Job Results:
Ligand
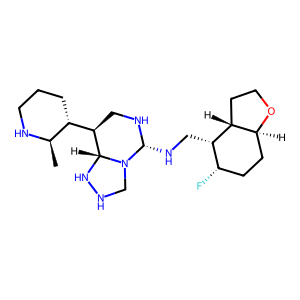
Structure
Job ID
b66da62373d29d285a275497218b65f3
Job name
NA
Time
2024-11-27 22:32:54
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | Intestinal maltase-glucoamylase (MGAM) | 3L4Y | 8.13 | |
Target general information Gen name MGAM Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms MGAM Protein family Glycosyl hydrolase 31 family Biochemical class Glycosylase Function May serve as an alternate pathway for starch digestion when luminal alpha-amylase activity is reduced because of immaturity or malnutrition. May play a unique role in the digestion of malted dietary oligosaccharides used in food manufacturing. Related diseases Hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia (HVLI) [MIM:618850]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by highly elevated plasma concentrations of valine and leucine/isoleucine. Affected individuals suffer from headache and mild memory impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. A patient with hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia was identified as compound heterozygote for Gln-170 (inherited from his father) and Lys-264 (inherited from his mother), both variants reduced the catalytic activity of the enzyme. After treatment with vitamin B6, a precursor of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, a BCAT2 cofactor, the blood levels of branched chain amino acids, especially valine, were decreased and brain lesions were improved. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00284; DB00491; DB04878 Interacts with Q13520; Q7Z7G2; Q96BA8; O15529; P14410; P54219-3; Q9NUH8 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Glycosidase; Hydrolase; Membrane; Multifunctional enzyme; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal-anchor; Sulfation; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 97779.4 Length 863 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 32.47 Isoelectric point 5.2 Charge (pH=7) -28.27 3D Binding mode Sequence VNELERINCIPDQPPTKATCDQRGCCWNPQGAVSVPWCYYSKNHSYHVEGNLVNTNAGFTARLKNLPSSPVFGSNVDNVLLTAEYQTSNRFHFKLTDQTNNRFEVPHEHVQSFSGNAAASLTYQVEISRQPFSIKVTRRSNNRVLFDSSIGPLLFADQFLQLSTRLPSTNVYGLGEHVHQQYRHDMNWKTWPIFNRDTTPNGNGTNLYGAQTFFLCLEDASGLSFGVFLMNSNAMEVVLQPAPAITYRTIGGILDFYVFLGNTPEQVVQEYLELIGRPALPSYWALGFHLSRYEYGTLDNMREVVERNRAAQLPYDVQHADIDYMDERRDFTYDSVDFKGFPEFVNELHNNGQKLVIIVDPAISNNSSSSKPYGPYDRGSDMKIWVNSSDGVTPLIGEVWPGQTVFPDYTNPNCAVWWTKEFELFHNQVEFDGIWIDMNEVSNFVDGSVSGCSTNNLNNPPFTPRILDGYLFCKTLCMDAVQHWGKQYDIHNLYGYSMAVATAEAAKTVFPNKRSFILTRSTFAGSGKFAAHWLGDNTATWDDLRWSIPGVLEFNLFGIPMVGPDICGFALDTPEELCRRWMQLGAFYPFSRNHNGQGYKDQDPASFGADSLLLNSSRHYLNIRYTLLPYLYTLFFRAHSRGDTVARPLLHEFYEDNSTWDVHQQFLWGPGLLITPVLDEGAEKVMAYVPDAVWYDYETGSQVRWRKQKVEMELPGDKIGLHLRGGYIFPTQQPNTTTLASRKNPLGLIIALDENKEAKGELFWDDGETKDTVANKVYLLCEFSVTQNRLEVNISQSTYKDPNNLAFNEIKILGTEEPSNVTVKHNGVPSTSPTVTYDSNLKVAIITDIDLLLGEAYTVEWAH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 42 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 (ADRBK1) | 3V5W | 8.12 | |
Target general information Gen name GRK2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms GRK2; G-protein coupled receptor kinase 2; BetaARK1; Beta-ARK-1; Beta ARK1 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, GPRK subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Specifically phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the beta-adrenergic and closely related receptors, probably inducing a desensitization of them. Key regulator of LPAR1 signaling. Competes with RALA for binding to LPAR1 thus affecting the signaling properties of the receptor. Desensitizes LPAR1 and LPAR2 in a phosphorylation-independent manner. Related diseases 3-ketothiolase deficiency (3KTD) [MIM:203750]: An autosomal recessive inborn error of isoleucine catabolism characterized by intermittent ketoacidotic attacks associated with unconsciousness. Some patients die during an attack or are mentally retarded. Urinary excretion of 2-methyl-3-hydroxybutyric acid, 2-methylacetoacetic acid, triglylglycine, butanone is increased. It seems likely that the severity of this disease correlates better with the environmental or acquired factors than with the ACAT1 genotype. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1346617, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1715688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7728148, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9744475}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00171 Interacts with P05067; P48730-2; P21860; P21462; Q9Y2X7; P35626; Q00987; P13591; P25963; Q13635; P0CG48 EC number EC 2.7.11.15 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ATP-binding; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Cytoplasm; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Synapse; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 38433.9 Length 337 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 52.17 Isoelectric point 7.36 Charge (pH=7) 1.05 3D Binding mode Sequence KNVELNIHLTMNDFSVHRIIGRGGFGEVYGCRKADTGKMYAMKCLDKKRIKMKQGETLALNERIMLSLVSTGDCPFIVCMSYAFHTPDKLSFILDLMNGGDLHYHLSQHGVFSEADMRFYAAEIILGLEHMHNRFVVYRDLKPANILLDEHGHVRISDLGLACDFSKKKPHASVGTHGYMAPEVLQKGVAYDSSADWFSLGCMLFKLLRGHSPFRQHKTKDKHEIDRMTLTMAVELPDSFSPELRSLLEGLLQRDVNRRLGCLGRGAQEVKESPFFRSLDWQMVFLQKYPPPLIPPRGEVNAADAFDKGIKLLDSDQELYRNFPLTISERWQQEVAE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 43 | Short transient receptor potential channel 5 (TRPC5) | 7WDB | 8.11 | |
Target general information Gen name TRPC5 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hTRP5; hTRP-5; TrpC5; Transient receptor protein 5; TRP-5 Protein family Transient receptor (TC 1.A.4) family, STrpC subfamily, TRPC5 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Transient receptor potential catioin channel Function Thought to form a receptor-activated non-selective calcium permeant cation channel. Probably is operated by a phosphatidylinositol second messenger system activated by receptor tyrosine kinases or G-protein coupled receptors. Has also been shown to be calcium-selective. May also be activated by intracellular calcium store depletion. Related diseases Loss-of-function variants in TRPC5 may be involved in a mental disorder characterized by maladaptive behavior, anxiety, autism, postpartum depression, extreme food-seeking and hoarding behavior, hyperphagia and obesity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38959890}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ANK repeat; Calcium; Calcium channel; Calcium transport; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 76850.6 Length 665 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 40.05 Isoelectric point 6.16 Charge (pH=7) -5.94 3D Binding mode Sequence RIPLQIVRAETELSAEEKAFLNAVEKGDYATVKQALQEAEIYYNVNINCMDPLGRSALLIAIENENLEIMELLLNHSVYVGDALLYAIRKEVVGAVELLLSYQFSEFTPDITPIMLAAHTNNYEIIKLLVQKRVTIPRPHQIRCNCVECVSSSEVDSLRHSRSRLNIYKALASPSLIALSSEDPILTAFRLGWELKELSKVENEFKAEYEELSQQCKLFAKDLLDQARSSRELEIILNHRDDLAKLKVAIKYHQKEFVAQPNCQQLLATLWYDGFPGWRRKHWVVKLLTCMTIGFLFPMLSIAYLISPRSNLGLFIKKPFIKFICHTASYLTFLFMLLLASQHVQGPPPTVVEWMILPWVLGFIWGEIKEMWDGGFTEYIHDWWNLMDFAMNSLYLATISLKIVAYVKYNGSRPREEWEMWHPTLIAEALFAISNILSSLRLISLFTANSHLGPLQISLGRMLLDILKFLFIYCLVLLAFANGLNQLYFYYETRAIDEPNNCKGIRCEKQNNAFSTLFETLQSLFWSVFGLLNLYVTNVKARHEFTEFVGATMFGTYNVISLVVLLNMLIAMMNNSYQLIADHADIEWKFARTKLWMSYFDEGGTLPPPFNIISLIQNQHYQEVIRNLVKRYVAAMIRNSKTTEENFKELKQDISSFRYEVLDLL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 44 | Cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2) | 6PT0 | 8.11 | |
