Job Results:
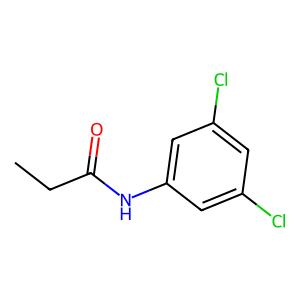
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
e8ee1117e51baec8034629c7ce0a1a1e
Job name
NA
Time
2025-12-29 08:34:20
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | Peptostreptococcal albumin-binding protein | 2VDB | 6.00 | |
Target general information Gen name pab Organism Finegoldia magna (Peptostreptococcus magnus) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family NA Biochemical class Protein binding Function Binds serum albumin. Related diseases LTC4 synthase deficiency is associated with a neurometabolic developmental disorder characterized by muscular hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, and microcephaly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10896305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9820300}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03600; DB00788 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell wall; Peptidoglycan-anchor; Secreted; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B Molecular weight (Da) 21751.6 Length 189 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 49.17 Isoelectric point 5.44 Charge (pH=7) -6.7 3D Binding mode Sequence EVAHRFKDLGEENFKALVLIAFAQYLQQCPFEDHVKLVNEVTEFAKTCVADESAENCDKSLHTLFGDKLCTVATLEMADCCAKQEPERNECFLQHKDDNPNLPRLVRPEVDVMCTAFHDNEETFLKKYLYEIARRHPYFYAPELLFFAKRYKAAFTECCQAADKAACLLPKLDELRDEGKASSAKQRLK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 22 | Cyclopropane mycolic acid synthase MmaA2 | 1TPY | 6.00 | |
Target general information Gen name mmaA2 Organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms Rv0644c;mma2 Protein family CFA/CMAS family Biochemical class Transferase Function Cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase activity.Methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 16 (OZEMA16) [MIM:617234]: A rare cause of female primary infertility. In affected women, ovulation and fertilization proceed normally but embryos are arrested at early stages of development. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27545678}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01718; DB01752 Interacts with NA EC number 2.1.1.79 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Methyltransferase; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32493.6 Length 285 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.61 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -10.17 3D Binding mode Sequence NDLTPHFEDVQAHYDLSDDFFRLFLDPTQTYSCAHFEREDMTLEEAQIAKIDLALGKLGLQPGMTLLDIGCGWGATMRRAIAQYDVNVVGLTLSKNQAAHVQKSFDEMDTPRDRRVLLAGWEQFNEPVDRIVSIGAFEHFGHDRHADFFARAHKILPPDGVLLLHTITGLTRQQMVDHGLPLTLWLARFLKFIATEIFPGGQPPTIEMVEEQSAKTGFTLTRRQSLQPHYARTLDLWAEALQEHKSEAIAIQSEEVYERYMKYLTGCAKLFRVGYIDVNQFTLAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 23 | Pseudomonas Transcriptional activator protein LasR (Pseudo LasR) | 3IX3 | 6.00 | |
Target general information Gen name Pseudo LasR Organism Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NA Protein family Autoinducer-regulated transcriptional regulatory protein family Biochemical class NA Function Transcriptional activator of elastase structural gene (LasB). Binds to the PAI autoinducer. Related diseases Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1A (IGHD1A) [MIM:262400]: An autosomal recessive, severe deficiency of growth hormone leading to dwarfism. Patients often develop antibodies to administered growth hormone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8364549}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 1B (IGHD1B) [MIM:612781]: An autosomal recessive deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Patients have low but detectable levels of growth hormone, significantly retarded bone age, and a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655557}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Kowarski syndrome (KWKS) [MIM:262650]: A syndrome clinically characterized by short stature associated with bioinactive growth hormone, normal or slightly increased growth hormone secretion, pathologically low insulin-like growth factor 1 levels, and normal catch-up growth on growth hormone replacement therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17519310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8552145, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9276733}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Growth hormone deficiency, isolated, 2 (IGHD2) [MIM:173100]: An autosomal dominant deficiency of growth hormone leading to short stature. Clinical severity is variable. Patients have a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11502836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9152628}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08324 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; DNA-binding; Quorum sensing; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 18305.5 Length 163 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.52 Isoelectric point 5.19 Charge (pH=7) -6.78 3D Binding mode Sequence FLELERSSGKLEWSAILQKMASDLGFSKILFGLLPKDSQDYENAFIVGNYPAAWREHYDRAGYARVDPTVSHCTQSVLPIFWEPSIYQTRKQHEFFEEASAAGLVYGLTMPLHGARGELGALSLSVEAENRAEANRFMESVLPTLWMLKDYALQSGAGLAFEH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 24 | Histamine H3 receptor (H3R) | 7F61 | 6.00 | |
Target general information Gen name HRH3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Histamine receptor 3; HH3R; GPCR97; G-protein coupled receptor 97; G protein-coupled receptor 97 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Signals through the inhibition of adenylate cyclase and displays high constitutive activity (spontaneous activity in the absence of agonist). Agonist stimulation of isoform 3 neither modified adenylate cyclase activity nor induced intracellular calcium mobilization. The H3 subclass of histamine receptors could mediate the histamine signals in CNS and peripheral nervous system. Related diseases Immunodeficiency 48 (IMD48) [MIM:269840]: A form of severe immunodeficiency characterized by a selective absence of CD8+ T-cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11123350, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11412303, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18509675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8124727, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8202713}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Autoimmune disease, multisystem, infantile-onset, 2 (ADMIO2) [MIM:617006]: An autosomal recessive, autoimmune disorder characterized by systemic manifestations including blistering skin disease, uncontrollable bullous pemphigoid, inflammatory colitis, autoimmune hypothyroidism, proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26783323}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01238; DB06698; DB05381; DB17087; DB05080; DB00768; DB11642 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34321.1 Length 301 Aromaticity 0.16 Instability index 32.22 Isoelectric point 9.63 Charge (pH=7) 15.11 3D Binding mode Sequence RGFSAAWTAVLAALMALLIVATVLGNALVMLAFVADSSLRTQNNFFLLNLAISDFLVGAFCIPLYVPYVLTGRWTFGRGLCKLWLVVDYLLCTSKAFNIVLISYDRFLSVTRAVSYRAQQGDTRRAVRKMLLVWVLAFLLYGPAILSWEYLSGGSSIPEGHCYAEFFYNWYFLITASTLEFFTPFLSVTFFNLSIYLNIQRRTRLRLDGAREAAGRFRLSRDRKVAKSLAVIVSIFGLCWAPYTLLMIIRAACHGHCVPDYWYETSFWLLWANSAVNPVLYPLCHHSFRRAFTKLLCPQKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 25 | Plasmepsin-2 | 2BJU | 5.99 | |
