Job Results:
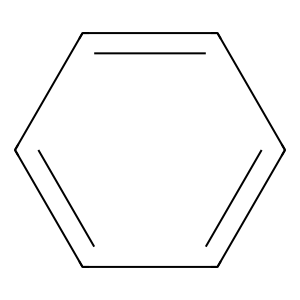
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
f587f6fdd815874cceb13aaa40f0b138
Job name
NA
Time
2025-01-22 15:24:13
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | Neprilysin | 1R1H | 5.10 | |
Target general information Gen name MME Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms EPN Protein family Peptidase M13 family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Endopeptidase activity.Exopeptidase activity.Metalloendopeptidase activity.Metallopeptidase activity.Peptide binding.Zinc ion binding. Related diseases Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, 2T (CMT2T) [MIM:617017]: An axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal degeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26991897, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27588448}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spinocerebellar ataxia 43 (SCA43) [MIM:617018]: A form of spinocerebellar ataxia, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of cerebellar disorders. Patients show progressive incoordination of gait and often poor coordination of hands, speech and eye movements, due to degeneration of the cerebellum with variable involvement of the brainstem and spinal cord. SCA43 is a slowly progressive, autosomal dominant form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27583304}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08575; DB02597; DB00616; DB11623; DB05796; DB06655; DB02558; DB02062; DB00886; DB02557; DB09292; DB13928; DB08626 Interacts with P05067; P21926; Q06787-7; P08107; P04792 EC number 3.4.24.11 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Metalloprotease; Myristate; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathy; Phosphoprotein; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal-anchor; Spinocerebellar ataxia; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 79435.8 Length 696 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 37.5 Isoelectric point 5.53 Charge (pH=7) -11.46 3D Binding mode Sequence GICKSSDCIKSAARLIQNMDATTEPCTDFFKYACGGWLKRNVIPETSSRYGNFDILRDELEVVLKDVLQEPKTEDIVAVQKAKALYRSCINESAIDSRGGEPLLKLLPDIYGWPVATENWEQKYGASWTAEKAIAQLNSKYGKKVLINLFVGTDDKNSVNHVIHIDQPRLGLPSRDYYECTGIYKEACTAYVDFMISVARLIRQEERLPIDENQLALEMNKVMELEKEIANATAKPEDRNDPMLLYNKMTLAQIQNNFSLEINGKPFSWLNFTNEIMSTVNISITNEEDVVVYAPEYLTKLKPILTKYSARDLQNLMSWRFIMDLVSSLSRTYKESRNAFRKALYGTTSETATWRRCANYVNGNMENAVGRLYVEAAFAGESKHVVEDLIAQIREVFIQTLDDLTWMDAETKKRAEEKALAIKERIGYPDDIVSNDNKLNNEYLELNYKEDEYFENIIQNLKFSQSKQLKKLREKVDKDEWISGAAVVNAFYSSGRNQIVFPAGILQPPFFSAQQSNSLNYGGIGMVIGHEITHGFDDNGRNFNKDGDLVDWWTQQSASNFKEQSQCMVYQYGNFSWDLAGGQHLNGINTLGENIADNGGLGQAYRAYQNYIKKNGEEKLLPGLDLNHKQLFFLNFAQVWCGTYRPEYAVNSIKTDVHSPGNFRIIGTLQNSAEFSEAFHCRKNSYMNPEKKCRVW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 22 | SPRY domain-containing SOCS box protein 2 (SSB-2) (Gene-rich cluster protein C9) | 3EMW | 5.10 | |
Target general information Gen name SPSB2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms GRCC9;SSB2 Protein family SPSB family Biochemical class NA Function Substrate recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin BC-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:15601820, PubMed:21199876). Negatively regulates nitric oxide (NO) production and limits cellular toxicity in activated macrophages by mediating the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of NOS2 (PubMed:21199876). Acts as a bridge which links NOS2 with the ECS E3 ubiquitin ligase complex components ELOC and CUL5 (PubMed:21199876). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15601820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21199876}." Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 2 (MRT2) [MIM:607417]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRT2 patients display mild intellectual disability with a standard IQ ranged from 50 to 70. IQ scores are lower in males than females. Developmental milestones are mildly delayed. There are no dysmorphic or autistic features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15557513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28143899}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with G5E9A7; Q15369; Q53EP0-3; O60333-2; Q16656-4; Q96IZ0; P16284; Q92569; O60260-5; Q99873; Q6P9E2; Q9Y3C5; Q96GM5; P61086; P08670; P09052 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Host-virus interaction; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 22703.1 Length 207 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 50.84 Isoelectric point 5.98 Charge (pH=7) -2.79 3D Binding mode Sequence LYFQSMPEGLEELLSAPPPDLGAQRRHGWNPKDCSENIEVKEGGLYFERRPVAQSTDGARGKRGYSRGLHAWEISWPLEQRGTHAVVGVATALAPLQTDHYAALLGSNSESWGWDIGRGKLYHQSKGPGAPQYPAGTQGEQLEVPERLLVVLDMEEGTLGYAIGGTYLGPAFRGLKGRTLYPAVSAVWGQCQVRIRYLGEDINNNNN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 23 | SPRY domain-containing SOCS box protein 2 (SSB-2) (Gene-rich cluster protein C9) | 3EMW | 5.10 | |
Target general information Gen name SPSB2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms GRCC9;SSB2 Protein family SPSB family Biochemical class NA Function Substrate recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin BC-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:15601820, PubMed:21199876). Negatively regulates nitric oxide (NO) production and limits cellular toxicity in activated macrophages by mediating the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of NOS2 (PubMed:21199876). Acts as a bridge which links NOS2 with the ECS E3 ubiquitin ligase complex components ELOC and CUL5 (PubMed:21199876). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15601820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21199876}." Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 2 (MRT2) [MIM:607417]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRT2 patients display mild intellectual disability with a standard IQ ranged from 50 to 70. IQ scores are lower in males than females. Developmental milestones are mildly delayed. There are no dysmorphic or autistic features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15557513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28143899}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with G5E9A7; Q15369; Q53EP0-3; O60333-2; Q16656-4; Q96IZ0; P16284; Q92569; O60260-5; Q99873; Q6P9E2; Q9Y3C5; Q96GM5; P61086; P08670; P09052 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Host-virus interaction; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 22703.1 Length 207 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 50.84 Isoelectric point 5.98 Charge (pH=7) -2.79 3D Binding mode Sequence LYFQSMPEGLEELLSAPPPDLGAQRRHGWNPKDCSENIEVKEGGLYFERRPVAQSTDGARGKRGYSRGLHAWEISWPLEQRGTHAVVGVATALAPLQTDHYAALLGSNSESWGWDIGRGKLYHQSKGPGAPQYPAGTQGEQLEVPERLLVVLDMEEGTLGYAIGGTYLGPAFRGLKGRTLYPAVSAVWGQCQVRIRYLGEDINNNNN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 24 | Mas-related gene 2 (MRGX2) | 7VV5 | 5.10 | |