Target general information Gen name CNR2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hCB2; Cannabinoid CB2 receptor; CX5; CB2B; CB2A; CB-2 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function May function in inflammatory response, nociceptive transmission and bone homeostasis. Heterotrimeric G protein-coupled receptor for endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol mediating inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Related diseases Factor V deficiency (FA5D) [MIM:227400]: A blood coagulation disorder leading to a hemorrhagic diathesis known as parahemophilia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10942390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12393490}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thrombophilia due to activated protein C resistance (THPH2) [MIM:188055]: A hemostatic disorder due to defective degradation of factor V by activated protein C. It is characterized by a poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C resulting in tendency to thrombosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10391209, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10942390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11435304, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11858490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14617013, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14695241, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16710414, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8164741, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9454742}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Budd-Chiari syndrome (BDCHS) [MIM:600880]: A syndrome caused by obstruction of hepatic venous outflow involving either the hepatic veins or the terminal segment of the inferior vena cava. Obstructions are generally caused by thrombosis and lead to hepatic congestion and ischemic necrosis. Clinical manifestations observed in the majority of patients include hepatomegaly, right upper quadrant pain and abdominal ascites. Budd-Chiari syndrome is associated with a combination of disease states including primary myeloproliferative syndromes and thrombophilia due to factor V Leiden, protein C deficiency and antithrombin III deficiency. Budd-Chiari syndrome is a rare but typical complication in patients with polycythemia vera. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9245936}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Ischemic stroke (ISCHSTR) [MIM:601367]: A stroke is an acute neurologic event leading to death of neural tissue of the brain and resulting in loss of motor, sensory and/or cognitive function. Ischemic strokes, resulting from vascular occlusion, is considered to be a highly complex disease consisting of a group of heterogeneous disorders with multiple genetic and environmental risk factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15534175}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Pregnancy loss, recurrent, 1 (RPRGL1) [MIM:614389]: A common complication of pregnancy, resulting in spontaneous abortion before the fetus has reached viability. The term includes all miscarriages from the time of conception until 24 weeks of gestation. Recurrent pregnancy loss is defined as 3 or more consecutive spontaneous abortions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11018168}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09061; DB00470; DB06202; DB14009; DB00486; DB14011; DB02955; DB16321; DB11755 Interacts with Q9UKJ8; Q15848; Q9NRZ5; P13236; P21964; Q14802-3; Q8N387; Q8IXM6; I3L0A0; Q96AA3; Q9Y6D0; Q6ICL7; Q9NP94; Q13501; Q96HH6; Q969S6; Q9NWH2; Q9H2L4; Q8N2M4; Q6ZT21; Q5TGU0; Q9Y548; Q9BSR8; Q96EC8 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Cell projection; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Inflammatory response; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 32999.2 Length 298 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 30.98 Isoelectric point 9.49 Charge (pH=7) 14.35 3D Binding mode Sequence MKDYMILSGPQKTAVAVLCTLLGLLSALENVAVLYLILSSHQLRRKPSYLFIGSLAGADFLASVVFACSFVNFHVFHGVDSKAVFLLKIGSVTMTFTASVGSLLLTAIDRYLCLRYPPSYKALLTRGRALVTLGIMWVLSALVSYLPLMGWTCCPRPCSELFPLIPNDYLLSWLLFIAFLFSGIIYTYGHVLWKAHQHVASLSGHQDRQVPGMARMRLDVRLAKTLGLVLAVLLICWFPVLALMAHSLATTLSDQVKKAFAFCSMLCLINSMVNPVIYALRSGEIRSSAHHCLAHWKK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 45 | Pol polyprotein | 5KAO | 8.10 | |
Target general information Gen name pol Organism Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family NA Biochemical class Hydrolase / hydrolase inhibitor Function Aspartic-type endopeptidase activity. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 16 (OZEMA16) [MIM:617234]: A rare cause of female primary infertility. In affected women, ovulation and fertilization proceed normally but embryos are arrested at early stages of development. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27545678}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00701; DB01072; DB04887; DB01264; DB01319; DB00224; DB01601; DB00503; DB01232; DB00932 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Aspartyl protease; Hydrolase; Protease Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 21411 Length 198 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 42.78 Isoelectric point 9.45 Charge (pH=7) 4.15 3D Binding mode Sequence PQVTLWQRPLVTIKIGGQLKEALLDTGADDTVLEEMSLPGRWKPKMIGGIGGFIKVRQYDQILIEIAGHKAIGTVLVGPTPVNIIGRNLLTQIGATLNFPQVTLWQRPLVTIKIGGQLKEALLDTGADDTVLEEMSLPGRWKPKMIGGIGGFIKVRQYDQILIEIAGHKAIGTVLVGPTPVNIIGRNLLTQIGATLNF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 46 | Phosphodiesterase 3A (PDE3A) | 7EG0 | 8.10 | |
Target general information Gen name PDE3A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms cGMP-inhibited 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase A; Phosphodiesterase 3A; Cyclic GMP-inhibited phosphodiesterase A; Cyclic GMP inhibited phosphodiesterase A; CGI-PDE A Protein family Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family, PDE3 subfamily Biochemical class Phosphoric diester hydrolase Function Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase with a dual-specificity for the second messengers cAMP and cGMP, which are key regulators of many important physiological processes. Related diseases Hypertension and brachydactyly syndrome (HTNB) [MIM:112410]: A syndrome characterized by brachydactyly type E, severe salt-independent but age-dependent hypertension, an increased fibroblast growth rate, neurovascular contact at the rostral-ventrolateral medulla, and altered baroreflex blood pressure regulation. It results in death from stroke before age 50 years when untreated. Brachydactyly type E is characterized by shortening of the fingers mainly in the metacarpals and metatarsals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25961942}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01223; DB01427; DB00261; DB00201; DB01166; DB04880; DB05266; DB00922; DB00235; DB01303; DB00277; DB08811; DB09283 Interacts with Q9Y6D6; Q9Y6D5 EC number EC 3.1.4.17 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; cAMP; cGMP; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Isopeptide bond; Manganese; Membrane; Metal-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 108171 Length 939 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 39.75 Isoelectric point 6.53 Charge (pH=7) -4.15 3D Binding mode Sequence KPILAPEPLVMDNLDSIMEQLNTWNFPIFDLVENIGRKCGRILSQVSYRLFEDMGLFEAFKIPIREFMNYFHALEIGYRDIPYHNRIHATDVLHAVWYLTTQPIPGLSTVGYVFSKTYNVTDDKYGCLSGNIPALELMALYVAAAMHDYDHPGRTNAFLVATSAPQAVLYNDRSVLENHHAAAAWNLFMSRPEYNFLINLDHVEFKHFRFLVIEAILATDLKKHFDFVAKFNGKVNDDVGIDWTNENDRLLVCQMCIKLADINGPAKCKELHLQWTDGIVNEFYEQGDEEASLGLPISPFMDRSAPQLANLQESFISHIVGPLCNSYDSAGLMPGKWVEKIYCQITQHLLQNHKMWKKVIEEEQRLAGIENQNISVDLETNYAELVLDVGRVTLGENSRKKMKDCKLRKKQNESVSRAMCALLNSGGGVIKAEIENEDYSYTKDGIGLDLENSFSNILLFVPEYLDFMQNGNYFLIFVKSWSLNTSGLRITTLSSNLYKRDITSAKVMNATAALEFLKDMKKTRGRLYLRPELLAKRPCVDIQEENNMKALAGVFFDRTELDRKEKLTFTESTHVEIKNFSTERLLQRIKEILPQYVSAFANTDGGYLFIGLNEDKEIIGFKAEMSDLDDLEREIEKSIRKMPVHHFCMEKKKINYSCKFLGVYDKGSLCGYVCALRVERFCCAVFAKEPDSWHVKDNRVMQLTRKEWIQFMVEAEPKFSSAYEEVISQINTSLPAPHSWPLLEWQRQRHHCPGLSGRITYTPENLCRKLFLQHEGLKQLICEEMSSVRKGSLIFSRSWSVDLGLQENHKVLCDALLISQDSPPVLYTFHMVQDEEFKGYSTQTALTLKQKLAKIGGYTKKVCVMTKIFYLSPEGMTSCQYDLRSQVIYPESYYFTRRKYLLKALFKALKRLKSLRDQFSFAENLYQIIGIDCFQKNDK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 47 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 (mGluR3) | 4XAR | 8.10 | |