Target general information Gen name N/A Organism Plasmodium falciparum (isolate HB3) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Peptidase A1 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Aspartic-type endopeptidase activity. Related diseases Short/branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (SBCADD) [MIM:610006]: Autosomal recessive disorder and consists of a defect in catabolism of L-isoleucine which is characterized by an increase of 2-methylbutyrylglycine and 2-methylbutyrylcarnitine in blood and urine. Affected individuals have seizures and psychomotor delay as the main clinical features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10832746, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11013134, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16317551}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04378; DB04373; DB11638; DB01218; DB02505; DB03063 Interacts with NA EC number 3.4.23.39 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Aspartyl protease; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Hydrolase; Membrane; Protease; Reference proteome; Signal-anchor; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Vacuole; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 36923.5 Length 329 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 44.31 Isoelectric point 4.67 Charge (pH=7) -17.94 3D Binding mode Sequence SSNDNIELVDFQNIMFYGDAEVGDNQQPFTFILDTGSANLWVPSVKCTTAGCLTKHLYDSSKSRTYEKDGTKVEMNYVSGTVSGFFSKDLVTVGNLSLPYKFIEVIDTNGFEPTYTASTFDGILGLGWKDLSIGSVDPIVVELKNQNKIENALFTFYLPVHDKHTGFLTIGGIEERFYEGPLTYEKLNHDLYWQITLDAHVGNIMLEKANCIVDSGTSAITVPTDFLNKMLQNLDVIKVPFLPFYVTLCNNSKLPTFEFTSENGKYTLEPEYYLQHIEDVGPGLCMLNIIGLDFPVPTFILGDPFMRKYFTVFDYDNHSVGIALAKKNL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 26 | N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE) | 4ZHT | 5.99 | |
Target general information Gen name GNE Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms UDPGlcNAc2epimerase/ManAc kinase; GNE; Bifunctional UDPNacetylglucosamine 2epimerase/Nacetylmannosamine kinase Protein family UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase family; ROK (NagC/XylR) family Biochemical class Kinase Function Regulates and initiates biosynthesis of N- acetylneuraminic acid (NeuAc), a precursor of sialic acids. Plays an essential role in early development. Required for normal sialylation in hematopoietic cells. Sialylation is implicated in cell adhesion, signal transduction, tumorigenicity and metastatic behavior of malignant cells. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10334995}. Related diseases Sialuria (SIALURIA) [MIM:269921]: In sialuria, free sialic acid accumulates in the cytoplasm and gram quantities of neuraminic acid are secreted in the urine. The metabolic defect involves lack of feedback inhibition of UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase by CMP-Neu5Ac, resulting in constitutive overproduction of free Neu5Ac. Clinical features include variable degrees of developmental delay, coarse facial features and hepatomegaly. Sialuria inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10330343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10356312, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11326336, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2808337}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Nonaka myopathy (NM) [MIM:605820]: An autosomal recessive myopathy characterized by early adult onset and progressive distal muscle weakness that preferentially affects the anterior tibial muscles, usually sparing the quadriceps femoris. Some individuals may have involvement of the upper limbs or proximal muscles. Muscle biopsy reveals presence of rimmed vacuoles. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11528398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11916006, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12177386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12325084, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12409274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12473753, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12473769, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12473780, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12497639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12811782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12913203, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14707127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15146476, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16503651}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thrombocytopenia 12 with or without myopathy (THC12) [MIM:620757]: A form of thrombocytopenia, a hematologic disorder defined by a decrease in the number of platelets in circulating blood, resulting in the potential for increased bleeding and decreased ability for clotting. THC12 is an autosomal recessive form manifesting from infancy or early childhood with bleeding episodes. Clinical features include petechiae, easy bruising, epistaxis, hematomas, menorrhagia, and increased bleeding after trauma or surgery. Rare patients may have thrombocytopenia without bleeding. Some affected individuals have myopathic features, usually apparent in the second or third decades of life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25257349, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30171045, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33198675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34788986, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34858435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35052006, ECO:0000269|PubMed:38237079}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P12814; Q6UY14-3; Q969Y2; Q15323; P60370; P60409; P60410; P60411; Q9BQ66; P26371; Q9BYQ4; Q7Z3S9; O43597; Q6UY14-3; Q6P5X5; P27918; A8MQ03; Q16610; Q9UHF1; P28799; P49639; Q5T749; Q15323; O76011; Q6A162; P78385; P78386; O43790; Q07627; Q8IUG1; P60409; P60410; Q8IUC1; P60328; Q52LG2; Q3SY46; Q9BYP8; Q3LHN2; Q3SYF9; Q9BYR8; Q9BYR6; Q9BYQ7; Q9BYQ6; Q9BYR3; P26371; Q3LI64; Q3LI66; Q3LI67; Q9BYQ4; Q9BYQ3; Q9BYQ0; Q99750; Q8IV28; P0DPK4; O15496; O43609; O43610; P14373; Q8IWZ5; Q15654; O14817; Q2TAL6; Q9BRX9; O76024; Q9NZC7-5 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Allosteric enzyme; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Kinase; Metal-binding; Multifunctional enzyme; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transferase; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 41589.2 Length 384 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 35.07 Isoelectric point 7.05 Charge (pH=7) 0.19 3D Binding mode Sequence NRKLRVCVATCNRADYSKLAPIXFGIKTEPEFFELDVVVLGSHLIDDYGNTYRXIEQDDFDINTRLHTIVRGEDEAAXVESVGLALVKLPDVLNRLKPDIXIVHGDRFDALALATSAALXNIRILHIEGGEVSGTIDDSIRHAITKLAHYHVCCTRSAEQHLISXCEDHDRILLAGCPSYDKLLSAKNKDYXSIIRXWLGDDVKSKDYIVALQHPVTTDIKHSIKXFELTLDALISFNKRTLVLFPNIDAGSKEXVRVXRKKGIEHHPNFRAVKHVPFDQFIQLVAHAGCXIGNSSCGVREVGAFGTPVINLGTRQIGRETGENVLHVRDADTQDKILQALHLQFGKQYPCSKIYGDGNAVPRILKFLKSIDLQEPLQKKFCFP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 27 | Helicobacter pylori Methylthioadenosine nucleosidase (HELPY mtnN) | 4BMZ | 5.99 | |