Target general information Gen name MRGPRX2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Masrelated Gprotein coupled receptormember X2; MRGPRX2 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, Mas subfamily Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function Mast cell-specific receptor for basic secretagogues (PubMed:25517090). Basic secretagogues are a set of cationic amphiphilic drugs, as well as endo- and exogenous peptides, which share basic head group combined with a hydrophobic core of the molecule. Recognizes and binds small molecules containing a cyclized a tetrahydroisoquinoline (THIQ), such as non-steroidal neuromuscular blocking drugs (NMBDs), including tubocurarine and atracurium. Mediates mast cell responsiveness and side effects of small-molecule therapeutic drugs by acting as a specific receptor for basic secretagogues drugs in mast cells: binding to drugs induces pseudo-allergic reactions characterized by histamine release, inflammation and airway contraction. Acts as a receptor for a number of ligands, including peptides: acts as a receptor of cortistatin-14, a regulator of sleep regulation locomotor activity, and cortical function (PubMed:12915402). Acts as a receptor for proadrenomedullin N- terminal peptides PAMP-12, and atlower extent PAMP-20 (PubMed:15823563). Acts as a receptor for antibacterial protein LL-37, promoting chemotaxis, degranulation and chemokine production in mast cells (PubMed:22069323). Acts as a receptor for PMX-53 peptide, a potent antagonist of C5AR1/CD88 (PubMed:21441599). Acts as a receptor for beta-defensins (PubMed:23698749). Acts as a receptor for complanadine A, an alkaloid (PubMed:24930830). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3UG50, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15823563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21441599, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22069323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23698749, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24930830, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25517090, ECO:0000305|PubMed:12915402}. Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder with macrocephaly, seizures, and speech delay (IDDMSSD) [MIM:618158]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impaired intellectual development, poor speech, postnatal macrocephaly, and seizures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30290153}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; G-protein coupled receptor; Membrane; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 30319.3 Length 268 Aromaticity 0.16 Instability index 32.43 Isoelectric point 8.8 Charge (pH=7) 6.89 3D Binding mode Sequence LLLLCGKETLIPVFLILFIALVGLVGNGFVLWLLGFRMRRNAFSVYVLSLAGADFLFLCFQIINCLVYLSNFFCSISINFPSFFTTVMTCAYLAGLSMLSTVSTERCLSVLWPIWYRCRRPRHLSAVVCVLLWALSLLLSILEGKFCGFLFSDGDSGWCQTFDFITAAWLIFLFMVLCGSSLALLVRILCGSRGLPLTRLYLTILLTVLVFLLCGLPFGIQWFLILWIWKDSDVLFCHIHPVSVVLSSLNSSANPIIYFFVGSFRKQW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 25 | Nitric-oxide synthase inducible (NOS2) | 3E7G | 5.09 | |
Target general information Gen name NOS2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms iNOS; Peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylase NOS2; Nitric oxide synthase, inducible; NOS2A; NOS type II; Inducible NOS; Inducible NO synthase; Hepatocyte NOS; HEP-NOS Protein family NOS family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Produces nitric oxide (NO) which is a messenger molecule with diverse functions throughout the body. In macrophages, NO mediates tumoricidal and bactericidal actions. Also has nitrosylase activity and mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of cytoplasmic target proteins such PTGS2/COX2 (By similarity). As component of the iNOS-S100A8/9 transnitrosylase complex involved in the selective inflammatory stimulus-dependent S-nitrosylation of GAPDH on 'Cys-247' implicated in regulation of the GAIT complex activity and probably multiple targets including ANXA5, EZR, MSN and VIM. Involved in inflammation, enhances the synthesis of proinflammatory mediators such as IL6 and IL8. Related diseases Cerebellar ataxia, impaired intellectual development, and dysequilibrium syndrome 3 (CAMRQ3) [MIM:613227]: An autosomal recessive, congenital cerebellar ataxia associated with dysarthia, quadrupedal gait and intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19461874}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07003; DB07007; DB07011; DB07405; DB08750; DB01997; DB07029; DB07008; DB08214; DB07002; DB01835; DB06879; DB04534; DB03100; DB02207; DB00125; DB00155; DB01234; DB14649; DB11327; DB00997; DB07306; DB07388; DB05252; DB01381; DB03366; DB05214; DB04400; DB09237; DB00244; DB01110; DB01017; DB03144; DB01686; DB03449; DB06916; DB07318; DB07389; DB02044; DB02644; DB05383; DB02234; DB03953; DB02462; DB08814 Interacts with P04406 EC number EC 1.14.13.39 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Calmodulin-binding; Cytoplasm; FAD; Flavoprotein; FMN; Heme; Iron; Metal-binding; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D Molecular weight (Da) 48633 Length 421 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.5 Isoelectric point 6.75 Charge (pH=7) -1.04 3D Binding mode Sequence RHVRIKNWGSGMTFQDTLHHKAKGILTCRSKSCLGSIMTPKSLTRGPRDKPTPPDELLPQAIEFVNQYYGSFKEAKIEEHLARVEAVTKEIETTGTYQLTGDELIFATKQAWRNAPRCIGRIQWSNLQVFDARSCSTAREMFEHICRHVRYSTNNGNIRSAITVFPQRSDGKHDFRVWNAQLIRYAGYQMPDGSIRGDPANVEFTQLCIDLGWKPKYGRFDVVPLVLQANGRDPELFEIPPDLVLEVAMEHPKYEWFRELELKWYALPAVANMLLEVGGLEFPGCPFNGWYMGTEIGVRDFCDVQRYNILEEVGRRMGLETHKLASLWKDQAVVEINIAVLHSFQKQNVTIMDHHSAAESFMKYMQNEYRSRGGCPADWIWLVPPMSGSITPVFHQEMLNYVLSPFYYYQVEAWKTHVWQD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 26 | Cocaine esterase | 3I2K | 5.09 | |
Target general information Gen name cocE Organism Rhodococcus sp. (strain MB1 Bresler) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family CocE/NonD hydrolase family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Carboxylic ester hydrolase activity.Dipeptidyl-peptidase activity. Related diseases Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 5, episodic encephalopathy type (THMD5) [MIM:614458]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder due to an inborn error of thiamine metabolism. The phenotype is highly variable, but in general, affected individuals have onset in early childhood of acute encephalopathic episodes associated with increased serum and CSF lactate. These episodes result in progressive neurologic dysfunction manifest as gait disturbances, ataxia, dystonia, and spasticity, which in some cases may result in loss of ability to walk. Cognitive function is usually preserved, although mildly delayed development has been reported. These episodes are usually associated with infection and metabolic decompensation. Some patients may have recovery of some neurologic deficits. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22152682}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03793; DB01795 Interacts with NA EC number 3.1.1.84 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Hydrolase; Serine esterase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 62127.9 Length 574 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 26.62 Isoelectric point 4.56 Charge (pH=7) -33.24 3D Binding mode Sequence VDGNYSVASNVMVPMRDGVRLAVDLYRPDADGPVPVLLVRNPYDKFDVFAWSTQSTNWLEFVRDGYAVVIQDTRGLFASEGEFVPHVDDEADAEDTLSWILEQAWCDGNVGMFGVSYLGVTQWQAAVSGVGGLKAIAPSMASADLYRAPWYGPGGALSVEALLGWSALIGTGLITSRSDARPEDAADFVQLAAILNDVAGAASVTPLAEQPLLGRLIPWVIDQVVDHPDNDESWQSISLFERLGGLATPALITAGWYDGFVGESLRTFVAVKDNADARLVVGPWSHSNLTGRNADRKFGIAATYPIQEATTMHKAFFDRHLRGETDALAGVPKVRLFVMGIDEWRDETDWPLPDTAYTPFYLGGSGAANTSTGGGTLSTSISGTESADTYLYDPADPVPSLGGTLLFHNGDNGPADQRPIHDRDDVLCYSTEVLTDPVEVTGTVSARLFVSSSAVDTDFTAKLVDVFPDGRAIALCDGIVRMRYRETLVNPTLIEAGEIYEVAIDMLATSNVFLPGHRIMVQVSSSNFPKYDRNSNTGGVIAREQLEEMCTAVNRIHRGPEHPSHIVLPIIKRK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 27 | Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) | 6MVD | 5.09 | |