Target general information Gen name GRM3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms mGLUR3; Group III metabotropic glutamate receptor; GPRC1C Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 3 family Biochemical class GPCR glutamate Function Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity. G-protein coupled receptor for glutamate. Related diseases Paramyotonia congenita (PMC) [MIM:168300]: An autosomal dominant channelopathy characterized by myotonia, increased by exposure to cold, intermittent flaccid paresis, not necessarily dependent on cold or myotonia, lability of serum potassium, non-progressive nature and lack of atrophy or hypertrophy of muscles. In some patients, myotonia is not increased by cold exposure (paramyotonia without cold paralysis). Patients may have a combination phenotype of PMC and HYPP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10369308, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10727489, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1310898, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1316765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1338909, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15318338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15790667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786525, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18166706, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18690054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19077043, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20076800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8242056, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8308722, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8388676, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8580427}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Periodic paralysis hypokalemic 2 (HOKPP2) [MIM:613345]: An autosomal dominant disorder manifested by episodic flaccid generalized muscle weakness associated with falls of serum potassium levels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10599760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10944223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11558801, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11591859, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16890191, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17898326, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18162704, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19118277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20522878, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21043388, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24549961}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Periodic paralysis hyperkalemic (HYPP) [MIM:170500]: An autosomal dominant channelopathy characterized by episodic flaccid generalized muscle weakness associated with high levels of serum potassium. Concurrence of myotonia is found in HYPP patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1659668, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1659948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20076800}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Periodic paralysis normokalemic (NKPP) [MIM:170500]: A disorder closely related to hyperkalemic periodic paralysis, but marked by a lack of alterations in potassium levels during attacks of muscle weakness. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15596759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18046642, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20522878}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Myotonia SCN4A-related (MYOSCN4A) [MIM:608390]: A phenotypically highly variable myotonia aggravated by potassium loading, and sometimes by cold. Myotonia is characterized by sustained muscle tensing that prevents muscles from relaxing normally. It causes muscle stiffness that can interfere with movement. In some people the stiffness is very mild, while in other cases it may be severe enough to interfere with walking, running, and other activities of daily life. Myotonia SCN4A-related includes myotonia permanens and myotonia fluctuans. In myotonia permanens, the myotonia is generalized and there is a hypertrophy of the muscle, particularly in the neck and the shoulder. Attacks of severe muscle stiffness of the thoracic muscles may be life threatening due to impaired ventilation. In myotonia fluctuans, the muscle stiffness may fluctuate from day to day, provoked by exercise. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10218481, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786525, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16832098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17212350, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17998485, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18203179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18337100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19015483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19347921, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20076800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27653901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8058156, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9392583}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 16 (CMS16) [MIM:614198]: A form of congenital myasthenic syndrome, a group of disorders characterized by failure of neuromuscular transmission, including pre-synaptic, synaptic, and post-synaptic disorders that are not of autoimmune origin. Clinical features are easy fatigability and muscle weakness. CMS16 is characterized by fatigable generalized weakness and recurrent attacks of respiratory and bulbar paralysis since birth. The fatigable weakness involves lid-elevator, external ocular, facial, limb and truncal muscles and an decremental response of the compound muscle action potential on repetitive stimulation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12766226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25707578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26659129}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Congenital myopathy 22A, classic (CMYO22A) [MIM:620351]: A form of congenital myopathy, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of muscle disorders characterized by hypotonia and muscle weakness apparent at birth, and specific pathological features on muscle biopsy. CMYO22A is an autosomal recessive form characterized by fetal hypokinesia, polyhydramnios, and severe neonatal hypotonia associated with respiratory insufficiency. Affected individuals who survive the neonatal period have delayed motor development, difficulty walking, proximal muscle weakness of the upper and lower limbs, facial and neck muscle weakness, easy fatigability, and mild limb contractures or foot deformities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26700687, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28262468, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36090556}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Congenital myopathy 22B, severe fetal (CMYO22B) [MIM:620369]: A severe congenital myopathy, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of muscle disorders characterized by hypotonia and muscle weakness apparent at birth, and specific pathological features on muscle biopsy. CMYO22B is an autosomal recessive form characterized by onset in utero. Affected individuals show fetal akinesia, and develop fetal hydrops with pulmonary hypoplasia, severe joint contractures, and generalized muscle hypoplasia. Death occurs in utero or soon after birth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26700687}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05096 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 50355.5 Length 445 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 38.26 Isoelectric point 6.52 Charge (pH=7) -1.53 3D Binding mode Sequence RREIKIEGDLVLGGLFPINEKGTGTEECGRINEDRGIQRLEAMLFAIDEINKDDYLLPGVKLGVHILDTCSRDTYALEQSLEFVRASLLLIAGVIGGSYSSVSIQVANLLRLFQIPQISYASTSAKLSDKSRYDYFARTVPPDFYQAKAMAEILRFFNWTYVSTVASEGDYGETGIEAFEQEARLRNISIATAEKVGRSNIRKSYDSVIRELLQKPNARVVVLFMRSDDSRELIAAASRANASFTWVASDGWGAQESIIKGSEHVAYGAITLELASQPVRQFDRYFQSLNPYNNHRNPWFRDFWEQKFQCSLRVCDKHLAIDSSNYEQESKIMFVVNAVYAMAHALHKMQRTLCPNTTKLCDAMKILDGKKLYKDYLLKINFTAPDADSIVKFDTFGDGMGRYNVFNFQNVGGKYSYLKVGHWAETLSLDVNSIHWSRNSVPTSE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 48 | Steroid 21-hydroxylase | 4Y8W | 8.10 | |
