Job Results:
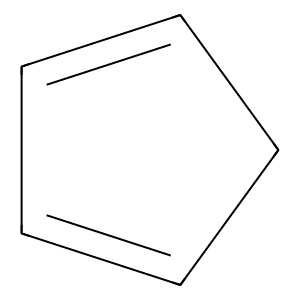
Ligand
Structure
Job ID
7f371ea108ffadeed56066fb8d4cae63
Job name
NA
Time
2024-12-09 11:06:55
| Rank | Target | PDB ID |
AirScore |
Detail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | Voltage-gated sodium channel alpha Nav1.7 (SCN9A) | 7W9M | 4.79 | |
Target general information Gen name SCN9A Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hNE-Na; Voltage-gated sodium channel subunit alpha Nav1.7; Sodium channel proteintype IX subunit alpha; Sodium channel proteintype 9 subunit alpha; Sodium channel protein type IX subunit alpha; Sodium Protein family Sodium channel (TC 1.A.1.10) family, Nav1.7/SCN9A subfamily Biochemical class Voltage-gated ion channel Function Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-sensitive Na(+) channel isoform. Plays a role in pain mechanisms, especially in the development of inflammatory pain. Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Related diseases Primary erythermalgia (PERYTHM) [MIM:133020]: Autosomal dominant disease characterized by recurrent episodes of severe pain associated with redness and warmth in the feet or hands. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14985375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15385606, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15955112, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15958509, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16216943, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16392115, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16702558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16988069, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18945915, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19369487, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24311784}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Indifference to pain, congenital, autosomal recessive (CIP) [MIM:243000]: A disorder characterized by congenital inability to perceive any form of pain, in any part of the body. All other sensory modalities are preserved and the peripheral and central nervous systems are apparently intact. Patients perceive the sensations of touch, warm and cold temperature, proprioception, tickle and pressure, but not painful stimuli. There is no evidence of a motor or sensory neuropathy, either axonal or demyelinating. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20635406}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder (PEXPD) [MIM:167400]: An autosomal dominant paroxysmal disorder of pain and autonomic dysfunction. The distinctive features are paroxysmal episodes of burning pain in the rectal, ocular, and mandibular areas accompanied by autonomic manifestations such as skin flushing. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17145499, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18945915, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25285947}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB09088; DB13746; DB05541; DB00564; DB01161; DB00907; DB13269; DB13961; DB06218; DB00555; DB00281; DB00776; DB11186; DB09345; DB01069; DB09342; DB00243; DB06201; DB09085; DB00273; DB00313; DB00909 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Epilepsy; Glycoprotein; Ion channel; Ion transport; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Sodium; Sodium channel; Sodium transport; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Ubl conjugation; Voltage-gated channel Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 162402 Length 1418 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 35.66 Isoelectric point 6.72 Charge (pH=7) -1.33 3D Binding mode Sequence GPQSFVHFTKQSLALIEQRIAERKSKEPKPSSDLEAGKQLPFIYGDIPPGMVSEPLEDLDPYYADKKTFIVLNKGKTIFRFNATPALYMLSPFSPLRRISIKILVHSLFSMLIMCTILTNCIFMTMNNPPDWTKNVEYTFTGIYTFESLVKILARGFCVGEFTFLRDPWNWLDFVVIVFAYLTEFVNNVSALRTFRVLRALKTISVIPGLKTIVGALIQSVKKLSDVMILTVFCLSVFALIGLQLFMGNLKHKCFRNSLENNETLESIMNTLESEEDFRKYFYYLEGSKDALLCGFSTDSGQCPEGYTCVKIGRNPDYGYTSFDTFSWAFLALFRLMTQDYWENLYQQTLRAAGKTYMIFFVVVIFLGSFYLINLILAVVAMAYKEQNQANIEEAKQKELEFQQMLDRLKKEQEPYWIKFKKCIYFIVMDPFVDLAITICIVLNTLFMAMEHHPMTEEFKNVLAIGNLVFTGIFAAEMVLKLIAMDPYEYFQVGWNIFDSLIVTLSLVELFLADVEGLSVLRSFRLLRVFKLAKSWPTLNMLIKIIGNSVGALGNLTLVLAIIVFIFAVVGMQLFGKSYKECVCKINDDCTLPRWHMNDFFHSFLIVFRVLCGEWIETMWDCMEVAGQAMCLIVYMMVMVIGNLVVLNLFLALLLSSFSSDNLTAIEEDPDANNLQIAVTRIKKGINYVKQTLREFILKAFGKIWWNIRKTCYKIVEHSWFESFIVLMILLSSGALAFEDIYIERKKTIKIILEYADKIFTYIFILEMLLKWIAYGYKTYFTNAWCWLDFLIVDVSLVTLVANTLGYSDLGPIKSLRTLRALRPLRALSRFEGMRVVVNALIGAIPSIMNVLLVCLIFWLIFSIMGVNLFAGKFYECINTTDGSRFPASQVPNRSECFALMNVSQNVRWKNLKVNFDNVGLGYLSLLQVATFKGWTIIMYAAVDSVNVDKQPKYEYSLYMYIYFVVFIIFGSFFTLNLFIGVIIDNFNQQKKKLGGQDIFMTEEQKKYYNAMKKLGSKKPQKPIPRPGNKIQGCIFDLVTNQAFDISIMVLICLNMVTMMVEKEGQSQHMTEVLYWINVVFIILFTGECVLKLISLRHYYFTVGWNIFDFVVVIISIVGMFLADLIETYFVSPTLFRVIRLARIGRILRLVKGAKGIRTLLFALMMSLPALFNIGLLLFLVMFIYAIFGMSNFAYVKKEDGINDMFNFETFGNSMICLFQITTSAGWDGLLAPILNSKPPDCDPKKVHPGSSVEGDCGNPSVGIFYFVSYIIISFLVVVNMYIAVILENFSVATEESTEPLSEDDFEMFYEVWEKFDPDATQFIEFSKLSDFAAALDPPLLIAKPNKVQLIAMDLPMVSGDRIHCLDILFAFTKRVLGESGEMDSLRSQMEERFMSANPSKVSYEPITTTLKRKQEDV Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 22 | Protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 (PTPN11) | 2SHP | 4.79 | |
Target general information Gen name PTPN11 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11; SHPTP2; SHP2; SHP-2; SH-PTP3; SH-PTP2; Protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP2; Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 2C; Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1D; PTP2C; PT Protein family Protein-tyrosine phosphatase family, Non-receptor class 2 subfamily Biochemical class Phosphoric monoester hydrolase Function Positively regulates MAPK signal transduction pathway. Dephosphorylates GAB1, ARHGAP35 and EGFR. Dephosphorylates ROCK2 at 'Tyr-722' resulting in stimulatation of its RhoA binding activity. Dephosphorylates CDC73. Acts downstream of various receptor and cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinases to participate in the signal transduction from the cell surface to the nucleus. Related diseases LEOPARD syndrome 1 (LPRD1) [MIM:151100]: A disorder characterized by lentigines, electrocardiographic conduction abnormalities, ocular hypertelorism, pulmonic stenosis, abnormalities of genitalia, retardation of growth, and sensorineural deafness. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12058348, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14961557, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15121796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15389709, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15520399, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15690106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16679933, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16733669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24891296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26742426}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Noonan syndrome 1 (NS1) [MIM:163950]: A form of Noonan syndrome, a disease characterized by short stature, facial dysmorphic features such as hypertelorism, a downward eyeslant and low-set posteriorly rotated ears, and a high incidence of congenital heart defects and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Other features can include a short neck with webbing or redundancy of skin, deafness, motor delay, variable intellectual deficits, multiple skeletal defects, cryptorchidism, and bleeding diathesis. Individuals with Noonan syndrome are at risk of juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, a myeloproliferative disorder characterized by excessive production of myelomonocytic cells. Some patients with NS1 develop multiple giant cell lesions of the jaw or other bony or soft tissues, which are classified as pigmented villonodular synovitis (PVNS) when occurring in the jaw or joints. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11704759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11992261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12161469, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12325025, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12529711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12634870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12717436, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12739139, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12960218, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15384080, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15889278, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15948193, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19020799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24891296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28074573}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Mutations in PTPN11 account for more than 50% of the cases.; DISEASE: Leukemia, juvenile myelomonocytic (JMML) [MIM:607785]: An aggressive pediatric myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative disorder characterized by malignant transformation in the hematopoietic stem cell compartment with proliferation of differentiated progeny. Patients have splenomegaly, enlarged lymph nodes, rashes, and hemorrhages. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12717436, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26742426}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Metachondromatosis (MC) [MIM:156250]: A skeletal disorder with radiologic features of both multiple exostoses and Ollier disease, characterized by the presence of exostoses, commonly of the bones of the hands and feet, and enchondromas of the metaphyses of long bones and iliac crest. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20577567}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB02779 Interacts with P10275; P32239; Q9BZW8; P20138; Q08345; P00533; P29317; P04626; Q8WU20; Q13480; Q9UQC2; P62993; P08069; P06213; P35568; P43628; P10721; P08581; O95297; Q15116; P09619; P16284; P49023; P49247; Q13049; P68105; Q71V39; P35570; P97710; Q6P1J9; Q13480; O75496; Q9UKI8 EC number EC 3.1.3.48 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Deafness; Disease variant; Hydrolase; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Protein phosphatase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; SH2 domain Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 56341.2 Length 491 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 41.37 Isoelectric point 7.76 Charge (pH=7) 2.43 3D Binding mode Sequence KSRRWFHPNITGVEAENLLLTRGVDGSFLARPSKSNPGDLTLSVRRNGAVTHIKIQNTGDYYDLYGGEKFATLAELVQYYMEHHGQLKEKNGDVIELKYPLNCADPTSERWFHGHLSGKEAEKLLTEKGKHGSFLVRESQSHPGDFVLSVRTGDNDGKSKVTHVMIRCQELKYDVGGGERFDSLTDLVEHYKKNPMVETLGTVLQLKQPLNTTRINAAEIESRVRELSKGFWEEFETLQQQECKLLYSRKEGQRQENKNKNRYKNILPFDHTRVVLHDSDYINANIIMPKKSYIATQGCLQNTVNDFWRMVFQENSRVIVMTTKEVERGKSKCVKYWPDEYALKEYGVMRVRNVKESAAHDYTLRELKLSKVGQGNTERTVWQYHFRTWPDHGVPSDPGGVLDFLEEVHHKQESIMDAGPVVVHCSAGIGRTGTFIVIDILIDIIREKGVDCDIDVPKTIQMVRSQRSGMVQTEAQYRSIYMAVQHYIETL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 23 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 | 2W96 | 4.78 | |
Target general information Gen name CDK4 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CDC2/CDKX subfamily Biochemical class Cell cycle Function ATP binding.Cyclin binding.Cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity.Cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity.Protein complex binding. Related diseases Melanoma, cutaneous malignant 3 (CMM3) [MIM:609048]: A malignant neoplasm of melanocytes, arising de novo or from a pre-existing benign nevus, which occurs most often in the skin but may also involve other sites. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7652577, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8528263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9311594, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9425228}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12001; DB03496; DB12010; DB09073; DB02733; DB11730; DB15442 Interacts with Q9UH17; P24385; P30279; P30281; Q16543; P50613; P38936; P46527; P49918; P42771; P42772; P42773; P55273; Q9UJC3; P08238; Q9UKT9; Q0VD86; P01106; Q9ULD0; P28749; Q08999; P09936; Q8N720 EC number 2.7.11.22 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Cell cycle; Cell division; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Nucleus; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Serine/threonine-protein kinase; Transferase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID B Molecular weight (Da) 30138.4 Length 267 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 36.2 Isoelectric point 5.78 Charge (pH=7) -5.83 3D Binding mode Sequence SRYEPVAEIGVGAYGTVYKARDPHSGHFVALKSVRVPNGEEGLPISTVREVALLRRLEAFEHPNVVRLMDVCATSRTDREIKVTLVFEHVDQDLRTYLDKAPPPGLPAETIKDLMRQFLRGLDFLHANCIVHRDLKPENILVTSGGTVKLADFGLARIYSYQMALDPVVVTLWYRAPEVLLQSTYATPVDMWSVGCIFAEMFRRKPLFCGNSEADQLGKIFDLIGLPPEDDWVPEMEESGAQLLLEMLTFNPHKRISAFRALQHSYL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 24 | Nitric-oxide synthase endothelial (NOS3) | 4D1P | 4.78 | |
Target general information Gen name NOS3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Nitric oxide synthase, endothelial; NOSIII; NOS,type III; NOS type III; Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; Endothelial NOS; ENOS; EC-NOS; Constitutive NOS; CNOS Protein family NOS family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function NO mediates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced angiogenesis in coronary vessels and promotes blood clotting through the activation of platelets. Produces nitric oxide (NO) which is implicated in vascular smooth muscle relaxation through a cGMP-mediated signal transduction pathway. Related diseases Variation Asp-298 in NOS3 may be associated with susceptibility to coronary spasm. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11740345, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9737779}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07001; DB02048; DB02911; DB02335; DB01997; DB03332; DB04534; DB07244; DB03100; DB03918; DB02207; DB03065; DB00125; DB02994; DB01833; DB00155; DB00997; DB07388; DB03974; DB02077; DB01821; DB09237; DB01110; DB03144; DB03305; DB01686; DB04559; DB02044; DB08019; DB08018; DB02027; DB02979; DB00435; DB04223; DB06154; DB03910; DB02141; DB03963; DB03707; DB02234; DB04018; DB00360; DB02589 Interacts with P60709; P63010-2; Q8N6T3-3; Q9Y575-3; Q96FT7-4; Q5SZD1; Q16543; Q9UNS2; Q8IUI8; P35222; Q05193; O15287; Q08379; Q71DI3; P69905; P61978; Q12891; Q9UKT9; Q9Y2M5; Q14525; Q6DKI2; P43364-2; Q8N6F8; O94851; A4FUJ8; Q8N594; Q8IVI9; Q6X4W1-6; O15381-5; Q9NV79; Q16549; Q5T2W1; O75925; Q96I34; Q6ZMI0-5; P57052; Q9GZR2; Q96D59; Q8N6K7-2; Q9GZS3; Q8IUW3; Q7Z699; Q7Z698; P50502; Q9BR01-2; Q9NVV9; Q86WT6-2; Q9H347; P58304; Q9NZC7-5; Q9UNY5; P14079 EC number EC 1.14.13.39 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Calmodulin-binding; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; FMN; Golgi apparatus; Heme; Iron; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Myristate; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 90790.1 Length 803 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 50.67 Isoelectric point 6.03 Charge (pH=7) -9.56 3D Binding mode Sequence FPRVKNWEVGSITYDTLSAQAQQDGPCTPRRCLGSLVFPAPEQLLSQARDFINQYYSSIKRSGSQAHEQRLQEVEAEVAATGTYQLRESELVFGAKQAWRNAPRCVGRIQWGKLQVFDARDCRSAQEMFTYICNHIKYATNRGNLRSAITVFPQRCPGRGDFRIWNSQLVRYAGYRQQDGSVRGDPANVEITELCIQHGWTPGNGRFDVLPLLLQAPDEPPELFLLPPELVLEVPLEHPTLEWFAALGLRWYALPAVSNMLLEIGGLEFPAAPFSGWYMSTEIGTRNLCDPHRYNILEDVAVCMDLDTRTTSSLWKDKAAVEINVAVLHSYQLAKVTIVDHHAATASFMKHLENEQKARGGCPADWAWIVPPISGSLTPVFHQEMVNYFLSPAFRYQPDPWKFPRVKNWEVGSITYDTLSAQAQQDGPCTPRRCLGSLVFPAPEQLLSQARDFINQYYSSIKRSGSQAHEQRLQEVEAEVAATGTYQLRESELVFGAKQAWRNAPRCVGRIQWGKLQVFDARDCRSAQEMFTYICNHIKYATNRGNLRSAITVFPQRCPGRGDFRIWNSQLVRYAGYRQQDGSVRGDPANVEITELCIQHGWTPGNGRFDVLPLLLQAPDEPPELFLLPPELVLEVPLEHPTLEWFAALGLRWYALPAVSNMLLEIGGLEFPAAPFSGWYMSTEIGTRNLCDPHRYNILEDVAVCMDLDTRTTSSLWKDKAAVEINVAVLHSYQLAKVTIVDHHAATASFMKHLENEQKARGGCPADWAWIVPPISGSLTPVFHQEMVNYFLSPAFRYQPDPW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 25 | SPRY domain-containing SOCS box protein 2 (SSB-2) (Gene-rich cluster protein C9) | 3EMW | 4.78 | |
