Job Results:
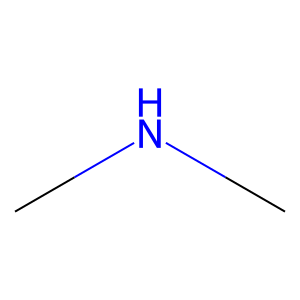
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
7689e25b6c3c7fc348a8f90b8451d3c4
Job name
NA
Time
2025-02-18 14:12:25
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit A | 1ZVT | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name parC Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b3019;JW2987 Protein family Type II topoisomerase GyrA/ParC subunit family, ParC type 1 subfamily Biochemical class Isomerase Function ATP binding.DNA binding.DNA topoisomerase type II (ATP-hydrolyzing) activity. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB11943; DB12924; DB00817 Interacts with P22523; P0A7K2 EC number 5.6.2.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; DNA-binding; Isomerase; Membrane; Reference proteome; Topoisomerase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 26490.3 Length 246 Aromaticity 0.04 Instability index 46.03 Isoelectric point 8.94 Charge (pH=7) 2.83 3D Binding mode Sequence SEPVTIVLSQMGWVRSAKGHDIDAPGLNYKAGDSFKAAVKGKSNQPVVFVDSTGRSYAIDPITLPSARGQGEPLTGKLTLPPGATVDHMLMESDDQKLLMASDAGYGFVCTFNDLVARNRAGKALITLPENAHVMPPVVIEDASDMLLAITQAGRMLMFPVSDLPQLSKGKGNKIINIPSAEAARGEDGLAQLYVLPPQSTLTIHVGKRKIKLRPEELQKVTGERGRRGTLMRGLQRIDRVEIDSP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 22 | Phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase-1 (PDPK1) | 5LVO | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name PDPK1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PDK1; HPDK1; 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1; 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1; 3'-phosphoinositide dependent kinase 1 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, PDPK1 subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Its targets include: protein kinase B (PKB/AKT1, PKB/AKT2, PKB/AKT3), p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RPS6KB1), p90 ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RPS6KA1, RPS6KA2 and RPS6KA3), cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PRKACA), protein kinase C (PRKCD and PRKCZ), serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK1, SGK2 and SGK3), p21-activated kinase-1 (PAK1), protein kinase PKN (PKN1 and PKN2). Plays a central role in the transduction of signals from insulin by providing the activating phosphorylation to PKB/AKT1, thus propagating the signal to downstream targets controlling cell proliferation and survival, as well as glucose and amino acid uptake and storage. Negatively regulates the TGF-beta-induced signaling by: modulating the association of SMAD3 and SMAD7 with TGF-beta receptor, phosphorylating SMAD2, SMAD3, SMAD4 and SMAD7, preventing the nuclear translocation of SMAD3 and SMAD4 and the translocation of SMAD7 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in response to TGF-beta. Activates PPARG transcriptional activity and promotes adipocyte differentiation. Activates the NF-kappa-B pathway via phosphorylation of IKKB. The tyrosine phosphorylated form is crucial for the regulation of focal adhesions by angiotensin II. Controls proliferation, survival, and growth of developing pancreatic cells. Participates in the regulation of Ca(2+) entry and Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels of mast cells. Essential for the motility of vascular endothelial cells (ECs) and is involved in the regulation of their chemotaxis. Plays a critical role in cardiac homeostasis by serving as a dual effector for cell survival and beta-adrenergic response. Plays an important role during thymocyte development by regulating the expression of key nutrient receptors on the surface of pre-T cells and mediating Notch-induced cell growth and proliferative responses. Provides negative feedback inhibition to toll-like receptor-mediated NF-kappa-B activation in macrophages. Isoform 3 is catalytically inactive. Serine/threonine kinase which acts as a master kinase, phosphorylating and activating a subgroup of the AGC family of protein kinases. Related diseases Hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia (HVLI) [MIM:618850]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by highly elevated plasma concentrations of valine and leucine/isoleucine. Affected individuals suffer from headache and mild memory impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. A patient with hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia was identified as compound heterozygote for Gln-170 (inherited from his father) and Lys-264 (inherited from his mother), both variants reduced the catalytic activity of the enzyme. After treatment with vitamin B6, a precursor of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, a BCAT2 cofactor, the blood levels of branched chain amino acids, especially valine, were decreased and brain lesions were improved. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25653144}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07132; DB06932; DB07300; DB07456; DB07457; DB07033; DB01933; DB03777; DB01946; DB00482; DB04522; DB12010; DB01863; DB02010 Interacts with P31749; Q00005; Q9Y4P3; O75385; P54252; P42858; Q8WXH2; Q8IUH5 EC number EC 2.7.11.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Activator; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cell junction; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Transferase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 32750.5 Length 286 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 40.9 Isoelectric point 8.55 Charge (pH=7) 3.58 3D Binding mode Sequence PRKKRPEDFKFGKILGEGSFSTVVLARELATSREYAIKILEKRHIIKENKVPYVTRERDVMSRLDHPFFVKLYFTFQDDEKLYFGLSYAKNGELLKYIRKIGSFDETCTRFYTAEIVSALEYLHGKGIIHRDLKPENILLNEDMHIQITDFGTAKVLSPESKQARANXFVGTAQYVSPELLTEKSACKSSDLWALGCIIYQLVAGLPPFRAGNEGLIFAKIIKLEYDFPEKFFPKARDLVEKLLVLDATKRLGCEEMEGYGPLKAHPFFESVTWENLHQQTPPKLT Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 23 | Flavodoxin/ferredoxin--NADP reductase | 1FDR | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name fpr Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms mvrA;b3924;JW3895 Protein family Ferredoxin--NADP reductase type 1 family Biochemical class Flavoprotein Function FAD binding.Ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase activity.Oxidoreductase activity. Related diseases Noonan syndrome 13 (NS13) [MIM:619087]: A form of Noonan syndrome, a disease characterized by short stature, facial dysmorphic features such as hypertelorism, a downward eyeslant and low-set posteriorly rotated ears, and a high incidence of congenital heart defects and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Other features can include a short neck with webbing or redundancy of skin, deafness, motor delay, variable intellectual deficits, multiple skeletal defects, cryptorchidism, and bleeding diathesis. Individuals with Noonan syndrome are at risk of juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, a myeloproliferative disorder characterized by excessive production of myelomonocytic cells. NS13 inheritance is autosomal dominant. There is considerable variability in severity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32721402}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147 Interacts with NA EC number 1.18.1.2; 1.19.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; NADP; Nucleotide-binding; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 27346.2 Length 244 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 30.68 Isoelectric point 7.25 Charge (pH=7) 0.42 3D Binding mode Sequence ADWVTGKVTKVQNWTDALFSLTVHAPVLPFTAGQFTKLGLEIRVQRAYSYVNSPDNPDLEFYLVTVPDGKLSPRLAALKPGDEVQVVSEAAGFFVLDEVPHCETLWMLATGTAIGPYLSILRLGKDLDRFKNLVLVHAARYAADLSYLPLMQELEKRYEGKLRIQTVVSRETAAGSLTGRIPALIESGELESTIGLPMNKETSHVMLCGNPQMVRDTQQLLKETRQMTKHLRRRPGHMTAEHYW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 24 | Xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase (XDH) | 2E1Q | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name XDH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Xanthine oxidase; Xanthine dehydrogenase; XDHA Protein family Xanthine dehydrogenase family Biochemical class CH/CH(2) oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine. Catalyzes the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. Contributes to the generation of reactive oxygen species. Has also low oxidase activity towards aldehydes (in vitro). Key enzyme in purine degradation. Related diseases Xanthinuria 1 (XAN1) [MIM:278300]: A disorder characterized by excretion of very large amounts of xanthine in the urine and a tendency to form xanthine stones. Uric acid is strikingly diminished in serum and urine. XAN1 is due to isolated xanthine dehydrogenase deficiency. Patients can metabolize allopurinol. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10844591, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11379872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14551354, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9153281}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00640; DB00041; DB00437; DB00993; DB00958; DB01136; DB00856; DB00515; DB00746; DB03328; DB00997; DB03516; DB12466; DB04854; DB03147; DB04335; DB01020; DB00583; DB00170; DB01033; DB00157; DB03841; DB00336; DB01250; DB05262; DB06478; DB01168; DB00339; DB00127; DB01685; DB00831 Interacts with Q9Y3R0-3 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 2Fe-2S; 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; FAD; Flavoprotein; Iron; Iron-sulfur; Metal-binding; Molybdenum; NAD; Oxidoreductase; Peroxisome; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 143697 Length 1307 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 37.9 Isoelectric point 8.01 Charge (pH=7) 7.07 3D Binding mode Sequence ADKLVFFVNGRKVVEKNADPETTLLAYLRRKLGLSGTKLGCGEGGCGACTVMLSKYDRLQNKIVHFSANACLAPICSLHHVAVTTVEGIGSTKTRLHPVQERIAKSHGSQCGFCTPGIVMSMYTLLRNQPEPTMEEIENAFQGNLCRCTGYRPILQGFRTFARDGSPSLFKPEEFTPLDPTQEPIFPPELLRLKDTPRKQLRFEGERVTWIQASTLKELLDLKAQHPDAKLVVGNTEIGIEMKFKNMLFPMIVCPAWIPELNSVEHGPDGISFGAACPLSIVEKTLVDAVAKLPAQKTEVFRGVLEQLRWFAGKQVKSVASVGGNIITASPISDLNPVFMASGAKLTLVSRGTRRTVQMDHTFFPGYRKTLLSPEEILLSIEIPYSREGEYFSAFKQASRREDDIAKVTSGMRVLFKPGTTEVQELALCYGGMANRTISALKTTQRQLSKLWKEELLQDVCAGLAEELHLPPDAPGGMVDFRCTLTLSFFFKFYLTVLQKLGQENLEDKCGKLDPTFASATLLFQKDPPADVQLFQEVPKGQSEEDMVGRPLPHLAADMQASGEAVYCDDIPRYENELSLRLVTSTRAHAKIKSIDTSEAKKVPGFVCFISADDVPGSNITGICNDETVFAKDKVTCVGHIIGAVVADTPEHTQRAAQGVKITYEELPAIITIEDAIKNNSFYGPELKIEKGDLKKGFSEADNVVSGEIYIGGQEHFYLETHCTIAVPKGEAGEMELFVSTQNTMKTQSFVAKMLGVPANRIVVRVKRMGGGFGGKVTRSTVVSTAVALAAYKTGRPVRCMLDRDEDMLITGGRHPFLARYKVGFMKTGTVVALEVDHFSNVGNTQDLSQSIMERALFHMDNCYKIPNIRGTGRLCKTNLPSNTAFRGFGGPQGMLIAECWMSEVAVTCGMPAEEVRRKNLYKEGDLTHFNQKLEGFTLPRCWEECLASSQYHARKSEVDKFNKENCWKKRGLCIIPTKFGISFTVPFLNQAGALLHVYTDGSVLLTHGGTEMGQGLHTKMVQVASRALKIPTSKIYISETSTNTVPNTSPTAASVSADLNGQAVYAACQTILKRLEPYKKKNPSGSWEDWVTAAYMDTVSLSATGFYRTPNLGYSFETNSGNPFHYFSYGVACSEVEIDCLTGDHKNLRTDIVMDVGSSLNPAIDIGQVEGAFVQGLGLFTLEELHYSPEGSLHTRGPSTYKIPAFGSIPIEFRVSLLRDCPNKKAIYASKAVGEPPLFLAASIFFAIKDAIRAARAQHTGNNVKELFRLDSPATPEKIRNACVDKFTTLCVTGVPENCKPWSVRV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 25 | Aminoacylase-1 | 1Q7L | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name ACY1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Peptidase M20A family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Aminoacylase activity.Identical protein binding.Metal ion binding.Metallopeptidase activity. Related diseases Aminoacylase-1 deficiency (ACY1D) [MIM:609924]: An enzymatic deficiency resulting in encephalopathy, unspecific psychomotor delay, psychomotor delay with atrophy of the vermis and syringomyelia, marked muscular hypotonia or normal clinical features. Epileptic seizures are a frequent feature. All affected individuals exhibit markedly increased urinary excretion of several N-acetylated amino acids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16274666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16465618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17562838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21414403}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06151; DB00128; DB09130 Interacts with Q03154; O75934; Q96HA8; P36639; P36639-2; Q8TCT1; P0CG20; Q96A09; P54274; O43711; Q9UPN9; Q9NZC7-5 EC number 3.5.1.14 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 31172.2 Length 275 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 36.46 Isoelectric point 6 Charge (pH=7) -5.26 3D Binding mode Sequence NPWWAAFSRVCKDMNLTLEPEIMPAAGDNRYIRAVGVPALGFSPMNRTPVLLHDHDERLHEAVFLRGVDIYTRLLPALASVPALPEEHPSVTLFRQYLRIRTVQPKPDYGAAVAFFEETARQLGLGCQKVEVAPGYVVTVLTWPGTNPTLSSILLNSHTDVVPVFKEHWSHDPFEAFKDSEGYIYARGAQDMKCVSIQYLEAVRRLKVEGHRFPRTIHMTFVPDEEVGGHQGMELFVQRPEFHALRAGFALDEGIANPTDAFTVFYSERSPWWVR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 26 | Aminoacylase-1 | 1Q7L | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name ACY1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Peptidase M20A family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Aminoacylase activity.Identical protein binding.Metal ion binding.Metallopeptidase activity. Related diseases Aminoacylase-1 deficiency (ACY1D) [MIM:609924]: An enzymatic deficiency resulting in encephalopathy, unspecific psychomotor delay, psychomotor delay with atrophy of the vermis and syringomyelia, marked muscular hypotonia or normal clinical features. Epileptic seizures are a