Job Results:
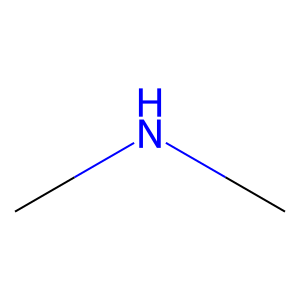
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
500380c02188392c5ec501006b89ab5f
Job name
NA
Time
2025-02-18 14:12:25
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | S-adenosylmethionine synthase isoform type-1 | 2OBV | 4.03 | |
Target general information Gen name MAT1A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms MATA1;AMS1 Protein family AdoMet synthase family Biochemical class Transferase Function ATP binding.Identical protein binding.Metal ion binding.Methionine adenosyltransferase activity.Selenomethionine adenosyltransferase activity. Related diseases Methionine adenosyltransferase deficiency (MATD) [MIM:250850]: An inborn error of metabolism resulting in isolated hypermethioninemia. Most patients have no clinical abnormalities, although some neurologic symptoms may be present in rare cases with severe loss of methionine adenosyltransferase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10677294, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7560086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8770875, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9042912}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03191; DB00118; DB03611; DB00134 Interacts with P05067; P42858; Q00266; P31153 EC number 2.5.1.6 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ATP-binding; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Magnesium; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; One-carbon metabolism; Potassium; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; S-nitrosylation; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 42222.9 Length 381 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 41.95 Isoelectric point 6.14 Charge (pH=7) -4.58 3D Binding mode Sequence MGVFMFTSESVGEGHPDKICDQISDAVLDAHLKQDPNAKVACETVCKTGMVLLCGEITSMAMVDYQRVVRDTIKHIGYDDSAKGFDFKTCNVLVALEQQSPDIAQCVHLDRNEEDVGAGDQGLMFGYATDETEECMPLTIILAHKLNARMADLRRSGLLPWLRPDSKTQVTVQYMQDNGAVIPVRIHTIVISVQHNEDITLEEMRRALKEQVIRAVVPAKYLDEDTVYHLQPSGRFVIGGPQGDAGVTGRKIIVDTYGGWGAHGGGAFSGKDYTKVDRSAAYAARWVAKSLVKAGLCRRVLVQVSYAIGVAEPLSISIFTYGTSQKTERELLDVVHKNFDLRPGVIVRDLDLKKPIYQKTACYGHFGRSEFPWEVPRKLVF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 22 | Kallikrein-5 (KLK5) | 6QFE | 4.03 | |
Target general information Gen name KLK5 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms UNQ570/PRO1132; Stratum corneum tryptic enzyme; SCTE; Kallikrein-like protein 2; KLK-L2 Protein family Peptidase S1 family, Kallikrein subfamily Biochemical class Peptidase Function May be involved in desquamation. Related diseases Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 8 (FPLD8) [MIM:620679]: An autosomal dominant form of partial lipodystrophy, a disorder characterized by abnormal subcutaneous fat distribution. FPLD8 patients show selective loss of subcutaneous adipose tissue from the limbs, beginning around 13 to 15 years of age, and abnormal accumulation of subcutaneous adipose tissue in the dorsal neck and face, as well as in the posterior thoracic and abdominal regions. The disorder is associated with metabolic abnormalities, including diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27376152}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P20930; Q9NQG1 EC number EC 3.4.21.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Serine protease; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 50299.2 Length 454 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 40.74 Isoelectric point 9.25 Charge (pH=7) 23.09 3D Binding mode Sequence IINGSDCDMHTQPWQAALLLRPNQLYCGAVLVHPQWLLTAAHCRKKVFRVRLGHYSLSPVYESGQQMFQGVKSIPHPGYSHPGHSNDLMLIKLNRRIRPTKDVRPINVSSHCPSAGTKCLVSGWGTTKSPQVHFPKVLQCLNISVLSQKRCEDAYPRQIDDTMFCAGDKAGRDSCQGDSGGPVVCNGSLQGLVSWGDYPCARPNRPGVYTNLCKFTKWIQETIQANSIINGSDCDMHTQPWQAALLLRPNQLYCGAVLVHPQWLLTAAHCRKKVFRVRLGHYSLSPVYESGQQMFQGVKSIPHPGYSHPGHSNDLMLIKLNRRIRPTKDVRPINVSSHCPSAGTKCLVSGWGTTKSPQVHFPKVLQCLNISVLSQKRCEDAYPRQIDDTMFCAGDKAGRDSCQGDSGGPVVCNGSLQGLVSWGDYPCARPNRPGVYTNLCKFTKWIQETIQANS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 23 | Lysine-specific demethylase 7A (KDM7A) | 3KVB | 4.03 | |
Target general information Gen name KDM7A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Lysine-specific demethylase 7; KIAA1718; KDM7; JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 1D; JHDM1D Protein family JHDM1 histone demethylase family, JHDM1D subfamily Biochemical class NA Function Histone demethylase required for brain development. Specifically demethylates dimethylated 'Lys-9' and 'Lys-27' (H3K9me2 and H3K27me2, respectively) of histone H3 and monomethylated histone H4 'Lys-20' residue (H4K20Me1), thereby playing a central role in histone code. Specifically binds trimethylated 'Lys-4' of histone H3 (H3K4me3), affecting histone demethylase specificity: in presence of H3K4me3, it has no demethylase activity toward H3K9me2, while it has high activity toward H3K27me2. Demethylates H3K9me2 in absence of H3K4me3. Has activity toward H4K20Me1 only when nucleosome is used as a substrate and when not histone octamer is used as substrate. Related diseases MUC1/CA 15-3 is used as a serological clinical marker of breast cancer to monitor response to breast cancer treatment and disease recurrence (PubMed:20816948). Decreased levels over time may be indicative of a positive response to treatment. Conversely, increased levels may indicate disease progression. At an early stage disease, only 21% of patients exhibit high MUC1/CA 15-3 levels, that is why CA 15-3 is not a useful screening test. Most antibodies target the highly immunodominant core peptide domain of 20 amino acid (APDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTS) tandem repeats. Some antibodies recognize glycosylated epitopes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20816948}.; DISEASE: Tubulointerstitial kidney disease, autosomal dominant, 2 (ADTKD2) [MIM:174000]: A form of autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease, a genetically heterogeneous disorder characterized by slowly progressive loss of kidney function, bland urinary sediment, hyperuricemia, absent or mildly increased albuminuria, lack of severe hypertension during the early stages, and normal or small kidneys on ultrasound. Renal histology shows variable abnormalities including interstitial fibrosis with tubular atrophy, microcystic dilatation of the tubules, thickening of tubular basement membranes, medullary cysts, and secondary glomerulosclerotic or glomerulocystic changes with abnormal glomerular tufting. There is significant variability, as well as incomplete penetrance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23396133}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.14.11.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Dioxygenase; Iron; Metal-binding; Neurogenesis; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 42365.5 Length 366 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 41.95 Isoelectric point 6.3 Charge (pH=7) -3.09 3D Binding mode Sequence PVQAGTRTFIKELRSRVFPSADEIIIKMHGSQLTQRYLEKHGFDVPIMVPKLDDLGLRLPSPTFSVMDVERYVGGDKVIDVIDVARQADSKMTLHNYVKYFMNPNRPKVLNVISLEFSDTKMSELVEVPDIAKKLSWVENYWPDDSVFPKPFVQKYCLMGVQDSYTDFHIDFGGTSVWYHVLWGEKIFYLIKPTDENLARYESWSSSVTQSEVFFGDKVDKCYKCVVKQGHTLFVPTGWIHAVLTSQDCMAFGGNFLHNLNIGMQLRCYEMEKRLKTPDLFKFPFFEAICWFVAKNLLETLKELREDGFQPQTYLVQGVKALHTALKLWMKKELVSEHAFEIPDNVRPGHLIKELSKVIRAIEEEN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 24 | Plasmodium DOXP reductoisomerase (Malaria DXR) | 3AU9 | 4.03 | |