Target general information Gen name CYP21A2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CYP21;CYP21B Protein family Cytochrome P450 family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Heme binding.Iron ion binding.Steroid 21-monooxygenase activity.Steroid binding.Steroid hydroxylase activity. Related diseases Adrenal hyperplasia 3 (AH3) [MIM:201910]: A form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, a common recessive disease due to defective synthesis of cortisol. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is characterized by androgen excess leading to ambiguous genitalia in affected females, rapid somatic growth during childhood in both sexes with premature closure of the epiphyses and short adult stature. Four clinical types: 'salt wasting' (SW, the most severe type), 'simple virilizing' (SV, less severely affected patients), with normal aldosterone biosynthesis, 'non-classic form' or late-onset (NC or LOAH) and 'cryptic' (asymptomatic). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10051010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10094562, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10198222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10364682, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10391209, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10408778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10408786, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10443693, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10496074, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10720040, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11232002, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11598371, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11600539, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11746135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12213891, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12222711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12788866, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12887291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12915679, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1406699, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1406709, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14676460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14715874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1496017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15110320, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15126570, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16046588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1644925, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16984992, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18319307, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18381579, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18445671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1864962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1937474, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20080860, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2072928, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21169732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22014889, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2303461, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27721825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29328376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3038528, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3257825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3260007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3267225, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3497399, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3871526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7749410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8478006, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8485582, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8989258, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9067760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9187661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9497336}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01026; DB05667 Interacts with NA EC number 1.14.14.16 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Congenital adrenal hyperplasia; Disease variant; Endoplasmic reticulum; Heme; Iron; Lipid metabolism; Lipid-binding; Membrane; Metal-binding; Microsome; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Steroid-binding; Steroidogenesis Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 50326.2 Length 442 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 50.06 Isoelectric point 7.79 Charge (pH=7) 2.07 3D Binding mode Sequence KLPPLAPGFLHLLQPDLPIYLLGLTQKFGPIYRLHLGLQDVVVLNSKRTIEEAMVKKWADFAGRPEPLTYKLVSRNYPDLSLGDYSLLWKAHKKLTRSALLLGIRDSMEPVVEQLTQEFCERMRAQPGTPVAIEEEFSLLTCSIICYLTFGDKIKDDNLMPAYYKCIQEVLKTWSHWSIQIVDVIPFLRFFPNPGLRRLKQAIEKRDHIVEMQLRQHKESLVAGQWRDMMDYMLQGVAGQLLEGHVHMAAVDLLIGGTETTANTLSWAVVFLLHHPEIQQRLQEELDHESRVPYKDRARLPLLNATIAEVLRLRPVVPLALPHRTTRPSSISGYDIPEGTVIIPNLQGAHLDETVWERPHEFWPDRFLEPGKNSRALAFGCGARVCLGEPLARLELFVVLTRLLQAFTLLPSGDALPSLQPLPHCSVILKMQPFQVRLQPRG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 49 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 (EPHA7) | 3DKO | 8.09 | |
Target general information Gen name EPHA7 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hEK11; EPH-like kinase 11; EPH homology kinase 3; EK11; EHK3; EHK-3 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, Ephrin receptor subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Among GPI-anchored ephrin-A ligands, EFNA5 is a cognate/functional ligand for EPHA7 and their interaction regulates brain development modulating cell-cell adhesion and repulsion. Has a repellent activity on axons and is for instance involved in the guidance of corticothalamic axons and in the proper topographic mapping of retinal axons to the colliculus. May also regulate brain development through a caspase(CASP3)-dependent proapoptotic activity. Forward signaling may result in activation of components of the ERK signaling pathway including MAP2K1, MAP2K2, MAPK1 AND MAPK3 which are phosphorylated upon activation of EPHA7. Receptor tyrosine kinase which binds promiscuously GPI-anchored ephrin-A family ligands residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. Related diseases WHIM syndrome 2 (WHIMS2) [MIM:619407]: An autosomal recessive form of WHIM syndrome, a primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by warts, hypogammaglobulinemia, infections, and myelokathexis. Myelokathexis is a unique form of non-cyclic severe congenital neutropenia caused by accumulation of mature and degenerating neutrophils in the bone marrow. Monocytopenia and lymphopenia, especially B lymphopenia, also commonly occur. There is significant phenotypic variation among patients, such that some individuals may have an incomplete form of the disorder in which one or more of the classic tetrad features are not present. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24777453}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07970; DB12010 Interacts with P07333; P52803; P29317; P29320; P29323; P54760; Q16288; P52793 EC number EC 2.7.10.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Apoptosis; ATP-binding; Cell membrane; Developmental protein; Glycoprotein; Kinase; Membrane; Neurogenesis; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tyrosine-protein kinase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 31250.7 Length 275 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 28.85 Isoelectric point 6.44 Charge (pH=7) -1.92 3D Binding mode Sequence TYIDPETYEDPNRAVHQFAKELDASCIKIERVIGAEFGEVCSGRLKLPGKRDVAVAIKTLKVGYTEKQRRDFLCEASIMGQFDHPNVVHLEGVVTRGKPVMIVIEFMENGALDAFLRKHDGQFTVIQLVGMLRGIAAGMRYLADMGYVHRDLAARNILVNSNLVCKVSDFGPVRWTAPEAIQYRKFTSASDVWSYGIVMWEVMSYGERPYWDMSNQDVIKAIEEGYRLPAPMDCPAGLHQLMLDCWQKERAERPKFEQIVGILDKMIRNPNSAHH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 50 | Extracellular lysophospholipase D (E-NPP2) | 4ZGA | 8.09 | |
Target general information Gen name ENPP2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms LysoPLD; Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 2; E-NPP 2; Autotaxin; ATX Protein family Nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family Biochemical class Phosphoric diester hydrolase Function Hydrolyzes lysophospholipids to produce the signaling molecule lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) in extracellular fluids. Major substrate is lysophosphatidylcholine. Also can act on sphingosylphosphorylcholine producing sphingosine-1-phosphate, a modulator of cell motility. Can hydrolyze, in vitro, bis-pNPP, to some extent pNP-TMP, and barely ATP. Involved in several motility-related processes such as angiogenesis and neurite outgrowth. Acts as an angiogenic factor by stimulating migration of smooth muscle cells and microtubule formation. Stimulates migration of melanoma cells, probably via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. May have a role in induction of parturition. Possible involvement in cell proliferation and adipose tissue development (Probable). Tumor cell motility-stimulating factor. Related diseases Anemia, non-spherocytic hemolytic, due to G6PD deficiency (NSHA) [MIM:300908]: A disease characterized by G6PD deficiency, acute hemolytic anemia, fatigue, back pain, and jaundice. In most patients, the disease is triggered by an exogenous agent, such as some drugs, food, or infection. Increased unconjugated bilirubin, lactate dehydrogenase, and reticulocytosis are markers of the disorder. Although G6PD deficiency can be life-threatening, most patients are asymptomatic throughout their life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12524354, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1303180, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1303182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1536798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1611091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1889820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1945893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20007901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26479991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2836867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2912069, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30988594, ECO:0000269|PubMed:38066190, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7858267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7959695, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8193373, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8490627, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8533762, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8733135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452072}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Deficiency of G6PD is associated with hemolytic anemia in two different situations. First, in areas in which malaria has been endemic, G6PD-deficiency alleles have reached high frequencies (1% to 50%) and deficient individuals, though essentially asymptomatic in the steady state, have a high risk of acute hemolytic attacks. Secondly, sporadic cases of G6PD deficiency occur at a very low frequencies, and they usually present a more severe phenotype. Several types of NSHA are recognized. Class-I variants are associated with severe NSHA; class-II have an activity <10% of normal; class-III have an activity of 10% to 60% of normal; class-IV have near normal activity. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.1.4.39 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Chemotaxis; Cleavage on pair of basic residues; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lipid degradation; Lipid metabolism; Metal-binding; Obesity; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 85397.4 Length 740 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 58.63 Isoelectric point 7.16 Charge (pH=7) 1.02 3D Binding mode Sequence GSCKGRCFELCRCDNLCKSYTSCCHDFDELCLKTARGWECTKDRCGNEENACHCEDCLARGDCCTNYQVVCKGESHWVDDDCEEIKAAECPAGFVRPPLIIFSVDGFRASYMKKGSKVMPNIEKLRSCGTHSPYMRPVYPTKTFPNLYTLATGLYPESHGIVGNSMYDPVFDATFHLRGREKFNHRWWGGQPLWITATKQGVKAGTFFWSVVIPHERRILTILQWLTLPDHERPSVYAFYSEQPDFSGHKYGPFGPEMTNPLREIDKIVGQLMDGLKQLKLHRCVNVIFVGDHGMEDVTCDRTEFLSNYLTNVDDITLVPGTLGRIRSKFDPKAIIANLTCKKPDQHFKPYLKQHLPKRLHYANNRRIEDIHLLVERRWHVARKPFFQGDHGFDNKVNSMQTVFVGYGSTFKYKTKVPPFENIELYNVMCDLLGLKPAPNNGTHGSLNHLLRTNTFRPTMPEEVTRPNYPGIMYLQSDFDLGTEERHLLYGRPAVLYRTRYDILYHTDFESGYSEIFLMPLWTSYTVSKQACVRPDVRVSPSFSQNCLAYKNDKQMSYGFLFPPYLSSSPEAKYDAFLVTNMVPMYPAFKRVWNYFQRVLVKKYASERNGVNVISGPIFDYDYDGLHDTEDKIKQYVEGSSIPVPTHYYSIITSCLDFTQPADKCDGPLSVSSFILPHRPDNEESCNSSEDESKWVEELMKMHTARVRDIEHLTSLDFFRKTSRSYPEILTLKTYLHTYE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 51 | Transferrin (TF) | 1RYO | 8.09 | |
Target general information Gen name TF Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Siderophilin; Serotransferrin; PRO1400; Beta-1 metal-binding globulin Protein family Transferrin family Biochemical class Transferrin Function It is responsible for the transport of iron from sites of absorption and heme degradation to those of storage and utilization. Serum transferrin may also have a further role in stimulating cell proliferation. Transferrins are iron binding transport proteins which can bind two Fe(3+) ions in association with the binding of an anion, usually bicarbonate. Related diseases Atransferrinemia (ATRAF) [MIM:209300]: A rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by abnormal synthesis of transferrin leading to iron overload and microcytic hypochromic anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11110675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15466165}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01370; DB14517; DB14518; DB01294; DB14526; DB14527; DB11136; DB14528; DB14529; DB14530; DB00515; DB09130; DB11397; DB13949; DB14490; DB14491; DB14488; DB14501; DB14489; DB13257; DB06215; DB06784; DB05260; DB01592; DB00893; DB00677; DB06757; DB11182; DB14520; DB01593; DB14487; DB14533; DB14548 Interacts with O43315; O00501; Q7Z7G2; Q9GZR5; Q9Y282; Q96KR6; P01350; P08034; Q8NBJ4; O15529; Q8TED1; Q7Z5P4; A8MZ59; O15173; Q96TC7; Q3KNW5; Q9BXS9-3; Q99523; O43278-2; Q8N9I0; P02786; Q4KMG9; Q9K0U9; Q09057; Q9K0V0; P02786 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Ion transport; Iron; Iron transport; Metal-binding; Methylation; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 35854.5 Length 324 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 34.17 Isoelectric point 7.58 Charge (pH=7) 1.42 3D Binding mode Sequence KTVRWCAVSEHEATKCQSFRDHMKSVIPSDGPSVACVKKASYLDCIRAIAANEADAVTLDAGLVYDAYLAPNNLKPVVAEFYGSKEDPQTFYYAVAVVKKDSGFQMNQLRGKKSCHTGLGRSAGWNIPIGLLYCDLPEPRKPLEKAVANFFSGSCAPCADGTDFPQLCQLCPGCGCSTLNQYFGYSGAFKCLKDGAGDVAFVKHSTIFENLANKADRDQYELLCLDNTRKPVDEYKDCHLAQVPSHTVVARSMGGKEDLIWELLNQAQEHFGKDKSKEFQLFSSPHGKDLLFKDSAHGFLKVPPRMDAKMYLGYEYVTAIRNLR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 52 | Zinc finger protein Helios (IKZF2) | 7LPS | 8.08 | |