frequent feature. All affected individuals exhibit markedly increased urinary excretion of several N-acetylated amino acids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16274666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16465618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17562838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21414403}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06151; DB00128; DB09130 Interacts with Q03154; O75934; Q96HA8; P36639; P36639-2; Q8TCT1; P0CG20; Q96A09; P54274; O43711; Q9UPN9; Q9NZC7-5 EC number 3.5.1.14 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 31172.2 Length 275 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 36.46 Isoelectric point 6 Charge (pH=7) -5.26 3D Binding mode Sequence NPWWAAFSRVCKDMNLTLEPEIMPAAGDNRYIRAVGVPALGFSPMNRTPVLLHDHDERLHEAVFLRGVDIYTRLLPALASVPALPEEHPSVTLFRQYLRIRTVQPKPDYGAAVAFFEETARQLGLGCQKVEVAPGYVVTVLTWPGTNPTLSSILLNSHTDVVPVFKEHWSHDPFEAFKDSEGYIYARGAQDMKCVSIQYLEAVRRLKVEGHRFPRTIHMTFVPDEEVGGHQGMELFVQRPEFHALRAGFALDEGIANPTDAFTVFYSERSPWWVR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 27 | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 | 2YL2 | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name ACACA Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms ACAC;ACCA;ACC1 Protein family NA Biochemical class Ligase Function Acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity.ATP binding.Biotin carboxylase activity.Identical protein binding.Metal ion binding. Related diseases Acetyl-CoA carboxylase-alpha deficiency (ACACAD) [MIM:613933]: An autosomal recessive inborn error of de novo fatty acid synthesis associated with severe brain damage, persistent myopathy and poor growth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:6114432}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00121 Interacts with Q13085; O60218; P38398; Q96EB6; Q9CQ20; P02654; Q92915-2; Q6NTF9-3 EC number 6.4.1.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Allosteric enzyme; Alternative promoter usage; ATP-binding; Biotin; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Fatty acid biosynthesis; Fatty acid metabolism; Ligase; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Magnesium; Manganese; Metal-binding; Multifunctional enzyme; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 54237.7 Length 486 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 39.18 Isoelectric point 6.37 Charge (pH=7) -2.46 3D Binding mode Sequence VASPAEFVTRFGGNKVIEKVLIANNGIAAVKCMRSIRRWSYEMFRNERAIRFVVMVTPEDLKANAEYIKMADHYVPVPGGPNNNNYANVELILDIAKRIPVQAVWAGWGHASENPKLPELLLKNGIAFMGPPSQAMWALGDKIASSIVAQTAGIPTLPWSGSGLRVDWSKRILNVPQELYEKGYVKDVDDGLQAAEEVGYPVMIKASEGGGGKGIRKVNNADDFPNLFRQVQAEVPGSPIFVMRLAKQSRHLEVQILADQYGNAISLFGRDCSVQRRHQKIIEEAPATIATPAVFEHMEQCAVKLAKMVGYVSAGTVEYLYSQDGSFYFLELNPRLQVEHPCTEMVADVNLPAAQLQIAMGIPLYRIKDIRMMYGVSPWGDSPIDFEDSAHVPCPRGHVIAARITGTVQELNFRSNKNVWGYFSVQFGHCFSWGENREEAISNMVVALKELSIRGDFRTTVEYLIKLLETESFQMNRIDTGWLDRL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 28 | Lysine--tRNA ligase | 4YCU | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name KARS Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms KARS;KIAA0070 Protein family Class-II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family Biochemical class ligase / ligase inhibitor Function Amino acid binding.ATP adenylyltransferase activity.ATP binding.Identical protein binding.Lysine-tRNA ligase activity.Protein homodimerization activity.TRNA binding. Related diseases Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, recessive intermediate B (CMTRIB) [MIM:613641]: A form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Recessive intermediate forms of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease are characterized by clinical and pathologic features intermediate between demyelinating and axonal peripheral neuropathies, and motor median nerve conduction velocities ranging from 25 to 45 m/sec. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20920668}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Deafness, autosomal recessive, 89 (DFNB89) [MIM:613916]: A form of non-syndromic deafness characterized by bilateral, prelingual, moderate to severe hearing loss affecting all frequencies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23768514}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Deafness, congenital, and adult-onset progressive leukoencephalopathy (DEAPLE) [MIM:619196]: An autosomal recessive, complex neurodegenerative disorder characterized by congenital sensorineural deafness, and progressive motor and cognitive decline apparent in young adulthood. Brain imaging shows diffuse white matter abnormalities affecting various brain regions, consistent with a progressive leukoencephalopathy. More variable additional features may include visual impairment and axonal peripheral neuropathy. Premature death may occurr in some patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28887846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30737337, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31116475}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukoencephalopathy, progressive, infantile-onset, with or without deafness (LEPID) [MIM:619147]: An autosomal recessive, complex neurodegenerative disorder apparent from infancy. LEPID is characterized by early-onset progressive leukoencephalopathy with brainstem and spinal cord calcifications, sensorineural deafness in most patients, global developmental delay with cognitive impairment and poor or absent speech, developmental regression, and neurologic deterioration. Additional more variable features may include poor overall growth with microcephaly, seizures, visual loss, microcytic anemia, and hepatic enlargement or abnormal liver enzymes. Premature death is common. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25330800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29615062, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30252186, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30715177}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00123 Interacts with Q13155; P07814; Q15046; P08865; P00441; Q13155 EC number 2.7.7.