Job Results:
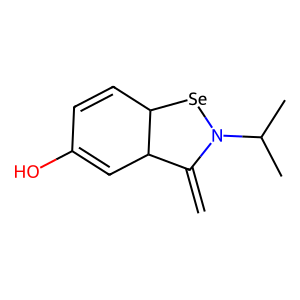
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
6035497cf04470e01d5d7dbbed13b512
Job name
NA
Time
2025-10-13 17:35:32
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | Hyperpolarization cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 2 (HCN2) | 3U10 | 5.82 | |
Target general information Gen name HCN2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 2; Brain cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 2; BCNG2; BCNG-2 Protein family Potassium channel HCN family Biochemical class Voltage-gated ion channel Function Contributes to the native pacemaker currents in heart (If) and in neurons (Ih). Can also transport ammonium in the distal nephron. Produces a large instantaneous current. Modulated by intracellular chloride ions and pH; acidic pH shifts the activation to more negative voltages. Hyperpolarization-activated ion channel exhibiting weak selectivity for potassium over sodium ions. Related diseases Epilepsy, idiopathic generalized 17 (EIG17) [MIM:602477]: A form of idiopathic generalized epilepsy, a disorder characterized by recurring generalized seizures in the absence of detectable brain lesions and/or metabolic abnormalities. Generalized seizures arise diffusely and simultaneously from both hemispheres of the brain. Seizure types include juvenile myoclonic seizures, absence seizures, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Both autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive EIG17 inheritance have been reported. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22131395, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29064616}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Febrile seizures, familial, 2 (FEB2) [MIM:602477]: Seizures associated with febrile episodes in childhood without any evidence of intracranial infection or defined pathologic or traumatic cause. It is a common condition, affecting 2-5% of children aged 3 months to 5 years. The majority are simple febrile seizures (generally defined as generalized onset, single seizures with a duration of less than 30 minutes). Complex febrile seizures are characterized by focal onset, duration greater than 30 minutes, and/or more than one seizure in a 24 hour period. The likelihood of developing epilepsy following simple febrile seizures is low. Complex febrile seizures are associated with a moderately increased incidence of epilepsy. FEB2 transmission pattern is consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24324597}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02527; DB02315; DB09083 Interacts with Q9UL51; Q4ACU6-1 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Ammonia transport; cAMP; cAMP-binding; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Epilepsy; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Methylation; Nucleotide-binding; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Potassium; Potassium channel; Potassium transport; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Sodium; Sodium channel; Sodium transport; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Voltage-gated channel Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23672.9 Length 202 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 38.05 Isoelectric point 8.85 Charge (pH=7) 4.11 3D Binding mode Sequence DSSRRQYQEKYKQVEQYMSFHKLPADFRQKIHDYYEHRYQGKMFDEDSILGELNGPLREEIVNFNCRKLVASMPLFANADPNFVTAMLTKLKFEVFQPGDYIIREGTIGKKMYFIQHGVVSVLTKGNKEMKLSDGSYFGEICLLTRGRRTASVRADTYCRLYSLSVDNFNEVLEEYPMMRRAFETVAIDRLDRIGKKNSILL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 22 | Folate receptor alpha (FOLR1) | 4LRH | 5.82 | |
Target general information Gen name FOLR1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Ovarian tumorassociated antigen MOv18; KB cells FBP; Folate receptor, adult; Folate receptor 1; FRalpha; FOLR1; Adult folatebinding protein Protein family Folate receptor family Biochemical class Folate receptor Function Binds to folate and reduced folic acid derivatives and mediates delivery of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and folate analogs into the interior of cells. Has high affinity for folate and folic acid analogs at neutral pH. Exposure to slightly acidic pHafter receptor endocytosis triggers a conformation change that strongly reduces its affinity for folates and mediates their release. Required for normal embryonic development and normal cell proliferation. Related diseases Neurodegeneration due to cerebral folate transport deficiency (NCFTD) [MIM:613068]: An autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder resulting from brain-specific folate deficiency early in life. Onset is apparent in late infancy with severe developmental regression, movement disturbances, epilepsy and leukodystrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19732866}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05595; DB00158; DB00563; DB12489; DB15413; DB05168 Interacts with Q8N357 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Endosome; Folate-binding; Glycoprotein; GPI-anchor; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Neurodegeneration; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 24216 Length 207 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 49.36 Isoelectric point 8.14 Charge (pH=7) 3.41 3D Binding mode Sequence RTELLNVCMNAKHHKEKPGPEDKLHEQCRPWRKNACCSTNTSQEAHKDVSYLYRFNWNHCGEMAPACKRHFIQDTCLYECSPNLGPWIQQVDQSWRKERVLNVPLCKEDCEQWWEDCRTSYTCKSNWHKGWNWTSGFNKCAVGAACQPFHFYFPTPTVLCNEIWTHSYKVSNYSRGSGRCIQMWFDPAQGNPNEEVARFYAAAMSGT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 23 | Erbb3 tyrosine kinase receptor (Erbb-3) | 6OP9 | 5.82 | |
Target general information Gen name ERBB3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER3; Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3; Proto-oncogene-like protein c-ErbB-3; HER3; C-erbB3; C-erbB-3 protein Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, EGF receptor subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Binds to neuregulin-1 (NRG1) and is activated by it; ligand-binding increases phosphorylation on tyrosine residues and promotes its association with the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. May also be activated by CSPG5. Involved in the regulation of myeloid cell differentiation. Tyrosine-protein kinase that plays an essential role as cell surface receptor for neuregulins. Related diseases Lethal congenital contracture syndrome 2 (LCCS2) [MIM:607598]: A form of lethal congenital contracture syndrome, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by degeneration of anterior horn neurons, extreme skeletal muscle atrophy, and congenital non-progressive joint contractures (arthrogryposis). The contractures can involve the upper or lower limbs and/or the vertebral column, leading to various degrees of flexion or extension limitations evident at birth. LCCS2 patients manifest craniofacial/ocular findings, lack of hydrops, multiple pterygia, and fractures, as well as a normal duration of pregnancy and a unique feature of a markedly distended urinary bladder (neurogenic bladder defect). The phenotype suggests a spinal cord neuropathic etiology. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17701904}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Erythroleukemia, familial (FERLK) [MIM:133180]: An autosomal dominant myeloproliferative disorder characterized by neoplastic proliferation of erythroblastic and myeloblastic elements with atypical erythroblasts and myeloblasts in the peripheral blood. Disease penetrance is incomplete. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27416908}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Visceral neuropathy, familial, 1, autosomal recessive (VSCN1) [MIM:243180]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by intestinal dysmotility due to aganglionosis (Hirschsprung disease), hypoganglionosis, and/or chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Additional variable features are progressive peripheral neuropathy, arthrogryposis, hypoplasia or aplasia of the olfactory bulb and of the external auditory canals, microtia or anotia, and facial dysmorphism. Some patients present structural cardiac anomalies and arthrogryposis with multiple pterygia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33497358}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB11652 Interacts with P42684; P46108; P46109; P00533; P04626; P21860; Q15303; P62993; Q14451; P25098; P08631; P08238; Q96JA1; O43639; Q02297-6; Q02297-7; P42336; P27986; O00459; Q92569; P19174; P20936; Q13671; P26447; P04271; Q9UQQ2; P29353; Q92529; P12931; P43405; Q63HR2; Q68CZ2 EC number EC 2.7.10.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tyrosine-protein kinase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 31061 Length 276 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 35.43 Isoelectric point 8.31 Charge (pH=7) 2.6 3D Binding mode Sequence VLARIFKETELRKLKVLGSGVFGTVHKGVWIPEGESIKIPVCIKVIEDKSGRQSFQAVTDHMLAIGSLDHAHIVRLLGLCPGSSLQLVTQYLPLGSLLDHVRQHRGALGPQLLLNWGVQIAKGMYYLEEHGMVHRNLAARNVLLKSPSQVQVADFGVADLLPPDDKQAKTPIKWMALESIHFGKYTHQSDVWSYGVTVWELMTFGAEPYAGLRLAEVPDLLEKGERLAQPQICTIDVYMVMVKCWMIDENIRPTFKELANEFTRMARDPPRYLVIK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 24 | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) | 5J89 | 5.82 | |
Target general information Gen name CD274 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hPD-L1; Programmed death ligand 1; PDL1; PDCD1LG1; PDCD1L1; PDCD1 ligand 1; B7H1; B7-H1; B7 homolog 1 Protein family Immunoglobulin superfamily, BTN/MOG family Biochemical class Immunoglobulin Function As a ligand for the inhibitory receptor PDCD1/PD-1, modulates the activation threshold of T-cells and limits T-cell effector response. Through a yet unknown activating receptor, may costimulate T-cell subsets that predominantly produce interleukin-10 (IL10). Plays a critical role in induction and maintenance of immune tolerance to self. Related diseases Truncation of the 3'-untranslated (3'-UTR) region of CD274 transcripts leads to elevated expression of CD274 in multiple cancers including T-cell leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and stomach adenocarcinoma (PubMed:27281199). Disruption of 3'-UTR region is caused by structural variants that stabilize CD274 transcripts, leading to overexpression (PubMed:27281199). Increased expression in tumors promotes immune evasion and tumor cell growth by allowing malignant cells to escape destruction by the immune system (PubMed:27281199). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27281199}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB15773; DB11595; DB15771; DB11945; DB15772; DB14776; DB15770; DB11714; DB15769; DB09035; DB09037; DB00203; DB00313 Interacts with P33681; Q8IZR5; Q9NX76; Q15116; Q15116 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Endosome; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Immunoglobulin domain; Membrane; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Secreted; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C,D Molecular weight (Da) 28335.2 Length 249 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 35.39 Isoelectric point 6.15 Charge (pH=7) -3.43 3D Binding mode Sequence AFTVTVPKDLYVVEYGSNMTIECKFPVEKQLDLAALIVYWEMEDKNIIQFVHGEEDLKVQHSSYRQRARLLKDQLSLGNAALQITDVKLQDAGVYRCMISYGGADYKRITVKVNAPYAAALEHHHAFTVTVPKDLYVVEYGSNMTIECKFPVEKQLDLAALIVYWEMEDKNIIQFVHGEEDLKVQHSSYRQRARLLKDQLSLGNAALQITDVKLQDAGVYRCMISYGGADYKRITVKVNAPYAAALEHH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 25 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-2 | 5FJV | 5.81 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-2/CHRNA2 sub-subfamily Biochemical class NA Function After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane." Related diseases Epilepsy, nocturnal frontal lobe, 4 (ENFL4) [MIM:610353]: An autosomal dominant focal epilepsy characterized by nocturnal seizures associated with fear sensation, tongue movements, and nocturnal wandering, closely resembling nightmares and sleep walking. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16826524}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Seizures, benign familial infantile, 6 (BFIS6) [MIM:610353]: A form of benign familial infantile epilepsy, a neurologic disorder characterized by afebrile seizures occurring in clusters during the first year of life, without neurologic sequelae. BFIS6 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25847220}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00732; DB00237; DB00411; DB00565; DB01245; DB00514; DB01135; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB00483; DB08960; DB00657; DB01336; DB00416; DB01226; DB00184; DB01337; DB01338; DB00721; DB00728; DB05740; DB00202; DB01199; DB01339 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Epilepsy; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E Molecular weight (Da) 120584 Length 1031 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 32.21 Isoelectric point 5.62 Charge (pH=7) -17.58 3D Binding mode Sequence DRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLPEDRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLPEDRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLPEDRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLPEDRLFKHLFRGYNRWARPVPNTSDVVIVRFGLSIAQLIDVDEKNQMMTTNVWLKQEWSDYKLRWNPTDFGNITSLRVPSEMIWIPDIVLYNNADGEFAVTHMTKAHLFSTGTVHWVPPAIYKSSCSIDVTFFPFDQQNCKMKFGSWTYDKAKIDLEQMEQTVDLKDYWESGEWAIVNATGTYNSKKYDCCAEIYPDVTYAFVIRRLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 26 | SEC14-like protein 3 | 4UYB | 5.81 | |