Target general information Gen name IKZF2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Ikaros family zinc finger protein 2 Protein family Ikaros C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family Biochemical class NA Function Associates with Ikaros at centromeric heterochromatin. Related diseases Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 25, with amelogenesis imperfecta (DEE25) [MIM:615905]: An autosomal recessive disease characterized by subclinical seizures appearing in the first days of life, evolving to severe epileptic disease. Affected individuals have profound or severe delayed development with lack of speech, and most patients do not acquire the ability to sit. Additional variable features include axial hypotonia, peripheral hypertonia, and abnormal involuntary movements such as dystonia and choreoathetosis. Dental abnormalities, including delayed eruption, hypodontia, tooth hypoplasia, yellow discoloration, thin enamel, and enamel chipping are observed in most patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24995870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26384929, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30054523}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P29972; P56545; P56545-3; Q17RB8; P09022; Q8N8B7-2 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Activator; Alternative splicing; DNA-binding; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B,C Molecular weight (Da) 47006.6 Length 410 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 44.28 Isoelectric point 7.23 Charge (pH=7) 0.69 3D Binding mode Sequence INFDTSLPTSHTYLGADMEEFHGRTLHDDDSCQVIPVLPQVMMILIPGQTLPLQLFHPQEVSMVRNLIQKDRTFAVLAYSNVQEREAQFGTTAEIYAYREEQDFGIEIVKVKAIGRQRFKVLELRTQSDGIQQAKVQILPECVLPSTMSAVQLESLNKCQIFPCSYKWWQKYQKRKFHCANLTSWPRWLYSLYDAETLMDRIKKQLREWDENLKDDSLPSNPIDFSYRVAACLPIDDVLRIQLLKIGSAIQRLRCELDIMNKCTSLCCKQCQETEITTKNEIFSLSLCGPMAAYVNPHGYVHETLTVYKACNLNLIGRPSTEHSWFPGYAWTVAQCKICASHIGWKFTATKKDMSPQKFWGLTRSALLPTIPDTEDEISPDGERPFHCNQCGASFTQKGNLLRHIKLHSG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 53 | Choline O-acetyltransferase | 2FY3 | 8.07 | |
Target general information Gen name CHAT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Carnitine/choline acetyltransferase family Biochemical class Transferase Function Choline O-acetyltransferase activity. Related diseases Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 6, presynaptic (CMS6) [MIM:254210]: A form of congenital myasthenic syndrome, a group of disorders characterized by failure of neuromuscular transmission, including pre-synaptic, synaptic, and post-synaptic disorders that are not of autoimmune origin. Clinical features are easy fatigability and muscle weakness affecting the axial and limb muscles (with hypotonia in early-onset forms), the ocular muscles (leading to ptosis and ophthalmoplegia), and the facial and bulbar musculature (affecting sucking and swallowing, and leading to dysphonia). The symptoms fluctuate and worsen with physical effort. CMS6 affected individuals have myasthenic symptoms since birth or early infancy, negative tests for anti-AChR antibodies, and abrupt episodic crises with increased weakness, bulbar paralysis, and apnea precipitated by undue exertion, fever, or excitement. CMS6 inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11172068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12756141}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00122; DB14006; DB00184 Interacts with Q6H8Q1-8; Q8N302-2; Q9NXL2-1; Q6XD76; Q9UII2; Q8TBE0; Q9UQB8-6; Q9ULD4-2; Q9NSI6-4; Q6P5X5; Q96LL4; P20807-4; O00257-3; Q6ZP82-1; O95674; Q9H3R5; Q8WUX9; Q9H2A9; Q3SX64; Q92782-2; Q14117; O14641; Q658K8; Q6UXG2-3; O00472; Q6NXG1; Q15910-2; Q8IZU1; P15407; P55318; Q06547-3; P23769-2; P23771; Q15486; Q8IV36; Q4VB01; Q53GQ0; P10809; P41134; Q9NZH6; Q8NA54; Q86U28; P17275; Q8N5Z5; Q6P597; P08727; Q14525; Q8IUC2; Q6IAA8; Q14847-2; P27338; Q9GZQ8; Q53S70; Q5JXC2; A0A0A0MR05; Q8NEH6; Q8TCY5; Q6IN84-2; Q96H12; P01106; P41271-2; P14598; Q9GZM8; Q5BJF6-2; Q9H8K7; Q9NR21-5; Q5VU43-8; Q13956; Q5SXH7-1; Q96T60; Q96I34; Q86UA1; Q15311; Q8TBY0; Q04206; P47804-3; Q9H0X6; P62899; Q66K80; Q9BY12-3; Q86SQ7-2; Q7Z6I5; Q496A3; Q7Z698; Q9C004; Q92783-2; Q8N4C7; O75528; Q15814; O15273; Q96A09; Q8WTV1; Q53NU3; Q71RG4-4; Q86WT6-2; Q9Y3Q8; Q99598; P49459; P11441; Q9H270; P19544-6; Q53FD0-2; Q3KNS6-3 EC number 2.3.1.6 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acyltransferase; Alternative splicing; Congenital myasthenic syndrome; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Neurotransmitter biosynthesis; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 66365.9 Length 595 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 53.36 Isoelectric point 8.16 Charge (pH=7) 4.64 3D Binding mode Sequence SEESGLPKLPVPPLQQTLATYLQCMRHLVSEEQFRKSQAIVQQFGAPGGLGETLQQKLLERQEKTANWVSEYWLNDMYLNNRLALPVNSSPAVIFARQHFPGTDDQLRFAASLISGVLSYKALLDSHSIPTDCAKGQPLCMKQYYGLFSSYRLPGHTQDTLVAQNSSIMPEPEHVIVACCNQFFVLDVVINFRRLSEGDLFTQLRKIVKMASNAAARLPPIGLLTSDGRSEWAEARTVLVKDSTNRDSLDMIERCICLVCLDAPGGVELSDTHRALQLLHGGGYSKNGANRWYDKSLQFVVGRDGTCGVVCEHSPFDGIVLVQCTEHLLKHMTQPELVRSPMVPLPAPRRLRWKCSPEIQGHLASSAEKLQRIVKNLDFIVYKFDNYGKTFIKKQKCSPDAFIQVALQLAFYRLHRRLVPTYESASIRRFQEGRVDNIRSATPEALAFVRAVTDHKAAVPASEKLLLLKDAIRAQTAYTVMAITGMAIDNHLLALRELARAMCAALPEMFMDETYLMSNRFVLSTSQVPTTTEMFCCYGPVVPNGYGACYNPQPETILFCISSFHSCAATSSSKFAKAVEESLIDMRDLCSLLPP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 54 | Prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 (PTGDR2) | 6D26 | 8.06 | |
Target general information Gen name PTGDR2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PTGDR2; Chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on Th2 cells; CD294 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Receptor for prostaglandin D2 (PGD2). Coupled to the G(i)-protein. Receptor activation may result in pertussis toxin- sensitive decreases in cAMP levels and Ca(2+) mobilization. PI3K signaling is also implicated in mediating PTGDR2 effects. PGD2 induced receptor internalization. CRTH2 internalization can be regulated by diverse kinases such as, PKC, PKA, ADRBK1/GRK2, GPRK5/GRK5 and GRK6. Receptoractivation is responsible, at least in part, in immune regulation and allergic/inflammation responses. Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder with seizures, hypotonia, and brain imaging abnormalities (NEDSHBA) [MIM:618922]: An autosomal recessive neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by global developmental delay, hypotonia, severe to profound intellectual disability, early-onset epilepsy, and microcephaly. Neuroimaging shows cerebral atrophy, thin corpus callosum and hypomyelination in a majority of cases. Death in childhood may occur. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27435318, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28097321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32286009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33476302, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33500274}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00770; DB12789; DB00917; DB01088; DB00328; DB02056; DB13036; DB00605; DB04828 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 49740.6 Length 447 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.89 Isoelectric point 10.13 Charge (pH=7) 21.88 3D Binding mode Sequence ATLKPLCPILEQMSRLQSHSATSIRYIDHAAVLLHGLASLLGLVENGVILFVVGCRMRQTVVTTWVLHLALSDLLASASLPFFTYFLAVGHSWELGTTFCKLHSSIFFLNMFASGFLLSAISLDRCLQVVRPVWAQNHRTVAAAHKVCLVLWALAVLNTVPYFVFRDTISRLDGRIMCYYNVLLLNPGPDRDATCNSRQAALAVSKFLLAFLVPLAIIASSHAAVSLRLQHRADLGLQHRNIFEMLRIDEGGGSGGDEAEKLFNQDVDAAVRGILRNAKLKPVYDSLDAVRRAALINMVFQMGETGVAGFTNSLRMLQQKRWDEAAVNLAKSRWYNQTPNRAKRVITTFRTGTWDAYRRRPGRFVRLVAAVVAAFALCWGPYHVFSLLEARAHANPGLRPLVWRGLPFVTSLAFFNSVANPVLYVLTXPDMLRKLRRSLRTVLESVL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 55 | Oxygen-insensitive NADPH nitroreductase | 3QDL | 8.06 | |