-; 6.1.1.6 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; ATP-binding; Cell membrane; Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; Cytoplasm; Deafness; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Host-virus interaction; Intellectual disability; Ligase; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathy; Non-syndromic deafness; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Protein biosynthesis; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 37110.4 Length 323 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 50.17 Isoelectric point 4.92 Charge (pH=7) -17.53 3D Binding mode Sequence IIRSKIITYIRSFLDELGFLEIETPMMNIIPGGAVAKPFITYHNELDMNLYMRIAPELYHKMLVVGGIDRVYEIGRQFRNEGIDLTHNPEFTTCEFYMAYADYHDLMEITEKMVSGMVKHITGSYKVTYHPDGPEGQAYDVDFTPPFRRINMVEELEKALGMKLPETNLFETEETRKILDDICVAKAVECPPPRTTARLLDKLVGEFLEVTCINPTFICDHPQIMSPLAKWHRSKEGLTERFELFVMKKEICNAYTELNDPMRQRQLFEEQAKAKAAGDDEAMFIDENFCTALEYGLPPTAGWGMGIDRVAMFLTDSNNIKEV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 29 | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | 4LY1 | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name HDAC2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms HD2 Protein family Histone deacetylase family, HD type 1 subfamily Biochemical class Carbon-nitrogen hydrolase Function Gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. Forms transcriptional repressor complexes by associating with MAD, SIN3, YY1 and N-COR. Interacts in the late S-phase of DNA-replication with DNMT1 in the other transcriptional repressor complex composed of DNMT1, DMAP1, PCNA, CAF1. Deacetylates TSHZ3 and regulates its transcriptional repressor activity. Component of a RCOR/GFI/KDM1A/HDAC complex that suppresses, via histone deacetylase (HDAC) recruitment, a number of genes implicated in multilineage blood cell development. May be involved in the transcriptional repression of circadian target genes, such as PER1, mediated by CRY1 through histone deacetylation. Involved in MTA1-mediated transcriptional corepression of TFF1 and CDKN1A. Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Related diseases Ventricular tachycardia, catecholaminergic polymorphic, 1, with or without atrial dysfunction and/or dilated cardiomyopathy (CPVT1) [MIM:604772]: An arrhythmogenic disorder characterized by stress-induced, bidirectional ventricular tachycardia that may degenerate into cardiac arrest and cause sudden death. Patients present with recurrent syncope, seizures, or sudden death after physical activity or emotional stress. CPVT1 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11157710, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11159936, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11208676, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12093772, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12106942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14571276, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15046072, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15046073, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15466642, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15544015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16188589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24793461, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25372681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27733687}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Ventricular arrhythmias due to cardiac ryanodine receptor calcium release deficiency syndrome (VACRDS) [MIM:115000]: An autosomal dominant arrhythmogenic disorder characterized by syncope, cardiac arrest and/or sudden unexpected death, often in association with physical exertion or acute emotional stress. Patients who survive manifest polymorphic ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. Unlike typical catecholaminergic ventricular tachycardia, arrhythmias are not reproducible on exercise stress testing or adrenaline challenge. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12093772, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17984046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33536282}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12565; DB01223; DB01076; DB05015; DB01262; DB11841; DB01095; DB12645; DB00227; DB11830; DB01303; DB06603; DB06819; DB05223; DB00175; DB03766; DB12847; DB06176; DB00641; DB00277; DB09091; DB00313; DB02546 Interacts with Q9C0K0; Q9HCU9; P68400; Q9UER7; P51610; Q13547; Q9UIS9; Q13330; P01106; P06748; P48382; Q96ST3; O95863; Q9HD15; O43463; Q9H3M7; Q92618; Q17R98; Q2HR82; PRO_0000449623 [P0DTD1] EC number EC 3.5.1.98 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Biological rhythms; Chromatin regulator; Cytoplasm; Hydrolase; Isopeptide bond; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repressor; S-nitrosylation; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 42020.5 Length 366 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 29.52 Isoelectric point 6.52 Charge (pH=7) -2.16 3D Binding mode Sequence KKKVCYYYDGDIGNYYYGQGHPMKPHRIRMTHNLLLNYGLYRKMEIYRPHKATAEEMTKYHSDEYIKFLRSIRPDNMSEYSKQMQRFNVGEDCPVFDGLFEFCQLSTGGSVAGAVKLNRQQTDMAVNWAGGLHHAKKSEASGFCYVNDIVLAILELLKYHQRVLYIDIDIHHGDGVEEAFYTTDRVMTVSFHKYGEYFPGTGDLRDIGAGKGKYYAVNFPMRDGIDDESYGQIFKPIISKVMEMYQPSAVVLQCGADSLSGDRLGCFNLTVKGHAKCVEVVKTFNLPLLMLGGGGYTIRNVARCWTYETAVALDCEIPNELPYNDYFEYFGPDFKLHISPSNMTNQNTPEYMEKIKQRLFENLRML Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 30 | Mycobacterium Isocitrate lyase (MycB icl) | 1F8M | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name MycB icl Organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Isocitratase; Isocitrase; ICL Protein family Isocitrate lyase/PEP mutase superfamily, Isocitrate lyase family Biochemical class Carbon-carbon lyase Function Catalyzes the formation of succinate and glyoxylate from isocitrate, a key step of the glyoxylate cycle. May be involved in the assimilation of one-carbon compounds via the isocitrate lyase- positive serine pathway. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 80, with variant lissencephaly (MRT80) [MIM:620653]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by global developmental delay, mildly to moderately impaired intellectual development, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder, hypotonia, seizure, poor social skills, and autistic traits. Brain imaging shows fronto-temporal lissencephaly and pachygyria. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:37880421}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04343 Interacts with NA EC number EC 4.1.3.