Target general information Gen name SPSB2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms GRCC9;SSB2 Protein family SPSB family Biochemical class NA Function Substrate recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin BC-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:15601820, PubMed:21199876). Negatively regulates nitric oxide (NO) production and limits cellular toxicity in activated macrophages by mediating the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of NOS2 (PubMed:21199876). Acts as a bridge which links NOS2 with the ECS E3 ubiquitin ligase complex components ELOC and CUL5 (PubMed:21199876). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15601820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21199876}." Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 2 (MRT2) [MIM:607417]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRT2 patients display mild intellectual disability with a standard IQ ranged from 50 to 70. IQ scores are lower in males than females. Developmental milestones are mildly delayed. There are no dysmorphic or autistic features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15557513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28143899}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with G5E9A7; Q15369; Q53EP0-3; O60333-2; Q16656-4; Q96IZ0; P16284; Q92569; O60260-5; Q99873; Q6P9E2; Q9Y3C5; Q96GM5; P61086; P08670; P09052 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Host-virus interaction; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 22703.1 Length 207 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 50.84 Isoelectric point 5.98 Charge (pH=7) -2.79 3D Binding mode Sequence LYFQSMPEGLEELLSAPPPDLGAQRRHGWNPKDCSENIEVKEGGLYFERRPVAQSTDGARGKRGYSRGLHAWEISWPLEQRGTHAVVGVATALAPLQTDHYAALLGSNSESWGWDIGRGKLYHQSKGPGAPQYPAGTQGEQLEVPERLLVVLDMEEGTLGYAIGGTYLGPAFRGLKGRTLYPAVSAVWGQCQVRIRYLGEDINNNNN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 26 | SPRY domain-containing SOCS box protein 2 (SSB-2) (Gene-rich cluster protein C9) | 3EMW | 4.78 | |
Target general information Gen name SPSB2 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms GRCC9;SSB2 Protein family SPSB family Biochemical class NA Function Substrate recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin BC-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:15601820, PubMed:21199876). Negatively regulates nitric oxide (NO) production and limits cellular toxicity in activated macrophages by mediating the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of NOS2 (PubMed:21199876). Acts as a bridge which links NOS2 with the ECS E3 ubiquitin ligase complex components ELOC and CUL5 (PubMed:21199876). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15601820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21199876}." Related diseases Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 2 (MRT2) [MIM:607417]: A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRT2 patients display mild intellectual disability with a standard IQ ranged from 50 to 70. IQ scores are lower in males than females. Developmental milestones are mildly delayed. There are no dysmorphic or autistic features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15557513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28143899}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with G5E9A7; Q15369; Q53EP0-3; O60333-2; Q16656-4; Q96IZ0; P16284; Q92569; O60260-5; Q99873; Q6P9E2; Q9Y3C5; Q96GM5; P61086; P08670; P09052 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Host-virus interaction; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Ubl conjugation pathway Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 22703.1 Length 207 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 50.84 Isoelectric point 5.98 Charge (pH=7) -2.79 3D Binding mode Sequence LYFQSMPEGLEELLSAPPPDLGAQRRHGWNPKDCSENIEVKEGGLYFERRPVAQSTDGARGKRGYSRGLHAWEISWPLEQRGTHAVVGVATALAPLQTDHYAALLGSNSESWGWDIGRGKLYHQSKGPGAPQYPAGTQGEQLEVPERLLVVLDMEEGTLGYAIGGTYLGPAFRGLKGRTLYPAVSAVWGQCQVRIRYLGEDINNNNN Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 27 | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) | 3IJJ | 4.78 | |
Target general information Gen name MIF Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Phenylpyruvate tautomerase; MMIF; L-dopachrome tautomerase; L-dopachrome isomerase; Glycosylation-inhibiting factor; GLIF; GIF Protein family MIF family Biochemical class Intramolecular oxidoreductase Function Involved in the innate immune response to bacterial pathogens. The expression of MIF at sites of inflammation suggests a role as mediator in regulating the function of macrophages in host defense. Counteracts the anti-inflammatory activity of glucocorticoids. Has phenylpyruvate tautomerase and dopachrome tautomerase activity (in vitro), but the physiological substrate is not known. It is not clear whether the tautomerase activity has any physiological relevance, and whether it is important for cytokine activity. Pro-inflammatory cytokine. Related diseases Rheumatoid arthritis systemic juvenile (RASJ) [MIM:604302]: An inflammatory articular disorder with systemic onset beginning before the age of 16. It represents a subgroup of juvenile arthritis associated with severe extraarticular features and occasionally fatal complications. During active phases of the disorder, patients display a typical daily spiking fever, an evanescent macular rash, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, serositis, myalgia and arthritis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11508429}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01880; DB07888; DB08334; DB08335; DB08333; DB07718; DB08765; DB02728 Interacts with O43521-2; P00533; Q92743; P14174; Q96HA8 EC number EC 5.3.2.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Cytokine; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Immunity; Inflammatory response; Innate immunity; Isomerase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,C Molecular weight (Da) 24671.9 Length 228 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 31.45 Isoelectric point 8.37 Charge (pH=7) 2.26 3D Binding mode Sequence PMFIVNTNVPRASVPDGFLSELTQQLAQATGKPPQYIAVHVVPDQLMAFGGSSEPCALCSLHSIGKIGGAQNRSYSKLLCGLLAERLRISPDRVYINYYDMNAANVGWNNSTFAPMFIVNTNVPRASVPDGFLSELTQQLAQATGKPPQYIAVHVVPDQLMAFGGSSEPCALCSLHSIGKIGGAQNRSYSKLLCGLLAERLRISPDRVYINYYDMNAANVGWNNSTFA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 28 | Voltage-gated calcium channel alpha Cav3.3 (CACNA1I) | 7WLL | 4.78 | |