Target general information Gen name rdxA Organism Helicobacter pylori (strain ATCC 700392 / 26695) (Campylobacter pylori) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms HP_0954 Protein family Nitroreductase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Oxidoreductase activity. Related diseases Hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia (HVLI) [MIM:618850]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by highly elevated plasma concentrations of valine and leucine/isoleucine. Affected individuals suffer from headache and mild memory impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. A patient with hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia was identified as compound heterozygote for Gln-170 (inherited from his father) and Lys-264 (inherited from his mother), both variants reduced the catalytic activity of the enzyme. After treatment with vitamin B6, a precursor of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, a BCAT2 cofactor, the blood levels of branched chain amino acids, especially valine, were decreased and brain lesions were improved. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00916 Interacts with NA EC number 1.-.-.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Antibiotic resistance; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 40094.3 Length 352 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 55.15 Isoelectric point 6.72 Charge (pH=7) -0.86 3D Binding mode Sequence MQRLESYILMKFLDQEKRRQLLNERHSCKMFDSHYEFSSTELEEIAEIARLSPSSYNTQPWHFVMVTDKDLKKQIAAHSYFNEEMIKSASALMVVCSLSYILEQCYIAVGQICMGVSLMGLDSCIIGGFDPLKVGEVLEERINPKIACLIALGKRVAEASQKSRKSKVDAITWLMKFLDQEKRRQLLNERHSCKMFDSHYEFSSTELEEIAEIARLSPSSYNTQPWHFVMVTDKDLKKQIAAHSYFNEEMIKSASALMVVCSLRPSELLPMQRLESYILEQCYIAVGQICMGVSLMGLDSCIIGGFDPLKVGEVLEERINKPKIACLIALGKRVAEASQKSRKSKVDAITWL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 56 | Angiopoietin 1 receptor (TEK) | 3BEA | 8.06 | |
Target general information Gen name TEK Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hTIE2; VMCM1; VMCM; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TIE-2; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TEK; Tyrosine kinase with Ig and EGF homology domains-2; Tunica interna endothelial cell kinase; TIE2; P140 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, Tie subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Has anti-inflammatory effects by preventing the leakage of proinflammatory plasma proteins and leukocytes from blood vessels. Required for normal angiogenesis and heart development during embryogenesis. Required for post-natal hematopoiesis. After birth, activates or inhibits angiogenesis, depending on the context. Inhibits angiogenesis and promotes vascular stability in quiescent vessels, where endothelial cells have tight contacts. In quiescent vessels, ANGPT1 oligomers recruit TEK to cell-cell contacts, forming complexes with TEK molecules from adjoining cells, and this leads to preferential activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and the AKT1 signaling cascades. In migrating endothelial cells that lack cell-cell adhesions, ANGT1 recruits TEK to contacts with the extracellular matrix, leading to the formation of focal adhesion complexes, activation of PTK2/FAK and of the downstream kinases MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1, and ultimately to the stimulation of sprouting angiogenesis. ANGPT1 signaling triggers receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation at specific tyrosine residues that then serve as binding sites for scaffold proteins and effectors. Signaling is modulated by ANGPT2 that has lower affinity for TEK, can promote TEK autophosphorylation in the absence of ANGPT1, but inhibits ANGPT1-mediated signaling by competing for the same binding site. Signaling is also modulated by formation of heterodimers with TIE1, and by proteolytic processing that gives rise to a soluble TEK extracellular domain. The soluble extracellular domain modulates signaling by functioning as decoy receptor for angiopoietins. TEK phosphorylates DOK2, GRB7, GRB14, PIK3R1; SHC1 and TIE1. Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for ANGPT1, ANGPT2 and ANGPT4 and regulates angiogenesis, endothelial cell survival, proliferation, migration, adhesion and cell spreading, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, but also maintenance of vascular quiescence. Related diseases Dominantly inherited venous malformations (VMCM) [MIM:600195]: An error of vascular morphogenesis characterized by dilated, serpiginous channels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10369874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19079259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19888299, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8980225}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Somatic mutations of TEK are associated with solitary and multiple sporadic venous malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19079259}.; DISEASE: May play a role in a range of diseases with a vascular component, including neovascularization of tumors, psoriasis and inflammation.; DISEASE: Glaucoma 3, primary congenital, E (GLC3E) [MIM:617272]: An autosomal dominant form of primary congenital glaucoma (PCG). PCG is characterized by marked increase of intraocular pressure at birth or early childhood, large ocular globes (buphthalmos) and corneal edema. It results from developmental defects of the trabecular meshwork and anterior chamber angle of the eye that prevent adequate drainage of aqueous humor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27270174}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00415; DB12010; DB08221; DB08901; DB08896; DB14840; DB11800; DB05294 Interacts with Q15389; O15123; O15123-1; Q16678; Q05209; P23467; P08575; Q12913; Q15262; Q16827 EC number EC 2.7.10.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Angiogenesis; ATP-binding; Cell junction; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; EGF-like domain; Glaucoma; Glycoprotein; Immunoglobulin domain; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34965.9 Length 310 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 43.57 Isoelectric point 8.39 Charge (pH=7) 3.42 3D Binding mode Sequence QVRWKIIESYEGNSYTFIDPTQLPYNEKWEFPRNNLQFGKTLGAGAFGKVVEATAFGLGKEDAVLKVAVKMLKSTAHADEKEALMSELKIMSHLGQHENIVNLLGACTHGGPVLVITEYCCYGDLLNFLRRKSRVLSTLSTRDLLHFSSQVAQGMAFLASKNCIHRDVAARNVLLTNGHVAKIGDFGLARDIMNDSNYIVKGNARLPVKWMAPESIFDCVYTVQSDVWSYGILLWEIFSLGLNPYPGILVNSKFYKLVKDGYQMAQPAFAPKNIYSIMQACWALEPTHRPTFQQICSFLQEQAQEDRRER Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 57 | Bifunctional aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (EPRS) | 4HVC | 8.06 | |