Target general information Gen name LCAT Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Phospholipidcholesterolacyltransferase; Phospholipid-cholesterol acyltransferase; Phosphatidylcholinesterol acyltransferase; Phosphatidylcholine-sterol acyltransferase Protein family AB hydrolase superfamily, Lipase family Biochemical class Acyltransferase Function Synthesized mainly in the liver and secreted into plasma where it converts cholesterol and phosphatidylcholines (lecithins) to cholesteryl esters and lysophosphatidylcholines on the surface of high and low density lipoproteins (HDLs and LDLs). The cholesterol ester is then transported back to the liver. Has a preference for plasma 16:0-18:2 or 18:O-18:2 phosphatidylcholines. Also produced in the brain by primary astrocytes, and esterifies free cholesterol on nascent APOE-containing lipoproteins secreted from glia and influences cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) APOE- and APOA1 levels. Together with APOE and the cholesterol transporter ABCA1, plays a key role in the maturation of glial-derived, nascent lipoproteins. Required for remodeling high-density lipoprotein particles into their spherical forms. Central enzyme in the extracellular metabolism of plasma lipoproteins. Related diseases Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency (LCATD) [MIM:245900]: A disorder of lipoprotein metabolism characterized by inadequate esterification of plasmatic cholesterol. Two clinical forms are recognized: complete LCAT deficiency and fish-eye disease. LCATD is generally referred to the complete form which is associated with absence of both alpha and beta LCAT activities resulting in esterification anomalies involving both HDL (alpha-LCAT activity) and LDL (beta-LCAT activity). It causes a typical triad of diffuse corneal opacities, target cell hemolytic anemia, and proteinuria with renal failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11423760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12957688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15994445, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16051254, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16216249, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1681161, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1859405, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2370048, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7607641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7711728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8318557, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8432868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8807342, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9007616, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9741700}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Fish-eye disease (FED) [MIM:136120]: A disorder of lipoprotein metabolism due to partial lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency that affects only alpha-LCAT activity. FED is characterized by low plasma HDL and corneal opacities due to accumulation of cholesterol deposits in the cornea ('fish-eye'). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1516702, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1571050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15994445, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1737840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21901787, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8620346, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9261271}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P02647; O76024 EC number EC 2.3.1.43 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acyltransferase; Cholesterol metabolism; Corneal dystrophy; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lipid metabolism; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Steroid metabolism; Sterol metabolism; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 42715.4 Length 376 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 42.05 Isoelectric point 5.69 Charge (pH=7) -9.12 3D Binding mode Sequence HTRPVILVPGCLGNQLEAKLDKPDVVNWMCYRKTEDFFTIWLDLNMFLPLGVDCWIDNTRVVYNRSSGLVSNAPGVQIRVPGFGKTYSVEYLDSSKLAGYLHTLVQNLVNNGYVRDETVRAAPYDWRLEPGQQEEYYRKLAGLVEEMHAAYGKPVFLIGHSLGCLHLLYFLLRQPQAWKDRFIDGFISLGAPWGGSIKPMLVLASGDNQGIPIMSSIKEEQRITTTSPWMFPSRMAWPEDHVFISTPSFNYTGRDFQRFFADLHFEEGWYMWLQSRDLLAGLPAPGVEVYCLYGVGLPTPRTYIYDHGFPYTDPVGVLYEDGDDTVATRSTELCGLWQGRQPQPVHLLPLHGIQHLNMVFSNLTLEHINAILLGAH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 28 | Adrenergic receptor alpha-2A (ADRA2A) | 7EJ8 | 5.09 | |
Target general information Gen name ADRA2A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Alpha-2AAR; Alpha-2A adrenoreceptor; Alpha-2A adrenoceptor; Alpha-2A adrenergic receptor; Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtype C10; ADRAR; ADRA2R Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, Adrenergic receptor subfamily, ADRA2A sub-subfamily Biochemical class GPCR rhodopsin Function The rank order of potency for agonists of this receptor is oxymetazoline > clonidine > epinephrine > norepinephrine > phenylephrine > dopamine > p-synephrine > p-tyramine > serotonin = p-octopamine. For antagonists, the rank order is yohimbine > phentolamine = mianserine > chlorpromazine = spiperone = prazosin > propanolol > alprenolol = pindolol. Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. Related diseases Lipodystrophy, familial partial, 8 (FPLD8) [MIM:620679]: An autosomal dominant form of partial lipodystrophy, a disorder characterized by abnormal subcutaneous fat distribution. FPLD8 patients show selective loss of subcutaneous adipose tissue from the limbs, beginning around 13 to 15 years of age, and abnormal accumulation of subcutaneous adipose tissue in the dorsal neck and face, as well as in the posterior thoracic and abdominal regions. The disorder is associated with metabolic abnormalities, including diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27376152}. The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01472; DB00321; DB00543; DB00182; DB00714; DB00964; DB09229; DB01238; DB14185; DB06216; DB00865; DB00217; DB00484; DB01200; DB00248; DB01136; DB04846; DB00477; DB09202; DB00575; DB00363; DB01151; DB00633; DB01576; DB11273; DB13345; DB00320; DB00449; DB11278; DB09167; DB04855; DB06262; DB01363; DB05492; DB00751; DB00668; DB01049; DB00696; DB01175; DB06678; DB09194; DB00800; DB06623; DB00629; DB01018; DB00502; DB11577; DB00555; DB06707; DB00589; DB04948; DB09195; DB00408; DB08815; DB00934; DB01365; DB01577; DB01403; DB00968; DB06148; DB00370; DB09205; DB09242; DB06711; DB01149; DB00368; DB00540; DB06229; DB00935; DB01267; DB00715; DB01186; DB01608; DB00925; DB00692; DB00397; DB09286; DB09244; DB06153; DB00413; DB00457; DB00433; DB01069; DB00852; DB01224; DB11124; DB11738; DB00268; DB09304; DB06764; DB13025; DB00697; DB00797; DB00193; DB00656; DB00726; DB11477; DB06694; DB01392; DB00246; DB01624 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Methylation; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID R Molecular weight (Da) 30303.9 Length 263 Aromaticity 0.16 Instability index 35.08 Isoelectric point 9.66 Charge (pH=7) 16.82 3D Binding mode Sequence YSLQVTLTLVCLAGLLMLLTVFGNVLVIIAVFTSRALKAPQNLFLVSLASADILVATLVIPFSLANEVMGYWYFGKAWCEIYLALDVLFCTSSIVHLCAISLDRYWSITQAIEYNLKRTPRRIKAIIITVWVISAVISFPPRCEINDQKWYVISSCIGSFFAPCLIMILVYVRIYQIAKRRTRRGRQNREKRFTFVLAVVIGVFVVCWFPFFFTYTLTAVGCSVPRTLFKFFFWFGYCNSSLNPVIYTIFNHDFRRAFKKILC Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 29 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 (EPHB3) | 5L6O | 5.09 | |
Target general information Gen name EPHB3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hEK2; Tyrosine-protein kinase TYRO6; TYRO6; Embryonic kinase 2; ETK2; EPH-like tyrosine kinase 2; EPH-like kinase 2; EK2 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, Ephrin receptor subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Generally has an overlapping and redundant function with EPHB2. Like EPHB2, functions in axon guidance during development regulating for instance the neurons forming the corpus callosum and the anterior commissure, 2 major interhemispheric connections between the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. In addition to its role in axon guidance plays also an important redundant role with other ephrin-B receptors in development and maturation of dendritic spines and the formation of excitatory synapses. Controls other aspects of development through regulation of cell migration and positioning. This includes angiogenesis, palate development and thymic epithelium development for instance. Forward and reverse signaling through the EFNB2/EPHB3 complex also regulate migration and adhesion of cells that tubularize the urethra and septate the cloaca. Finally, plays an important role in intestinal epithelium differentiation segregating progenitor from differentiated cells in the crypt. Receptor tyrosine kinase which binds promiscuously transmembrane ephrin-B family ligands residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. Related diseases A chromosomal aberration involving TRIM24/TIF1 is found in papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs). Translocation t(7;10)(q32;q11) with RET. The translocation generates the TRIM24/RET (PTC6) oncogene. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10439047}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with P37235; O75031 EC number EC 2.7.10.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Angiogenesis; ATP-binding; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Developmental protein; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Kinase; Membrane; Neurogenesis; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 30412.9 Length 267 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 37.42 Isoelectric point 7.74 Charge (pH=7) 1 3D Binding mode Sequence CVKIEEVIGAGEVCRGRLKQPGRREVFVAIKTLKVGYTERQRRDFLSEASIMGQFDHPNIIRLEGVVTKSRPVMILTEFMENCALDSFLRLNDGQFTVIQLVGMLRGIAAGMKYLSEMNYVHRDLAARNILVNSNLVCKVSDFGLEDDPSDPTYTSSLGGKIPIRWTAPEAIAYRKFTSASDVWSYGIVMWEVMSYGERPYWDMSNQDVINAVEQDYRLPPPMDCPTALHQLMLDCWVRDRNLRPKFSQIVNTLDKLIRNPASLKVI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 30 | Steroid 11-beta-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) | 7E7F | 5.09 | |
Target general information Gen name CYP11B1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms S11BH; P450C11; P-450c11; CYPXIB1; CYP11B1 Protein family Cytochrome P450 family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Has steroid 11-beta-hydroxylase activity. In addition to this activity, the 18 or 19-hydroxylation of steroids and the aromatization of androstendione to estrone have also been ascribed to cytochrome P450 XIB. Related diseases Adrenal hyperplasia 4 (AH4) [MIM:202010]: A form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, a common recessive disease due to defective synthesis of cortisol. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is characterized by androgen excess leading to ambiguous genitalia in affected females, rapid somatic growth during childhood in both sexes with premature closure of the epiphyses and short adult stature. Four clinical types: 'salt wasting' (SW, the most severe type), 'simple virilizing' (SV, less severely affected patients), with normal aldosterone biosynthesis, 'non-classic form' or late-onset (NC or LOAH) and 'cryptic' (asymptomatic). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16046588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20089618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2022736, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20331679, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20947076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23940125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24022297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24536089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24987415, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26053152, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26476331, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9302260}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Hyperaldosteronism, familial, 1 (HALD1) [MIM:103900]: A disorder characterized by hypertension, variable hyperaldosteronism, and abnormal adrenal steroid production, including 18-oxocortisol and 18-hydroxycortisol. There is significant phenotypic heterogeneity, and some individuals never develop hypertension. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The molecular defect causing hyperaldosteronism familial 1 is an anti-Lepore-type fusion of the CYP11B1 and CYP11B2 genes. The hybrid gene has the promoting part of CYP11B1, ACTH-sensitive, and the coding part of CYP11B2. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04630; DB00501; DB01234; DB14649; DB00292; DB00741; DB14539; DB14540; DB14543; DB14545; DB14544; DB01026; DB05667; DB01011; DB01388; DB01110; DB00648; DB11837; DB00252; DB00421 Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.14.15.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Congenital adrenal hyperplasia; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Heme; Iron; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Membrane; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Steroid biosynthesis; Steroidogenesis; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 54077 Length 472 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 46.85 Isoelectric point 9.31 Charge (pH=7) 10.15 3D Binding mode Sequence VPRTVLPFEAMPRRPGNRRNRLNQIRREQGYEDLHLEVHQTFQELGPIFRYDLGGAGMVCVMLPEDVEKLQQVDSLHPHRMSLEPWVAYRQHRGHKCGVFLLNGPEWRFNRLRLNPEVLSPNAVQRFLPMVDAVARDFSQALKKKVLQNARGSLTLDVQPSIFHYTIEASNLALFGERLGLVGHSPSSASLNFLHALEVMFKSTVQLMFMPRSNSRNTSPKVWKEHFEAWDCIFQYGDNCIQKIYQELAFSRPQQYTSIVAELLLNAELSPDAIKANSMELTAGSVDTTVFPLLMTLFELARNPNVQQALRQESLAAAASISEHPQKATTELPLLRAALKETLRLYPVGLFLERVASSDLVLQNYHIPAGTLVRVFLYSLGRNPALFPRPERYNPQRWLDIRGSGRNFYHVPFGFGMRQCLGRRLAEAEMLLLLHHVLKHLQVETLTQEDIKMVYSFILRPSMFPLLTFRAI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 31 | Natriuretic peptides B | 1YK1 | 5.08 | |