Target general information Gen name Malaria DXR Organism Plasmodium falciparum (isolate HB3) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms IspC; DXR; DXP reductoisomerase; DOXP reductoisomerase; 2-C-Methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate synthase; 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase Protein family DXR family Biochemical class Short-chain dehydrogenases reductase Function Catalyzes the NADP-dependent rearrangement and reduction of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP) to 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP). Related diseases Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive 11 (ARCI11) [MIM:602400]: A form of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis, a disorder of keratinization with abnormal differentiation and desquamation of the epidermis, resulting in abnormal skin scaling over the whole body. The main skin phenotypes are lamellar ichthyosis (LI) and non-bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (NCIE), although phenotypic overlap within the same patient or among patients from the same family can occur. Lamellar ichthyosis is a condition often associated with an embedment in a collodion-like membrane at birth; skin scales later develop, covering the entire body surface. Non-bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma characterized by fine whitish scaling on an erythrodermal background; larger brownish scales are present on the buttocks, neck and legs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17273967, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18843291}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.1.1.267 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Apicoplast; Isoprene biosynthesis; Magnesium; Manganese; Metal-binding; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Plastid; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 46644.4 Length 410 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 36.77 Isoelectric point 6.95 Charge (pH=7) -0.14 3D Binding mode Sequence PINVAIFGSTGSIGTNALNIIRECNKIENVFNVKALYVNKSVNELYEQAREFLPEYLCIHDKSVYEELKELVKNIKDYKPIILCGDEGMKEICSSNSIDKIVIGIDSFQGLYSTMYAIMNNKIVALANKESIVSAGFFLKKLLNIHKNAKIIPVDSEHSAIFQCLDNNKVLKTKCLQDNFSKINNINKIFLCSSGGPFQNLTMDELKNVTSENALKHPKWKMGKKITIDSATMMNKGLEVIETHFLFDVDYNDIEVIVHKECIIHSCVEFIDKSVISQMYYPDMQIPILYSLTWPDRIKTNLKPLDLAQVSTLTFHKPSLEHFPCIKLAYQAGIKGNFYPTVLNASNEIANNLFLNNKIKYFDISSIISQVLESFNSQKVSENSEDLMKQILQIHSWAKDKATDIYNKHN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 25 | Protoporphyrinogen oxidase (PPOX) | 3NKS | 4.03 | |
Target general information Gen name PPOX Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PPO Protein family Protoporphyrinogen/coproporphyrinogen oxidase family, Protoporphyrinogen oxidase subfamily Biochemical class NA Function Catalyzes the 6-electron oxidation of protoporphyrinogen-IX to form protoporphyrin-IX. Related diseases Variegate porphyria (VP) [MIM:176200]: A form of porphyria. Porphyrias are inherited defects in the biosynthesis of heme, resulting in the accumulation and increased excretion of porphyrins or porphyrin precursors. They are classified as erythropoietic or hepatic, depending on whether the enzyme deficiency occurs in red blood cells or in the liver. Variegate porphyria is an acute hepatic form characterized by partial reduction of protoporphyrinogen oxidase activity, increased photosensitivity, skin blistering and scarring of sun-exposed areas, skin hyperpigmentation, abdominal pain, and neuropsychiatric symptoms. High fecal levels of protoporphyrin and coproporphyrin, increased urine uroporphyrins and iron overload are typical markers of the disease. Inheritance is autosomal dominant with incomplete penetrance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10486317, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11074242, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11102990, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11348478, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11350188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11474578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12380696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655566, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12859407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12922165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14669009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16433813, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16621625, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16922948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16947091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18350656, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18570668, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19320019, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21048046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23430901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23467411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24073655, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8817334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8852667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9763307}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Mutations leading to severe PPOX deficiency cause the rare homozygous variant form of VP. Missense mutations that preserve 10%-25% of wild-type activity may not cause clinically overt VP in heterozygotes (PubMed:9811936). Mutations with intermediate effect on catalytic activity may cause VP, but with a low clinical penetrance (PubMed:10486317). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10486317, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9811936}.; DISEASE: Variegate porphyria, childhood-onset (VPCO) [MIM:620483]: An autosomal recessive form of variegate porphyria, a disorder of heme biosynthesis that results from diminished activity of protoporphyrinogen oxidase. VPCO is characterized by severe protoporphyrinogen oxidase deficiency, onset of photosensitization by porphyrins in early childhood, skin scarring and hyperpigmentation, and skeletal abnormalities of the hand. Additional variable features are short stature, impaired intellectual development, and seizures. VPCO patients rarely experience acute neuropsychiatric or abdominal attacks. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10870850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11286631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33159949, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8673113, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9541112, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9811936}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.3.3.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Disease variant; FAD; Flavoprotein; Heme biosynthesis; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Oxidoreductase; Porphyrin biosynthesis; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 49470.2 Length 465 Aromaticity 0.05 Instability index 48.23 Isoelectric point 7.8 Charge (pH=7) 1.98 3D Binding mode Sequence GRTVVVLGGGISGLAASYHLSRAPCPPKVVLVESSERLGGWIRSVRGPNGAIFELGPRGIRPAGALGARTLLLVSELGLDSEVLPVRGDHPAAQNRFLYVGGALHALPTGLRGPSPPFSKPLFWAGLRELTKPRGKEPDETVHSFAQRRLGPEVASLAMDSLCRGVFAGNSRELSIRSCFPSLFQAEQTHRSILLGLLLGQPDSALIRQALAERWSQWSLRGGLEMLPQALETHLTSRGVSVLRGQPVCGLSLQAEGRWKVSLRDSSLEADHVISAIPASVLSELLPAEAAPLARALSAITAVSVAVVNLQYQGAHLPVQGFGHLVPSSEDPGVLGIVYDSVAFPEQDGSPPGLRVTVMLGGSWLQTLEASGCVLSQELFQQRAQEAAATQLGLKEMPSHCLVHLHKNCIPQYTLGHWQKLESARQFLTAHRLPLTLAGASYEGVAVNDCIESGRQAAVSVLGTE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 26 | Deubiquitinating enzyme 1 (USP1) | 7ZH4 | 4.03 | |