Target general information Gen name HELPY mtnN Organism Helicobacter pylori (strain ATCC 700392 / 26695) (Campylobacter pylori) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms MTAN; MTA/SAH nucleosidase; Aminofutalosine nucleosidase; Aminodeoxyfutalosine nucleosidase; AFL nucleosidase; 6-amino-6-deoxyfutalosine N-ribosylhydrolase; 5'-methylthioadenosine/S-adenosylhomocystei Protein family PNP/UDP phosphorylase family Biochemical class NA Function Catalyzes the direct conversion of aminodeoxyfutalosine (AFL) into dehypoxanthine futalosine (DHFL) and adenine via the hydrolysis of the N-glycosidic bond; this reaction seems to represent an essential step in the menaquinone biosynthesis pathway in Helicobacter species. Can also probably catalyzes the hydrolysis of 5'-methylthioadenosine (MTA) and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) to adenine and the corresponding thioribose, 5'-methylthioribose and S-ribosylhomocysteine, respectively. These other activities highlight the tremendous versatility of the enzyme, which also plays key roles in S-adenosylmethionine recycling and in the biosynthesis of the quorum-sensing molecule autoinducer-2. Does not act on futalosine (FL) as substrate. Related diseases Progressive familial heart block 1B (PFHB1B) [MIM:604559]: A cardiac bundle branch disorder characterized by progressive alteration of cardiac conduction through the His-Purkinje system, with a pattern of a right bundle-branch block and/or left anterior hemiblock occurring individually or together. It leads to complete atrio-ventricular block causing syncope and sudden death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19726882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20562447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21887725}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva 6 (EKVP6) [MIM:618531]: A form of erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva, a genodermatosis characterized by the coexistence of two independent skin lesions: transient erythema and hyperkeratosis that is usually localized but occasionally occurs in its generalized form. Clinical presentation varies significantly within a family and from one family to another. Palmoplantar keratoderma is present in around 50% of cases. EKVP6 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30528822}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Amino-acid biosynthesis; Hydrolase; Menaquinone biosynthesis; Methionine biosynthesis; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 50547.6 Length 464 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 26.92 Isoelectric point 5.13 Charge (pH=7) -20.92 3D Binding mode Sequence VQKIGILGAMREEITPILELFGVDFEEIPLGGNVFHKGVYHNKEIIVAYSKIGKVHSTLTTTSMILAFGVQKVLFSGVAGSLVKDLKINDLLVAIQLVQHDVDLSAFDHPLGFIPESAIFIETSESLNALAKEVANEQHIVLKEGVIASGDQFVHSKERKEFLVSEFKASAVEMEGASVAFVCQKFGVPCCVLRSISNNADEEANMSFDAFLEKSAQTSAKFLKSMVDELGSHMVQKIGILGAMREEITPILELFGVDFEEIPLGGNVFHKGVYHNKEIIVAYSKIGKVHSTLTTTSMILAFGVQKVLFSGVAGSLVKDLKINDLLVAIQLVQHDVDLSAFDHPLGFIPESAIFIETSESLNALAKEVANEQHIVLKEGVIASGDQFVHSKERKEFLVSEFKASAVEMEGASVAFVCQKFGVPCCVLRSISNNADEEANMSFDAFLEKSAQTSAKFLKSMVDEL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 28 | Neprilysin | 1R1H | 5.98 | |
Target general information Gen name MME Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms EPN Protein family Peptidase M13 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Endopeptidase activity.Exopeptidase activity.Metalloendopeptidase activity.Metallopeptidase activity.Peptide binding.Zinc ion binding. Related diseases Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, 2T (CMT2T) [MIM:617017]: An axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal degeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26991897, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27588448}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spinocerebellar ataxia 43 (SCA43) [MIM:617018]: A form of spinocerebellar ataxia, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of cerebellar disorders. Patients show progressive incoordination of gait and often poor coordination of hands, speech and eye movements, due to degeneration of the cerebellum with variable involvement of the brainstem and spinal cord. SCA43 is a slowly progressive, autosomal dominant form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27583304}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08575; DB02597; DB00616; DB11623; DB05796; DB06655; DB02558; DB02062; DB00886; DB02557; DB09292; DB13928; DB08626 Interacts with P05067; P21926; Q06787-7; P08107; P04792 EC number 3.4.24.11 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Myristate; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathy; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal-anchor; Spinocerebellar ataxia; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 79435.8 Length 696 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.5 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -11.46 3D Binding mode Sequence GICKSSDCIKSAARLIQNMDATTEPCTDFFKYACGGWLKRNVIPETSSRYGNFDILRDELEVVLKDVLQEPKTEDIVAVQKAKALYRSCINESAIDSRGGEPLLKLLPDIYGWPVATENWEQKYGASWTAEKAIAQLNSKYGKKVLINLFVGTDDKNSVNHVIHIDQPRLGLPSRDYYECTGIYKEACTAYVDFMISVARLIRQEERLPIDENQLALEMNKVMELEKEIANATAKPEDRNDPMLLYNKMTLAQIQNNFSLEINGKPFSWLNFTNEIMSTVNISITNEEDVVVYAPEYLTKLKPILTKYSARDLQNLMSWRFIMDLVSSLSRTYKESRNAFRKALYGTTSETATWRRCANYVNGNMENAVGRLYVEAAFAGESKHVVEDLIAQIREVFIQTLDDLTWMDAETKKRAEEKALAIKERIGYPDDIVSNDNKLNNEYLELNYKEDEYFENIIQNLKFSQSKQLKKLREKVDKDEWISGAAVVNAFYSSGRNQIVFPAGILQPPFFSAQQSNSLNYGGIGMVIGHEITHGFDDNGRNFNKDGDLVDWWTQQSASNFKEQSQCMVYQYGNFSWDLAGGQHLNGINTLGENIADNGGLGQAYRAYQNYIKKNGEEKLLPGLDLNHKQLFFLNFAQVWCGTYRPEYAVNSIKTDVHSPGNFRIIGTLQNSAEFSEAFHCRKNSYMNPEKKCRVW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 29 | Dopamine beta-hydroxylase | 4ZEL | 5.98 | |