Target general information Gen name CACNA1I Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Voltage-gated calcium channel subunit alpha Cav3.3; Voltage-dependent T-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1I; KIAA1120; Ca(v)3.3 Protein family Calcium channel alpha-1 subunit (TC 1.A.1.11) family, CACNA1I subfamily Biochemical class Voltage-gated ion channel Function Voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCC) mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell motility, cell division and cell death. This channel gives rise to T-type calcium currents. T-type calcium channels belong to the "low-voltage activated (LVA)" group and are strongly blocked by nickel and mibefradil. A particularity of this type of channels is an opening at quite negative potentials, and a voltage-dependent inactivation. T-type channels serve pacemaking functions in both central neurons and cardiac nodal cells and support calcium signaling in secretory cells and vascular smooth muscle. They may also be involved in the modulation of firing patterns of neurons which is important for information processing as well as in cell growth processes. Gates in voltage ranges similar to, but higher than alpha 1G or alpha 1H (By similarity). Related diseases Neurodevelopmental disorder with speech impairment and with or without seizures (NEDSIS) [MIM:620114]: An autosomal dominant disorder with variable manifestations. Severely affected individuals have profound global developmental delay, hypotonia, delayed or absent walking, absent speech, feeding difficulties, cortical visual impairment, and onset of hyperexcitability and seizures in the first months or years of life. Some patients manifest a milder phenotype characterized by mild to moderate cognitive impairment and mild speech delay, usually without seizures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33704440}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB01118; DB00381; DB09231; DB13746; DB11148; DB11093; DB11348; DB14481; DB09061; DB00568; DB09235; DB00228; DB00153; DB04841; DB09238; DB14009; DB01388; DB14011; DB00622; DB01115; DB06712; DB06152; DB00617; DB09498; DB09089; DB00661; DB00909 Interacts with Q8NEC5; Q96P56 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Calcium channel; Calcium transport; Disease variant; Glycoprotein; Intellectual disability; Ion channel; Ion transport; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport; Voltage-gated channel Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 130104 Length 1135 Aromaticity 0.12 Instability index 41.15 Isoelectric point 8.25 Charge (pH=7) 8.02 3D Binding mode Sequence TSPRNWCIKMVCNPWFECVSMLVILLNCVTLGMYQPCDDMDCLSDRCKILQVFDDFIFIFFAMEMVLKMVALGIFGKKCYLGDTWNRLDFFIVMAGMVEYSLDLQNINLSAIRTVRVLRPLKAINRVPSMRILVNLLLDTLPMLGNVLLLCFFVFFIFGIIGVQLWAGLLRNRCFLEENFTIQGDVALPPYYQPEEDDEMPFICSLSGDNGIMGCHEIPPLKCVNWNRYYNVCRTGSANPHKGAINFDNIGYAWIVIFQVITLEGWVEIMYYVMDAHSFYNFIYFILLIIVGSFFMINLCLVVIATQFSETKQREHRLMLRETRAKLRGIVDSKYFNRGIMMAILVNTVSMGIEHHEQPEELTNILEICNVVFTSMFALEMILKLAAFGLFDYLRNPYNIFDSIIVIISIWEIVGQADGGLSVLRTFRLLRVLKLVRFMPALRRQLVVLMKTMDNVATFCMLLMLFIFIFSILGMHIFGCKFSLRTDTGDTVPDRKNFDSLLWAIVTVFQILTQEDWNVVLYNGMASTSPWASLYFVALMTFGNYVLFNLLVAILVEGFQQTIIAHKLFDYVVLAFIFLNCITIALERPQIEAGSTERIFLTVSNYIFTAIFVGEMTLKVVSLGLYFGEQAYLRSSWNVLDGFLVFVSIIDIVVSLASAGGAKILGVLRVLRLLRTLRPLRVISRAPGLKLVVETLISSLKPIGNIVLICCAFFIIFGILGVQLFKGKFYHCLGVDTRNITNRSDCMAANYRWVHHKYNFDNLGQALMSLFVLASKDGWVNIMYNGLDAVAVDQQPVTNHNPWMLLYFISFLLIVSFFVLNMFVGVVVENFHKCRQHQEAEEARRREEKRLRRLEKKRRKAQRLPYYATYCHTRLLIHSMCTSHYLDIFITFIICLNVVTMSLEHYNQPTSLETALKYCNYMFTTVFVLEAVLKLVAFGLRRFFKDRWNQLDLAIVLLSVMGITLEEIEINAALPINPTIIRIMRVLRIARVLKLLKMATGMRALLDTVVQALPQVGNLGLLFMLLFFIYAALGVELFGKLVCNDENPCEGMSRHATFENFGMAFLTLFQVSTGDNWNGIMKDTLRDCTHDERSCLSSLQFVSPLYFVSFVLTAQFVLINVVVAVLMKHLDDSNK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 29 | Steroid 11-beta-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) | 7E7F | 4.78 | |
Target general information Gen name CYP11B1 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms S11BH; P450C11; P-450c11; CYPXIB1; CYP11B1 Protein family Cytochrome P450 family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function Has steroid 11-beta-hydroxylase activity. In addition to this activity, the 18 or 19-hydroxylation of steroids and the aromatization of androstendione to estrone have also been ascribed to cytochrome P450 XIB. Related diseases Adrenal hyperplasia 4 (AH4) [MIM:202010]: A form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, a common recessive disease due to defective synthesis of cortisol. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is characterized by androgen excess leading to ambiguous genitalia in affected females, rapid somatic growth during childhood in both sexes with premature closure of the epiphyses and short adult stature. Four clinical types: 'salt wasting' (SW, the most severe type), 'simple virilizing' (SV, less severely affected patients), with normal aldosterone biosynthesis, 'non-classic form' or late-onset (NC or LOAH) and 'cryptic' (asymptomatic). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16046588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20089618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2022736, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20331679, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20947076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23940125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24022297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24536089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24987415, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26053152, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26476331, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9302260}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Hyperaldosteronism, familial, 1 (HALD1) [MIM:103900]: A disorder characterized by hypertension, variable hyperaldosteronism, and abnormal adrenal steroid production, including 18-oxocortisol and 18-hydroxycortisol. There is significant phenotypic heterogeneity, and some individuals never develop hypertension. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The molecular defect causing hyperaldosteronism familial 1 is an anti-Lepore-type fusion of the CYP11B1 and CYP11B2 genes. The hybrid gene has the promoting part of CYP11B1, ACTH-sensitive, and the coding part of CYP11B2. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB04630; DB00501; DB01234; DB14649; DB00292; DB00741; DB14539; DB14540; DB14543; DB14545; DB14544; DB01026; DB05667; DB01011; DB01388; DB01110; DB00648; DB11837; DB00252; DB00421 Interacts with NA EC number EC 1.14.15.4 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Congenital adrenal hyperplasia; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Heme; Iron; Lipid biosynthesis; Lipid metabolism; Membrane; Metal-binding; Mitochondrion; Mitochondrion inner membrane; Monooxygenase; Oxidoreductase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Steroid biosynthesis; Steroidogenesis; Transit peptide Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 54077 Length 472 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 46.85 Isoelectric point 9.31 Charge (pH=7) 10.15 3D Binding mode Sequence VPRTVLPFEAMPRRPGNRRNRLNQIRREQGYEDLHLEVHQTFQELGPIFRYDLGGAGMVCVMLPEDVEKLQQVDSLHPHRMSLEPWVAYRQHRGHKCGVFLLNGPEWRFNRLRLNPEVLSPNAVQRFLPMVDAVARDFSQALKKKVLQNARGSLTLDVQPSIFHYTIEASNLALFGERLGLVGHSPSSASLNFLHALEVMFKSTVQLMFMPRSNSRNTSPKVWKEHFEAWDCIFQYGDNCIQKIYQELAFSRPQQYTSIVAELLLNAELSPDAIKANSMELTAGSVDTTVFPLLMTLFELARNPNVQQALRQESLAAAASISEHPQKATTELPLLRAALKETLRLYPVGLFLERVASSDLVLQNYHIPAGTLVRVFLYSLGRNPALFPRPERYNPQRWLDIRGSGRNFYHVPFGFGMRQCLGRRLAEAEMLLLLHHVLKHLQVETLTQEDIKMVYSFILRPSMFPLLTFRAI Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 30 | Argininosuccinate lyase | 1K62 | 4.77 | |