Target general information Gen name SEC14L3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms TAP2 Protein family NA Biochemical class Transport protein Function Lipid binding.Transporter activity. Related diseases Chondrodysplasia with platyspondyly, distinctive brachydactyly, hydrocephaly, and microphthalmia (CDP-PBHM) [MIM:300863]: A disease characterized by chondrodysplasia, severe platyspondyly, hydrocephaly, and facial features with microphthalmia. Bone abnormalities include a distinctive metaphyseal cupping of the metacarpals, metatarsals, and phalanges. Affected females show a milder phenotype with small stature, sometimes associated with body asymmetry and mild intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20181727}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB14003; DB14001; DB14002; DB11635; DB11251; DB00163 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Lipid-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 46148.7 Length 401 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 45.19 Isoelectric point 5.79 Charge (pH=7) -5.94 3D Binding mode Sequence SMSGRVGDLSPKQAETLAKFRENVQDVLPALPNPDDYFLLRWLRARNFDLQKSEALLRKYMEFRKTMDIDHILDWQPPEVIQKYMPGGLCGYDRDGCPVWYDIIGPLDPKGLLFSVTKQDLLKTKMRDCERILHECDLQTERLGKKIETIVMIFDCEGLGLKHFWKPLVEVYQEFFGLLEENYPETLKFMLIVKATKLFPVGYNLMKPFLSEDTRRKIIVLGNNWKEGLLKLISPEELPAQFGGTLTDPDGNPKCLTKINYGGEIPKSMYVRDQVKTQYEHSVQINRGSSHQVEYEILFPGCVLRWQFSSDGADIGFGVFLKTKMGERQRAGEMTEVLPSQRYNAHMVPEDGNLTCSEAGVYVLRFDNTYSFVHAKKVSFTVEVLLPDEGMQKYDKELTPV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 27 | Bromodomain-containing protein 7 (BRD7) | 6V1H | 5.81 | |
Target general information Gen name BRD7 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Protein CELTIX-1; CELTIX1; BP75; 75 kDa bromodomain protein Protein family NA Biochemical class Bromodomain Function May play a role in chromatin remodeling. Activator of the Wnt signaling pathway in a DVL1-dependent manner by negatively regulating the GSK3B phosphotransferase activity. Induces dephosphorylation of GSK3B at 'Tyr-216'. Down-regulates TRIM24-mediated activation of transcriptional activation by AR. Transcriptional corepressor that down-regulates the expression of target genes. Binds to target promoters, leading to increased histone H3 acetylation at 'Lys-9' (H3K9ac). Binds to the ESR1 promoter. Recruits BRCA1 and POU2F1 to the ESR1 promoter. Coactivator for TP53-mediated activation of transcription of a set of target genes. Required for TP53-mediated cell-cycle arrest in response to oncogene activation. Promotes acetylation of TP53 at 'Lys-382', and thereby promotes efficient recruitment of TP53 to target promoters. Inhibits cell cycle progression from G1 to S phase. Acts both as coactivator and as corepressor. Related diseases Involved in the epigenetic regulation of ESR1 expression in breast cancer in a TFAP2C, IFI16 and HDAC4/5/6-dependent manner. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24413532}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q09472; Q9BUJ2; Q9H8W4; P04637 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Bromodomain; Cell cycle; Chromosome; Coiled coil; Isopeptide bond; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Tumor suppressor; Ubl conjugation; Wnt signaling pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 13703.8 Length 117 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 44.32 Isoelectric point 8.98 Charge (pH=7) 3.01 3D Binding mode Sequence EQTPLQEALNQLMRQLQRKDPSAFFSFPVTDFIAPGYSMIIKHPMDFSTMKEKIKNNDYQSIEELKDNFKLMCTNAMIYNKPETIYYKAAKKLLHSGMKILSQERIQSLKQSIDFMA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 28 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-3 | 4ZK4 | 5.80 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NACHRA3 Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-3/CHRNA3 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Acetylcholine binding protein Function Acetylcholine binding.Acetylcholine-gated cation-selective channel activity.Acetylcholine receptor activity.Ligand-gated ion channel activity.Serotonin-gated cation-selective channel activity. Related diseases Bladder dysfunction, autonomic, with impaired pupillary reflex and secondary CAKUT (BAIPRCK) [MIM:191800]: An autosomal recessive disease characterized by impaired innervation and autonomic dysfunction of the urinary bladder, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, small kidneys, recurrent urinary tract infections, and progressive renal insufficiency. Additional autonomic features are impaired pupillary reflex and orthostatic hypotension. The disease manifests in utero or early childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31708116}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00915; DB01156; DB00237; DB00565; DB09028; DB00514; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB05710; DB01227; DB00848; DB00333; DB00184; DB01090; DB00202; DB01273 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E Molecular weight (Da) 46391.5 Length 408 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 30.23 Isoelectric point 4.6 Charge (pH=7) -22.73 3D Binding mode Sequence LHSQANLMRLKSDLFYPGPTKDDPLTVTLGFTLQDIVKADSSTNEVDLVYWEQQRWKLNSLMWDPNEYGNITDFRTSAADIWTPDITAYSSTRPVQVLSPQIAVVTHDGSVMFIPAQRLSFMCDPTGVDSEEGATCAVKFGSWVYSGFEIDLKTDTDQVDLSSYYASSKYEILSATQYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDVVLVVKFRERRLHSQANLMRLKSDLFNRYPGPTKDDPLTVTLGFTLQDIVKADSSTNEVDLVYWEQQRWKLNSLMWDPNEYGNITDFRTSAADIWTPDITAYSSTRPVQVLSPQIAVVTHDGSVMFIPAQRLSFMCDPTGVDSEEGATCAVKFGSWVYSGFEIDLKTDTDQVDLSSYYASSKYEILSATQYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDVVLVVKFRE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 29 | Acyloxyacyl hydrolase (neutrophil) | 5W7C | 5.80 | |
Target general information Gen name AOAH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Acyloxyacyl hydrolase Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Removes the secondary (acyloxyacyl-linked) fatty acyl chains from the lipid A region of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. By breaking down LPS, terminates the host response to bacterial infection and prevents prolonged and damaging inflammatory responses (By similarity). In peritoneal macrophages, seems to be important for recovery from a state of immune tolerance following infection by Gram-negative bacteria (By similarity). Related diseases Major depressive disorder (MDD) [MIM:608516]: A common psychiatric disorder. It is a complex trait characterized by one or more major depressive episodes without a history of manic, mixed, or hypomanic episodes. A major depressive episode is characterized by at least 2 weeks during which there is a new onset or clear worsening of either depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure in nearly all activities. Four additional symptoms must also be present including changes in appetite, weight, sleep, and psychomotor activity; decreased energy; feelings of worthlessness or guilt; difficulty thinking, concentrating, or making decisions; or recurrent thoughts of death or suicidal ideation, plans, or attempts. The episode must be accompanied by distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15229186}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q15700 EC number EC 3.1.1.77 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lipid metabolism; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C Molecular weight (Da) 47779.7 Length 420 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.45 Isoelectric point 7.72 Charge (pH=7) 2.1 3D Binding mode Sequence GSDICSLPVLAKICQKIKLAMEQSVPFKDVDSDKYSVFPTLRGYHWRGRDCNDSDESVYPGRRPNNWDVHQDSNCNGIWGVDPKDGVPYEKKFCEGSQPRGIILLGDAAGAHFHISPEWITASQMSLNSFINLPTALTNELDWPQLSGATGFLDSTVGIKEKSIYLRLWKRNHCNHRDYQNISRNGASSRNLKKFIESLSRNKVLDYPAIVIYAMIGNDVCSGKSDPVPAMTTPEKLYSNVMQTLKHLNSHLPNGSHVILYGLPDGTFLWDNLHNRYHPLGQLNKDMTYAQLYSFLNCLQVSPCHGWMSSNKTLRTLTSERAEQLSNTLKKIAASEKFTNFNLFYMDFAFHEIIQEWQKRGGQPWQLIEPVDGFHPNEVALLLLADHFWKKVQLQWPQILGKENPFNPQIKQVFGDQGGH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 30 | Bromodomain-containing protein 9 (BRD9) | 6V0X | 5.80 | |