Target general information Gen name DBH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Copper type II ascorbate-dependent monooxygenase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Catalytic activity.Copper ion binding.Dopamine beta-monooxygenase activity.L-ascorbic acid binding. Related diseases Orthostatic hypotension 1 (ORTHYP1) [MIM:223360]: A form of orthostatic hypotension due to congenital dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a finding defined as a 20-mm Hg decrease in systolic pressure or a 10-mm Hg decrease in diastolic pressure occurring 3 minutes after a person has risen from supine to standing. Symptoms include dizziness, blurred vision, and sometimes syncope. ORTHYP1 is an autosomal recessive condition apparent from infancy or early childhood and characterized by low plasma and urinary levels of norepinephrine and epinephrine, and episodic hypoglycemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11857564}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00126; DB06774; DB09130; DB05394; DB00822; DB00988; DB00968; DB00550 Interacts with P00352; P63010-2; Q04656; Q8WUW1; Q9UNS2; Q71DI3; P61978; Q9Y2M5; Q92876; P08727; Q14693; P0DPK4; Q6GQQ9-2; P27986-2; Q9ULX5; Q96D59; Q8N6K7-2; Q9GZS3; Q8IUW3; Q86WT6-2 EC number 1.14.17.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Catecholamine biosynthesis; Copper; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal-anchor; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Vitamin C Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 123694 Length 1094 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 51.85 Isoelectric point 5.84 Charge (pH=7) -24.5 3D Binding mode Sequence PLPYHIPLDPEGSLELSWNVSYTQEAIHFQLLVRRLKAGVLFGMSDRGELENADLVVLWTDGDAYFADAWSDQKGQIHLDPQQDYQLLQVQRTPEGLTLLFKRPFGTCDPKDYLIEDGTVHLVYGILEEPFRSLEAINGSGLQMGLQRVQLLKPNIPEPELPSDACTMEVQAPNIQIPSQETTYWCYIKELPKGFSRHHIIKYEPIVTKGNEALVHHMEVFQCAPEMDSVPHFSGPCDSKMKPDRLNYCRHVLAAWALGAKAFYYPEEAGLAFGGPGSSRYLRLEVHYHNPLVIEGRNDSSGIRLYYTAKLRRFNAGIMELGLVYTPVMAIPPRETAFILTGYCTDKCTQLALPPSGIHIFASQLHTHLTGRKVVTVLVRDGREWEIVNQDNHYSPHFQEIRMLKKVVSVHPGDVLITSCTYNTEDRELATVGGFGILEEMCVNYVHYYPQTQLELCKSAVDAGFLQKYFHLINRFNNEDVCTCPQASVSQQFTSVPWNSFNRDVLKALYSFAPISMHCNKSSAVRFQGEWNLQPLPKVISTLEEPTVVSPLPYHIPLDPEGSLELSWNVSYTQEAIHFQLLVRRLKAGVLFGMSDRGELENADLVVLAYFADAWSDQKGQIHLDPQQDYQLLQVQRTPEGLTLLFKRPFGTCDPKDYLIEDGTVHLVYGILEEPFRSLEAINGSGLQMGLQRVQLLKPNIPEPELPSDACTMEVQAPNIQIPSQETTYWCYIKELPKGFSRHHIIKYEPIVTKGNEALVHHMEVFQCAPEVPHFSGPCDSKMLNYCRHVLAAWALGAKAFYYPEEAGLAFGGPGSSRYLRLEVHYHNPLVIEGRNDSSGIRLYYTAKLRRFNAGIMELGLVYTPVMAIPPRETAFILTGYCTDKCTQLALPPSGIHIFASQLHTHLTGRKVVTVLVRDGREWEIVNQDNHYSPHFQEIRMLKKVVSVHPGDVLITSCTYNTEDRELATVGGFGILEEMCVNYVHYYPQTQLELCKSAVDAGFLQKYFHLINRFNNEDVCTCPQASVSQQFTSVPWNSFNRDVLKALYSFAPISMHCNKSSAVRFQGEWNLQPLPKVISTLEEPTPQCVVSIGG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 30 | Serine Racemase (SRR) | 3L6B | 5.98 | |
Target general information Gen name SRR Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms L-serine dehydratase; L-serine ammonia-lyase; D-serine dehydratase; D-serine ammonia-lyase Protein family Serine/threonine dehydratase family Biochemical class Racemases and epimerase Function D-serine is a key coagonist with glutamate at NMDA receptors. Has dehydratase activity towards both L-serine and D-serine. Catalyzes the synthesis of D-serine from L-serine. Related diseases Cornelia de Lange syndrome 5 (CDLS5) [MIM:300882]: A form of Cornelia de Lange syndrome, a clinically heterogeneous developmental disorder associated with malformations affecting multiple systems. It is characterized by facial dysmorphisms, abnormal hands and feet, growth delay, cognitive retardation, hirsutism, gastroesophageal dysfunction and cardiac, ophthalmologic and genitourinary anomalies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22885700, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22889856}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00114; DB00133 Interacts with Q9H4P4; Q9GZT4 EC number EC 5.1.1.18 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Allosteric enzyme; ATP-binding; Direct protein sequencing; Isomerase; Lyase; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Proteomics identification; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34613.6 Length 322 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 31.62 Isoelectric point 6.35 Charge (pH=7) -1.7 3D Binding mode Sequence AQYDISFADVEKAHINIRDSIHLTPVLTSSILNQLTGRNLFFKCELFQKTGSFKIRGALNAVRSLVRKPKAVVTHSSGNHGQALTYAAKLEGIPAYIVVPQTAPDCKKLAIQAYGASIVYCEPSDESRENVAKRVTEETEGIMVHPNQEPAVIAGQGTIALEVLNQVPLVDALVVPVGGGGMLAGIAITVKALKPSVKVYAAEPSNADDCYQSKLKGKLMPNLYPPETIADGVKSSIGLNTWPIIRDLVDDIFTVTEDEIKCATQLVWERMKLLIEPTAGVGVAAVLSQHFQTVSPEVKNICIVLSGGNVDLTSSITWVKQA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 31 | Mycobacterium Cytochrome p450 121 (MycB cyp121) | 5EDT | 5.98 | |
Target general information Gen name MycB cyp121 Organism Mycobacterium bovis (strain ATCC BAA-935 / AF2122/97) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Cytochrome P450 MT2; Cytochrome P450 121 Protein family Cytochrome P450 family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the formation of an intramolecular C-C bond between two tyrosyl carbon atoms of Cyy. Related diseases Long QT syndrome 1 (LQT1) [MIM:192500]: A heart disorder characterized by a prolonged QT interval on the ECG and polymorphic ventricular arrhythmias. They cause syncope and sudden death in response to exercise or emotional stress, and can present with a sentinel event of sudden cardiac death in infancy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10024302, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10220144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10220146, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10367071, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10409658, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10482963, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10728423, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10973849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11799244, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12442276, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15840476, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16414944, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16556865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16922724, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18165683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18400097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19540844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19716085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19808498, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21241800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24184248, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24269949, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24713462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25037568, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25139741, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25705178, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28096388, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