Job Results:
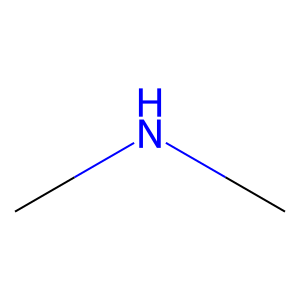
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
4d96340bab84003cd843e60272b3611c
Job name
NA
Time
2025-02-13 15:23:33
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | Lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase (EC 1.14.13.70) | 4G3J | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name Tb11.02.4080 Organism Trypanosoma brucei brucei (strain 927/4 GUTat10.1) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Cytochrome P450 family Biochemical class NA Function NA Related diseases LTC4 synthase deficiency is associated with a neurometabolic developmental disorder characterized by muscular hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, and microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10896305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9820300}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 1.14.13.70 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Heme; Iron; Metal-binding; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID D Molecular weight (Da) 50691.4 Length 448 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 54.09 Isoelectric point 6.99 Charge (pH=7) -0.03 3D Binding mode Sequence GKLPPVYPVTVPILGHIIQFGKSPLGFMQECKRQLKSGIFTINIVGKRVTIVGDPHEHSRFFLPRNEVLSPREVYSFMVPVFGEGVAYAAPYPRMREQLNFLAEELTIAKFQNFVPAIQHEVRKFMAANWDKDEGEINLLEDCSTMIINTACQCLFGEDLRKRLDARRFAQLLAKMESSLIPAAVFLPILLKLPLPQSARCHEARTELQKILSEIIIARKEEEVNKDSSTSDLLSGLLSAVYRDGTPMSLHEVCGMIVAAMFAGQHTSSITTTWSMLHLMHPANVKHLEALRKEIEEFPAQLNYNNVMDEMPFAERCARESIRRDPPLLMLMRKVMADVKVGSYVVPKGDIIACSPLLSHHDEEAFPEPRRWDPERDEKVEGAFIGFGAGVHKCIGQKFGLLQVKTILATAFRSYDFQLLRDEVPDPDYHTMVVGPTASQCRVKYIRR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 42 | Alr1529 protein | 1Z8H | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name alr1529 Organism Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family NA Biochemical class Hydrolase Function NA Related diseases Desbuquois dysplasia 1 (DBQD1) [MIM:251450]: A chondrodysplasia characterized by severe prenatal and postnatal growth retardation (less than -5 SD), joint laxity, short extremities, progressive scoliosis, round face, midface hypoplasia, prominent bulging eyes. The main radiologic features are short long bones with metaphyseal splay, a 'Swedish key' appearance of the proximal femur (exaggerated trochanter), and advance carpal and tarsal bone age. Two forms of Desbuquois dysplasia are distinguished on the basis of the presence or absence of characteristic hand anomalies: an extra ossification center distal to the second metacarpal, delta phalanx, bifid distal thumb phalanx, and phalangeal dislocations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19853239, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20425819, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21037275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21412251, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21654728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22539336}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epiphyseal dysplasia, multiple, 7 (EDM7) [MIM:617719]: A form of multiple epiphyseal dysplasia, a generalized skeletal dysplasia associated with significant morbidity. Joint pain, joint deformity, waddling gait, and short stature are the main clinical signs and symptoms. Radiological examination of the skeleton shows delayed, irregular mineralization of the epiphyseal ossification centers and of the centers of the carpal and tarsal bones. Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia is broadly categorized into the more severe Fairbank and the milder Ribbing types. The Fairbank type is characterized by shortness of stature, short and stubby fingers, small epiphyses in several joints, including the knee, ankle, hand, and hip. The Ribbing type is confined predominantly to the hip joints and is characterized by hands that are normal and stature that is normal or near-normal. EDM7 inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28742282}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 45603.2 Length 401 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 49.26 Isoelectric point 7.67 Charge (pH=7) 1.26 3D Binding mode Sequence KTQIRICFVGDSFVNGTGDPECLGWTGRVCVNANKKGYDVTYYNLGIRRDTSSDIAKRWLQEVSLRLHKEYNSLVVFSFGLNDTTLENGKPRVSIAETIKNTREILTQAKKLYPVLXISPAPYIEQQDPGRRRRTIDLSQQLALVCQDLDVPYLDVFPLLEKPSVWLHEAKANDGVHPQAGGYTEFARIVENWDAWLNWFRKTQIRICFVGDSFVNGTGDPECLGWTGRVCVNANKKGYDVTYYNLGIRRDTSSDIAKRWLQEVSLRLHKEYNSLVVFSFGLNDTTLENGKPRVSIAETIKNTREILTQAKKLYPVLXISPAPYIEQQDPGRRRRTIDLSQQLALVCQDLDVPYLDVFPLLEKPSVWLHEAKANDGVHPQAGGYTEFARIVENWDAWLNWF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 43 | Protein cereblon (CRBN) | 5FQD | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name CRBN Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein cereblon Protein family CRBN family Biochemical class NA Function Substrate recognition component of a DCX (DDB1-CUL4-X-box) E3 protein ligase complex that mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins, such as MEIS2. Normal degradation of key regulatory proteins is required for normal limb outgrowth and expression of the fibroblast growth factor FGF8. May play a role in memory and learning by regulating the assembly and neuronal surface expression of large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in brain regions involved in memory and learning via its interaction with KCNT1. Binding of pomalidomide and other thalidomide-related drugs changes the substrate specificity of the human protein, leading to decreased degradation of MEIS2 and other target proteins and increased degradation of MYC, IRF4, IKZF1 and IKZF3. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 2 (MRT2) [MIM:607417]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRT2 patients display mild intellectual disability with a standard IQ ranged from 50 to 70. IQ scores are lower in males than females. Developmental milestones are mildly delayed. There are no dysmorphic or autistic features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15557513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28143899}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00480; DB08910; DB01041 Interacts with Q96A83-2; P48729; Q16531; O14901; Q8IVT2; Q9P286; A0A6Q8PF08; Q93062; Q16531; Q13422-7 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation; Ubl conjugation pathway; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B,E Molecular weight (Da) 38245.7 Length 337 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 40.62 Isoelectric point 5.7 Charge (pH=7) -6.53 3D Binding mode Sequence EFIVGGKYKLNITNGEEVAVINFDTSLPTSHTYLGADMEEFHGRTLHDDDSCQVIPVLPQVMMILIPGQTLPLQLFHPQEVSMVRNLIQKDRTFAVLAYSNVQEREAQFGTTAEIYAYREEIVKVKAIGRQRFKVLEQQAKVQILPECVLAETLMDRIKKQLREWDENLKDDSLPSNPIDFSYRVAACLPIDDVLRIQLLKIGSAIQRLRCELDIMNKCTSLCCKQCQETEITTKNEIFSLSLCGPMAAYVNPHGYVHETLTVYKACNLNLIGRPSTEHSWFPGYAWTVAQCKICASHIGWKFTATKKDMSPQKFWGLTRSALLPTIPDTEDEISPD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 44 | Plasmodium Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (Malaria DHOdehase) | 1TV5 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name Malaria DHOdehase Organism Plasmodium falciparum (isolate 3D7) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PFF0160c; Mitochondrially bound dihydroorotate-ubiqui oxidoreductase; Dihydroorotate oxidase of Plasmodium falciparum; Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase of Plasmodium falciparum; DHOdehase of Plasmodium fa Protein family Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase family, Type 2 subfamily Biochemical class CH-CH donor oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the conversion of dihydroorotate to orotate with quinone as electron acceptor. Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 33 (COXPD33) [MIM:617713]: An autosomal recessive disorder caused by multiple mitochondrial respiratory chain defects and impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism. Clinical manifestations are highly variable. Affected infants present with cardiomyopathy accompanied by multisystemic features involving liver, kidney, and brain. Death in infancy is observed in some patients. Children and adults present with myopathy and progressive external ophthalmoplegia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28942965}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01117 Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.3.5.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Flavoprotein; FMN; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Oxidoreductase; Pyrimidine biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Transit peptide; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 41846.8 Length 371 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.25 Isoelectric point 8.21 Charge (pH=7) 3.13 3D Binding mode Sequence FESYNPEFFLYDIFLKFCLKYIDGEICHDLFLLLGKYNILPYDTSNDSIYACTNIKHLDFINPFGVAAGFDKNGVCIDSILKLGFSFIEIGTITPRGQTGNAKPRIFRDVESRSIINSCGFNNMGCDKVTENLILFRKRQEEDKLLSKHIVGVSIGKNKDTVNIVDDLKYCINKIGRYADYIAINVSSPNTPGLRDNQEAGKLKNIILSVKEEIDNLEFLWFNTTKKKPLVFVKLAPDLNQEQKKEIADVLLETNIDGMIISNTTTQINDIKSFENKKGGVSGAKLKDISTKFICEMYNYTNKQIPIIASGGIFSGLDALEKIEAGASVCQLYSCLVFNGMKSAVQIKRELNHLLYQRGYYNLKEAIGRKH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 45 | Orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase (UMPS) | 3MI2 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name UMPS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Uridine 5'-monophosphate synthase; UMP synthase Protein family Purine/pyrimidine phosphoribosyltransferase family; OMP decarboxylase family Biochemical class Pentosyltransferase Function Catalyses the formation of uridine monophosphate (UMP), an energy-carrying molecule in many important biosynthetic pathways. Related diseases Orotic aciduria 1 (ORAC1) [MIM:258900]: A disorder of pyrimidine metabolism resulting in megaloblastic anemia and orotic acid crystalluria that is frequently associated with some degree of physical and intellectual disability. A minority of cases have additional features, particularly congenital malformations and immune deficiencies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9042911}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02890; DB00544 Interacts with P54764; P11172-1 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Decarboxylase; Disease variant; Glycosyltransferase; Lyase; Multifunctional enzyme; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Pyrimidine biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 55844 Length 514 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 22.7 Isoelectric point 6.44 Charge (pH=7) -2.99 3D Binding mode Sequence KELSFGARAELPRIHPVASKLLRLMQKKETNLCLSADVSLARELLQLADALGPSICMLKTHVDILNDFTLDVMKELITLAKXHEFLIFEDRKFADIGNTVKKQYEGGIFKIASWADLVNAHVVPGSGVVKGLQEVGLPLHRGCLLIAEMSSTGSLATGDYTRAAVRMAEEHSEFVVGFISGSRVSMKPEFLHLTPGVQLEAGGDNLGQQYNSPQEVIGKRGSDIIIVGRGIISAADRLEAAEMYRKAAWEAYLSRLGKELSFGARAELPRIHPVASKLLRLMQKKETNLCLSADVSLARELLQLADALGPSICMLKTHVDILNDFTLDVMKELITLAKXHEFLIFEDRKFADIGNTVKKQYEGGIFKIASWADLVNAHVVPGSGVVKGLQEVGLPLHRGCLLIAEMSSTGSLATGDYTRAAVRMAEEHSEFVVGFISGSRVSMKPEFLHLTPGVQLEAGGDNLGQQYNSPQEVIGKRGSDIIIVGRGIISAADRLEAAEMYRKAAWEAYLSRLG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 46 | N-acetylgalactosamine 6 sulfatase (GALNS) | 4FDJ | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name GALNS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase; N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase; Galactose-6-sulfate sulfatase; GalNAc6S sulfatase; GalN6S; Chondroitinsulfatase; Chondroitinase Protein family Sulfatase family Biochemical class Sulfuric ester hydrolase Function Catalyzes the chemical reaction of cleaving off the 6-sulfate groups of the N-acetyl-D-galactosamine 6-sulfate units of the macromolecule chondroitin sulfate and, similarly, of the D-galactose 6-sulfate units of the macromolecule keratan sulfate. Related diseases Mucopolysaccharidosis 4A (MPS4A) [MIM:253000]: A form of mucopolysaccharidosis type 4, an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease characterized by intracellular accumulation of keratan sulfate and chondroitin-6-sulfate. Key clinical features include short stature, skeletal dysplasia, dental anomalies, and corneal clouding. Intelligence is normal and there is no direct central nervous system involvement, although the skeletal changes may result in neurologic complications. There is variable severity, but patients with the severe phenotype usually do not survive past the second or third decade of life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1522213, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16287098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24726177, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7581409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7633425, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7668283, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7795586, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8651279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8826435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9298823, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9375852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9521421}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09301 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.1.6.