Target general information Gen name USP1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hUBP; Ubiquitin-specific-processing protease 1; Ubiquitin thioesterase 1; Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 Protein family Peptidase C19 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Involved in PCNA-mediated translesion synthesis (TLS) by deubiquitinating monoubiquitinated PCNA. Has almost no deubiquitinating activity by itself and requires the interaction with WDR48 to have a high activity. Negative regulator of DNA damage repair which specifically deubiquitinates monoubiquitinated FANCD2. Related diseases Brachydactyly A2 (BDA2) [MIM:112600]: A form of brachydactyly. Brachydactyly defines a group of inherited malformations characterized by shortening of the digits due to abnormal development of the phalanges and/or the metacarpals. In brachydactyly type A2 shortening of the middle phalanges is confined to the index finger and the second toe, all other digits being more or less normal. Because of a rhomboid or triangular shape of the affected middle phalanx, the end of the second finger usually deviates radially. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19327734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357617}. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. Duplications of a cis-regulatory element located approximately 110 kb downstream of BMP2 have been found in BDA2 families. They likely cause altered BMP2 expression with pathological consequences. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19327734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357617}.; DISEASE: Short stature, facial dysmorphism, and skeletal anomalies with or without cardiac anomalies 1 (SSFSC1) [MIM:617877]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by short stature, facial dysmorphism, skeletal anomalies, and variable cardiac defects. Distinctive facial features include midface retrusion, short upturned nose, long philtrum, high-arched or cleft palate, and variable degrees of micrognathia and dental crowding. Skeletal anomalies include patterning defects of the axial skeleton, characterized by 11 pairs of ribs and brachydactyly of the fifth ray. Congenital heart defects are variably observed and appear to involve primarily the cardiac outflow tract. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29198724}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q8TAF3; Q8TAF3-1 EC number EC 3.4.19.12 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Autocatalytic cleavage; DNA damage; DNA repair; Hydrolase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Thiol protease; Ubl conjugation; Ubl conjugation pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID D Molecular weight (Da) 32426 Length 285 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 50.73 Isoelectric point 5.85 Charge (pH=7) -4.67 3D Binding mode Sequence GLNNLGNTSYLNSILQVLYFCPGFKSGVKHLFNIISRKKYELICSLQSLIISVEQLQASFLLNPLQHDAQEVLQCILGNIQETCQLLKKGFELVEKLFQGQLVLRTRCLECESLTERREDFQDISVPVQEDMKTLRWAISQFASVERIVGEDKYFCENCHHYTEAERSLLFDKMPEVITIHLKCFAASGLSKINTPLLTPLKLSLEEWSTKPTNDSYGLFAVVMHSGITISSGHYTASVKVTYEGKWLLFDDSEVKVTEEKDFLNSLSPSTSPTSTPYLLFYKKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 27 | Lysine-specific demethylase 4C (KDM4C) | 4XDO | 4.03 | |
Target general information Gen name KDM4C Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms KIAA0780; Jumonji domain-containing protein 2C; JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 3C; JMJD2C; JHDM3C; Gene amplified in squamous cell carcinoma 1 protein; GASC1; GASC-1 protein Protein family JHDM3 histone demethylase family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Does not demethylate histone H3 'Lys-4', H3 'Lys-27' nor H4 'Lys-20'. Demethylates trimethylated H3 'Lys-9' and H3 'Lys-36' residue, while it has no activity on mono- and dimethylated residues. Demethylation of Lys residue generates formaldehyde and succinate. Histone demethylase that specifically demethylates 'Lys-9' and 'Lys-36' residues of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code. Related diseases Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) [MIM:144700]: Renal cell carcinoma is a heterogeneous group of sporadic or hereditary carcinoma derived from cells of the proximal renal tubular epithelium. It is subclassified into clear cell renal carcinoma (non-papillary carcinoma), papillary renal cell carcinoma, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, collecting duct carcinoma with medullary carcinoma of the kidney, and unclassified renal cell carcinoma. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma is the most common subtype. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20054297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23622243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23792563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25728682}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Defects of SETD2 are associated with loss of DNA methylation at non-promoter regions (PubMed:23792563). SETD2 defects lead to aberrant and reduced nucleosome compaction and chromatin association of key replication proteins, such as MCM7 and DNA polymerase delta, leading to hinder replication fork progression and prevent loading of RAD51 homologous recombination repair factor at DNA breaks (PubMed:25728682). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23792563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25728682}.; DISEASE: Luscan-Lumish syndrome (LLS) [MIM:616831]: An autosomal dominant syndrome with a variable phenotype. Clinical features include macrocephaly, distinctive facial appearance, postnatal overgrowth, various degrees of learning difficulties, autism spectrum disorder, and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23160955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24852293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26084711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27317772}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute lymphoblastic (ALL) [MIM:613065]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. ALL is a malignant disease of bone marrow and the most common malignancy diagnosed in children. The malignant cells are lymphoid precursor cells (lymphoblasts) that are arrested in an early stage of development. The lymphoblasts replace the normal marrow elements, resulting in a marked decrease in the production of normal blood cells. Consequently, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia occur to varying degrees. The lymphoblasts also proliferate in organs other than the marrow, particularly the liver, spleen, and lymphnodes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24509477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24662245}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML) [MIM:601626]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. AML is a malignant disease of bone marrow characterized by maturational arrest of hematopoietic precursors at an early stage of development. Clonal expansion of myeloid blasts occurs in bone marrow, blood, and other tissue. Myelogenous leukemias develop from changes in cells that normally produce neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils and monocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16314571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24509477}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting distinct genetic loci, including the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 70 (MRD70) [MIM:620157]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by mild global developmental delay, moderately impaired intellectual disability with speech difficulties, and behavioral abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32710489}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Rabin-Pappas syndrome (RAPAS) [MIM:620155]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by severely impaired global development, intellectual disability, microcephaly, facial dysmorphism, and variable congenital anomalies affecting the skeletal, genitourinary, cardiac, and other organ systems. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32710489}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.14.11.- Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Dioxygenase; Iron; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 39355.6 Length 338 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 38.34 Isoelectric point 8.04 Charge (pH=7) 2.41 3D Binding mode Sequence LNPSCKIMTFRPSMEEFREFNKYLAYMESKGAHRAGLAKVIPPKEWKPRQCYDDIDNLLIPAPIQQMVTGQSGLFTQYNIQKKAMTVKEFRQLANSGKYCTPRYLDYEDLERKYWKNLTFVAPIYGADINGSIYDEGVDEWNIARLNTVLDVVEEECGISIEGVNTPYLYFGMWKTTFAWHTEDMDLYSINYLHFGEPKSWYAIPPEHGKRLERLAQGFFPSSSQGCDAFLRHKMTLISPSVLKKYGIPFDKITQEAGEFMITFPYGYHAGFNHGFNCAESTNFATVRWIDYGKVAKLCTCRKDMVKISMDIFVRKFQPDRYQLWKQGKDIYTIDHTK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 28 | Cerebroside-sulfatase (ARSA) | 1E2S | 4.03 | |
Target general information Gen name ARSA Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Cerebrosidesulfatase; Arylsulfatase A component C; ASA; ARSA Protein family Sulfatase family Biochemical class Sulfuric ester hydrolase Function Hydrolyzes cerebroside sulfate. Related diseases Metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD) [MIM:250100]: An autosomal recessive disease caused by abnormal intralysosomal accumulation of cerebroside-3-sulfate in central and peripheral nervous systems, as well as other organs. MLD is clinically characterized by leukodystrophy, progressive demyelination and a variety of neurological symptoms, including gait disturbances, ataxias, optical atrophy, dementia, seizures, and spastic tetraparesis. Decreased arylsulfatase A activity is detected in urine, leukocytes, and fibroblasts of affected individuals. Several forms of the disease can be distinguished according to the age at onset and disease severity: late infantile, juvenile and adult forms, partial cerebroside sulfate deficiency, and pseudoarylsulfatase A deficiency. Individuals with pseudoarylsulfatase A deficiency have low arylsulfatase A activity but lack neurological manifestations and are apparently healthy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10220151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10381328, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10477432, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10533072, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10751093, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11020646, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11061266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11456299, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11941485, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12503099, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12788103, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1353340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14517960, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14680985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15026521, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15326627, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15710861, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1670590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1673291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1678251, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18693274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19606494, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20339381, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21265945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2574462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7581401, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7825603, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7860068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7902317, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7906588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7909527, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8095918, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8101038, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8101083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8104633, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8891236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9090526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9272717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452102, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9490297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9600244, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9819708}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Multiple sulfatase deficiency (MSD) [MIM:272200]: A clinically and biochemically heterogeneous disorder caused by the simultaneous impairment of all sulfatases, due to defective post-translational modification and activation. It combines features of individual sulfatase deficiencies such as metachromatic leukodystrophy, mucopolysaccharidosis, chondrodysplasia punctata, hydrocephalus, ichthyosis, neurologic deterioration and developmental delay. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15146462}. The protein represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. Arylsulfatase A activity is impaired in multiple sulfatase deficiency due to mutations in SUMF1 (PubMed:15146462). SUMF1 mutations result in defective post-translational modification of ARSA at residue Cys-69 that is not converted to 3-oxoalanine (PubMed:7628016). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15146462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7628016}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03821; DB01800; DB01141; DB04786 Interacts with P50995; Q6P5X5; Q13554-3; O60826; Q96D98; Q9H0I2; Q12951-2; Q16512; P28069; O75360; Q9BQY4; Q15645; O95231 EC number EC 3.1.6.8 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Ichthyosis; Leukodystrophy; Lipid metabolism; Lysosome; Metachromatic leukodystrophy; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID P Molecular weight (Da) 51173.7 Length 481 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 47.42 Isoelectric point 5.59 Charge (pH=7) -12.84 3D Binding mode Sequence RPPNIVLIFADDLGYGDLGCYGHPSSTTPNLDQLAAGGLRFTDFYVPVSLATPSRAALLTGRLPVRMGMYPGVLVPSSRGGLPLEEVTVAEVLAARGYLTGMAGKWHLGVGPEGAFLPPHQGFHRFLGIPYSHDQGPCQNLTCFPPATPCDGGCDQGLVPIPLLANLSVEAQPPWLPGLEARYMAFAHDLMADAQRQDRPFFLYYASHHTHYPQFSGQSFAERSGRGPFGDSLMELDAAVGTLMTAIGDLGLLEETLVIFTADNGPETMRMSRGGCSGLLRCGKGTTYEGGVREPALAFWPGHIAPGVTHELASSLDLLPTLAALAGAPLPNVTLDGFDLSPLLLGTGKSPRQSLFFYPSYPDEVRGVFAVRTGKYKAHFFTQGSAHSDTTADPACHASSSLTAHEPPLLYDLSKDPGENYNLLGATPEVLQALKQLQLLKAQLDAAVTFGPSQVARGEDPALQICCHPGCTPRPACCHCP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 29 | Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase type 5 | 2BQ8 | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name ACP5 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Metallophosphoesterase superfamily, Purple acid phosphatase family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Acid phosphatase activity.Ferric iron binding.Ferrous iron binding. Related diseases Spondyloenchondrodysplasia with immune dysregulation (SPENCDI) [MIM:607944]: A disease characterized by vertebral and metaphyseal dysplasia, spasticity with cerebral calcifications, and strong predisposition to autoimmune diseases. The skeletal dysplasia is characterized by radiolucent and irregular spondylar and metaphyseal lesions that represent islands of chondroid tissue within bone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21217752, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21217755}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. ACP5 inactivating mutations result in a functional excess of phosphorylated osteopontin causing deregulation of osteopontin signaling and consequential autoimmune disease. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number 3.1.3.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Iron; Lysosome; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID X Molecular weight (Da) 34330.6 Length 304 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 42.3 Isoelectric point 9.11 Charge (pH=7) 6.75 3D Binding mode Sequence ATPALRFVAVGDWGGVPNAPFHTAREMANAKEIARTVQILGADFILSLGDNFYFTGVQDINDKRFQETFEDVFSDRSLRKVPWYVLAGNHDHLGNVSAQIAYSKISKRWNFPSPFYRLHFKIPQTNVSVAIFMLDTVTLCGNSDDFLSQQPERPRDVKLARTQLSWLKKQLAAAREDYVLVAGHYPVWSIAEHGPTHCLVKQLRPLLATYGVTAYLCGHDHNLQYLQDENGVGYVLSGAGNFMDPSKRHQRKVPNGYLRFHYGTEDSLGGFAYVEISSKEMTVTYIEASGKSLFKTRLPRRARP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 30 | DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit A | 1ZVT | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name parC Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b3019;JW2987 Protein family Type II topoisomerase GyrA/ParC subunit family, ParC type 1 subfamily Biochemical class Isomerase Function ATP binding.DNA binding.DNA topoisomerase type II (ATP-hydrolyzing) activity. Related diseases Pigmentary disorder, reticulate, with systemic manifestations, X-linked (PDR) [MIM:301220]: An X-linked recessive disorder characterized by recurrent infections and sterile inflammation in various organs. Diffuse skin hyperpigmentation with a distinctive reticulate pattern is universally evident by early childhood. This is later followed in many patients by hypohidrosis, corneal inflammation and scarring, enterocolitis that resembles inflammatory bowel disease, and recurrent urethral strictures. Melanin and amyloid deposition is present in the dermis. Affected males also have a characteristic facies with frontally upswept hair and flared eyebrows. Female carriers have only restricted pigmentary changes along Blaschko's lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. XLPDR is caused by a recurrent intronic mutation that results in missplicing and reduced POLA1 expression. This leads to a decrease in cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids and constitutive activation of type I interferon responses, but has no effect on cell replication. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27019227}.; DISEASE: Van Esch-O'Driscoll syndrome (VEODS) [MIM:301030]: An X-linked recessive syndrome characterized by different degrees of intellectual disability, moderate to severe short stature, microcephaly, hypogonadism, and variable congenital malformations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006512}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB11943; DB12924; DB00817 Interacts with P22523; P0A7K2 EC number 5.6.2.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; DNA-binding; Isomerase; Membrane; Reference proteome; Topoisomerase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 26490.3 Length 246 Aromaticity 0.04 Instability index 46.03 Isoelectric point 8.94 Charge (pH=7) 2.83 3D Binding mode Sequence SEPVTIVLSQMGWVRSAKGHDIDAPGLNYKAGDSFKAAVKGKSNQPVVFVDSTGRSYAIDPITLPSARGQGEPLTGKLTLPPGATVDHMLMESDDQKLLMASDAGYGFVCTFNDLVARNRAGKALITLPENAHVMPPVVIEDASDMLLAITQAGRMLMFPVSDLPQLSKGKGNKIINIPSAEAARGEDGLAQLYVLPPQSTLTIHVGKRKIKLRPEELQKVTGERGRRGTLMRGLQRIDRVEIDSP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 31 | Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (PLAU) | 4JNI | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name PLAU Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms UPA; U-plasminogen activator Protein family Peptidase S1 family Biochemical class Peptidase Function Specifically cleaves the zymogen plasminogen to form the active enzyme plasmin. Related diseases Quebec platelet disorder (QPD) [MIM:601709]: An autosomal dominant bleeding disorder due to a gain-of-function defect in fibrinolysis. Although affected individuals do not exhibit systemic fibrinolysis, they show delayed onset bleeding after challenge, such as surgery. The hallmark of the disorder is markedly increased PLAU levels within platelets, which causes intraplatelet plasmin generation and secondary degradation of alpha-granule proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20007542}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07129; DB07122; DB01905; DB02287; DB03729; DB01725; DB08072; DB07625; DB07626; DB08697; DB03136; DB01977; DB07076; DB03082; DB02705; DB02473; DB02398; DB02551; DB03865; DB06855; DB06856; DB03046; DB04059; DB04172; DB00594; DB03127; DB02526; DB03159; DB05254; DB03782; DB06857; DB16701; DB03876; DB03476 Interacts with Q9UKQ2; P05067; Q03405-1; P05121; P55000 EC number EC 3.4.21.73 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Blood coagulation; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; EGF-like domain; Fibrinolysis; Glycoprotein; Hemostasis; Hydrolase; Kringle; Pharmaceutical; Phosphoprotein; Plasminogen activation; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Serine protease; Signal; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID U Molecular weight (Da) 25825.3 Length 229 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 47.36 Isoelectric point 8.65 Charge (pH=7) 5.38 3D Binding mode Sequence IIGGEFTTIENQPWFAAIYRRSVTYVCGGSLISPCWVISATHCFPKKEDYIVYLGRSRLNSNTQGEMKFEVENLILHKDYSALAHHNDIALLKIRRCAQPSRTIQTIALPSMYNDPQFGTSCEITGFGKEQSTDYLYPEQLKMTVVKLISHRECQQHYYGSEVTTKMLCAAQWKTDSCQGDSGGPLVCSLQGRMTLTGIVSWGRGCALDKPGVYTRVSHFLPWIRSHTK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 32 | Flavodoxin/ferredoxin--NADP reductase | 1FDR | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name fpr Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms mvrA;b3924;JW3895 Protein family Ferredoxin--NADP reductase type 1 family Biochemical class Flavoprotein Function FAD binding.Ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase activity.Oxidoreductase activity. Related diseases Noonan syndrome 13 (NS13) [MIM:619087]: A form of Noonan syndrome, a disease characterized by short stature, facial dysmorphic features such as hypertelorism, a downward eyeslant and low-set posteriorly rotated ears, and a high incidence of congenital heart defects and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Other features can include a short neck with webbing or redundancy of skin, deafness, motor delay, variable intellectual deficits, multiple skeletal defects, cryptorchidism, and bleeding diathesis. Individuals with Noonan syndrome are at risk of juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, a myeloproliferative disorder characterized by excessive production of myelomonocytic cells. NS13 inheritance is autosomal dominant. There is considerable variability in severity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32721402}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03147 Interacts with NA EC number 1.18.1.2; 1.19.1.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; NADP; Nucleotide-binding; Oxidoreductase; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 27346.2 Length 244 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 30.68 Isoelectric point 7.25 Charge (pH=7) 0.42 3D Binding mode Sequence ADWVTGKVTKVQNWTDALFSLTVHAPVLPFTAGQFTKLGLEIRVQRAYSYVNSPDNPDLEFYLVTVPDGKLSPRLAALKPGDEVQVVSEAAGFFVLDEVPHCETLWMLATGTAIGPYLSILRLGKDLDRFKNLVLVHAARYAADLSYLPLMQELEKRYEGKLRIQTVVSRETAAGSLTGRIPALIESGELESTIGLPMNKETSHVMLCGNPQMVRDTQQLLKETRQMTKHLRRRPGHMTAEHYW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 33 | Aminoacylase-1 | 1Q7L | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name ACY1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Peptidase M20A family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Aminoacylase activity.Identical protein binding.Metal ion binding.Metallopeptidase activity. Related diseases Aminoacylase-1 deficiency (ACY1D) [MIM:609924]: An enzymatic deficiency resulting in encephalopathy, unspecific psychomotor delay, psychomotor delay with atrophy of the vermis and syringomyelia, marked muscular hypotonia or normal clinical features. Epileptic seizures are a frequent feature. All affected individuals exhibit markedly increased urinary excretion of several N-acetylated amino acids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16274666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16465618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17562838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21414403}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06151; DB00128; DB09130 Interacts with Q03154; O75934; Q96HA8; P36639; P36639-2; Q8TCT1; P0CG20; Q96A09; P54274; O43711; Q9UPN9; Q9NZC7-5 EC number 3.5.1.14 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 31172.2 Length 275 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 36.46 Isoelectric point 6 Charge (pH=7) -5.26 3D Binding mode Sequence NPWWAAFSRVCKDMNLTLEPEIMPAAGDNRYIRAVGVPALGFSPMNRTPVLLHDHDERLHEAVFLRGVDIYTRLLPALASVPALPEEHPSVTLFRQYLRIRTVQPKPDYGAAVAFFEETARQLGLGCQKVEVAPGYVVTVLTWPGTNPTLSSILLNSHTDVVPVFKEHWSHDPFEAFKDSEGYIYARGAQDMKCVSIQYLEAVRRLKVEGHRFPRTIHMTFVPDEEVGGHQGMELFVQRPEFHALRAGFALDEGIANPTDAFTVFYSERSPWWVR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 34 | Kynureninase (KYNU) | 3E9K | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name KYNU Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms L-kynurenine hydrolase; KYNU Protein family Kynureninase family Biochemical class Carbon-carbon bonds hydrolase Function Catalyzes the cleavage of L-kynurenine (L-Kyn) and L-3- hydroxykynurenine (L-3OHKyn) into anthranilic acid (AA) and 3- hydroxyanthranilic acid (3-OHAA), respectively. Has a preference for the L-3-hydroxy form. Also has cysteine-conjugate-beta-lyase activity. Related diseases Hydroxykynureninuria (HYXKY) [MIM:236800]: An inborn error of amino acid metabolism characterized by massive urinary excretion of large amounts of kynurenine, 3-hydroxykynurenine and xanthurenic acid. Affected individuals manifest renal tubular dysfunction, metabolic acidosis, psychomotor retardation, non-progressive encephalopathy, and muscular hypertonia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17334708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28792876}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Vertebral, cardiac, renal, and limb defects syndrome 2 (VCRL2) [MIM:617661]: An autosomal recessive congenital malformation syndrome characterized by vertebral segmentation abnormalities, congenital cardiac defects, renal defects, and distal mild limb defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28792876}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00160; DB07069; DB00114 Interacts with Q8WUE5; P56545-3; Q9NVL1-2; P61968; P59942; Q8TDC0; P78356-2; Q86WH2 EC number EC 3.7.1.3 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Proteomics identification; Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis; Pyridoxal phosphate; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 50204.5 Length 446 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 39.91 Isoelectric point 6.36 Charge (pH=7) -4.59 3D Binding mode Sequence LELPADTVQRIAAELKCHPTDERVALHLDEEDKLRHFREXFYIPKIQDLPPVDLSLVNKDENAIYFLGNSLGLQPKMVKTYLEEELDKWAKIAAYGHEVGKRPWITGDESIVGLMKDIVGANEKEIALMNALTVNLHLLMLSFFKPTPKRYKILLEAKAFPSDHYAIESQLQLHGLNIEESMRMIKPREGEETLRIEDILEVIEKEGDSIAVILFSGVHFYTGQHFNIPAITKAGQAKGCYVGFDLAHAVGNVELYLHDWGVDFACWCSYKYLNAGAGGIAGAFIHEKHAHTIKPALVGWFGHELSTRFKMDNKLQLIPGVCGFRISNPPILLVCSLHASLEIFKQATMKALRKKSVLLTGYLEYLIKHNYGVVNIITPSHVEERGCQLTITFSVPNKDVFQELEKRGVVCDKRNPNGIRVAPVPLYNSFHDVYKFTNLLTSILDS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 35 | Aminoacylase-1 | 1Q7L | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name ACY1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Peptidase M20A family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Aminoacylase activity.Identical protein binding.Metal ion binding.Metallopeptidase activity. Related diseases Aminoacylase-1 deficiency (ACY1D) [MIM:609924]: An enzymatic deficiency resulting in encephalopathy, unspecific psychomotor delay, psychomotor delay with atrophy of the vermis and syringomyelia, marked muscular hypotonia or normal clinical features. Epileptic seizures are a frequent feature. All affected individuals exhibit markedly increased urinary excretion of several N-acetylated amino acids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16274666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16465618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17562838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21414403}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06151; DB00128; DB09130 Interacts with Q03154; O75934; Q96HA8; P36639; P36639-2; Q8TCT1; P0CG20; Q96A09; P54274; O43711; Q9UPN9; Q9NZC7-5 EC number 3.5.1.14 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 31172.2 Length 275 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 36.46 Isoelectric point 6 Charge (pH=7) -5.26 3D Binding mode Sequence NPWWAAFSRVCKDMNLTLEPEIMPAAGDNRYIRAVGVPALGFSPMNRTPVLLHDHDERLHEAVFLRGVDIYTRLLPALASVPALPEEHPSVTLFRQYLRIRTVQPKPDYGAAVAFFEETARQLGLGCQKVEVAPGYVVTVLTWPGTNPTLSSILLNSHTDVVPVFKEHWSHDPFEAFKDSEGYIYARGAQDMKCVSIQYLEAVRRLKVEGHRFPRTIHMTFVPDEEVGGHQGMELFVQRPEFHALRAGFALDEGIANPTDAFTVFYSERSPWWVR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 36 | Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) | 4LY1 | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name HDAC2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms HD2 Protein family Histone deacetylase family, HD type 1 subfamily Biochemical class Carbon-nitrogen hydrolase Function Gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. Forms transcriptional repressor complexes by associating with MAD, SIN3, YY1 and N-COR. Interacts in the late S-phase of DNA-replication with DNMT1 in the other transcriptional repressor complex composed of DNMT1, DMAP1, PCNA, CAF1. Deacetylates TSHZ3 and regulates its transcriptional repressor activity. Component of a RCOR/GFI/KDM1A/HDAC complex that suppresses, via histone deacetylase (HDAC) recruitment, a number of genes implicated in multilineage blood cell development. May be involved in the transcriptional repression of circadian target genes, such as PER1, mediated by CRY1 through histone deacetylation. Involved in MTA1-mediated transcriptional corepression of TFF1 and CDKN1A. Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Related diseases Ventricular tachycardia, catecholaminergic polymorphic, 1, with or without atrial dysfunction and/or dilated cardiomyopathy (CPVT1) [MIM:604772]: An arrhythmogenic disorder characterized by stress-induced, bidirectional ventricular tachycardia that may degenerate into cardiac arrest and cause sudden death. Patients present with recurrent syncope, seizures, or sudden death after physical activity or emotional stress. CPVT1 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11157710, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11159936, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11208676, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12093772, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12106942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14571276, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15046072, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15046073, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15466642, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15544015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16188589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24793461, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25372681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27733687}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Ventricular arrhythmias due to cardiac ryanodine receptor calcium release deficiency syndrome (VACRDS) [MIM:115000]: An autosomal dominant arrhythmogenic disorder characterized by syncope, cardiac arrest and/or sudden unexpected death, often in association with physical exertion or acute emotional stress. Patients who survive manifest polymorphic ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. Unlike typical catecholaminergic ventricular tachycardia, arrhythmias are not reproducible on exercise stress testing or adrenaline challenge. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12093772, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17984046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33536282}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12565; DB01223; DB01076; DB05015; DB01262; DB11841; DB01095; DB12645; DB00227; DB11830; DB01303; DB06603; DB06819; DB05223; DB00175; DB03766; DB12847; DB06176; DB00641; DB00277; DB09091; DB00313; DB02546 Interacts with Q9C0K0; Q9HCU9; P68400; Q9UER7; P51610; Q13547; Q9UIS9; Q13330; P01106; P06748; P48382; Q96ST3; O95863; Q9HD15; O43463; Q9H3M7; Q92618; Q17R98; Q2HR82; PRO_0000449623 [P0DTD1] EC number EC 3.5.1.98 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Biological rhythms; Chromatin regulator; Cytoplasm; Hydrolase; Isopeptide bond; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repressor; S-nitrosylation; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C Molecular weight (Da) 42020.5 Length 366 Aromaticity 0.13 Instability index 29.52 Isoelectric point 6.52 Charge (pH=7) -2.16 3D Binding mode Sequence KKKVCYYYDGDIGNYYYGQGHPMKPHRIRMTHNLLLNYGLYRKMEIYRPHKATAEEMTKYHSDEYIKFLRSIRPDNMSEYSKQMQRFNVGEDCPVFDGLFEFCQLSTGGSVAGAVKLNRQQTDMAVNWAGGLHHAKKSEASGFCYVNDIVLAILELLKYHQRVLYIDIDIHHGDGVEEAFYTTDRVMTVSFHKYGEYFPGTGDLRDIGAGKGKYYAVNFPMRDGIDDESYGQIFKPIISKVMEMYQPSAVVLQCGADSLSGDRLGCFNLTVKGHAKCVEVVKTFNLPLLMLGGGGYTIRNVARCWTYETAVALDCEIPNELPYNDYFEYFGPDFKLHISPSNMTNQNTPEYMEKIKQRLFENLRML Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 37 | Pectate lyase | 1R76 | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name pelA Organism Niveispirillum irakense (Azospirillum irakense) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family NA Biochemical class Lyase Function Lyase activity. Related diseases A chromosomal aberration involving ALK is found in a form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Translocation t(2;5)(p23;q35) with NPM1. The resulting chimeric NPM1-ALK protein homodimerize and the kinase becomes constitutively activated. The constitutively active fusion proteins are responsible for 5-10% of non-Hodgkin lymphomas. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15938644}.; DISEASE: A chromosomal aberration involving ALK is associated with inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors (IMTs). Translocation t(2;11)(p23;p15) with CARS; translocation t(2;4)(p23;q21) with SEC31A. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12112524, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16161041}.; DISEASE: A chromosomal aberration involving ALK is associated with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL). Translocation t(2;17)(p23;q25) with ALO17. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12112524}.; DISEASE: Neuroblastoma 3 (NBLST3) [MIM:613014]: A common neoplasm of early childhood arising from embryonic cells that form the primitive neural crest and give rise to the adrenal medulla and the sympathetic nervous system. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18724359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18923523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18923525, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21242967, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22932897}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: The ALK signaling pathway plays an important role in glioblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor of adults and one of the most lethal cancers. It regulates both glioblastoma migration and growth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15908427}.; DISEASE: A chromosomal aberration involving ALK is found in one subject with colorectal cancer. Translocation t(2;2)(p23.1;p23.3). A 5 million base pair tandem duplication generates an in-frame WDCP-ALK gene fusion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22327622}.; DISEASE: A chromosomal aberration involving ALK has been identified in a subset of patients with non-small-cell lung carcinoma. This aberration leads to the production of a fusion protein between the N-terminus of EML4 et the C-terminus of ALK. It is unclear whether the fusion protein is caused by a simple inversion within 2p (inv(2)(p21p23)) or whether the chromosome translocation involving 2p is more complex. When tested in a heterologous system, the fusion protein EML4-ALK possesses transforming activity that is dependent on ALK catalytic activity, possibly due to spontaneous dimerization mediated by the EML4 moiety, leading to ALK kinase activation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17625570}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Lyase; Signal Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 41907.5 Length 384 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 