Target general information Gen name ASL Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family Lyase 1 family, Argininosuccinate lyase subfamily Biochemical class Lyase Function Argininosuccinate lyase activity.Identical protein binding. Related diseases Argininosuccinic aciduria (ARGINSA) [MIM:207900]: An autosomal recessive disorder of the urea cycle. The disease is characterized by mental and physical retardation, liver enlargement, skin lesions, dry and brittle hair showing trichorrhexis nodosa microscopically and fluorescing red, convulsions, and episodic unconsciousness. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11747432, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11747433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12408190, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1705937, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17326097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19703900, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22081021, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2263616, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24166829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9045711}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The phenotype heterogeneity among patients is associated with interallelic complementation resulting in either complete loss of activity or partial regeneration of functional active sites in the heterotetrameric mutant protein. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11747433}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03814; DB00125; DB02267 Interacts with P04424; Q9BTE3-2; Q96HA8; O75382 EC number 4.3.2.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Acetylation; Alternative splicing; Amino-acid biosynthesis; Arginine biosynthesis; Disease variant; Lyase; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Urea cycle Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 51364.1 Length 459 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 35.82 Isoelectric point 6.66 Charge (pH=7) -1.25 3D Binding mode Sequence GKLWGGRFVGAVDPIMEKFNASIAYDRHLWEVDVQGSKAYSRGLEKAGLLTKAEMDQILHGLDKVAEEWAQGTFKLNSNDEDIHTANERRLKELIGATAGKLHTGRSRNDQVVTDLRLWMRQTCSTLSGLLWELIRTMVDRAEAERDVLFPGYTHLQRAQPIRWSHWILSHAVALTRDSERLLEVRKRINVLPLGSGAIAGNPLGVDRELLRAELNFGAITLNSMDATSERDFVAEFLFWRSLCMTHLSRMAEDLILYCTKEFSFVQLSDAYSTGSSLMPRKKNPDSLELIRSKAGRVFGRCAGLLMTLKGLPSTYNKDLQEDKEAVFEVSDTMSAVLQVATGVISTLQIHQENMGQALSPDMLATDLAYYLVRKGMPFRQAHEASGKAVFMAETKGVALNQLSLQELQTISPLFSGDVICVWDYRHSVEQYGALGGTARSSVDWQIRQVRALLQAQQA Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 31 | Sodium channel subunit beta-2 | 5FEB | 4.77 | |
Target general information Gen name SCN2B Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms UNQ326/PRO386 Protein family Sodium channel auxiliary subunit SCN2B (TC 8.A.17) family Biochemical class Membrane protein Function Sodium channel regulator activity.Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential. Related diseases Atrial fibrillation, familial, 14 (ATFB14) [MIM:615378]: A familial form of atrial fibrillation, a common sustained cardiac rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity and ineffective atrial contraction promoting blood stasis in the atria and reduces ventricular filling. It can result in palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19808477}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Genetic variations in SCN2B may be involved in Brugada syndrome (PubMed:23559163). This tachyarrhythmia is characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs, the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23559163}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB05541; DB00907; DB13269; DB13961; DB00776; DB00243; DB00313; DB00909 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Atrial fibrillation; Brugada syndrome; Cell membrane; Cell projection; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Immunoglobulin domain; Ion transport; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Signal; Sodium; Sodium transport; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Transport Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 14190 Length 122 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 37.04 Isoelectric point 6.39 Charge (pH=7) -1.21 3D Binding mode Sequence SNAMEVTVPATLNVLNGSDARLPCTFNSAYTVNHKQFSLNWTYQECNNCSEEMFLQFRMKIINLKLERFQDRVEFSGNPSKYDVSVMLRNVQPEDEGIYNCYIMNPPDRHRGHGKIHLQVLM Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 32 | P2Y purinoceptor 12 | 4PXZ | 4.77 | |
Target general information Gen name P2RY12 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms HORK3 Protein family G-protein coupled receptor 1 family Biochemical class Membrane protein Function ADP receptor activity.G-protein coupled adenosine receptor activity.Guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Related diseases Bleeding disorder, platelet-type, 8 (BDPLT8) [MIM:609821]: A condition characterized by mild to moderate mucocutaneous bleeding, and excessive bleeding after surgery or trauma. The defect is due to severe impairment of platelet response to ADP resulting in defective platelet aggregation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11196645, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12578987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25428217}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06441; DB00758; DB06350; DB01240; DB06209; DB01069; DB05553; DB15163; DB08816; DB00208; DB00374; DB16349 Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Blood coagulation; Cell membrane; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; G-protein coupled receptor; Glycoprotein; Hemostasis; Membrane; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transducer; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 28830.4 Length 248 Aromaticity 0.17 Instability index 24.19 Isoelectric point 9.39 Charge (pH=7) 10.55 3D Binding mode Sequence SLCTRDYKITQVLFPLLYTVLFFVGLITNGLAMRIFFQIRSKSNFIIFLKNTVISDLLMILTFPFKILSDAKLGTGPLRTFVCQVTSVIFYFTMYISISFLGLITIDPKNLLGAKILSVVIWAFMFLLSLPNMILTNRQPRDKNVKKCSFLKSEFGLVWHEIVNYICQVIFWINFLIVVKVFIIIAVFFICFVPFHFARIPYTLSQTRDVFDCTAENTLFYVKESTLWLTSLNACLNPFIYFFLCKSF Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 33 | Cocaine esterase | 3I2K | 4.77 | |
Target general information Gen name cocE Organism Rhodococcus sp. (strain MB1 Bresler) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms NA Protein family CocE/NonD hydrolase family Biochemical class Hydrolase Function Carboxylic ester hydrolase activity.Dipeptidyl-peptidase activity. Related diseases Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 5, episodic encephalopathy type (THMD5) [MIM:614458]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder due to an inborn error of thiamine metabolism. The phenotype is highly variable, but in general, affected individuals have onset in early childhood of acute encephalopathic episodes associated with increased serum and CSF lactate. These episodes result in progressive neurologic dysfunction manifest as gait disturbances, ataxia, dystonia, and spasticity, which in some cases may result in loss of ability to walk. Cognitive function is usually preserved, although mildly delayed development has been reported. These episodes are usually associated with infection and metabolic decompensation. Some patients may have recovery of some neurologic deficits. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22152682}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03793; DB01795 Interacts with NA EC number 3.1.1.84 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cytoplasm; Direct protein sequencing; Hydrolase; Serine esterase Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 62127.9 Length 574 Aromaticity 0.09 Instability index 26.62 Isoelectric point 4.56 Charge (pH=7) -33.24 3D Binding mode Sequence VDGNYSVASNVMVPMRDGVRLAVDLYRPDADGPVPVLLVRNPYDKFDVFAWSTQSTNWLEFVRDGYAVVIQDTRGLFASEGEFVPHVDDEADAEDTLSWILEQAWCDGNVGMFGVSYLGVTQWQAAVSGVGGLKAIAPSMASADLYRAPWYGPGGALSVEALLGWSALIGTGLITSRSDARPEDAADFVQLAAILNDVAGAASVTPLAEQPLLGRLIPWVIDQVVDHPDNDESWQSISLFERLGGLATPALITAGWYDGFVGESLRTFVAVKDNADARLVVGPWSHSNLTGRNADRKFGIAATYPIQEATTMHKAFFDRHLRGETDALAGVPKVRLFVMGIDEWRDETDWPLPDTAYTPFYLGGSGAANTSTGGGTLSTSISGTESADTYLYDPADPVPSLGGTLLFHNGDNGPADQRPIHDRDDVLCYSTEVLTDPVEVTGTVSARLFVSSSAVDTDFTAKLVDVFPDGRAIALCDGIVRMRYRETLVNPTLIEAGEIYEVAIDMLATSNVFLPGHRIMVQVSSSNFPKYDRNSNTGGVIAREQLEEMCTAVNRIHRGPEHPSHIVLPIIKRK Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 34 | Helicobacter pylori Methylthioadenosine nucleosidase (HELPY mtnN) | 4BMZ | 4.77 | |