Target general information Gen name NPPB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Natriuretic peptide family Biochemical class Hormone / growth factor receptor Function Diuretic hormone activity.Hormone activity.Peptide hormone receptor binding.Receptor binding. Related diseases Multiple fibroadenomas of the breast (MFAB) [MIM:615554]: A benign breast disease marked by lobuloalveolar growth with abnormally high proliferation of the epithelium, and characterized by the presence of more than 3 fibroadenomas in one breast. Fibroadenomas are adenomas containing fibrous tissue. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18779591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Hyperprolactinemia (HPRL) [MIM:615555]: A disorder characterized by increased levels of prolactin in the blood not associated with gestation or the puerperium. HPRL may result in infertility, hypogonadism, and galactorrhea. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24195502}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01136; DB06412 Interacts with A8MQ03; P57678; Q6A162; P60411; Q7Z3S9; P25788; Q9UJW9 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hormone; Pharmaceutical; Proteoglycan; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Vasoactive; Vasodilator Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID E Molecular weight (Da) 46353.1 Length 415 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.91 Isoelectric point 5.51 Charge (pH=7) -12.09 3D Binding mode Sequence GCFGRKMDRISSSSGLGCKVLALPPQKIEVLVLLPQDDSYLFSLTRVRPAIEYALRSVEGLLPPGTRFQVAYEDSDCGNRALFSLVDRVAAARGAKPDLILGPVCEYAAAPVARLASHWDLPMLSAGALAAGFQHKDSEYSHLTRVAPAYAKMGEMMLALFRHHHWSRAALVYSDDKLERNCYFTLEGVHEVFQEEGLHTSIYSFDETKDLDLEDIVRNIQASERVVIMCASSDTIRSIMLVAHRHGMTSGDYAFFNIELFNSSSYGDGSWKRGDKHDFEAKQAYSSLQTVTLLRTVKPEFEKFSMEVKSSVEKQGLNMEDYVNMFVEGFHDAILLYVLALHEVLRAGYSKKDGGKIIQQTWNRTFEGIAGQVSIDANGDRYGDFSVIAMTDVEAGTQEVIGDYFGKEGRFEMRP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 32 | Lethal(3)malignant brain tumor-like 3 (L3MBTL3) | 4FL6 | 5.08 | |
Target general information Gen name L3MBTL3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms MBT1; MBT-1; Lethal(3)malignant brain tumor-like protein 3; L(3)mbt-like protein 3; KIAA1798; H-l(3)mbt-like protein 3 Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Putative Polycomb group (PcG) protein. PcG proteins maintain the transcriptionally repressive state of genes, probably via a modification of chromatin, rendering it heritably changed in its expressibility. Required for normal maturation of myeloid progenitor cells (By similarity). Related diseases Spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive, with axonal neuropathy 1 (SCAN1) [MIM:607250]: A form of spinocerebellar ataxia, a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of cerebellar disorders. Patients show progressive incoordination of gait and often poor coordination of hands, speech and eye movements, due to degeneration of the cerebellum with variable involvement of the brainstem and spinal cord. SCAN1 is an autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia (ARCA) associated with peripheral axonal motor and sensory neuropathy, distal muscular atrophy, pes cavus and steppage gait as seen in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy. All affected individuals have normal intelligence. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12244316, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15647511, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15920477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16141202, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17948061}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9NWX5; Q8N9N5; Q13895; Q96JK2; Q16531; P26358; Q01094; O00716; Q96JM7; Q9Y4Z0; P45984; Q9UBU8; Q15014; Q9NPG2; Q9UMX2; P18545; Q8IXK0; Q8N381; Q96S99; Q9H8W4; P62875; Q13131; P54646; P14678-2; P23497; G2XKQ0; P10827; Q6DKK2; P54253; A0A0S2Z5G4; Q13895; Q9BXJ3; Q8IUI8; Q14203-5; Q9H4E7; Q8NFF5-2; Q53EP0-3; O95995; O75031; P42858; Q14005-2; Q63ZY3; Q96JM7-2; P61968; P45984; P55081; Q9UBU8-2; Q15014; Q9NPG2; Q16656-4; Q96HA8; Q96BD5; Q92569; Q96S99; Q9H8W4; O60568; A0A6Q8PF08; P67775; P54646; P63000; O94955; Q5VUG0; P37840; P00441; Q5MJ10; Q9UMX1; Q13148; Q86TI0; Q8N8B7-2; Q9Y228; Q5T7W7; Q6DKK2; P09936; P31930; P61758; A0A0S2Z6A9; Q9H0M4-4; P36508 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Chromatin regulator; Isopeptide bond; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 71079 Length 615 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 29.71 Isoelectric point 6.42 Charge (pH=7) -6.56 3D Binding mode Sequence AWCWASYLEEEKAVAVPAKLFKEHQSFPYNKNGFKVGMKLEGVDPEHQSVYCVLTVAEVCGYRIKLHFDGYSDCYDFWVNADALDIHPVGWCEKTGHKLHPPKGYKEEEFNWQTYLKTCKAQAAPKSLFEVIPSGFRVGMKLEAVDKKNPSFICVATVTDMVDNRFLVHFDNWDESYDYWCEASSPHIHPVGWCKEHRRTLITPPGYPNVKHFSWDKYLEETNSLPAPARAFKVKPPHGFQKKMKLEVVDKRNPMFIRVATVADTDDHRVKVHFDGWNNCYDYWIDADSPDIHPVGWCSKTGHPLQPPLAWCWASYLEEEKAVAVPAKLFKEHQSFPYNKNGFKVGMKLEGVDPEHQSVYCVLTVAEVCGYRIKLHFDGYSDCYDFWVNADALDIHPVGWCEKTGHKLHPPKGYKEEEFNWQTYLKTCKAQAAPKSLFENSGFRVGMKLEAVDKKNPSFICVATVTDMVDNRFLVHFDNWDESYDYWCEASSPHIHPVGWCKEHRRTLITPPGYPNVHFSWDKYLEETNSLPAPARAFKVKPPHGFQKKMKLEVVDKRNPMFIRVATVADTDDHRVKVHFDGWNNCYDYWIDADSPDIHPVGWCSKTGHPLQPPL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 33 | Natriuretic peptides B | 1YK1 | 5.07 | |