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Calcium; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Dwarfism; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lysosome; Metal-binding; Mucopolysaccharidosis; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 55013.8 Length 493 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 35.46 Isoelectric point 6.14 Charge (pH=7) -6.48 3D Binding mode Sequence PQPPNILLLLMDDMGWGDLGVYGEPSRETPNLDRMAAEGLLFPNFYSANPLXSPSRAALLTGRLPIRNGFYTTNAHARNAYTPQEIVGGIPDSEQLLPELLKKAGYVSKIVGKWHLGHRPQFHPLKHGFDEWFGSPNCHFGPYDNKARPNIPVYRDWEMVGRYYEEFPINLKTGEANLTQIYLQEALDFIKRQARHHPFFLYWAVDATHAPVYASKPFLGTSQRGRYGDAVREIDDSIGKILELLQDLHVADNTFVFFTSDNGAALISAPEQGGSNGPFLCGKQTTFEGGMREPALAWWPGHVTAGQVSHQLGSIMDLFTTSLALAGLTPPSDRAIDGLNLLPTLLQGRLMDRPIFYYRGDTLMAATLGQHKAHFWTWTNSWENFRQGIDFCPGQNVSGVTTHNLEDHTKLPLIFHLGRDPGERFPLSFASAEYQEALSRITSVVQQHQEALVPAQPQLNVCNWAVMNWAPPGCEKLGKCLTPPESIPKKCLW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 47 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) | 6YND | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name GAPDH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylase GAPDH; OK/SW-cl.12; GAPD; D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; CDABP0047 Protein family Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Aldehyde/oxo donor oxidoreductase Function Participates in nuclear events including transcription, RNA transport, DNA replication and apoptosis. Nuclear functions are probably due to the nitrosylase activity that mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of nuclear target proteins such as SIRT1, HDAC2 and PRKDC. Modulates the organization and assembly of the cytoskeleton. Facilitates the CHP1-dependent microtubule and membrane associations through its ability to stimulate the binding of CHP1 to microtubules. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is a key enzyme in glycolysis that catalyzes the first step of the pathway by converting D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) into 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate. Component of the GAIT (gamma interferon-activated inhibitor of translation) complex which mediates interferon-gamma-induced transcript-selective translation inhibition in inflammation processes. Upon interferon-gamma treatment assembles into the GAIT complex which binds to stem loop-containing GAIT elements in the 3'-UTR of diverse inflammatory mRNAs (such as ceruplasmin) and suppresses their translation. Has both glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and nitrosylase activities, thereby playing a role in glycolysis and nuclear functions, respectively. Related diseases Bone marrow failure and diabetes mellitus syndrome (BMFDMS) [MIM:620044]: A form of bone marrow failure syndrome, a heterogeneous group of life-threatening disorders characterized by hematopoietic defects in association with a range of variable extra-hematopoietic manifestations. BMFDMS is an autosomal recessive form characterized by various degrees of bone marrow failure, ranging from dyserythropoiesis to bone marrow aplasia, with onset in infancy or early childhood, and non-autoimmune insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus appearing in the first or second decades. Many patients show pigmentary skin abnormalities and short stature. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28073829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35611808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35931051}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07347; DB02059; DB11638; DB09130; DB00157; DB03893; DB09092 Interacts with Q6UY14-3; Q9UIJ7; P05067; Q9UQM7; Q14194; P35222; Q9BPW9-4; P00533; O00471; O75344; P06241; P04406; O14556; Q8NEA9; P42858; Q92993-2; P42695; P35228; P12004; P00558; P48147; P17612; Q8WUY3; Q9UHX1-2; P15927; P05109; Q96GZ6; P00441; Q9BSI4; P10599 EC number EC 1.2.1.12 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; ADP-ribosylation; Alternative splicing; Apoptosis; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; Glycolysis; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Innate immunity; Isopeptide bond; Membrane; Methylation; NAD; Nucleus; Oxidation; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation; Transferase; Translation regulation; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35818.4 Length 333 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 13.69 Isoelectric point 8.64 Charge (pH=7) 3.64 3D Binding mode Sequence GKVKVGVNGFGRIGRLVTRAAFNSGKVDIVAINDPFIDLNYMVYMFQYDSTHGKFHGTVKAENGKLVINGNPITIFQERDPSKIKWGDAGAEYVVESTGVFTTMEKAGAHLQGGAKRVIISAPSADAPMFVMGVNHEKYDNSLKIISNASTTNCLAPLAKVIHDNFGIVEGLMTTVHAITATQKTVDGPSGKLWRDGRGALQNIIPASTGAAKAVGKVIPELNGKLTGMAFRVPTANVSVVDLTCRLEKPAKYDDIKKVVKQASEGPLKGILGYTEHQVVSSDFNSDTHSSTFDAGAGIALNDHFVKLISWYDNEFGYSNRVVDLMAHMASKE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 48 | Membrane copper amine oxidase (AOC3) | 4BTX | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name AOC3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Vascular adhesion protein-1; Vascular adhesion protein 1; VAP1; VAP-1; Semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase; SSAO; Membrane primary amine oxidase; HPAO; Copper amine oxidase Protein family Copper/topaquinone oxidase family Biochemical class CH-NH(2) donor oxidoreductase Function Has semicarbazide-sensitive (SSAO) monoamine oxidase activity. May play a role in adipogenesis. Cell adhesion protein that participates in lymphocyte extravasation and recirculation by mediating the binding of lymphocytes to peripheral lymph node vascular endothelial cells in an L-selectin-independent fashion. Related diseases Glioma (GLM) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19117336, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. Mutations affecting Arg-132 are tissue-specific, and suggest that this residue plays a unique role in the development of high-grade gliomas. Mutations of Arg-132 to Cys, His, Leu or Ser abolish magnesium binding and abolish the conversion of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate. Instead, alpha-ketoglutarate is converted to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate. Elevated levels of R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate are correlated with an elevated risk of malignant brain tumors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646}.; DISEASE: Genetic variations are associated with cartilaginous tumors such as enchondroma or chondrosarcoma. Mutations of Arg-132 to Cys, Gly or His abolish the conversion of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate. Instead, alpha-ketoglutarate is converted to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26161668}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04334; DB01275; DB00780 Interacts with Q3SXY8; O95484; Q7Z7G2; Q96BA8; Q6PI48; Q8TBE3; Q7Z5P4; P42858; O43765; Q16623 EC number EC 1.4.3.21 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Cell adhesion; Cell membrane; Copper; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal-anchor; TPQ; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 157266 Length 1415 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 39.94 Isoelectric point 6 Charge (pH=7) -23.49 3D Binding mode Sequence PGQSQLFADLSREELTAVMRFLTQRLGPGLVDAAQARPSDNCVFSVELQLPPKAAALAHLDRGSPPPAREALAIVFFGRQPQPNVSELVVGPLPHPSYMRDVTVERHGGPLPYHRRPVLFQEYLDIDQMIFNRELPQASGLLHHCCFYKHRGRNLVTMTTAPRGLQSGDRATWFGLYYNISGAGFFLHHVGLELLVNHKALDPARWTIQKVFYQGRYYDSLAQLEAQFEAGLVNVVLIPDNGTGGSWSLKSPVPPGPAPPLQFYPQGPRFSVQGSRVASSLWTFSFGLGAFSGPRIFDVRFQGERLVYEISLQEALAIYGGNSPAAMTTRYVDGGFGMGKYTTPLTRGVDCPYLATYVDWHFLLESQAPKTIRDAFCVFEQNQGLPLRRHHSDLYSHYFGGLAETVLVVRSMSTLLNXDYVWDTVFHPSGAIEIRFYATGYISSAFLFGATGKYGNQVSEHTLGTVHTHSAHFKVDLDVAGLENWVWAEDMVFVPMAVPWSPEHQLQRLQVTRKLLEMEEQAAFLVGSATPRYLYLASNHSNKWGHPRGYRIQMLSFAGEPLPQNSSMARGFSWERYQLAVTQRKEEEPSSSSVFNQNDPWAPTVDFSDFINNETIAGKDLVAWVTAGFLHIPHAEDIPNTVTVGNGVGFFLRPYNFFDEDPSFYSADSIYFRGDQDAGACEVNPLACLPQAAACAPDLPAFSHGGFSHSQLFADLSREELTAVMRFLTQRLGPGLVDAAQARPSDNCVFSVELQLPPKAAALAHLDRGSPPPAREALAIVFFGRQPQPNVSELVVGPLPHPSYMRDVTVERHGGPLPYHRRPVLFQEYLDIDQMIFNRELPQASGLLHHCCFYKHRGRNLVTMTTAPRGLQSGDRATWFGLYYNISGAGFFLHHVGLELLVNHKALDPARWTIQKVFYQGRYYDSLAQLEAQFEAGLVNVVLIPDNGTGGSWSLKSPVPPGPAPPLQFYPQGPRFSVQGSRVASSLWTFSFGLGAFSGPRIFDVRFQGERLVYEISLQEALAIYGGNSPAAMTTRYVDGGFGMGKYTTPLTRGVDCPYLATYVDWHFLLESQAPKTIRDAFCVFEQNQGLPLRRHHSDLYSHYFGGLAETVLVVRSMSTLLNXDYVWDTVFHPSGAIEIRFYATGYISSAFLFGATGKYGNQVSEHTLGTVHTHSAHFKVDLDVAGLENWVWAEDMVFVPMAVPWSPEHQLQRLQVTRKLLEMEEQAAFLVGSATPRYLYLASNHSNKWGHPRGYRIQMLSFAGEPLPQNSSMARGFSWERYQLAVTQRKEEEPSSSSVFNQNDPWAPTVDFSDFINNETIAGKDLVAWVTAGFLHIPHAEDIPNTVTVGNGVGFFLRPYNFFDEDPSFYSADSIYFRGDQDAGACEVNPLACLPQAAACAPDLPAFSHGGFSH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 