Target general information Gen name HELPY mtnN Organism Helicobacter pylori (strain ATCC 700392 / 26695) (Campylobacter pylori) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms MTAN; MTA/SAH nucleosidase; Aminofutalosine nucleosidase; Aminodeoxyfutalosine nucleosidase; AFL nucleosidase; 6-amino-6-deoxyfutalosine N-ribosylhydrolase; 5'-methylthioadenosine/S-adenosylhomocystei Protein family PNP/UDP phosphorylase family Biochemical class NA Function Catalyzes the direct conversion of aminodeoxyfutalosine (AFL) into dehypoxanthine futalosine (DHFL) and adenine via the hydrolysis of the N-glycosidic bond; this reaction seems to represent an essential step in the menaquinone biosynthesis pathway in Helicobacter species. Can also probably catalyzes the hydrolysis of 5'-methylthioadenosine (MTA) and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) to adenine and the corresponding thioribose, 5'-methylthioribose and S-ribosylhomocysteine, respectively. These other activities highlight the tremendous versatility of the enzyme, which also plays key roles in S-adenosylmethionine recycling and in the biosynthesis of the quorum-sensing molecule autoinducer-2. Does not act on futalosine (FL) as substrate. Related diseases Progressive familial heart block 1B (PFHB1B) [MIM:604559]: A cardiac bundle branch disorder characterized by progressive alteration of cardiac conduction through the His-Purkinje system, with a pattern of a right bundle-branch block and/or left anterior hemiblock occurring individually or together. It leads to complete atrio-ventricular block causing syncope and sudden death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19726882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20562447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21887725}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva 6 (EKVP6) [MIM:618531]: A form of erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva, a genodermatosis characterized by the coexistence of two independent skin lesions: transient erythema and hyperkeratosis that is usually localized but occasionally occurs in its generalized form. Clinical presentation varies significantly within a family and from one family to another. Palmoplantar keratoderma is present in around 50% of cases. EKVP6 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30528822}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with NA EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Amino-acid biosynthesis; Hydrolase; Menaquinone biosynthesis; Methionine biosynthesis; Reference proteome Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 50547.6 Length 464 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 26.92 Isoelectric point 5.13 Charge (pH=7) -20.92 3D Binding mode Sequence VQKIGILGAMREEITPILELFGVDFEEIPLGGNVFHKGVYHNKEIIVAYSKIGKVHSTLTTTSMILAFGVQKVLFSGVAGSLVKDLKINDLLVAIQLVQHDVDLSAFDHPLGFIPESAIFIETSESLNALAKEVANEQHIVLKEGVIASGDQFVHSKERKEFLVSEFKASAVEMEGASVAFVCQKFGVPCCVLRSISNNADEEANMSFDAFLEKSAQTSAKFLKSMVDELGSHMVQKIGILGAMREEITPILELFGVDFEEIPLGGNVFHKGVYHNKEIIVAYSKIGKVHSTLTTTSMILAFGVQKVLFSGVAGSLVKDLKINDLLVAIQLVQHDVDLSAFDHPLGFIPESAIFIETSESLNALAKEVANEQHIVLKEGVIASGDQFVHSKERKEFLVSEFKASAVEMEGASVAFVCQKFGVPCCVLRSISNNADEEANMSFDAFLEKSAQTSAKFLKSMVDEL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 35 | Bifunctional protein PutA | 3E2Q | 4.76 | |
Target general information Gen name putA Organism Escherichia coli (strain K12) Uniprot ID TTD ID NA Synonyms b1014;poaA;JW0999 Protein family Proline dehydrogenase family; Aldehyde dehydrogenase family Biochemical class Oxidoreductase Function 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase activity.Bacterial-type RNA polymerase core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding.DNA binding.Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding.Identical protein binding.Proline dehydrogenase activity.Sequence-specific DNA binding.Transcriptional repressor activity, bacterial-type RNA polymerase core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding. Related diseases Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency (FBP1D) [MIM:229700]: An autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by impaired gluconeogenesis, and episodes of hypoglycemia and metabolic acidosis that can be lethal in newborn infants or young children. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12126934, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25601412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9382095}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB03051; DB03147; DB04398 Interacts with P09546 EC number 1.2.1.88; 1.5.5.2 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; DNA-binding; FAD; Flavoprotein; Multifunctional enzyme; NAD; Oxidoreductase; Proline metabolism; Reference proteome; Repressor; Transcription; Transcription regulation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 45567.7 Length 407 Aromaticity 0.08 Instability index 33.2 Isoelectric point 7.22 Charge (pH=7) 0.47 3D Binding mode Sequence QSVSRAAITAAYRRPETEAVSMLLEQARLPQPVAEQAHKLAYQLADKLRRLMGEQFVTGETIAEALANARKLEEKGFRYSYDMLGEAALTAADAQAYMVSYQQAIHAIGKASNGRGIYEGPGISIKLSALHPRYSRAQYDRVMEELYPRLKSLTLLARQYDIGINIDAEESDRLEISLDLLEKLCFEPELAGWNGIGFVIQAYQKRCPLVIDYLIDLATRSRRRLMIRLVKGAYWDSEIKRAQMDGLEGYPVYTRKVYTDVSYLACAKKLLAVPNLIYPQFATHNAHTLAAIYQLAGQNYYPGQYEFQCLHGMGEPLYEQVTGKVADGKLNRPCRISAPVGTHETLLAYLVRRLLENGANTSFVNRIADTSLPLDELVADPVTAVEKLAQQEGQTGLPHPKIPLPRD Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 36 | Vitamin D3 receptor (VDR) | 3B0T | 4.76 | |
Target general information Gen name VDR Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Vitamin D(3) receptor; Nuclear vitamin D receptor; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 1; NR1I1; 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily Biochemical class Nuclear hormone receptor Function Enters the nucleus upon vitamin D3 binding where it forms heterodimers with the retinoid X receptor/RXR. The VDR-RXR heterodimers bind to specific response elements on DNA and activate the transcription of vitamin D3-responsive target genes. Plays a central role in calcium homeostasis. Nuclear receptor for calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D3 which mediates the action of this vitamin on cells. Related diseases Rickets vitamin D-dependent 2A (VDDR2A) [MIM:277440]: A disorder of vitamin D metabolism resulting in severe rickets, hypocalcemia and secondary hyperparathyroidism. Most patients have total alopecia in addition to rickets. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1652893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17970811, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2177843, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2849209, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28698609, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7828346, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8106618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8381803, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8392085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8675579, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8961271, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9005998}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07530; DB08742; DB01436; DB04891; DB00146; DB02300; DB00136; DB00169; DB04540; DB05024; DB11672; DB14635; DB01070; DB06410; DB05295; DB06194; DB00153; DB04796; DB03451; DB00910; DB04258; DB11094 Interacts with P35222; Q09472; Q15648; P50222; Q15788; P26045; P19793; Q13573; Q13501; P04637; Q15645; Q9JLI4; P28700; X5D778; Q96HA8; Q01804; Q96S38; P48443 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Cytoplasm; Disease variant; DNA-binding; Metal-binding; Nucleus; Proteomics identification; Receptor; Reference proteome; Transcription; Transcription regulation; Ubl conjugation; Zinc; Zinc-finger Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 28781 Length 254 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 47.69 Isoelectric point 6.15 Charge (pH=7) -3.44 3D Binding mode Sequence ALRPKLSEEQQRIIAILLDAHHKTYDPTYSDFCQFRPPVRVNDGGGSVTLELSQLSMLPHLADLVSYSIQKVIGFAKMIPGFRDLTSEDQIVLLKSSAIEVIMLRSNESFTMDDMSWTCGNQDYKYRVSDVTKAGHSLELIEPLIKFQVGLKKLNLHEEEHVLLMAICIVSPDRPGVQDAALIEAIQDRLSNTLQTYIRCRHPPPGSHLLYAKMIQKLADLRSLNEEHSKQYRCLSFQPECSMKLTPLVLEVFG Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 37 | Nitric-oxide synthase endothelial (NOS3) | 4D1P | 4.76 | |
Target general information Gen name NOS3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Nitric oxide synthase, endothelial; NOSIII; NOS,type III; NOS type III; Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; Endothelial NOS; ENOS; EC-NOS; Constitutive NOS; CNOS Protein family NOS family Biochemical class Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase Function NO mediates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced angiogenesis in coronary vessels and promotes blood clotting through the activation of platelets. Produces nitric oxide (NO) which is implicated in vascular smooth muscle relaxation through a cGMP-mediated signal transduction pathway. Related diseases Variation Asp-298 in NOS3 may be associated with susceptibility to coronary spasm. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11740345, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9737779}. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB07001; DB02048; DB02911; DB02335; DB01997; DB03332; DB04534; DB07244; DB03100; DB03918; DB02207; DB03065; DB00125; DB02994; DB01833; DB00155; DB00997; DB07388; DB03974; DB02077; DB01821; DB09237; DB01110; DB03144; DB03305; DB01686; DB04559; DB02044; DB08019; DB08018; DB02027; DB02979; DB00435; DB04223; DB06154; DB03910; DB02141; DB03963; DB03707; DB02234; DB04018; DB00360; DB02589 Interacts with P60709; P63010-2; Q8N6T3-3; Q9Y575-3; Q96FT7-4; Q5SZD1; Q16543; Q9UNS2; Q8IUI8; P35222; Q05193; O15287; Q08379; Q71DI3; P69905; P61978; Q12891; Q9UKT9; Q9Y2M5; Q14525; Q6DKI2; P43364-2; Q8N6F8; O94851; A4FUJ8; Q8N594; Q8IVI9; Q6X4W1-6; O15381-5; Q9NV79; Q16549; Q5T2W1; O75925; Q96I34; Q6ZMI0-5; P57052; Q9GZR2; Q96D59; Q8N6K7-2; Q9GZS3; Q8IUW3; Q7Z699; Q7Z698; P50502; Q9BR01-2; Q9NVV9; Q86WT6-2; Q9H347; P58304; Q9NZC7-5; Q9UNY5; P14079 EC number EC 1.14.13.39 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Calmodulin-binding; Cell membrane; Cytoplasm; Cytoskeleton; Direct protein sequencing; FAD; Flavoprotein; FMN; Golgi apparatus; Heme; Iron; Lipoprotein; Membrane; Metal-binding; Myristate; NADP; Oxidoreductase; Palmitate; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Zinc Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A,B Molecular weight (Da) 90790.1 Length 803 Aromaticity 0.11 Instability index 50.67 Isoelectric point 6.03 Charge (pH=7) -9.56 3D Binding mode Sequence FPRVKNWEVGSITYDTLSAQAQQDGPCTPRRCLGSLVFPAPEQLLSQARDFINQYYSSIKRSGSQAHEQRLQEVEAEVAATGTYQLRESELVFGAKQAWRNAPRCVGRIQWGKLQVFDARDCRSAQEMFTYICNHIKYATNRGNLRSAITVFPQRCPGRGDFRIWNSQLVRYAGYRQQDGSVRGDPANVEITELCIQHGWTPGNGRFDVLPLLLQAPDEPPELFLLPPELVLEVPLEHPTLEWFAALGLRWYALPAVSNMLLEIGGLEFPAAPFSGWYMSTEIGTRNLCDPHRYNILEDVAVCMDLDTRTTSSLWKDKAAVEINVAVLHSYQLAKVTIVDHHAATASFMKHLENEQKARGGCPADWAWIVPPISGSLTPVFHQEMVNYFLSPAFRYQPDPWKFPRVKNWEVGSITYDTLSAQAQQDGPCTPRRCLGSLVFPAPEQLLSQARDFINQYYSSIKRSGSQAHEQRLQEVEAEVAATGTYQLRESELVFGAKQAWRNAPRCVGRIQWGKLQVFDARDCRSAQEMFTYICNHIKYATNRGNLRSAITVFPQRCPGRGDFRIWNSQLVRYAGYRQQDGSVRGDPANVEITELCIQHGWTPGNGRFDVLPLLLQAPDEPPELFLLPPELVLEVPLEHPTLEWFAALGLRWYALPAVSNMLLEIGGLEFPAAPFSGWYMSTEIGTRNLCDPHRYNILEDVAVCMDLDTRTTSSLWKDKAAVEINVAVLHSYQLAKVTIVDHHAATASFMKHLENEQKARGGCPADWAWIVPPISGSLTPVFHQEMVNYFLSPAFRYQPDPW Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 38 | Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT-3) | 1RJB | 4.76 | |
Target general information Gen name FLT3 Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Stem cell tyrosine kinase 1; STK1; STK-1; Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3; Fetal liver kinase-2; FLT-3; FLK2; FLK-2; FL cytokine receptor; CD135 Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily Biochemical class Kinase Function Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for the cytokine FLT3LG and regulates differentiation, proliferation and survival of hematopoietic progenitor cells and of dendritic cells. Promotes phosphorylation of SHC1 and AKT1, and activation of the downstream effector MTOR. Promotes activation of RAS signaling and phosphorylation of downstream kinases, including MAPK1/ERK2 and/or MAPK3/ERK1. Promotes phosphorylation of FES, FER, PTPN6/SHP, PTPN11/SHP-2, PLCG1, and STAT5A and/or STAT5B. Activation of wild-type FLT3 causes only marginal activation of STAT5A or STAT5B. Mutations that cause constitutive kinase activity promote cell proliferation and resistance to apoptosis via the activation of multiple signaling pathways. Related diseases Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML) [MIM:601626]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. AML is a malignant disease of bone marrow characterized by maturational arrest of hematopoietic precursors at an early stage of development. Clonal expansion of myeloid blasts occurs in bone marrow, blood, and other tissue. Myelogenous leukemias develop from changes in cells that normally produce neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils and monocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11090077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11290608, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11442493, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14504097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16266983, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18305215, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8946930, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9737679}. The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis. Somatic mutations that lead to constitutive activation of FLT3 are frequent in AML patients. These mutations fall into two classes, the most common being in-frame internal tandem duplications of variable length in the juxtamembrane region that disrupt the normal regulation of the kinase activity. Likewise, point mutations in the activation loop of the kinase domain can result in a constitutively activated kinase. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB12742; DB12267; DB12500; DB12010; DB12141; DB06469; DB06080; DB06595; DB11763; DB09079; DB11697; DB12978; DB08901; DB15822; DB12874; DB00398; DB01268; DB05465; DB11800; DB05014 Interacts with P00519; P42684; P46108; P46109; P06241; Q13322; Q9Y6K9; P06239; P27986; P20936; P43405; Q8R4L0 EC number EC 2.7.10.1 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; ATP-binding; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Endoplasmic reticulum; Glycoprotein; Host-virus interaction; Immunoglobulin domain; Kinase; Membrane; Nucleotide-binding; Phosphoprotein; Proteomics identification; Proto-oncogene; Receptor; Reference proteome; Signal; Transferase; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tyrosine-protein kinase; Ubl conjugation Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 34209.2 Length 298 Aromaticity 0.14 Instability index 39.68 Isoelectric point 5.57 Charge (pH=7) -4.02 3D Binding mode Sequence YESQLQMVQVTGSSDNEYFYVDFREYEYDLKWEFPRENLEFGKVLGSGAFGKVMNATAYGISKTGVSIQVAVKMLKEREALMSELKMMTQLGSHENIVNLLGACTLSGPIYLIFEYCCYGDLLNYLRSKREKFLTFEDLLCFAYQVAKGMEFLEFKSCVHRDLAARNVLVTHGKVVKICDFGLARDIMSDSNYVVRGNARLPVKWMAPESLFEGIYTIKSDVWSYGILLWEIFSLGVNPYPGIPVDANFYKLIQNGFKMDQPFYATEEIYIIMQSCWAFDSRKRPSFPNLTSFLGCQL Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 39 | Acyloxyacyl hydrolase (neutrophil) | 5W7C | 4.76 | |