34398675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8528244, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8818942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8872472, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9024139, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9272155, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9302275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9312006, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9323054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9386136, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9482580, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9570196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9641694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9693036, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9702906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9799083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9927399, ECO:0000269|Ref.36}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome 1 (JLNS1) [MIM:220400]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by congenital deafness, prolongation of the QT interval, syncopal attacks due to ventricular arrhythmias, and a high risk of sudden death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10090886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10728423, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18400097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18441444, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25705178, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9781056}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Atrial fibrillation, familial, 3 (ATFB3) [MIM:607554]: An autosomal dominant form of atrial fibrillation, a common sustained cardiac rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity and ineffective atrial contraction promoting blood stasis in the atria and reduces ventricular filling. It can result in palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12522251}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Short QT syndrome 2 (SQT2) [MIM:609621]: An autosomal dominant form of short QT syndrome, a heart disorder characterized by idiopathic persistently and uniformly short QT interval on ECG in the absence of structural heart disease in affected individuals. It can cause syncope and sudden death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15159330}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) [MIM:125853]: A multifactorial disorder of glucose homeostasis caused by a lack of sensitivity to insulin. Affected individuals usually have an obese body habitus and manifestations of a metabolic syndrome characterized by diabetes, insulin resistance, hypertension and hypertriglyceridemia. The disease results in long-term complications that affect the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and blood vessels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18711366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18711367, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24390345}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.14.-.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Heme; Iron; Metal-binding; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 43023.2 Length 394 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 39.15 Isoelectric point 6.23 Charge (pH=7) -2.55 3D Binding mode Sequence ATVLLEVPFSARGDRIPDAVAELRTREPIRKVRTITGAEAWLVSSYALCTQVLEDRRFSMKETAAAGAPRLNALTVPPEVVNNMGNIADAGLRKAVMKAITPKAPGLEQFLRDTANSLLDNLITEGAPADLRNDFADPLATALHCKVLGIPQEDGPKLFRSLSIAFMSSADPIPAAKINWDRDIEYMAGILENPNITTGLMGELSRLRKDPAYSHVSDELFATIGVTFFGAGVISTGSFLTTALISLIQRPQLRNLLHEKPELIPAGVEELLRINLSFADGLPRLATADIQVGDVLVRKGELVLVLLEGANFDPEHFPNPGSIELDRPNPTSHLAFGRGQHFCPGSALGRRHAQIGIEALLKKMPGVDLAVPIDQLVWRTRFQRRIPERLPVLW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 32 | Peroxiredoxin-4 (PRDX4) | 4RQX | 5.98 | |
Target general information Gen name PRDX4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Thioredoxindependent peroxide reductase A0372; Thioredoxin peroxidase AO372; PrxIV; Peroxiredoxin4; Peroxiredoxin IV; PRDX4; Antioxidant enzyme AOE372; AOE372 Protein family Peroxiredoxin family, AhpC/Prx1 subfamily Biochemical class Peroxidases Function Probably involved in redox regulation of the cell. Regulates the activation of NF-kappa-B in the cytosol by a modulation of I-kappa-B-alpha phosphorylation. Related diseases May be involved in T-cell exhaustion associated with chronic viral infections such as with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitic C virus (HCV). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19001139, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19587053}.; DISEASE: T-cell lymphoma, subcutaneous panniculitis-like (SPTCL) [MIM:618398]: An uncommon form of T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, in which cytotoxic CD8+ T-cells infiltrate subcutaneous adipose tissue, and rimming adipocytes in a lace-like pattern. Affected individuals typically present with multiple subcutaneous nodules, systemic B-cell symptoms, and, in a subset of cases, autoimmune disorders, most commonly systemic lupus erythematosus. A subset of patients develop hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. SPTCL transmission pattern is consistent with autosomal recessive inheritance with incomplete penetrance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30374066, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30792187, ECO:0000269|Ref.2}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P54253; P18428; P07237; P30101; Q15084; Q06830; P21731; Q8NBS9 EC number EC 1.11.1.15 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Antioxidant; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Oxidoreductase; Peroxidase; Proteomics identification; Redox-active center; Reference proteome; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 18846.2 Length 166 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 30.43 Isoelectric point 5.54 Charge (pH=7) -3.89 3D Binding mode Sequence GTAKISKPAPYWEGTAVIDGEFKELKLTDYRGKYLVFFFYPLDFTFVCPTEIIAFGDRLEEFRSINTEVVACSVDSQFTHLAWINTPRRQGGLGPIRIPLLSDLTHQISKDYGVYLEDSGHTLRGLFIIDDKGILRQITLNDLPVGRSVDETLRLVQAFQYTDKHG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 33 | Guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase | 3ORH | 5.97 | |