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Glyoxylate bypass; Isopeptide bond; Lyase; Magnesium; Manganese; Metal-binding; Reference proteome; Tricarboxylic acid cycle; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 93759.5 Length 854 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 28.02 Isoelectric point 4.98 Charge (pH=7) -34.53 3D Binding mode Sequence ASVVGTPKSAEQIQQEWDTNPRWKDVTRTYSAEDVVALQGSVVEEHTLARRGAEVLWEQLHDLEWVNALGALTGNMAVQQVRAGLKAIYLSGWQVAGDANLSGHTYPDQSLYPANSVPQVVRRINNALQRADQIAKIEGDTSVENWLAPIVADGEAGFGGALNVYELQKALIAAGVAGSHWEDQLASEKKCGHLGGKVLIPTQQHIRTLTSARLAADVADVPTVVIARTDAEAATLITSDVDERDQPFITGERTREGFYRTKNGIEPCIARAKAYAPFADLIWMETGTPDLEAARQFSEAVKAEYPDQMLAYNCSPSFNWKKHLDDATIAKFQKELAAMGFKFQFITLAGFHALNYSMFDLAYGYAQNQMSAYVELQEREFAAEERGYTATKHQREVGAGYFDRIATTVDPNSSTTALTGSTEEGQFASVVGTPKSAEQIQQEWDTNPRWKDVTRTYSAEDVVALQGSVVEEHTLARRGAEVLWEQLHDLEWVNALGALTGNMAVQQVRAGLKAIYLSGWQVAGDANLSGHTYPDQSLYPANSVPQVVRRINNALQRADQIAKIEGDTSVENWLAPIVADGEAGFGGALNVYELQKALIAAGVAGSHWEDQLASEKKCGHLGGKVLIPTQQHIRTLTSARLAADVADVPTVVIARTDAEAATLITSDVDERDQPFITGERTREGFYRTKNGIEPCIARAKAYAPFADLIWMETGTPDLEAARQFSEAVKAEYPDQMLAYNCSPSFNWKKHLDDATIAKFQKELAAMGFKFQFITLAGFHALNYSMFDLAYGYAQNQMSAYVELQEREFAAEERGYTATKHQREVGAGYFDRIATTVDPNSSTTALTGSTEEGQF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 31 | Trypanosoma Cruzipain (Trypano CYSP) | 1EWM | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name Trypano CYSP Organism Trypanosoma cruzi Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Cruzaine; Major cysteine proteinase Protein family Peptidase C1 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function The cysteine protease may play an important role in the development and differentiation of the parasites at several stages of their life cycle. Related diseases Sick sinus syndrome 2 (SSS2) [MIM:163800]: The term 'sick sinus syndrome' encompasses a variety of conditions caused by sinus node dysfunction. The most common clinical manifestations are syncope, presyncope, dizziness, and fatigue. Electrocardiogram typically shows sinus bradycardia, sinus arrest, and/or sinoatrial block. Episodes of atrial tachycardias coexisting with sinus bradycardia ('tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome') are also common in this disorder. SSS occurs most often in the elderly associated with underlying heart disease or previous cardiac surgery, but can also occur in the fetus, infant, or child without heart disease or other contributing factors. SSS2 onset is in utero or at birth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15123648, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16407510, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20662977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23103389}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Brugada syndrome 8 (BRGDA8) [MIM:613123]: A tachyarrhythmia characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs, the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19165230}. The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Epilepsy, idiopathic generalized 18 (EIG18) [MIM:619521]: An autosomal dominant form of idiopathic generalized epilepsy, a disorder characterized by recurring generalized seizures in the absence of detectable brain lesions and/or metabolic abnormalities. Generalized seizures arise diffusely and simultaneously from both hemispheres of the brain. Seizure types include juvenile myoclonic seizures, absence seizures, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. EIG18 is characterized by onset of myoclonic seizures in infancy. Although the seizures remit, some patients may have later speech or cognitive impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30127718}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02200; DB02051; DB01871; DB01810; DB02128; DB03536; DB04427; DB03691; DB04502; DB03573 Interacts with NA EC number EC 3.4.22.51 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Autocatalytic cleavage; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Protease; Signal; Thiol protease; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 22703 Length 215 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 28.98 Isoelectric point 4.37 Charge (pH=7) -13.9 3D Binding mode Sequence APAAVDWRARGAVTAVKDQGQCGSCWAFSAIGNVECQWFLAGHPLTNLSEQMLVSCDKTDSGCSGGLMNNAFEWIVQENNGAVYTEDSYPYASGEGISPPCTTSGHTVGATITGHVELPQDEAQIAAWLAVNGPVAVAVDASSWMTYTGGVMTSCVSEQLDHGVLLVGYNDSAAVPYWIIKNSWTTQWGEEGYIRIAKGSNQCLVKEEASSAVVG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 32 | Plasmodium DOXP reductoisomerase (Malaria DXR) | 3AU9 | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name Malaria DXR Organism Plasmodium falciparum (isolate HB3) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms IspC; DXR; DXP reductoisomerase; DOXP reductoisomerase; 2-C-Methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate synthase; 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase Protein family DXR family Biochemical class Short-chain dehydrogenases reductase Function Catalyzes the NADP-dependent rearrangement and reduction of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP) to 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP). Related diseases Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive 11 (ARCI11) [MIM:602400]: A form of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis, a disorder of keratinization with abnormal differentiation and desquamation of the epidermis, resulting in abnormal skin scaling over the whole body. The main skin phenotypes are lamellar ichthyosis (LI) and non-bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (NCIE), although phenotypic overlap within the same patient or among patients from the same family can occur. Lamellar ichthyosis is a condition often associated with an embedment in a collodion-like membrane at birth; skin scales later develop, covering the entire body surface. Non-bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma characterized by fine whitish scaling on an erythrodermal background; larger brownish scales are present on the buttocks, neck and legs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17273967, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18843291}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.1.1.267 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Apicoplast; Isoprene biosynthesis; Magnesium; Manganese; Metal-binding; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Plastid; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 46644.4 Length 410 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 36.77 Isoelectric point 6.95 Charge (pH=7) -0.14 3D Binding mode Sequence PINVAIFGSTGSIGTNALNIIRECNKIENVFNVKALYVNKSVNELYEQAREFLPEYLCIHDKSVYEELKELVKNIKDYKPIILCGDEGMKEICSSNSIDKIVIGIDSFQGLYSTMYAIMNNKIVALANKESIVSAGFFLKKLLNIHKNAKIIPVDSEHSAIFQCLDNNKVLKTKCLQDNFSKINNINKIFLCSSGGPFQNLTMDELKNVTSENALKHPKWKMGKKITIDSATMMNKGLEVIETHFLFDVDYNDIEVIVHKECIIHSCVEFIDKSVISQMYYPDMQIPILYSLTWPDRIKTNLKPLDLAQVSTLTFHKPSLEHFPCIKLAYQAGIKGNFYPTVLNASNEIANNLFLNNKIKYFDISSIISQVLESFNSQKVSENSEDLMKQILQIHSWAKDKATDIYNKHN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 33 | Tankyrase-2 (TNKS-2) | 3U9H | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name TNKS2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tankyrase-related