Target general information Gen name AOAH Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms Acyloxyacyl hydrolase Protein family NA Biochemical class NA Function Removes the secondary (acyloxyacyl-linked) fatty acyl chains from the lipid A region of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. By breaking down LPS, terminates the host response to bacterial infection and prevents prolonged and damaging inflammatory responses (By similarity). In peritoneal macrophages, seems to be important for recovery from a state of immune tolerance following infection by Gram-negative bacteria (By similarity). Related diseases Major depressive disorder (MDD) [MIM:608516]: A common psychiatric disorder. It is a complex trait characterized by one or more major depressive episodes without a history of manic, mixed, or hypomanic episodes. A major depressive episode is characterized by at least 2 weeks during which there is a new onset or clear worsening of either depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure in nearly all activities. Four additional symptoms must also be present including changes in appetite, weight, sleep, and psychomotor activity; decreased energy; feelings of worthlessness or guilt; difficulty thinking, concentrating, or making decisions; or recurrent thoughts of death or suicidal ideation, plans, or attempts. The episode must be accompanied by distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15229186}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Drugs (DrugBank ID) NA Interacts with Q15700 EC number EC 3.1.1.77 Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Alternative splicing; Calcium; Cytoplasmic vesicle; Direct protein sequencing; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hydrolase; Lipid metabolism; Metal-binding; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Secreted; Signal; Zymogen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID C Molecular weight (Da) 47779.7 Length 420 Aromaticity 0.1 Instability index 43.45 Isoelectric point 7.72 Charge (pH=7) 2.1 3D Binding mode Sequence GSDICSLPVLAKICQKIKLAMEQSVPFKDVDSDKYSVFPTLRGYHWRGRDCNDSDESVYPGRRPNNWDVHQDSNCNGIWGVDPKDGVPYEKKFCEGSQPRGIILLGDAAGAHFHISPEWITASQMSLNSFINLPTALTNELDWPQLSGATGFLDSTVGIKEKSIYLRLWKRNHCNHRDYQNISRNGASSRNLKKFIESLSRNKVLDYPAIVIYAMIGNDVCSGKSDPVPAMTTPEKLYSNVMQTLKHLNSHLPNGSHVILYGLPDGTFLWDNLHNRYHPLGQLNKDMTYAQLYSFLNCLQVSPCHGWMSSNKTLRTLTSERAEQLSNTLKKIAASEKFTNFNLFYMDFAFHEIIQEWQKRGGQPWQLIEPVDGFHPNEVALLLLADHFWKKVQLQWPQILGKENPFNPQIKQVFGDQGGH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||
| 40 | Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 1 (EPCAM) | 4MZV | 4.76 | |
Target general information Gen name EPCAM Organism Homo sapiens (Human) Uniprot ID TTD ID Synonyms hEGP314; TROP1; TACSTD1; Major gastrointestinal tumor-associated protein GA733-2; MIC18; M4S1; M1S2; KSA; KS 1/4 antigen; Gastrointestinal carcinoma antigen GA733; GA733-2; Epithelial glycoprotein 314 Protein family EPCAM family Biochemical class NA Function Plays a role in embryonic stem cells proliferation and differentiation. Up-regulates the expression of FABP5, MYC and cyclins A and E. May act as a physical homophilic interaction molecule between intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) and intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) at the mucosal epithelium for providing immunological barrier as a first line of defense against mucosal infection. Related diseases Diarrhea 5, with tufting enteropathy, congenital (DIAR5) [MIM:613217]: An intractable diarrhea of infancy characterized by villous atrophy and absence of inflammation, with intestinal epithelial cell dysplasia manifesting as focal epithelial tufts in the duodenum and jejunum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18572020, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24142340}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lynch syndrome 8 (LYNCH8) [MIM:613244]: A form of Lynch syndrome, an autosomal dominant disease associated with marked increase in cancer susceptibility. It is characterized by a familial predisposition to early-onset colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and extra-colonic tumors of the gastrointestinal, urological and female reproductive tracts. Lynch syndrome is reported to be the most common form of inherited colorectal cancer in the Western world. Clinically, it is often divided into two subgroups. Type I is characterized by hereditary predisposition to colorectal cancer, a young age of onset, and carcinoma observed in the proximal colon. Type II is characterized by increased risk for cancers in certain tissues such as the uterus, ovary, breast, stomach, small intestine, skin, and larynx in addition to the colon. Diagnosis of classical Lynch syndrome is based on the Amsterdam criteria: 3 or more relatives affected by colorectal cancer, one a first degree relative of the other two; 2 or more generation affected; 1 or more colorectal cancers presenting before 50 years of age; exclusion of hereditary polyposis syndromes. The term 'suspected Lynch syndrome' or 'incomplete Lynch syndrome' can be used to describe families who do not or only partially fulfill the Amsterdam criteria, but in whom a genetic basis for colon cancer is strongly suspected. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19098912}. The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. LYNCH8 results from heterozygous deletion of 3-prime exons of EPCAM and intergenic regions directly upstream of MSH2, resulting in transcriptional read-through and epigenetic silencing of MSH2 in tissues expressing EPCAM. Drugs (DrugBank ID) DB06607; DB11075; DB05831; DB05319; DB09336 Interacts with P27797; P12830; Q15078; P36957; Q8TDX7 EC number NA Uniprot keywords 3D-structure; Cell junction; Cell membrane; Direct protein sequencing; Disease variant; Disulfide bond; Glycoprotein; Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer; Membrane; Proteomics identification; Reference proteome; Repeat; Signal; Tight junction; Transmembrane; Transmembrane helix; Tumor antigen Protein physicochemical properties Chain ID A Molecular weight (Da) 27439.8 Length 243 Aromaticity 0.07 Instability index 33.77 Isoelectric point 6.03 Charge (pH=7) -1.99 3D Binding mode Sequence XEECVCENYKLAVNCFVNNNRQCQCTSVGAQNTVICSKLAAKCLVMKAEMQGSKLGRRAKPEGALQNNDGLYDPDCDESGLFKAKQCQGTSTCWCVNTAGVRRTDKDTEITCSERVRTYWIIIELKHKAREKPYDSKSLRTALQKEITTRYQLDPKFITSILYENNVITIDLVQQSSQKTQNDVDIADVAYYFEKDVKGESLFHSKKMDLTVNGEQLDLDPGQTLIYYVDEKAPEFSMQGLKH Hydrogen bonds contact Hydrophobic contact | ||||