Target general information Gen name GAMT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, RMT2 methyltransferase family Biochemical class Transferase Function Guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase activity.Methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 2 (CCDS2) [MIM:612736]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by developmental delay and regression, intellectual disability, severe disturbance of expressive and cognitive speech, intractable seizures, movement disturbances, severe depletion of creatine and phosphocreatine in the brain, and accumulation of guanidinoacetic acid in brain and body fluids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12468279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15108290, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15651030, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16293431, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16855203, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17101918, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17466557, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19388150, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23660394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24415674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8651275}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00148; DB02751; DB00536; DB13191; DB01752 Interacts with O95363; Q969Q5; Q9HCM9-2 EC number 2.1.1.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Disease variant; Methyltransferase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 24656 Length 219 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 46.5 Isoelectric point 5.91 Charge (pH=7) -4.34 3D Binding mode Sequence PAWGAAPAAYDAADTHLRILGKPVMERWETPYMHALAAAASSKGGRVLEVGFGMAIAASKVQEAPIDEHWIIECNDGVFQRLRDWAPRQTHKVIPLKGLWEDVAPTLPDGHFDGILYDTYPLSEETWHTHQFNFIKNHAFRLLKPGGVLTYCNLTSWGELMKSKYSDITIMFEETQVPALLEAGFRRENIRTEVMALVPPADCRYYAFPQMITPLVTKG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 34 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 8 (CDK8) | 3RGF | 5.97 | |
Target general information Gen name CDK8 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein kinase K35; Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit CDK8; Mediator complex subunit CDK8; Cell division protein kinase 8 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CDC2/CDKX subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Mediator functions as a bridge to convey information from gene-specific regulatory proteins to the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Mediator is recruited to promoters by direct interactions with regulatory proteins and serves as a scaffold for the assembly of a functional preinitiation complex with RNA polymerase II and the general transcription factors. Phosphorylates the CTD (C-terminal domain) of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAp II), which may inhibit the formation of a transcription initiation complex. Phosphorylates CCNH leading to down-regulation of the TFIIH complex and transcriptional repression. Recruited through interaction with MAML1 to hyperphosphorylate the intracellular domain of NOTCH, leading to its degradation. Component of the Mediator complex, a coactivator involved in regulated gene transcription of nearly all RNA polymerase II-dependent genes. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder with hypotonia and behavioral abnormalities (IDDHBA) [MIM:618748]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder with onset in infancy. IDDHBA is characterized by hypotonia, global developmental delay, learning disability, and behavioral abnormalities, such as autistic features and attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Additional variable features may include non-specific facial dysmorphism, congenital heart defects, ocular anomalies, and poor feeding. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30905399}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03496 Interacts with P24863; Q01094; P02489; Q14204; Q92876 EC number EC 2.7.11.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Autism spectrum disorder; Disease variant; Intellectual disability; Kinase; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repressor; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 37655.2 Length 321 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.04 Isoelectric point 8.56 Charge (pH=7) 5.13 3D Binding mode Sequence DKMDYDFKVKLSSERERVEDLFEYEGCKVGHVYKAKRKDGKDDKDYALKQIEGTGISMSACREIALLRELKHPNVISLQKVFLSHADRKVWLLFDYAEHDLWHIIKFHRASKLPRGMVKSLLYQILDGIHYLHANWVLHRDLKPANILVMGEGPERGRVKIADMGFARVTFWYRAPELLLGARHYTKAIDIWAIGCIFAELLTSEPIFHCRQNPYHHDQLDRIFNVMGFPADKDWEDIKKMPEHSTLMKDFRRNTYTNCSLIKYMEKHKVKPDSKAFHLLQKLLTMDPIKRITSEQAMQDPYFLEDPLPTSDVFAGCQIPY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 35 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor alpha-2 (CHRNA2) | 5FJV | 5.97 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CHRNA2 Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-2/CHRNA2 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. Related diseases Epilepsy, nocturnal frontal lobe, 4 (ENFL4) [MIM:610353]: An autosomal dominant focal epilepsy characterized by nocturnal seizures associated with fear sensation, tongue movements, and nocturnal wandering, closely resembling nightmares and sleep walking. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16826524}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Seizures, benign familial infantile, 6 (BFIS6) [MIM:610353]: A form of benign familial infantile epilepsy, a neurologic disorder characterized by afebrile seizures occurring in clusters during the first year of life, without neurologic sequelae. BFIS6 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25847220}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00732; DB00237; DB00411; DB00565; DB01245; DB00514; DB01135; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB00483; DB08960; DB00657; DB01336; DB00416; DB01226; DB00184; DB01337; DB01338; DB00721; DB00728; DB05740; DB00202; DB01199; DB01339 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Epilepsy; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 48323.4 Length 413 Aromaticity 0.15 Instability index 32 Isoelectric point 5.69 Charge (pH=7) -6.58 3D Binding mode Sequence DRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLPEDRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 36 | Free fatty acid receptor 1 | 4PHU | 5.96 | |