Target general information Gen name EPRS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms QPRS; QARS; ProlinetRNA ligase; PIG32; GlutamatylprolyltRNA synthetase; Glutamatyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase; GluRS; EPRS; Cell proliferationinducing gene 32 protein; Cell proliferation-inducing gene 32 Protein family Class-I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family, Glutamate--tRNA ligase type 2 subfamily; Class-II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family Biochemical class Carbon-oxygen ligase Function The phosphorylation of EPRS, induced by interferon-gamma, dissociates the protein from the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase multienzyme complex and recruits it to the GAIT complex that binds to stem loop-containing GAIT elements in the 3'-UTR of diverse inflammatory mRNAs (such as ceruplasmin), suppressing their translation. Interferon-gamma can therefore redirect, in specific cells, the EPRS function from protein synthesis to translation inhibition. Also functions as an effector of the mTORC1 signaling pathway by promoting, through SLC27A1, the uptake of long-chain fatty acid by adipocytes. Thereby, it also plays a role in fat metabolism and more indirectly influences lifespan. Multifunctional protein which is primarily part of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase multienzyme complex, also know as multisynthetase complex, that catalyzes the attachment of the cognate amino acid to the corresponding tRNA in a two-step reaction: the amino acid is first activated by ATP to form a covalent intermediate with AMP and is then transferred to the acceptor end of the cognate tRNA. Related diseases Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, 15 (HLD15) [MIM:617951]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by hypomyelinating leukodystrophy with thinning of the corpus callosum. Clinical features include motor and cognitive impairment appearing in the first or second decade of life, dystonia, ataxia, spasticity, and dysphagia. Most patients develop severe optic atrophy, and some have hearing loss. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29576217}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02684; DB02510; DB03376; DB00142; DB00172 Interacts with P07814; Q8IWL3; P41252; Q15046; P42695; P54136; O60506 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Leukodystrophy; Ligase; Membrane; Metal-binding; Methylation; Multifunctional enzyme; Neurodegeneration; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Protein biosynthesis; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; RNA-binding; Translation regulation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 55039.7 Length 483 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 39.15 Isoelectric point 5.92 Charge (pH=7) -6.4 3D Binding mode Sequence GLEAKKEENLADWYSQVITKSEMIEYHDISGCYILRPWAYAIWEAIKDFFDAEIKKLGVENCYFPMFVSQSALEKEKTHVADFAPEVAWVTRSGKTELAEPIAIRPTSETVMYPAYAKWVQSHRDLPIKLNQWCNVVRWEFKHPQPFLRTREFLWQEGHSAFATMEEAAEEVLQILDLYAQVYEELLAIPVVKGRKTEKEKFAGGDYTTTIEAFISASGRAIQGGTSHHLGQNFSKMFEIVFEDPKIPGEKQFAYQNSWGLTTRTIGVMTMVHGDNMGLVLPPRVACVQVVIIPCGISEEDKEALIAKCNDYRRRLLSVNIRVRADLRDNYSPGWKFNHWELKGVPIRLEVGPRDMKSCQFVAVRRDTGEKLTVAENEAETKLQAILEDIQVTLFTRASEDLKTHMVVANTMEDFQKILDSGKIVQIPFCGEIDCEDWIKKTTAMGAKSLCIPFKPLCELQPGAKCVCGKNPAKYYTLFGRSY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 58 | Fatty acid-binding protein 5 (FABP5) | 5UR9 | 8.06 | |
Target general information Gen name FABP5 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Psoriasis-associated fatty acid-binding protein homolog; PA-FABP; Fatty acid-binding protein, epidermal; Fatty Acid BindingProtein mal1; Epidermal-type fatty acid-binding protein; E-FABP Protein family Calycin superfamily, Fatty-acid binding protein (FABP) family Biochemical class Fatty acid binding protein Function Intracellular carrier for long-chain fatty acids and related active lipids, such as the endocannabinoid, that regulates the metabolism and actions of the ligands they bind. In addition to the cytosolic transport, selectively delivers specific fatty acids from the cytosol to the nucleus, wherein they activate nuclear receptors. Delivers retinoic acid to the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta; which promotes proliferation and survival. May also serve as a synaptic carrier of endocannabinoid at central synapses and thus controls retrograde endocannabinoid signaling. Modulates inflammation by regulating PTGES induction via NF-kappa-B activation, and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) biosynthesis during inflammation. May be involved in keratinocyte differentiation. Related diseases Erythrocytosis, familial, 4 (ECYT4) [MIM:611783]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by elevated serum hemoglobin and hematocrit, and normal platelet and leukocyte counts. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18184961, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18378852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19208626, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22367913}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03796 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Lipid transport; Lipid-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Synapse; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 15033.1 Length 134 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 28.26 Isoelectric point 6.83 Charge (pH=7) -0.14 3D Binding mode Sequence ATVQQLEGRWRLVDSKGFDEYMKELGVGIALRKMGAMAKPDCIITCDGKNLTIKTESTLKTTQFSCTLGEKFEETTADGRKTQTVCNFTDGALVQHQEWDGKESTITRKLKDGKLVVECVMNNVTCTRIYEKVE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 59 | Ecdysone receptor (20-hydroxy-ecdysone receptor) (EcRH) (Ecdysteroid receptor) (Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group H member 1) | 3IXP | 8.05 | |
Target general information Gen name NA Organism Helicoverpa armigera (Cotton bollworm) (Heliothis armigera) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily Biochemical class NA Function NA Related diseases NA Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; DNA-binding; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Receptor; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,D Molecular weight (Da) 52799.1 Length 462 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 51.97 Isoelectric point 8.09 Charge (pH=7) 2.37 3D Binding mode Sequence QELSIERLLEMESLVADPSEEFQFLRVGPDSNVPPKFRAPVSSLCQIGNKQIAALVVWARDIPHFSQLEMEDQILLIKGSWNELLLFAIAWRSMEFLTSPPQLMCLMPGMTLHRNSALQAGVGQIFDRVLSELSLKMRTLRVDQAEYVALKAIILLNPDVKGLKNRQEVEVLREKMFLCLDEYCRRSRSSEEGRFAALLLRLPALRSISLKSFEHLFFFHLVADTSIAGYIRDALRNHAPPIVPPLTANQKSLIARLVYYQEGYEQMPFRQITEMTILTVQLIVEFAKGLPGFSKISQSDQITLLKACSSEVMMLRVARRYDAATDSVLFANNQAYTRDNYRKAGMAYVIEDLLHFCRCMYSMMMDNVHYALLTAIVIFSDRPGLEQPSLVEEIQRYYLNTLRVYILNQNSASPRSAVIFGKILGILTEIRTLGMQNSNMCISLKLKNRKLPPFLEEIWDVA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 60 | Melanoma derived growth regulator (MIA) | 5IXB | 8.03 | |
Target general information Gen name MIA Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Melanoma-derived growth regulatory protein; Melanoma inhibitory activity protein Protein family MIA/OTOR family Biochemical class NA Function Elicits growth inhibition on melanoma cells in vitro as well as some other neuroectodermal tumors, including gliomas. Related diseases Hypertriglyceridemia, transient infantile (HTGTI) [MIM:614480]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by onset of moderate to severe transient hypertriglyceridemia in infancy that normalizes with age. The hypertriglyceridemia is associated with hepatomegaly, moderately elevated transaminases, persistent fatty liver, and the development of hepatic fibrosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22226083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24549054}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Growth factor; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; SH3 domain; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 11955.6 Length 105 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 26.45 Isoelectric point 8.7 Charge (pH=7) 2.64 3D Binding mode Sequence MPKLADRKLCADQECSHPISMAVALQDYMAPDCRFLTIHRGQVVYVFSKLKGRGRLFWGGSVQGDYYGDLAARLGYFPSSIVREDQTLKPGKVDVKTDKWDFYCQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||