Target general information Gen name NPPB Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Natriuretic peptide family Biochemical class Hormone / growth factor receptor Function Diuretic hormone activity.Hormone activity.Peptide hormone receptor binding.Receptor binding. Related diseases Multiple fibroadenomas of the breast (MFAB) [MIM:615554]: A benign breast disease marked by lobuloalveolar growth with abnormally high proliferation of the epithelium, and characterized by the presence of more than 3 fibroadenomas in one breast. Fibroadenomas are adenomas containing fibrous tissue. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18779591}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Hyperprolactinemia (HPRL) [MIM:615555]: A disorder characterized by increased levels of prolactin in the blood not associated with gestation or the puerperium. HPRL may result in infertility, hypogonadism, and galactorrhea. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24195502}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01136; DB06412 Interacts with A8MQ03; P57678; Q6A162; P60411; Q7Z3S9; P25788; Q9UJW9 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hormone; Pharmaceutical; Proteoglycan; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Vasoactive; Vasodilator Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID E Molecular weight (Da) 46353.1 Length 415 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.91 Isoelectric point 5.51 Charge (pH=7) -12.09 3D Binding mode Sequence GCFGRKMDRISSSSGLGCKVLALPPQKIEVLVLLPQDDSYLFSLTRVRPAIEYALRSVEGLLPPGTRFQVAYEDSDCGNRALFSLVDRVAAARGAKPDLILGPVCEYAAAPVARLASHWDLPMLSAGALAAGFQHKDSEYSHLTRVAPAYAKMGEMMLALFRHHHWSRAALVYSDDKLERNCYFTLEGVHEVFQEEGLHTSIYSFDETKDLDLEDIVRNIQASERVVIMCASSDTIRSIMLVAHRHGMTSGDYAFFNIELFNSSSYGDGSWKRGDKHDFEAKQAYSSLQTVTLLRTVKPEFEKFSMEVKSSVEKQGLNMEDYVNMFVEGFHDAILLYVLALHEVLRAGYSKKDGGKIIQQTWNRTFEGIAGQVSIDANGDRYGDFSVIAMTDVEAGTQEVIGDYFGKEGRFEMRP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 34 | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1 | 4O42 | 5.07 | |
Target general information Gen name CHD1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family SNF2/RAD54 helicase family Biochemical class Dna binding protein / viral protein Function ATP binding.ATP-dependent DNA helicase activity.DNA binding.Methylated histone binding. Related diseases Pilarowski-Bjornsson syndrome (PILBOS) [MIM:617682]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by developmental delay, speech apraxia, intellectual disability, autism, and facial dysmorphic features. Some patients may have seizures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28866611}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with O60341-1; B2BUF1; P28799; O76024 EC number 3.6.4.12 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Chromatin regulator; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; DNA-binding; Helicase; Hydrolase; Intellectual disability; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 20969.1 Length 180 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 46.35 Isoelectric point 5.88 Charge (pH=7) -2.83 3D Binding mode Sequence EFETIERFMDCRIGRKGATGATTTIYAVEADGDPNAGFEKNKEPGEIQYLIKWKGWSHIHNTWETEETLKQQNVRGMKKLDNYKKKDQETKRWLKNASPEDVEYYNCQQELTDDLHKQYQIVERIIAHSNQKSAAGYPDYYCKWQGLPYSECSWEDGALISKKFQACIDEYFSRTARSXV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 35 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-3 | 4ZK4 | 5.07 | |
Target general information Gen name CHRNA3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NACHRA3 Protein family Ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family, Acetylcholine receptor (TC 1.A.9.1) subfamily, Alpha-3/CHRNA3 sub-subfamily Biochemical class Acetylcholine binding protein Function Acetylcholine binding.Acetylcholine-gated cation-selective channel activity.Acetylcholine receptor activity.Ligand-gated ion channel activity.Serotonin-gated cation-selective channel activity. Related diseases Bladder dysfunction, autonomic, with impaired pupillary reflex and secondary CAKUT (BAIPRCK) [MIM:191800]: An autosomal recessive disease characterized by impaired innervation and autonomic dysfunction of the urinary bladder, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, small kidneys, recurrent urinary tract infections, and progressive renal insufficiency. Additional autonomic features are impaired pupillary reflex and orthostatic hypotension. The disease manifests in utero or early childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31708116}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB00915; DB01156; DB00237; DB00565; DB09028; DB00514; DB07720; DB00898; DB00472; DB05710; DB01227; DB00848; DB00333; DB00184; DB01090; DB00202; DB01273 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Glycoprotein; Golgi apparatus; Ion channel; Ion transport; Ligand-gated ion channel; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Postsynaptic cell membrane; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Synapse; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B,C,D,E Molecular weight (Da) 46391.5 Length 408 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 30.23 Isoelectric point 4.6 Charge (pH=7) -22.73 3D Binding mode Sequence LHSQANLMRLKSDLFYPGPTKDDPLTVTLGFTLQDIVKADSSTNEVDLVYWEQQRWKLNSLMWDPNEYGNITDFRTSAADIWTPDITAYSSTRPVQVLSPQIAVVTHDGSVMFIPAQRLSFMCDPTGVDSEEGATCAVKFGSWVYSGFEIDLKTDTDQVDLSSYYASSKYEILSATQYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDVVLVVKFRERRLHSQANLMRLKSDLFNRYPGPTKDDPLTVTLGFTLQDIVKADSSTNEVDLVYWEQQRWKLNSLMWDPNEYGNITDFRTSAADIWTPDITAYSSTRPVQVLSPQIAVVTHDGSVMFIPAQRLSFMCDPTGVDSEEGATCAVKFGSWVYSGFEIDLKTDTDQVDLSSYYASSKYEILSATQYKHDIKYNCCEEIYPDVVLVVKFRE Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 36 | Nitric-oxide synthase endothelial (NOS3) | 4D1P | 5.07 | |
Target general information Gen name NOS3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Nitric oxide synthase, endothelial; NOSIII; NOS,type III; NOS type III; Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; Endothelial NOS; ENOS; EC-NOS; Constitutive NOS; CNOS Protein family NOS family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function NO mediates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced angiogenesis in coronary vessels and promotes blood clotting through the activation of platelets. Produces nitric oxide (NO) which is implicated in vascular smooth muscle relaxation through a cGMP-mediated signal transduction pathway. Related diseases Variation Asp-298 in NOS3 may be associated with susceptibility to coronary spasm. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11740345, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9737779}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07001; DB02048; DB02911; DB02335; DB01997; DB03332; DB04534; DB07244; DB03100; DB03918; DB02207; DB03065; DB00125; DB02994; DB01833; DB00155; DB00997; DB07388; DB03974; DB02077; DB01821; DB09237; DB01110; DB03144; DB03305; DB01686; DB04559; DB02044; DB08019; DB08018; DB02027; DB02979; DB00435; DB04223; DB06154; DB03910; DB02141; DB03963; DB03707; DB02234; DB04018; DB00360; DB02589 Interacts with P60709; P63010-2; Q8N6T3-3; Q9Y575-3; Q96FT7-4; Q5SZD1; Q16543; Q9UNS2; Q8IUI8; P35222; Q05193; O15287; Q08379; Q71DI3; P69905; P61978; Q12891; Q9UKT9; Q9Y2M5; Q14525; Q6DKI2; P43364-2; Q8N6F8; O94851; A4FUJ8; Q8N594; Q8IVI9; Q6X4W1-6; O15381-5; Q9NV79; Q16549; Q5T2W1; O75925; Q96I34; Q6ZMI0-5; P57052; Q9GZR2; Q96D59; Q8N6K7-2; Q9GZS3; Q8IUW3; Q7Z699; Q7Z698; P50502; Q9BR01-2; Q9NVV9; Q86WT6-2; Q9H347; P58304; Q9NZC7-5; Q9UNY5; P14079 EC number EC 1.14.13.39 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Calmodulin-binding; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; FMN; Golgi apparatus; Heme; Iron; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Myristate; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 90790.1 Length 803 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 50.67 Isoelectric point 6.03 Charge (pH=7) -9.56 3D Binding mode Sequence FPRVKNWEVGSITYDTLSAQAQQDGPCTPRRCLGSLVFPAPEQLLSQARDFINQYYSSIKRSGSQAHEQRLQEVEAEVAATGTYQLRESELVFGAKQAWRNAPRCVGRIQWGKLQVFDARDCRSAQEMFTYICNHIKYATNRGNLRSAITVFPQRCPGRGDFRIWNSQLVRYAGYRQQDGSVRGDPANVEITELCIQHGWTPGNGRFDVLPLLLQAPDEPPELFLLPPELVLEVPLEHPTLEWFAALGLRWYALPAVSNMLLEIGGLEFPAAPFSGWYMSTEIGTRNLCDPHRYNILEDVAVCMDLDTRTTSSLWKDKAAVEINVAVLHSYQLAKVTIVDHHAATASFMKHLENEQKARGGCPADWAWIVPPISGSLTPVFHQEMVNYFLSPAFRYQPDPWKFPRVKNWEVGSITYDTLSAQAQQDGPCTPRRCLGSLVFPAPEQLLSQARDFINQYYSSIKRSGSQAHEQRLQEVEAEVAATGTYQLRESELVFGAKQAWRNAPRCVGRIQWGKLQVFDARDCRSAQEMFTYICNHIKYATNRGNLRSAITVFPQRCPGRGDFRIWNSQLVRYAGYRQQDGSVRGDPANVEITELCIQHGWTPGNGRFDVLPLLLQAPDEPPELFLLPPELVLEVPLEHPTLEWFAALGLRWYALPAVSNMLLEIGGLEFPAAPFSGWYMSTEIGTRNLCDPHRYNILEDVAVCMDLDTRTTSSLWKDKAAVEINVAVLHSYQLAKVTIVDHHAATASFMKHLENEQKARGGCPADWAWIVPPISGSLTPVFHQEMVNYFLSPAFRYQPDPW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 37 | Oxysterols receptor LXR-alpha (NR1H3) | 3IPQ | 5.07 | |