protein; Tankyrase-like protein; Tankyrase II; TRF1-interacting ankyrin-related ADP-ribose polymerase 2; TNKL; TANK2; Protein poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase tankyrase-2; Poly [ADP-ribos Protein family ARTD/PARP family Biochemical class Glycosyltransferases Function Acts as an activator of the Wnt signaling pathway by mediating poly-ADP-ribosylation of AXIN1 and AXIN2, 2 key components of the beta-catenin destruction complex: poly-ADP-ribosylated target proteins are recognized by RNF146, which mediates their ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. Also mediates poly-ADP-ribosylation of BLZF1 and CASC3, followed by recruitment of RNF146 and subsequent ubiquitination. Mediates poly-ADP-ribosylation of TERF1, thereby contributing to the regulation of telomere length. Stimulates 26S proteasome activity. Poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase involved in various processes such as Wnt signaling pathway, telomere length and vesicle trafficking. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder with macrocephaly, seizures, and speech delay (IDDMSSD) [MIM:618158]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impaired intellectual development, poor speech, postnatal macrocephaly, and seizures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30290153}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with O15084; Q7Z6K5-1; O15169; Q9NWV8; P11274; Q13698; Q9NRI5; Q6V0I7; Q9NWT6; P14652; Q9UIQ6; Q14980; Q9BZL4; Q92698; P78314; O43815; P54274; Q9C0C2; Q9UHP3; Q06649 EC number EC 2.4.2.30 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ADP-ribosylation; ANK repeat; Chromosome; Cytoplasm; Glycosyltransferase; Golgi apparatus; Hydroxylation; Membrane; Metal-binding; NAD; Nucleotidyltransferase; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Telomere; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Wnt signaling pathway; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23695.5 Length 208 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 47.61 Isoelectric point 8.28 Charge (pH=7) 2.88 3D Binding mode Sequence GTILIDLSPDDKEFQSVEEEMQSTVREHRDGGHAGGIFNRYNILKIQKVCNKKLWERYTHRRKEVSEENHNHANERMLFHGSPFVNAIIHKGFDERHAYIGGMFGAGIYFAENSSKSNQYVYGIGGGTGCPVHKDRSCYICHRQLLFCRVTLGKSFLQFSAMAHSPPGHHSVTGRPSVNGLALAEYVIYRGEQAYPEYLITYQIMRPE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 34 | Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH) | 7WGR | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name OGDH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms OGDC-E1; 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial; 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex component E1 Protein family Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Aldehyde/oxo donor oxidoreductase Function The 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of 2-oxoglutarate to succinyl-CoA and CO(2). The 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex is mainly active in the mitochondrion. A fraction of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex also localizes in the nucleus and is required for lysine succinylation of histones: associates with KAT2A on chromatin and provides succinyl-CoA to histone succinyltransferase KAT2A. 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (E1) component of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, which mediates the decarboxylation of alpha-ketoglutarate. Related diseases Postaxial acrofacial dysostosis (POADS) [MIM:263750]: POADS is characterized by severe micrognathia, cleft lip and/or palate, hypoplasia or aplasia of the posterior elements of the limbs, coloboma of the eyelids and supernumerary nipples. POADS is a very rare disorder: only 2 multiplex families, each consisting of 2 affected siblings born to unaffected, nonconsanguineous parents, have been described among a total of around 30 reported cases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19915526}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00157; DB00313; DB09092 Interacts with P54253; P42858 EC number EC 1.2.4.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Glycolysis; Isopeptide bond; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Thiamine pyrophosphate; Transit peptide; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 192730 Length 1700 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 43.47 Isoelectric point 5.97 Charge (pH=7) -29.2 3D Binding mode Sequence AVQSLIRAYQIRGHHVAQLDPLGILDADLDSSVPADIISSTDKLGFYGLDESDLDKVFHLPTTTFIGGQESALPLREIIRRLEMAYCQHIGVEFMFINDLEQCQWIRQKFETPGIMQFTNEEKRTLLARLVRSTRFEEFLQRKWSSEKRFGLEGCEVLIPALKTIIDKSSENGVDYVIMGMPHRGRLNVLANVIRKELEQIFCQFDSKLEAADEGSGDNITLSLVANPSHLEAADPVVMGKTKAEQFYCGDTEGKKVMSILLHGDAAFAGQGIVYETFHLSDLPSYTTHGTVHVVVNNQIGFTTDPRMARSSPYPTDVARVVNAPIFHVNSDDPEAVMYVCKVAAEWRSTFHKDVVVDLVCYRRNGHNEMDEPMFTQPLMYKQIRKQKPVLQKYAELLVSQGVVNQPEYEEEISKYDKICEEAFARSKMSCPSTGLTEDILTHIGNVASSVPVENFTIHGGLSRILKTRGEMVKNRTVDWALAEYMAFGSLLKEGIHIRLSGQDVERGTFSHRHHVLHDQNVDKRTCIPMNHLWPNQAPYTVCNSSLSEYGVLGFELGFAMASPNALVLWEAQFGDFHNTAQCIIDQFICPGQAKWVRQNGIVLLLPHGMEGMGPEHSSARPERFLQMCNDDPDVLPDLKEANFDINQLYDCNWVVVNCSTPGNFFHVLRRQILLPFRKPLIIFTPKSLLRHPEARSSFDEMLPGTHFQRVIPEDGPAAQNPENVKRLLFCTGKVYYDLTRERKARDMVGQVAITRIEQLSPFPFDLLLKEVQKYPNAELAWCQEEHKNQGYYDYVKPRLRTTISRAKPVWYAGRDPAAAPATGNKKTHLTELQRLLDTAFDLDVFKNFSAVQSLIRAYQIRGHHVAQLDPLGILDADLDSSVPADIISSTDKLGFYGLDESDLDKVFHLPTTTFIGGQESALPLREIIRRLEMAYCQHIGVEFMFINDLEQCQWIRQKFETPGIMQFTNEEKRTLLARLVRSTRFEEFLQRKWSSEKRFGLEGCEVLIPALKTIIDKSSENGVDYVIMGMPHRGRLNVLANVIRKELEQIFCQFDSKLEAADEGSGDNITLSLVANPSHLEAADPVVMGKTKAEQFYCGDTEGKKVMSILLHGDAAFAGQGIVYETFHLSDLPSYTTHGTVHVVVNNQIGFTTDPRMARSSPYPTDVARVVNAPIFHVNSDDPEAVMYVCKVAAEWRSTFHKDVVVDLVCYRRNGHNEMDEPMFTQPLMYKQIRKQKPVLQKYAELLVSQGVVNQPEYEEEISKYDKICEEAFARSKMSCPSTGLTEDILTHIGNVASSVPVENFTIHGGLSRILKTRGEMVKNRTVDWALAEYMAFGSLLKEGIHIRLSGQDVERGTFSHRHHVLHDQNVDKRTCIPMNHLWPNQAPYTVCNSSLSEYGVLGFELGFAMASPNALVLWEAQFGDFHNTAQCIIDQFICPGQAKWVRQNGIVLLLPHGMEGMGPEHSSARPERFLQMCNDDPDVLPDLKEANFDINQLYDCNWVVVNCSTPGNFFHVLRRQILLPFRKPLIIFTPKSLLRHPEARSSFDEMLPGTHFQRVIPEDGPAAQNPENVKRLLFCTGKVYYDLTRERKARDMVGQVAITRIEQLSPFPFDLLLKEVQKYPNAELAWCQEEHKNQGYYDYVKPRLRTTISRAKPVWYAGRDPAAAPATGNKKTHLTELQRLLDTAFDLDVFKNFS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 35 | Cathepsin D (CTSD) | 4OC6 | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name CTSD Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CPSD; CD Protein family Peptidase A1 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Plays a role in APP processing following cleavage and activation by ADAM30 which leads to APP degradation. Involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases such as breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer disease. Acid protease active in intracellular protein breakdown. Related diseases Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, 10 (CLN10) [MIM:610127]: A form of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis with onset at birth or early childhood. Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses are progressive neurodegenerative, lysosomal storage diseases characterized by intracellular accumulation of autofluorescent liposomal material, and clinically by seizures, dementia, visual loss, and/or cerebral atrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16670177, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16685649, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21990111}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03028; DB03096; DB07542; DB08740; DB02216 Interacts with P05067; Q9P1A6-3; I6L9I8; Q9H6S3; Q7Z602; P28799; PRO_0000012695 [P28799]; PRO_0000012696 [P28799]; PRO_0000012697 [P28799]; PRO_0000012698 [P28799]; PRO_0000012699 [P28799]; PRO_0000012700 [P28799]; PRO_0000012701 [P28799]; P68431; Q9Y6F6-3; Q12756; Q5TA79; Q86VF5-3; O15130-2; Q96LB9; P09565; Q9C004; Q8NBJ7; Q9BQG1; P28347-2; P45880; Q15007-2; O00308; Q5W0Z9-4; Q6ZNH5 EC number EC 3.4.23.5 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alzheimer disease; Aspartyl protease; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lysosome; Neurodegeneration; Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 37264.2 Length 341 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 32.32 Isoelectric point 5.6 Charge (pH=7) -4.86 3D Binding mode Sequence GPIPEVLKNYMDAQYYGEIGIGTPPQCFTVVFDTGSSNLWVPSIHCKLLDIACWIHHKYNSDKSSTYVKNGTSFDIHYGSGSLSGYLSQDTVSVPCQSGGVKVERQVFGEATKQPGITFIAAKFDGILGMAYPRISVNNVLPVFDNLMQQKLVDQNIFSFYLSRDPDAQPGGELMLGGTDSKYYKGSLSYLNVTRKAYWQVHLDQVEVASGLTLCKEGCEAIVDTGTSLMVGPVDEVRELQKAIGAVPLIQGEYMIPCEKVSTLPAITLKLGGKGYKLSPEDYTLKVSQAGKTLCLSGFMGMDIPPPSGPLWILGDVFIGRYYTVFDRDNNRVGFAEAARL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 36 | Complement C1s component (C1S) | 1ELV | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name C1S Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Complement component 1 subcomponent s; Complement C1s subcomponent; C1-esterase; C1 esterase Protein family Peptidase S1 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function C1r activates C1s so that it can, in turn, activate C2 and C4. C1s B chain is a serine protease that combines with C1q and C1r to form C1, the first component of the classical pathway of the complement system. Related diseases Complement component C1s deficiency (C1SD) [MIM:613783]: A rare defect resulting in C1 deficiency and impaired activation of the complement classical pathway. C1 deficiency generally leads to severe immune complex disease with features of systemic lupus erythematosus and glomerulonephritis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11390518}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, periodontal type, 2 (EDSPD2) [MIM:617174]: A form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, a connective tissue disorder characterized by hyperextensible skin, atrophic cutaneous scars due to tissue fragility and joint hyperlaxity. EDSPD2 is characterized by the association of typical features of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with gingival recession and severe early-onset periodontal disease, leading to premature loss of permanent teeth. EDSPD2 transmission pattern is consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27745832}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02371; DB09228; DB09130; DB12831; DB06404; DB14996; DB01593; DB14487; DB14533; DB14548 Interacts with P00736; P09871; P06681; O43889-2; Q9H6H4; P05155 EC number EC 3.4.21.42 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Calcium; Complement pathway; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; EGF-like domain; Ehlers-Danlos syndrome; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Hydroxylation; Immunity; Innate immunity; Metal-binding; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Serine protease; Signal; Sushi Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 33278.6 Length 303 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 33.69 Isoelectric point 5.16 Charge (pH=7) -7.95 3D Binding mode Sequence LDCGIPESIENGKVEDPESTLFGSVIRYTCEEPYYYMEGGGEYHCAGNGSWVNEVLGPELPKCVPVCGVPREPFIIGGSDADIKNFPWQVFFDNPWAGGALINEYWVLTAAHVVEGNREPTMYVGSTSVQKMLTPEHVFIHPGWKLLAVPEGRTNFDNDIALVRLKDPVKMGPTVSPICLPGTSSDYNLMDGDLGLISGWGRTEKRDRAVRLKAARLPVAPLRKCKEVAYVFTPNMICAGGEKGMDSCKGDSGGAFAVQDPNDKTKFYAAGLVSWGPQCGTYGLYTRVKNYVDWIMKTMQENS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 37 | Cathepsin G (CTSG) | 1KYN | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name CTSG Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms CG Protein family Peptidase S1 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Cleaves complement C3. Has antibacterial activity against the Gram-negative bacterium P. aeruginosa, antibacterial activity is inhibited by LPS from P. aeruginosa, Z-Gly-Leu-Phe-CH2Cl and phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Serine protease with trypsin- and chymotrypsin-like specificity. Related diseases Lethal congenital contracture syndrome 2 (LCCS2) [MIM:607598]: A form of lethal congenital contracture syndrome, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by degeneration of anterior horn neurons, extreme skeletal muscle atrophy, and congenital non-progressive joint contractures (arthrogryposis). The contractures can involve the upper or lower limbs and/or the vertebral column, leading to various degrees of flexion or extension limitations evident at birth. LCCS2 patients manifest craniofacial/ocular findings, lack of hydrops, multiple pterygia, and fractures, as well as a normal duration of pregnancy and a unique feature of a markedly distended urinary bladder (neurogenic bladder defect). The phenotype suggests a spinal cord neuropathic etiology. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17701904}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Erythroleukemia, familial (FERLK) [MIM:133180]: An autosomal dominant myeloproliferative disorder characterized by neoplastic proliferation of erythroblastic and myeloblastic elements with atypical erythroblasts and myeloblasts in the peripheral blood. Disease penetrance is incomplete. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27416908}. Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Visceral neuropathy, familial, 1, autosomal recessive (VSCN1) [MIM:243180]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by intestinal dysmotility due to aganglionosis (Hirschsprung disease), hypoganglionosis, and/or chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Additional variable features are progressive peripheral neuropathy, arthrogryposis, hypoplasia or aplasia of the olfactory bulb and of the external auditory canals, microtia or anotia, and facial dysmorphism. Some patients present structural cardiac anomalies and arthrogryposis with multiple pterygia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33497358}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04016; DB02360 Interacts with A8MQ03; Q15323; Q7Z3S9; Q9NRD5 EC number EC 3.4.21.20 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Antibiotic; Antimicrobial; Cell membrane; Chemotaxis; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lysosome; Membrane; Nucleus; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Serine protease; Signal; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 25353.8 Length 223 Aromaticity 0.06 Instability index 66.1 Isoelectric point 11.51 Charge (pH=7) 23.24 3D Binding mode Sequence IIGGRESRPHSRPYMAYLQIQSPAGQSRCGGFLVREDFVLTAAHCWGSNINVTLGAHNIQRRENTQQHITARRAIRHPQYNQRTIQNDIMLLQLSRRVRRNRNVNPVALPRAQEGLRPGTLCTVAGWGRVSMRRGTDTLREVQLRVQRDRQCLRIFGSYDPRRQICVGDRRERKAAFKGDSGGPLLCNNVAHGIVSYGKSSGVPPEVFTRVSSFLPWIRTTMR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 38 | Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase type 5 | 2BQ8 | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name ACP5 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Metallophosphoesterase superfamily, Purple acid phosphatase family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Acid phosphatase activity.Ferric iron binding.Ferrous iron binding. Related diseases Spondyloenchondrodysplasia with immune dysregulation (SPENCDI) [MIM:607944]: A disease characterized by vertebral and metaphyseal dysplasia, spasticity with cerebral calcifications, and strong predisposition to autoimmune diseases. The skeletal dysplasia is characterized by radiolucent and irregular spondylar and metaphyseal lesions that represent islands of chondroid tissue within bone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21217752, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21217755}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. ACP5 inactivating mutations result in a functional excess of phosphorylated osteopontin causing deregulation of osteopontin signaling and consequential autoimmune disease. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 3.1.3.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Iron; Lysosome; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID X Molecular weight (Da) 34330.6 Length 304 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 42.3 Isoelectric point 9.11 Charge (pH=7) 6.75 3D Binding mode Sequence ATPALRFVAVGDWGGVPNAPFHTAREMANAKEIARTVQILGADFILSLGDNFYFTGVQDINDKRFQETFEDVFSDRSLRKVPWYVLAGNHDHLGNVSAQIAYSKISKRWNFPSPFYRLHFKIPQTNVSVAIFMLDTVTLCGNSDDFLSQQPERPRDVKLARTQLSWLKKQLAAAREDYVLVAGHYPVWSIAEHGPTHCLVKQLRPLLATYGVTAYLCGHDHNLQYLQDENGVGYVLSGAGNFMDPSKRHQRKVPNGYLRFHYGTEDSLGGFAYVEISSKEMTVTYIEASGKSLFKTRLPRRARP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 39 | Penicillin-binding protein 2B | 2WAD | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name penA Organism Streptococcus pneumoniae (strain ATCC BAA-255 / R6) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms spr1517;pbp2b Protein family Transpeptidase family Biochemical class Peptide binding protein Function Penicillin binding. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01163; DB00415; DB08795; DB01140; DB00456; DB01066; DB00493; DB01331; DB01212; DB00567; DB03313; DB00485; DB00739; DB01603; DB00607; DB00713; DB00319 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Antibiotic resistance; Cell membrane; Cell shape; Cell wall biogenesis/degradation; Membrane; Peptidoglycan synthesis; Reference proteome; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 65444.4 Length 607 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 30.15 Isoelectric point 4.95 Charge (pH=7) -20.68 3D Binding mode Sequence SQTKVTTSSARGEIYDASGKPLVENTLKQVVSFTRSNKMTATDLKEIAKKLLTYVSISSPNLTERQLADYYLADPEIYKKTVEALPSESELYNNAVDSVPTSQLNYTEDEKKEIYLFSQLNAVGNFATGTIATDPLNDSQVAVIASISKEMPGISISTSWDRKILETSLSSIVGSVSSEKAGLPAEEAESYLKKGYSLNDRVGTSYLEKQYEEVLQGKRPVKEIHLDKHGDMESVENIEEGSKGKNIKLTIDLAFQDSVDALLKSYFNSELGNGGAKYSEGVYAVALNPQTGAVLSMSGLKHDLKTGELTPDSLGTVTNVFVPGSVVKAATISSGWENGVLSGNQTLTDQPIVFQGSAPIYSWYKLAYGSFPITAVEALEYSSNAYVVQTALGIMGQTYQPNMFVGTSNLESAMGKLRSTFGEYGLGSATGIDLPDESTGLVPKEYNFANFITNAFGQFDNYTPMQLAQYVATIANNGVRLAPHIVEGIYDNNDKGGLGELIQAIDTKEINKVNISESDMAILHQGFYQVSHGTSPLTTGRAFSDGATVSISGKTGTNTNAVAYAPTENPQIAVAVVFPHNTNLTKNVGPAIARDIINLYNQHHPMN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 40 | Deoxyribodipyrimidine photo-lyase | 1OWL | 4.01 | |
Target general information Gen name phr Organism Synechococcus sp. (strain ATCC 27144 / PCC 6301 / SAUG 1402/1) (Anacystis nidulans) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms phrA;syc1392_c Protein family DNA photolyase class-1 family Biochemical class Lyase Function Deoxyribodipyrimidine photo-lyase activity.DNA binding.Nucleotide binding. Related diseases Myeloperoxidase deficiency (MPOD) [MIM:254600]: A disorder characterized by decreased myeloperoxidase activity in neutrophils and monocytes that results in disseminated candidiasis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:37198333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7904599, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8142659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8621627, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9354683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9637725}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147 Interacts with NA EC number 4.1.99.3 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Chromophore; Direct protein sequencing; DNA damage; DNA repair; DNA-binding; FAD; Flavoprotein; Lyase; Nucleotide-binding Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 53346.9 Length 473 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 53.22 Isoelectric point 6.92 Charge (pH=7) -0.23 3D Binding mode Sequence APILFWHRRDLRLSDNIGLAAARAQSAQLIGLFCLDPQILQSADMAPARVAYLQGCLQELQQRYQQAGSRLLLLQGDPQHLIPQLAQQLQAEAVYWNQDIEPYGRDRDGQVAAALKTAGIRAVQLWDQLLHSPDQILSGSGNPYSVYGPFWKNWQAQPKPTPVATPTELVDLSPEQLTAIAPLLLSELPTLKQLGFDWDGGFPVEPGETAAIARLQEFCDRAIADYDPQRNFPAEAGTSGLSPALKFGAIGIRQAWQAASAAHALSRSDEARNSIRVWQQELAWREFYQHALYHFPSLADGPYRSLWQQFPWENREALFTAWTQAQTGYPIVDAAMRQLTETGWMHNRCRMIVASFLTKDLIIDWRRGEQFFMQHLVDGDLAANNGGWQWSASSGMDPKPLRIFNPASQAKKFDATATYIKRWLPELRHVHPKDLISGEITPIERRGYPAPIVNHNLRQKQFKALYNQLKAAI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||