma levels of N-acetylputrescine, with otherwise normal polyamine levels, in affected individuals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30475435}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06243; DB04263; DB03856; DB04083; DB02824; DB01917; DB00114; DB02209; DB00203; DB00127; DB00313 Interacts with Q9H8Y8; Q92993; Q9UMX2; Q9UMX2-2 EC number EC 4.1.1.17 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Decarboxylase; Disease variant; Hypotrichosis; Lyase; Phosphoprotein; Polyamine biosynthesis; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 45682.9 Length 410 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 40.93 Isoelectric point 5.61 Charge (pH=7) -6.68 3D Binding mode Sequence LMNNFGNEEFDCHFLDEGFTAKDILDQKINEVSSSDDKDAFYVADLGDILKKHLRWLKALPRVTPFYAVKCNDSKAIVKTLAATGTGFDCASKTEIQLVQSLGVPPERIIYANPCKQVSQIKYAANNGVQMMTFDSEVELMKVARAHPKAKLVLRIATDDSKAVCRLSVKFGATLRTSRLLLERAKELNIDVVGVSFHVGSGCTDPETFVQAISDARCVFDMGAEVGFSMYLLDIGGGFPGSEDVKLKFEEITGVINPALDKYFPSDSGVRIIAEPGRYYVASAFTLAVNIIAKKIVLEQTFMYYVNDGVYGSFNCILYDHAHVKPLLQKRPKPDEKYYSSSIWGPTCDGLDRIVERCDLPEMHVGDWMLFENMGAYTVAAASTFNGFQRPTIYYVMSGPAWQLMQQFQN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 60 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] | 3EYA | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name poxB Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b0871;JW0855 Protein family TPP enzyme family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.Identical protein binding.Lipid binding.Magnesium ion binding.Pyruvate dehydrogenase (quinone) activity.Thiamine pyrophosphate binding. Related diseases Glycogen storage disease 6 (GSD6) [MIM:232700]: A metabolic disorder characterized by mild to moderate hypoglycemia, mild ketosis, growth retardation, and prominent hepatomegaly. Heart and skeletal muscle are not affected. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9529348}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P07003 EC number 1.2.5.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell inner membrane; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; Lipid-binding; Magnesium; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Oxidoreductase; Pyruvate; Reference proteome; Thiamine pyrophosphate; Ubiquinone Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I,J,K,L Molecular weight (Da) 113027 Length 1046 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 35.99 Isoelectric point 5.75 Charge (pH=7) -24.38 3D Binding mode Sequence MKQTVAAYIAKTLESAGVKRIWGVTGDSLNGLSDSLNRMGTIEWMSTRHEEVAAFAAGAEAQLSGELAVCAGSCGPGNLHLINGLFDCHRNHVPVLAIAAHIPSSEIGSGYFQETHPQELFRECSHYCELVSSPEQIPQVLAIAMRKAVLNRGVSVVVLPGDVALKPAPEGATMHWYHAPQPVVTPEEEELRKLAQLLRYSSNIALMCGSGCAGAHKELVEFAGKIKAPIVHALRGKEHVEYDNPYDVGMTGLIGFSSGFHTMMNADTLVLLGTQFPYRAFYPTDAKIIQIDINPASIGAHSKVDMALVGDIKSTLRALLPLVEEKADRKFLDKALEDYRDARKGLDDLAKPSEKAIHPQYLAQQISHFAADDAIFTCDVGTPTVWAARYLKMNGKRRLLGSFNHGSMANAMPQALGAQATEPERQVVAMCGDGGFSMLMGDFLSVVQMKLPVKIVVFNNSVLGFDGTELHDTNFARIAEACGITGIRVEKASEVDEALQRAFSIDGPVLVDVVVAKEELAIPMKQTVAAYIAKTLESAGVKRIWGVTGDSLNGLSDSLNRMGTIEWMSTRHEEVAAFAAGAEAQLSGELAVCAGSCGPGNLHLINGLFDCHRNHVPVLAIAAHIPSSEIGSGYFQETHPQELFRECSHYCELVSSPEQIPQVLAIAMRKAVLNRGVSVVVLPGDVALKPAPEGATMHWYHAPQPVVTPEEEELRKLAQLLRYSSNIALMCGSGCAGAHKELVEFAGKIKAPIVHALRGKEHVEYDNPYDVGMTGLIGFSSGFHTMMNADTLVLLGTQFPYRAFYPTDAKIIQIDINPASIGAHSKVDMALVGDIKSTLRALLPLVEEKADRKFLDKALEDYRDARKGLDDLAKPSEKAIHPQYLAQQISHFAADDAIFTCDVGTPTVWAARYLKMNGKRRLLGSFNHGSMANAMPQALGAQATEPERQVVAMCGDGGFSMLMGDFLSVVQMKLPVKIVVFNNSVLGFVGTELHDTNFARIAEACGITGIRVEKASEVDEALQRAFSIDGPVLVDVVVAKEELAIP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||