Target general information Gen name BRD9 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Rhabdomyosarcoma antigen MU-RMS-40.8 Protein family NA Biochemical class Bromodomain Function Plays a role in chromatin remodeling and regulation of transcription. Acts as a chromatin reader that recognizes and binds acylated histones: binds histones that are acetylated and/or butyrylated. Component of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling subcomplex GBAF that carries out key enzymatic activities, changing chromatin structure by altering DNA-histone contacts within a nucleosome in an ATP-dependent manner. Related diseases Major depressive disorder (MDD) [MIM:608516]: A common psychiatric disorder. It is a complex trait characterized by one or more major depressive episodes without a history of manic, mixed, or hypomanic episodes. A major depressive episode is characterized by at least 2 weeks during which there is a new onset or clear worsening of either depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure in nearly all activities. Four additional symptoms must also be present including changes in appetite, weight, sleep, and psychomotor activity; decreased energy; feelings of worthlessness or guilt; difficulty thinking, concentrating, or making decisions; or recurrent thoughts of death or suicidal ideation, plans, or attempts. The episode must be accompanied by distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15229186}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q7Z7H3; Q7Z7H3 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Bromodomain; Chromatin regulator; Isopeptide bond; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 11491.3 Length 99 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 13.58 Isoelectric point 9.24 Charge (pH=7) 3.8 3D Binding mode Sequence STPIQQLLEHFLRQLQRKDPHGFFAFPVTDAIAPGYSMIIKHPMDFGTMKDKIVANEYKSVTEFKADFKLMCDNAMTYNRPDTVYYKLAKKILHAGFKM Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 31 | T-cell surface glycoprotein CD1a (CD1A) | 6NUX | 5.80 | |
Target general information Gen name CD1A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hTa1 thymocyteantigen; hTa1 thymocyte antigen; T-cell surfaceantigen T6/Leu-6; T-cell surface antigen T6/Leu-6; CD1a Protein family NA Biochemical class Immunoglobulin Function Antigen-presenting protein that binds self and non-self lipid and glycolipid antigens and presents them to T-cell receptors on natural killer T-cells. Related diseases Pulmonary hypertension, primary, 1 (PPH1) [MIM:178600]: A rare disorder characterized by plexiform lesions of proliferating endothelial cells in pulmonary arterioles. The lesions lead to elevated pulmonary arterial pression, right ventricular failure, and death. The disease can occur from infancy throughout life and it has a mean age at onset of 36 years. Penetrance is reduced. Although familial pulmonary hypertension is rare, cases secondary to known etiologies are more common and include those associated with the appetite-suppressant drugs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10903931, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10973254, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11015450, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11115378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12045205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12358323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15965979, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24936649, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25187962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28507310}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Pulmonary venoocclusive disease 1, autosomal dominant (PVOD1) [MIM:265450]: A disease characterized by widespread fibrous obstruction and intimal thickening of septal veins and preseptal venules, a low diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide, occult alveolar hemorrhage, and nodular ground-glass opacities, septal lines and lymph node enlargement showed by high-resolution computed tomography of the chest. It is frequently associated with pulmonary capillary dilatation and proliferation, and is a rare and devastating cause of pulmonary hypertension. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12446270, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16429395}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00098 Interacts with P61769 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Adaptive immunity; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Endosome; Glycoprotein; Immunity; Immunoglobulin domain; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 30867.3 Length 270 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 37.45 Isoelectric point 6.16 Charge (pH=7) -4.5 3D Binding mode Sequence SFHVIWIASFYNHSWKQNLVSGWLSDLQTHTWDSNSSTIVFLWPWSRGNFSNEWKELETLFRIRTIRSFEGIRRYAHELQFEYPFEIQVTGGCESGSFLQLAYQGSDFVSFQNNSWLPYPVAGNMAKHFCKVLNQNQHENDITHNLLSDTCPRFILGLLDAGKAHLQRQVKPEAWLSHGPSPGPGHLQLVCHVSGFYPKPVWVMWMRGEQEQQGTQRGDILPSADGTWYLRATLEVAAGEAADLSCRVKHSSLEGQDIVLYWEGSLVPRG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 32 | Histamine H3 receptor (H3R) | 7F61 | 5.79 | |
Target general information Gen name HRH3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Histamine receptor 3; HH3R; GPCR97; G-protein coupled receptor 97; G protein-coupled receptor 97 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Signals through the inhibition of adenylate cyclase and displays high constitutive activity (spontaneous activity in the absence of agonist). Agonist stimulation of isoform 3 neither modified adenylate cyclase activity nor induced intracellular calcium mobilization. The H3 subclass of histamine receptors could mediate the histamine signals in CNS and peripheral nervous system. Related diseases Immunodeficiency 48 (IMD48) [MIM:269840]: A form of severe immunodeficiency characterized by a selective absence of CD8+ T-cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11123350, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11412303, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18509675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8124727, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8202713}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Autoimmune disease, multisystem, infantile-onset, 2 (ADMIO2) [MIM:617006]: An autosomal recessive, autoimmune disorder characterized by systemic manifestations including blistering skin disease, uncontrollable bullous pemphigoid, inflammatory colitis, autoimmune