49 | Cathepsin F (CTSF) | 1M6D | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name CTSF Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CATSF Protein family Peptidase C1 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Has also been implicated in tumor invasion and metastasis. Thiol protease which is believed to participate in intracellular degradation and turnover of proteins. Related diseases Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, 13 (Kufs type) (CLN13) [MIM:615362]: A form of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis characterized by adult onset of progressive cognitive decline and motor dysfunction leading to dementia and often early death. Some patients develop seizures. Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses are progressive neurodegenerative, lysosomal storage diseases characterized by intracellular accumulation of autofluorescent liposomal material. CLN13 inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23297359}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02243; DB01871; DB01810; DB08775; DB03536; DB07913; DB03691; DB03573 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.4.22.41 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lysosome; Neurodegeneration; Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal; Thiol protease; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23634.4 Length 214 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 39.11 Isoelectric point 5.82 Charge (pH=7) -2.9 3D Binding mode Sequence APPEWDWRSKGAVTKVKDQGMCGSCWAFSVTGNVEGQWFLNQGTLLSLSEQELLDCDKMDKACMGGLPSNAYSAIKNLGGLETEDDYSYQGHMQSCQFSAEKAKVYIQDSVELSQNEQKLAAWLAKRGPISVAINAFGMQFYRHGISRPLRPLCSPWLIDHAVLLVGYGQRSDVPFWAIKNSWGTDWGEKGYYYLHRGSGACGVNTMASSAVVD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 50 | Triggering receptor expressed on monocytes 1 (TREM1) | 1Q8M | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name Trem1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Trem1; TREM-1 Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Stimulates neutrophil and monocyte-mediated inflammatory responses. Triggers release of pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines, as well as increased surface expression of cell activation markers. Amplifier of inflammatory responses that are triggered by bacterial and fungal infections and is a crucial mediator of septic shock. Related diseases GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 1 (GLUT1DS1) [MIM:606777]: A neurologic disorder showing wide phenotypic variability. The most severe 'classic' phenotype comprises infantile-onset epileptic encephalopathy associated with delayed development, acquired microcephaly, motor incoordination, and spasticity. Onset of seizures, usually characterized by apneic episodes, staring spells, and episodic eye movements, occurs within the first 4 months of life. Other paroxysmal findings include intermittent ataxia, confusion, lethargy, sleep disturbance, and headache. Varying degrees of cognitive impairment can occur, ranging from learning disabilities to severe intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10227690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10980529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11136715, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11603379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12325075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15622525, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19901175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20129935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20221955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20574033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24847886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30197081}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 2 (GLUT1DS2) [MIM:612126]: A clinically variable disorder characterized primarily by onset in childhood of paroxysmal exercise-induced dyskinesia. The dyskinesia involves transient abnormal involuntary movements, such as dystonia and choreoathetosis, induced by exercise or exertion, and affecting the exercised limbs. Some patients may also have epilepsy, most commonly childhood absence epilepsy. Mild intellectual disability may also occur. In some patients involuntary exertion-induced dystonic, choreoathetotic, and ballistic movements may be associated with macrocytic hemolytic anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14605501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18451999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19630075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19798636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20129935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20574033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20621801, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20830593, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21204808}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epilepsy, idiopathic generalized 12 (EIG12) [MIM:614847]: A disorder characterized by recurring generalized seizures in the absence of detectable brain lesions and/or metabolic abnormalities. Generalized seizures arise diffusely and simultaneously from both hemispheres of the brain. Seizure types include juvenile myoclonic seizures, absence seizures, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. In some EIG12 patients seizures may remit with age. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19798636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22282645, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23280796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Dystonia 9 (DYT9) [MIM:601042]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder characterized by childhood onset of paroxysmal choreoathetosis and progressive spastic paraplegia. Most patients show some degree of cognitive impairment. Other variable features may include seizures, migraine headaches, and ataxia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21832227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Stomatin-deficient cryohydrocytosis with neurologic defects (SDCHCN) [MIM:608885]: A rare form of stomatocytosis characterized by episodic hemolytic anemia, cold-induced red cells cation leak, erratic hyperkalemia, neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, hepatosplenomegaly, cataracts, seizures, intellectual disability, and movement disorder. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21791420, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22492876}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01694 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Immunoglobulin domain; Innate immunity; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 28186.2 Length 242 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 45.2 Isoelectric point 6.1 Charge (pH=7) -3.8 3D Binding mode Sequence MELRAATKLTEEKYELKEGQTLDVKCDYTLEKFASSQKAWQIIRDGEMPKTLACTERPSKNSHPVQVGRIILEDYHDHGLLRVRMVNLQVEDSGLYQCVIYQPPKEPHMLFDRIRLVVTLEMELRAATKLTEEKYELKEGQTLDVKCDYTLEKFASSQKAWQIIRDGEMPKTLACTERPSKNSHPVQVGRIILEDYHDHGLLRVRMVNLQVEDSGLYQCVIYQPPKEPHMLFDRIRLVVTLE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 51 | NAPE-hydrolyzing phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD) | 4QN9 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name NAPEPLD Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NAPE-PLD; N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolyzing phospholipase D; N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D; C7orf18 Protein family NAPE-PLD family Biochemical class NA Function Hydrolyzes N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamines (NAPEs) to produce N-acylethanolamines (NAEs) and phosphatidic acid. Responsible for the generation of these bioactive fatty acid ethanolamides (FAEs), including anandamide (N-arachidonoylethanolamine), the ligand of cannabinoid and vanilloid receptors. As a regulator of lipid metabolism in the adipose tissue, mediates the crosstalk between adipocytes, gut microbiota and immune cells to control body temperature and weight. In particular, regulates energy homeostasis by promoting cold-induced brown or beige adipocyte differentiation program to generate heat from fatty acids and glucose (By similarity). Related diseases Glioma (GLM) [MIM:137800]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539269}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. H3F3A mutations affecting residues involved in post-translational modifications of histone H3.3 are recurrent in malignant, aggressive gliomas including glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) (PubMed:22286061, PubMed:22286216). The mechanism through which mutations lead to tumorigenesis involves altered histones methylation, impaired regulation of Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) activity, and aberrant epigenetic regulation of gene expression (PubMed:23539183, PubMed:23539269, PubMed:23603901). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22286216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23539269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23603901}.; DISEASE: Bryant-Li-Bhoj neurodevelopmental syndrome 1 (BRYLIB1) [MIM:619720]: An autosomal dominant disorder predominantly characterized by global developmental delay, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and delayed motor milestones. Clinical manifestations are highly variable, including abnormal head shape, dysmorphic facial features, oculomotor abnormalities, feeding problems, and non-specific brain imaging abnormalities. Additional features may include hearing loss, seizures, short stature, and mild skeletal defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BRYLIB1 is caused by variants in H3-3A. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}.; DISEASE: Bryant-Li-Bhoj neurodevelopmental syndrome 2 (BRYLIB2) [MIM:619721]: An autosomal dominant disorder predominantly characterized by global developmental delay, impaired intellectual development, poor or absent speech, and delayed motor milestones. Clinical manifestations are highly variable, including abnormal head shape, dysmorphic facial features, oculomotor abnormalities, feeding problems, and non-specific brain imaging abnormalities. Additional features may include hearing loss, seizures, short stature, and mild skeletal defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. BRYLIB2 is caused by variants in H3-3B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34876591}.; DISEASE: H3F3A and H3F3B mutations affecting residues involved in post-translational modifications of histone H3.3 are implicated in the pathogenesis of some bone and cartilage neoplasms. Mutations have been found with high prevalence in chondroblastoma and giant cell tumors of bone, and with low frequency in osteosarcoma, conventional chondrosarcoma and clear cell chondrosarcoma. Chondroblastoma samples frequently carry a H3F3B mutation affecting residue Lys-37 (H3K36), although H3F3A is mutated in some cases. Most giant cell tumors of bone harbor H3F3A mutations affecting residue Gly-35 (H3G34). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24162739}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB14009 Interacts with Q6IQ20 EC number EC 3.1.4.54 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Endosome; Golgi apparatus; Hydrolase; Lipid degradation; Lipid metabolism; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phospholipid degradation; Phospholipid metabolism; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 74256.5 Length 643 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 48.34 Isoelectric point 5.65 Charge (pH=7) -17.61 3D Binding mode Sequence SKKGKDGRFVNPWPTWKNPSIPNSSVPSSKEELDKELPVLKPYFITNPEEAGVREAGLRVTWLGHATVMVEMDELIFLTDPIFSSRASPSQYMGPKRFRRSPCTISELPPIDAVLISHNHYDHLDYNSVIALNERFGNELRWFVPLGLLDWMQKCGCENVIELDWWEENCVPGHDKVTFVFTPSQHWCKRTLMDDNKVLWGSWSVLGPWNRFFFAGDTGYCPAFEEIGKRFGPFDLAAIPIGAYEPRWFMKYQHVDPEEAVRIHTDVQTKKSMAIHWGTFALANEHYLEPPVKLNEALERYGLNAEDFFVLKHGESRYLNNSKKGKDGRFVNPWPTWKNPSIPNSSVPSSKEELDKELPVLKPYFITNPEEAGVREAGLRVTWLGHATVMVEMDELIFLTDPIFSSRASPSQYMGPKRFRRSPCTISELPPIDAVLISHNHYDHLDYNSVIALNERFGNELRWFVPLGLLDWMQKCGCENVIELDWWEENCVPGHDKVTFVFTPSQHWCKRTLMDDNKVLWGSWSVLGPWNRFFFAGDTGYCPAFEEIGKRFGPFDLAAIPIGAYEPRWFMKYQHVDPEEAVRIHTDVQTKKSMAIHWGTFALANEHYLEPPVKLNEALERYGLNAEDFFVLKHGESRYLNND Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 52 | Neprilysin | 1R1H | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name MME Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms EPN Protein family Peptidase M13 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Endopeptidase activity.Exopeptidase activity.Metalloendopeptidase activity.Metallopeptidase activity.Peptide binding.Zinc ion binding. Related diseases Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, 2T (CMT2T) [MIM:617017]: An axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal degeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26991897, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27588448}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spinocerebellar ataxia 43 (SCA43) [MIM:617018]: A form of spinocerebellar ataxia, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of cerebellar disorders. Patients show progressive incoordination of gait and often poor coordination of hands, speech and eye movements, due to degeneration of the cerebellum with variable involvement of the brainstem and spinal cord. SCA43 