Target general information Gen name FFAR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms GPR40 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class Fatty acid binding protein / hydrolase Function Bioactive lipid receptor activity.G-protein coupled receptor activity.Guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity.Lipid binding. Related diseases Refsum disease (RD) [MIM:266500]: A rare autosomal recessive peroxisomal disorder characterized by the accumulation of the branched-chain fatty acid, phytanic acid, in blood and tissues. Cardinal clinical features are retinitis pigmentosa, peripheral neuropathy, cerebellar ataxia, and elevated protein levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Half of all patients exhibit generalized, mild to moderate ichthyosis resembling ichthyosis vulgaris. Less constant features are nerve deafness, anosmia, skeletal abnormalities, cataracts and cardiac impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10709665, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10767344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14974078, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9326939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9326940}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00159 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Lipid-binding; Membrane; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 28319.1 Length 272 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 27.3 Isoelectric point 9.07 Charge (pH=7) 6.85 3D Binding mode Sequence MDLPPQLSFGLYVAAFALGFPLNVLAIRGATAHARLRLTPSAVYALNLGCSDLLLTVSLPLKAVEALASGAWPLPASLCPVFAVAHFAPLYAGGGFLAALSAARYLGAAFPPCYSWGVCAAIWALVLCHLGLVFGLEAPGGWLDHSNTSLGINTPVNGSPVCLEAWDPASAGPARFSLSLLLFFLPLAITAFCFVGCLRALARGSLTHRRKLRAAWVAGGALLTLLLCVGPYNASNVASFLYPNLGGSWRKLGLITGAWSVVLNPLVTGYLG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 37 | Histone acetyltransferase p300 (EP300) | 5LKX | 5.96 | |
Target general information Gen name EP300 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms p300 HAT; Protein propionyltransferase p300; P300; Histone crotonyltransferase p300; Histone butyryltransferase p300; E1Aassociated protein p300; E1A-associated protein p300 Protein family NA Biochemical class Acyltransferase Function Acetylates all four core histones in nucleosomes. Histone acetylation gives an epigenetic tag for transcriptional activation. Mediates cAMP-gene regulation by binding specifically to phosphorylated CREB protein. Mediates acetylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-122' (H3K122ac), a modification that localizes at the surface of the histone octamer and stimulates transcription, possibly by promoting nucleosome instability. Mediates acetylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-27' (H3K27ac). Also functions as acetyltransferase for non-histone targets, such as ALX1, HDAC1, PRMT1 or SIRT2. Acetylates 'Lys-131' of ALX1 and acts as its coactivator. Acetylates SIRT2 and is proposed to indirectly increase the transcriptional activity of TP53 through acetylation and subsequent attenuation of SIRT2 deacetylase function. Acetylates HDAC1 leading to its inactivation and modulation of transcription. Acts as a TFAP2A-mediated transcriptional coactivator in presence of CITED2. Plays a role as a coactivator of NEUROD1-dependent transcription of the secretin and p21 genes and controls terminal differentiation of cells in the intestinal epithelium. Promotes cardiac myocyte enlargement. Can also mediate transcriptional repression. Acetylates FOXO1 and enhances its transcriptional activity. Acetylates BCL6 wich disrupts its ability to recruit histone deacetylases and hinders its transcriptional repressor activity. Participates in CLOCK or NPAS2-regulated rhythmic gene transcription; exhibits a circadian association with CLOCK or NPAS2, correlating with increase in PER1/2 mRNA and histone H3 acetylation on the PER1/2 promoter. Acetylates MTA1 at 'Lys-626' which is essential for its transcriptional coactivator activity. Acetylates XBP1 isoform 2; acetylation increases protein stability of XBP1 isoform 2 and enhances its transcriptional activity. Acetylates PCNA; acetylation promotes removal of chromatin-bound PCNA and its degradation during nucleotide excision repair (NER). Acetylates MEF2D. Acetylates and stabilizes ZBTB7B protein by antagonizing ubiquitin conjugation and degragation, this mechanism may be involved in CD4/CD8 lineage differentiation. In addition to protein acetyltransferase, can use different acyl-CoA substrates, such as (2E)-butenoyl-CoA (crotonyl-CoA), butanoyl-CoA (butyryl-CoA) or propanoyl-CoA (propionyl-CoA), and is able to mediate protein crotonylation, butyrylation or propionylation, respectively. Acts as a histone crotonyltransferase; crotonylation marks active promoters and enhancers and confers resistance to transcriptional repressors. Histone crotonyltransferase activity is dependent on the concentration of (2E)-butenoyl-CoA (crotonyl-CoA) substrate and such activity is weak when (E)-but-2-enoyl-CoA (crotonyl-CoA) concentration is low. Also acts as a histone butyryltransferase; butyrylation marks active promoters. Functions as a transcriptional coactivator for SMAD4 in the TGF-beta signaling pathway. Acetylates PCK1 and promotes PCK1 anaplerotic activity. Functions as histone acetyltransferase and regulates transcription via chromatin remodeling. Related diseases Defects in EP300 may play a role in epithelial cancer.; DISEASE: Chromosomal aberrations involving EP300 may be a cause of acute myeloid leukemias. Translocation t(8;22)(p11;q13) with KAT6A.; DISEASE: Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2 (RSTS2) [MIM:613684]: A disorder characterized by craniofacial abnormalities, postnatal growth deficiency, broad thumbs, broad big toes, intellectual disability and a propensity for development of malignancies. Some individuals with RSTS2 have less severe mental impairment, more severe microcephaly, and a greater degree of changes in facial bone structure than RSTS1 patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15706485}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Menke-Hennekam syndrome 2 (MKHK2) [MIM:618333]: A form of Menke-Hennekam syndrome, a congenital autosomal dominant disease characterized by developmental delay, growth retardation, and craniofacial dysmorphism. Patients have intellectual disability of variable severity, speech delay, autistic behavior, short stature and microcephaly. Main facial characteristics include short palpebral fissures, telecanthi, depressed nasal ridge, short nose, anteverted nares, short columella and long philtrum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29460469}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9NXW9; P27695; Q9UBL3; Q8WXX7; Q9NPI1; P24941; Q99967; P61201; P16220-1; P17844; Q01844; P35637; Q00403; Q16665; Q9H2X6; Q92831; P55209; O60934; P20265; Q96KQ4; Q8WUF5; Q13761; Q96EB6; Q13309; O95863; P42226; Q9UL17; P56279; P05549; P04637; Q13625; O15350; P11473; P67809; K4P3M7; P03122; P06422; P06790; Q61221; Q9QXM1; P04608; P03070; P03255; P03255-2; P03259 EC number EC 2.3.1.48 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Acyltransferase; Biological rhythms; Bromodomain; Cell cycle; Chromosomal rearrangement; Chromosome; Citrullination; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Host-virus interaction; Intellectual disability; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Methylation; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 64477.2 Length 554 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 45.78 Isoelectric point 7.01 Charge (pH=7) 0.05 3D Binding mode Sequence KKIFKPEELRQALMPTLEALYRQDPESLPFRQPVDPQLLGIPDYFDIVKSPMDLSTIKRKLDTGQYQEPWQYVDDIWLMFNNAWLYNRKTSRVYKYCSKLSEVFEQEIDPVMQSLGYCCGRKLEFSPQTLCCYGKQLCTIPRDATYYSYQNRYHFCEKCFNEIQGESVSLGQTTINKEQFSKRKNDTLDPELFVECTECGRKMHQICVLHHEIIWPAGFVCDGCLKKSARTRKENKFSAKRLPSTRLGTFLENRVNDFLRRQNHPESGEVTVRVVHASDKTVEVKPGMKARFVDSGEMAESFPYRTKALFAFEEIDGVDLCFFGMHVQEYGSDCPPPNQRRVYISYLDSVHFFRPKCLRTAVYHEILIGYLEYVKKLGYTTGHIWACPPSEGDDYIFHCHPPDQKIPKPKRLQEWFKKMLDKAVSERIVHDYKDIFKQATEDRLTSAKELPYFEGDFWPNVLEESIKESGGSGSQKLYATMEKHKEVFFVIRLIAGPAANSLPPIVDPDPLIPCDLMDGRDAFLTLARDKHLEFSSLRRAQWSTMCMLVELHTQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 38 | Phosphoribosylaminoimidazolecarboxamide formyltransferase (ATIC) | 1PKX | 5.95 | |