hypothyroidism, proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26783323}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01238; DB06698; DB05381; DB17087; DB05080; DB00768; DB11642 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34321.1 Length 301 Aromaticity 0.16 Instability index 32.22 Isoelectric point 9.63 Charge (pH=7) 15.11 3D Binding mode Sequence RGFSAAWTAVLAALMALLIVATVLGNALVMLAFVADSSLRTQNNFFLLNLAISDFLVGAFCIPLYVPYVLTGRWTFGRGLCKLWLVVDYLLCTSKAFNIVLISYDRFLSVTRAVSYRAQQGDTRRAVRKMLLVWVLAFLLYGPAILSWEYLSGGSSIPEGHCYAEFFYNWYFLITASTLEFFTPFLSVTFFNLSIYLNIQRRTRLRLDGAREAAGRFRLSRDRKVAKSLAVIVSIFGLCWAPYTLLMIIRAACHGHCVPDYWYETSFWLLWANSAVNPVLYPLCHHSFRRAFTKLLCPQKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 33 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor beta-4 (CHRNB4) | 6PV7 | 5.79 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNB4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CHRNB4; Beta-4 nAChR Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Beta-4/CHRNB4 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. Related diseases Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) [MIM:144700]: Renal cell carcinoma is a heterogeneous group of sporadic or hereditary carcinoma derived from cells of the proximal renal tubular epithelium. It is subclassified into clear cell renal carcinoma (non-papillary carcinoma), papillary renal cell carcinoma, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, collecting duct carcinoma with medullary carcinoma of the kidney, and unclassified renal cell carcinoma. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma is the most common subtype. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20054297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23622243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23792563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25728682}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Defects of SETD2 are associated with loss of DNA methylation at non-promoter regions (PubMed:23792563). SETD2 defects lead to aberrant and reduced nucleosome compaction and chromatin association of key replication proteins, such as MCM7 and DNA polymerase delta, leading to hinder replication fork progression and prevent loading of RAD51 homologous recombination repair factor at DNA breaks (PubMed:25728682). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23792563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25728682}.; DISEASE: Luscan-Lumish syndrome (LLS) [MIM:616831]: An autosomal dominant syndrome with a variable phenotype. Clinical features include macrocephaly, distinctive facial appearance, postnatal overgrowth, various degrees of learning difficulties, autism spectrum disorder, and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23160955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24852293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26084711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27317772}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute lymphoblastic (ALL) [MIM:613065]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. ALL is a malignant disease of bone marrow and the most common malignancy diagnosed in children. The malignant cells are lymphoid precursor cells (lymphoblasts) that are arrested in an early stage of development. The lymphoblasts replace the normal marrow elements, resulting in a marked decrease in the production of normal blood cells. Consequently, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia occur to varying degrees. The lymphoblasts also proliferate in organs other than the marrow, particularly the liver, spleen, and lymphnodes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24509477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24662245}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML) [MIM:601626]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. AML is a malignant disease of bone marrow characterized by maturational arrest of hematopoietic precursors at an early stage of development. Clonal expansion of myeloid blasts occurs in bone marrow, blood, and other tissue. Myelogenous leukemias develop from changes in cells that normally produce neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils and monocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16314571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24509477}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 70 (MRD70) [MIM:620157]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by mild global developmental delay, moderately impaired intellectual disability with speech difficulties, and behavioral abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32710489}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Rabin-Pappas syndrome (RAPAS) [MIM:620155]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by severely impaired global development, intellectual disability, microcephaly, facial dysmorphism, and variable congenital anomalies affecting the skeletal, genitourinary, cardiac, and other organ systems. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32710489}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00237; DB00565; DB00514; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB01227; DB00184; DB01090; DB00202 Interacts with Q6FHY5 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 89661.2 Length 775 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 35.11 Isoelectric point 6.07 Charge (pH=7) -5.67 3D Binding mode Sequence SEAEHRLFERLFEDYNEIIRPVANVSDPVIIHFEVSMSQLVKVDEVNQIMETNLWLKQIWNDYKLKWNPSDYGGAEFMRVPAQKIWKPDIVLYNNAVGDFQVDDKTKALLKYTGEVTWIPPAIFKSSCKIDVTYFPFDYQNCTMKFGSWSYDKAKIDLVLIGSSMNLKDYWESGEWAIIKAPGYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDITYSLYIRRLPLFYTINLIIPCLLISFLTVLVFYLPSDCGEKVTLCISVLLSLTVFLLVITETIPSTSLVIPLIGEYLLFTMIFVTLSIVITVFVLNVHYRTPTTHTMPSWVKTVFLNLLPRVMFMTRIKEAIQSVKYIAENMKAQNEAKEIQDDWKYVAMVIDRIFLWVFTLVCILGTAGLFLQPLMRVANAEEKLMDDLLNKTRYNNLIRPATSSSQLISIKLQLSLAQLISVNEREQIMTTNVWLKQEWTDYRLTWNSSRYEGVNILRIPAKRIWLPDIVLYNNADGTYEVSVYTNLIVRSNGSVLWLPPAIYKSACKIEVKYFPFDQQNCTLKFRSWTYDHTEIDMVLMTPTASMDDFTPSGEWDIVALPGRRTVNPQDPSYVDVTYDFIIKRKPLFYTINLIIPCVLTTLLAILVFYLPSDCGEKMTLCISVLLALTFFLLLISKIVPPTSLDVPLIGKYLMFTMVLVTFSIVTSVCVLNVHHRSPSTHTMAPWVKRCFLHKLPTFLFMKRRQDVQEALEGVSFIAQHMKNDDEDQSVVEDWKYVAMVVDRLFLWVFMFVCVLGTVGLFLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 34 | Leucine carboxyl methyltransferase 1 | 3IEI | 5.78 | |