is a slowly progressive, autosomal dominant form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27583304}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08575; DB02597; DB00616; DB11623; DB05796; DB06655; DB02558; DB02062; DB00886; DB02557; DB09292; DB13928; DB08626 Interacts with P05067; P21926; Q06787-7; P08107; P04792 EC number 3.4.24.11 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Myristate; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathy; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal-anchor; Spinocerebellar ataxia; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 79435.8 Length 696 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.5 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -11.46 3D Binding mode Sequence GICKSSDCIKSAARLIQNMDATTEPCTDFFKYACGGWLKRNVIPETSSRYGNFDILRDELEVVLKDVLQEPKTEDIVAVQKAKALYRSCINESAIDSRGGEPLLKLLPDIYGWPVATENWEQKYGASWTAEKAIAQLNSKYGKKVLINLFVGTDDKNSVNHVIHIDQPRLGLPSRDYYECTGIYKEACTAYVDFMISVARLIRQEERLPIDENQLALEMNKVMELEKEIANATAKPEDRNDPMLLYNKMTLAQIQNNFSLEINGKPFSWLNFTNEIMSTVNISITNEEDVVVYAPEYLTKLKPILTKYSARDLQNLMSWRFIMDLVSSLSRTYKESRNAFRKALYGTTSETATWRRCANYVNGNMENAVGRLYVEAAFAGESKHVVEDLIAQIREVFIQTLDDLTWMDAETKKRAEEKALAIKERIGYPDDIVSNDNKLNNEYLELNYKEDEYFENIIQNLKFSQSKQLKKLREKVDKDEWISGAAVVNAFYSSGRNQIVFPAGILQPPFFSAQQSNSLNYGGIGMVIGHEITHGFDDNGRNFNKDGDLVDWWTQQSASNFKEQSQCMVYQYGNFSWDLAGGQHLNGINTLGENIADNGGLGQAYRAYQNYIKKNGEEKLLPGLDLNHKQLFFLNFAQVWCGTYRPEYAVNSIKTDVHSPGNFRIIGTLQNSAEFSEAFHCRKNSYMNPEKKCRVW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 53 | Coagulation factor VII (F7) | 4YLQ | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name F7 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Serum prothrombin conversion accelerator; SPCA; Proconvertin; Eptacog alfa Protein family Peptidase S1 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Initiates the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. Serine protease that circulates in the blood in a zymogen form. Factor VII is converted to factor VIIa by factor Xa, factor XIIa, factor IXa, or thrombin by minor proteolysis. In the presence of tissue factor and calcium ions, factor VIIa then converts factor X to factor Xa by limited proteolysis. Factor VIIa will also convert factor IX to factor IXa in the presence of tissue factor and calcium. Related diseases Factor VII deficiency (FA7D) [MIM:227500]: A hemorrhagic disease with variable presentation. The clinical picture can be very severe, with the early occurrence of intracerebral hemorrhages or repeated hemarthroses, or, in contrast, moderate with cutaneous-mucosal hemorrhages (epistaxis, menorrhagia) or hemorrhages provoked by a surgical intervention. Finally, numerous subjects are completely asymptomatic despite very low factor VII levels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10862079, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11091194, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11129332, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12472587, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14717781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1634227, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18976247, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19432927, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19751712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2070047, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21206266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21372693, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26761581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7974346, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7981691, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8043443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8204879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8242057, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8364544, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8652821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8844208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8883260, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8940045, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9414278, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452082, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9576180}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04590; DB07207; DB04758; DB04606; DB04593; DB07376; DB07247; DB08232; DB06552; DB13151; DB00100; DB13152; DB00036; DB09332; DB04767; DB13933 Interacts with P13726 EC number EC 3.4.21.21 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Blood coagulation; Calcium; Cleavage on pair of basic residues; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; EGF-like domain; Gamma-carboxyglutamic acid; Glycoprotein; Hemostasis; Hydrolase; Hydroxylation; Pharmaceutical; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Serine protease; Signal; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID H Molecular weight (Da) 26492.2 Length 240 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 34.61 Isoelectric point 6.81 Charge (pH=7) -0.52 3D Binding mode Sequence IVGGKVCPKGECPWQVLLLVNGAQLCGGTLINTIWVVSAAHCFNWRNLIAVLGEHDLSEHDGDEQSRRVAQVIIPSTYVPGTTNHDIALLRLHQPVVLTDHVVPLCLPERTFTLAFVRFSLVSGWGQLLDRGATALELMVLNVPRLMTQDCEASFPGKITEYMFCGYSDSKDSCKGDSGGPHATHYRGTWYLTGIVSWGQGCATVGHFGVYTRVSQYIEWLQKLMRSEPRPGVLLRAPFP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 54 | DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit A | 1ZVT | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name parC Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b3019;JW2987 Protein family Type II topoisomerase GyrA/ParC subunit family, ParC type 1 subfamily Biochemical class Isomerase Function ATP binding.DNA binding.DNA topoisomerase type II (ATP-hydrolyzing) activity. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB11943; DB12924; DB00817 Interacts with P22523; P0A7K2 EC number 5.6.2.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; DNA-binding; Isomerase; Membrane; Reference proteome; Topoisomerase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 26490.3 Length 246 Aromaticity 0.04 Instability index 46.03 Isoelectric point 8.94 Charge (pH=7) 2.83 3D Binding mode Sequence SEPVTIVLSQMGWVRSAKGHDIDAPGLNYKAGDSFKAAVKGKSNQPVVFVDSTGRSYAIDPITLPSARGQGEPLTGKLTLPPGATVDHMLMESDDQKLLMASDAGYGFVCTFNDLVARNRAGKALITLPENAHVMPPVVIEDASDMLLAITQAGRMLMFPVSDLPQLSKGKGNKIINIPSAEAARGEDGLAQLYVLPPQSTLTIHVGKRKIKLRPEELQKVTGERGRRGTLMRGLQRIDRVEIDSP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 55 | Cytochrome b (Complex III subunit 3) (Complex III subunit III) (Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 3) (Ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase complex cytochrome b subunit) | 4G6H | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name MT-CYB Organism Bos taurus (Bovine) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CYTB;MTCYB;COB Protein family Cytochrome b family Biochemical class NA Function Component of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex (complex III or cytochrome b-c1 complex) that is part of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The b-c1 complex mediates electron transfer from ubiquinol to cytochrome c. Contributes to the generation of a proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane that is then used for ATP synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1327781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20025846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9485330, ECO:0000305|PubMed:189810}." Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 6 (COXPD6) [MIM:300816]: A mitochondrial disease resulting in a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by psychomotor delay, hypotonia, areflexia, muscle weakness and wasting. Some patients manifest prenatal ventriculomegaly and severe postnatal encephalomyopathy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20362274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22019070, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25583628, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26004228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26173962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27178839}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, X-linked recessive, 4, with or without cerebellar ataxia (CMTX4) [MIM:310490]: A neuromuscular disorder characterized by progressive sensorimotor axonal neuropathy, distal sensory impairment, difficulty walking due to peripheral neuropathy and/or cerebellar ataxia, and deafness due to auditory neuropathy. Additional features include cognitive impairment, cerebellar atrophy, dysarthria, abnormal extraocular movements, tremor, dysmetria and spasticity. The age at onset ranges from infancy to young adulthood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23217327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26004228}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Deafness, X-linked, 5, with peripheral neuropathy (DFNX5) [MIM:300614]: A form of hearing loss characterized by absent or severely abnormal auditory brainstem response, abnormal middle ear reflexes, abnormal speech discrimination, loss of outer hair cell function, and cochlear nerve hypoplasia. DFNX5 patients manifest auditory neuropathy with childhood onset, associated with distal sensory impairment affecting the peripheral nervous system. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25986071}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, X-linked, with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy (SEMDHL) [MIM:300232]: An X-linked recessive developmental disorder characterized by slowly progressive skeletal and neurologic abnormalities, including short stature, large and deformed joints, significant motor impairment, visual defects, and sometimes cognitive deficits. Affected individuals typically have normal early development in the first year or so of life, followed by development regression and the development of symptoms. Brain imaging shows white matter abnormalities consistent with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842795}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Electron transport; Heme; Iron; Membrane; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Reference proteome; Respiratory chain; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubiquinone Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 105644 Length 944 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37 Isoelectric point 9.24 Charge (pH=7) 19.42 3D Binding mode Sequence TMKVIDPQHSDKPNVLILGSGWGAISFLKHIDTKKYNVSIISPRSYFLFTPLLPSAPVGTVDEKSIIEPIVNFALKKKGNVTYYEAEATSINPDRNTVTIKSLSAVSQLYQPENHLGLHQAEPAEIKYDYLISAVGAEPNTFGIPGVTDYGHFLKEIPNSLEIRRTFAANLEKANLLPKGDPERRRLLSIVVVGGGPTGVEAAGELQDYVHQDLRKFLPALAEEVQIHLVEALPIVLNMFEKKLSSYAQSHLENTSIKVHLRTAVAKVEEKQLLAKTKHEDGKITEETIPYGTLIWATGNKARPVITDLFKKIPEQNSSKRGLAVNDFLQVKGSNNIFAIGDNAFAGLPPTAQVAHQEAEYLAKNFDKMAQIPNFQKNLSSRKDKIDLLFEENNFKPFKYNDLGALAYLGSERAIATIRSGKRTFYTGGGLMTFYLWRILYLSMILSARSRLKVFFDWIKLAFFKRDFFKGLTMKVIDPQHSDKPNVLILGSGWGAISFLKHIDTKKYNVSIISPRSYFLFTPLLPSAPVGTVDEKSIIEPIVNFALKKKGNVTYYEAEATSINPDRNTVTIKSLSAVSQLYQPENHLGLHQAEPAEIKYDYLISAVGAEPNTFGIPGVTDYGHFLKEIPNSLEIRRTFAANLEKANLLPKGDPERRRLLSIVVVGGGPTGVEAAGELQDYVHQDLRKFLPALAEEVQIHLVEALPIVLNMFEKKLSSYAQSHLENTSIKVHLRTAVAKVEEKQLLAKTKHEDGKITEETIPYGTLIWATGNKARPVITDLFKKIPEQNSSKRGLAVNDFLQVKGSNNIFAIGDNAFAGLPPTAQVAHQEAEYLAKNFDKMAQIPNFQKNLSSRKDKIDLLFEENNFKPFKYNDLGALAYLGSERAIATIRSGKRTFYTGGGLMTFYLWRILYLSMILSARSRLKVFFDWIKLAFFKRDFFKGL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 56 | Endolysin | 1AM7 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name R Organism Escherichia phage lambda (Bacteriophage lambda) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Glycosyl hydrolase 24 family Biochemical class Glycosidase Function Lyase activity.Lysozyme activity.Lytic transglycosylase activity. Related diseases Estrogen resistance (ESTRR) [MIM:615363]: A disorder characterized by partial or complete resistance to estrogens, in the presence of elevated estrogen serum levels. Clinical features include absence of the pubertal growth spurt, delayed bone maturation, unfused epiphyses, reduced bone mineral density, osteoporosis, continued growth into adulthood and very tall adult stature. Glucose intolerance, hyperinsulinemia and lipid abnormalities may also be present. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23841731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27754803}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04206 Interacts with NA EC number 4.2.2.n2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Antimicrobial; Bacteriolytic enzyme; Cytolysis; Direct protein sequencing; Host cell lysis by virus; Host cytoplasm; Lyase; Reference proteome; Viral release from host cell Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 49834.9 Length 462 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 18.78 Isoelectric point 9.6 Charge (pH=7) 18.29 3D Binding mode Sequence MVEINNQRKAFLDMLAXSEGTDNGRQKTRNHGYDVIVGGELFTDYSDHPRKLVTLNPKLKSTGAGRYQLLSRXXDAYRKQLGLKDFSPKSQDAVALQQIKERGALPMIDRGDIRQAIDRCSNIXASLPGAGYGQFEHKADSLIAKFKEAGGTVRMVEINNQRKAFLDMLAXSEGTDNGRQKTRNHGYDVIVGGELFTDYSDHPRKLVTLNPKLKSTGAGRYQLLSRXXDAYRKQLGLKDFSPKSQDAVALQQIKERGALPMIDRGDIRQAIDRCSNIXASLPGAGYGQFEHKADSLIAKFKEAGGTVRMVEINNQRKAFLDMLAXSEGTDNGRQKTRNHGYDVIVGGELFTDYSDHPRKLVTLNPKLKSTGAGRYQLLSRXXDAYRKQLGLKDFSPKSQDAVALQQIKERGALPMIDRGDIRQAIDRCSNIXASLPGAGYGQFEHKADSLIAKFKEAGGTVR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 57 | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 | 2JJK | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name FBP1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms FBP Protein family FBPase class 1 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function AMP binding.Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate 1-phosphatase activity.Identical protein binding.Metal ion binding.Monosaccharide binding. Related diseases Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency (FBP1D) [MIM:229700]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by impaired gluconeogenesis, and episodes of hypoglycemia and metabolic acidosis that can be lethal in newborn infants or young children. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12126934, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25601412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9382095}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02778; DB07312; DB07321; DB08484; DB00131; DB04493; DB05518; DB05053; DB04175; DB07270; DB02848 Interacts with O00499; Q99814; P09467; O00757; P51116; Q16665; P42858 EC number 3.1.3.11 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Allosteric enzyme; Carbohydrate metabolism; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Gluconeogenesis; Hydrolase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 69197.4 Length 634 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 25.2 Isoelectric point 7.84 Charge (pH=7) 2.55 3D Binding mode Sequence DVNTLTRFVMEEGRKARGTGELTQLLNSLCTAVKAISSAVRKAGIAHLYGIAGKLDVLSNDLVMNMLKSSFATCVLVSEEDKHAIIVEPEKRGKYVVCFDPLDGSSNIDCLVSVGTIFGIYRKKSTDEPSEKDALQPGRNLVAAGYALYGSATMLVLAMDCGVNCFMLDPAIGEFILVDKDVKIKKKGKIYSLNEGYAKDFDPAVTEYIQRKKFPPDNSAPYGARYVGSMVADVHRTLVYGGIFLYPANKKSPNGKLRLLYECNPMAYVMEKAGGMATTGKEAVLDVIPTDIHQRAPVILGSPDDVLEFLKVYEKHSDVNTLTRFVMEEGRKARGTGELTQLLNSLCTAVKAISSAVRKAGIAHLYGIAGKLDVLSNDLVMNMLKSSFATCVLVSEEDKHAIIVEPEKRGKYVVCFDPLDGSSNIDCLVSVGTIFGIYRKKSTDEPSEKDALQPGRNLVAAGYALYGSATMLVLAMDCGVNCFMLDPAIGEFILVDKDVKIKKKGKIYSLNEGYAKDFDPAVTEYIQRKKFPPDNSAPYGARYVGSMVADVHRTLVYGGIFLYPANKKSPNGKLRLLYECNPMAYVMEKAGGMATTGKEAVLDVIPTDIHQRAPVILGSPDDVLEFLKVYEKHS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 58 | mRNA-capping enzyme | 2C46 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name RNGTT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CAP1A Protein family Non-receptor class of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase family; Eukaryotic GTase family Biochemical class Transferase Function GTP binding.MRNA guanylyltransferase activity.Polynucleotide 5'-phosphatase activity.Protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity.Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity.RNA guanylyltransferase activity.Triphosphatase activity. Related diseases Atrial fibrillation, familial, 14 (ATFB14) [MIM:615378]: A familial form of atrial fibrillation, a common sustained cardiac rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity and ineffective atrial contraction promoting blood stasis in the atria and reduces ventricular filling. It can result in palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19808477}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Genetic variations in SCN2B may be involved in Brugada syndrome (PubMed:23559163). This tachyarrhythmia is characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs, the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23559163}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q92624; P16333-1 EC number 2.7.7.50; 3.6.1.74 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; GTP-binding; Host-virus interaction; Hydrolase; mRNA capping; mRNA processing; Multifunctional enzyme; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleotidyltransferase; Nucleus; Protein phosphatase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 21849.8 Length 189 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 53.71 Isoelectric point 5.89 Charge (pH=7) -2.91 3D Binding mode Sequence NKIPPRWLNCPRRGQPVAGRFLPLKTMLGPRYDSQVAEENRFHPSMLSNYLKSVKMGLLVDLTNTSRFYDRNDIEKEGIKYIKLQCKGHGECPTTENTETFIRLCERFELIGVHCTHGFNRTGFLICAFLVEKMDWSIEAAVATFAQARPPGIYKGDYLKELFRRYGDIEEAPPPPLLPDWCFEDDEDE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 59 | Aspartate aminotransferase, mitochondrial | 5AX8 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name GOT2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms KYAT4 Protein family Class-I pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent aminotransferase family Biochemical class Transferase Function 4-hydroxyglutamate transaminase activity.Amino acid binding.Enzyme binding.Kynurenine-oxoglutarate transaminase activity.L-aspartate:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity.L-phenylalanine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity.Phospholipid binding.Protein homodimerization activity.Pyridoxal phosphate binding.RNA binding. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 82 (DEE82) [MIM:618721]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of severe early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE82 is an autosomal recessive metabolic encephalopathy characterized by epilepsy from the first year of life, global developmental delay, hypotonia and feeding difficulties apparent soon after birth, and intellectual and motor disabilities. Other features include poor overall growth, progressive microcephaly and biochemical abnormalities, including increased serum lactate and ammonia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31422819}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02783; DB00128; DB00151; DB00142; DB00114 Interacts with NA EC number 2.6.1.1; 2.6.1.7 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Aminotransferase; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Epilepsy; Lipid transport; Membrane; Methylation; Mitochondrion; Nitration; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome; Transferase; Transit peptide; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 44694.8 Length 401 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 26.15 Isoelectric point 8.98 Charge (pH=7) 8.22 3D Binding mode Sequence SSWWTHVEMGPPDPILGVTEAFKRDTNSKKMNLGVGAYRDDNGKPYVLPSVRKAEAQIAAKNLDKEYLPIGGLAEFCKASAELALGENSEVLKSGRFVTVQTISGTGALRIGASFLQRFFKFSRDVFLPKPTWGNHTPIFRDAGMQLQGYRYYDPKTCGFDFTGAVEDISKIPEQSVLLLHACAHNPTGVDPRPEQWKEIATVVKKRNLFAFFDMAYQGFASGDGDKDAWAVRHFIEQGINVCLCQSYAKNMGLYGERVGAFTMVCKDADEAKRVESQLKILIRPMYSNPPLNGARIAAAILNTPDLRKQWLQEVKGMADRIIGMRTQLVSNLKKEGSTHNWQHITDQIGMFCFTGLKPEQVERLIKEFSIYMTKDGRISVAGVTSSNVGYLAHAIHQVTK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 60 | Hydrogen peroxide-inducible genes activator | 1I69 | 4.00 | |
Target general information Gen name oxyR Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b3961;mor;momR;JW3933 Protein family LysR transcriptional regulatory family Biochemical class Transcription Function Bacterial-type RNA polymerase core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding.Transcription factor activity, bacterial-type RNA polymerase core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; DNA-binding; Glutathionylation; Oxidation; Reference proteome; Repressor; S-nitrosylation; Stress response; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 46013 Length 412 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 44.76 Isoelectric point 5.57 Charge (pH=7) -14.52 3D Binding mode Sequence ETMSGPLHIGLIPTVGPYLLPHIIPMLHQTFPKLEMYLHEAQTHQLLAQLDSGKLDAVILALVKESEAFIEVPLFDEPMLLAIYEDHPWANREAVPMADLAGEKLLMLEDGHSLRDQAMGFCFDTHFRATSLETLRNMVAAGSGITLLPALAVPPERKRDGVVYLPAIKPEPRRTIGLVYRPGSPLRSRYEQLAEAIRARMDGHFDETMSGPLHIGLIPTVGPYLLPHIIPMLHQTFPKLEMYLHEAQTHQLLAQLDSGKLDAVILALVKESEAFIEVPLFDEPMLLAIYEDHPWANREAVPMADLAGEKLLMLEDGHSLRDQAMGFCFETHFRATSLETLRNMVAAGSGITLLPALAVPPERKRDGVVYLPAIKPEPRRTIGLVYRPGSPLRSRYEQLAEAIRARMDGHFD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||