Target general information Gen name NR1H3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group H member 3; Nuclear receptor LXRalpha; Nuclear orphan receptor LXR-alpha; Liver X receptor alpha; LXRalpha; LXRA Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily Biochemical class Nuclear hormone receptor Function Interaction with retinoic acid receptor (RXR) shifts RXR from its role as a silent DNA-binding partner to an active ligand-binding subunit in mediating retinoid responses through target genes defined by LXRES. LXRES are DR4-type response elements characterized by direct repeats of two similar hexanuclotide half-sites spaced by four nucleotides. Plays an important role in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis, regulating cholesterol uptake through MYLIP-dependent ubiquitination of LDLR, VLDLR and LRP8. Interplays functionally with RORA for the regulation of genes involved in liver metabolism. Nuclear receptor that exhibits a ligand-dependent transcriptional activation activity. Related diseases Okur-Chung neurodevelopmental syndrome (OCNDS) [MIM:617062]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by developmental delay, intellectual disability, behavioral problems, hypotonia, speech problems, microcephaly, pachygyria and variable dysmorphic features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27048600}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08175; DB08063; DB11994; DB07929; DB13174; DB07080 Interacts with O60869; O60341; Q99750; Q15788; O75376; Q07869; Q07869-1; Q03181; P37231; P19793; P28702; P48443; O43463; P42858; Q99750; O95817; G5E9A7; O95872; P02545; Q99750; P28702; P28702-3; P48443; Q7Z699 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Activator; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; DNA-binding; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 25389.9 Length 220 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 46.42 Isoelectric point 5.51 Charge (pH=7) -6.58 3D Binding mode Sequence QLSPEQLGMIEKLVAAQQTPWPEARQQRFAHFTELAIVSVQEIVDFAKQLPGFLQLSREDQIALLKTSAIEVMLLETSRRYNPGSESITFLKDFSYNREDFAKAGLQVEFINPIFEFSRAMNELQLNDAEFALLIAISIFSADRPNVQDQLQVERLQHTYVEALHAYVSIHHPHDRLMFPRMLMKLVSLRTLSSVHSEQVFALRLQDKKLPPLLSEIWDV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 38 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 9 (DPP-9) | 6EOR | 5.07 | |
Target general information Gen name DPP9 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Dipeptidyl peptidase-like protein 9; Dipeptidyl peptidase IX; Dipeptidyl peptidase IV-related protein 2; DPRP2; DPRP-2; DPP IX; DPLP9; DP9 Protein family Peptidase S9B family, DPPIV subfamily Biochemical class Peptidase Function Dipeptidyl peptidase that cleaves off N-terminal dipeptides from proteins having a Pro or Ala residue at position 2. Related diseases Hatipoglu immunodeficiency syndrome (HATIS) [MIM:620331]: An autosomal recessive immunologic disorder manifesting in infancy or early childhood, and characterized by failure to thrive, short stature, skin pigmentation abnormalities, pancytopenia, and susceptibility to recurrent infections. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:36112693}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q9NXR5; Q86TI2; Q6NUP5; P46379-2; Q8WUW1; Q96A83-2; O75190-2; O14645; Q01658; P29692-2; Q06787-7; Q9Y5Q9; O14901; Q9BVL2; Q96CV9; Q06830; P14678-2; P49458; Q11203; Q13148; P14927 EC number EC 3.4.14.5 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Aminopeptidase; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Nucleus; Protease; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine protease Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 92797.4 Length 808 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 37.45 Isoelectric point 6.34 Charge (pH=7) -8.98 3D Binding mode Sequence AARFQVQKHSWDGLRSIIHGSRKAPHDFQFVQKSGPHSHRLYYLGMPYRENSLLYSEIPKLLLSWKQMLDHFQATPHHGVYSREEELLRERKRLGVFGITSYDFHSESGLFLFQASNSLFHCRDGGKNGFMVSPMKPLEIKTQCSGPRMDPKICPADPAFFSFINNSDLWVANIETGEERRLTFCHQNVLDDPKSAGVATFVIQEEFDRFTGYWWCPTASWEGLKTLRILYEEVDESEVEVIHVPSPALEERKTDSYRYPRTGSKNPKIALKLAEFQTDSQGKIVSTQEKELVQPFSSLFPKVEYIARAGWTRDGKYAWAMFLDRPQQWLQLVLLPPALFIPSTENEEQRLASARAVPRNVQPYVVYEEVTNVWINVHDIFYPFPQLCFLRANECKTGFCHLYKVTAVLKSQGYDWSEPFSPGEDEFKCPIKEEIALTSGEWEVLARHGSKIWVNEETKLVYFQGTKDTPLEHHLYVVSYEAAGEIVRLTTPGFSHSCSMSQNFDMFVSHYSSVSTPPCVHVYKLSGPDDDPLHKQPRFWASMMEADYVPPEIFHFHTRSDVRLYGMIYKPHALQPGKKHPTVLFVYGGPQVQLVNNSFKGIKYLRLNTLASLGYAVVVIDGRGSCQRGLRFEGALKNQMGQVEIEDQVEGLQFVAEKYGFIDLSRVAIHGWSYGGFLSLMGLIHKPQVFKVAIAGAPVTVWMAYDTGYTERYMDVPENNQHGYEAGSVALHVEKLPNEPNRLLILHGFLDENVHFFHTNFLVSQLIRAGKPYQLQIYPNERHSIRCPESGEHYEVTLLHFLQEYLHH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 39 | RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT2) | 3D0E | 5.07 | |
Target general information Gen name AKT2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms RAC-PK-beta; Protein kinase B beta; Protein kinase Akt-2; PKB beta Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, RAC subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function AKT2 is one of 3 closely related serine/threonine-protein kinases (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3) called the AKT kinase, and which regulate many processes including metabolism, proliferation, cell survival, growth and angiogenesis. This is mediated through serine and/or threonine phosphorylation of a range of downstream substrates. Over 100 substrate candidates have been reported so far, but for most of them, no isoform specificity has been reported. AKT is responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake by mediating insulin-induced translocation of the SLC2A4/GLUT4 glucose transporter to the cell surface. Phosphorylation of PTPN1 at 'Ser-50' negatively modulates its phosphatase activity preventing dephosphorylation of the insulin receptor and the attenuation of insulin signaling. Phosphorylation of TBC1D4 triggers the binding of this effector to inhibitory 14-3-3 proteins, which is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. AKT regulates also the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen by phosphorylating GSK3A at 'Ser-21' and GSK3B at 'Ser-9', resulting in inhibition of its kinase activity. Phosphorylation of GSK3 isoforms by AKT is also thought to be one mechanism by which cell proliferation is driven. AKT regulates also cell survival via the phosphorylation of MAP3K5 (apoptosis signal-related kinase). Phosphorylation of 'Ser-83' decreases MAP3K5 kinase activity stimulated by oxidative stress and thereby prevents apoptosis. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 at 'Ser-939' and 'Thr-1462', thereby activating mTORC1 signaling and leading to both phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and in activation of RPS6KB1. AKT is involved in the phosphorylation of members of the FOXO factors (Forkhead family of transcription factors), leading to binding of 14-3-3 proteins and cytoplasmic localization. In particular, FOXO1 is phosphorylated at 'Thr-24', 'Ser-256' and 'Ser-319'. FOXO3 and FOXO4 are phosphorylated on equivalent sites. AKT has an important role in the regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription and positively regulates the activity of CREB1 (cyclic AMP (cAMP)-response element binding protein). The phosphorylation of CREB1 induces the binding of accessory proteins that are necessary for the transcription of pro-survival genes such as BCL2 and MCL1. AKT phosphorylates 'Ser-454' on ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), thereby potentially regulating ACLY activity and fatty acid synthesis. Activates the 3B isoform of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE3B) via phosphorylation of 'Ser-273', resulting in reduced cyclic AMP levels and inhibition of lipolysis. Phosphorylates PIKFYVE on 'Ser-318', which results in increased PI(3)P-5 activity. The Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC1 is another substrate and its phosphorylation is implicated in the regulation cell proliferation and cell growth. AKT plays a role as key modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway controlling the tempo of the process of newborn neurons integration during adult neurogenesis, including correct neuron positioning, dendritic development and synapse formation. Signals downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI(3)K) to mediate the effects of various growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). AKT mediates the antiapoptotic effects of IGF-I. Essential for the SPATA13-mediated regulation of cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly. May be involved in the regulation of the placental development. Related diseases Defects in AKT2 are a cause of susceptibility to breast cancer (BC). AKT2 promotes metastasis of tumor cells without affecting the latency of tumor development. May play a role in glioblastoma cell survival (PubMed:20167810). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20167810}.; DISEASE: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) [MIM:125853]: A multifactorial disorder of glucose homeostasis caused by a lack of sensitivity to insulin. Affected individuals usually have an obese body habitus and manifestations of a metabolic syndrome characterized by diabetes, insulin resistance, hypertension and hypertriglyceridemia. The disease results in long-term complications that affect the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and blood vessels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15166380, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19164855}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Hypoinsulinemic hypoglycemia with hemihypertrophy (HIHGHH) [MIM:240900]: A disorder characterized by hypoglycemia, low insulin levels, low serum levels of ketone bodies and branched-chain amino acids, left-sided hemihypertrophy, neonatal macrosomia, reduced consciousness and hypoglycemic seizures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21979934}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB08073; DB07859; DB12218; DB07947; DB07812 Interacts with P31749; P49841; P08238; Q6FHY5; Q9NRD5; Q04864-2; O60504; P53804; Q9C0C9; P08670; Q15118-1 EC number EC 2.7.11.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Apoptosis; ATP-binding; Carbohydrate metabolism; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Developmental protein; Diabetes mellitus; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endosome; Glucose metabolism; Glycogen biosynthesis; Glycogen metabolism; Glycoprotein; Kinase; Manganese; Membrane; Metal-binding; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Proto-oncogene; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Sugar transport; Transferase; Translation regulation; Transport; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 37380.5 Length 324 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 29.68 Isoelectric point 6.19 Charge (pH=7) -3.43 3D Binding mode Sequence KVTMNDFDYLKLLGKGTFGKVILVREKATGRYYAMKILRKEVIIAKDEVAHTVTESRVLQNTRHPFLTALKYAFQTHDRLCFVMEYANGGELFFHLSRERVFTEERARFYGAEIVSALEYLHSRDVVYRDIKLENLMLDKDGHIKITDFGLCKEGISDGATMKXFCGTPEYLAPEVLEDNDYGRAVDWWGLGVVMYEMMCGRLPFYNQDHERLFELILMEEIRFPRTLSPEAKSLLAGLLKKDPKQRLGGGPSDAKEVMEHRFFLSINWQDVVQKKLLPPFKPQVTSEVDTRYFDDEFTAQSITIXPPDQRTHFPQFDYSASIR Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 40 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase NIK (MAP3K14) | 4IDV | 5.07 | |
Target general information Gen name MAP3K14 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms NIK; NF-kappa-beta-inducing kinase; Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 14; HsNIK Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family, MAP kinase kinase kinase subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Promotes proteolytic processing of NFKB2/P100, which leads to activation of NF-kappa-B via the non-canonical pathway. Could act in a receptor-selective manner. Lymphotoxin beta-activated kinase which seems to be exclusively involved in the activation of NF-kappa-B and its transcriptional activity. Related diseases Immunodeficiency 112 (IMD112) [MIM:620449]: An autosomal recessive, primary immunologic disorder characterized by variable abnormalities affecting lymphoid immunity, including hypogammaglobulinemia, lymphopenia or paradoxical lymphocytosis, and recurrent bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25406581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29230214}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q16543; O15111; P01112; P07900; P08238; O14920; Q9Y6K9; Q14974; P36578; Q02878; P62917; P62280; P62277; Q12933; Q13114; P62258; Q60680-2 EC number EC 2.7.11.25 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; ATP-binding; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Kinase; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 36970.9 Length 335 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 41.12 Isoelectric point 6.18 Charge (pH=7) -5.06 3D Binding mode Sequence FSVEEYLVHALQGSVSSGQAHSLTSLAKTWAARTEDNEGVLLTEKLKPVDYEYREEVHWATHQLRLGRGSFGEVHRMEDKQTGFQCAVKKVRLEVFRAEELMACAGLTSPRIVPLYGAVREGPWVNIFMELLEGGSLGQLVKEQGCLPEDRALYYLGQALEGLEYLHSRRILHGDVKADNVLLSSDGSHAALCDFGHAVCLQPDGLGKSLLTGDYIPGTETHMAPEVVLGRSCDAKVDVWSSCCMMLHMLNGCHPWTQFFRGPLCLKIASEPPPVREIPPSCAPLTAQAIQEGLRKEPIHRVSAAELGGKVNRALQQVGGLKSPWRGEYKEPRHP Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||