Target general information Gen name LCMT1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CGI-68;LCMT Protein family Methyltransferase superfamily, LCMT family Biochemical class Transferase Function Protein C-terminal carboxyl O-methyltransferase activity.Protein C-terminal leucine carboxyl O-methyltransferase activity.S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase activity. Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder, mitochondrial, with abnormal movements and lactic acidosis, with or without seizures (NEMMLAS) [MIM:617710]: An autosomal recessive, mitochondrial disorder with a broad phenotypic spectrum ranging from severe neonatal lactic acidosis, encephalomyopathy and early death to an attenuated course with milder manifestations. Clinical features include delayed psychomotor development, intellectual disability, hypotonia, dystonia, ataxia, and spasticity. Severe combined respiratory chain deficiency may be found in severely affected individuals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28236339, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28650581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28905505, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30920170, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35074316}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Parkinsonism-dystonia 3, childhood-onset (PKDYS3) [MIM:619738]: An autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder with onset in infancy or early childhood. Affected individuals present with progressive movement abnormalities, including parkinsonism with tremor, dystonia, myoclonus ataxia, and hyperkinetic movements such as ballismus. The parkinsonism features may be responsive to treatment with levodopa, although many patients develop levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Some patients may have mild cognitive impairment or psychiatric disturbances. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29120065, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31970218, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34890876}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00149 Interacts with P51116 EC number 2.1.1.233 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Methyltransferase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-adenosyl-L-methionine; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H Molecular weight (Da) 35803 Length 310 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 42.77 Isoelectric point 6.13 Charge (pH=7) -3.58 3D Binding mode Sequence GVRGTCEDASLCKRFAVSIGYWHDPYIQHFVRLSKERKAPEINRGYFARVHGVSQLIKAFLRKTECHCQIVNLGAGMDTTFWRLKDEDLLSSKYFEVDFPMIVTRKLHSIKCKPPLSSPILELHSEDTLQMDGHILDSKRYAVIGADLRDLSELEEKLKKCNMNTQLPTLLIAECVLVYMTPEQSANLLKWAANSFERAMFINYEQVNMGDRFGQIMIENLRRRQCDLAGVETCKSLESQKERLLSNGWETASAVDMMELYNRLPRAEVSRIESLEFLDEMELLEQLMRHYCLCWATKGGNELGLKEITY Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 35 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor alpha-3/beta-4 (CHRNA3/B4) | 6PV7 | 5.78 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA3-CHRNB4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Neuronal acetylcholine receptor Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-3/CHRNA3 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Neurotransmitter receptor Function A type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting of 3 and 4 subunits. Related diseases Bladder dysfunction, autonomic, with impaired pupillary reflex and secondary CAKUT (BAIPRCK) [MIM:191800]: An autosomal recessive disease characterized by impaired innervation and autonomic dysfunction of the urinary bladder, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, small kidneys, recurrent urinary tract infections, and progressive renal insufficiency. Additional autonomic features are impaired pupillary reflex and orthostatic hypotension. The disease manifests in utero or early childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31708116}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00915; DB01156; DB00237; DB00565; DB09028; DB00514; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB05710; DB01227; DB00848; DB00333; DB00184; DB01090; DB00202; DB01273 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 89661.2 Length 775 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 35.11 Isoelectric point 6.07 Charge (pH=7) -5.67 3D Binding mode Sequence SEAEHRLFERLFEDYNEIIRPVANVSDPVIIHFEVSMSQLVKVDEVNQIMETNLWLKQIWNDYKLKWNPSDYGGAEFMRVPAQKIWKPDIVLYNNAVGDFQVDDKTKALLKYTGEVTWIPPAIFKSSCKIDVTYFPFDYQNCTMKFGSWSYDKAKIDLVLIGSSMNLKDYWESGEWAIIKAPGYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDITYSLYIRRLPLFYTINLIIPCLLISFLTVLVFYLPSDCGEKVTLCISVLLSLTVFLLVITETIPSTSLVIPLIGEYLLFTMIFVTLSIVITVFVLNVHYRTPTTHTMPSWVKTVFLNLLPRVMFMTRIKEAIQSVKYIAENMKAQNEAKEIQDDWKYVAMVIDRIFLWVFTLVCILGTAGLFLQPLMRVANAEEKLMDDLLNKTRYNNLIRPATSSSQLISIKLQLSLAQLISVNEREQIMTTNVWLKQEWTDYRLTWNSSRYEGVNILRIPAKRIWLPDIVLYNNADGTYEVSVYTNLIVRSNGSVLWLPPAIYKSACKIEVKYFPFDQQNCTLKFRSWTYDHTEIDMVLMTPTASMDDFTPSGEWDIVALPGRRTVNPQDPSYVDVTYDFIIKRKPLFYTINLIIPCVLTTLLAILVFYLPSDCGEKMTLCISVLLALTFFLLLISKIVPPTSLDVPLIGKYLMFTMVLVTFSIVTSVCVLNVHHRSPSTHTMAPWVKRCFLHKLPTFLFMKRRQDVQEALEGVSFIAQHMKNDDEDQSVVEDWKYVAMVVDRLFLWVFMFVCVLGTVGLFLP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 36 | Cytochrome b (Complex III subunit 3) (Complex III subunit III) (Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 3) (Ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase complex cytochrome b subunit) | 1SQB | 5.77 | |
Target general information Gen name MT-CYB Organism Bos taurus (Bovine) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms CYTB;MTCYB;COB Protein family Cytochrome b family Biochemical class NA Function Component of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex (complex III or cytochrome b-c1 complex) that is part of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The b-c1 complex mediates electron transfer from ubiquinol to cytochrome c. Contributes to the generation of a proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane that is then used for ATP synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1327781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20025846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9485330, ECO:0000305|PubMed:189810}." Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 6 (COXPD6) [MIM:300816]: A mitochondrial disease resulting in a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by psychomotor delay, hypotonia, areflexia, muscle weakness and wasting. Some patients manifest prenatal ventriculomegaly and severe postnatal encephalomyopathy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20362274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22019070, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25583628, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26004228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26173962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27178839}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, X-linked recessive, 4, with or without cerebellar ataxia (CMTX4) [MIM:310490]: A neuromuscular disorder characterized by progressive sensorimotor axonal neuropathy, distal sensory impairment, difficulty walking due to peripheral neuropathy and/or cerebellar ataxia, and deafness due to auditory neuropathy. Additional features include cognitive impairment, cerebellar atrophy, dysarthria, abnormal extraocular movements, tremor, dysmetria and spasticity. The age at onset ranges from infancy to young adulthood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23217327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26004228}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Deafness, X-linked, 5, with peripheral neuropathy (DFNX5) [MIM:300614]: A form of hearing loss characterized by absent or severely abnormal auditory brainstem response, abnormal middle ear reflexes, abnormal speech discrimination, loss of outer hair cell function, and cochlear nerve hypoplasia. DFNX5 patients manifest auditory neuropathy with childhood onset, associated with distal sensory impairment affecting the peripheral nervous system. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25986071}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, X-linked, with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy (SEMDHL) [MIM:300232]: An X-linked recessive developmental disorder characterized by slowly progressive skeletal and neurologic abnormalities, including short stature, large and deformed joints, significant motor impairment, visual defects, and sometimes cognitive deficits. Affected individuals typically have normal early development in the first year or so of life, followed by development regression and the development of symptoms. Brain imaging shows white matter abnormalities consistent with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842795}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Electron transport; Heme; Iron; Membrane; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Reference proteome; Respiratory chain; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubiquinone Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C,D,F,G,H Molecular weight (Da) 99281.2 Length 866 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 43.81 Isoelectric point 8.32 Charge (pH=7) 7.12 3D Binding mode Sequence VSASSRWLEGIRKWYYNAAGFNKLGLMRDDTIHENDDVKEAIRRLPENLYDDRVFRIKRALDLSMRQQILPKEQWTKYEEDKSYLEPYLKEVIRERKEREEWAKKELVDPLTTVREQCEQLEKCVKARERLELCDERVSSRSQTEEDCTEELLDFLHARDHCVAHKLFNSLKTNIRKSHPLMKIVNNAFIDLPAPSNISSWWNFGSLLGICLILQILTGLFLAMHYTSDTTTAFSSVTHICRDVNYGWIIRYMHANGASMFFICLYMHVGRGLYYGSYTFLETWNIGVILLLTVMATAFMGYVLPWGQMSFWGATVITNLLSAIPYIGTNLVEWIWGGFSVDKATLTRFFAFHFILPFIIMAIAMVHLLFLHETGSNNPTGISSDVDKIPFHPYYTIKDILGALLLILALMLLVLFAPDLLGDPDNYTPANPLNTPPHIKPEWYFLFAYAILRSIPNKLGGVLALAFSILILALIPLLHTSKQRSMMFRPLSQCLFWALVADLLTLTWIGGQPVEHPYITIGQLASVLYFLLILVLMPTAGTIENKLLKWSDLELHPPSYPWSHRGLLSSLDHTSIRRGFQVYKQVCSSCHSMDYVAYRHLVGVCYTEDEAKALAEEVEVQDGPNEDGEMFMRPGKLSDYFPKPYPNPEAARAANNGALPPDLSYIVRARHGGEDYVFSLLTGYCEPPTGVSLREGLYFNPYFPGQAIGMAPPIYNEVLEFDDGTPATMSQVAKDVCTFLRWAAEPEHDHRKRMGLKMLLMMGLLLPLVYAMKRHKWSVLKSRKLAYRPPKGRQFGHLTRVRHVITYSLSPFEQRAFPHYFSKGIPNVLRRTRACILRVAPPFVAFYLVYTWGTQEFEKSKRKNPA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 37 | Estrogen-related receptor-beta (ESRRB) | 6LIT | 5.77 | |
Target general information Gen name ESRRB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Steroid hormone receptor ERR2; Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group B member 2; NR3B2; Estrogen-related receptor beta; Estrogen receptor-like 2; ESRL2; ERRB2; ERR-beta; ERR beta-2 Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR3 subfamily Biochemical class Nuclear hormone receptor Function Isoform 3: Transcription factor that binds a canonical ESRRB recognition (ERRE) sequence 5'TCAAGGTCA-3' localized on promoter and enhancer of targets genes regulating their expression or their transcription activity. Plays a role, in a LIF-independent manner, in maintainance of self-renewal and pluripotency of embryonic and trophoblast stem cells through different signaling pathways including FGF signaling pathway and Wnt signaling pathways. Upon FGF signaling pathway activation, interacts with KDM1A by directly binding to enhancer site of ELF5 and EOMES and activating their transcription leading to self-renewal of trophoblast stem cells. Also regulates expression of multiple rod-specific genes and is required for survival of this cell type (By similarity). Plays a role as transcription factor activator of GATA6, NR0B1, POU5F1 and PERM1. Plays a role as transcription factor repressor of NFE2L2 transcriptional activity and ESR1 transcriptional activity. During mitosis remains bound to a subset of interphase target genes, including pluripotency regulators, through the canonical ESRRB recognition (ERRE) sequence, leading to their transcriptional activation in early G1 phase. Can coassemble on structured DNA elements with other transcription factors like SOX2, POU5F1, KDM1A and NCOA3 to trigger ESRRB-dependent gene activation. This mechanism, in the case of SOX2 corecruitment prevents the embryonic stem cells (ESCs) to epiblast stem cells (EpiSC) transition through positive regulation of NR0B1 that inhibits the EpiSC transcriptional program. Also plays a role inner ear development by controlling expression of ion channels and transporters and in early placentation (By similarity). Related diseases Deafness, autosomal recessive, 35 (DFNB35) [MIM:608565]: A form of non-syndromic deafness characterized by non-progressive, prelingual hearing loss. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18179891}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00255; DB07776; DB01645 Interacts with P62508-3 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Chromosome; Cytoplasm; Deafness; Disease variant; DNA-binding; Metal-binding; Non-syndromic deafness; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 22767.3 Length 198 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 56.41 Isoelectric point 5.76 Charge (pH=7) -5.51 3D Binding mode Sequence GDIKALTTLCDLADRELVVIIGWAKHIPGFSSLSLGDQMSLLQSAWMEILILGIVYRSLPYDDKLVYAEDYIMDEEHSRLAGLLELYRAILQLVRRYKKLKVEKEEFVTLKALALANSDSMHIEDLEAVQKLQDLLHEALQDYELSQHHEEPWRTGKLLLTLPLLRQTAAKAVQHFYSVKLQGKVPMHKLFLEMLEAK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 38 | Hepatitis B virus Capsid protein (HBV C) | 7PZL | 5.77 | |
Target general information Gen name HBV C Organism Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate France/Tiollais/1979) (HBV-D) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Core antigen; Core protein; HBcAg; p21.5 Protein family Orthohepadnavirus core antigen family Biochemical class NA Function Self assembles to form an icosahedral capsid. Most capsid appear to be large particles with an icosahedral symmetry of T=4 and consist of 240 copies of capsid protein, though a fraction forms smaller T=3 particles consisting of 180 capsid proteins. Entering capsid are transported along microtubules to the nucleus. Phosphorylation of the capsid is thought to induce exposure of nuclear localization signal in the C-terminal portion of the capsid protein that allows binding to the nuclear pore complex via the importin (karyopherin-) alpha and beta. Capsids are imported in intact form through the nuclear pore into the nuclear basket, where it probably binds NUP153. Only capsids that contain the mature viral genome can release the viral DNA and capsid protein into the nucleoplasm. Immature capsids get stucked in the basket. Capsids encapsulate the pre-genomic RNA and the P protein. Pre-genomic RNA is reverse transcribed into DNA while the capsid is still in the cytoplasm. The capsid can then either be directed to the nucleus, providing more genome for transcription, or bud through the endoplasmic reticulum to provide new virions. Related diseases Oocyte/zygote/embryo maturation arrest 14 (OZEMA14) [MIM:620276]: An autosomal recessive female infertility disorder characterized by oocyte maturation arrest, fertilization failure, and/or early embryonic arrest. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32666501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33683667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33898437, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34218387}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative initiation; Capsid protein; Cytoplasmic inwards viral transport; DNA-binding; Host cytoplasm; Host-virus interaction; Microtubular inwards viral transport; Phosphoprotein; Reference proteome; Repeat; RNA-binding; T=4 icosahedral capsid protein; Viral penetration into host nucleus; Virion; Virus entry into host cell Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 32388.9 Length 286 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 42.05 Isoelectric point 5.06 Charge (pH=7) -11.81 3D Binding mode Sequence MDIDPYKEFGATVELLSFLPSDFFPSVRDLLDTASALYREALESPEHCSPHHTALRQAIVCWGELMTLATWVGVNLEDPASRDLVVSYVNTNMGLKFRQLLWFHISCLTFGRETVIEYLVSFGVWIRTPPAYRPPNAPILSTLMDIDPYKEFGATVELLSFLPSDFFPSVRDLLDTASALYREALESPEHCSPHHTALRQAIVCWGELMTLATWVGVNLEDPASRDLVVSYVNTNMGLKFRQLLWFHISCLTFGRETVIEYLVSFGVWIRTPPAYRPPNAPILSTL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 39 | Fibrinogen gamma chain | 1DUG | 5.76 | |
Target general information Gen name FGG Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms PRO2061 Protein family NA Biochemical class transferase Function Cell adhesion molecule binding.Metal ion binding.Protein binding, bridging.Protein homodimerization activity.Receptor binding.Structural molecule activity. Related diseases Congenital afibrinogenemia (CAFBN) [MIM:202400]: Rare autosomal recessive disorder is characterized by bleeding that varies from mild to severe and by complete absence or extremely low levels of plasma and platelet fibrinogen. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25427968}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Patients with congenital fibrinogen abnormalities can manifest different clinical pictures. Some cases are clinically silent, some show a tendency toward bleeding and some show a predisposition for thrombosis with or without bleeding.; DISEASE: Dysfibrinogenemia, congenital (DYSFIBRIN) [MIM:616004]: A disorder characterized by qualitative abnormalities (dysfibrinogenemia) of the circulating fibrinogen. Affected individuals are frequently asymptomatic, but some patients have bleeding diathesis, thromboembolic complications, or both. In some cases, dysfibrinogenemia is associated with low circulating fibrinogen levels (hypodysfibrinogenemia). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15632207, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2257302, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2976995, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3708159}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00009; DB11571; DB00364; DB11300; DB11572 Interacts with P75358 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Blood coagulation; Calcium; Coiled coil; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hemostasis; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Sulfation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 54170 Length 468 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 35.94 Isoelectric point 6.08 Charge (pH=7) -7.16 3D Binding mode Sequence SPILGYWKIKGLVQPTRLLLEYLEEKYEEHLYERDEGDKWRNKKFELGLEFPNLPYYIDGDVKLTQSMAIIRYIADKHNMLGGCPKERAEISMLEGAVLDIRYGVSRIAYSKDFETLKVDFLSKLPEMLKMFEDRLCHKTYLNGDHVTHPDFMLYDALDVVLYMDPMCLDAFPKLVCFKKRIEAIPQIDKYLKSSKYIAWPLQGWQATFGGGDHPPKSDPQQHHLGGAKQAGDVSPILGYWKIKGLVQPTRLLLEYLEEKYEEHLYERDEGDKWRNKKFELGLEFPNLPYYIDGDVKLTQSMAIIRYIADKHNMLGGCPKERAEISMLEGAVLDIRYGVSRIAYSKDFETLKVDFLSKLPEMLKMFEDRLCHKTYLNGDHVTHPDFMLYDALDVVLYMDPMCLDAFPKLVCFKKRIEAIPQIDKYLKSSKYIAWPLQGWQATFGGGDHPPKSDPQQHHLGGAKQAGDV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 40 | Estrogen-related receptor-gamma (ESRRG) | 2E2R | 5.76 | |
Target general information Gen name ESRRG Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group B member 3; NR3B3; KIAA0832; Estrogen-related receptor gamma; Estrogen receptor-related protein 3; ERRG2; ERR3; ERR gamma-2 Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR3 subfamily Biochemical class Nuclear hormone receptor Function Binds specifically to an estrogen response element and activates reporter genes controlled by estrogen response elements. Induces the expression of PERM1 in the skeletal muscle. Orphan receptor that acts as transcription activator in the absence of bound ligand. Related diseases WHIM syndrome 1 (WHIMS1) [MIM:193670]: An autosomal dominant immunologic disease characterized by neutropenia, hypogammaglobulinemia and extensive human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Despite the peripheral neutropenia, bone marrow aspirates from affected individuals contain abundant mature myeloid cells, a condition termed myelokathexis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12692554, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15536153}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: CXCR4 mutations play a role in the pathogenesis of Waldenstroem macroglobulinemia (WM) and influence disease presentation and outcome, as well as response to therapy. WM is a B-cell lymphoma characterized by accumulation of malignant lymphoplasmacytic cells in the bone marrow, lymph nodes and spleen, and hypersecretion of monoclonal immunoglobulin M (IgM). Excess IgM production results in serum hyperviscosity, tissue infiltration, and autoimmune-related pathology. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24366360, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24553177}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06884; DB04468; DB06973; DB07485; DB02659; DB00255; DB13952; DB13953; DB13954; DB13955; DB13956; DB06902; DB00675; DB00197 Interacts with Q05D60; Q9BVG8; P50222; P51843; Q12769; Q9UBK2; A0MZ66; G2XKQ0; Q8NFM4; Q13315; Q86WA6-2; Q9BZE7; Q13555-5; Q05D60; Q5JST6; P11474; O95718-2; P62508-3; Q15024; O95990-4; Q8IZU1; Q14296; P23508; Q6IN84; P51843; Q15466; P48552; P26367; Q9NPJ4; P01189; Q9UBK2; P62195; Q8N0T1-2; Q04864-2; Q6NUQ1; A0MZ66-4; Q8TAD8; P19237; P48788; Q96PN7; Q96S82; Q5SQQ9-2; Q7Z4V0 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Activator; Alternative splicing; DNA-binding; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 25755.7 Length 227 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 55.31 Isoelectric point 5.09 Charge (pH=7) -10.6 3D Binding mode Sequence KPYNKIVSHLLVAEPEKIYAMPDPTVPDSDIKALTTLCDLADRELVVIIGWAKHIPGFSTLSLADQMSLLQSAWMEILILGVVYRSLSFEDELVYADDYIMDEDQSKLAGLLDLNNAILQLVKKYKSMKLEKEEFVTLKAIALANSDSMHIEDVEAVQKLQDVLHEALQDYEAGQHMEDPRRAGKMLMTLPLLRQTSTKAVQHFYNIKLEGKVPMHKLFLEMLEAKV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||