43.72 Isoelectric point 6.11 Charge (pH=7) -3.46 3D Binding mode Sequence AVIGMNEAASALTPSRVSSLPDTQRAAWQEYLARSEAQLSRDKASLAAELAPGQPLPPPPAEGKGADTMPLDKPAAWYTSKAARHVADVIVSFQTPAGGWGKNQPRDGALRLPGQHYTGENVAKVKRDRDWHYVGTIDNDATVTEIRFLAQVVSQLAPEEAAPYRDAALKGIEYLLASQFPNGGWPQVWPLEGGYHDAITYNDDALVHVAELLSDIAAGRDGFGFVPPAIRTRALEATNAAIHCIVETQVVQDGKRLGWGQQHDALTLRPTSARNFEPAALSSTESARILLFLMEIEAPSDAVKQAIRGGVAWLNTSVIRDQGAKPLWSRFYSLDGNKPVFGDRDKTIHDDVMGISQERRTGYAWYTTSPQKALSAFTKWEKRS Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 38 | Plasmodium Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (Malaria DHOdehase) | 1TV5 | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name Malaria DHOdehase Organism Plasmodium falciparum (isolate 3D7) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms PFF0160c; Mitochondrially bound dihydroorotate-ubiqui oxidoreductase; Dihydroorotate oxidase of Plasmodium falciparum; Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase of Plasmodium falciparum; DHOdehase of Plasmodium fa Protein family Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase family, Type 2 subfamily Biochemical class CH-CH donor oxidoreductase Function Catalyzes the conversion of dihydroorotate to orotate with quinone as electron acceptor. Related diseases Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 33 (COXPD33) [MIM:617713]: An autosomal recessive disorder caused by multiple mitochondrial respiratory chain defects and impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism. Clinical manifestations are highly variable. Affected infants present with cardiomyopathy accompanied by multisystemic features involving liver, kidney, and brain. Death in infancy is observed in some patients. Children and adults present with myopathy and progressive external ophthalmoplegia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28942965}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01117 Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.3.5.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Flavoprotein; FMN; Membrane; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Oxidoreductase; Pyrimidine biosynthesis; Reference proteome; Transit peptide; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 41846.8 Length 371 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.25 Isoelectric point 8.21 Charge (pH=7) 3.13 3D Binding mode Sequence FESYNPEFFLYDIFLKFCLKYIDGEICHDLFLLLGKYNILPYDTSNDSIYACTNIKHLDFINPFGVAAGFDKNGVCIDSILKLGFSFIEIGTITPRGQTGNAKPRIFRDVESRSIINSCGFNNMGCDKVTENLILFRKRQEEDKLLSKHIVGVSIGKNKDTVNIVDDLKYCINKIGRYADYIAINVSSPNTPGLRDNQEAGKLKNIILSVKEEIDNLEFLWFNTTKKKPLVFVKLAPDLNQEQKKEIADVLLETNIDGMIISNTTTQINDIKSFENKKGGVSGAKLKDISTKFICEMYNYTNKQIPIIASGGIFSGLDALEKIEAGASVCQLYSCLVFNGMKSAVQIKRELNHLLYQRGYYNLKEAIGRKH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 39 | Tankyrase-2 (TNKS-2) | 3U9H | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name TNKS2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tankyrase-related protein; Tankyrase-like protein; Tankyrase II; TRF1-interacting ankyrin-related ADP-ribose polymerase 2; TNKL; TANK2; Protein poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase tankyrase-2; Poly [ADP-ribos Protein family ARTD/PARP family Biochemical class Glycosyltransferases Function Acts as an activator of the Wnt signaling pathway by mediating poly-ADP-ribosylation of AXIN1 and AXIN2, 2 key components of the beta-catenin destruction complex: poly-ADP-ribosylated target proteins are recognized by RNF146, which mediates their ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. Also mediates poly-ADP-ribosylation of BLZF1 and CASC3, followed by recruitment of RNF146 and subsequent ubiquitination. Mediates poly-ADP-ribosylation of TERF1, thereby contributing to the regulation of telomere length. Stimulates 26S proteasome activity. Poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase involved in various processes such as Wnt signaling pathway, telomere length and vesicle trafficking. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder with macrocephaly, seizures, and speech delay (IDDMSSD) [MIM:618158]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impaired intellectual development, poor speech, postnatal macrocephaly, and seizures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30290153}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with O15084; Q7Z6K5-1; O15169; Q9NWV8; P11274; Q13698; Q9NRI5; Q6V0I7; Q9NWT6; P14652; Q9UIQ6; Q14980; Q9BZL4; Q92698; P78314; O43815; P54274; Q9C0C2; Q9UHP3; Q06649 EC number EC 2.4.2.30 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ADP-ribosylation; ANK repeat; Chromosome; Cytoplasm; Glycosyltransferase; Golgi apparatus; Hydroxylation; Membrane; Metal-binding; NAD; Nucleotidyltransferase; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Telomere; Transferase; Ubl conjugation; Wnt signaling pathway; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 23695.5 Length 208 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 47.61 Isoelectric point 8.28 Charge (pH=7) 2.88 3D Binding mode Sequence GTILIDLSPDDKEFQSVEEEMQSTVREHRDGGHAGGIFNRYNILKIQKVCNKKLWERYTHRRKEVSEENHNHANERMLFHGSPFVNAIIHKGFDERHAYIGGMFGAGIYFAENSSKSNQYVYGIGGGTGCPVHKDRSCYICHRQLLFCRVTLGKSFLQFSAMAHSPPGHHSVTGRPSVNGLALAEYVIYRGEQAYPEYLITYQIMRPE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 40 | Histamine H3 receptor (H3R) | 7F61 | 4.02 | |
Target general information Gen name HRH3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Histamine receptor 3; HH3R; GPCR97; G-protein coupled receptor 97; G protein-coupled receptor 97 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Signals through the inhibition of adenylate cyclase and displays high constitutive activity (spontaneous activity in the absence of agonist). Agonist stimulation of isoform 3 neither modified adenylate cyclase activity nor induced intracellular calcium mobilization. The H3 subclass of histamine receptors could mediate the histamine signals in CNS and peripheral nervous system. Related diseases Immunodeficiency 48 (IMD48) [MIM:269840]: A form of severe immunodeficiency characterized by a selective absence of CD8+ T-cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11123350, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11412303, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18509675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8124727, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8202713}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Autoimmune disease, multisystem, infantile-onset, 2 (ADMIO2) [MIM:617006]: An autosomal recessive, autoimmune disorder characterized by systemic manifestations including blistering skin disease, uncontrollable bullous pemphigoid, inflammatory colitis, autoimmune hypothyroidism, proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26783323}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01238; DB06698; DB05381; DB17087; DB05080; DB00768; DB11642 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34321.1 Length 301 Aromaticity 0.16 Instability index 32.22 Isoelectric point 9.63 Charge (pH=7) 15.11 3D Binding mode Sequence RGFSAAWTAVLAALMALLIVATVLGNALVMLAFVADSSLRTQNNFFLLNLAISDFLVGAFCIPLYVPYVLTGRWTFGRGLCKLWLVVDYLLCTSKAFNIVLISYDRFLSVTRAVSYRAQQGDTRRAVRKMLLVWVLAFLLYGPAILSWEYLSGGSSIPEGHCYAEFFYNWYFLITASTLEFFTPFLSVTFFNLSIYLNIQRRTRLRLDGAREAAGRFRLSRDRKVAKSLAVIVSIFGLCWAPYTLLMIIRAACHGHCVPDYWYETSFWLLWANSAVNPVLYPLCHHSFRRAFTKLLCPQKL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||