Target general information Gen name ATIC Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PURH; OK/SW-cl.86; Bifunctional purine biosynthesis protein PURH Protein family PurH family Biochemical class Methyltransferase Function Bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes 2 steps in purine biosynthesis. Related diseases AICA-ribosuria due to ATIC deficiency (AICAR) [MIM:608688]: A neurologically devastating inborn error of purine biosynthesis. Patients excrete massive amounts of AICA-riboside in the urine and accumulate AICA-ribotide and its derivatives in erythrocytes and fibroblasts. Clinical features include profound intellectual disability, epilepsy, dysmorphic features and congenital blindness. AICAR inheritance is autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15114530}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02309; DB03442; DB01700; DB01972; DB00563; DB04057; DB00642; DB00116 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Epilepsy; Hydrolase; Intellectual disability; Multifunctional enzyme; Proteomics identification; Purine biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 41584.9 Length 386 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 42 Isoelectric point 5.6 Charge (pH=7) -7.51 3D Binding mode Sequence GQLALFSVSDKTGLVEFARNLTALGLNLVASGGTAKALRDAGLAVRDVSELTGFPEMLGGRVKTLHPAVHAGILARNIPEDNADMARLDFNLIRVVACNLYPFVKTVASPGVTVEEAVEQIDIGGVTLLRAAAKNHARVTVVCEPEDYVVVSTEMQSSESKDTSLETRRQLALKAFTHTAQYDEAISDYFRKQGQLALFSVSDKTGLVEFARNLTALGLNLVASGGTAKALRDAGLAVRDVSELTGFPEMLGGRVKTLHPAVHAGILARNIPEDNADMARLDFNLIRVVACNLYPFVKTVASPGVTVEEAVEQIDIGGVTLLRAAAKNHARVTVVCEPEDYVVVSTEMQSSESKDTSLETRRQLALKAFTHTAQYDEAISDYFRKQ Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 39 | p53-binding protein Mdm4 (MDM4) | 6Q9Y | 5.95 | |
Target general information Gen name MDM4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein Mdmx; Mdm2-like p53-binding protein; Double minute 4 protein Protein family MDM2/MDM4 family Biochemical class MDM2/MDM4 family Function Inhibits p53/TP53- and TP73/p73-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by binding its transcriptional activation domain. Inhibits degradation of MDM2. Can reverse MDM2-targeted degradation of TP53 while maintaining suppression of TP53 transactivation and apoptotic functions. Related diseases Bone marrow failure syndrome 6 (BMFS6) [MIM:618849]: A form of bone marrow failure syndrome, a heterogeneous group of life-threatening disorders characterized by hematopoietic defects in association with a range of variable extra-hematopoietic manifestations. BMFS6 is an autosomal dominant form characterized by intermittent neutropenia, lymphopenia, or anemia associated with hypocellular bone marrow, and increased susceptibility to cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32300648}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9NX04; P10415; Q7Z479; O95971; P48729; Q00987; Q13064; P41227; P06400; Q9Y4L5; P23297; P29034; P33763; P04271; P31947; P04637; P62837; Q93009; O14972; P61964; P62258; P61981; P63104; Q9BRR0; A0A0S2Z6X0; Q3YBA8; P03255-2 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Disease variant; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 19722 Length 173 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 50.78 Isoelectric point 8.48 Charge (pH=7) 2.27 3D Binding mode Sequence QVRPKLPLLKILHAAGAQGEMFTVKEVMHYLGQYIMVKQLYDQQEQHMVYCGGDLLGELLGRQSFSVKDPSPLYDMLRKNLVTLAQINQVRPKLPLLKILHAAGAQGEMFTVKEVMHYLGQYIMVKQLYDQQEQHMVYCGGDLLGELLGRQSFSVKDPSPLYDMLRKNLVTLA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 40 | Dopamine beta-hydroxylase | 4ZEL | 5.94 | |
Target general information Gen name DBH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Copper type II ascorbate-dependent monooxygenase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function Catalytic activity.Copper ion binding.Dopamine beta-monooxygenase activity.L-ascorbic acid binding. Related diseases Orthostatic hypotension 1 (ORTHYP1) [MIM:223360]: A form of orthostatic hypotension due to congenital dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a finding defined as a 20-mm Hg decrease in systolic pressure or a 10-mm Hg decrease in diastolic pressure occurring 3 minutes after a person has risen from supine to standing. Symptoms include dizziness, blurred vision, and sometimes syncope. ORTHYP1 is an autosomal recessive condition apparent from infancy or early childhood and characterized by low plasma and urinary levels of norepinephrine and epinephrine, and episodic hypoglycemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11857564}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00126; DB06774; DB09130; DB05394; DB00822; DB00988; DB00968; DB00550 Interacts with P00352; P63010-2; Q04656; Q8WUW1; Q9UNS2; Q71DI3; P61978; Q9Y2M5; Q92876; P08727; Q14693; P0DPK4; Q6GQQ9-2; P27986-2; Q9ULX5; Q96D59; Q8N6K7-2; Q9GZS3; Q8IUW3; Q86WT6-2 EC number 1.14.17.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Catecholamine biosynthesis; Copper; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal-anchor; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Vitamin C Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 123694 Length 1094 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 51.85 Isoelectric point 5.84 Charge (pH=7) -24.5 3D Binding mode Sequence PLPYHIPLDPEGSLELSWNVSYTQEAIHFQLLVRRLKAGVLFGMSDRGELENADLVVLWTDGDAYFADAWSDQKGQIHLDPQQDYQLLQVQRTPEGLTLLFKRPFGTCDPKDYLIEDGTVHLVYGILEEPFRSLEAINGSGLQMGLQRVQLLKPNIPEPELPSDACTMEVQAPNIQIPSQETTYWCYIKELPKGFSRHHIIKYEPIVTKGNEALVHHMEVFQCAPEMDSVPHFSGPCDSKMKPDRLNYCRHVLAAWALGAKAFYYPEEAGLAFGGPGSSRYLRLEVHYHNPLVIEGRNDSSGIRLYYTAKLRRFNAGIMELGLVYTPVMAIPPRETAFILTGYCTDKCTQLALPPSGIHIFASQLHTHLTGRKVVTVLVRDGREWEIVNQDNHYSPHFQEIRMLKKVVSVHPGDVLITSCTYNTEDRELATVGGFGILEEMCVNYVHYYPQTQLELCKSAVDAGFLQKYFHLINRFNNEDVCTCPQASVSQQFTSVPWNSFNRDVLKALYSFAPISMHCNKSSAVRFQGEWNLQPLPKVISTLEEPTVVSPLPYHIPLDPEGSLELSWNVSYTQEAIHFQLLVRRLKAGVLFGMSDRGELENADLVVLAYFADAWSDQKGQIHLDPQQDYQLLQVQRTPEGLTLLFKRPFGTCDPKDYLIEDGTVHLVYGILEEPFRSLEAINGSGLQMGLQRVQLLKPNIPEPELPSDACTMEVQAPNIQIPSQETTYWCYIKELPKGFSRHHIIKYEPIVTKGNEALVHHMEVFQCAPEVPHFSGPCDSKMLNYCRHVLAAWALGAKAFYYPEEAGLAFGGPGSSRYLRLEVHYHNPLVIEGRNDSSGIRLYYTAKLRRFNAGIMELGLVYTPVMAIPPRETAFILTGYCTDKCTQLALPPSGIHIFASQLHTHLTGRKVVTVLVRDGREWEIVNQDNHYSPHFQEIRMLKKVVSVHPGDVLITSCTYNTEDRELATVGGFGILEEMCVNYVHYYPQTQLELCKSAVDAGFLQKYFHLINRFNNEDVCTCPQASVSQQFTSVPWNSFNRDVLKALYSFAPISMHCNKSSAVRFQGEWNLQPLPKVISTLEEPTPQCVVSIGG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||